




For nearly 75 years, Uhlmann has been a Partner to the Pharmaceutical Industry across the globe for it’s packaging requirements with innovative and futuristic packaging solutions
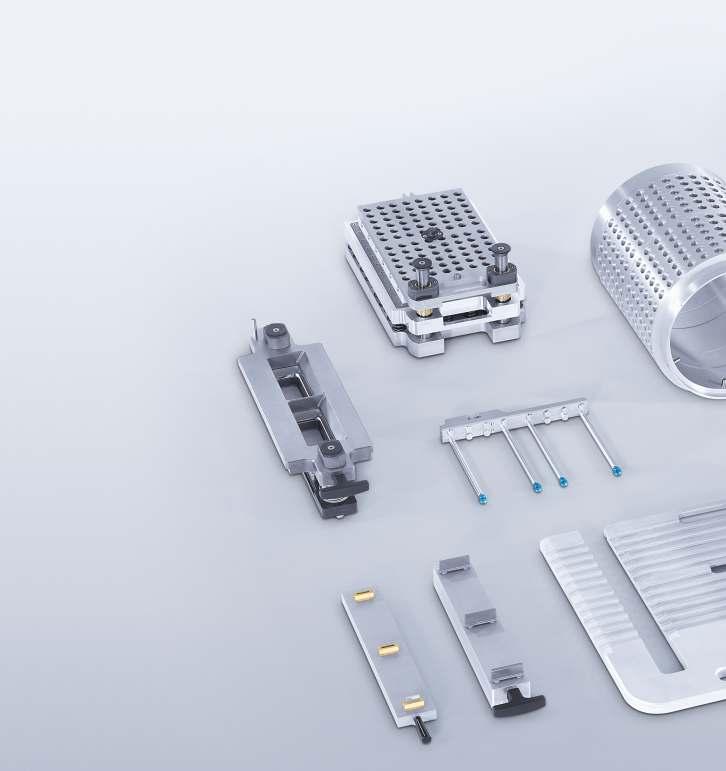
Backed with Uhlmann’s Corporate philosophy of being Strong, Open Minded, and Reliable, Uhlmann o�ers a wide range of Blister cartoning solutions from small batches to campaign batch requirements
Higher productivity requires quality format parts apart from e�cient machines. Tools and format parts produced by Uhlmann are designed, extensively tested, and run under simulated production.
Promoting“local for local”, Uhlmann manufacture it’s Format parts in India for selected equipment, helping in achieving:

Improved lead time, reliability & overall e�ciency.
Faster and easy changeovers resulting in reduced turnaround time
Accurately designed, reliable precision tools and harmonized format parts – tailored for your requirements. Higher return on investments with long life cycles, continuous productivity, and high overall e�ciency


ProcessingandpackagingsolutionsfromAxomatic,OmagandComasarenowavailableintheIndian Sub-continentwithcomprehensivelocalknowledgeandservicessupportincludingfastdeliveryofspares.







US FDAapproved cGMPdesign · Tolless change over · compatible with all leading bottle vial suppliers · 100 % checkweighing or sample checkweigher options · out put speed from 60bpm to 240 bpm · complete line solution

CAM has manufactured and successfully installed the Complete Packing line for Syringes and Vial in India.The Line Machines consist of:
DNRS - DE-NESTER AND RE-NESTER
• TUB Loading / Buffer • Robotic Pick & Place • Empty TUB transfer
nMX-F- BLISTER PACKING MACHINE
• Integration with De-Nester including Buffer Unit • Robotic Pick & Place for placing PFS in cavity
• Online Blister Inspection System • Online TIJ Printing & Its Verification (OCV/OCR)
S205
PRE-FILLED SYRINGE ASSEMBLY
• Mono Block Machine – for 400 Syringes / min • Plunger Rod
Insertion / Placing • Back
Stopper • Online TIJ Printing & Its Verification (OCV/OCR) • Can handle 0.5 ml to 10 ml
Pre-Filled Syringes
Complete Line is with cGMP Standard and having 21 CFR Part 11
Compliance
TTS
ONLINE TRACK AND TRACE SYSTEM
SMP INTEGRATED HORIZONTAL CASE PACKER
• Up to 10 cases / min
• Matrix Formation
• Labelling – Print & Apply
• OCR / OCV for Label
• Trackability Matrix
HV/2- AUTO CARTONING MACHINE
• Robotic Pick & Place – for single or multiple PFS in Carton • Leaflet Feeder– Pre-folded / GUK • Booklet Feeder • Barcode / Pharma Code Reader
• Integrated with Blister Machine
• Online TIJ Printing & Its Verification (OCV/OCR) • Vial Feeder • Glue Unit Attachment (Optional)
ASB38
ONLINE COLLATION WITH STRETCH BANDING / OVER-WRAPPING
ZP1 PALLETIZER FOR SHIPPERS
CAMPAK India Private Limited W-326, TTC Industrial Area, MIDC, Rabale, Navi Mumbai – 400 701 sales@camindia.co.in / www.campackaging.it




Dear Pharma Pals, Cleanroom validation plays a pivotal role in industries where product quality, safety, and regulatory compliance are paramount It confirms that these environments meet specific standards and consistently function as intended, safeguarding product integrity and consumer well-being

Pradip Bhalerao, a respected figure in the Indian pharmaceutical project industry, writes on Cleanroom Validation in the exclusive in this issue
For a successful validation, it is of utmost importance to have an all-inclusive and well-thought-of design for the cleanroom The essence of any successful cleanroom validation lies in adopting Quality by Design principles
When designing a cleanroom, it's important to take into account the amount of space its mechanical equipment takes up In the design stages, keeping flexibility in mind is essential, as this helps with issues of expansion and modification further down the line, as well as with the addition of new equipment and tools as necessary Read on the requirements to consider when designing a new cleanroom. The article also reminds us that the impact of a failed cleanroom validation on the cost of a project can be significant and multi-faceted as the majority of resources are consumed by the project by the time it reaches the validation stage
In recent years, formulations based on pellets have been the trend New technologies make it possible to circumvent property rights for active ingredients and are therefore very popular with pharmaceutical customers The article by Klaus Möller, Head of Business Development, Glatt Process Technology, discusses the technologies that are the most important.
Harjit Singh Dhaul Publisher & EditorPUBLISHER & EDITOR
Harjit Singh Dhaul
Editorial Office
Global Vision

Ensuring Quality and Compliance in Controlled Environments
Exclusive on the pivotal role that cleanroom validation plays in industries where product quality, safety, and regulatory compliance are paramount.
Renaissance of pellets is promoting innovative technologies
Klaus Möller, Head of Business Development, Glatt Process Technology Pharma, writes
PHARMA 4.0
Digital Transformation for the 21st Century

Exploring the potential of Pharma 4.0 to revolutionize the pharmaceutical industry in the 21st century

26-B, Rebellow Cottage, Gaon Devi Road, Poinsur (E), Kandivli 400 101, E-mail:info@pharmamachines.com
Advertisement/Circulation/
Subscription enquiries:
Mobile: +91 93 24 577012 / +91 77 15 957717
E-mail:info@pharmamachines.com
Website: www.pharmamachines.com Printed
Article by Prof. Frank Sullivan, Director, Radiation Oncology, Prostate Cancer Institute (PCI) NUIG, Galway Clinic, and founding CMO of Whyze Health.
Driving digitalization of products and supply chains
Antares Vision Group is driving digitalization by leading traceability, inspection, and integrated data management





Health Ministry inspected over 150 pharmaceutical factories in India and found that there was a prominent lack of safeguards, including an absence of internal product quality review as well as a lack of professionally qualified employees.
These reports come after multiple Indian pharmaceutical companies came under the government's scanner following deaths linked to faulty cough syrup manufactured in the country and shipped overseas. Faulty medicines were linked to the deaths of at least 95 children overseas.
According to the Health Ministry, the investigation also revealed that there was an absence of "quality failure investigation," as well as a lack of testing of raw materials.
The Ministry, after inspecting 162 pharmaceutical factories and 14 public laboratories, pointed to infrastructural deficiencies that play a crucial role in cross-contamination at drug factories. The investigation also flagged faulty design of manufacturing and testing areas at these factories.
The Union Health Ministry has proposed that either the Centre or state authorities be empowered to regulate the manufacture of drugs and cosmetics, changing its earlier proposal of allowing only the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) to do so.
As of now, all manufacturing activities relating to drugs and cosmetics are regulated by only the state governments through their drug control organizations.
The draft bill also mentions that the Central government may regulate, restrict or prohibit selling, stocking, exhibiting or offering sale or distribution of any drug online by notification. The latest draft of the New Drugs, Medical Devices and Cosmetics Bill, 2023, which seeks to replace the Drugs and Cosmetics Act of 1940, is yet to be
approved by the Cabinet.
The Union Health Ministry has also proposed a separate chapter for regulating cosmetics. Besides, regulations for conducting clinical trials for new drugs and medical devices have been brought under the draft bill. It also provides for regulation of clinical trials of new drugs and investigational new drugs.
The government has approved the export of BCG vaccine manufactured by the Serum Institute of India to Canada for immunotherapy to treat bladder cancer.
BCG as immunotherapy is a live freeze-dried preparation derived from attenuated strain of Mycobacterium bovis (Bacillus Calmette Guerin). The product is for intravesical instillation and is available from the Serum Institute in 40 mg and 80 mg presentations.
As part of the therapy, the vaccine is administered into the bladder through a catheter where it stays in the lining of the bladder for a specific duration affecting the cells and fighting cancer without impacting other body parts.

India's pharmaceuticals industry is the third largest by volume and the 13th largest by value in the world producing more than 60,000 generic drugs across 60 therapeutic categories, stated Minister of State (MoS) for Chemicals and Fertilizers, Bhagwant Khuba.
The statement from the minister came as a written reply on questions relating to the consumption of generic drugs in the last five years. The reply also included the annual turnover of Indian pharmaceutical sector during the last five years. The turnover for FY22 stood at Rs 3,44,125 crore.
According to rating agency ICRA, the revenue of India's top domestic pharmaceutical companies is expected to grow by 7-9 per cent in the current fiscal. The growth will be supported by an 8-10 per cent expansion in the domestic market and a 6-8 per cent rise in the US market, while revenues from the European and emerging markets are expected to increase by 3-5 per cent and 8-10 per cent. August-September 2023




India's pharma industry is heavily dependent on China for bulk drug imports, with 43% of total pharma imports originating from China, according to a report by CareEdge. This raises concerns due to the on-going geopolitical tensions between the two Asian countries.
Among India's overall pharma imports, bulk drugs continue to contribute 55-66 per cent and dependency on China for the same is expected to remain high in the coming years
The contribution of bulk drug imports from China has exhibited significant growth in both value and volume terms, increasing from 64% and 62% during FY14 to 71% and 75% during FY23, respectively," the report said.
India's dependency on Key Starting Materials (KSM) from Beijing exceeds 50%. India also imports certain formulations which account to 30 per cent to 35 per cent along Ayush and Herbal, and Surgical products, accounting to the rest.
Import dependency is on a high despite maximum project completions. The total project completions in the drugs and pharmaceuticals industry during FY24 are expected to be around $516 million which is the highest registered during the last decade, as per the CareEdge report.
"The date for implementation of track and trace system for exports of drug formulations with respect to maintaining the parent-child relationship in packaging levels and its uploading on central portal has been extended up to February 1, 2024 for both SSI and non-SSI manufactured drugs," the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) said in a public notice
Earlier also, the dates have been extended from time to time. The manufacturer or the exporter of drug formulations would have to print the barcode as per global standards at different packaging levels -primary, secondary and tertiary -- to facilitate tracking and tracing of their products.
Barcode helps in tracking and tracing the origin of drugs, which minimises the chances of genuine medicines being considered spurious, sub-standard or counterfeit.
According to the Pharmaceuticals Export Promotion Council of India (Pharmexcil), India's pharmaceutical exports this fiscal year are set to grow nearly twice as fast as last year to hit sales of $27 billion, driven by strong U.S. buying, despite deaths linked to Indianmade cough syrups.
The robust forecast comes against the backdrop of earlier concerns from the government that last year's deaths of dozens of children in Gambia, which the WHO linked to drugs made in India, had "adversely impacted the image of India's pharmaceutical products across the globe"
Sales to the United States, India's biggest market with 30% of its overall pharma sales, rose 6.2% to $7.5 billion last fiscal year. India's overall pharma exports in the April-June quarter rose 5% to $6.58 billion.
India is seeing good overall demand for drugs for central nervous system conditions, cardiovascular and oncology.
Pharmexcil delegations have visited countries including Nigeria, Egypt and Russia in recent months to allay any concerns about Indian drugs
Researchers are set to conduct a first-of-its-kind clinical trial in India to investigate the effectiveness of administering the antioxidant glutathione orally against early Alzheimer's disease (AD).
The initiative aims to not only treat but also potentially delay the onset of the progressive neurological disease that destroys memory and other important mental functions and, eventually, the ability to carry out the simplest tasks
Titled "Impact of Glutathione (GSH) Supplementation in Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) Patients: A Randomized Control Trial", the study is funded by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), approved by the Drugs Controller General of India and is listed on Clinical Trials Registry-India (CTRI).
Glutathione is a chemical and an antioxidant present in the brain. The brain consumes oxygen for its normal functioning and in the process, creates charged particles from metals, including iron, naturally present in the brain. These charged particles tend to combine to form radicals, which contribute to creating oxidative stress in the brain, which can damage brain cells, or neurons, resulting in their death.

