(BPD)
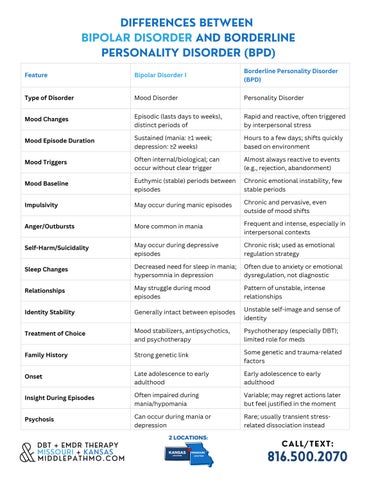
Feature
Type of Disorder
Mood Changes
Mood Episode Duration
Mood Triggers
Mood Baseline
Impulsivity
Anger/Outbursts
Self-Harm/Suicidality
Sleep Changes
Relationships
Identity Stability
Treatment of Choice
Family History
Onset
Bipolar Disorder I
Mood Disorder
Episodic (lasts days to weeks), distinct periods of
Sustained (mania: ≥1 week; depression: ≥2 weeks)
Often internal/biological; can occur without clear trigger
Euthymic (stable) periods between episodes
May occur during manic episodes
More common in mania
May occur during depressive episodes
Decreased need for sleep in mania; hypersomnia in depression
May struggle during mood episodes
Generally intact between episodes
Mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, and psychotherapy
Strong genetic link
Late adolescence to early hood

n impaired during a/hypomania
occur during mania or ession
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)
Personality Disorder
Rapid and reactive, often triggered by interpersonal stress
Hours to a few days; shifts quickly based on environment
Almost always reactive to events (e g , rejection, abandonment)
Chronic emotional instability, few stable periods
Chronic and pervasive, even outside of mood shifts
Frequent and intense, especially in interpersonal contexts
Chronic risk; used as emotional regulation strategy
Often due to anxiety or emotional dysregulation, not diagnostic
Pattern of unstable, intense relationships
Unstable self-image and sense of identity
Psychotherapy (especially DBT); limited role for meds
Some genetic and trauma-related factors
Early adolescence to early adulthood
Variable; may regret actions later but feel justified in the moment
Rare; usually transient stressrelated dissociation instead