port folio


















This completed project involves the redevelopment of a selected site, specifically an island in the backwater area of Kochi. The project focuses on designing a low-energy building with sustainable characteristics, specifically a proposal for a central public library. Throughout the design process, relevant planning policies, regulations, and legislation have been applied and utilized as justifications for design decisions.
The initial design concept involved a rectangular plan with voids strategically incorporated to maximize sunlight penetration, while an 80% glass facade was implemented to enhance natural lighting. The design was created using Autocad Revit and further refined in Google Sketchup, which facilitated the development of a double facade design. Energy simulations were conducted using elmhurst DesignBuilder to inform the design process and ensure optimal energy performance.
To address heat gain, a thermal wall was implemented on the west side of the building, effectively reducing thermal transfer. Additionally, perforated panels were incorporated as a double facade on the north and south sides to minimize glare and optimize visual comfort within the building.



Overall, this project showcases a sustainable and energy-efficient building design for the proposed central public library on the selected site in Kochi. The design decisions were guided by planning policies, regulations, and legislation, and were supported by advanced modeling and simulation tools to achieve an environmentally conscious and visually appealing outcome.

Meeting Rooms

Lecture Halls
Lounge Lounge Area
Viewing Gallery(Mezzanine)


Book Processing/Office


Cafe/Sunken Space
Reception/Information





This completed project focuses on producing a scheme proposal informed by site analysis, local planning policies, and sustainable principles. The project demonstrates a critical analysis of planning policy and showcases the decision-making process throughout. Various presentation techniques, including manual and computer-based simulations, diagrams, sketches, graphs, photos, and images, have been utilized to fulfill the project brief. The report includes an introduction, conclusion, aims and objectives statement, and references. The assessment is based on the critique of the proposal, evidence of background reading and research, and the presentation of the building project from sustainable site appraisal to the final outcome. Key elements addressed in the scheme proposal include strategic proposals, analysis of planning policies, integration of environmental design and energy systems, proposed interventions for enhancing energy performance, viability of technologies, adherence to sustainable codes and standards, and effective visual presentation.







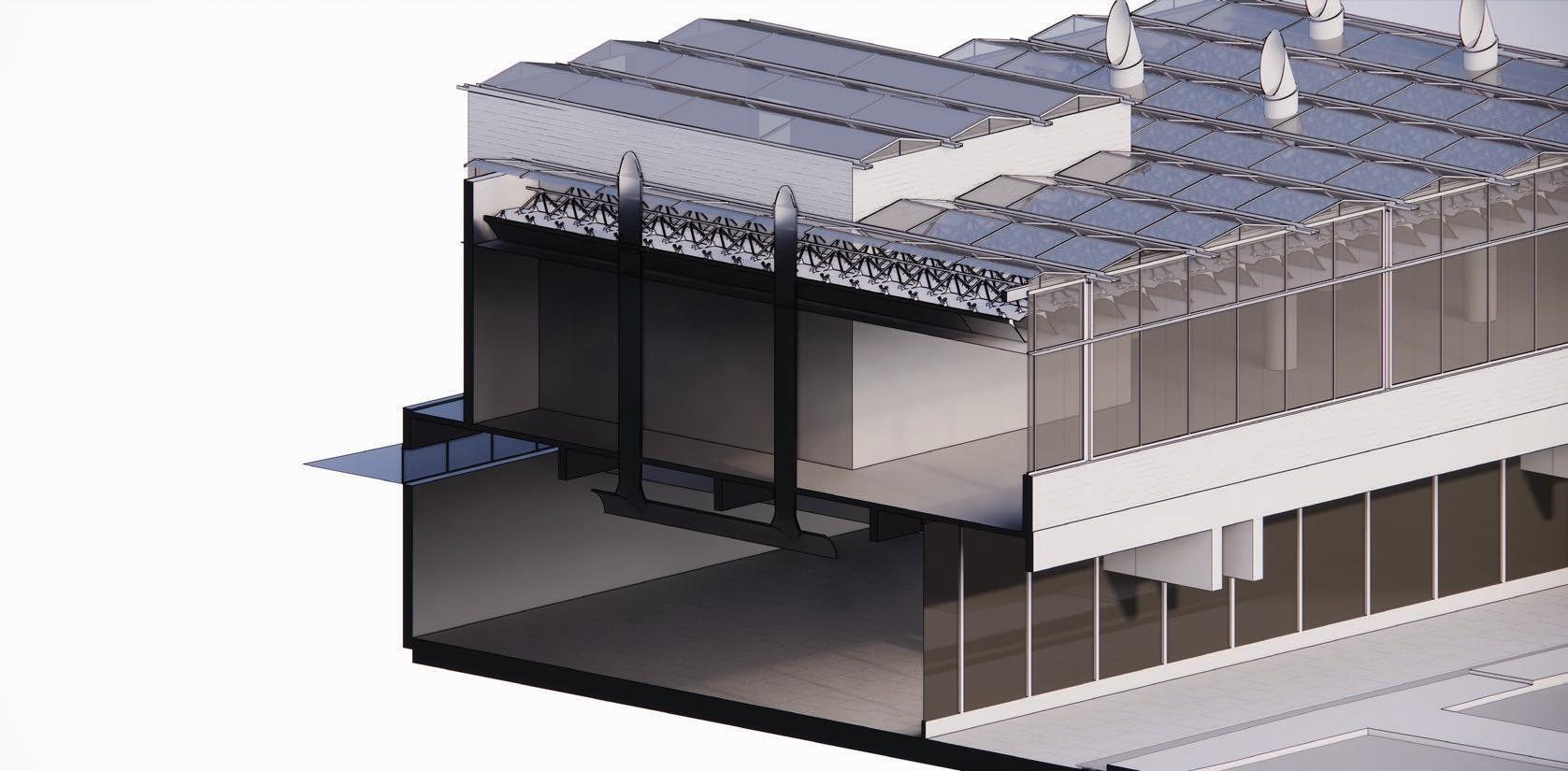
Glass roof system and the daylight diffusing leaves made out of ferro-cement have been used in areas proposed to be used as museum.