Tyra Biosciences has received orphan drug designation (ODD) from the USFDA for TYRA-300 to treat achondroplasia, a common form of dwarfism.
Individuals with achondroplasia encounter significant skeletal complications including sleep apnoea, hydrocephalus and cranial and spinal stenosis.
Originating from the company's in-house SNÅP platform, TYRA-300 is an investigational, oral, FGFR3-selective inhibitor currently being developed to treat cancer and skeletal dysplasias including achondroplasia.
It is under assessment in an open-label and multi-centre Phase I/II clinical trial for untreated and resistant FGFR3+ advanced solid tumours (SURF301).
The study is enrolling adults with advanced urothelial carcinoma and other solid tumours with FGFR3 gene alterations.
TYRA-300 has also shown positive preclinical results in skeletal dysplasias.
BlueRock Therapeutics has signed a collaboration and option agreement with bit.bio to discover and manufacture iPSC (induced pluripotent stem cell)derived regulatory T cells (Tregs)-based therapies.
bit.bio will detect transcription factor (TF) combinations to reprogramme iPSCs into Tregs by leveraging its machine learning (ML) powered discovery platform.
The agreement also provides BlueRock options to license bit.bio's opti-ox precision cell programming technology, which is used for controlling the expression of TF combinations within Treg cell therapies.
The opti-ox technology leverages a dual genomic, safe harbour approach to cell programming. By deploying opti-ox, bit.bio will rapidly facilitate the TF-mediated transformation of iPSCs into highly defined cell types.
BlueRock is tasked with the global development and commercialisation of therapeutic candidates resulting from the partnership.
Oncolytic immunotherapy company CG Oncology has secured $105m in a crossover funding round to advance its clinical-stage bladder cancer programmes.
The financing round was led jointly by new investors Foresite Capital and TCGX. BVF Partners, Avidity Partners and Janus Henderson Investors joined them.
Current investors Acorn Bioventures, Decheng Capital, Ally Bridge Group, Malin Corporation, RA Capital Management and Longitude Capital also took part in the round.
The programmes include the single-arm, Phase III BOND003 monotherapy clinical trial of cretostimogene grenadenorepvec. This could potentially treat patients with high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) not responsive to bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG).
Cretostimogene grenadenorepvec is an oncolytic immunotherapy agent administered intravesically. It is being evaluated in a Phase II trial along with Keytruda (pembrolizumab) for the same indication.
The agent is also being analysed along with Opdivo (nivolumab) for the treatment of other bladder cancer types.
Ionis Pharmaceuticals has signed a collaboration and licence agreement with Novartis to advance a nextgeneration programme targeting lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)) for cardiovascular disease (CVD).
The partnership will discover, develop and commercialise the medicine for patients with Lp(a)driven CVD.
Lp(a) is a lipoprotein particle in the liver that comprises a particle similar to low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and apolipoprotein(a).
The agreement is based on the companies' ongoing collaboration in the development and commercialisation of pelacarsen.
Ionis first discovered pelacarsen in 2019 and granted exclusive global rights for its development, production and commercialisation to Novartis.
The investigational antisense medicine cuts the production of apolipoprotein(a) in the liver to decrease circulating Lp(a) levels.
Novartis is currently assessing pelacarsen's potential in a Phase III cardiovascular outcome study. Novartis will also assume exclusive responsibility for the development, manufacturing and potential commercialisation activities of the next generation Lp(a) therapy.





USFDA has granted approval for an expanded indication of Merck's (MSD) Ebola vaccine, Ervebo, for usage in paediatric populations aged 12 months and above. The vaccine prevents Zaire ebolavirus-caused Ebola disease. The company noted that the vaccine does not offer protection against other ebolavirus or Marburgvirus species.
Ervebo initially received approval in December 2019 for its usage in those aged 18 and above. Ebola virus disease is contagious and potentially deadly in both children and adults.
In July 2023, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency recommended granting expanded approval to the vaccine for usage in children aged one year and above.
The vaccine has already received marketing authorisation in the European Union for use in people aged 18 years and above.
The European Commission will take into account the opinion of the CHMP. Its final decision is anticipated in the third quarter of 2023.
ABM Therapeutics has received orphan drug designation (ODD) from the USFDA for ABM-1310 to treat patients with glioblastoma (GBM) harbouring the BRAF V600 mutation.
A small-molecule BRAF inhibitor, ABM-1310 is an orally administered medicine with high BRAF mutation selectivity, blood-brain barrier permeability and water solubility.
The inhibitor is currently in Phase I trials at clinical sites in China and the US, targeting advanced solid tumours with the BRAF V600 mutation.
Interim results from the US Phase I trial showed that ABM-1310 exhibited promising anti-cancer activity and a good safety profile in patients with advanced solid tumours, including primary brain tumours such as GBM and other gliomas.
In China, a new Phase I clinical study focused specifically on GBM has recently commenced.
GBM is a hard-to-treat and extremely aggressive brain tumour. Its treatment remains a significant challenge owing to tumorigenesis complexities and resistance to the therapy.
Traditional treatments such as surgical resection, radiation therapy and chemotherapy have limitations.
Taiho Oncology and Taiho Pharmaceutical have received approval from the USFDA for Lonsurf to treat adult patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). The approval is intended for using Lonsurf either as a single agent or with bevacizumab in patients previously treated with oxaliplatin, fluoropyrimidine and irinotecanbased chemotherapy, an anti-VEGF biological therapy, and if RAS wild-type [without mutations], with an antiEGFR therapy.
Taiho Pharmaceutical discovered and developed Lonsurf, an oral nucleoside antitumour agent.
It contains trifluridine, a nucleoside analogue based on thymidine, along with tipiracil, an inhibitor of thymidine phosphorylase (TP). This combination enhances exposure to trifluridine by inhibiting its metabolism by TP. Based on data from the Phase III SUNLIGHT study, the FDA granted approval for the combination of Lonsurf and bevacizumab
This combination showed improvements in progressionfree survival and overall survival in patients with mCRC after disease progression or who could not tolerate two previous chemotherapy regimens. These results were compared to the outcomes using LONSURF alone
The UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) has opened a vaccine development and evaluation centre (VDEC) to globally bolster pandemic preparedness
Located at the Porton Down site of the UKHSA, the facility is spread over 2,800m² of laboratory space. The centre will have more than 200 scientists, who will work on almost 100 projects
VDEC will facilitate the development of new vaccines by testing and assessing them against a range of threats that can lead to a health emergency
The facility will operate throughout the vaccine lifecycle, from product design to the assessment of effectiveness with the emergence of new variants
The key focus will be on pathogens for which there currently exist no vaccines, or for which vaccines are not regulated in the UK, including avian influenza and monkeypox.
VDEC is a unique facility in the UK, delivering multiple critical early pre and post-clinical research and evaluation studies in a single research facility








Approximately 2.8 million US adults are impacted by heart failure with iron deficiency or iron deficiency anaemia, which can affect their daily lives and activities.
Thousands of older adults across Europe suffer serious respiratory illness due to RSV respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) each year.
Alzheimer disease is the most common form of dementia and may contribute to 60–70 percent of cases.
Dementia is currently the seventh leading cause of death and one of the major causes of disability and dependency among older people globally.
Approximately 15% of adults aged 60 and over suffer from a mental disorder. Mental health and wellbeing are as important in older age as at any other time of life.
Around 2.4 billion people worldwide cook using open fires or inefficient stoves fuelled by kerosene, biomass and coal, which generates harmful household air pollution
Medication now accounts for more than half of all abortions in the US. (This figure doesn't include the increasing number of women who use unapproved suppliers as more states limit access to the drugs).
Trade generics are branded medicines that are not promoted to physicians but are directly sold through retailers and distributors. In India, trade generics have a market share of 20% by volume and 5-6% by value.
Diabetic Neuropathy is a condition that results in nerve damage in peripheral areas of the body. It's a prevalent condition affecting over 2% of the global population.
India has a high prevalence of diabetes, with an estimated 77 million adults living with the disease, projected to rise to 101.2 million by 2030.
Type 2 diabetes accounts for about 90-95% of all cases in India and is often associated with lifestyle factors such as poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and obesity.
An annual additional investment of less than US$ 1.40 per person is needed to scale up ear and hearing care services globally.
More than 1 million people are affected with echinococcosis, a parasitic disease caused by tapeworms, at any one time.
It is estimated that up to 70% of people living with epilepsy could live seizure-free if properly diagnosed and treated.
Trachoma, a disease of the eye, is a public health problem in 42 countries, and is responsible for the blindness or visual impairment of about 1.9 million people.
US$ 110 billion is lost each year in productivity and medical expenses resulting from unsafe food in low- and middle-income countries.



Pradip Bhalerao, Founder and Director of Pharmadeep Turnkey Consultants & Engineers Pvt. Ltd., is a respected �gure in the Indian pharmaceutical project industry, with an impressive experience spanning over 35 years. He has worked on a wide range of pharmaceutical projects, progressing from middle management to the esteemed position of Project Director. His expertise covers various aspects, from OSD manufacturing to vaccines and biosimilar Products.
Pradip has played a crucial role in enhancing the status of the Indian pharmaceutical project industry. He has been instrumental in helping several companies establish state-of-the-art manufacturing plants. His project work extends to major Asian countries, 14 African countries, and 2 European countries, showcasing his global reach and impact.
 By Pradip Bhalerao
By Pradip Bhalerao
Cleanroom validation plays a pivotal role in industries where product quality, safety, and regulatory compliance are paramount. These controlled environments, equipped to maintain low levels of airborne particles and contaminants, are crucial in pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, microelectronics, aerospace, and healthcare. Cleanroom validation con�rms that these environments meet speci�c standards and consistently function as intended, safeguarding product integrity andconsumerwell-being.
Cleanrooms, by de�nition, are designed to control airborne particulate and environmental conditions. Cleanrooms can be positive or negative pressure environments that sweep a speci�ed area with HEPA-�ltered air.
For a successful validation, it is of utmost importance to have an all-inclusive and wellthought-of design for the cleanroom. The essence of any successful cleanroom validation lies in adopting Quality by Design principles.


Assisting Pradip is a competent team of employees and associates based in India and Europe, who work together to serve an impressive list of clients.
In summary, Pradip Bhalerao's remarkable journey in the pharmaceutical projects domain has left a signi�cant mark in the industry. In recognition of his dedication, leadership, and exceptional contributions to the �eld of pharmaceutical project management, he was bestowed with an honorary doctorate.
When designing a cleanroom, it's important to take into account the amount of space its mechanical equipment takes up. In the design stages, keeping �exibility in mind is essential, as this helps with issues of expansion and modi�cation further down the line, as well as with the addition of new equipment and tools as necessary. Here are some requirements to consider when designing a new cleanroom: Room Flexibility: Additionally, a �exible cleanroom design means a quicker change-over of equipment, resulting in increased productivity, reduced cost, and minimal risk of contamination in the long term. When it comes to �exibility, there are several design elements you can employ to help make a cleanroom more “future-ready”.
as it helps provide the correct conditions needed for materials and instruments. Meanwhile, the control of humidity is needed to assure product handling conditions, stop work surface condensation, and reduce static electricity.
Pressurization: The cleanroom should be maintained at a static pressure higher than atmospheric pressure in order to prevent in�ltration by the wind for most of the applications. Additionally, the air pressure should be set up in a way that the air moves from clean to less clean areas. The exception to the positive differential pressure rule is biopharmaceutical facilities, which require the facility to be at a negative pressure when dealing with certain hazardous materials.
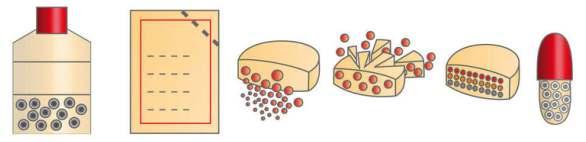
High-Efficiency particulate �lters: Practically a necessity when it comes to cleanroom design, these �lters are essential to controlling contamination since they �lter incredibly small particles with a 99.999% minimum particle-collective efficiency.

