back
Figure 5: S. Eubayanus was first isolated from Nothofagus, also known as the southern beeches, found in temerate areas of Patagonia Credit: Diego Libkind, Institute for Biodiversity and Environment Research, Bariloche, Argentina
to
bas i cs
s e r i a l
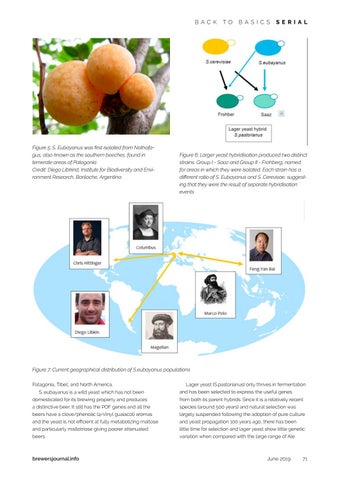
Figure 6: Larger yeast hybridisation produced two distinct strains. Group I - Saaz and Group II - Frohberg, named for areas in which they were isolated. Each strain has a different ratio of S. Eubayanus and S. Cerevisae, suggesting that they were the result of separate hybridisation events
Figure 7: Current geographical distribution of S.eubayanus populations Patagonia, Tibet, and North America. S. eubayanus is a wild yeast which has not been
Lager yeast (S.pastorianus) only thrives in fermentation and has been selected to express the useful genes
domesticated for its brewing property and produces
from both its parent hybrids. Since it is a relatively recent
a distinctive beer. It still has the POF genes and all the
species (around 500 years) and natural selection was
beers have a clove/phenolic (4-Vinyl guaiacol) aromas
largely suspended following the adoption of pure culture
and the yeast is not efficient at fully metabolizing maltose
and yeast propagation 100 years ago, there has been
and particularly maltotriose giving poorer attenuated
little time for selection and lager yeast show little genetic
beers.
variation when compared with the large range of Ale
brewersjournal.info
June 2019
71