International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

1Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar, India 2,3,4,5,6Diploma Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar, India ***
1. Abstract Now day people are facing some problems regarding traveling or transportationinthe sangli islampur city because of the bad condition of the road. There are potholes on road due to black cotton soil is proved to be seriously founded on it. It has high swelling and shrinkage properties. Because of its high swelling due to water percolation in the rainy season and shrinkage due to water evaporating in the summer season, when we construct the structure on black cotton soil, it gets cracked. In the past decades, we found stabilization techniques to reduce the swelling and shrinkage property of soil. So in this project, we stabilize the soil using brick dust and also find the causes of road cracks and remedial measures of it.
Key Words: Black cotton soil, brick dust, causes of settlement of road, remedial measures of it.

Recently,trafficandtransportationsystemsareincreased in the Sangli district. So most of the vehicles are goes on SangliIslampurroad.Recentlythisroadisconvertedintoa national highway. So it is necessary to keep it in good conditionandmaintenance. Mostofthetimethat roadis constructedbutthatroadisfrequentlydeterioratedandget cracks. So people are facing problems while traveling on thatroad.Tosolvethatproblemwechoosethisproject,so inthisproject,wewillfindthecausesofroaddeterioration andremedialmeasuresofit.
3.1 Objective:
1) Tostudyofcurrentconditionofroadandsurrounding area.
2) Tostudyofblackcottonsoil.
3) To study causes of settlement and suggest remedial measuresforthatroad.
3.2 Scope:
1)Permanentsolutionforblackcottonsoilroad.
2)Newtechnicsusedinsoilstabilization.
WesurveyedSangli Islampurroadandfoundthatitturns out that the road is damaged in little little patches throughoutentireitsspan.
Followingarethefailuresoccurredinroad:
Fig 1 : BeforeRainfall
1) Fatiguecracks 2) Longitudinalcracks 3) Edgecracks 4) Potholes.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Fatigue crack is also called as map cracking. It is the mostcommontypeofdistressinflexiblepavement.Itis commonlyfoundatinterconnectionandtrafficloading.
Slippagecracksarecrescent shapedorcrescent shaped crackswithtwoendsrunningawayfromtraffic.They formwhenthesidewalksurfaceslidesanddeformsdue tobrakingorturningwheels.

Longitudinalcracksbecomesimilartothemidlineofthe roadway. They can be caused by: poorly constructed joint,Asphaltlayershrinkage,Cracksreflectedfromthe underlying layer, And longitudinal separation due to improperpavingoperation.


Fig 4 : Longitudinalcracking
Edgecrackstravelwithinoneortwofeetoftheinternal edgeoftheroadwaysurface.Themostcommoncauseof thistypeofcrackisunfortunatedrainageconditionsand lack of support on the sidewalk. As a result, the base materialbecomesstagnantandweak.

Duetoinsufficientstrengthinsingleormorelayersof roadway,usuallyduetotheoccurrenceofwater,pitsare formedwhenthepavementdegradesintheloadingof traffic.Mostofthepitswillnothappeniftherootcause isrepairedbeforethepitsdevelop.


