
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
FIELD SURVEY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
Anshul Borkar1 , Atharva Degwekar2 , Chaitanya Khotele3 , Prof. Prashant Govardhan4
1,2,3Student, Computer Science and Engineering Department, Priyadarshini College of Engineering, Nagpur-440019 4Professor, Computer Science and Engineering Department, Priyadarshini College of Engineering, Nagpur-440019, Maharashtra, India ***
Abstract- Inthiseraoftechnologicalleaps,ensuringthe sanctity of data collection stands as a formidable challenge. This research embarks on a profound expedition, aiming to cultivate sincerity and thoroughness among officials, safeguarding the very essence of data integrity. Through meticulouscraftsmanship,asophisticatedcross-platformfield survey management system is meticulously sculpted, emphasizing personal visits to specific locales, thereby heraldinganunparallelederaofdataauthenticity.Thispaper meticulouslydissectsthearchitecturalintricaciesofthesystem, embracing avant-garde cross-platform development methodologies, critically analysing historical fieldwork managementparadigms,exploringpioneeringdatacollection methods, probing into real-time monitoring marvels, and contemplating the subtleties of sincerity assessment methodologieslaudedbyindustrystalwarts.
Keywords Cross-platform Development, Fieldwork Management System, Data Collection Integrity, Realtime Monitoring, Sincerity Assessment
1.INTRODUCTION
In today's data-driven economy, where information is the foundationforeducateddecision-makingacrossindustries, the integrity and quality of collected data is critical. Traditional fieldwork management approaches frequently failtoensuredatareliability,emphasizingtheneedfornovel solutionsthatgobeyondtechnologydevelopments.
The proposed Cross-Platform Fieldwork Management Systemoffersaparadigmshiftindatacollectionmethods, stressingthemutuallybeneficialinteractionbetweendata collectorsandthecommunitiestheyserve.Unliketraditional systems that focus primarily on technology tools, this methodologyrecognizestheinherentvalueofhumancontact ingatheringtrueandusefuldata.
At the heart of this transformational perspective is an understandingthatdatacollectors'sincerityanddiligence have a substantial impact on the authenticity and dependability of acquired data. By prioritizing personal visits to certain places, the method hopes to promote a bettergraspoflocalsettingsandnuances,henceimproving thequalityofacquireddata.
This technique is based on the concept of data collection integrity,whichgoesbeyondthemechanicalactofacquiring
information. It requires ensuring that data collectors are bothtechnicallycompetentandethicallydedicatedtotheir roles. The system aims to bridge the gap between technologicalimprovementsandthehumanfactorinherent in data collection operations by combining technological innovationandhuman-centereddesignprinciples.
Furthermore, the suggested approach provides a flexible framework that may be adjusted to meet a wide range of survey requirements, from large-scale national studies to community-focusedresearchefforts.Byprovidingmanagers with tools for tracking fieldworker actions and closely monitoring the data they generate, the system enhances operationalefficacyandaccountabilitythroughoutthedata gatheringprocess.
Beyonditsimmediateusesindatacollection,thesuggested technologyhastransformativepotentialinavarietyoffields. Policymakerscanusetheinsightsgainedfromcollecteddata toaddresssignificantsocietalissuesanddevelopevidencebased policy. Similarly, corporations can make strategic decisions based on credible market research data, and researchers can expedite scientific advancement by accessingextensiveandtrustworthydatasets.
The Cross-Platform Fieldwork Management System, in its essence, is more than just a technical fix; it symbolizes a changeinthedirectionofagenuineandopencultureindata gatheringprocedures.Thesystemcreatestheconditionsfor evidence-based decision-making and the advancement of society in the digital age by encouraging cooperation, stimulating innovation, and providing stakeholders with trustworthydata.
2.AIM AND OBJECTIVES
Create a reliable Cross-Platform Fieldwork Management Systemtoimprovedatacollectionintegrityandoperational efficiencyinvarioussurveyscenarios.