The glass roof extends both outdoors and within the building. Small supports on top of the truss structure underneath keep it in place.

Sun-shading fins have trusses running the length of them.
Interior and external areas are both shaded by sun-shading fins. Creates a smooth transition between inside and outdoors, as well as modulating the light for the exhibition spaces.
 1.Glass roof system:
2. Truss system:
3. Sun shading system:
1. Glass Roof and Gutter System
2. Structural Truss System
3. Fins / Leaves
O rthographic Section of Glass roof.
xonometric diagram of proposed roof.
P roposed Roof Detail.
1.Glass roof system:
2. Truss system:
3. Sun shading system:
1. Glass Roof and Gutter System
2. Structural Truss System
3. Fins / Leaves
O rthographic Section of Glass roof.
xonometric diagram of proposed roof.
P roposed Roof Detail.
Semi Transparent Photo-Voltaic Facade



South facing PV panels on roof

Light Shelves

The primary objective of this project is to thoroughly analyze and improve the energy performance and sustainability of an existing corporate o ce building. The building, which was constructed in 2015, showcases a unique blend of contemporary and traditional architectural styles, making it an ideal setting for exploring and implementing sustainable strategies. To achieve this, a comprehensive site appraisal and analysis was conducted to identify speci c areas within the building where energy e ciency can be enhanced, and occupant comfort can be improved.


To enhance sustainability and mitigate heat gain from the western sunlight, an imposing thermal barrier wall is strategically incorporated on the building's western side, utilizing advanced shading techniques to reduce thermal transfer, minimize glare, and optimize energy efficiency.






In addition to the thermal barrier wall, the design incorporates a thoughtful solution for glare reduction by implementing a screen wall on both the front and west side. The front facade showcases an engaging pattern of trellises, intelligently crafted to filter the intense sunlight, ensuring optimal natural ventilation while creating an aesthetically pleasing environment. This integration promotes comfort, energy efficiency, and a harmonious blend of sustainable design principles.
Recognizing the challenges of the hot tropical climate, the terrace is ingeniously transformed into a lush garden and inviting lounge area. This innovative addition provides an additional protective layer against the heat, effectively shielding the interiors and fostering a refreshing and cool environment. The garden not only enhances the aesthetic appeal but also promotes natural cooling through greenery, creating a harmonious synergy between nature, comfort, and sustainability.
Proposed Elevation - Existing Structure Orthographic View - Existing. Orthographic View - Proposed Design Elevation - Proposed Design





 AXONOMETRIC SITE PLAN WITH GF.
AXONOMETRIC SITE PLAN WITH GF.

