The most common testing performed during a cleanroom validation is indicated in Table 1 and commonly described below:
Airlocks: Since there can be a lot of dust, dirt particles, harmful chemicals, and other contaminants in these kinds of protected environments, airlocks can help minimize or prevent any changes in pressure that may compromise the work�ow.
Electrostatic Discharge: During the day-to-day use of a cleanroom, even something as innocuous as a person walking across the room can create turboelectric charges, which may inadvertently affect or damage certain things present in the room.
Temperature and Humidity: These two factors are integral to the design and function of a cleanroom. Temperature control is a must-have in any cleanroom



Air�ow or smoke pattern: For the evaluation of this parameter, a smoke generation device is used to add a visible fume in front of the HEPA Filters or in the area in which the product shall be exposed. The distribution of smoke is observed, documented, and recorded. It should be uniform following a laminar �ow pattern in the exit direction to return ducts without any major turbulence.
Air�ow velocity and changes per hour: For this test, the area of HVAC is divided into hypothetical grids, and the air velocity is measured at each grid and then the average air velocity (V) is calculated. The area of the HEPA �lter inlet (A) is calculated in feet and the total air volume (T) is then calculated by multiplying the average velocity of the air and the area of the inlet (T = A × V). After this, the volume of the room is calculated and the air changes per hour are obtained by dividing the total air change by the volume of the room.
Filter leak test: For the leak test of the HEPA �lter, a velometer is placed at the front of the AHU system and the air velocity is checked. The air velocity should be within the higher limit of the HEPA �lter.
Particle count: A particle counter is used to conduct the test. Particle count is taken at static conditions before the operation as well as operational working conditions. The particle count should be within the range as per the standards of particle classi�cation, for example, ISO Class 7, etc.
Viable particle monitoring: Viable monitoring is performed on a daily basis by employing the swab test and using a nutrient agar medium for the incubation of microorganisms. The different media plates are exposed in every manufacturing section. The microorganism count should be within the range otherwise, an investigation must be initiated to evaluate the root cause, effective corrective and preventive actions
Filter integrity test: The HEPA �lter integrity is tested by injecting particles of a predetermined size (0.2 um or greater) using an aerosol generator into the HEPA �lters to determine if they are retaining the aerosol particles. The 100% upward �ow of the aerosol must be captured into the HEPA �lter. A receptor probe that detects the aerosol is used to determine if they are passing through the HEPA �lter or not. Each HEPA �lter
must be tested and monitored periodically (e.g. annually or every six months). It is important to know if they are broken. Therefore, the amount of the aerosol detected passing through it is monitored and documented as part of the quali�cation. No residues or traces of aerosol must be detected after the HEPA �lter to pass the acceptance criteria of the �lter integrity test.
Pressure difference: It is calculated by making use of the mechanical gauges or pressure transmitters attached to the walls of the adjacent area. The pressure difference is generally kept positive from the cleanest area to the less clean area in the range from 10 and 30 mmHg pressure depending on the class of air and nature of operations.
Recovery test: The recovery of temperature and humidity conditions is checked after losing operational power conditions or doors opening. For example, the humidity and temperature are checked at the off position of the HVAC system. Then, the HVAC system is turned on to verify how much time it takes to recover the expected conditions, and the time required to stabilize the temperature and humidity is noted. Also, this test can be done, by opening the doors during some predetermined amount of time, then documenting the amount of time it takes to reach the expected environmental conditions.
Temperature and humidity uniformity test: The uniformity of temperature and humidity is monitored by employing a calibrated data logger, chart recorder, thermocouples, thermometer etc. The two parameters are monitored in a continuous manner, documented in the format, and stabilization is ensured within the speci�ed limit.
Fresh air determination: The fresh air intake is observed at the inlet on the fresh air damper. The total air change is calculated. The intake of fresh air is divided by the total air change in the room and multiplied by 100 to obtain the percent fresh air intake on each cycle by the HVAC system in all the individual rooms.
The cleanroom validation process is a comprehensive and rigorous procedure as described in Table 2 that comprises four key stages:


1. Design Quali�cation (DQ):
This phase ensures that the cleanroom's design aligns with the intended requirements and meets industry standards. It encompasses evaluating the cleanroom layout, air handling systems, and �ltration efficiency.
2. Installation Quali�cation (IQ): During IQ, the cleanroom's installation, calibration, and con�guration are meticulously tested and veri�ed. This step con�rms that the cleanroom equipment is correctly installed and performs as expected.
3. Operational Quali�cation (OQ): Under normal operating conditions, OQ assesses the cleanroom's functionality. Parameters such as air�ow patterns, temperature, humidity, and differential pressures are examined to validate the system's performance.
4. Performance Quali�cation (PQ): PQ evaluates the cleanroom's ability to consistently maintain the desired environmental conditions while operational.
This phase is critical in demonstrating that the cleanroom complies with industry standards.
Cleanroom validation must adhere to stringent regulatory guidelines, such as current good manufacturing practices (cGMP). Documentation, data analysis, and comprehensive reporting are essential throughout the validation process. Precise record-keeping ensures that the cleanroom remains compliant during audits and inspections. Regulatory Standards: Cleanroom validation is guided by various regulatory standards, including:
ISO 14644: This standard classi�es cleanrooms based on airborne particle concentrations.
US FDA Guidelines: The FDA provides comprehensive guidance for cleanrooms in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries.
EU GMP Annex 1: This document outlines the requirements for sterile medicinal products, including cleanroom speci�cations.
ICH Guidelines: The International Council for Harmonization offers guidance on pharmaceutical cleanrooms.
Cleanrooms are classi�ed based on the maximum allowable airborne particle concentrations per cubic meter. This is further elaborated in Table 3.
3
• Production size model
• 21 CFR Part 11
• Prevent powder inow with dust seal

• Improve durability

• Minimize noise and vibration
• Optimized design of powder duct

• 21 CFR Part 11
• Reinforce cleaning and maintenance
• Jacket type pan module
• 21 CFR Part 11
Sejong Pharmatech, a leading global market company that produces advanced pharmaceutical equipment with more than 30 years of accumulated know-how and excellent technology - increases the value of pharmaceutical machines by understanding the diversity and expertise required by the market beyond simple machine manufacturing.


are high productivity equipment and value for money, has always been.Tablet Press Vantix P Series Capsule Filling Machines F Series Automatic Tablet Coating
Cleanroom testing involves various procedures to assess performance and cleanliness. Some common tests include:
• Airborne Particle Count: This measures the concentration of particles in the air.
• Air�ow Velocity and Direction: Ensures proper air distribution and containment.
• Recovery and Leak Tests: Veri�es cleanroom integrity after brief disruptions.
• Non-Viable Particle Monitoring: Determines levels of airborne dust and contaminants.
• Microbial Monitoring: Checks for microbial contamination in the cleanroom environment.
Cleanroom Validation Challenges
Despite their critical importance, cleanrooms face several challenges in monitoring, testing, and maintaining compliance:
Equipment and Instrumentation: Ensuring monitoring equipment accuracy and calibration.
Human Contamination: Training personnel to prevent inadvertent contamination.
Facility Upgrades: Incorporating modi�cations without compromising cleanroom integrity.
Cleaning and Disinfection: Maintaining cleanliness to prevent particle generation.
Data Management: Handling and analyzing vast amounts of validation data. To address these challenges, organizations can adopt various solutions, including:
Robust Training Programs: Educating staff on cleanroom procedures and contamination control.
Regular Equipment Calibration: Ensuring monitoring instruments are accurate and reliable.
Stringent Cleaning Protocols: Developing thorough cleaning and disinfection procedures.
Periodic Revalidation: Regularly revalidating cleanrooms to ensure ongoing compliance.
Automation: Implementing automated systems for data collection and analysis.
Dos and Don'ts
Maintaining a cleanroom environment necessitates
adherence to certain dos and don'ts. The biggest variable in a cleanroom is the people. Despite all efforts and controls put into place, people are more prone to error than a set air �ltration system, or the workings of a stepper. Hence strict adherence to procedures is the �rst step for maintaining clean rooms.
Dos:
• Follow proper gowning procedures to prevent contamination.
• Maintain good personal hygiene and cleanliness.
• Use approved cleaning agents and procedures.
• Regularly inspect and maintain equipment and facilities.
• Adhere to cleanroom protocols and procedures.
• Do use only appropriate writing paper and pens
• Do use best practices when it comes to air�ow. Remember that the product gets air �rst.
• Do try to get to the service area, or gowning room, to blow your nose.
• Use the utmost precautions when sneezing and coughing.
Don'ts:
• Avoid bringing unnecessary items into the cleanroom.
• Refrain from eating, drinking, or smoking inside the cleanroom.
• Avoid opening cleanroom doors unnecessarily.
• Minimize excessive movements that may generate particles.
• Do not disregard deviations from cleanroom procedures.
• Wear any cosmetics in the cleanroom. This includes mascara, eyeliner, hair products, aftershaves, perfumes, and �ngernail polish.
• No leaning on surfaces or equipment.
• Allow unauthorized personnel into the room.
• Touch anything other than what you are working on, this means even scratching your face is prohibited!
The impact of a failed cleanroom validation on the


cost of a project can be signi�cant and multi-faceted as the majority of resources are consumed by the project by the time it reaches the validation stage. This is demonstrated in Table 4. Here are some of the potential consequences:
1. Rework and Redo Costs: When a cleanroom fails validation, it will likely require additional work, modi�cations, and improvements to meet the required standards. This could involve redesigning aspects of the cleanroom, purchasing new equipment, or retesting processes, all of which will incur extra expenses.
con�dence in the project if it experiences validation failures. This loss of trust can have long-term effects, affecting future project funding, partnerships, and customer relationships, which can indirectly impact the overall project's success and �nancial viability.
6. Resource Allocation: Addressing cleanroom validation issues may require diverting resources (�nancial, human, and time) away from other project aspects. This reallocation can disrupt budgeting plans and overall resource management, potentially leading to increased costs in other areas of the project. Overall, a failed validation of a cleanroom can have far-reaching implications, affecting not only the immediate costs of resolving the issues but also impacting the project's overall �nancial performance, reputation, and success. It underscores the importance of thorough planning, adherence to Quality by Design principles, and rigorous validation procedures to mitigate the risk of failure and its associated costs.
2. Production Delays: Failed validation means the cleanroom cannot be used for its intended purpose until the issues are resolved. This delay can lead to project timelines being extended, which in turn can increase costs due to longer operational overhead, additional labor expenses, and postponed revenue generation.
3. Compliance and Regulatory Costs: A failed validation may necessitate involvement with regulatory authorities to rectify the situation. This can lead to additional costs associated with compliance activities, potential �nes, and possible penalties if the failure is severe enough to violate regulations.
4. Loss of Productivity: If the cleanroom is a critical part of the project's operations, its failure can result in reduced productivity and efficiency. This can impact the overall project output, leading to potential losses in revenue or increased expenses to compensate for the reduced productivity.
5. Reputation and Customer Con�dence: Project stakeholders, investors, and customers may lose
Validation failures resulting from changes in validation criteria can be a serious concern with potential rami�cations for the project. Here's how such failures can impact the cleanroom validation process:
1. Inconsistent Standards: Changes in validation criteria can lead to confusion and inconsistency among the team members responsible for executing the validation. If the new criteria are not properly communicated or understood, it may result in deviations from the intended validation process, increasing the likelihood of failure.
2. Budget Overruns: When validation criteria change, it may require additional resources to meet the new requirements. This could include investing in new equipment, conducting extra testing, or extending the validation timeline. The unexpected expenses can lead to budget overruns and �nancial strain on the project.
3. Time Delays: Modi�cations to validation criteria often necessitate retesting and reassessment of the cleanroom processes. As a result, the validation process can be delayed, potentially impacting the project's overall schedule and causing delays in product development or manufacturing.






