voroflora
astudyonbiomimicrydesignwithin hospitalityarchitecture


Type Academic
Level Graduate
Location Shiraz,Iran
PlotArea 50,000sqft
Instructor Dr DebajoyotiPati
Team LadanKhalvati
Roleinteam Analysis,design, graphics,presentation
Software:




“biomimicryarchitectureistakinga designchallenge,findinganecosystem thathassolvedthatchallenge,andthen translatingitintoaphysicalspace”
Biomimicry is a technical approach to architecture that studies nature’s models and then emulates these forms, processes, systems, and strategies to solve human challenges sustainably The objective for this project was to redesign a previous building site to be more sustainable and regenerative This includes exploring natural architecture concepts and using fundamental concepts of LEED to guide the design process
VoroFlora is a redesigned hotel in Shiraz, Iran that blends traditional Persian architecture with modern and sustainable design applications The project hosts eight floors including an underground parking level and a rooftop garden Located within a semi-arid climate zone, the design requires to address the climatic challenges of high energy usage, water conservation, and ventilation and cooling strategies. Inspired by the biomimicry of natural cell patterns, VoroFlora adopts the Voronoi cell pattern to optimize efficiency and function throughout the design, as seen through the interiors, site landscape, and the highlighted responsive façade. The responsive façade is designed to detect environmental changes such as light, heat, humidity and air quality within the region and adjust the shape and orientation of the Voronoi cells in the façade to optimize natural light and temperature control within the building.
1stPlaceinthe2023ASIDCelebratingDesignTexasAwards,StudentDesignCommercialCategory