 DUPLEX - 2020
DUPLEX - 2020
RENOVATION PROJECT - 2020
JEWELLERY FACADE DESIGN - 2021
JEWELLERY FACADE DESIGN - 2021
JEWELLERY FACADE DESIGN - 2021
F
COMMERCIAL BLDG CONCEPT - 2021
COMMERCIAL BLDG CONCEPT - 2021
DUPLEX - 2020
DUPLEX - 2020
RENOVATION PROJECT - 2020
JEWELLERY FACADE DESIGN - 2021
JEWELLERY FACADE DESIGN - 2021
JEWELLERY FACADE DESIGN - 2021
F
COMMERCIAL BLDG CONCEPT - 2021
COMMERCIAL BLDG CONCEPT - 2021
The aim of this project is to raise awareness about Puthurvayal, a biodiverse hotspot, by establishing an Agricultural Institute under the MS Swaminathan Research Foundation (MSSRF). The project aims to highlight the site's natural signi cance while promoting sustainable development and preserving traditional agricultural practices. The objectives of the project include emphasizing the importance of the site's biodiversity, creating employment opportunities for the tribal population, educating people about biodiversity conservation, and facilitating the protection of endangered and local plant species.
The scope of the project involves utilizing the institute to educate locals, students, and tourists about the site's indigenous vegetation and the signi cance of agriculture in biodiversity conservation. The institute is envisioned as a platform for disseminating knowledge and technology, supporting sustainable and traditional farming practices, and keeping farmers updated on the latest advancements. However, it is important to note that the project has limitations, particularly in terms of construction processes that must be carefully executed to minimize disruption to the site's biodiversity.
The proposed site for the project is located in Puthurvayal, a village in South Wayanad, with an area of 49.7 acres. By establishing the MSSRF Agricultural Institute, the project aims to leverage the expertise of the foundation, promote research and technology, and train students in sustainable and traditional agricultural practices. Additionally, the institute can serve as a platform for knowledge exchange and capacity building among local farmers.


















