
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04| Apr2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04| Apr2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1Kumar Shukla, 2Nimeshkumar Patel, 3Hirenkumar Mistry
1Principal Network Engineer, 2Sr.Network Engineer, 3 Senior Linux System Administrator ***
Abstract: Asmoderncomputingenvironmentsincreasingly rely on cloud technology, ensuring the security of cloudbasedsystemshasbecomeparamount.Thispaperexplores various strategies and innovations in network security specificallytailoredforcloudcomputingenvironments.We delve into the unique challenges posed by cloud infrastructures, including data privacy, confidentiality, integrity, and availability concerns. Drawing on recent advancements in network security, we discussencryption techniques,accesscontrolmechanisms,intrusiondetection and prevention systems, and other proactive measures aimedatsafeguardingcloud-basedassets.Additionally,we examine emerging trends such as Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV)andtheirimplicationsforenhancingcloudsecurity. Byanalyzingtheintersectionofnetworksecurityprinciples andcloudcomputingparadigms,thispaperoffersinsights and recommendations to stakeholders seeking to fortify theircloudinfrastructuresagainstevolvingcyberthreats.
Index Terms – Cloud Security, Network Security, Modern Computing,CybersecurityInnovation
The rapid rise of cloud computing has fundamentally alteredhoworganizationsmanagedata,runapplications,and accessresources.However,thistransformationcomeswitha significant responsibility: ensuring the security of these critical assets in the cloud. Unlike traditional on-premise environmentswhereorganizationsretaincompletecontrol over infrastructure, cloud computing adopts a shared responsibility model. While cloud providers offer robust security features, the ultimate burden of securing data, applications,andaccesscontrolslieswiththeorganization utilizing the service [1]. This necessitates a multi-layered approachtocloudsecurity,withnetworksecurityforming thefoundation.
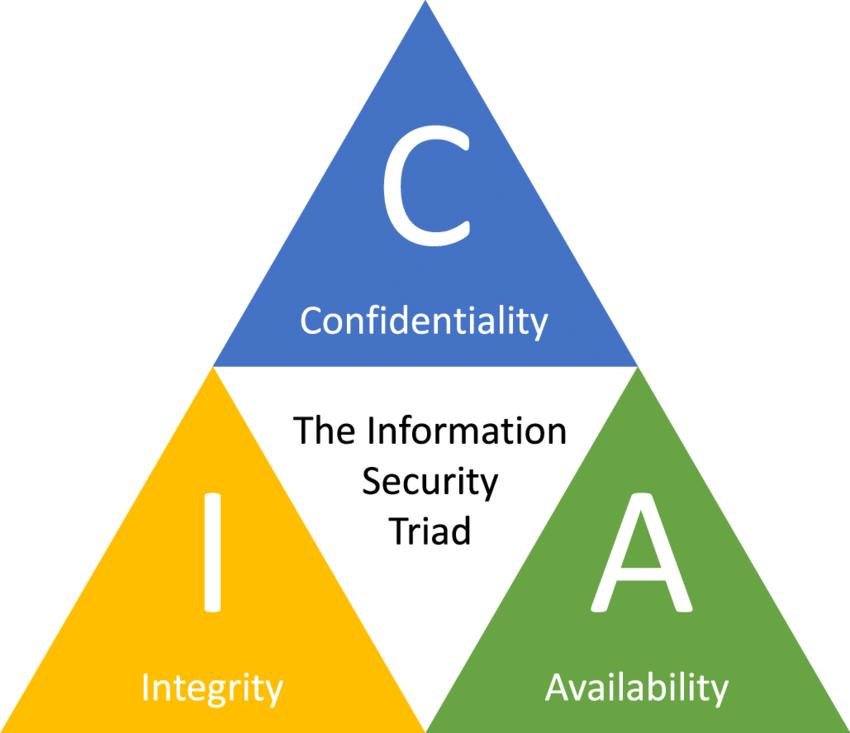
Networksecurityinthecloudfocusesonprotectingthe communication channels between users, applications, and cloudresources.ItensurestheCIAtriad:
Confidentiality: Data remains accessible only to authorizedusersandapplications.
Integrity: Data isn't tampered with or altered duringtransmission.
Availability: Authorized users can reliably access cloudresourcesandapplications.
Severalestablishedstrategiescanfortifyacloudnetwork securityposture.OnecrucialpracticeisIdentityandAccess Management (IAM). IAM involves establishing clear user identities, defining access controls (who can access what resources), and implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for added security. This ensures only authorized individualshaveaccesstospecificcloudresourcesbasedon theirrolewithintheorganization[2]
Another critical layer of protection is data encryption. Encryptingdataatrest(storedinthecloud)andintransit (being transmitted) safeguards its confidentiality even if interceptedbyunauthorizedparties[3].Encryptionrenders thedataunreadablewithouttheappropriatedecryptionkey, significantlymitigatingtheriskofdatabreaches.
