LYMPHATIC SYSTEM TRAINING MANUAL

contents
Introduction
Healthy lymphatic system
Lymphatic system Conditions
Where is the Lymphatic System?
What does it do?
The lymphatic system
What is the Lymphatic System?
Lymphatic vessels
The Lymph

Lymph nodes
The Spleen
The thymus
Beauty & the lymphatic system
Facial lymphatic drainage
Treatment directions
Body Contouring
Weight Gain
Lymphatic treatments
Contraindications
Techniques to stimulate the system
Lymphatic drainage massage
Treatment directions
Lymphedema
Conclusion
INTRODUCTION
The lymphatic system is a network of vessels, nodes, and organs responsible for maintaining fluid balance, aiding immune function, and eliminating waste products from the body. It works with the circulatory system to ensure proper fluid circulation and immune response Understanding the lymphatic system's role is important when considering non-invasive body contouring techniques, as some methods aim to optimize lymphatic drainage and enhance fat cell elimination Here are some key points about the lymphatic system about body contouring:

It
is imperative
one knows the significance of understanding the Lymphatic System in the Beauty Industry
This article underscores the significance of comprehending the lymphatic system in the beauty industry. It stresses the importance of moving beyond external treatments and delving deeper into the body's inner workings to improve genuine beauty and wellness. Beauty therapists can unlock a new level of radiance and sculpting effects by utilizing lymphatic drainage techniques Furthermore, understanding the lymphatic system helps promote optimal fluid flow, reduces inflammation, and nurtures the body's inner vitality, which radiates through the skin

Introduction
The Importance of a Healthy Lymphatic System
There are several reasons why it's crucial to maintain a healthy lymphatic system:
Immune Function: The lymphatic system is vital to the body's immune response. It contains specialized immune cells identify and destroy pathogens, bacteria, viruses, and abnormal cells A healthy lymphatic system enhances the body's ability to defend against infections and diseases, supporting optimal immune function
Fluid Balance: Maintaining fluid balance is another essential lymphatic system function. It collects excess fluids, waste products, and toxins from the tissues and transports them away If the lymphatic system is not functioning correctly, it can lead to swelling, edema, and discomfort. A healthy lymphatic system ensures proper fluid drainage and contributes to overall well-being..
Detoxification: Eliminating waste products and toxins from the body is a significant function of the lymphatic system. It helps to remove cellular waste, metabolic by-products, and harmful substances from the tissues. An impaired lymphatic system can accumulate toxins, which may affect overall health and increase the risk of various health issues
Why is it important to have a healthy lymphatic system?
Nutrient absorption: The lymphatic system is involved in the absorption of dietary fats and fat-soluble vitamins from the digestive system The lymphatic vessels called lacteals in the small intestine collect dietary fats and transport them to the bloodstream, where the body can utilize them A healthy lymphatic system ensures efficient absorption and transportation of essential nutrients.
Tissue health and healing: A well-functioning lymphatic system supports tissue health and healing processes It helps to remove cellular debris, damaged cells, and inflammatory substances from the tissues, promoting faster healing and reducing inflammation
Adequate lymphatic drainage is essential for tissue repair and recovery after injury or surgery.
Prevention of lymphedema: A healthy lymphatic system helps to prevent the development of lymphedema, a condition characterized by persistent swelling, usually in the arms or legs. Lymphed1. Consider breaking up the text into shorter par2 Add specific examples or case studies to illustrate the benefits of a healthy lymphatic system, making the content more engaging and relatable for readers
An unhealthy lymphatic system can contribute to various skin conditions due to its role in waste removal, immune response, and fluid balance. While an unhealthy lymphatic system can contribute to skin and body conditions, it can also be influenced by other factors and underlying causes. Addressing lymphatic system health and appropriate treatment and management of specific skin conditions can help improve skin health and alleviate symptoms If you suspect issues with your lymphatic system or experience persistent skin concerns, it is advisable to consult a Healthcare professional or dermatologist for proper evaluation and guidance
Here are some skin conditions that may be associated with impaired lymphatic system function:
Lymphedema: Lymphedema results from impaired lymphatic drainage leading to persistent swelling in the affected limbs or

Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that can occur when bacteria enter through breaks or cracks in the skin A compromised lymphatic system may reduce the body's ability to fight off these infections, increasing the risk of cellulitis. It typically causes redness, warmth, swelling, and pain in the affected area

Chronic edema
Chronic edema refers to long-term fluid retention in the tissues, often affecting the limbs. When the lymphatic system fails to remove excess fluid efficiently, it can lead to persistent swelling, skin changes, and discomfort.