ImprovingDataCollectionIntegrity:Establishsystems to evaluate and assure the honesty and diligence of officials involved in data collection activities. Include elements that encourage personal visits to defined places, resulting in a better comprehension of the obtained data and increased validity. Implement validation processes to ensure the correctness and

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
validityofobtaineddata,whileminimizingerrorsand biases.
Streamlined Data Collection Procedures: CreateanintuitiveuserexperienceforbothAndroidand webplatforms,allowingauthoritiestointeractandinput data seamlessly. Create effective data management solutions to organize and categorize acquired data, while streamlining storage and retrieval operations. Providereal-timesynchronizationcapabilities.
FosteringTechnologicalInnovation:Usecross-platform developmentmethodstoprovideinteroperabilityand accessibility across several devices and operating systems. Use advanced data analytics techniques to extract meaningful insights from collected data, providing decision-makers with useful information. Investigate upcoming technologies such as AI and machine learning to automate repetitive jobs and improvedatacollectionmethods.
3. LITERATURE REVIEW
[1] M. Nagappan and E. Shihab: "Future Trends in Software Engineering Research for Mobile Apps":
This study offers a fascinating look at present and future trends in software engineering. It covers the rapidly increasingnumberofmobiledevicesandtheresultingboom in software programs, or 'apps.' The article stresses the critical relevance of non-functional needs, with a nuanced focusontheseveralstagesofthesoftwaredevelopmentlifecycle, including requirements, design and development, testing, and maintenance. It looks into the vital themes of energy and security in particular, recognizing the specific problems encountered by mobile app developers, particularlythosenotlinkedwithhugeorganizations.The articlepromotesitselfasaguidingbeaconforacademicsand developersnavigatingthedelicateareaofmobilesoftware engineeringbyprovidingacompleteassessmentofcurrent advancements,problems,andfuturepotential.
[2] R. Nunkesser: "Beyond Web/Native/Hybrid: A New Taxonomy for Mobile App Development":
This landmark research provides a fresh classification system in response to the usual taxonomy of mobile app development. The research presents six new categories basedonfundamentaldifferencesintoolsandprogramming languages,departingfromthetraditionalWebApps,Native Apps, and Hybrid Apps paradigm. The taxonomy, which includesEndemicApps,WebApps,HybridWebApps,Hybrid BridgedApps,SystemLanguageApps,andForeignLanguage Apps,aimstogiveamorerealisticandnuancedpictureof modern multi-platform development. Not only does the article address the requirement for precision in classification,butitalsoestablishesthreeprimarycategories
withsevensubcategories,givingamoredetailedframework forthevariegatedterrainofmobileappdevelopment.
[3] A. Charland, B. Leroux: "Mobile Application Development: Web vs. Native":
Thisarticleprovidesahistoricalperspectiveonthehistory of mobile devices by reflecting on the revolutionary influenceofApple'siPhonedebutonmobileexperiences.It harkensbacktoatimewhenmobiledevicesweredubbed "dumb" because they lacked sophisticated touch displays andpowerfulbrowsers.Thestoryfollowsthekeymoment whenApple'siPhonechangedmobileexpectations,altering thecourseofmobileinteractions.Recognizingthisparadigm change,thepaperemphasizesthedramatictransitionfrom simpletextdisplaystorichanddynamicmobileplatforms.It highlights the paradigm shift that influenced the present landscapeofmobileappdevelopment,usheringinanewera ofmobileexperiences.
[4] M. Latif, Y. Lakhrissi, E. H. Nfaoui, and N. Es-Sbai: "Review of Mobile Cross-Platform and Research Orientations":
Thisincisivestudyexaminesthelandscapeofmobilecrossplatformtechniquesandtoolsinthecontextoftheproblems facedbyplatform-specificmobiledevelopment.Recognizing thetimeandfinancialrestrictionsinvolvedwithcreatingfor multiple platforms, the study promotes cross-platform techniquesasafeasiblealternativethatisgainingsupport among businesses. The comprehensive assessment goes beyondcurrentliterature,providinganin-depthlookatthe most recent tools and platforms linked with each crossplatformstrategy.Thestudyattemptstoaidresearchersand practitionersinmakinginformedjudgmentsbydivinginto the benefits and limits of each strategy. The work foreshadows future research paths, notably in the exploration of ontology requirements and the transformation of the unified model into administrative coresofcloudinfrastructures.