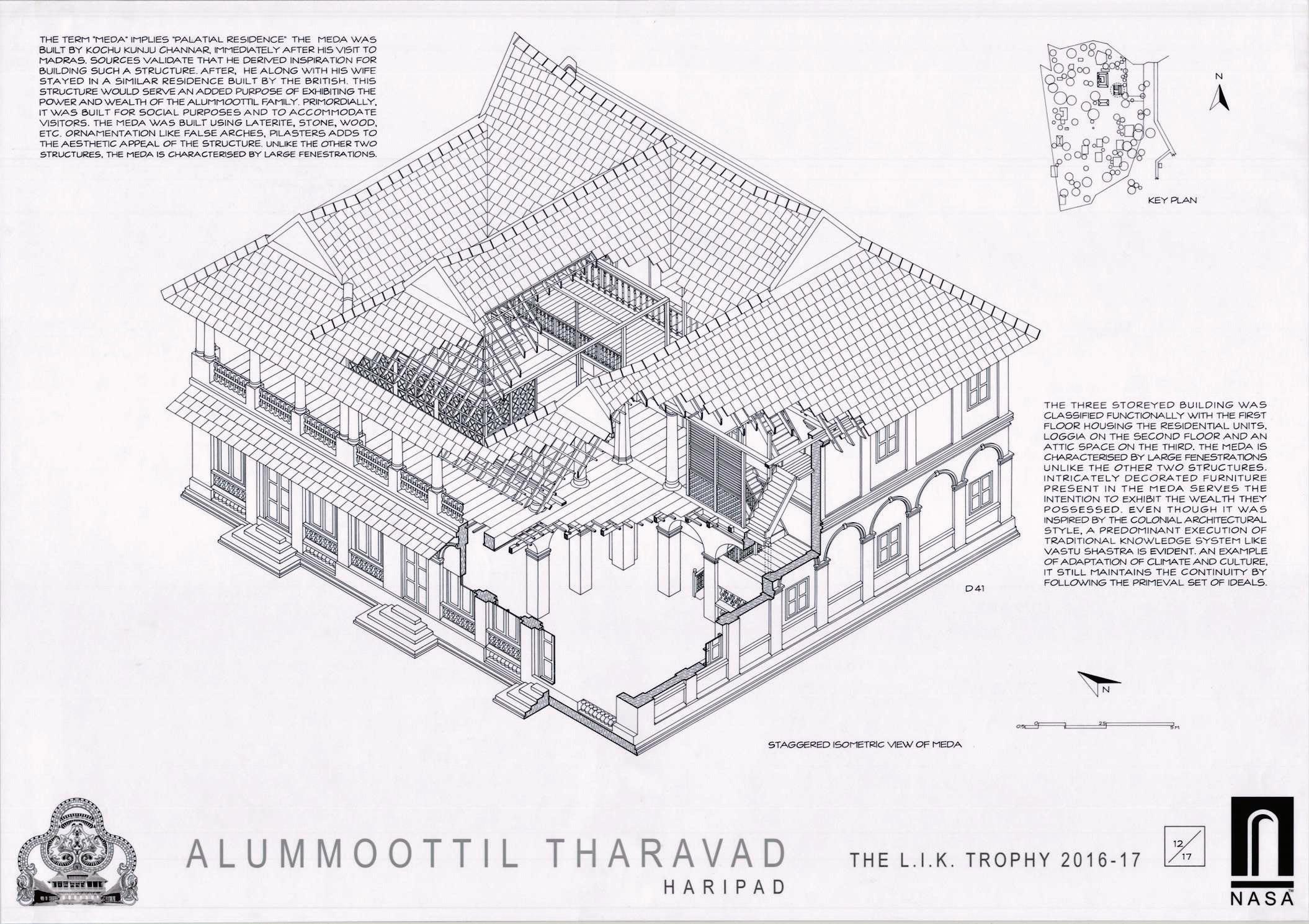

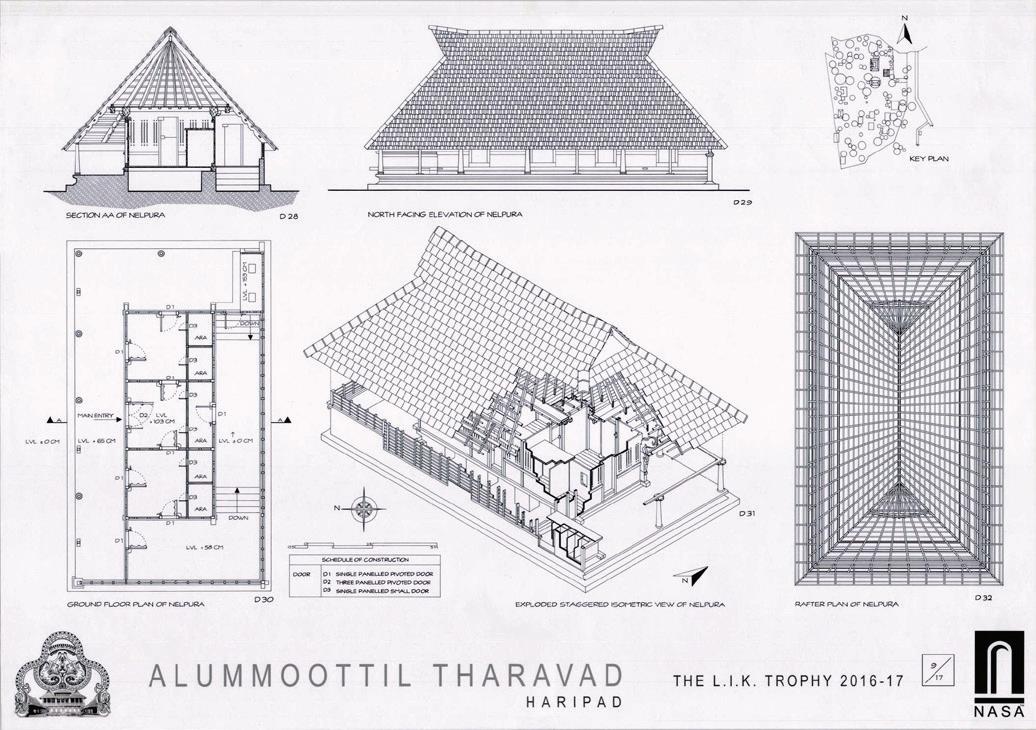
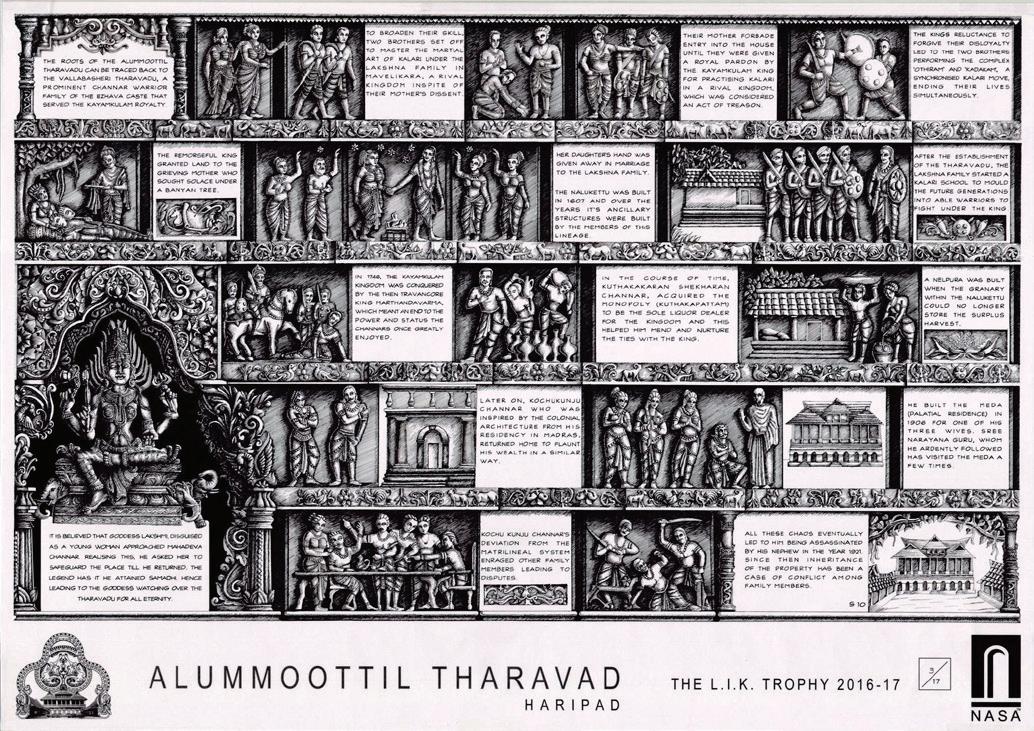
