Introduction to World War 1 The reasons/ causes
World War 1 was known as ‘The Great War’ and started on the 28th of July 1914. The main causes were Militarism, Alliance, Imperialism and Nationalism. Militarism as there was a rise in military and naval forces. Alliances as there was two main alliances the triple entente that included Great Britain, France and Russia and the triple alliance which included Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy. Imperialism as the growth in European countries caused tension. Last Nationalism where they were taking pride in their countries power and culture.



The Overall cause was the assassination of the Archduke of Franz Fernandez this was showing threats to the so called ‘Mother Country’, Britain. Australia fought and got involved to show their loyalty to Britain.

Why
the soldiers enlisted
Some soldiers enlisted for the need for extra pay, the desire to adventure, some wanted to escape from their normal lives, and some wanted to do their duty to fight alongside Britain.


Where they fought and the way they called for enlistment
Australian fought in many areas of the war such as the Western Front the area between Belgium and France, the Middle East and in the Gallipoli Peninsula in Turkey. The way they would call for enlistment was with post cards, posters and trade cards.




https://www.awm.gov.au/collection/C
969707
Intro to the Soldiers who fought on Gallipoli

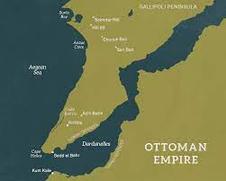
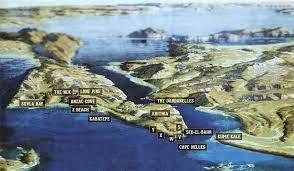
Soldiers who fought at Gallipoli arrived at Anzac Cove on the 25th of April 4:15 am for the hopes that they could force their way through the narrow straits also known as the Dardanelles to conquer Turkey and relieve pressure on their ally country Russia who were fighting on the Eastern Front. However, a lot of malfunctions caused one of the three main boats went off course and one of the chimneys sparked which caused Turkey soldiers to spot them. This caused for a rain of bullets on arrival causing 2,000 soldiers out of the 16000 soldiers to die on day 1. Even though a lot of soldiers died on arrival the soldiers remaining still pushed up the mountains to claim the lower trenches. This was extremely dangerous because some of the trenches were barely four metres apart in some areas. The soldiers who fought in Gallipoli were later called the ANZACs (Australian New Zealand Army Corporation) due to their mate ship, courage and persistence.

This was the location where they arrived: https://earth.google.com/web/@40.2449389,26.2818756,6.94 227993a,1000.00000001d,30y,0h,0.0000451t,0r

The experience the soldiers faced at war
Some of the experiences that the soldiers faced, either in the trenches, on the war grounds and with their mental and physical health were bad and unhealthy.
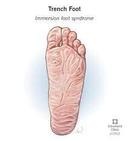
The first experience was inside the trenches where it was muddy, cold, stinky and infested with rats and lice. The mud and wetness caused something called ‘Trench foot’. Trench foot was what happened when you’d have your feet exposed to water or mud consistently for long periods of time without drying them.
Another experience was one of their orders which was when the captain yelled “over the top” which meant they had to climb out of their trenches carrying their equipment and run through the enemies firing area over and under barbed wire fencing and sticking low to t The enemies’ firing area was land’.
When the soldiers arrived at Gallipoli

25th of April 1915 4:15am






James (Jim) Martin

One of the soldiers who chose to fight in Gallipoli was James (Jim) Martin he was born on the 3rd of January 1901 in New South Wales. As a kid his dad was rejected from the army and he was determined to fill his spot. He threatened to run away from if his parents if they did not sign the permission note to join the army and to completely cut off communication with them. James (Jim) faked his age to get into the army and enlisted for the AIF (Australian Imperial Force) at the age of 14 years old on the 12th of April 1915 against the wishes of his family.
According to The Australian War Memorial a website created in 1980 stated that he was in the 21st infantry battalion and on the way over to Gallipoli the transport boat they were aboard was torpedoed by a German Submarine and James (Jim) and several others spent several hours in the water before being rescued. He arrived in the early hours of the 7th of September 1915 serving in the area between ANZAC cove and Gallipoli Peninsula.

The area he fought:
https://earth.google.com/web/search/wire+gully+gallipoli/@40.33 045559,26.50919828,148.37127365a,87557.02843772d,35y,0h, 0t,0r/data=CigiJgokCXq0KmpH0RAERGZVqMKH0RAGVkjfGv9STpAIVHxKpRURjpA

How he died:
James (Jim) got sick with a disease called Typhoid throughout service and refused to get help or seek medical attention. Typhoid disease is a bacterial disease spread through contaminated food, water or close contact. He survived 6 weeks in active service before passing on the 25th of October was titled as the youngest soldier to die in active service, dying at the young age of 14 years 9 months and 22 days from heart failure.
James (Jim) Martin Life time line

Short term and Long term impacts of WW1
on the Soldiers:

Some of the long term and shortterm impacts that impacted these types of soldiers were brutal and deadly. The first impact was a long-term impact, ‘Shell Shock’ which is a form of PTSD (post-traumatic stress disorder). Shell shock was caused by the sounds of bullets, bombs and other explosives when hitting something or someone. This would impact the soldiers really bad and would cause them to be very anxious and jumpy.

One of the short-term impacts were when they arrived at ANZAC cove they had a bullet fire which got rid of 2000 of their soldiers on their first day.


Bibliography:
“Armistice.” National WWI Museum and Memorial, www.theworldwar.org/learn/aboutwwi/armistice#:~:text=On%20Nov.
Australian War Memorial. “Home | the Australian War Memorial.” Awm.gov.au, 4 Feb. 2019, www.awm.gov.au/.
“British Library.” Www.bl.uk, www.bl.uk/world-warone/articles/combat-and-soldiers-experiencesm. Accessed 29 May 2023.
corporateName =Department of Veterans’ Affairs; address=21 Genge St, Civic/Canberra City.
“Timeline of Australians and the Gallipoli Campaign | Anzac Portal.” Anzacportal.dva.gov.au, 30 June 2022, anzacportal.dva.gov.au/wars-andmissions/ww1/where-australiansserved/gallipoli/timeline.
“Google Earth.” Earth.google.com, earth.google.com/web/@40.30074506. Accessed 29 May 2023.
Norwich University Online. “Six Causes of World War I.” Norwich University Online, Norwich University, 1 Aug. 2017, online.norwich.edu/academicprograms/resources/six-causes-of-world-wari#:~:text=The%20expansion%20of%20European%2 0nations.
Study.com, 2023, study.com/academy/lesson/diplomacy-of-worldwar-one-secret-agreements-diplomaticarrangements.html#:~:text=World%20War%20I%2 0Alliances%20were.