[5] T. Zohud, S. Zein: “A Systematic Mapping Study of Cross-Platform Mobile Apps”:
This fundamental work, published in the Journal of Computer Science, undertakes a painstakingly built SystematicMappingwork(SMS)tocategorizeandgraspthe complex terrain in a comprehensive analysis of crossplatform mobile app development. The SMS methodically maps30researchtoathoroughcategorizationframework, with a focused focus on contributions, problems, and successes. Key study gaps are observed, emphasizing the crucial necessity for more comprehensive and real-world appinvestigations.Thestudycorrectlyemphasizesthatthe distinction between cross-platform and native programs remainsvague,necessitatingmoreclarification.Thisstudy establishes the groundwork for future breakthroughs by serving as a rallying cry for further research efforts,

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
particularlyintheareasoftestingandmaintenancewithin thecross-platformmobileappdevelopmentparadigm.
4. METHODOLOGY
Oursolution,whichmakesuseofcutting-edgetechnology, provides unparalleled data integrity for well-informed decision-making while revolutionizing fieldwork management.Crucialelements
GPS technology verifies fieldworkers' presence, which ensuresdataauthenticity.
Robust databases Utilizes Google's widely recognized Firebaseplatformforefficientandadaptabledataarchiving. Strong programming languages are used in advanced programming to analyze and modify data in a reliable manner.Interfacesthatareeasytouse:Carefullythoughtout interfaces made with industry-standard development toolsprovideaseamlessuserexperienceonPCsandmobile devicesforreal-timedatacollection.
Analysis of Requirements: Using workshops and interviews, compile requirements from stakeholders. Determine the necessary features, giving operational effectivenessanddataintegrityfirstpriority.
System Architecture: Create a cross-platform architecturethatguaranteesusabilityandcompatibility. Create user-friendly interfaces with an emphasis on accessibilityformanagersandfieldpersonnel.
ChoiceofTechnology:Assessbackendtechnologiesand cross-platform development frameworks. Take into account automation and enhanced analytics using AI andmachinelearning.
Implementation: Createonlineandmobile appswhile adhering to security and design standards. Integrate synchronization, authentication, and data storage backendservices.
QualityControlandTesting:Performthoroughtesting, which should include usability and unit testing. Put automated testing frameworks for cross-platform reliabilityintopractice.
Implementation and Implementation: Forscalability,deploythesystemtocloud-basedhosting infrastructures. Set up pipelines for continuous deploymenttoensuresmoothupgrades.
5. SYSTEM DESIGNING
5.1 Cross-Platform Architecture:
The cross-platform architecture of the system enables the creation of applications that function flawlessly on boththewebandAndroidplatforms.
By allowing code, resources, and functionality to be shared between the web and mobile applications, this architecture ensures consistency across platforms and cutsdownondevelopmenttimeandeffort.
Through the utilization of cross-platform development frameworkslikeReactNativeorFlutter,thesystemcan get performance and user experience comparable to nativeonbothwebandAndroidplatforms.
5.2 Compatibility and Usability:
Compatibilityandusabilityaregiventoppriorityinthe design, guaranteeing that users can easily access and utilizetheapplicationsonavarietyofdevicesandscreen sizes.
Best practices for web and mobile applications are followedwhiledesigninguserinterfaces(UIs),withan emphasison responsive designconceptsthatadjust to differentscreenresolutionsandorientations.
Becausethenavigationandinteractionpatternsarethe same on all platforms, users may switch between the mobile and web interfaces without experiencing any usabilityproblems.
5.3 Data Management and Synchronization:
Effective data management and synchronization techniquesthatpermitsmoothdatasharingandupdating betweenfieldworkers,managers,andadministratorsare essentialcomponentsofthesystemdesign.