Dermatitis
Dermatitis refers to inflammation of the skin, which can manifest in various forms, such as contact dermatitis, atopic dermatitis (eczema), or seborrheic dermatitis. While the exact cause of dermatitis can vary, impaired lymphatic drainage may hinder the removal of irritants or allergens from the skin, contributing to the development or exacerbation of dermatitis symptoms.

Acne can be caused by inadequate lymphatic drainage, which leads to poor elimination of toxins and clogged pores. When lymphatic flow is sluggish, it can hinder the clearance of sebum, dead skin cells, and impurities, creating an environment that favors acne development

A compromised lymphatic system can lead to dry and dull skin due to insufficient delivery of nutrients and hydration, resulting in flakiness and a lackluster complexion. Inadequate lymphatic drainage can also disrupt the fluid balance, impairing the skin's ability to maintain moisture and nourishment

Tonsils and adenoids are small masses of lymphatic tissue that help to trap and remove pathogens, acting as the body's first line of defense Tonsils are located at the back of the throat, while adenoids are located behind the nose in the upper part of the throat.
The lymphatic system supports immune responses, circulates and filters lymph, and eliminates waste products
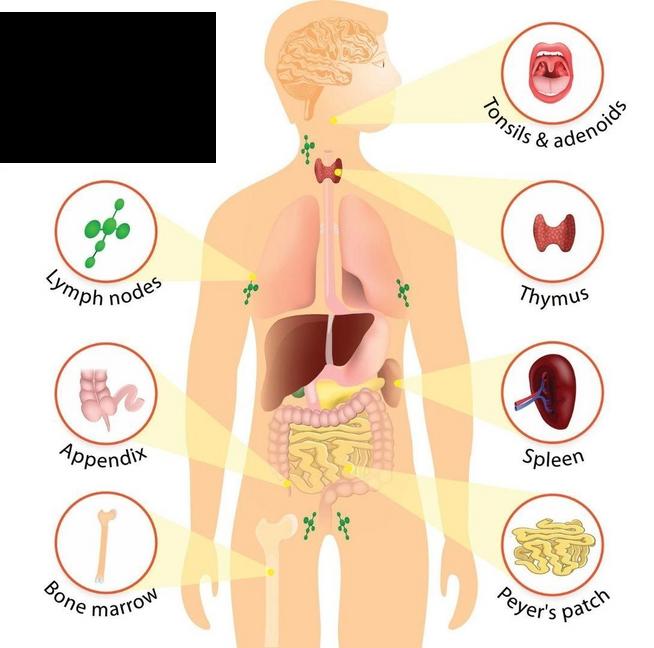
Fluid balance: The lymphatic system maintains fluid balance by collecting excess fluids, proteins, and other substances from blood vessels and tissues, transporting them through lymphatic vessels, and filtering them through lymph nodes This helps prevent tissue swelling and maintain proper organ and tissue function.
Immune defense: The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in the body's defense against infections Lymph nodes are small beanshaped structures that contain immune cells that help identify and eliminate foreign substances, such as bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells When an infection or injury occurs, immune cells in the lymph nodes become activated, initiating an immune response to fight off pathogens and support healing

THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM

WHAT DOES IT DO?
Waste removal: Besides removing excess fluids, the lymphatic system also eliminates waste products, cellular debris, and toxins from tissues
These waste materials are transported through lymphatic vessels and eventually processed and filtered by lymph nodes. By clearing waste materials, the lymphatic system helps maintain tissue health and function
Understanding the lymphatic system
The lymphatic system removes waste products, fights infections, and transports fats from the digestive system Beauty therapists need to understand how it works to improve clients' health
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM & TRANSPORT OF LIPIDS
While the lymphatic system's primary function is to transport lymph fluid and aid in immune defense, it also plays a role in the transport of lipids, specifically dietary fats. Lipids are transported through specialized lymphatic vessels called lacteals, which are present in the small intestine.
After we consume a meal that contains dietary fats, these fats are absorbed by the cells lining the small intestine Within these cells, the fats are packaged into small droplets called chylomicrons Chylomicrons are too large to be directly absorbed into the bloodstream, so they enter the lacteals within the intestinal villi (finger-like projections in the small intestine) instead.
The chylomicrons and other fat-soluble vitamins and lipids enter the lymphatic vessels and are transported through the lymphatic system The lymphatic vessels converge into larger lymphatic ducts, eventually reaching the thoracic duct, the main collecting duct of the lymphatic system
The thoracic duct then empties the lymph, chylomicrons, and other lipids into the bloodstream at a point near the left subclavian vein in the neck From there, the chylomicrons and lipids can circulate in the bloodstream, delivering essential fats and nutrients to various tissues and organs throughout the body.
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM & TRANSPORT OF LIPIDS
This transport of dietary lipids through the lymphatic system ensures efficient absorption and distribution, preventing the overwhelming entry of large fat molecules into the bloodstream and adverse effects on the liver Endogenous fats are primarily mobilized and transported through the bloodstream by lipoproteins such as LDL and HDL cholesterol.