Networksegmentationfurtherstrengthenscloudsecurity. This approach divides the cloud network into isolated segments,limitingthepotentialspreadofsecuritythreats.By creatingseparatesegmentsforcriticalapplicationsanddata, the impact of a security breach in one segment can be contained,preventingitfromcompromisingtheentirecloud environment[4]
Traditionalsecuritytoolsalsoplayavitalrole.Firewalls actasthefirstlineofdefense,filteringincomingandoutgoing networktrafficbasedonpredefinedsecurityrules.Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) continuously monitornetworktrafficformaliciousactivityandcaneither detectorblockunauthorizedaccessattempts[5].
However, cloud security is a dynamic field constantly evolving with new technologies. Machine Learning (ML) offers innovative solutions by analyzing network traffic patternstodetectanomaliesandidentifypotentialthreatsin real-time.Thisallowsforproactiveidentificationofsecurity breachesbeforetheycancausesignificantdamage[6]
Blockchain technology presents another promising avenueforenhancingcloudsecurity.Blockchaincanbeused to create tamper-proof records of data access and transactions, further bolstering data integrity and auditability. The Zero-Trust security model is another emergingconceptgainingtraction.Thismodelassumesno userordeviceisinherentlytrustworthywithinthenetwork.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04| Apr2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
It enforces continuous verification for access control, requiring users toconstantly re-authenticate regardless of theirlocationordevice[7] Byunderstandingtheevolving securitylandscape,implementingestablishedstrategies,and embracingtheseinnovations,organizationscanbuildrobust cloud network security. This comprehensive approach ensures a secure and reliable foundation for modern computingenvironmentsinthecloud.
Cloudcomputinghasemergedasafundamentalpillarof modern information technology, revolutionizing the way organizations procure, manage, and leverage computing resources.AsdefinedbytheNationalInstituteofStandards and Technology (NIST), cloud computing refers to the deliveryofcomputingservices includingservers,storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics over the internetonapay-as-you-gobasis[1].Thisparadigmshifthas ledtoadeparturefromtraditional,on-premisedatacenters towardsadecentralizedandflexiblemodel,whereresources are dynamically allocated and scaled to meet changing demands.
Thesignificanceofcloudcomputinginmoderncomputing environments cannot be overstated. It offers unparalleled agility,scalability,andcost-efficiency,enablingbusinessesto rapidly innovate, scale operations, and respond to market dynamics [9]. Moreover, cloud computing democratizes accesstoadvancedtechnologiesandcapabilities,levelingthe playing field for organizations of all sizes and industries. Fromstartupstomultinationalcorporations,fromhealthcare to finance, virtually every sector has embraced cloud computingasastrategicenablerofdigitaltransformation.
However,amidstthemyriadbenefitsofcloudcomputing lies the paramount importance of cloud security. As organizations increasingly migrate sensitive data, critical applications,andbusinessprocessestothecloud,ensuring theconfidentiality,integrity,andavailabilityoftheseassets becomesimperative[10].Thesharedresponsibilitymodel, whereincloudserviceproviders(CSPs)areresponsiblefor thesecurityofthecloudinfrastructurewhilecustomersare accountable for securing their data and applications, underscoresthecollaborativeeffortrequiredtomaintaina securedcloudecosystem[11].

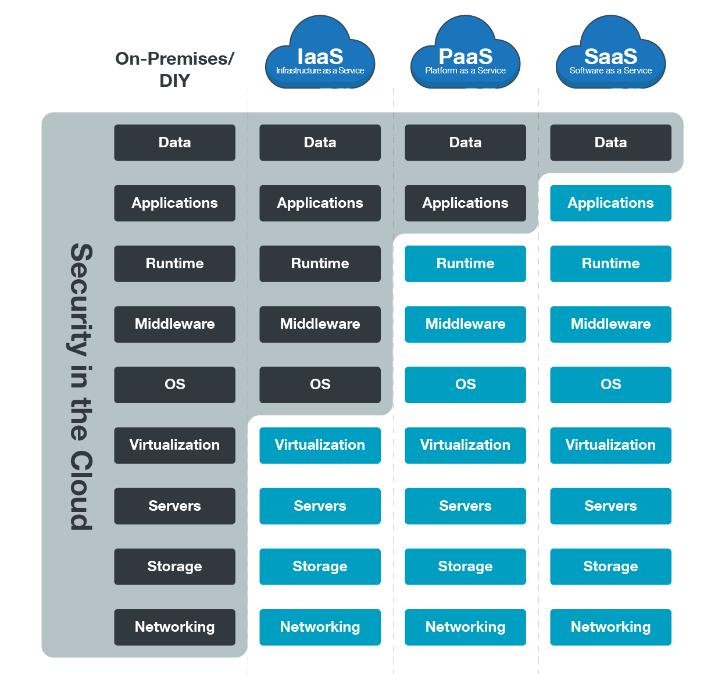
Cloudcomputingoffersavarietyofservicemodels,eachwith itsownsecurityimplications[1]:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):While IaaS providesthefoundationallayer(virtualizedservers, storage,networking),thesecurityresponsibilityfalls on the user to secure the operating systems, applications, and data deployed on top [12]. This necessitates robust security practices like encryption, access controls, and vulnerability management.