Roads run on black cotton soils are known for poor conditionandunpredictablebehaviorforwhichthenature ofthesoilcontributestosomeextent.Thenatureofblack cottonsoilisdiscussedhere.
BCsoilsabsorblargeamountsofwater,swell,soften,lose strength,areeasily compressed,andtendtogerminatein wetconditions.
BC soils are depleted and fall apart in summer. They are characterizedbyextremehardnessandcrackingwhendries.
Whenthefreeswellindexismorethan50%,thesoiliscalled highexpander.Largechangesoccurinsuchsoilsthatcause
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
sidewalkstodeform,crack,andcausegeneralunevenness duetoseasonalwetnessanddryness.
BC produces 2 to 5% CBR value if the soil is efficiently compacted.
Thereisnodrainagesystem.Sothewaterthatfallsonthe road.Thatwaterisstoredontheroadanditispercolateinto the road. Percolated water create movement in sub grade course (i.e changes properties of black cotton soil). And cracksandpotholesformintheroad.
thisvomitparadox.Thewetonesarenarrowatthebottom andwideatthebottom.Thebasicconditionofthesoilwasto buildinsuchsoils.Aspecialmethodoflayingthefoundation isrequiredinsuchsoils.
Fig 7 : NoDrainagesystem
Every surface, including asphalt, is exposed to weather. Although the sun's intense rays can damage the asphalt, torrentialrainsandexcessiverainfallcancauseevenmore damage.Thelastthingyouneedismoisturetogetintoyour tar.Temperaturechangesthatcausefreezingandthawing can also affect asphalt. Due to temperature water is evaporated,soilisshrinkageandduetoheavyrainfallwater ispercolatedinsoilanditisswelled.
Definition:
Blackcottonsoilisheavyclaysoil,varyingfromclaytoclay; itisusuallylighttodarkgrayincolor.Cottongrowsinsuch soils.Thissoiliscommonlyfoundincentral andsouthern parts of India. The most important feature of soil is that when it is dry it shrinks and is as hard as stone and its endurance is very high. Large cracks form in the soil. The entireareasplitsandcracksformuptoadepthof3.0to3.5 m and a width of 150 mm. But when the soil is moist, it expands,becomestoosoftandlosesitsabilitytohold.Dueto its wide character, it increases from 20% to 30% of the originalsizeandbringspressure.Theupwardpressureisso greatthatitliftsthebaseupwards.Foundationsareaddedto
Fig 7 : Blackcottonsoil
4.9 Properties of black cotton soil:
1) IthashighswellingandshrinkageLimit.
2) Clayeytextureandhighfertile.
3) Highretentiveofmoisturecontent.
4) Extremelycompactandforcefulwhenwet.
Contractibleanddevelopdeepwidecracksondrying.
5.1 Test on black cotton soil
5.1.1 Liquid limit test on black cotton soil.
Liquid limit (WL): The liquid limit is conceptually definedasthewatercontentatwhichthebehaviorofa clayey soil changes from plastic to liquid. But experimentally it is defined as the minimum water content at which two separated grooved soil parts mixedtogetherunder25blowsofCasagrande’sLiquid LimitApparatus.
Fig 8 : Liquidlimittest
Procedure :
1) Take about 120 grams. Sample of air dried soil passingthrough425micronISsieveMetaltray.
2) Add20%distilledwatertothesoilsampletomakea uniformclaypaste.
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal





International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
3) Place this clay paste in the brass cup of Cassagrande's tool and spread horizontally In part withafewstrokesofthespatula.
4) Trimthesoiltoadepthof1cmandremoveexcess soil.
5) Makestrongstrokesalongthesideofthegrooving toolintwopartsofthesoilsampleBrasscupinthe centerofthediametersothattherightsharpgroove willbecleanDimensionsarecreated.
6) Rotate the handle of the Cassagrande device at a speedof2cyclespersecond.Thetwopiecesofsoil willcomeincontactwitheachotherforalengthof about12mmOnlybyflow.
7) Measurethenumberofturnsrequiredtoclosethe grooveuptoabout12mm.ThisisitRecordedasn.
8) To determine the amount of water, take a representativepartofthesoilw%.
9) Repeatalltheabovestepsbychangingthewaterin thesoilsampletogetthenumberofstrokesBetween 10 and 50. Record the number of strokes and the amountofwaterassociatedvarioustests.
10) Draw the flow curve is the number of strokes requiredagainsttheabscess(logscale)the amount ofwaterdeterminedasanordinate(naturalscale)on asemi logarithmicgraph paper.
11) Find the amount of water corresponding to 25 strokesfromthegraphasaliquidlimit (WL)ofa givensoilsample.
Maximum Dry Density (M.D.D): It is the Maximum value of dry density obtained in compaction curve, is knownasMaximumDryDensity.

OptimumMoistureContent(O.M.C):Itisthewatercontent corresponding to maximum dry density of soil, is calledasOptimumMoisterContent.
1) Take about 5 kg. De aerated soil through a 20 mm sieveinthetray.
2) Addabout4%water(approximately120ml)tothe soilandmixwellwithatrowelandcoverthesoilwith adampclothfor24hourstoensurethatthewateris completelymixed.

3) Notethedimensionsoftheproctormold,collarand baseplate.
4) Taketheemptyweightofthemold(withoutcollarand baseplate).
5) Applyathinlayerofgreaseontheinsideofthemold.
6) Putthemoldonthebaseplatewiththehelpofwing nuts,putthecollaronthemold.
7) Determinethedensityoftheproctorandgiveuntilthe soilinthemoldinthreeequallayers.Usingastandard hammer, hit each layer 25 times. Scrape on the compactedtopsurfaceLayerbeforeplacingthenext layerofsoil.MakesureafterthirdcompactionLayer, compacted soil level slightly above the top of the mold.
8) Removethecollar,trimthe soilwithstraightedges, disconnectthemoldfromthebaseplateandtakeits weight.
9) Removethecompactionsoilfromthemold.
10) Collect a sample in the middle of the mold to determinetheamountofwater.
11) Repeatsteps5to10,takingfreshsampleofthesame soil, adding 3 to 4% more water than previously
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