WHAT IS THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM?
The lymphatic system comprises several key components that work together to perform its functions. These components include:
Lymphatic vessels: These vessels form an extensive network throughout the body, similar to blood vessels Lymphatic vessels are finer and have thinner walls than blood vessels. They carry lymph, a colorless fluid, throughout the body.
Lymph: Lymph is a fluid that flows through the lymphatic vessels It is derived from the plasma that leaves the blood vessels and surrounds the body's tissues. Lymph contains waste products, toxins, excess water, and immune cells
Lymph nodes: Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures located along the lymphatic vessels. They act as filters, trapping and removing foreign substances from the lymph fluid, such as bacteria, viruses, damaged cells, and cancer cells Lymph nodes also contain white blood cells, primarily lymphocytes, crucial for immune responses.
Spleen: The spleen is an organ located in the upper left side of the abdomen It filters the blood and removes old or damaged red blood cells The spleen also helps to detect and fight infections by producing immune cells and antibodies.
Thymus: The thymus is a gland in the upper chest, behind the breastbone It plays a vital role in developing and maturing certain types of white blood cells called T lymphocytes or T cells T cells are essential for immune responses against specific pathogens.
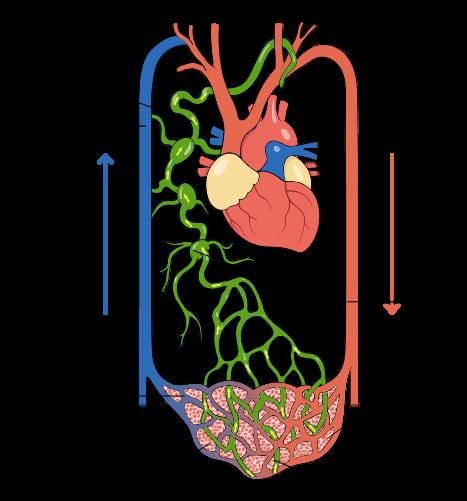
LYMPHATIC VESSELS
Lymphatic vessels form a network of thin-walled tubes throughout the body, carrying clear fluid lymph They have one-way valves and small smooth muscles to propel lymph forward Found in tissues and organs, they transport lymph from tissues to lymph nodes and back to the bloodstream.
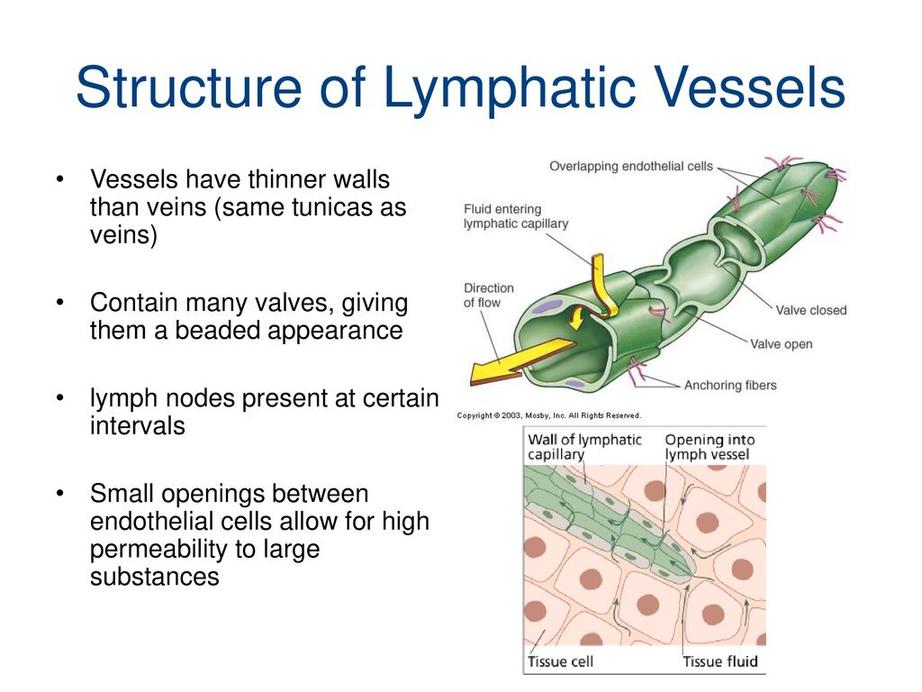
LYMPHATIC VESSELS
The lymphatic vessels gradually converge and form larger vessels called lymphatic trunks. There are several major lymphatic trunks in the body, including the jugular trunks, subclavian trunks, bronchomediastinal trunks, intestinal trunks, and lumbar trunks These trunks merge to form two main collecting vessels: the thoracic duct and the right lymphatic duct
The thoracic duct is the larger of the two and drains lymph from the lower body, left upper body, and left side of the head and neck It begins near the abdomen and ascends through the thoracic cavity before emptying into the left subclavian vein, where lymph rejoins the bloodstream.
The right lymphatic duct is more petite and drains lymph from the right upper body, including the right arm, right side of the head, and right side of the neck. It empties into the right subclavian vein.
The lymphatic vessels are critical in maintaining fluid balance and immune function They collect excess fluid, waste products, toxins, and immune cells from the body tissues and transport them to the lymph nodes, where harmful substances are filtered, and immune responses are initiated
Lymphatic vessels form an extensive network that collects and transports lymph throughout the body. They have one-way valves and muscle contractions to ensure proper lymph flow. These vessels are vital for maintaining fluid balance, removing waste products, and supporting immune function
THE LYMPH
Lymph is a clear fluid that circulates through the lymphatic system It originates from plasma, which leaks out of blood vessels and bathes the body's tissues. When plasma leaves blood vessels, it becomes tissue fluid, eventually entering lymphatic vessels and turning into lymph Lymph contains water, proteins, fats, waste products, toxins, immune cells, and cellular debris. It is similar to interstitial fluid, which surrounds cells and provides them with nutrients and oxygen. However, lymph also contains immune cells that play a crucial role in the body's defense against infections