Backend services are employed to enable safe data synchronization, storage, and access control, guaranteeing that every user has instant access to the mostrecentdata.
Inconsistenciesandconflictsarehandledgentlybydata synchronization protocols, reducing the possibility of datalossordamageduringsynchronizationprocedures.
5.4 Security and Authentication:
The system architecture places a high priority on security,usingstrongauthenticationandauthorization procedurestosafeguardprivateinformationandsystem resources.
SecureprotocolslikeOAuthandJSONWebTokens(JWT) are used to enforce user authentication, guaranteeing thatonlyauthorizeduserscanaccessthesystemandits features.
Administratorscaneffectivelymanageaccessrightsby defininggranularpermissionsandprivilegesfordistinct userrolesthroughtheuseofrole-basedaccesscontrol (RBAC).

2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
5.5 System Architecture
The system architecture for the Field Survey ManagementSystemisdesignedtofacilitateseamless integration between the website application and the mobile application, ensuring efficient data collection, management,andanalysis.Atthecore,thearchitecture comprisesmultiplelayers,eachplayingacrucialrolein maintaining the system’s functionality and performance. The client layer includes the website application for managers, featuring an intuitive user interface for task assignment, survey creation, data monitoring, and reporting. Meanwhile, the mobile application, tailored for field agents, offers a streamlinedinterfacefortaskmanagement,attendance marking, survey form filling, and real-time location tracking,withofflinefunctionalitytoensurecontinuous operationwithoutinternetconnectivity.
Thebusinesslogiclayerhandlescoreoperationssuchas task and survey management, data validation, and processing. An API gateway bridges the website and mobile applications, ensuring secure and efficient data exchange through the integration layer, which also includesservicesforreal-timedatasynchronizationand userauthentication.Data is securelystoredina cloudbasedFirestoredatabase,whichsupportsscalabilityand consistency,whilesecuritymeasuressuchasencryption, role-based access control, and compliance with data privacyregulationssafeguardtheintegrityofthesystem. This integrated architecture ensures that all data collectedviathemobileappisinstantlyreflectedonthe website,providingmanagerswithreal-timeinsightsand facilitatinginformeddecision-making.

Figure 5: System Architecture
6. APPLICATION DESIGN
Theprogramdesignincludesseveralinterfaces,includinga loginpage,adashboardformanagers,asurveyinterfacefor field workers, and an informative "About" page. These interfaces leverage the Ionic platform's cross-platform featurestooffersmoothaccessibilityandconsistencyacross a wide range of operating systems and devices, including Android, iOS, and Windows. The application's design prioritizes usability, accessibility, and cross-platform compatibility, offering users intuitive interfaces and seamlessexperiencesacrossmultipledevicesandoperating systems.
6.1LoginPage:
Users, including fieldworkers and supervisors, can access the Cross-Platform Fieldwork Management System by entering their individual username and passwordontheloginscreen.
Aftersuccessfulauthentication,usersaregrantedaccess totheirparticulardashboardsorfunctionalityinsidethe program.
If the credentials entered are invalid, users are promptedtoseekassistancebyclickingthe"GetHelp" button,whichtakesthemtoasupportpageorcontact information.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Login Page
6.2AttendancePage:
Fieldworkers use the mobile application's attendance screen to record their presence at specific survey locations.
When fieldworkers arrive at a survey site, they can recordtheirattendancebyselectingtheirnamefroma listorscanningaQRcodeconnectedwiththelocation.
