

Understanding Female Infertility


What is Infertility?
Infertility: The inability to conceive naturally after 1 year of trying (or 6 months if over 35).
Can be due to female factors, male factors, or a combination of both.
Causes of Female Infertility

·Ovulation Disorders: Irregular or absent ovulation (PCOS, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome; POI, Premature Ovarian Insufficiency). Fallopian Tube Blockage: Caused by pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or scar tissue (adhesions).
Uterine Issues: Fibroids, polyps, or endometriosis (tissue lining the uterus grows outside it).
Age-related decline: Egg quality and quantity decrease with age.
Signs and Symptoms

Irregular or absent periods
Pelvic pain during menstruation or intercourse
Difficulty maintaininga Pregnancy (miscarriages)
Diagnosis of Infertility
Consultation with a healthcare professional specializing in reproductive health.

Pelvic exam to assess the reproductive organs. Blood tests to check hormone levels and ovarian reserve.
Imaging tests: Ultrasound for uterine health, HSG (hysterosalpingography) to check fallopian tubes.
Treatment Options
Medication: To stimulate ovulation or regulate menstrual cycles.
Surgery: To remove fibroids, repair tubal blockage, or treat endometriosis.
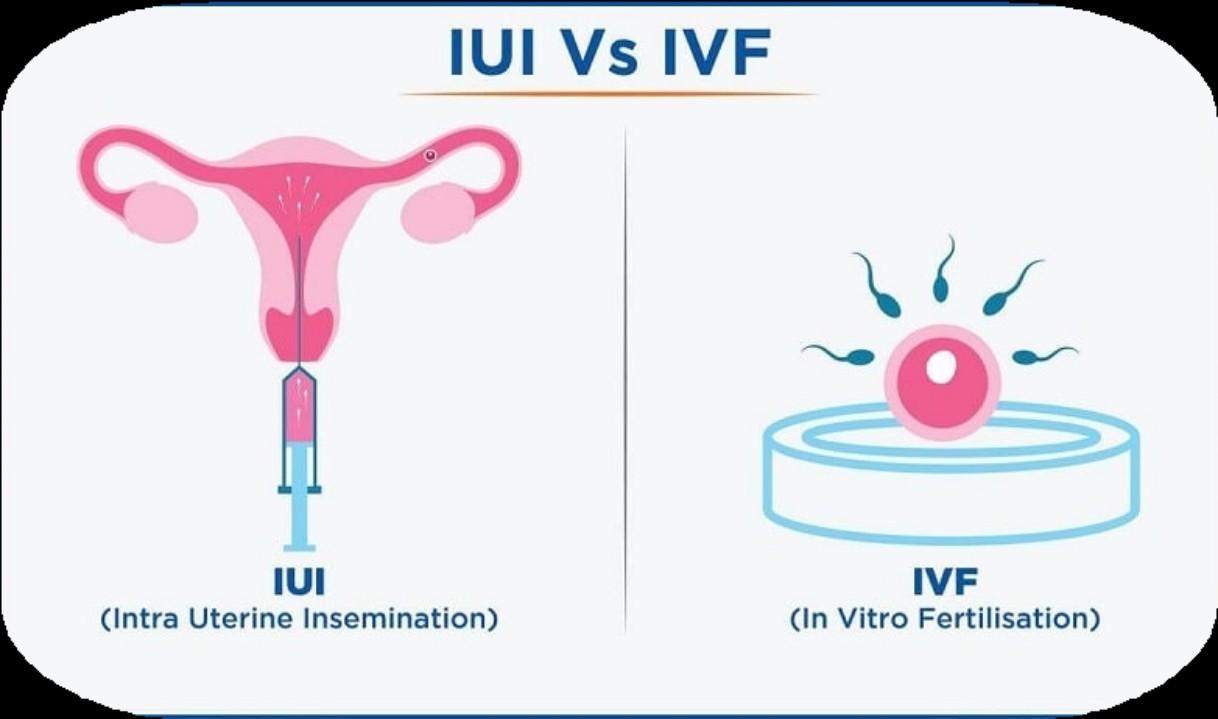
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART): Options include Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) and In Vitro Fertilization (IVF).
Emotional Impact of Infertility
Infertility can cause stress, anxiety, and depression.
Support systems from family, friends, and support groups are crucial.
Conclusion
Infertility is a common challenge, but there is hope.
Seek medical advice to explore treatment options.
Building a family is possible through various paths.