THE LYMPH
The lymphatic vessels collect lymph from the tissues and transport it toward the lymph nodes. Along the way, lymph passes through numerous lymph nodes, acting as filters The lymph nodes contain specialized immune cells, primarily lymphocytes, which help identify and eliminate foreign substances, such as bacteria, viruses, and abnormal cells, in the lymph.
The lymph nodes play a significant role in the body's immune response When harmful substances are detected in the lymph, lymphocytes within the lymph nodes are activated. These lymphocytes help identify and destroy pathogens or abnormal cells, preventing them from spreading further in the body
As lymph continues its journey through the lymphatic system, it eventually reaches larger lymphatic vessels called lymphatic trunks. The lymphatic trunks merge to form the thoracic and right lymphatic ducts, which empty the lymph back into the bloodstream, specifically into the subclavian veins
From there, the lymph rejoins the circulation and becomes part of the blood plasma The waste products and toxins the lymph carries are ultimately filtered and eliminated from the body through various excretory organs, such as the kidneys.
The lymph serves as a crucial medium for transporting immune cells, waste products, toxins, and cellular debris away from the tissues It plays a vital role in maintaining fluid balance, immune function, and the removal of harmful substances from the body.
LYMPH NODES
Lymph nodes are small bean-shaped structures that function as filters in the lymphatic system. They are located throughout the body and are connected by lymphatic vessels Lymph nodes play an essential role in the immune system's defense against infections and diseases by trapping and destroying pathogens and other foreign substances in the lymph fluid before it returns to the bloodstream

LYMPH NODES
The lymph nodes contain lymphoid follicles that house lymphocytes Immune cells in follicles detect foreign particles in the lymph fluid and trigger an immune response, producing antibodies and mobilizing immune cells to fight infections. Lymph nodes cluster in specific body areas and may become swollen, tender, or painful during immune challenges

THE SPLEEN
The spleen, located in the upper left abdomen under the ribcage, is a vital component of the lymphatic system, performing various functions It is composed of red pulp and white pulp.

THE SPLEEN
The white pulp of the spleen contains specialized immune cells, primarily lymphocytes, which help to initiate immune responses It acts as a surveillance system, detecting and responding to foreign substances, such as bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens, present in the bloodstream.
One of the primary functions of the spleen is its involvement in the body's immune defense It acts as a filter for the blood, removing bacteria, viruses, and other harmful microorganisms. The spleen also helps to identify and destroy damaged or abnormal cells, including old or defective red blood cells, preventing them from circulating in the bloodstream.
Additionally, the spleen serves as a reservoir for red blood cells and platelets In times of increased demand, such as during physical exertion or in cases of blood loss, the spleen contracts and releases stored red blood cells and platelets into circulation, helping to maintain adequate levels of these cells in the body
The spleen also has a role in the production of specific immune cells It is a site for developing and maturing some white blood cells, including lymphocytes These lymphocytes play a critical role in immune responses and help to defend the body against infections.
THE SPLEEN
In some diseases or conditions, such as infections, autoimmune disorders, or blood disorders, the spleen may enlarge (splenomegaly) or require surgical removal (splenectomy) However, the body can still function without it, as other organs and tissues can compensate for its absence. The spleen plays a crucial role in immune responses, blood filtration, and storage of red blood cells and platelets, contributing to overall bodily function

THE THYMUS
The thymus, an essential organ of the immune system, is located in the upper chest behind the sternum It consists of two lobes and contains two types of tissue: the cortex and the medulla During childhood, the thymus is most active and gradually decreases in size during adulthood The cortex contains immature T cells that undergo positive and negative selection to prevent autoimmune reactions.