addedwater.Repeatthesestepsforno.Timesforsoil weightlossforatleasttwoconsecutivereadings.
12) Measurethebulkdensityofcompactedsoilforeach test.
13) Determine the maximum dry density and optimum humidityrelativetostandardProctercompactionby plottinggraphwatercontentv/s.Drydensity.Also plot constant degrees of saturation lines for 100%, 90%,80%saturationonthesamegraph.Calculatethe degree of saturation relative to the maximum dry densityasOMCandMDDofagivensoilsample.
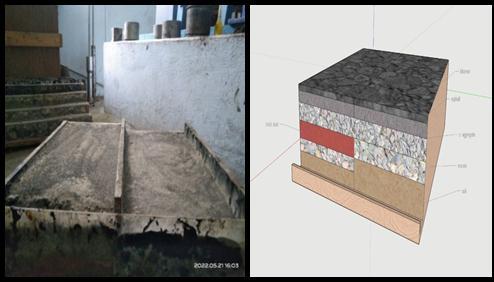
1) Firstwepreparethetowroadsectionusingply.
2) Infirstsectionspreadblackcottonsoilupto25mm thicklayerandcompactedit.
3) Secondspreadmurumupto25mmthicklayerand compactedit.
4) Thenweapplycoarseaggregate25mmlayeronthe murumandcompactedit.
5) Thenweapply15mmthicklayerofasphalt.
6) Thenwespreadbitumenlayerof10mmthickon thetopofthesurface
4) Thenweapplybrickdustlayerupto25mmthickon themurumandcompactedit.
5) Thenweapplycoarse aggregate25 mm layer on the murumandcompactedit.
6) Thenweapply15mmthicklayerofasphalt.
7) Thenwespreadbitumenlayerof10mmthickonthe topofthesurface
Fig
1) Firstwepreparethetowroadsectionusingply.
2) Insecondsectionspreadblackcottonsoilupto25mm thicklayerandcompactedit.
3) Second spread murum up to 25 mm thick layer and compactedit.
7. RESULTS
7.1 Test on black cotton soil
Sr.No. Name of Tests Result
1 Liquidlimitin(%) 54.33 2 Optimummoisture content(%) 17.96 3 Drydensity (gm/cc) 1.80
Chart No. 1

7.2 Liquid limit test of black cotton soil + brick dust
Sr. No. Samples Liquid limit in (%)
1
Blackcottonsoil 54.33 2
Blackcottonsoil(90%) +brickdust(10%): 50.53 3
Blackcottonsoil(80%) +brickdust(20%): 48.00 4 Blackcottonsoil(70%) +brickdust(30%): 42.55
Chart No. 2
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Chartshowseffectofbrickdustonliquidlimitofblack cottonsoil.
1) “AStudyonEngineeringBehaviorofBlackCottonSoil anditsStabilizationby UseofLime”,BrajeshMishra, International Journal of Science and Research in Engineering.
2) “ReviewOnComparativeStudyOnSoilStabilization Using Natural Materials”, Tehsin Kazi1 ,Shabiimam M.A2,OmerBaig3andFerozMachlcuri4
Chart No. 3
Procedure :
1) Weretained500mlwateronbothroadsectionsupto 24hours.
2) After24hoursweobserved,thewaterispercolateinto roadsectionwherebrickdustisnotused.
3) “AReviewAndStudyOnStabilizationOfExapansive SoilUsingBrickDust”,S.LakshmanTeja1,S.Shravan Kumar2 ,Dr.S.Needhiasan3,International Journal of Scientific&Engineering.
4) “PROBLEMS AND TREATMENT OF BLACK COTTON SOIL”, Rajesh Prasad Shukla,Niraj Singh, Pravar Yadav, Nitesh Mankotia, 50 th INDIAN GEOTECHNICAL CONFERENCE 17th 19th DECEMBER 2015, Pune, Maharashtra, India Venue: CollegeofEngineering(Estd.1854),Pune,India
5) “StudyofSuitableFoundationsforBlackCottonSoil”, Prof. A. R. Gupta1, Ms. Roochira R. Bobde2, InternationalJournalforResearchinAppliedScience & Engineering Technology (IJRASET) ISSN: 2321 9653;ICValue:45.98;SJImpactFactor:7.177Volume 7IssueV,May2019 Availableatwww.ijraset.com
Fig 12 : Waterpercolationtestonmodel
1) We visit the Islampur Sangli road and we studied the current condition of road and surrounding area we foundthattotallyareaiscoveredwithblackcottonsoil.
2) We took sample of black cotton soil and check the variouspropertiesofblackcottonsoillikeliquidlimit, OMC,MDD.Wefoundthatduetoblackcottonproperties shrinkageandswellingoccursandroadsettlementdue toheavyloadvehicles.
3) Blackcottonsoilismaincauseofsettlementofroadso weneedtoimprovestabilityofblackcottonsoil.


4) Withthehelpofbrickdustweimprovethestabilityof black cotton soil and it is observed that brick dust partiallymixwithblackcottonsoilandreducethewater content.
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page47