4. Resource Reallocation: Changes in validation criteria might require reallocating resources, both human and material, to accommodate the new requirements. This could disrupt the project's work�ow and create inefficiencies, leading to higher operational costs.
5. Regulatory Non-Compliance: If the changes in validation criteria are not adequately understood or addressed, the cleanroom might fail to meet the updated regulatory standards. This can result in noncompliance issues, potential �nes, and delays in gaining regulatory approvals, all of which can further escalate costs.
6. Reputational Impact: Frequent changes in validation criteria may raise concerns among stakeholders about the project's reliability and adherence to quality standards. This could negatively affect the project's reputation and erode con�dence in its success, leading to difficulties in securing future investments or partnerships.
To mitigate the impact of validation failures due to changes in criteria, it's crucial to follow best practices: Clear Communication: Ensure that any changes in validation criteria are communicated clearly to relevant team members and stakeholders. Everyone involved should understand the new requirements and their implications.
Thorough Planning: Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment before implementing changes to validation criteria. This can help identify potential pitfalls and provide opportunities for proactive solutions.
Incremental Changes: If possible, implement changes to validation criteria in a phased manner rather than all at once. This approach allows for better adaptation and reduces the likelihood of unexpected failures.
Collaboration and Expertise: Involve experts and experienced personnel in the validation process to ensure that changes are well-founded and aligned with industry best practices.
Documentation: Keep detailed records of validation procedures, criteria, and any changes made. This documentation is essential for traceability and for identifying the root cause of any validation failures.
By taking these precautions, the risk of cleanroom validation failures due to changes in validation criteria can be minimized, leading to a more successful and cost-effective project outcome.
Changing validation methods to economize on the cost of validation can lead to potential cost savings in several ways:
1. Reduced Testing Requirements: By adopting alternative validation methods, certain expensive or time-consuming tests may be replaced with more efficient and cost-effective ones. This can lead to savings in terms of labor, equipment, and materials required for testing.
2. Resource Optimization: Some validation methods might require specialized equipment or highly skilled personnel. Switching to more economical methods that utilize existing resources or less specialized personnel can result in cost savings.
3. Faster Validation Process: Certain validation methods can expedite the validation process, leading to shorter timelines and reduced operational overhead. Faster validation means quicker integration of the cleanroom into the project, which can result in cost savings.
4. Simpli�ed Documentation: Some validation methods may require less extensive documentation compared to others. Simpli�ed documentation can save time and effort, reducing administrative costs.
5. Risk-Based Approach: Implementing a risk-based approach to validation allows focusing on critical aspects while potentially omitting non-critical ones. This targeted approach can lead to cost savings by allocating resources where they are most needed.
6. Standardization: Adopting standardized validation methods can be cost-effective as it allows leveraging existing knowledge, templates, and best practices, reducing the need for custom solutions.
7. Regulatory Compliance Efficiency: Certain validation methods might align better with regulatory requirements, leading to smoother compliance processes and fewer rework costs due to noncompliance issues.
8. Training Costs: If the new validation methods are




more straightforward and require less specialized training, the costs associated with training personnel can be reduced.
Table 5 elaborates on the relationship between the costs of change in validation criteria v/s possible cost reductions in the validation process. It is important to note that while cost-saving is a valid consideration, any changes to validation methods should not compromise the integrity and quality of the validation process.
Validation is critical for ensuring the cleanroom's functionality, safety, and compliance with industry

Conclusion
Cleanroom validation is a critical process that ensures controlled environments maintain the highest levels of cleanliness and functionality. By adhering to regulatory standards, implementing continuous monitoring, and overcoming challenges through robust solutions, industries can con�dently produce high quality, contamination-free products while safeguarding consumer safety and meeting compliance requirements.
standards and regulations. Therefore, any cost-saving measures should be thoroughly evaluated and approved by relevant stakeholders, ensuring that they do not jeopardize the reliability and effectiveness of the cleanroom.
Additionally, the potential cost savings should be balanced against the risk of potential failures or noncompliance issues that might arise from changes in validation methods. Proper risk assessment and validation expertise are essential in making informed decisions that lead to both cost efficiency and maintaining high standards of validation.
Introduction: This technical case study delves into the cleanroom validation process carried out at a cutting-edge nanotechnology research facility. The facility specializes in the development of nanoscale materials and devices, where even the tiniest contamination can signi�cantly impact experimental outcomes. The stringent cleanroom validation aimed to maintain ISO 14644-1 Class 1 cleanliness standards, allowing a maximum of only 10 particles of 0.1 μm or larger per cubic meter.
Background: The nanotechnology research facility had invested substantial resources in designing and constructing a state-of-the-art cleanroom to ensure an ultra-clean environment for conducting sensitive experiments. Given the facility's focus on nanoscale research, ensuring the highest level of cleanliness and strict compliance with regulatory standards was crucial to the success of their research endeavors.



1. Design Quali�cation (DQ): The cleanroom validation process commenced with a design quali�cation phase. A multidisciplinary team of experts, including engineers, physicists, and validation specialists, thoroughly reviewed the cleanroom's architectural plans and equipment layout. Computational �uid dynamics (CFD) simulations were employed to assess air�ow patterns, particle dispersion, and identify potential contamination risks.
2. Installation Quali�cation (IQ): Following the construction phase, the installation quali�cation stage focused on rigorous testing and calibration of cleanroom equipment. The high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) and ultra-low penetration air (ULPA) �lters were subjected to challenging performance tests to verify their effectiveness in removing particles of speci�ed sizes. Precision instruments, such as laser particle counters and differential pressure sensors, were calibrated to ensure accurate data collection.
3. Operational Quali�cation (OQ): The operational quali�cation phase involved comprehensive testing under various operating conditions. The facility's HVAC system underwent extensive veri�cation to ensure optimal air�ow velocities, temperature uniformity, and humidity control. Pressure differentials between different cleanroom areas were carefully measured and validated to prevent cross-contamination.
4. Performance Quali�cation (PQ): The �nal stage of cleanroom validation, performance quali�cation, focused on the facility's day-to-day operations. Over an extended period, the cleanroom environment was continuously monitored, and data from particle counters, air samplers, and microbial tests were analyzed. The cleanroom's ability to consistently maintain ISO Class 1 cleanliness standards was closely scrutinized to ensure the success of nanoscale experiments.
The nanotechnology research facility encountered several complex challenges during the cleanroom validation process:
1. Particle Control at Nanoscale: Achieving ISO Class 1 cleanliness standards required rigorous control over nanoscale particles, which demanded specialized �ltration and cleaning techniques.
2. Instrument Calibration: Calibrating particle counters and other monitoring instruments at nanoscale accuracy levels posed signi�cant technical difficulties.
3. Microbial Contamination Control: Preventing microbial contamination at the nanoscale demanded stringent sterilization protocols and continuous monitoring.
Solutions Implemented
To overcome these technical challenges, the facility implemented the following solutions:
1. Advanced Filtration Technology: Cutting-edge ULPA and nano-�ltration systems were employed to achieve maximum particle removal efficiency at the nanoscale.
2. Nanoscale Calibration Standards: The facility collaborated with calibration laboratories to develop nanoscale calibration standards for precise instrument calibration.
3. Sterile Protocol Implementation: Rigorous aseptic techniques, automated sterilization, and continuous microbial monitoring were instituted to minimize microbial contamination risks.
The nanotechnology research facility successfully completed the cleanroom validation process, achieving ISO 14644-1 Class 1 cleanliness standards. The facility's cleanroom demonstrated exceptional performance, maintaining ultra-clean conditions and meeting the stringent requirements for nanoscale research.










Antares Vision Group is driving digitalization of products and supply chains by leading traceability, inspection, and integrated data management. AV Group helps companies and institutions to achieve safety,quality,efficiency,andsustainability,enablingTrustparency®.
It guarantees the quality and integrity of products, from production to market, by creating a unique digital identity for each saleable item. AV Group enables traceability from raw materials to the end user while ensuring compliance with regulatory authorities.
In Life Science industry Antares Vision Group providescomprehensive solutions, including hardware and software, to meet global regulatory compliance requirements across the supply chain, from manufacturing to logistics and veri�cation operations, distribution and retail.
Tracking and Tracing products at any point in the value chain is bene�cial for any industry. Track & Trace solutions for pharmaceutical improve product safety
by reducing the possibilities of counterfeiting and guarantee the reliability of the supply chain. By implementing lifetime traceability with Track & Trace solutions, it is possible to follow and monitor products throughout their life cycle.
A complete Track & Trace process, made of serialization and aggregation, represents the best possible control, as it could tell the whole history of any given product - from the manufacturer to the point of dispense, giving lifetime traceability across the supply chain.
The unique identi�er becomes the “digital passport” that not only enhances the protection of brands but also enables production line monitoring and




minimize recalled products and guaranteeing several bene�ts:
· Compliance with worldwide regulations and directives
· Get information from line to optimize production and distribution efficiency
· Facilitate recall operations
· Control product diversion
· Guarantee quality and originality of the product
· Ensure transparency of supply chain
· Get information about end users and shelf life
Serialization and Aggregation Solutions
Antares Vision Serialization and Aggregation
Equipments are designed to manage operations in production plants and warehouses:
· Compact, standalone serialization modules optionally combining advanced packaging functions (eg. Checkweigher, Tamper Evident Labelling) for quick deployment and line space saving.
· Print & Check Serialization kit integrated on 3rd party OEM equipment.
· Stand-alone automatic unit that performs all
serialization functions, including marking, recording and verifying all serialization data, ensuring data consistency and security under all conditions.
· Semi-automatic or Manual
Standalone Aggregation Modules for end-of-line packaging operations.
· Automatic Aggregation kits designed for installation on bundling machines, case packers and palletizing stations.
Track & Trace Software Solutions
Based on its unparalleled experience in installing track & trace on manufacturing lines, Antares Vision Group has developed ATS - Antares Tracking System - the fully integrated software platform to manage all serialization, aggregation, data storage and exchange activities.
ATS has proven its functionality and efficiency across thousands of serialization lines deployed worldwide. This includes current serialization and aggregation regulations in Turkey, South Korea, Argentina, China, EU-FMD, DSCSA and other international pharmaceutical product safety regulations.
ATS can manage all tracking data at line, plant or corporate level. Antares Tracking System coordinates line-level serialization of individual pharmaceutical packs, cases up to pallet. At plant and corporate level, ATS can interface with the internal ERP to manage order handling and exchange of serialization data with external supply chains and regulatory agencies
Key Bene�ts:
· Worldwide Regulation Compliance Expertise: Most widely installed solution
· Overall Scalability: Corporate, Production, and Warehouse Environment can be integrated with existing solutions
· Total Flexibility: New Devices, Procedures and Business Rules can be easily changed or added, and Independently Validated
· User-friendly Interface



In recent years, formulations based on pellets have been the trend. New technologies make it possible to circumvent property rights for active ingredients and are therefore very popular with pharmaceutical customers.Butwhichtechnologiesarethemostimportant?
Pellets are the jack-of-all-trades of solid dosage forms. Positioned somewhere between powder and granulate, they make bitter medicine more palatable and can even awaken a child's instinct to play when the dosage forms are imaginative enough. One wellknown example is the Xstraw, a plastic tube shaped like a drinking straw which is �lled with pellets of active ingredient, through which children or elderly people can take in the medicine with water. Pellets in tablets are also making a splash - hybrids which combine all the advantages of both dosage forms.
The pioneers in the development of these formulations, known as Multiple Unit Pellet Systems (or MUPS for short), was Astra Zeneca in 1999. Their move to embed the proton pump inhibitor Omeprazole in micropellets and then compress these pellets into immediate release tablets was an awardwinning one at the time. The development of MUPS
and Xstraw symbolizes the impetus pellets have fueled in recent years. Klaus N. Möller, Head of Business Development at Glatt in Binzen /Germany, explains: “New excipients, coating materials and sophisticated processes allow us to extend the patent protection period and to make the dosage form more attractive.“

The number of patents registered yearly for pelletbased formulations has increased exponentially and is set to continue. According to research performed by IMS Health, the market for OSD (Oral Solid Dosage Forms) is growing by 6 to 8 percent every year. The number of drugs approved by the FDA also re�ects this trend: in 2015, more than half were solid products.
Pellets, as de�ned by pharmacy guru Prof. Peter Kleinbudde are “an isometric agglomerate of powder particles in an approximate spherical or cylindrical form”, and are a task for perfectionists. The smoother






Process Solutions for:

