115
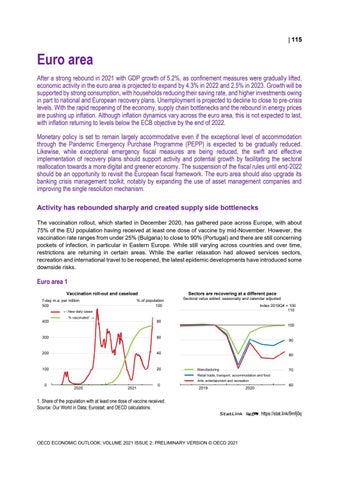
Euro area After a strong rebound in 2021 with GDP growth of 5.2%, as confinement measures were gradually lifted, economic activity in the euro area is projected to expand by 4.3% in 2022 and 2.5% in 2023. Growth will be supported by strong consumption, with households reducing their saving rate, and higher investments owing in part to national and European recovery plans. Unemployment is projected to decline to close to pre-crisis levels. With the rapid reopening of the economy, supply chain bottlenecks and the rebound in energy prices are pushing up inflation. Although inflation dynamics vary across the euro area, this is not expected to last, with inflation returning to levels below the ECB objective by the end of 2022. Monetary policy is set to remain largely accommodative even if the exceptional level of accommodation through the Pandemic Emergency Purchase Programme (PEPP) is expected to be gradually reduced. Likewise, while exceptional emergency fiscal measures are being reduced, the swift and effective implementation of recovery plans should support activity and potential growth by facilitating the sectoral reallocation towards a more digital and greener economy. The suspension of the fiscal rules until end-2022 should be an opportunity to revisit the European fiscal framework. The euro area should also upgrade its banking crisis management toolkit, notably by expanding the use of asset management companies and improving the single resolution mechanism. Activity has rebounded sharply and created supply side bottlenecks The vaccination rollout, which started in December 2020, has gathered pace across Europe, with about 75% of the EU population having received at least one dose of vaccine by mid-November. However, the vaccination rate ranges from under 25% (Bulgaria) to close to 90% (Portugal) and there are still concerning pockets of infection, in particular in Eastern Europe. While still varying across countries and over time, restrictions are returning in certain areas. While the earlier relaxation had allowed services sectors, recreation and international travel to be reopened, the latest epidemic developments have introduced some downside risks.
Euro area 1 Vaccination roll-out and caseload 7-day m.a. per million 500
Sectors are recovering at a different pace Sectoral value added, seasonally and calendar adjusted
% of population 100
Index 2019Q4 = 100 110
← New daily cases
400
% vaccinated¹ →
80
300
60
200
40
100
20
100
90
80
Manufacturing
70
Retail trade, transport, accommodation and food Arts, entertainment and recreation
0
2020
2021
0
0
2019
2020
60
1. Share of the population with at least one dose of vaccine received. Source: Our World in Data; Eurostat; and OECD calculations. StatLink 2 https://stat.link/9mfj0q
OECD ECONOMIC OUTLOOK, VOLUME 2021 ISSUE 2: PRELIMINARY VERSION © OECD 2021