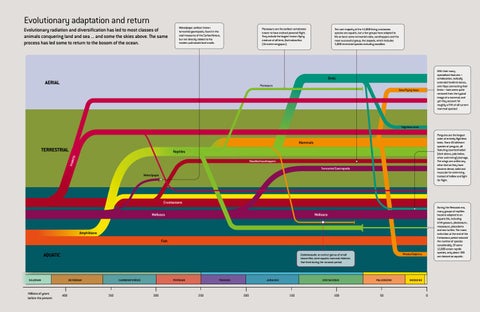
Evolutionary adaptation and return Evolutionary radiation and diversification has led to most classes of animals conquering land and sea ... and some the skies above. The same process has led some to return to the bosom of the ocean.
Maturipupa: earliest known terrestrial gastropods, found in the coal measures of the Carboniferous, but not directly related to the modern pulmonate land snails.
Pterosaurs are the earliest vertebrates known to have evolved powered flight. They include the largest known flying creature of all time, Quetzalcoatlus (16-metre wingspan).
The vast majority of the 44,000 living crustacean species are aquatic, but a few groups have adapted to life on land: some terrestrial crabs, sandhoppers and the most successful group, the isopods, which includes 5,000 terrestrial species including woodlice.
With their many specialised features – echolocation, radically extended forelimb bones, skin flaps connecting their limbs – bats seem quite removed from the typical image of a mammal, and yet they account for roughly a fifth of all current mammal species!
Birds
AERIAL
Pterosaurs Bats/Flying foxes
Flightless birds Penguins are the largest order of entirely flightless birds. There 20 different species of penguin, all featuring countershaded (dark above, pale below, when swimming) plumage. The wings are unlike any other bird as they have become dense, solid and muscular for swimming, instead of hollow and light for flight.
Mammals
TERRESTRIAL Insec
ts
Reptiles Woodlice/sandhoppers
Terrestrial Gastropods Maturipupa
Crustaceans Molluscs
During the Mesozoic era, many groups of reptiles became adapted to an aquatic life, including ichthyosaurs, plesiosaurs , mosasaurs, placodonts and sea turtles. The mass extinction at the end of the Cretaceous period reduced the number of species considerably. Of some 12,000 extant reptile species, only about 100 are classed as aquatic.
Molluscs
Amphibians Fish
AQUATIC
SILURIAN
Millions of years before the present
Whales/Dolphins
Castorocauda: an extinct genus of small beaver-like, semi-aquatic mammal relatives that lived during the Jurassic period.
DEVONIAN
400
CARBONIFEROUS
350
PERMIAN
300
TRIASSIC
250
JURASSIC
200
CRETACEOUS
150
100
PALEOGENE
50
NEOGENE
0