Mouth Matters
Oral Health Before, During &After Cancer Treatment
Jill Meyer-Lippert, RDH




What I thought would happen


What really happened




Oral Health Fast Facts from the CDC
• Oral health is essential to general health and well-being.
• Oral disease can cause pain and infections that may lead to problems with eating, speaking, and learning. It can also affect social interaction and employment potential.
• The three oral conditions that most affect overall health and quality of life are cavities, severe gum disease, and severe tooth loss
https://www.cdc.gov/oralhealth/fast-facts/index.html
What determines oral health or oral disease?
The Oral Microbiome


We’renotallbad!


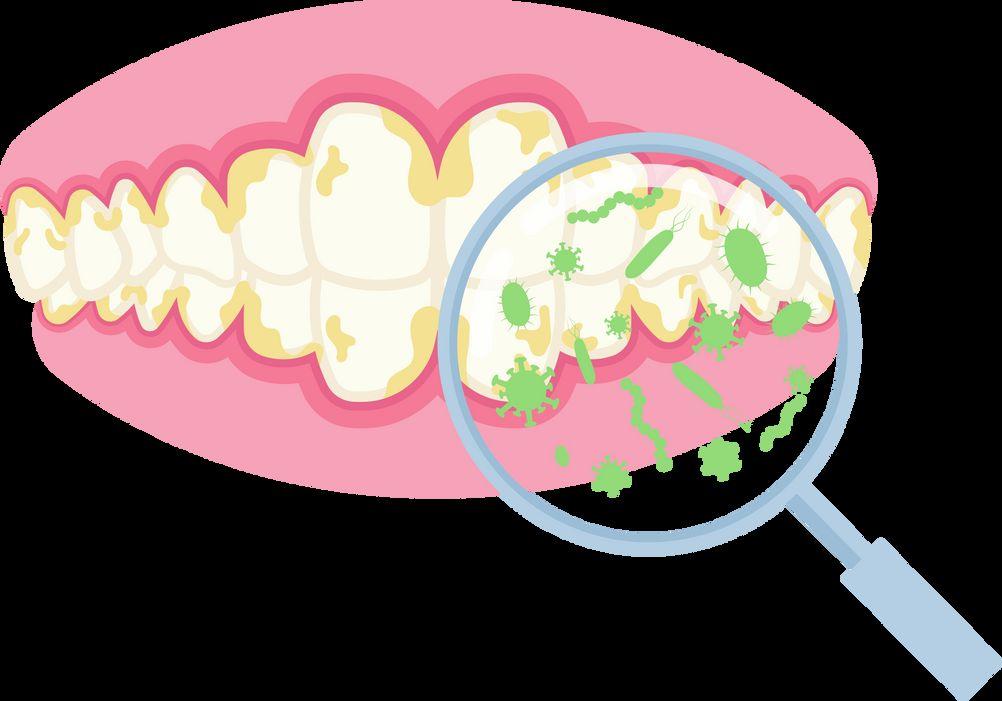





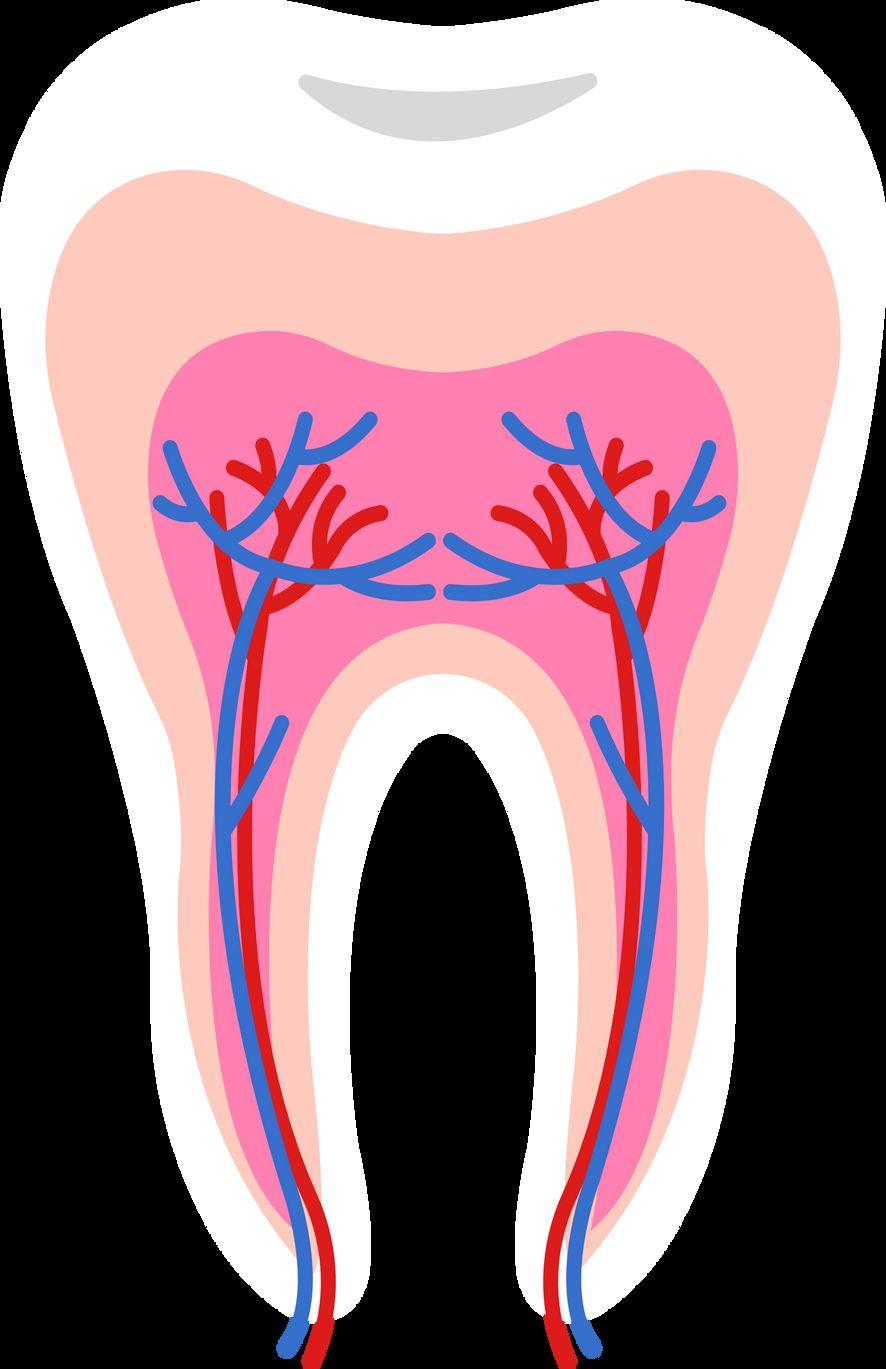
Tooth anatomy & cavities
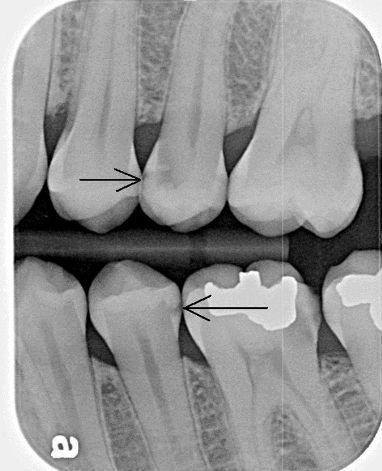
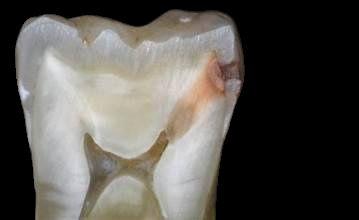
Bacteria produce acidic byproducts
Acid removes minerals from teeth