Theattendancescreenshowsreal-timedataon
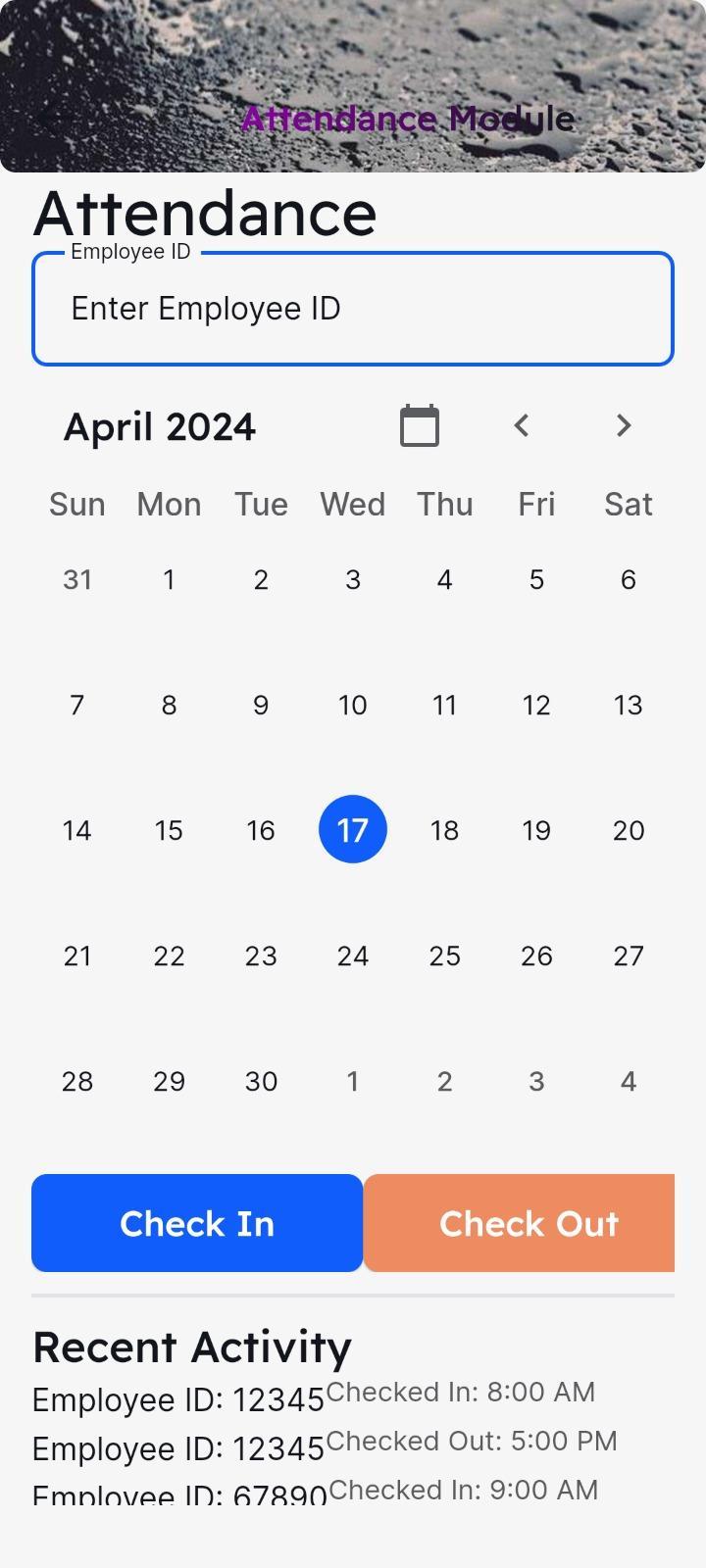
6.2: Attendance Page
6.3 Survey Screen:
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2024, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.226 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page1215
Fieldworkerscanusethemobileapp'ssurveyscreento collectdatafromrespondentsinthefield.fieldworkers can examine a list of assigned surveys and select the one to administer to respondents. The survey screen offers a simple interface for entering survey replies, capturingmultimediadata(suchasimagesorvideos), andrecordinggeographicalinformation.

Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

Managerscandrilldownintoindividualdatasetsand filterdatabycriteriasuchas
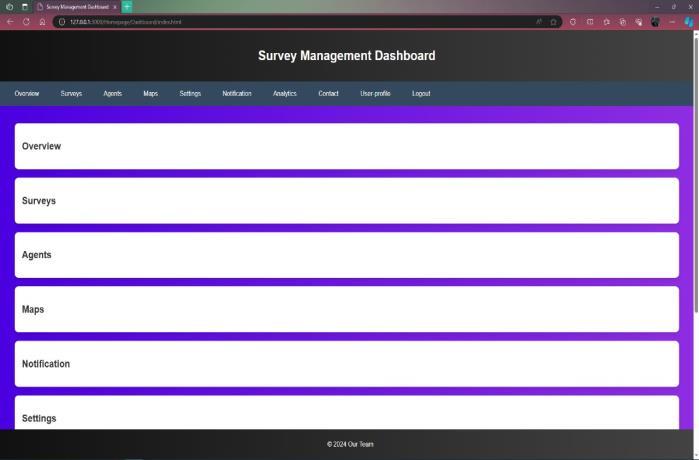
7. Conclusion:
Managers can access a full dashboard on the web application,whichprovidesanoverviewoffieldwork activities,surveyresults,anddatainsights.
The dashboard includes customized widgets and statistics that show critical performance factors including survey completion rates, geographical distributionofdatagathering,andchangesovertime.
TheCross-PlatformFieldworkManagementSystemprovides substantialbenefitsinsatisfyingthedifferentneedsofusers involvedindatagathering.Thetechnologyacceleratesdata collectionmethodsandimprovesoperationalefficiencyfor both fieldworkers and management by including a smart mobile application as well as a web interface. The key advantageofusingasmartmobileapplicationistheeaseand quicknesswithwhichrequestsmaybeconfirmed,reducing unnecessary work for consumers. Furthermore, a welldesignedinterfaceimprovestheuserexperienceandmakes iteasiertopublishresearchfindings.Lookingahead,there arepotentialtoexpandandimprovethesystem.Oneoption forexpansionistoincludemorecollegesandinstitutionsto increasetheareaofresearchpublicationandcollaboration. Furthermore,theadditionofmultilingualcapabilities,such as Arabic, may attract a more diversified user base and improve accessibility. Suggestions for future development includecontinuousimprovementoffunctionalityandquality to meet changing user needs. This involves providing a broaderrangeofoperationswithintheapplication,suchas allowing users to select alternatives from a menu and smoothlyfilloutformsbasedontheirrequirements.Adding achatoptioncouldalsohelpstaff,students,andsupervisors communicatemoreeffectively,ensuringthatquestionsand responsesareclarifiedinatimelymanner.Furthermore,the system's ability to connect colleges from diverse nations creates opportunities for worldwide collaboration and knowledge exchange. The system promotes increased collaborationandsynergyinresearcheffortsbyemploying technology to connect people across geographical boundaries.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
REFERENCES
[1] J.Z.Blanco,D.Lucrédio,Aholisticapproachforcrossplatformsoftwaredevelopment,JournalofSystemsand Software,Volume179,2021,110985,ISSN0164-1212
[2] Hakro, A., 2017. Research Management System [Interview](10April2017).
[3] E.F.Watson,P.P.Chawda,B.McCarthy,M.J.Drevna, and R. P. Sadowski, “A Simulation Metamodel for response-timeplanning,”DecisionSciences,vol.29,pp. 217-241,1998.
[4] Yiqing Lin, Arthur Hsu, and Ravi Rajamani, “A SimulationModelforFieldServicewithConditionBased Maintenance,” Proceedings of the 2002 Winter Simulation Conference, Dec. 8-11, 2002, pp. 1885 –1890.
[5] Yu-Ting Lin, and Tony Ambler, “A knowledge-based dispatchingmodelforfieldservices,”TheUniversityof TexasatAustin,USA.
[6] DrAlokAggarwal,DataanalyticsoutsourcingtoIndia: Doestheemperorhaveanyclues?Nov18,2014
[7] T.Zohud,S.Zein,“Asystematicmappingstudyofcrossplatform mobile apps,” Journal ofComputer Science, vol.
[8] YiqingLin,A.HsuandR.Rajamani,"Asimulationmodel forfieldservicewithcondition-basedmaintenance".
