29
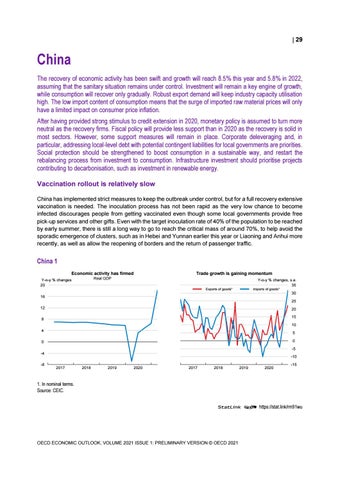
China The recovery of economic activity has been swift and growth will reach 8.5% this year and 5.8% in 2022, assuming that the sanitary situation remains under control. Investment will remain a key engine of growth, while consumption will recover only gradually. Robust export demand will keep industry capacity utilisation high. The low import content of consumption means that the surge of imported raw material prices will only have a limited impact on consumer price inflation. After having provided strong stimulus to credit extension in 2020, monetary policy is assumed to turn more neutral as the recovery firms. Fiscal policy will provide less support than in 2020 as the recovery is solid in most sectors. However, some support measures will remain in place. Corporate deleveraging and, in particular, addressing local-level debt with potential contingent liabilities for local governments are priorities. Social protection should be strengthened to boost consumption in a sustainable way, and restart the rebalancing process from investment to consumption. Infrastructure investment should prioritise projects contributing to decarbonisation, such as investment in renewable energy. Vaccination rollout is relatively slow China has implemented strict measures to keep the outbreak under control, but for a full recovery extensive vaccination is needed. The inoculation process has not been rapid as the very low chance to become infected discourages people from getting vaccinated even though some local governments provide free pick-up services and other gifts. Even with the target inoculation rate of 40% of the population to be reached by early summer, there is still a long way to go to reach the critical mass of around 70%, to help avoid the sporadic emergence of clusters, such as in Hebei and Yunnan earlier this year or Liaoning and Anhui more recently, as well as allow the reopening of borders and the return of passenger traffic.
China 1 Economic activity has firmed
Trade growth is gaining momentum
Real GDP
Y-o-y % changes 20
Y-o-y % changes, s.a. 35
Exports of goods¹
Imports of goods¹
30
16
25 12
20 15
8
10 4
5 0
0
-5 -4 -8
-10 2017
2018
2019
2020
0
0
2017
2018
2019
2020
-15
1. In nominal terms. Source: CEIC. StatLink 2 https://stat.link/rm91wu
OECD ECONOMIC OUTLOOK, VOLUME 2021 ISSUE 1: PRELIMINARY VERSION © OECD 2021