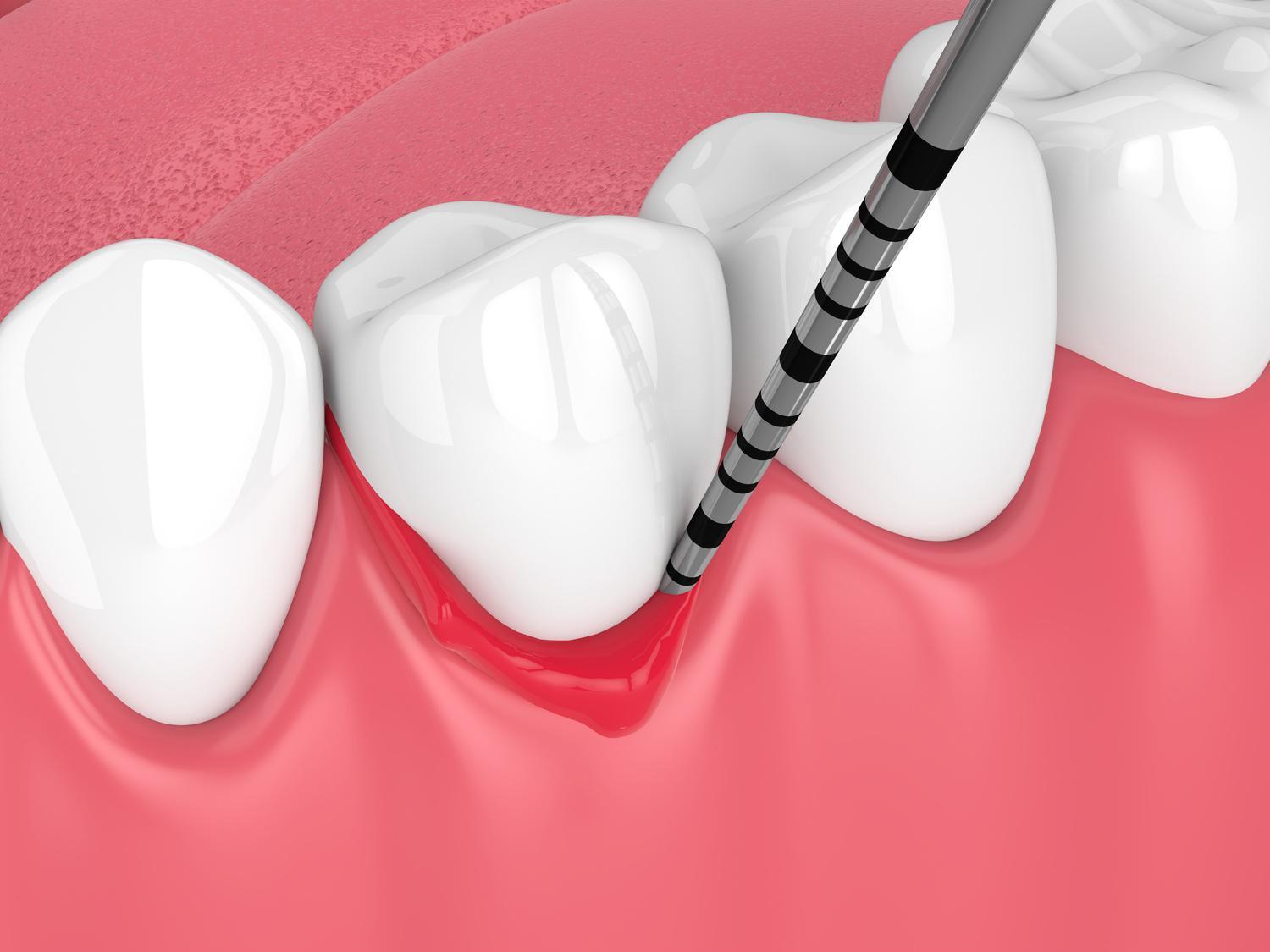
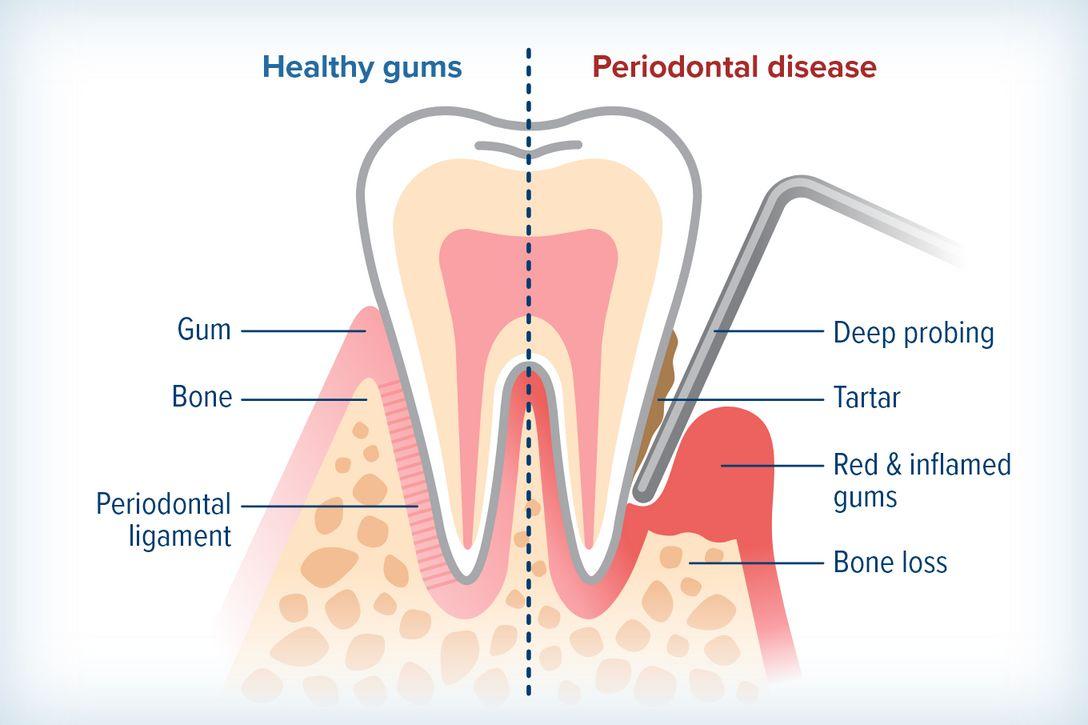
Gum disease (gingivitis & periodontal disease)
What influences your oral microbiome?