THE THYMUS
Once T cells complete the maturation process, they migrate to the medulla of the thymus. The medulla contains mature T cells and specialized cells called thymic epithelial cells, which provide support and guidance for the T cells The mature T cells leave the thymus and travel to other lymphoid organs, such as the lymph nodes and spleen, where they participate in immune responses
The thymus also produces various hormones, including thymosin, thymopoietin, and interleukins, which help regulate the development and function of T cells These hormones contribute to the overall maturation and differentiation of T cells, ensuring they can recognize and respond to specific pathogens and foreign substances.
Although the thymus gradually decreases in size and activity with age, it continues to play a role in immune function throughout life However, the exact extent of its contribution to immune responses in adulthood is still being researched.
The thymus is a specialized gland of the immune system responsible for T cells' maturation and development. Through positive and negative selection processes, the thymus ensures that mature T cells are capable of recognizing foreign antigens while avoiding harmful immune reactions against selfantigens The thymus's hormones and thymic epithelial cells support this maturation process, ultimately contributing to a well-functioning immune system.
BEAUTY & THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
Understanding the lymphatic system when offering beauty and noninvasive body contouring treatments is vital for client safety, treatment customization, enhanced results, minimizing side effects, client education, and collaboration with other healthcare professionals It ensures a holistic and informed treatment approach, promoting aesthetic goals and overall lymphatic health.

BEAUTY & THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
Safety and contraindications: The lymphatic system is interconnected with the circulatory and immune systems By understanding the lymphatic system, beauty and body contouring professionals can identify any contraindications or precautions related to lymphatic conditions or compromised lymphatic function. This knowledge helps ensure clients' safety by avoiding treatments that could potentially worsen or negatively impact their lymphatic health
Treatment customization: The lymphatic system plays a significant role in fluid balance, waste removal, and immune response. When offering beauty and body contouring treatments, the lymphatic system allows professionals to customize the treatments according to the client's needs. This may involve adjusting techniques, pressures, or treatment modalities to optimize lymphatic drainage, reduce swelling, and enhance overall treatment outcomes
Enhanced results: The lymphatic system removes waste products, toxins, and excess fluid from the body. Efficient lymphatic drainage can help reduce post-treatment swelling, promote better healing, and enhance overall treatment results By incorporating techniques that support lymphatic flow, beauty, and body contouring professionals can improve treatment outcomes, minimize downtime, and optimize client satisfaction.
BEAUTY & THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
Minimizing side effects: Certain beauty and body contouring treatments, such as massages, lymphatic drainage techniques, or devices that promote lymphatic movement, directly target the lymphatic system. Understanding how these treatments affect lymphatic flow allows professionals to minimize potential side effects and maximize client benefits. It ensures that treatments are performed correctly and in a manner that supports the body's natural detoxification and waste elimination processes
Client education and aftercare: Educating clients about the lymphatic system's role in beauty and body contouring treatments empowers them to participate actively in their well-being. Professionals can guide selfcare practices that support the lymphatic system, such as hydration, gentle exercises, and proper skincare By understanding the importance of the lymphatic system, clients can make informed decisions and follow appropriate aftercare recommendations to optimize treatment results and maintain their lymphatic health
Referral and collaboration: Sometimes, clients may present with signs or symptoms that suggest underlying lymphatic issues or conditions. Recognizing these indications allows beauty and body contouring professionals to refer clients to healthcare providers or specialists with expertise in lymphatic health Collaboration between professionals can provide comprehensive care and better outcomes for clients with lymphatic concerns.
WHAT IS FACIAL LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE?
Facial lymphatic drainage is a gentle technique that stimulates the lymphatic system in the face and neck area, promoting lymphatic flow and reducing swelling or congestion. The technique involves gentle, rhythmic movements and manual manipulation to encourage the movement of lymphatic fluid, which can improve overall skin health
**NOTE: Facial lymphatic drainage is generally considered safe and non-invasive However, individuals with certain medical conditions, such as active infections, skin conditions, or lymphatic disorders, should consult a healthcare professional before undergoing or performing facial lymphatic drainage to ensure it is appropriate for their situation.
FACIAL LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE
Here's a breakdown of facial lymphatic drainage:
Technique: Facial lymphatic drainage typically involves gentle, lightpressure movements using the fingertips or palms of the hands The moves follow the natural direction of lymphatic flow, typically towards the lymph nodes in the neck area.
Starting point: The practitioner often begins at the center of the face, such as the forehead or the area between the eyebrows. From there, they move outward and downward, following the contours of the face, using slow, gliding motions The aim is to encourage lymphatic fluid to drain towards the lymph nodes
Key areas: The technique focuses on specific areas of the face where lymph nodes are located, including the sides of the neck, behind the ears, and under the jawline By targeting these areas, the practitioner aims to facilitate the elimination of waste products and toxins, reduce puffiness, and enhance the overall appearance of the skin.
Light pressure: The pressure applied during facial lymphatic drainage is generally soft and gentle, as the lymphatic vessels are close to the skin's surface The intention is to avoid discomfort or damage to delicate facial structures.
FACIAL LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE

THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM & BODY CONTOURING
The lymphatic system plays a significant role in the results of non-invasive body contouring procedures. Non-invasive body contouring treatments, such as laser therapy, radiofrequency, or ultrasound, aim to reduce fat and improve specific body areas' overall shape and appearance
These procedures target and disrupt fat cells, causing them to break down and be eliminated from the body Once the fat cells are disrupted, they release fatty acids and triglycerides into the surrounding tissue This is where the lymphatic system comes into play.

The lymphatic system helps to remove the by-products of fat cell breakdown The released fatty acids and triglycerides are picked up by the lymphatic vessels and transported through the lymphatic system. The lymphatic vessels carry these waste products to the lymph nodes, where they are filtered and processed
When the lymphatic system is functioning optimally, it efficiently eliminates waste products, aiding in removing the broken-down fat cells from the body This helps improve the overall results of non-invasive body contouring procedures by eliminating fat and reducing swelling or inflammation in the treated areas.
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM & BODY CONTOURING
However, if the lymphatic system is compromised or not functioning properly, it may hinder the effectiveness of the body contouring treatment If the lymphatic system is overwhelmed or congested, it may struggle to remove the waste products efficiently, leading to slower results or prolonged swelling.
To optimize the outcomes of non-invasive body contouring, supporting the lymphatic system's function is important. This can be done through various methods such as lymphatic massage, compression garments, exercise, hydration, and a healthy lifestyle These practices can help stimulate lymphatic circulation, improve lymphatic drainage, and enhance the body's natural ability to eliminate waste products.

THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM & BODY CONTOURING

Non-invasive body contouring and the lymphatic system: Certain noninvasive body contouring techniques recognize the importance of optimizing lymphatic function for effective fat reduction and body shaping These techniques aim to enhance lymphatic drainage and eliminate fat cells For example:
Lymphatic massage: Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) techniques involve gentle massage and rhythmic movements that stimulate lymphatic flow and help remove excess fluid and waste products This can enhance the lymphatic system's efficiency and support the elimination of fat cells after body contouring treatments.
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM & WEIGHT GAIN