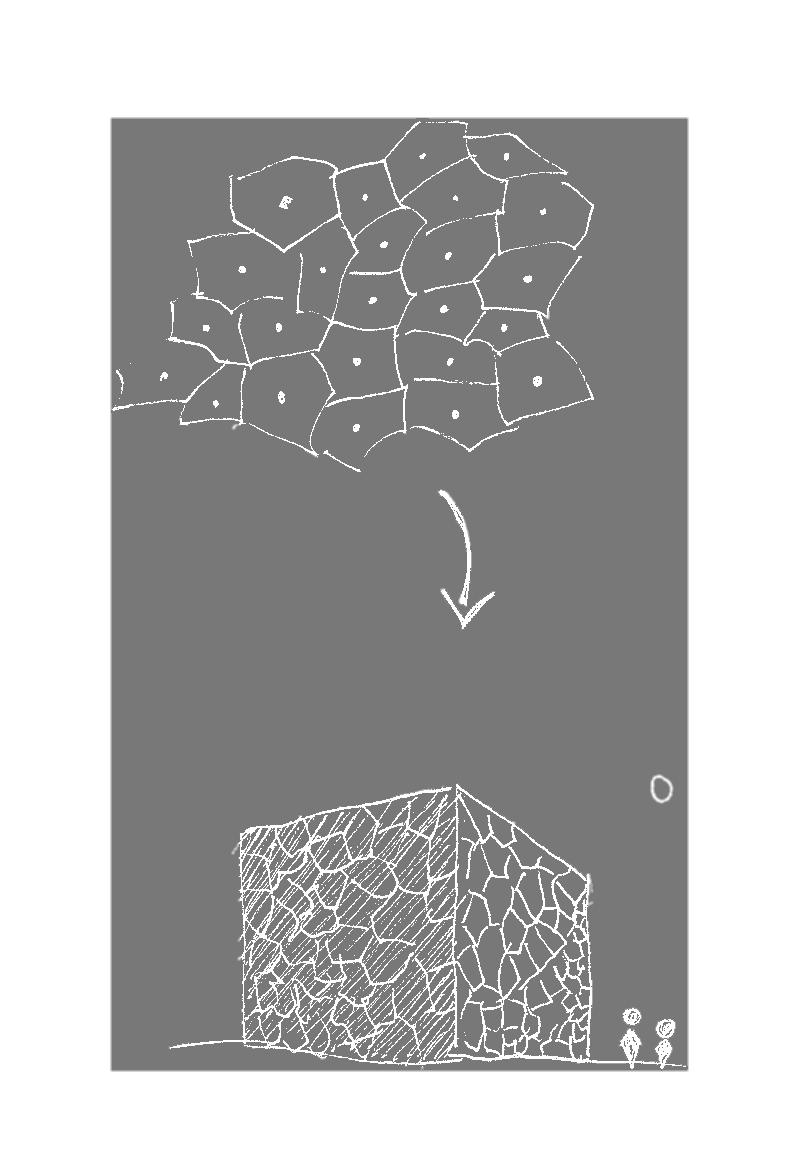

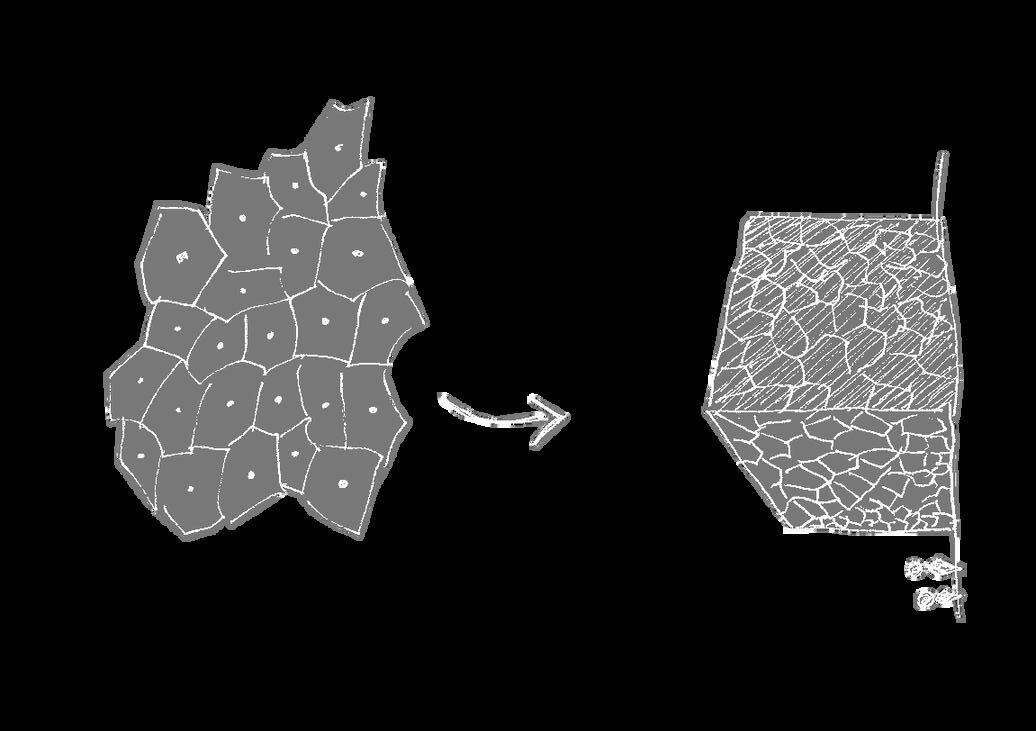


In living organisms, cells are arranged to optimize the distribution of nutrients, waste, and other essential materials. This is achieved through a complex system of intercellular communication and signaling, ultimately creating a network of cells that are arranged in a pattern that maximizes efficiency, known as the Voronoi pattern
The responsive façade in this design adopts the Voronoi pattern and its processes to optimize overall building energy consumption The Voronoi facade cells change shape in response to environmental factors such as light, heat, and humidity. This, as well as reorienting the building to optimize sunlight from the east-west faces, cools the thermal mass of the building, allows temperature and light control within the interiors, and reduces the demand of mechanical cooling systems

Shiraz has a semi-arid climate The region hosts comfortable levels of humidity annually, allowing natural ventilation strategies to occur
Average Humidity (%)
Little to no rain within the annual year, water conservation strategies can play a role in offsetting the building's energy usage