Genetics

Sharing germs

Professional Dental Care
Oral Hygiene


Diet, Lifstyle Choices
Medications & Other Medical Conditions
The oral-systemic link

Heart disease Strokes
Erectile dysfunction

Astma and respiratory infections
Alzheimer’s Disease
Diabetes


Pre-term & low
birthweight babies
Certain cancers
What therapies can affect oral health?
• Chemotherapy
• Radiation therapy
• Surgery
⚬ Oral hygiene limitations
• Hormone suppresion
• Targeted therapies/Immunotherapy
⚬ Antiangiogenics
• Corticosteroids
• Antiresorptive Medications
• Antianxiety/antidepressants
• Diet (Ensure, Gatorade, etc.)
• Pain medications


Early Intervention and Patient Education are Key
Anticipate potential problems and start treating them before they have a chance to start!
Oral Health Risks
**Depending on type of cancer & type of treatments**

• Hyposalivation/Xerostomia (dry mouth)
• Oral Mucositis/Stomatitis (mouth sores)
• Caries (cavities)
• Periodontal Disease (gum disease)
• Enamel Erosion
• Infections (bacterial, fungal and viral)
• Dysgeusia (taste changes)
• Dysphasia (trouble swallowing)
• Trismus (limits jaw opening)
• Osteonecrosis of the Jaw from Radiation to the head & neck or from certain medications
• Graft vs. Host Disease after bone marrow
Dry Mouth (quantity and quality of saliva)
More than a comfort issue
• Tissue lubrication
• Wound Healing
• Infection prevention
• Buffers oral pH
• Remineralized teeth
• First step in food digestion
• Plays a role in taste

Dry Mouth - Simple Tips
• Stay hydrated
• Diet changes
⚬ Avoid caffeine & alcohol
⚬ Avoid dry, crusty foods
⚬ Use sauces & gravies
• Breathe through nose
• Use humidifier


Rx and OTC Dry Mouth products
• No “one size fits all”
Think long-term effects vs. just masking symptoms
Oral pH and oral diseases
Demineralization/Remineralization

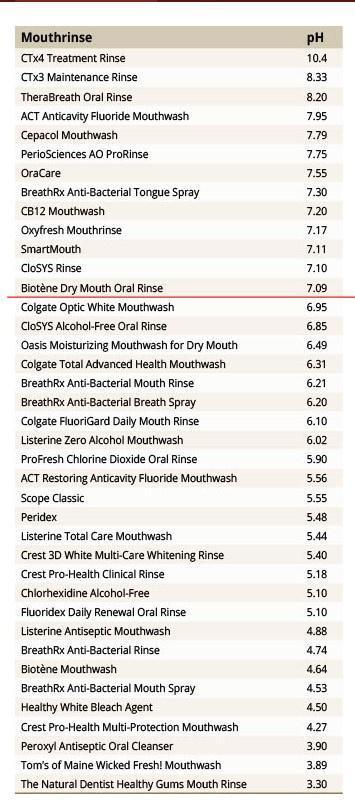
Florida study evaluates acidity levels in oral lozenges
https://www.dentistryiq.com/dental-hygiene/article/16367852/florida-study-evaluates-acidity-levels-in-oral-lozenges

•DenTek OraMoist, pH 2.9
•Cotton Mouth Lozenges, pH 3.1
•MedActive Oral Relief Lozenges, pH 3.2
•Hager Pharma Dry Mouth Drops, pH 4.44
•Rite Aid Dry Mouth Discs, pH 5.1
•CVS Dry Mouth Discs, pH 5.3
•ACT Dry Mouth Lozenges, pH 5.7
•TheraBreath Dry Mouth Lozenges, pH 5.82

Oral Mucositis

Treatment and prevention are primarily aimed at reducing modifiable RISK FACTORS:
Dry Mouth
Existing Dental Issues
Poor Oral Hygiene

Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
• What is it?
• What medications put us at risk?
• Signs and symptoms
• What initiates most cases?
FOCUS
ON PREVENTION
⚬ Good communication is vital
• Treatment options
Toothbrush Basics

Size/shape of brush
Softness of bristles
When to replace
Protecting from germs
How is brush stored
Sharing is not caring
Detergent s
Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (SLS)
• Known to penetrate skin and cause cutaneous irritation
Cocamidopropyl betaine
• Allergy to CAPB is most commonly seen in a head and neck distribution, although other patterns have been identified.”
American Journal of Contact Dermatitis
2001
• American Contact Dermatitis Society Allergen of the Year 2004
Drying & Irritating Ingredients

The Scoop On Sugars
Xylitol & Erythritol
• Improve oral microbiome
• Buffers oral pH
• Exposure/dosage
• Introduce slowly into diet
• Safe for diabetics

• Keep away from pets
Systemic vs. topical
OTC vs. Prescription
Recommended vs. reality • Check for potentially irritating detergents
image courtesy of bmjopen.bmj.com/content/10/9/e038606
Prebiotics vs. probiotics


“My hair will grow back, my teeth won’t”




Over-the-counter products