Biologics & Complex Sterile injectables
Complete Contained Solutions
Continuous Manufacturing
Drug layering
Functional coating
Integrated Granulation
Operational excellence
Glatt, whose portfolio comprises all granulation and pellet manufacturing techniques, has spent recent years developing additional ways of“�ne tuning”the pellet process and has opened up a range of new, interesting possibilities for the lifecycle management of active ingredients.
con�gure �uidized bed machines on request to be multipurpose installations which then allow the continuous manufacturing of pellets The individual process modules for direct pelletization with rotor technology, for layering active ingredient and for pellet coating with Wurster technology or the simple drying of wet granulates can be added as necessary”
Wurster technology has been used in practice for many years: it is a �uidized bed technique in which starter cores or active ingredient pellets are sprayed with a insists. Möller says: “This method is robust and, because the process is so stable, it's generally the most popular way to process pellets”
Depending on the composition of the tablets, processing can last anywhere between eight and ten hours The knack is knowing how to optimize the efficiency and times of the production process Additionally, Möller recommends timely expert assistance during the development of the pellet formulation and the production process: “Right from the beginning, it will help to avoid mistakes and to keep an eye on process times and manufacturing costs”
Glatt's development team demonstrated how to re�ne an established process with the �uidized bed agglomeration technique known as MicroPx. The trick is to use the Conti process, which was conceived in Pharmaceutical Services' laboratories in Binzen: �rst, the active ingredient/excipient liquid is spray-dried to a very �ne product dust in a �uidized bed and agglomerated into tiny primary particles The micropellets then build up, layer by layer, until the desired size is reached
The heart of this technology is a zigzag classi�er which continuously ejects particles of sufficient size from the process, while simultaneously allowing smaller particles to reenter the process chamber
where they continue to grow. Möller explains that the result of this method is high dosage active ingredient pellets in the size range of 100 to 400 μm with a narrow particle size distribution and content uniformity of a consistent 90 to 95 percent.
This means that one signi�cant limitation of former times is now no longer an issue: for many years, the volume of a pellet-�lled capsule was larger – and therefore much harder to swallow – than the equivalent tablet with the same dose and composition. The use of microencapsulation, which changes bitter-tasting active ingredients into tasteless microparticles, means the taste is much improved now, too
Micropellets can be also pressed into tablets or MUPS tablets which already begin disintegration in the mouth. But the reason pharmaceutical companies �nd the MicroPx process so exciting is that it makes completely new formulations possible and therefore allows the legal circumvention of property rights The technology experts have long known the secret to the perfect pellet, too, an answer provided by Complex Perfect Spheres Technology (CPS). CPS is a souped-up rotor process for �uidized bed machines that uses direct pelletization to yield functionalized pellets and micropellets which are perfectly round and smooth.
Unlike classic rotor technology, the modi�ed technique uses a tapered rotating disc which allows the movement of particles to be directed and pelletization to be performed to a de�ned endpoint. The results are perfectly spherical pellets of exactly de�ned sizes of between 100 and 1500 μm and extremely narrow size distribution. This is how Glatt's own Cellets of microcrystalline cellulose are created, which are used as starter cores for pellets and in the Wurster process, for example – thus completing the formulation cycle
But what differentiates the manufacturing of granulates from the manufacturing of pellets?
From a pharmaceutical point of view, both processes are closely related and are only separated by the form of the particle, since the ideal shape for pellets is a sphere. There are also de�nite commonalities in procedure.
and rounder the pellets, the better they are at ful�lling their purpose. The equipment manufacturer Glatt and their specialists from Pharmaceutical Services have been actively pursuing the subject for years.
There are two fundamental ways of making active ingredient pellets: direct pelletization, in which the powdered active ingredient and excipient combine in a matrix, and active ingredient layering, in which uses side spray or Wurster technology to apply the active ingredient to a starter core of sugar or microcrystalline cellulose.
One interesting process variant for matrix pellets is the extrusion of wet granulate in a basket extruder and subsequent rounding in a spheronizer. Möller elucidates: “Continuous wet granulation, followed by extrusion, spheronization and drying now make it possible to perform continuous processes”. Active
ingredient pellets made like this can then be covered with a functional coating, be continuously mixed with excipients and be directly compressed into a MUPS tablet. The challenge is to avoid separation of the ingredients and destruction of the tablets during pressing.
Glatt, whose portfolio comprises all granulation and pellet manufacturing techniques, has spent recent years developing additional ways of “�ne tuning” the pellet process and has opened up a range of new, interesting possibilities for the lifecycle management of active ingredients.
One well-known example is the Xstraw, a plastic tube shaped like a drinking straw which is �lled with pellets of active ingredient, through which children or elderly people can take in the medicine with water. Pellets in tablets are also making a splash.
Drug Layering / Coating
Fluidized bed technologies such as Wurster technology and side spray technology
Uniformly round pellets with low to medium active ingredient payloads, homogenous functional coating layers, high content uniformity
Enteric-coated / prolonged release / controlled release / taste masked pellets; suitable for capsules, Xstraw, sachets, stickpacks, MUPS
Powder Layering Direct pelletization
Fluidized bed rotor technology
Uniform, round pellets with high active ingredient payloads, high degree of content uniformity, particularly suitable for active ingredients which are sensitive to moisture
Further processing to become enteric- coated / prolonged release / controlled release pellets
Fluidized bed technologies such as Micro- Px, ProCell and PCS
Uniformly round, high dosage active ingredient pellets in the size range of 100 to 400 μm with a very narrow particle size distribution, 90 to 95 % active ingredient content is possible with a high content uniformity
MUPS, ODT (Orally Disintegrating Tablets), capsules, Xstraw, sachets, stickpacks
Extrusion / spheronizationg
Basket extruders and spheronizers
But what differentiates the manufacturing of granulates from the manufacturing of pellets? From a pharmaceutical point of view, both processes are closely related and are only separated by the form of
Low to high dosage pellets in the size range of 0.5 to 2 mm, low porosity and a high content uniformity
Further processing to become enteric- coated/ prolonged release / controlled release pellets
the particle, since the ideal shape for pellets is a sphere. There are also de�nite commonalities in procedure.
As Möller explains: “The �uidized bed can be used for both granulation and pelletization. This is why we
Pellets and micropellets can be further processed into a wide range of
Pellet and Micropellet products
‘A
The new Innovation Center in Binzen was inaugurated last Fall What can you offer customers there?
Klaus Möller: We offer the customers a technical playground of 7000 m2 with state-of-the art machine technology The customer can perform batch and continuous processes in a non-GMP environment. The highly �exible machines can be con�gured as needed for granulation, pelletization and coating processes, from laboratory to production scale with batch sizes of up to 150 kg
A Glatt Modcos process machine is available, in which powder can be processed up to the �nished tablet in a fully-automated process. A whole range of modular processing equipment is available that can be arranged into a fullyautomated process line. Up to 6 processes can be performed in parallel.
What do you think is the most important unique feature?
Klaus Möller: The combination of Pharmaceutical Services' competences in the development of

The technology experts have long known the secret to the perfect pellet, too, an answer provided by Complex Perfect Spheres Technology (CPS). CPS is a souped-up rotor process for �uidized bed machines that uses direct pelletization to yield functionalized pellets and micropellets which are perfectly round and smooth.
formulations, processes and technology, the Innovation Center and the possibility to manufacture clinical samples under GMP conditions is, as far as we know, a range of services which only we can provide. Our technical capacities allow us to scale up from laboratory to commercial production scale seamlessly under GMP conditions This means we accompany the customer from the initial product idea to market launch.
In which speci�c problems can you offer assistance?
Klaus Möller: The development of processes and formulations is a massive playing �eld and places the customer before a huge range of challenges Our specialty is the development of solid dosage forms with a focus on complex formulations and we have great expertise in multiparticular systems This is why customers frequently come to us with matters such as product and process development or even the registration of a product.
connect with our experts at sales-pharma.india@glatt.com

Steriline and INCOME are two names, synonymous with each other, and for quality and service for the past three decades in the pharmaceutical industry in India. It is only a natural progression that the two companies together create an ecosystem to rapidly enhance their footprint on the Indian subcontinent to become more responsive to the ever changing and evolving needs of the industry, by forming Steriline Asia Pvt. Ltd.
Steriline Srl is an Italian company, established in 1989, specializing in the design, manufacturing, and installation of complete lines for the pharmaceutical industry. With a strong presence in the global market, Steriline has established itself as a leading provider of advanced solutions for the aseptic processing of pharmaceutical products.
INCOME, established in 1987, is an organization dedicated to the sale and service of pharmaceutical machines in India. “Good people to work with…” has been the motto of INCOME since the past three and a half decades which has resulted in a strong customer relationship which has lasted over many years.
Steriline offers a comprehensive range of products and services that cater to various stages of pharmaceutical production, including washing machines, sterilization tunnels, �lling machines, and capping machines. These machines are designed to meet the stringent regulatory requirements of the pharmaceutical industry and are known for their reliability, efficiency, and compliance with international standards.
As a testament to its success, Steriline has established
a global presence, serving customers in over 80 countries worldwide. Its customer base includes leading pharmaceutical companies, biotech �rms, and contract manufacturing organizations.
India remains one of the key markets for Steriline with an installed base of about 100 lines and 850+ machines.
The Indian pharmaceutical industry is today at a cusp of transformation in terms of technology and Steriline / INCOME pledge to continue to be at the forefront of the same; offering solutions which are value for money propositions and engineered for Indian operations.
Steriline Asia Pvt. Ltd will be based out of Mumbai with support offices based in regional cities of India.
The excitement on the formation of Steriline Asia Pvt Ltd, and the reasons behind the bold move was shared at an exclusive evening of networking cocktails and dinner on 23rd June 2023atHotelLeMERIDIEN,Hyderabad.




In an exclusive interview with Pharma Machines & Technology, Chiranjeevi Kondapaka, CEO, Steriline Asia Pvt Ltd, speaks on the coming together of Steriline and INCOME, the achievements and milestones in the last three decades, opportunities and challenges in the Indian market, objectives of the collaboration, and what more the Indian pharmaceutical industry can expect from Steriline Asia.

“As a testament to its commitment to R &D and technological innovation, in 2014 Steriline became a pioneer by introducing the �rst robotic application in the aseptic processing market: a groundbreaking solution that was built based on a“zero-loss philosophy”with no need of format parts.”
Q. What are your achievements and milestones in the last three decades?
A. Steriline was founded in 1989 in the Lake Como area (Italy), where its headquarters and manufacturing facilities are still based. First established as a manufacturer of washing machines and depyrogenation tunnels, Steriline launched its �rst complete line including isolators and �lling + capping machines in 2007. Since then, Steriline has been able to signi�cantly evolve into a single-source supplier of equipment solutions for the primary packaging of injectable drugs, ranging from complete lines to stand-alone machines.
As a testament to its commitment to Research & Development and technological innovation, in 2014 Steriline became a pioneer by introducing the �rst robotic application in the aseptic processing market: a groundbreaking solution that was built based on a “zero-loss philosophy” with no need of format parts.
Steriline currently develops, manufactures, and supplies a comprehensive range of solutions to pharmaceutical companies worldwide, including both mechanical and robotic applications for aseptic processing. These applications are compatible with vials, ampoules, cartridges and syringes and can
handle toxic or non-toxic products in both liquid and powder form.
Q. What led to the formation of Steriline Asia Private Limited?
A. Having collaborated for over a quarter century, INCOME and Steriline have fostered a relationship that goes well beyond a conventional Agent-Principal dynamics, evolving into a deep and robust partnership.
Recognizing the value of this long-standing association, we have made the decision to formalize and strengthen these bonds. By doing so, we aim to leverage the collective strengths of both organizations, enabling us to progress at an accelerated pace.
Q. What are the opportunities and challenges before you?
A. Steriline, as the numbers mentioned above indicate, has probably the largest base for European machines in India for the Sterile / Injectables. This itself provides challenges and opportunities.
The major challenge remains to ensure that each of this machine meets the regulatory standards which have evolved dramatically over the past 2 decades.
‘We aim to leverage collective strengths of both organizations'









Some of our machines are over 2 decades old but are still in operation by our customers! These machines need constant upgradation to comply with audits. Our engineering team has to come up with new and innovative solutions to ensure that our equipment doesn't become obsolete.
There is an industry saying that “If you are in the Generic Medicine Business, and are not in India, then you are not in the Generic Medicine business!”This statement sums up the opportunities available for any equipment supplier to be a part of the growth story in the Indian Pharmaceutical Industry! The challenge for Steriline Asia will remain to leverage on this opportunity on the ground level to create value for itself and its customers.
Q. Now that you have come together, what more can the Indian pharmaceutical industry expect from you?
A. The main objective behind any collaboration is to achieve a result that surpasses the individual capabilities of each organization involved. Every organization has its own strengths and weaknesses. By joining forces, the strengths are ampli�ed, and the weaknesses are mitigated. Consequently, our customers can anticipate signi�cantly improved products and services.
We are currently undergoing a substantial recruitment drive, actively seeking Software Engineers, Mechanical Engineers, and Design Engineers. With a larger team in place, we expect to enhance our response time to customers.
Previously, software support was provided from Italy, posing challenges due to different time zones, but now it will be provided locally, ensuring more efficient assistance.
Overall, I am con�dent that Steriline Asia will not only meet but exceed customer expectations in numerous aspects.
Q. What are your specializations in machinery / technology solutions?
A. Pharmaceutical machinery, especially from Europe, has reached a very high standard of technology, quality and reliability. The differentiation and specialization remains in customizations. Steriline machines are tailormade for every customer and provide unique operational advantages.
Kindly allow me to elaborate on the same with an example.
Some years back, a customer came to us with a unique requirement. They wanted to have a single machine which could process vials, pre�lled syringes and cartridges on a single machine as they had to cater to their market in all the three formats and their volumes were very low. Steriline rose to the challenge and developed and supplied a single machine which could handle all the 3 formats and yet comply to all requirements of GMP and efficiency.
Q. What are your expectations from the Indian market?
A. In simple words – “Continue to challenge us!”
Such challenges ignite the spark for our design team to develop “out of the box” solutions! Such challenges which motivate our support teams to do what is above and beyond what is merely written in a Business Contract!
Such challenges help us erase the words “Not Possible” from our lexicon!
Q. What are your projections for the future, any plan to set up manufacturing facilities in India?
A. Steriline acknowledges India's immense potential to emerge as a global manufacturing and service hub across various sectors, particularly in pharmaceuticals. Steriline Asia recognizes this opportunity and aims to actively contribute to India's growth trajectory.
In the initial phase, Steriline Asia will focus on serving and supporting clients across India and the broader Asian region. Additionally, we aspire to harness India's "soft power" by leveraging software customization and AI development for our machines.
As we progress, the natural progression would involve design and manufacturing operations aligning with this vision.
“There is an industry saying that 'If you are in the Generic Medicine Business, and are not in India, then you are not in the Generic Medicine business!' This statement sums up the opportunities available for any equipment supplier to be a part of the growth story in the Indianpharmaceuticalindustry!”







Across Europe, we continue to see a declining trend in the number of clinical trials taking place, most notably since the European Union Clinical Trials Directive (CTD) was established in 2004. The decline in clinical trials in Ireland is a major concern, as it means that fewer people are given access to potentially life-saving treatments.
This can have long-term effects on the quality of care being provided, as well as making it harder for new treatments to be developed and tested. However, the CTD has long-felt rami�cations for European patients The regulatory burden and insurance requirements grew even more burdensome. At the same time, the global COVID-19 pandemic also affected the number of clinical trials, which decreased by 19.6% in Europe between August and October of 2020 compared to 2019.
However, the effects of this decrease in access to clinical trials are being felt more severely in countries like Ireland which have far fewer trials than their peers. In this article, we explore the causes of decreased access to groundbreaking trials in Ireland and how to improve the quality of health care to create a healthier, more efficient system that better serves the Irish population.
Despite Ireland's signi�cant spend in its healthcare system, diverse population, and heavy inbound investment from the pharma and med-tech sectors, Ireland is not able to keep up with its European counterparts in terms of clinical trial participation.

Despite Ireland's signi�cant spend in its healthcare system, diverse population, and heavy inbound investment from the pharma and med-tech sectors, Ireland is not able to keep up with its European counterparts in terms of clinical trial participation. According to the Central Statistics Office (CSO) of Ireland, the foreign direct investment (FDI) in Ireland increased by €109 billion to €1,208 billion in 2021, a large proportion of that coming from the pharmaceutical and med tech sectors. Compared to Finland and Denmark, which both have similar populations and economic wealth, Ireland has only seen 18% of the 2,290 clinical trials conducted between 2013 to 2021 in the three countries. In contrast, Finland and Denmark have respectively seen 29% and 53% of these clinical trials.
Ireland is not alone. The number of clinical trials in the UK has also declined signi�cantly in recent times, with the Association of British Pharmaceutical Industry reporting that the number of industry-backed clinical trials started




in the UK each year fell by 41% between 2017 and 2021. This steep drop is due largely to a combination of factors, including slow set-up times, increased staff fatigue and turnover, and a reduction in the NHS's research capacity. Unfortunately, this means that UK and Ireland is lagging behind many of their European counterparts in attracting clinical trials.
The main barrier for Ireland when it comes to clinical trials is the need for more resources, both in terms of funds and personnel. Clinical trials require a signi�cant amount of time from both researchers and practitioners to be successful. However, due to budgetary constraints, they are often forced to make do with limited personnel or wait for additional funding. Additionally, the infrastructure needed to support clinical trials is often expensive and difficult to obtain.
Another barrier in Ireland is the public's lack of awareness and understanding regarding clinical trials
Many people are unaware of both their purpose and potential bene�ts, so they do not see them as a worthwhile investment of time and effort. As such, recruitment for clinical trials becomes more difficult as fewer people are willing to participate. Finally, there is the problem of bureaucracy in Ireland when it comes to starting up clinical trials. It can be a lengthy process that requires navigating complex legal structures and regulatory requirements, which can be challenging
and time-consuming, and “off-putting” for established healthcare providers

A further barrier to trials expansion in Ireland is the lack of digitization and coordination in the health records. Patient records are often still paper based, and fragmented and silo'd, which makes the process of identifying suitable trial candidates difficult, time consuming and expensive There is urgent need to reform Ireland's digital health landscape
Overall, the current landscape of research and clinical trials in Ireland is hindered by these various factors. If these barriers are not addressed, it will become increasingly difficult for Ireland to keep up with its European and global counterparts regarding clinical trial participation and access to ground-breaking treatments
Dr Rebecca Cramp has been appointed scienti�c and regulatory affairs manager with the Irish Pharmaceutical Healthcare Association (IPHA), which represents the international research-based pharmaceutical industry in Ireland. She believes that Ireland should be able to attract more clinical trials given the size of its biopharmaceutical manufacturing footprint. To make this a reality, she believes that further standardization in the clinical trials space is needed to help Ireland catch up with Finland and Denmark, and improve its ability to host important studies that give people access to life-saving treatments.
The number of clinical trials in the UK has also declined signi�cantly in recent times, with the Association of British Pharmaceutical Industry reporting that the number of industry-backed clinical trials started in the UK each year fell by 41% between 2017 and 2021.


Bureaucratic impediments: To reverse the trend of declining clinical trials in Ireland, the government has taken steps to address the administrative barriers to clinical trial participation in Ireland. One signi�cant improvement is the centralization of ethics and standardizing the clinical trial process The National Clinical Trials Office (NCTO) was established to facilitate clinical trial research in Ireland The NCTO provides a centralized infrastructure to support the set-up and management of clinical trials, including a Clinical Trial Management System (CTMS), which allows researchers to track patient recruitment, trial progress, and data management.
Private-public expansion: Through the Health Research Board (HRB) infrastructure, Ireland has invested heavily in Clinical Research facilities, generally based in and around the public hospital university system, but penetration in the private healthcare delivery system is patchy at best. Up to one half of the Irish population carries health care insurance, and receives some or all of its healthcare in the private system. There is clear scope to expand the pool of patients accessing trials, through measures designed to include all eligible patients, treated in both the private as well as public sectors in Ireland
Data issues: Finally, there is a clear need to modernize the data infrastructure, to allow for advances in arti�cial intelligence (AI) and machine
learning to bring further increases in access and retention to clinical trials We will address this issue here
Of crucial importance to the issues discussed in the previous section, a signi�cant barrier to clinical trial participation in Ireland is the lack of patient access to digitized personal health records and control over their own medical data. Patients should have access to their medical records and be able to move from one treatment centre to another and to obtain access to trials This is particularly important for patients with rare diseases, who may need to travel outside their local area to access the best treatments and trials
The Whyze Health (WH) digital platform provides a solution to this problem by allowing patients to access their personal medical records and connect with their healthcare providers to learn about new treatments and clinical trials The platform also enables real-time (real-world) monitoring of patients' conditions, which can help patients and healthcare providers make more informed decisions about treatment options. Furthermore, the platform's digital asset management system encourages long-term patient participation in trials, providing a unique opportunity for healthcare providers to extend their reach and increase their revenue through research and clinical trial involvement.
The current landscape of research and clinical trials in Ireland is hindered by various factors. If these barriers are not addressed, it will become increasingly difficult for Ireland to keep up with its European and global counterparts regarding clinical trial participation and access to ground-breaking treatments

Up to one half of the Irish population carries health care insurance, and receives some or all of its healthcare in the private system. There is clear scope to expand the pool of patients accessing trials, through measures designed to include all eligible patients, treated in both the private as well as public sectors.
There are good clinical reasons to promote this activity. Evidence suggests that being treated in a centre where trials are offered is associated with better patient outcomes. Patients who are treated at centres with clinical trials have access to the latest treatments and technologies, which can improve their health outcomes. Better outcomes lead to better value to the overall health sector Therefore, improving access to clinical trials in Ireland is critical for improving the quality and value of care provided to Irish patients
The WH platform is designed to unify health and research to advance both knowledge areas The patient-centered solution encourages patients to connect with their healthcare providers, allowing them access to information about new treatments and clinical trials and real-time monitoring of their conditions This access is particularly bene�cial for those who may not have been previously aware that participation in clinical trials was a viable option, or who had yet to be invited by their healthcare providers
Increasing the quality of the health interventions through clinical trials improves patients' outcomes Improved outcomes lead to improved value to the overall system. Improved value through clinical trials leverages the substantial FDI incoming to Ireland through the pharmaceutical and med tech investments.
In addition to providing resources and information to patients, the Whyze platform also provides a unique opportunity for healthcare providers to extend their reach and increase their revenue through research and clinical trial involvement. Healthcare providers can now link their patients more directly to relevant studies and trials, enabling more people to bene�t from state-of-the-art treatments
In closing, the Whyze Health Platform collects data in a digital health and research data lake that is used for post-market surveillance of medical products, further improving patient outcomes, and increasing the overall quality of the healthcare delivered in Ireland As new treatments are used in the country, the payers can track the longer term effects of these interventions, to ensure only the best treatments continue to receive �nancial support. As the platform grows and continues to incentivize patient participation, it can help bridge the gap between high-performing healthcare systems in Europe and their counterparts in America and Asia, allowing patients access to ground-breaking treatments and creating improved health outcomes for all This ampli�es the return on investment Ireland derives from the substantial FDI from pharmaceutical and med tech sectors Through its unique patient-centred approach, Whyze has provided a much-needed solution to the problems posed by a lack of European access to clinical trials This is truly the time for a change, and Ireland can rise in the forefront meeting these challenges
Increasing clinical trials activity in Ireland is a healthcare priority. Direct bene�ts include improved outcomes and value for the patients and the healthcare system. By products are increase in return on FDI investment for Ireland. Improvements in digital health platforms including AI and machine learning can help drive this important change
Increasing the quality of the health interventions through clinical trials improves patients' outcomes. Improved outcomes lead to improved value to the overall system. Improved value through clinical trials leverages the substantial FDI incoming to Ireland through the pharmaceutical and med tech investments.



This article explores the potential of Pharma 4.0 to revolutionize the pharmaceutical industry in the 21st century, providing an in-depth look at the latest advancements in the �eld and how they can be used to improve patientoutcomes.
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, businesses across industries are increasingly considering digital transformation to stay competitive and meet the changing needs of their customers The concept of Pharma 4.0 digital transformation refers to the integration of digital technologies and processes in the pharmaceutical industry to enhance productivity, efficiency, and innovation. This transformation encompasses various aspects of the pharmaceutical value chain, including research and development, manufacturing, supply chain management, and patient engagement.
The digital revolution has drastically changed the way we live, work, and interact with one another With the advent of technologies such as arti�cial intelligence, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things, businesses are now faced with the challenge of adapting to this rapidly evolving digital landscape This is where digital transformation comes into play
Digitalization, an important component of Pharma 4.0, will connect everything, creating new levels of transparency and adaptivity for a “smart” plant �oor This will enable faster decision-making and provide inline and on-time control over business, operations, quality, and regulatory compliance. Notably, this new connectedness will require higher levels of security,
By Rameshwar Vermasince linked systems heighten vulnerability
Pharma 4.0 introduces more connectivity, increased productivity, simpli�ed compliance, and the ability to leverage production information to respond to problems as they emerge
Pharma 4.0 is more than just an approach to digital technologies: It's a shift in mindset. Manufacturers need to �nd new ways to identify problems and implement advanced technology to increase efficiency and effectiveness in meeting compliance requirements
From connecting workers to introducing more human-centric work�ows to driving shifts in company culture, humans are at the core of Pharma 4.0. As such, companies must do more than automating processes.
• Application of digital technologies to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and improve patient outcomes
• Part of the larger trend of Industry 4.0.
• Embracing of cloud computing, big data, and the
The concept of Pharma 4.0 digital transformation refers to the integration of digital technologies and processes in the pharmaceutical industry to enhanceproductivity,efficiency,andinnovation.


Internet of Things (IoT).
Key Components/ Pillars of Pharma 4.0
1. Internet of Things (IoT)
2. Arti�cial Intelligence (AI)
3. Big Data Analytics
4. Robotics and Automation
5. Cloud storage
6. Blockchain
7. Remote communication technologies
Pillars of Pharma 4.0
Bene�ts of Pharma 4.0
They try to help organizations achieve “business goals by operating faster, reducing costs, and being more competitive and agile
• Decreased costs
• Improved efficiency
• Increased patient outcomes
• Increased opportunities for innovation.
• Improved collaboration and communication. To achieve this level of operation, you must consider the following:
• A shift to a risk-based and integrated approach for validation.
• The implementation of a holistic control strategy secured to validation.
• The increased focus on data for quality assurance and compliance
• The elimination of paper-based processes and paper documentation.
• The elimination of data store with better communication across the lifecycle of drugs
• A lower-touch relationship with regulatory bodies as data collection and sharing improves Ladders to Reach Pharma 4.0
Stages of Digital Maturity: Digital maturity, the transformation must begin now – starting with computerization to make operations more efficient.
To ensure success, manufacturers must take a
Pharma 4.0 is more than just an approach to digital technologies: It's a shift in mindset. Manufacturers need to �nd new ways to identify problems and implement advanced technology to increase efficiency and effectiveness in meetingcompliancerequirements.
methodical approach in which each stage builds upon the previous one:
1. Computerization: Creating the basis for a digital infrastructure
2. Connectivity: Enabling staff members to accomplish tasks more efficiently
3. Visibility: Connected people, machines, and processes create a substantial digital record of production that can be used to make real-time, data-driven decisions
4. Transparency: With more data, new insights about complex systems become available. Advanced analytics provide you with evolving opportunities for improvement.
5. Predictability: Detail production records enable manufacturers to correct problems before they happen.
6. Adaptability: Systems anticipate problems and initiate the proper action by themselves. At their most advanced, these systems become autonomous and self-correcting
Data integrity is one of the areas in which Pharma 4.0 can contribute the most. In fact, the ISPE outlines “Data Integrity by Design” as a desired outcome of digital maturity
Despite knowing this, many pharmaceutical companies continue to trust on error-prone, paperbased documentation. During manufacturing, engineers record machine states, batch information, and production schedules in paper forms These logs are labour thorough, prone to transcription error, and difficult to reference. Mistakes caught at the end of the process often leave few options available for corrections
With Pharma 4.0 solutions, manufacturers can implement process checks on the most critical data and catch deviations in real time This makes it

possible to manufacture with a right the-�rst-time approach – saving time in exception handling
Electronic logbooks automatically document relevant production information – reorganization a manual process while dramatically improving data integrity These logbooks can compile and integrate information from machines and operators, increasing process visibility
Further, electronic logs can integrate photos, notes, reason codes, device history records, and locations –providing a more holistic record of production than paper-based forms
Electronic logbooks ensure that information is attributable, legible, contemporaneous, original, and accurate (ALCOA).
Because these logs are digital, they can be easily accessed to prove compliance
Many line clearance processes are complex, timeexhaustive changeovers With paper-based processes, workers may use a signi�cant amount of time looking for the next step or validating the execution of the previous one, reducing the amount of time they must progress through the procedure.
Collaborative, Digital line clearance applications can make line clearance easier to navigate. Digital, IoTenabled work instructions guide users through SOPs –increasing efficiency while ensuring that work is performed correctly and validated automatically The applications record how long each step of the process takes, serving to improve process visibility and enable engineers to locate areas for process improvement. Because these apps are collecting and communicating data in real time, engineers can view process status as work unfolds, leading to reduced downtime and more effective scheduling.
Batch record reviews require compiling and reviewing a large quantity of manufacturing data and process documentation.
Much of the labour spent in the review process comes from identifying incorrect or illegible entries and correcting records so that all production information is available for a given batch.
With Pharma 4.0 tools, manufacturers can make data collection and validation a continuous, seamless part of the manufacturing process. Information about manufacturing processes is automatically collected as operators and machines work, and all data is thereby attributable, legible, contemporaneous, original, and accurate.
When it's time for a batch record review, the necessary information is accessible and easy to read Manufacturers can spend more time ensuring the quality of a product and less time correcting transcription errors
Many manufacturing processes require a signi�cant investment in training This challenge is further made worse during periods of high employee turnover, which result in a loss of expert knowledge on the team. Training can be slow, as manufacturers often have a difficult time replicating real-life production scenarios in their training programs. Lengthy training times are expensive, decrease productivity, and reduce quality if technicians aren't trained properly Using manufacturing apps, manufacturers can design pharma-speci�c training applications to get employees on the line fast. If it's not possible to take workers off the line during reskilling periods, training applications can be con�gured to facilitate on-the-job training (OJT).
Manufacturers can even simulate processes by running training apps in a staging environment using Workspaces This sets up a separate environment that allows you to track operator performance without having training data impact your production data.
1. Regulatory compliance: Pharma 4.0 technologies involve the use of advanced systems and software, and regulators need to ensure that they meet the required standards. Ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements is a signi�cant challenge that pharma companies must address
2. Data privacy and security: With the increasing use of data analytics, arti�cial intelligence, and other advanced technologies, the pharma industry is generating vast amounts of data. However, ensuring data privacy and security is a major


challenge, as the data is often sensitive and subject to regulatory scrutiny
3. Integration of legacy systems: Many pharma companies still rely on outdated systems that cannot easily integrate with new digital technologies. Integrating legacy systems with modern digital technologies is a signi�cant challenge that requires careful planning and execution.
4. Talent acquisition and retention: Pharma 4.0 requires a new set of skills, including data analytics, arti�cial intelligence, and machine learning Attracting and retaining top talent with these skills is a signi�cant challenge for pharma companies
5. Cost: Implementing Pharma 4.0 technologies requires a signi�cant investment in infrastructure, software, and talent. Cost is a signi�cant challenge for smaller pharma companies or those with limited resources
Reference:
1. Bringing Industry 4.0 to Pharma: A Breakdown of How to Drive… | Tulip
2. Pharma 4.0 Operating Model | Industry 4.0 | ISPE | International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering
3. Pharma 4.0: The Future of Pharmaceutical Manufacturing (qbdgroup.com)

Rameshwar Verma is a part of the leadership team of an esteemed pharmaceutical company as an Executive - Packing (Serialization Specialist) with 8+ years of experience. He has good knowledge about serialization system, pharmaceutical packing, industry 4.0, QMS, electronic records and compliance. He is the author of the books: “Basic concept of track and trace system for pharmaceutical industry” and “Pharmaceutical track and trace system: A guide to optimizing efficiency and compliance”.



PDA India Chapter Annex 1 Conference, held from 16-18 August 2023 in Ahmedabad, featured engaging knowledge-sharing sessions by globally renowned subject matter experts on the revised requirements of Annex 1, Contamination Control Strategy, Pharmaceutical Quality System, Aseptic Processing, Environmental Monitoring, and so on.
The Parenteral Drug Association (PDA), a nonprofit organization headquartered in the United States, stands as a prominent worldwide source of scientific, technological, and regulatory insights, as well as education tailored to the pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical sectors Through its numerous Chapters, PDA effectively extends its reach and impact across the global industry. PDA plays a pivotal role in facilitating the advancement, assessment, and qualification of emerging technologies
The PDA also presents a valuable opportunity for hands-on training via its Training and Research Institute, ensuring practical learning experiences. Staying true to PDA's overarching vision for the decade, the India Chapter has taken a leading role in bridging the realms of regulations, scientific advancements, and individuals within the community Noteworthy are their dynamic efforts in organizing targeted workshops throughout the nation,
distinguished by innovative techniques for knowledge dissemination.
Established in 2013, the PDA India Chapter operates on a volunteer-based, nonprofit model, serving as a scientific hub. By fostering connections between people, scientific insights, and regulatory landscapes, the chapter aligns with the global mission of PDA Inc Moreover, the chapter actively fosters and supports locally conceived scientific projects and educational endeavors with the potential to make a significant impact on a global scale
Presently, the leadership of the PDA India Chapter is guided by Vishal Sharma, the co-founding director of Vienni Training & Consulting LLP, who serves as the President of the PDA India Chapter. Joining him in this endeavor are accomplished professionals from the pharmaceutical landscape, including:
The President Elect, Dr. Rustom Mody, Head & Vice President, Sunpharma Biologics R&D; Secretary, Rishikesh Jaiwant, Director at Baxter India; and Treasurer, Raghuram Chandra Rao, Vice President of Quality at Gland Pharma.
Pankaj Shitole, Cluster Head, Cipla Ltd; Sumitra Pillai, Vice President and R&D Head, Slayback Pharma; and S G Belapur, providing advisory expertise and representing the Indian Pharmaceutical Alliance are Members at Large
This dedicated group of individuals collaborates to drive the PDA India Chapter's mission of fostering knowledge exchange, partnership, and advancements within the pharmaceutical domain.







After successfully concluding roadshows in Ahmedabad and Chandigarh, Pharma Pro&Pack Expo 2023, analytica Anacon India and India Lab Expo conducted a roadshow on 'Pharma Engineering – A Way to Enhance Productivity, Quality & Compliance' in Bengaluru, on 14 July 2023 at Welcomhotel by ITC.

The triad event, Pharma Pro&Pack Expo, analytica Anacon India and India Lab Expo, is a key enabler in presenting ground-breaking innovations in pharma machinery, laboratory technologies and analytical instruments to user industries such as pharma, chemicals, F&B, etc. in India. The event brings top machinery manufacturers, suppliers of analytical instruments and laboratory equipment, leading pharma companies and industry experts under one roof to network and unlock business opportunities
The event is well-known for organizing multi-city roadshows that hold panel discussions on pressing pharma issues and recommending ways forward.
After successfully concluding roadshows in Ahmedabad and Chandigarh, Pharma Pro&Pack Expo 2023, analytica Anacon India and India Lab Expo conducted a roadshow on 'Pharma Engineering – A Way to Enhance Productivity, Quality & Compliance' in Bengaluru, which houses some of the largest pharma companies and exporters. The event was graced by leaders and decision-makers from these companies, thus facilitating business networking and attracting them to the three-day main event in Hyderabad The event witnessed a panel discussion on the latest pharma manufacturing trends led by leading pharma manufacturers and industry experts
The roadshow was organized in association with Indian Pharma Machinery Manufacturers' Association (IPMMA). Speaking about the success of the roadshow, Harshit Shah, President, IPMMA, said, “Bengaluru is a prominent hub for the pharma industry with several large pharma companies, research institutes and educational institutions We are overwhelmed by the response to our roadshow in Bengaluru, which successfully brought together key stakeholders, including pharma companies, associations, technology suppliers and industry experts, fostering meaningful interactions and networking opportunities”
Harish K. Jain, President, KDPMA and Director, Embiotic Laboratories, said, “Having attended this



roadshow for the last few years, I have seen it grow by leaps and bounds Today, the event saw 200+ attendees which is huge considering it is in Bangalore
The roadshow gives a glimpse of what to expect at the main event comprising Pharma Pro&Pack Expo, analytica Anacon India and India Lab Expo in Hyderabad in September The triad event is a huge marketplace if one is considering purchasing pharma machinery or equipment or understanding various technologies”
Avisha Desai, Business Unit Head - Consumer & Capital Goods and International Business, Member of Management Board, Messe Muenchen India, said, “Bengaluru is of strategic importance due to the presence of some of the leading pharma manufacturers and exporters Their presence at the event attracted various pharma stakeholders and technology suppliers, thus facilitating business networking. We are overwhelmed with the response to our roadshow in Bengaluru, where industry experts touched upon some of the key pharma issues and recommended the way forward using technology This roadshow will be instrumental in bringing pharma buyers from Bengaluru to the three-day main event in Hyderabad”
Productive business interactions at the buyer-seller networking tables: One of the main attractions of the Bengaluru roadshow was its buyer-seller interaction which provided exhibitors with an opportunity to build prior networks with the visitors before the main show in Hyderabad

The shows will be held on 14-16 September 2023 at the Hitex Exhibition Centre, Hyderabad The triad event, to be held in a 25,000 sqm exhibition space, is expected to attract 17,000+ visitors and 400+ technology suppliers from 10+ countries displaying 6000+ products
The event encourages the exchange of ideas by bringing domestic and international machine manufacturers, suppliers of laboratory technology and analytical instruments, laboratory users, consultants and key government officials under one roof to showcase their innovations
The well-curated conferences at the event focus on some of the trending topics. Apart from this, the event's hosted buyer and buyer-seller programs will enable business matchmaking through in-depth interaction between the buyer and seller communities
More roadshows scheduled to be held prior to the event are in Chennai on August 4, Vizag on August 18, and Hyderabad on September 1.
For further information and participation opportunities, contact Leonara Braganza (+91 97737 64118) leonara.braganza@mm-india.in


The inaugural regulatory program of Eminence Business Media, Pharma Regulatory Conclave 2023 set a very high benchmark for conferences based off learning and rejuvenation.

The program was designed with a unique framework with one day virtual day program on 30th June and a two-day in-person conference at Hilton Resort, North Goa on July 5th - 6th With the unique theme on the Day 2,“Patrao”, having dedicated Q/A rounds after every session, case study solving exercises, within the quaint locality in Goa amidst the monsoon, this regulatory program took a very distinctive and bold step by not only addressing current challenges of the pharma regulatory industry but also acknowledging the unaddressed yet crucial focus of emerging markets The virtual day was designed to give theoretical understanding to the delegates about the various required regulatory processes like Regulatory Intelligence, Dossier Filings and GDUFA III guidelines delivered by Mr Prafulla Nandi from Cadila Pharma, Ms Minoo Biju from Piramal Pharma Solutions and Mr Adam Freeman from exFDA Consultants
The program also included a very interesting panel discussion of international experts from regulatory bodies of USA, South Africa, and Latin America. Mr Larry Stevens from USFDA, Ms Emtia Perold from SAPHARA and MrIvan Calderón from COFEPRIS shared their experience and gave insights about the practicality of having a common dossier for emerging markets. Pharma industry veterans like Dr Udaykumar Rakibe from PharmaMantraTM and Dr Sanjit Singh Lamba from Biocuris Pharma were also a part of the discussion and presented the Indian Pharma perspective with their standing within the global market.
The unique design of the program facilitated Eminence Business Media's commitment to delivering excellence by learning The virtual program was corroborated with the in-person conference with a unique case study solving exercise which focused on emerging markets regulatory requirements The session was designed by Mr. Rajeev Mathur from Sun Pharma and was facilitated by Mr. Udaykumar Rakibe and Mr. Rahul Jain at the inperson conference. Delegates and attendees were
working in groups and solving the case study for over a week to present their solutions with the groups on Day 2 of the conference The group exercise was fruitful with unique frameworks being presented by the delegates as a solution to the cases
The two day in-person conference further thoroughly discussed topics like regulatory requirements of complex generics, drug approvals in ICH countries, life cycle management of a drug, post approval changes, among others. Experts like Mr. Rahul Gupta from USV, Ms Meenakshi Jain from Sandoz, Ms Adity Sen Pal from Indoco Remedies and Ms Vandana Singh from Biocon delivered the crucial topics and interacted with the audience by accommodating their questions. Mr Arani Chatterjee from Cadila Pharma and Mr Praveen Cherukupalli from Innovare Labs discussed the clinical trial regulatory requirements and the nitrosamine requirements which are the pain points for the industry The in-person conference also witnessed a panel discussion on the ever-evolving challenges of regulatory affairs moderated by Dr Sanjit Singh Lamba. The expert consisted of panel members like Dr Mayur Parmar from Govt of Gujarat, Dr Venkat R Naidu from Dr Reddy's Laboratories, Ms Adity Sen Pal, and Mr Rahul Gupta.
Having understood the unique requirements of the regulatory professionals to clarify their doubts and addresses their questions, the program accommodated a panel of experts namely, Mr Prafulla Nandi, Mr Arani Chatterjee and Mr Praveen Cherukupalli to solely address the queries of the delegates and attendees
The in-person conference also had sessions catering to gap mitigation between regulatory and other departments by having a dedicated session on soft skills delivered by Mr Sushil Barkur. Further, the rejuvenating activity of the program was also designed with the underline learning of importance of working in collaboration focusing more on regulatory professionals being facilitators than inspectors


Uhlmann is the One Stop Shop, a single source provider of Machine, Software and Service for Counting, �lling, checking and serializing in a continuous process. Our expertise lies in controlling complex lines in a comprehensive, user-friendly and reliable manner
At the 9th Pharma Pro&Pack Expo, Hyderabad on 14th to 16th September 2023 (Booth #J-21, Hall: 1-B), UhlmannGroup will be presenting their solids-in-bottle packaging line on a monoblock platform that covers the key product packaging processes within a single machine The packaging of solids in bottles is particularly popular in the growing segments of dietary supplements and alternative medicines but is also attracting increasing interest in the pharmaceutical industry
Uhlmann IBC 150 bottle line is aimed at being a highly automated, networked and �exible equipment designed to pack varying sized batches of solid dose products in bottles This monoblock line, processes on average up to 150 bottles and 24,000 tablets or capsules per minute Rapid product changeover and short ramp-up phases also make the line attractive for C M O s, C D M O s a n d m a n u f a c t u re r s o f fo o d supplements

Uhlmann IBC 150's integrated design without any belt conveyers and very short distances between function stations allows us to save up to 50% �oor space allowing for a much cleaner and GMP compliant operation. The machine central HMI operates all the functions seamlessly with its recipe driven format recall and also allows for automatic adjustment of transport rake to the bottle diameter This ensures that bottles and caps are handled carefully and accurately
Our Assured Efficiency is delivered through bene�ts like,
• Positive-guided bottle transport
• No Bottle can fall during transport in IBC 150
• Single Operator for multiple functions
• Every Bottle position with “Accept/Reject” status is tracked on HMI via the Master Shift Register Forhighpatientsafety and safe product handling in
t h e p a c k a g i n g
process, Uhlmann g u a r a n t e e s 1 0 0 % Count Accuracy with s e r v o r e g u l a t e d p r o d u c t transportation and an infrared counting system. These infrared c o u n t e r s a r e programmed with a self-compensating m e c h a n i s m t h a t
enable them to accurately handle even dusty products Further, we are able to equip the Counters with an integrated Camera for Product inspection.
This Compact line can also be equipped with a Single Tablet Reject function: This optional module checks the tablets already in the tablet counter and identi�es any damaged or incorrect products and foreign particles These are rejected whilst maintaining a high production speed.
Due to more stringent official guidelines in the Pharmaceutical Industry, the content of bottles must be checked for foreign particles in the packaging process before these are sealed Uhlmann has taken up this

challenge for pharmaceuticals manufacturers and integrated a metal detector in the bottle line IBC 150 –and it has done so without increasing the footprint of the monoblock
Our Counting Systems and Patient centric functions
offer bene�ts like,
• 100%CountAccuracy
• AutoCompensationforDustyProducts
• Integrated Camera Inspection + Single Tablet Rejection
• Integrated Metal Detection / Gross & Net Weighing
Forseamlesstraceability, Uhlmann's Pexcite Software offers an application solution with which users can network Uhlmann Pac-Systeme systems as well as machines and equipment from other manufacturers, according to their process requirements and thus centrally monitor and control them.
A Solid-in-bottle packaging lines consist of a multitude of mechanical and digital components In addition, there are high compliance requirements as well as speci�cations for counterfeit protection or traceability that must be implemented Networking these complex structures in such a way that processes run safely and efficiently is not trivial; interfaces have to be managed, data collected, exported and analysed. Uhlmann's PEXCITE Track & Trace solution including aggregation can be easily connected to the bottle line along with a suitable unscrambler, labelling, cartoning and end-ofline packaging machines, as required
Uhlmann Serialization Platform S 500 is compact and optimally designed either as a stand-alone solution or can be integrated in the packaging line. Depending on the challenge, pharmaceutical manufacturers can use the unit, which is free from format parts, in various

con�gurations, e.g for a 360° bottle inspection, for bottle labeling or serialization, whereby every bottle is identi�ed with a 2D code Since the code is very difficult to include on the 360° circumference of the bottle, an optional helper code can be printed on the base of the bottle This is checked in the follow-up process and assigned to the serialization code on the bottle label The basis for any track & trace application is the software Uhlmann's Pexcite platform offers a digital solution for recording, preparing and evaluating machine data – all independent of the manufacturer.
Pexcite offers various applications speci�cally for the control and operation of an entire plant:
• SupervisoryControl
• OEEMonitoring
• Track&TraceDataCollectionandReporting
• ToolMonitoring
Pexcite ensures connectivity across the entire �lling and packaging process of the solid dose bottle line, providing transparency on key process parameters such as waste, energy consumption, maintenance and spare parts requirements, enabling optimal processes.
Hence, with its new solids-in-bottle line, Uhlmann PacSysteme offers a line that addresses all requirements –and does so across all machines and interfaces in the complete process: from erecting and cleaning the bottles to �lling them with solids, desiccant or cotton wools, sealing the bottles, labeling and serialization.
The individual elements of the Uhlmann Pac-Systeme solutions, such as the below equipment can be optimally connected
• BU300BottleUnscrambler
• IBC150Bottleline
• S500Serializationplatform

Vivek Bansal from Biological E. then led an engaging session on "Change Control and Change Management," an essential topic for understanding the transition from CSV to CSA.
This two-day in-person event occurred at Novotel Mumbai, Juhu Beach, on June 22nd and 23rd, 2023. The conference's unique program design achieved a balance between CSV and CSA.
The conference commenced with a keynote address from Eminence Business Media's Managing Director, Ms Guneet Kaur Hayer. Her warm welcome set the expectations for the exceptional two-day learning program. The program began with an insightful Panel Discussion moderated by Mr. Ken Shitamoto, titled "CSV or CSA? CSV to CSA? CSV is CSA?" Esteemed panelists included Mr. Francisco Vicenty from USFDA, Dr. Mayur Parmar from Govt of Gujarat, Mr. Ravi Kalla from Anthem Biosciences, and Mr. Sanjeev Dharwadkar from Pharma Tech Consulting This session explored various aspects of CSA and CSV approaches in the pharmaceutical industry, providing valuable insights from a regulatory as well as manufacturing perspective.
Following the panel discussion, attendees had the opportunity to engage in a "Fireside Chat" with Mr Francisco Vicenty, enabling direct interaction and the chance to ask questions to the FDA. The day continued with a session delivered by Ms. Deepa Pangaonkar from Wockhardt, focusing on the challenging topic of "Quality Testing and Evidence" within CSA and CSV. Mr
During the conference, partners such as Persistent Systems, Techsol Life Sciences, RxCloud, Rephine, and Conval Group had the opportunity to participate in a unique networking session. Additionally, Mr Ravi Kalla designed a process activity for the delegates, promoting collaboration and emphasizing the importance of unified systems
The second day of the conference commenced with an intriguing session on Digital Validation Systems by Mr Khaled Moussally from Compliance Group This session highlighted the significance of going paperless and explored various platforms offering practical solutions. Subsequent sessions focused on facilitating the transition from CSV to CSA. Mr Ken Shitamoto delivered a vital talk on Critical Thinking, followed by Mr Pranav Gadre from Reliance Life Sciences, sharing his experiences working in IT and QA teams
The latter half of the day concentrated on topics such as Industry 4.0 and Data Integrity Risk Assessment (DIRA) designed by Mr Rajesh Thempadiyil from Dr Reddy's Laboratories through a group exercise that stimulated intense discussions and generated vital takeaways.
True to the distinctive nature of the Eminence Conference, the program concluded with a unique and invigorating activity designed to encourage delegates to ask questions in a rapid-fire fashion. The representatives debunked over 100 myths in an impressive feat within 45 minutes
The day concluded with a unique networking activity, where delegates and speakers could bond over cold beers and 360° Cam experiences
 The Pharma Computer Software Assurance 2023 conference's third edition set remarkably high session originality and creativity standards, providing attendees with an engaging program full of valuable learning opportunities
The Pharma Computer Software Assurance 2023 conference's third edition set remarkably high session originality and creativity standards, providing attendees with an engaging program full of valuable learning opportunities























