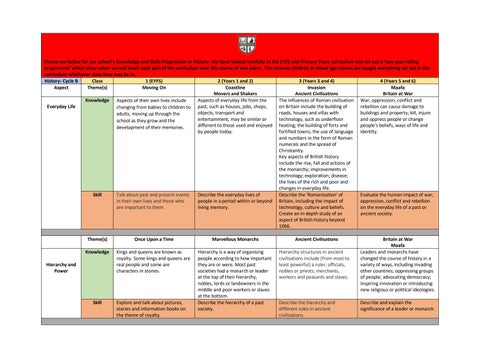
Please see below for our school’s Knowledge and Skills Progression in History. We have looked carefully at the EYFS and Primary Years curriculum and set out a ‘two year rolling programme’ which show when we will teach each part of the curriculum over the course of two years. This ensures children in mixed age classes are taught everything set out in the curriculum whichever class they may be in. History- Cycle B Class 1 (EYFS) 2 (Years 1 and 2) 3 (Years 3 and 4) 4 (Years 5 and 6) Aspect Theme(s) Moving On Coastline Invasion Maafa Movers and Shakers Ancient Civilisations Britain at War Knowledge Aspects of their own lives include Aspects of everyday life from the The influences of Roman civilisation War, oppression, conflict and Everyday Life on Britain include the building of rebellion can cause damage to changing from babies to children to past, such as houses, jobs, shops, objects, transport and roads, houses and villas with buildings and property; kill, injure adults, moving up through the entertainment, may be similar or technology, such as underfloor and oppress people or change school as they grow and the different to those used and enjoyed heating; the building of forts and people's beliefs, ways of life and development of their memories. by people today. fortified towns; the use of language identity. and numbers in the form of Roman numerals and the spread of Christianity. Key aspects of British history include the rise, fall and actions of the monarchy; improvements in technology; exploration; disease; the lives of the rich and poor and changes in everyday life. Skill Talk about past and present events Describe the everyday lives of Describe the 'Romanisation' of Evaluate the human impact of war, in their own lives and those who people in a period within or beyond Britain, including the impact of oppression, conflict and rebellion are important to them. living memory. technology, culture and beliefs. on the everyday life of a past or Create an in-depth study of an ancient society. aspect of British history beyond 1066. Theme(s)
Once Upon a Time
Marvellous Monarchs
Ancient Civilisations
Knowledge
Kings and queens are known as royalty. Some kings and queens are real people and some are characters in stories.
Hierarchy structures in ancient civilisations include (from most to least powerful) a ruler; officials, nobles or priests; merchants, workers and peasants and slaves.
Skill
Explore and talk about pictures, stories and information books on the theme of royalty.
Hierarchy is a way of organising people according to how important they are or were. Most past societies had a monarch or leader at the top of their hierarchy, nobles, lords or landowners in the middle and poor workers or slaves at the bottom. Describe the hierarchy of a past society.
Hierarchy and Power
Describe the hierarchy and different roles in ancient civilisations.
Britain at War Maafa Leaders and monarchs have changed the course of history in a variety of ways, including invading other countries; oppressing groups of people; advocating democracy; inspiring innovation or introducing new religious or political ideologies. Describe and explain the significance of a leader or monarch.