159
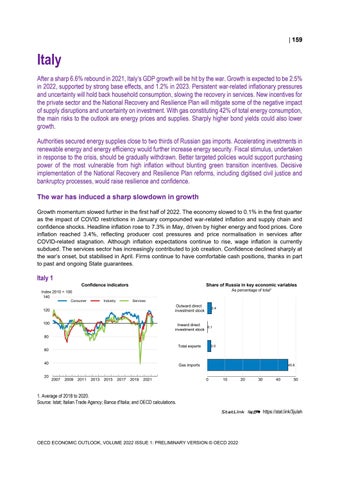
Italy After a sharp 6.6% rebound in 2021, Italy’s GDP growth will be hit by the war. Growth is expected to be 2.5% in 2022, supported by strong base effects, and 1.2% in 2023. Persistent war-related inflationary pressures and uncertainty will hold back household consumption, slowing the recovery in services. New incentives for the private sector and the National Recovery and Resilience Plan will mitigate some of the negative impact of supply disruptions and uncertainty on investment. With gas constituting 42% of total energy consumption, the main risks to the outlook are energy prices and supplies. Sharply higher bond yields could also lower growth. Authorities secured energy supplies close to two thirds of Russian gas imports. Accelerating investments in renewable energy and energy efficiency would further increase energy security. Fiscal stimulus, undertaken in response to the crisis, should be gradually withdrawn. Better targeted policies would support purchasing power of the most vulnerable from high inflation without blunting green transition incentives. Decisive implementation of the National Recovery and Resilience Plan reforms, including digitised civil justice and bankruptcy processes, would raise resilience and confidence. The war has induced a sharp slowdown in growth Growth momentum slowed further in the first half of 2022. The economy slowed to 0.1% in the first quarter as the impact of COVID restrictions in January compounded war-related inflation and supply chain and confidence shocks. Headline inflation rose to 7.3% in May, driven by higher energy and food prices. Core inflation reached 3.4%, reflecting producer cost pressures and price normalisation in services after COVID-related stagnation. Although inflation expectations continue to rise, wage inflation is currently subdued. The services sector has increasingly contributed to job creation. Confidence declined sharply at the war’s onset, but stabilised in April. Firms continue to have comfortable cash positions, thanks in part to past and ongoing State guarantees.
Italy 1 Confidence indicators
Share of Russia in key economic variables As percentage of total¹
Index 2010 = 100 140
Consumer
Industry
Services
Outward direct investment stock
120 100
2.4
Inward direct 0.1 investment stock
80 Total exports
60 40 20
2.0
Gas imports
2007
2009
2011
2013
2015
2017
2019
2021
0
45.6
0
10
20
30
40
50
1. Average of 2018 to 2020. Source: Istat; Italian Trade Agency; Banca d'Italia; and OECD calculations. StatLink 2 https://stat.link/3julah
OECD ECONOMIC OUTLOOK, VOLUME 2022 ISSUE 1: PRELIMINARY VERSION © OECD 2022