The lymphatic system itself does not directly cause weight gain However, disruptions or imbalances in the lymphatic system's function can contribute to fluid retention, possibly leading to temporary weight gain. Here's a closer look at the relationship between the lymphatic system and weight:
The lymphatic system is crucial in maintaining fluid balance within the body, removing waste products, and supporting the immune system. It comprises a network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, and lymphoid tissues The lymphatic system transports lymph, a fluid containing white blood cells and waste products, throughout the body
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM & WEIGHT GAIN
When the lymphatic system functions optimally, it helps to eliminate excess fluids, toxins, and cellular waste from the body tissues. However, if the lymphatic system becomes compromised or inefficient, fluid may accumulate in the tissues, leading to edema or swelling. This can cause a temporary increase in weight due to the additional fluid retention.
Factors that can disrupt the normal function of the lymphatic system and contribute to fluid retention include:
Lymphatic congestion: Blockages or obstructions in the lymphatic vessels can impede the normal flow of lymph, leading to fluid buildup in the tissues.
Inflammation: Inflammatory conditions can affect lymphatic flow and contribute to fluid retention. Inflammation may result from various causes, such as injury, infection, or chronic conditions.
Surgery or trauma: Surgical or physical trauma can disrupt the lymphatic system, leading to temporary swelling and fluid accumulation.
Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle can impair lymphatic circulation. Regular exercise and movement help stimulate lymphatic flow and promote optimal fluid drainage
While fluid retention related to lymphatic system issues may cause temporary weight gain, it is distinct from weight gain due to increased body fat Weight gain associated with increased body fat is typically a result of energy imbalance, where caloric intake exceeds caloric expenditure, leading to fat storage.
INCORPORATING LYMPHATIC TREATMENTS
Assessing a client's lymphatic system should be a routine part of their initial consultation This can be done through a combination of visual and tactile assessments Beauty therapists should also take note of any existing medical conditions that may affect lymphatic function.
Beauty therapists should be familiar with the techniques to stimulate the lymphatic system, including massage, dry brushing, and exercise These techniques should be incorporated into existing body contouring services, such as wrap treatments or vacuum therapy. Clients who receive lymphatic treatments may see better results from other body contouring services that they receive
Continued education and training on lymphatic treatments can help beauty therapists provide more comprehensive services for their clients. This includes learning about new techniques and equipment and staying up-todate with the latest research and developments in the field
It's important to remember that lymphatic treatments should not replace traditional body contouring services but should be used as complementary services to enhance the overall results for clients.
PRECAUTIONS AND CONTRAINDICATIONS FOR LYMPHATIC TREATMENTS
Beauty therapists should take proper precautions and be aware of contraindications when providing lymphatic treatments to their clients. Here are some important things to keep in mind:
Clients with lymph nodes removed or lymphatic issues should be referred to a medical professional before receiving lymphatic treatments.
Therapists should avoid applying too much pressure during lymphatic massage, which can damage delicate vessels
Clients who are pregnant or have a history of blood clots should speak with their doctor before receiving lymphatic treatments
Therapists should know any medications or supplements clients take that may affect lymphatic function.
Clients should drink plenty of water before and after lymphatic treatments to help flush out toxins and waste products
By following these precautions and being aware of contraindications, beauty therapists can help ensure the safety and effectiveness of lymphatic treatments for their clients.
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE FOR BODY CONTOURING
The lymphatic system is highly relevant to body contouring, as it plays a critical role in the body's natural detoxification processes Fat cells are broken down and released into the interstitial space between cells during body contouring treatments such as ultrasonic cavitation and vacuum therapy The lymphatic system then transports these fat cells to the liver, where they are metabolized and eliminated from the body.
However, if the lymphatic system is not functioning properly, the fat cells may not be effectively eliminated, leading to swelling, inflammation, and other complications In addition, some body contouring treatments, such as lymphatic drainage massage, are specifically designed to stimulate the lymphatic system and promote the elimination of excess fluids and toxins
Therefore, proper lymphatic system function is essential for achieving optimal results from body contouring treatments Clients may be advised to maintain a healthy diet, stay hydrated, and exercise regularly to support lymphatic system function and promote eliminating of excess fat cells. Somebody contouring clinics may offer lymphatic drainage massage or other lymphatic system treatments to help optimize the body's natural detoxification processes and promote the best possible results
TECHNIQUES TO STIMULATE THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
There are several techniques that beauty therapists can use to stimulate the lymphatic system and improve overall health:
Manual lymph drainage massage: This gentle massage technique can be done by hand or with a device. The massage stimulates lymphatic flow and reduces fluid buildup in the body The therapist uses light pressure to move lymphatic fluid toward the lymph nodes, which can be filtered and eliminated from the body.
Dry brushing involves using a firm-bristled brush to massage the skin in long strokes, which helps move lymphatic fluid and stimulate circulation Dry brushing also exfoliates the skin, leaving it soft and smooth.
Vacuum therapy: This non-invasive technique uses suction to stimulate lymphatic flow and break up cellulite The therapist applies a suction cup to the skin and moves it in circular motions, which can help improve skin tone and texture.
Wood therapy involves using specially designed wooden tools to massage the body and improve lymphatic flow The devices are shaped to fit different body parts and can break up cellulite, reduce fluid retention, and contour the body
BENEFITS OF LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE MASSAGE
Some of the benefits of lymphatic drainage massage after body contouring include:
Reduces swelling: Lymphatic drainage massage helps to reduce swelling and inflammation, which can occur after body contouring treatments. This can help improve the treated area's appearance and reduce discomfort.
Promotes healing: Lymphatic drainage massage can help to promote healing by increasing blood flow and oxygenation to the treated area This can help to speed up the healing process and reduce the risk of complications.
Improves skin tone and texture: Lymphatic drainage massage can help to improve skin tone and texture by increasing circulation and promoting lymphatic drainage. This can help reduce cellulite's appearance and improve the skin's overall appearance
Enhances results: Lymphatic drainage massage can help to enhance the results of body contouring treatments by promoting the elimination of excess fat cells and toxins from the body. This can help optimize the treatment results and improve overall body shape
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AND BODY CONTOURING

LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE TREATMENT MAP
Lymphatic drainage massage is a massage therapy designed to stimulate the lymphatic system and eliminate excess fluids and toxins from the body It is often recommended after body contouring treatments to help enhance the results and support the body's natural detoxification processes
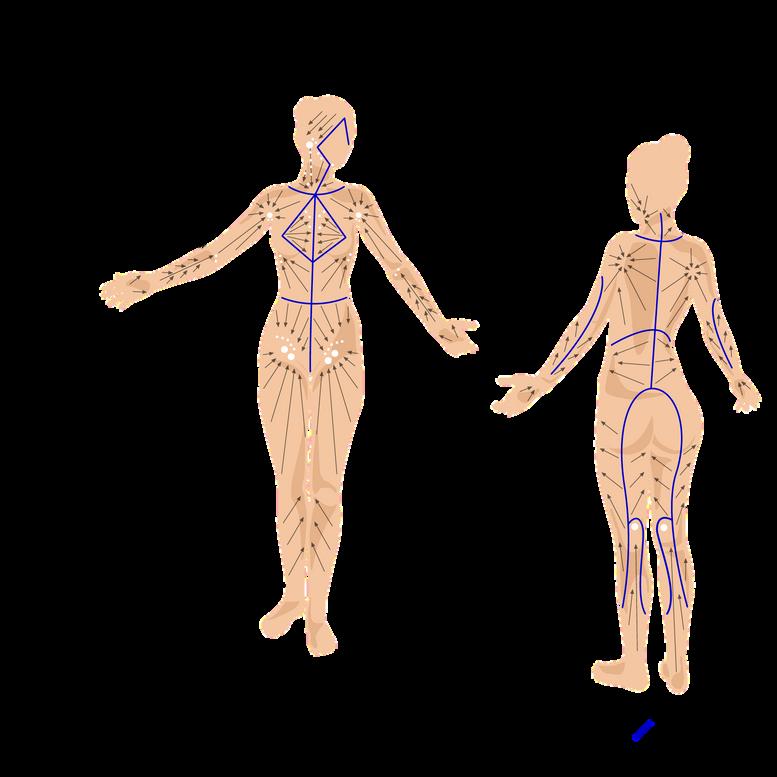
TREATMENT
Lymphatic drainage treatment is an important aspect of body contouring because it can help to reduce swelling and improve lymphatic circulation, which in turn can enhance the effectiveness of the body contouring treatment Lymphatic drainage massage works by manually stimulating the lymphatic system, which filters and removes waste products from the body
When performing body contouring treatments, the fat cells are broken down and eliminated from the body through the lymphatic system. However, if the lymphatic system is not functioning properly, the body may be unable to efficiently eliminate the waste products and excess fluid, resulting in swelling, inflammation, and discomfort.
Using lymphatic drainage treatment directions for body contouring can help to facilitate the removal of waste products and excess fluid from the body, which can improve the overall results of the treatment This may include using specific massage techniques to promote lymphatic flow and instructing the client to perform self-massage or other lymphatic drainage techniques at home
Incorporating lymphatic drainage treatment into a body contouring treatment plan can help to improve the client's overall experience and results while also minimizing the risk of adverse reactions or complications.
WHAT IS LYMPHEDEMA?

Lymphedema is a chronic condition characterized by persistent swelling, usually in the arms or legs, but it can also affect other body parts. It occurs when there is a disruption or impairment in the normal flow of lymphatic fluid, leading to its accumulation in the affected area
Early detection and prompt lymphedema management are important to minimize its impact and prevent progression If you suspect you have lymphedema or are at risk, seeking medical attention for proper evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment options is recommended
WHAT IS LYMPHEDEMA?
There are two main types of lymphedema:
Primary lymphedema: This type is rare and typically results from a developmental abnormality or genetic mutation affecting the lymphatic system. It may be present at birth or develop later in life, often during adolescence or adulthood Primary lymphedema can affect one or both limbs and may progress over time.
Secondary lymphedema: This type of lymphedema is more common and occurs due to damage or disruption to the lymphatic system It can develop after surgical procedures, such as lymph node removal or radiation therapy for cancer treatment, which can cause scarring or blockage of lymphatic vessels. Secondary lymphedema can also be caused by trauma, infection, or inflammation that affects the lymphatic system.
The hallmark symptom of lymphedema is swelling, which may range from mild to severe Other common symptoms include a feeling of heaviness or tightness in the affected limb, decreased flexibility, discomfort or pain, recurring infections, and changes in the skin texture (such as thickening or hardening).
Lymphedema can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life It can affect mobility, cause physical discomfort, and increase the risk of recurrent infections. Left untreated or poorly managed, it can lead to complications such as skin infections, cellulitis, and reduced limb function.
WHY IS IT IMPORTANT TO RECOGNISE LYMPHEDEMA?
It is crucial for a body contouring technician to recognize lymphedema for several reasons:

Lymphedema is a chronic condition that requires specialized care and management If a client has undiagnosed or untreated lymphedema and undergoes certain body contouring procedures, it can worsen their condition or lead to complications By recognizing the signs and symptoms of lymphedema, a technician can ensure the client's safety and well-being
In cases where lymphedema is suspected or confirmed, the technician needs to refer the client to a healthcare professional with expertise in lymphedema management
CONCLUSION
IIn conclusion, understanding the lymphatic system can help beauty therapists enhance their clients' physical beauty and promote optimal health.
































