76
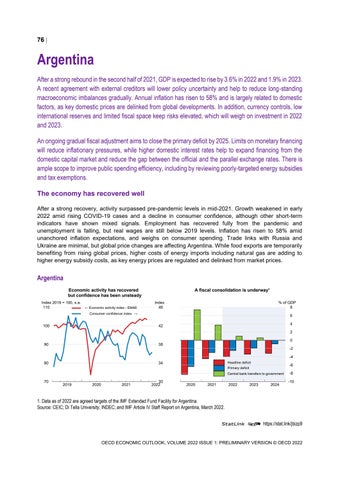
Argentina After a strong rebound in the second half of 2021, GDP is expected to rise by 3.6% in 2022 and 1.9% in 2023. A recent agreement with external creditors will lower policy uncertainty and help to reduce long-standing macroeconomic imbalances gradually. Annual inflation has risen to 58% and is largely related to domestic factors, as key domestic prices are delinked from global developments. In addition, currency controls, low international reserves and limited fiscal space keep risks elevated, which will weigh on investment in 2022 and 2023. An ongoing gradual fiscal adjustment aims to close the primary deficit by 2025. Limits on monetary financing will reduce inflationary pressures, while higher domestic interest rates help to expand financing from the domestic capital market and reduce the gap between the official and the parallel exchange rates. There is ample scope to improve public spending efficiency, including by reviewing poorly-targeted energy subsidies and tax exemptions. The economy has recovered well After a strong recovery, activity surpassed pre-pandemic levels in mid-2021. Growth weakened in early 2022 amid rising COVID-19 cases and a decline in consumer confidence, although other short-term indicators have shown mixed signals. Employment has recovered fully from the pandemic and unemployment is falling, but real wages are still below 2019 levels. Inflation has risen to 58% amid unanchored inflation expectations, and weighs on consumer spending. Trade links with Russia and Ukraine are minimal, but global price changes are affecting Argentina. While food exports are temporarily benefiting from rising global prices, higher costs of energy imports including natural gas are adding to higher energy subsidy costs, as key energy prices are regulated and delinked from market prices.
Argentina Economic activity has recovered but confidence has been unsteady Index 2019 = 100, s.a. 110
← Economic activity index - EMAE
A fiscal consolidation is underway¹ Index 46
% of GDP 8
Consumer confidence index →
100
6 4
42
2 90
38
80
34
0 -2 -4 Headline deficit
-6
Primary deficit Central bank transfers to government
70
2019
2020
2021
30 2022
0
2020
2021
2022
2023
2024
-8 -10
1. Data as of 2022 are agreed targets of the IMF Extended Fund Facility for Argentina. Source: CEIC; Di Tella University; INDEC; and IMF Article IV Staff Report on Argentina, March 2022. StatLink 2 https://stat.link/jbizp9
OECD ECONOMIC OUTLOOK, VOLUME 2022 ISSUE 1: PRELIMINARY VERSION © OECD 2022