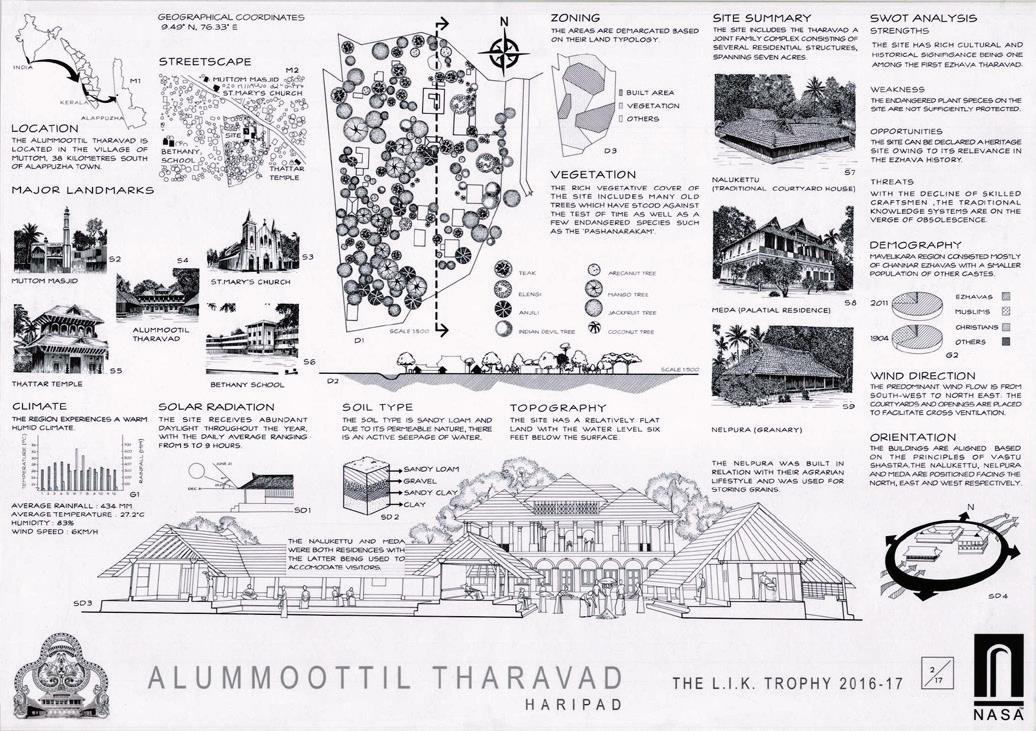
 Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner