

16th Annual
October 1, 2024


16th Annual October 1, 2024



16th Annual
October 1, 2024


16th Annual October 1, 2024




1. Google Maps/Waze to suggest a destination route
2. Use Facial recognition to unlock your phone or online account
3. Watch a video, listen to music, or streaming recommendation on Spotify/YouTube/Disney+/Netflix
4. Submit a Google search suggestion
5. Use Grammarly to suggest writing corrections
6. Ask Alexa or Siri to tell you the weather or answer a question
7. Use Siri, Gmail, or Outlook to predict the next word you’re writing
8. Scroll upon Instagram/Snap/Facebook/LinkedIn recommended links
9. Use Google or Apple photos for recognition, or touch-up editing
10. Any translation apps or resources





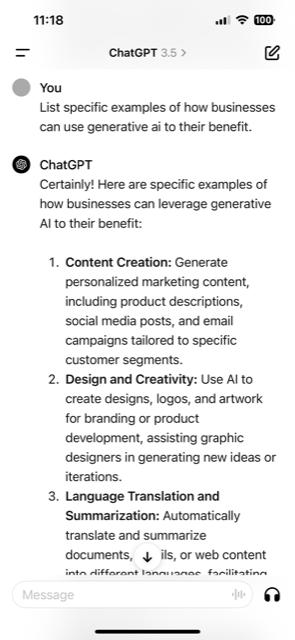
Generate personalized marketing content, including product descriptions, social media posts, and email campaigns tailored to specific customer segments.
Design and Creativity, Brainstorming Generally
Use AI to create designs, logos, and artwork for branding or product development, assisting graphic designers in generating new ideas or iterations.
Language Translation and Summarization
Language Translation and Automatically translate and summarize documents, emails, or web content into different languages, facilitating global communication and understanding.

Use productive analytics to analyze financial data and generate forecasts for better investment decisions or risk management.
Assist in designing customizable products by generating multiple iterations based on user preferences and requirements.
Develop AI-powered chatbots capable of engaging with customers, answering queries, and providing support 24/7, improving customer service experiences.

Enhances aspects such as content optimization, keyword research, and improve user experience. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patters and trends helping marketers to refine strategies. AI-driven tools can even provide personalized content recommendations.
Automation of routine processes, such as email campaigns, social media scheduling, and performance tracking. This empowers marketers to focus on strategy and creativity while AI handles repetitive operational tasks.
Create synthetic images or videos for advertising, virtual try-ons for fashion, or editing and enhancing visual content.
Utilize generative AI to build recommendation engines for personalized product recommendations or content suggestions based on user behavior and preferences.





• Information provided by generative AI may not be accurate.
• Be aware of hallucinations.
• Always verify and check information prior to finalizing.




Generative AI may collect or retain data
• This includes during conversations and information in the prompts
• Using sensitive data for AI training could lead to data breaches or privacy violations


• May use Generative AI to create templates or initial drafts without identifiable information.
• Personally Identifiable Information should be included manually after template generated.


• Learn from human-generated datasets.
• Absorb the biases present in the text, perpetuating stereotypes and discriminations.


• In 2014, Amazon attempted to automate its hiring process by building algorithm to identify top talent.
• Similar to how it rates products, Amazon’s hiring tool used artificial intelligence to give job candidates scores ranging from one to five stars.


• Part of the algorithm used resumes submitted to the company over a 10-year period.
• Since most came from men, the algorithm began to favor men.
• For example, it penalized resumes that included the word “women’s,” as in “women’s chess club captain.”


• Potential unforeseen outcomes or unintended consequences arising from the use of generative AI, impacting business operations or reputation.
• Failing to adhere to regulations and standards, especially in highly regulated industries such as healthcare or finance.


• Overreliance on AI systems may lead to decreased human involvement, impacting skill development and human judgment.
• Difficulty in understanding or explaining how AIgenerated outputs are created, leading to challenges in accountability and transparency.




• Prepare a workplace policy governing the use of Generative AI for employees.


• Establish a team of relevant personnel.
• The team should include collaboration from legal, IT, and business teams.
• Team must align business objectives, while addressing ethical, legal, and operational considerations.
• Take Inventory of Use Cases: Aggregate and assess what’s working, what’s not.


• Define the goals and objectives for using generative AI within the business, outlining what the AI should achieve and how it aligns with broader business strategies.


Include a clear list of authorized and intended uses.
• Examples:
• Draft emails, letters, memorandums or presentations
• Conducting research
• Creating marketing materials


• Implement risk management protocols to mitigate potential risks associated with AI, including bias detection and mitigation strategies.
• Vet any proposed AI, test for performance in a real-world context. Think “mock trial” and pilot programs.
• Assess your organization’s risk comfort level. None of this is without risk.


• Company should retain right to monitor employee’s use of AI


• Require employees review all AI inputs and outputs before use. This should include:
• Ensuring they don’t contain offensive or discriminatory material
• Do not contain personal or confidential information
• Information is accurate
• A general understanding of the provided information’s provenance, quality, appropriateness, and relevancy.
Using a representative data set?


• Establish mechanisms for continuous monitoring, evaluation, and auditing of AI systems to ensure they operate as intended and adhere to established policies.


• Define roles and responsibilities for individuals involved in implementing and overseeing AI systems, ensuring clear accountability.


• Recognize the evolving nature of AI technologies and the need to update policies regularly to address new challenges and opportunities.


• Provide training and awareness programs to employees, ensuring they understand AI's capabilities, limitations, and ethical considerations.


Training and Awareness
Training should include:
1. Explanation of the policy
2. How to use generative AI
3. Appropriate uses under the policy
4. Explanation of policy violations and consequences



• Generative AI was used to create this presentation.
• All material was reviewed, and corrections were made where appropriate.





























16th Annual October 1, 2024


Facts
Numbers
Dates/Times
“Personal Data” is any information linked or linkable to an identifiable person


Concept based upon autonomy and having control over your personal information; how it is collected and how it is used or disseminated
Rights given to Data Subjects
Obligations placed upon Businesses
Attendant Risk Management


1. Applicants and New Hires –submitting data
2.Existing Employee –updating data
3. HR Departments –managing data
4. Payroll Systems –accessing data systems
Employee personal data
5. Benefits Systems –evaluating data

45% of the U.S. Population
of World Population

Applies to Employment and B2B contexts
CCPA regulations in effect; updated final regulations in progress
Effective January 1, 2020, expanded & amended 20+ times
California Privacy Protection Agency (CPPA)
Applies to for-profit businesses that do business in CA and collect and control CA residents’ Personal Information, with certain triggers

Civil penalties up to $2,500 for each violation or $7,500 for each intentional & other types of violations
Limited private right of action when consumers’ unencrypted and nonredacted personal information is exposed after a data breach

Controllers that conduct business in NJ or produce products or service targeted to NJ residents
For profit and non-profit entities alike
100,000 consumers or 25,000 consumer (if revenue or discount from sale of personal data)
NJDPA does not include any form of revenue threshold for applicability so even businesses with relatively low revenues may be in scope


NJ government entities (or of any political subdivision of New Jersey)

Financial institutions and affiliates or data subject to the GrammLeach-Bliley Act (GLBA) [entity level & subject level exemption]
Protected health information (PHI) collected by a HIPAA covered entity [subject level exemption]
Insurance institutions [entity level]
Data subject to the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) [subject level exemption]

BUT, does not include a common exemption for educational data or data processed by non-profits or higher education institutions


The NJDPA gives consumers the following rights :
The right to confirm whether a controller is processing personal data and to access that data;
The right to correct inaccuracies in the personal data;
The right to delete personal data;
The right to obtain a portable copy of personal data; and
The right to opt out of the processing of data for purposes of targeted advertising, the sale of personal data, or, in certain circumstances, profiling


Transparency / Purpose Limitation
Specify purpose of processing (e.g.Privacy Notice requirement)
Minimization (adequate, relevant, reasonably necessary)
Administrative + Technical + Physical data security practices
Need consumer Consent to process Sensitive Data
Cannot process personal data of a known child (u13) unless COPPA
Cannot discriminate (for exercising rights or for effect)
Respond to a verified Data Subject Requests within 45 days



Targeted Advertising = displaying advertisements where the advertisement is selected based on personal data obtained or inferred from that consumer’s activities over time and across nonaffiliated Internet web sites or online applications to predict such consumer’s preferences or interests
Enforcement Example (from California):Sephora
Alleged to violate the CCPA by:
deceptively allowing third parties to track consumer information online in exchange for targeted advertisements
Failing to process visitor request to opt-out of sale via a Global Privacy Control setting
Failed to cure after notice

Sensitive Data in the NJDPA:
Personal data revealing…
Racial or ethnic origin
Religious beliefs
Mental or physical health condition, treatment or diagnosis
Financial information (account no., account log-in, financial account or credit or debit card number + access info to permit access)
Sex life or orientation
Citizenship or immigration status
Transgender / non-binary status
Genetic or biometric data that may be processed for the purpose of uniquely identifying an individual;
Personal data from a known child
Precise geolocation



WHERE DO WE OPERATE?

WHERE ARE OUR EMPLOYEES AND CONTRACTORS LOCATED?

WHERE ARE OUR DATA SUBJECTS LOCATED?

WHAT’S THE TERRITORIAL REACH OF FOREIGN PRIVACY AND DATA SECURITY LAWS?

FTC protects consumers from unfair or deceptive trade practices
FTC promulgates regulations, enforces privacy laws, and takes action against companies to protect consumers when such companies:
Fail to implement and maintain reasonable data security measures
Fail to comply with industry standards
Do not comply with a privacy policy/statement/notice
Use personal information in a manner not disclosed in a privacy statement
Fail to properly secure personal data
Collect, use/process, share, or sell personal data in violation of data privacy rights

FTC and HHS/OCR recent statements on privacy and data
“Companies have a responsibility to secure data they maintain and to delete data they no longer need.” –February2024,Blackbaudsettlement
“Protecting consumers’ sensitive health data is a high priority for the FTC.” –April2024,HBNRchangesannounced
“You should fully understand where all electronic protected health information exists across your organization - from software, to connected devices, legacy systems, and elsewhere across your network.” – February2022,OCRDirectorLisaPinto

Data Mapping and Inventorying
Undertake a data mapping exercise to understand the types of data the organization processes and maintains, the purposes for which the data is used, and whether all data is needed
Data is likely being collected on your Website
Does your organization utilize cookies or other trackers on its website(s)?
Does your business allow others to place cookies or other trackers there?



Do you know what Personal Data you have?
Do you know how Personal Data is being used or shared?
What are your Service Providers / Vendors / Affiliates doing with Personal Data?
If your organization sells personal data to third parties or processes personal data for targeted advertising or profiling purposes, such activities must be disclosed in the privacy notice and consumers must be afforded opportunity to opt-out
Review business relationships with third-party data processors to understand the role of each party and potential requirements

Proactive Prevention versusReactive Remediation
Leverage existing compliance infrastructure to adopt a proactive approach to data governance
Is Personal Data being processed for legitimate and lawful business purposes in accordance with policies, SOPs and applicable law?
Consider what tools are already in place
Policies related to how data is collected, used, and handled?
Is the company already acting transparently?
Notices and consents collected and maintained (consent management platforms)
Vendor Contract and Practices Management

Policies/Procedures
• External-Facing Privacy Policy
• Internal Data Privacy Compliance Policy
• Data Breach Response Policy/SOP
• IT Security Policy
Trainings
Contracts/Notices/Consents/ Authorizations
• General Privacy Trainings for all Personnel
• Targeted Trainings for Select Groups/Personnel
Monitoring and Auditing
• Data Processing Agreements/Addenda
• Contract Language
• Opt-In/Opt-Out Language
• Notices, Authorizations, and Consents
• Develop regular cadence of oversight into processes and compliance efforts












16th Annual October 1, 2024
Navigating State Taxation, Health Savings Accounts, Business Succession Planning, and the Corporate Transparency Act


Overview of State Taxation of Remote Workers
Triple Tax Benefit of Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
Essentials of Business Succession Planning
Implications of the Corporate Transparency Act

Impact of Remote Work on State Taxation
o Increased remote work post-pandemic: Complex state tax implications.
o Residency and Tax Obligations
NJ residents taxed on worldwide income (N.J.S.A. 54A:2-1).
Remote workers’ income from other states: Potential double taxation.
o Nexus Considerations
NJ's economic nexus: Tax authority without physical presence (N.J.S.A. 54:10A-2).

Navigating Multi-State Tax Obligations
o Consistent Policies for Remote Workers
Clear guidelines on work locations to manage tax liabilities.
Tracking where employees work.
o Payroll and Withholding Tax Considerations
NJ rules on withholding: Employers must withhold NJ income tax for NJ residents (N.J.A.C. 18:35-7.3).
Reciprocal agreements with PA: Residents pay income tax only in their state of residence (N.J.S.A. 54A:917).
o Managing Audits and State Tax Disputes
Prepare for audits with thorough records.
Consider voluntary disclosure agreements (VDAs) for past liabilities.
Some states will report their audit findings to other states.

PA 3.07% No
NY 4.5% -8.82% (progressive) No
-PA residents working fully remotely in PA are only subject to PA income tax.
-Reciprocal agreement simplifies filing, but NJ doesn’t tax PA remote work.
-NY residents working fully remotely in NY are taxed only by NY.
-No NJ tax liability unless work is physically performed in NJ. CA 1% -13.3% (progressive) No
-CA residents are subject to CA income tax only. -High CA tax rates apply to all income earned while residing in CA. FL 0% No
-FL residents have no state income tax liability. -NJ does not tax income unless work is physically performed in NJ.


-CA residents owe CA tax on worldwide income, including NJ-sourced income. - CA provides a credit for NJ taxes, but higher CA rates may result in additional taxes owed to CA.
-FL residents owe no state tax, but NJ taxes the income earned while working in
double taxation since FL has no

What Are Health Savings Accounts?
o Eligibility Criteria
Must be enrolled in HDHP, not in Medicare, and not a dependent.
o Contribution Limits
2024: $3,650 for individuals; $7,300 for families (IRC §223).
o Investment Options
Funds can be invested and grow tax-free.
o Tax Treatment
Contributions tax-deductible, earnings tax-free, withdrawals for medical expenses tax-free.

Tax Benefit Explanation Details
Tax-Free Contributions
Tax-Free Growth
Contributions deductible from federal gross income (IRC §223(b)(7)).
Tax-Free Withdrawals
Investment earnings accumulate tax-free (IRC §223(f)).
-Contributions to an HSA are made with pre-tax dollars, reducing your taxable income on the federal level.
-For 2024, the contribution limit is $4,150 for individuals and $8,300 for families.
-Note: NJ does not follow federal rules for HSA tax benefits, so contributions are not deductible for NJ state income tax purposes.
-The funds in an HSA can be invested in a variety of options (e.g., mutual funds, stocks, bonds), and the earnings grow tax-free.
- Unlike traditional investment accounts, there’s no tax on dividends, interest, or capital gains within the HSA account.
Retirement Planning
Withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free (IRC §223(f)(1)).
HSAs as an additional retirement account; unused funds roll over annually.
-Funds withdrawn for qualified medical expenses are completely tax-free, including both the contributions and any investment earnings.
-Qualified expenses include medical, dental, vision, and prescription costs.
-HSAs are a powerful retirement planning tool because funds never expire; they roll over year after year.
-After age 65, HSA funds can be withdrawn for non-medical expenses without penalty, though regular income tax applies to those withdrawals.

Ensuring Business Continuity and Legacy
o Identifying Potential Successors
Evaluate readiness and capability of successors.
o Structuring Buy-Sell Agreements
Legal agreements on how a partner’s share may be reassigned.
Funding via life insurance for liquidity.
o Valuation of Business Interests
Accurate valuation is critical for tax obligations (IRC §2031).

Owner Dies Without a Plan
Buy-Sell Agreements
Business ownership and control pass according to state laws or will, often leading to liquidation or sale.
-Simplifies decision-making for heirs.
-Avoids upfront planning costs.
Legal agreement between owners that outlines the terms for a buyout if an owner leaves or dies.
-Provides clear exit strategy.
-Establishes business continuity.
-Uncertain outcomes. -May result in higher estate taxes.
-Potential forced liquidation.
-Possible family disputes.
-Requires ongoing funding (e.g., insurance).
-Can be complex to negotiate and maintain.
-Business may be subject to probate, delaying distribution.
-Missed tax planning opportunities.
- Funded by life insurance, which is generally tax-free.
-Can lock in valuation for estate tax purposes.
Employee Equity Grants
Employees receive ownership stakes, usually through stock options or profit-sharing plans.
-Can set a fair market value.
-Aligns employee and business interests.
-Can incentivize long-term commitment.
-Dilutes existing ownership.
-Requires careful planning to avoid tax complications for employees.
-May have capital gains implications.
-May trigger immediate tax liabilities for employees.
-Capital gains treatment if stock is held long-term.
-Can reduce overall estate value if used in succession planning.

Owner Dies Without a Plan
Business ownership and control pass according to state laws or will, often leading to disputes or liquidation.
-Simplifies decision-making for heirs.
-Avoids upfront planning costs.
-Uncertain outcomes.
-Potential forced liquidation.
-Possible family disputes.
-Protects assets from creditors.
- Complex and expensive to set up and maintain.
-May result in higher estate taxes.
-Business may be subject to probate, delaying distribution.
-Missed tax planning opportunities.
-Transfers can utilize lifetime gift tax exemptions.
Family Buy-Sell Agreements
Business assets are transferred into a trust, managed by trustees for the benefit of heirs.
-Provides for structured, longterm control.
-Requires careful selection of trustees. - Trusts can help reduce estate tax liability.
-Can reduce estate taxes.
Agreement among family members on the terms and conditions for buying out an owner’s interest.
-Preserves family control.
-Establishes clear terms for succession.
-Can be funded with insurance.
-Requires agreement among all family members.
-May create tension if terms are perceived as unfair.
-Generation-skipping transfer tax (GSTT) may apply if grandchildren are beneficiaries.
-Can set a clear valuation for estate tax purposes.
-Life insurance funding is generally tax-free.
-Potential capital gains tax on sale of shares.

Enhancing Corporate Transparency
o Beneficial Ownership Reporting
Mandatory reporting to FinCEN for certain entities (31 U.S.C. §5336).
Beneficial owner: 25% ownership or substantial control.
o Implications for Private Businesses
Reporting applies to corporations, LLCs, and similar entities; certain exemptions.
o Compliance Deadlines
Existing entities: Report by Jan 1, 2025; new entities: Within 30 days of formation.

Compliance with the Corporate Transparency Act
o Identifying Beneficial Owners
Processes for gathering and verifying ownership information.
Ongoing monitoring and updates to records.
o Updating Corporate Records
Integrate compliance into corporate governance.
Regular updates to reflect ownership/control changes.
o Legal and Operational Challenges
Challenges in identifying and reporting beneficial owners for complex structures.
Seek legal counsel to mitigate non-compliance risks.








16th Annual October 1, 2024


Lisa N. Brown, Esq.











DEI backlash: Stay up-to-date on the latest legal and corporate challenges
Lowe’s ends some DEI policies, adding to trend


Utah lawmaker blames 'diversity' for Baltimore bridge collapse

Ford becomes the latest company to scale back its diversity and inclusion policies

As diversity, equity and inclusion comes under legal attack, companies quietly alter their programs



DEI efforts “advance our business objectives . . .”
David Cordani, CEO
Cigna Group
DEI is “aligned with shareholder value and improved financial performance.”
Ryan Lance, Chairman
ConocoPhillips
Tim Murphy, CAO Mastercard Remains “committed to creating a global corporate environment where all people . . . have equal access to opportunities and advancement.”




“It is good for business; it’s morally right; we’re quite good at it; we’re successful.”
Jamie Dimon, Chairman and CEO
Chase



Forced to adopt race-based grading system
Forced to attend anti-racism workshops
Forced to endure pervasive negative racial rhetoric

Ensure that diversity initiatives include nonracial points of diversity e.g., gender, disability, veteran status, and other lifeexperiences
Shift language to embrace “all-inclusive multiculturalism” and use inclusive language that highlights the benefits of DEI for all groups
Diversify decision-making groups and ensure equitable processes across all stages of employment
Implement privacy measures in feedback collection to ensure honest responses, without fear of identification
Use race-based offerings or exclusions
Use rhetoric that may alienate certain groups
Enforce strict numerical criteria tied to protected group membership
Neglect to assess programs for unintended disparate impact(s)










16th Annual
October 1, 2024










USSupremeCourtdeclareslateraltransfersthatcause“someharm”

US Supreme Court declares lateral transfers that cause “some harm” to be unlawful under federal law

Muldrowv.CityofSt.Louis
Plain clothes police officer was transferred to a ‘less prestigious’ position
Lateral position
Same rank and same pay / different duties and different hours
‘Some harm’ is enough to trigger liability
Raises many questions






Federal Trade Commission ban on non-competes was set to begin on September 4, 2024
Texas District Court issues injunction with nationwide effect
Appeal to the 5th Circuit likely
Cautiously continue lawful practices with respect to non-compete agreements, subject to state restrictions
Contact your attorney



You Don’t Discriminate. But Does Your A.I.?

Mobleyv.Workday,Inc.(N.D. Cal. 2024)
Can A.I. job screening tools unwittingly discriminate against certain job applicants?
What are the employer’s responsibilities to protect against this potential discrimination?
Intentional vs. disparateimpact discrimination.








NLRB precludes employer from enforcing dress code for customer-facing employee who wrote “Black Lives Matter”initialsoncompany-suppliedapron*
Can employers always enforce employee dress code policies?
Doesn’t protected concerted activity require that at least two employees act in concert?
How can employers increase their chances of enforcing their dress code policies?
Should we expect further incursion of political and social justice issues into the workplace?
*HomeDepot,USA,373NLRBNo.25(February21,2024)



Yannickv.KrogerCo.ofMich.(6th Cir. 2024)
No “magic words” necessary for accommodation request under the ADA.
Context is critical.
Training managers to spot requests will be key.
Reach out to counsel when there are close calls.





Written policy regarding return to work
Strict adherence to policy













16th Annual October 1, 2024

David M. Schloss

Boosts Employee Morale & Engagement
Enhanced Teamwork, Camaraderie & Communications
Requires Investment of Time and Money
Possibility of Alienation or Unease among Certain Employees
Stronger Bonds
Encourage Creativity
May Heighten Tension within the Team
Employee’s Exhibit Bad Behavior
Increased Productivity
Builds Trust
Helps Create a Positive Workplace Culture
Accidents, Injuries, or Property Damage
Alcohol, Alcohol, Alcohol


Compensation for Hourly Staff

Liability for Accidents and Injuries




• Canyou require it?
• Shouldyou require it?



“Our company made the ‘Company BBQ’ mandatory, and they held it at a park, we had one guy tear his ACL while playing flag football and another got bit by a stray dog . . . both claimed workers' comp”





Dazzling the Boss to Curry Favor and Promotion
Making a Dangerous Activity Seem Obligatory
‘Mandatory’ Fun
Discrimination by Gender Assumptions
Creating Tension and Hostility between Team Members

Risks to the Health & Safety of Employees
Leaders not Participating in Team Activities


The boss schedules a workplace outing full of fun teambuilding activities such as paintball, escape rooms, or scavenger hunts and does so on a Saturday afternoon in the fall. Of course, the outing is optional, and virtually all employees attended.

The boss schedules a team bowling tournament at a local venue and offers an open bar to all those who join in the fun. One employee has a bit too much fun and face plants on lane 7.

The Regional VP of sales arranges a pool party for all his sales reps and district managers. The alcohol flows and one district manager is seen hitting on a female sales rep and another must be carried back to his hotel room at the end of the evening.








16th Annual October 1, 2024
RatedR - Required watching for workers’
compliance



The Worker’s Compensation program was created as a social safety net through legislation to provide medical treatment, wage replacement, and permanent disability compensation to employees who suffer jobrelated injuries or illnesses, as well as death benefits to dependents of workers who have died as a result of their employment.
Employers are required by law to carry worker’s compensation insurance for employees.


Any work-related injury or illness that occurred in the course of the employee performing his/her duties or while on the employer’s premises for the benefit of the employer.
Any injury or illness caused by the negligence of the employer or a coworker (see exceptions to the exclusive remedy)
Occupational Illness
Death

Non-work related medical conditions or diseases that are not caused by nor exacerbated from working conditions.
Examples:
Kidney failure
Heart disease /attack (sometimes)
Diabetes
Appendicitis
Cancer (sometimes)
Mental Illness (sometimes)
Specialnoteforlawenforcement, publicsafety,andmedicalemergency workers

Medical
All necessary and reasonable medical treatment, prescriptions, and hospitalization services related to the work injury
Temporary Total Disability
Injured workers disabled for seven or more days, may be eligible to receive benefits at a rate of 70% of their average weekly wage.
Lump Sum Compensation
Permanent Partial Disability
Permanent Total Disability
Death Benefits





Workers’ compensation is a no-fault benefit ‘without regard to the negligence of the employer,’ and generally bars an employee from seeking damages for pain and suffering in court.
The only exception to the exclusive remedy is where the employee can prove (1) an employer’s act or omission was an intentional wrong, and (2) the wrongful behavior caused the employee’s work-related injury or illness.


Whether workers’ compensation is applicable to an employee’s injury often depends on special attending factors of
• Where …
• When …
• How … and
• Why … the injury occurred


Employees are only covered while they are performing duties for the employer.
Therefore, workers who are injured during their commute to or from work and home are usually ineligible.
However, if the job duties require the employee to travel, any injury that occurs while traveling in the course of employment is workrelated and subject to workers’ compensation laws.


An employee's employment begins when they arrive at the employer's place of work to begin scheduled work and ends when they leave the employer's premises.
The employer's premises includes any property that the employer owns or controls.



New Jersey's workers' compensation law covers mental and psychological conditions that arise from work-related events, including depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). To qualify for benefits, the condition must be severe enough to interfere with the employee's ability to perform their job.
There must be sufficient medical evidence that the condition was objectively work-related to be eligible for coverage.


A certain amount of horseplay is to be expected in any workplace and is generally always covered by WC
Unless the employer can show that the horseplay constituted a major deviation from the employee’s work duties


Workplace injuries caused by physical violence are covered under Workers’ compensation laws if the dispute giving rise to the physical altercation is work related.


Altercations arising from purely personal disputes are not covered.


If an employer requires employees to attend an event and an injury occurs, the injury is compensable.
However, there is a gray area where attendance to the event is not mandatory.

An employee who is on the premises, not for the benefit of the employer but for their own benefit, and is free of all duties, is not covered by WC for any injury they suffer. Again, the employer's premises includes any property that the employer owns or controls.


Generally, workers’ compensation benefits are tied to the job the employee was working when he or she was injured.
This is true even if the injuries prevent the employee from working both jobs.

No Double Feature Roles

The injured employee was intoxicated at the time of the injury (with blood or urine analysis)
Employers can challenge eligibility for worker’s compensation benefits if they can show 2 things:
And the intoxication was the sole cause of the injury

The Second Injury Fund makes benefit payments to injured workers who are totally and permanently disabled as a result of work-related injuries combined with pre-existing disabilities.
The Fund was established to encourage employers to hire disabled workers. The employer only pays for the work-related aspect of the total disability award.


The remedy for a temporary worker assigned through an agency is usually covered by workers’ compensation with the placement agency.
The agency normally contracts with its client to cover workers’ compensation claims of the employees it places with the client.

Check your Temp Agency Contract


The employer and their insurer have the right to select the doctor(s) an employee will see after a workplace injury
However, if the employee objects with the care given, they can obtain a second opinion and petition to change treatment plans and care providers

Employers may inquire with the treating physician if light duty is appropriate for transitioning the employee back to work early. If the employee refuses light duty, they can lose their WC temporary disability benefits.
All employers should require medical certification that the employee is medically fit to perform duties that theemployerhas identified in a written job description.
Employers may require a second medical opinion, with a provider of its choosing, if it questions the accuracy of a prior opinion regarding the employee’s condition.
Point of No Return
Once a doctor has certified an employee has reached maximum medical improvement (MMI), if they still cannot perform the essential duties of job they may lawfully be discharged.


It is unlawful for an employer to terminate or retaliate against an employee for making a workers’ compensation claim.


Communicate with Broker
Conduct Year-end Audits
Brokers can be an indispensable partner in helping to ensure full compliance and reduce WC costs through audits, assessments and return to work programs
Ensure the employer is being assessed on accurate payroll records so it is not overpaying in mandated WC insurance premiums
Worksite Safety Assessment
These can be arranged through the Broker to address common workplace hazards and reduce WC claims
Return to Work Programs
Programs designed to return employees to work as soon as possible in some capacity (light duty, reduced hours, etc.) have better outcomes overall









16th Annual
October 1, 2024


1.Would not have occurred but for the employee’s protected characteristic (i.e., sex, sexual orientation, gender, race);
3.A reasonable person in the same protected category would believe the conduct changed the conditions of employment; and
2.The harassment was severe or pervasive;
4.The conduct has changed the “conditions of employment” and rendered the “working environment hostile or abusive”

Formal Policy
Only employers who promulgate and support an anti-harassmentactive policy are entitled to protection under the law
Formal Notice
Informal notice of a complaint is sufficient for notice



• A single derogatory comment directed against a subordinate employee by a supervisor can create a hostile work environment
• Racial epithets are particularly egregious
• Who makes the comment matters; the higher up, the more pervasive



Inappropriate comments based on a protected classes can be the basis for a Hostile Work Environment claim, even if the comment is not made to, or in front of, a person in that protected class Discriminatory Comments
Not intended to mean or suggest a “civility code” in the workplace “where only language fit for polite society will be tolerated” Workplace Civility







Scan the QR code to access the Employment Law Forum 2024 event page to complete the evaluation form and view the slide deck, upcoming events, and additional resources!



16th Annual
October 1, 2024