Platform as a Service (PaaS):PaaS offers a preconfiguredplatformwithbuilt-insecurityfeatures. However, users still hold some responsibility for securing their applications and data [13] Understanding the security posture of the chosen PaaSprovideriscrucial.
Software as a Service (SaaS):SaaS offers the most managedservicemodel,withtheproviderhandling mostsecurityaspects.However,usersshouldstillbe awareofpotentialsecurityriskslikedatabreaches and ensure proper access controls for their data withintheSaaSapplication[14]

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04| Apr2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
2.2 Benefits of Cloud Computing in Modern IT, with SecurityinMind:
Cloud computing offers numerous advantages over traditionalon-premiseITinfrastructure,butsecurityremains paramount:
CostEfficiencyandSecurityOptimization: Cloud computingoffersapay-as-you-gomodel,eliminating upfronthardwareandsoftwarecosts,andreducing ongoing maintenance expenses [15]. Cloud providers often invest heavily in security infrastructure,offeringrobustsecurityfeaturesthat may be out of reach for smaller organizations onpremise.Thistranslatestoabalancebetweencost optimization and a potentially stronger security posture.
Scalability and Agility with Secure Resource Management: Cloudresourcescanbeeasilyscaled up or down based on changing business needs. However, this agility needs to be balanced with secureresourcemanagement.Implementingaccess controlsandmonitoringresourceusageensuresthat onlyauthorizedusersaccesscloudresources[16]
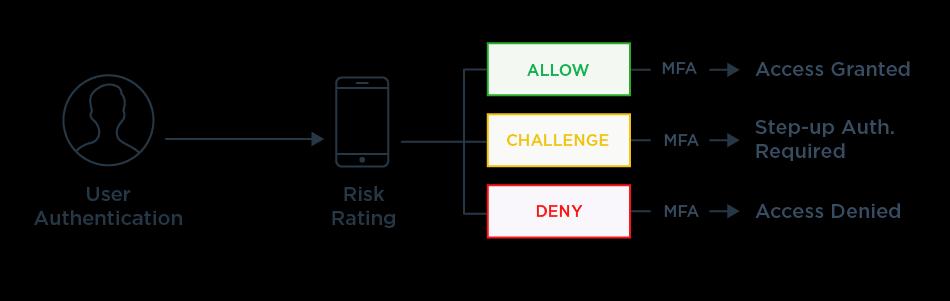
Improved Accessibility and Collaboration with Secure Access: Cloud-based resources can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, promoting remote work and collaboration.However,secureaccessprotocolslike multi-factor authentication (MFA) are crucial to preventunauthorizedaccess[2]
3. The Challenge of Cloud Security:
The shift from on-premise IT infrastructure to cloud computinghasfundamentallyalteredthesecuritylandscape. Traditionally,organizationsheldcompletecontrolovertheir physical data centers, wielding absolute authority over security policies and implementation. However, cloud computingintroducesasharedresponsibilitymodel,where the burden of security is distributed between the cloud providerandthesubscribingorganization[1].
3.1UnderstandingtheShared ResponsibilityModel:
While cloud providers invest heavily in securing their infrastructureandunderlyingplatforms,thespecificsecurity posture of cloud resources ultimately rests with the organization leveraging the services [14]. This shared responsibilitymodelcanbebrokendownintodistinctareas:
Cloud Provider Responsibility in Securing the Cloud Environment:
Cloudprovidersplayacriticalroleinsafeguarding the security of the cloud ecosystem. Their responsibilities encompass various aspects of the
underlying infrastructure and platform, offering a baseline level of security for organizations leveraging their services. Here's a detailed breakdownoftheirkeysecurityareas:
a) Physical Security of Data Centers: Cloud providers invest heavily in securing their physical data centers, which house the hardwareinfrastructurethatpowerstheircloud services.Thisincludesmeasureslike:
o Restricted access control: Implementing physical barriers, security personnel, and accesscontrolsystemstorestrictentryto unauthorizedindividuals[14]
o Environmental controls: Maintaining appropriatetemperature,humidity,andfire suppression systems to ensure optimal equipment functionality and prevent physicaldamage[17]
o Video surveillance: Utilizing CCTV camerasandothermonitoringsystemsto deter unauthorized activity and provide videoevidenceforsecurityincidents.
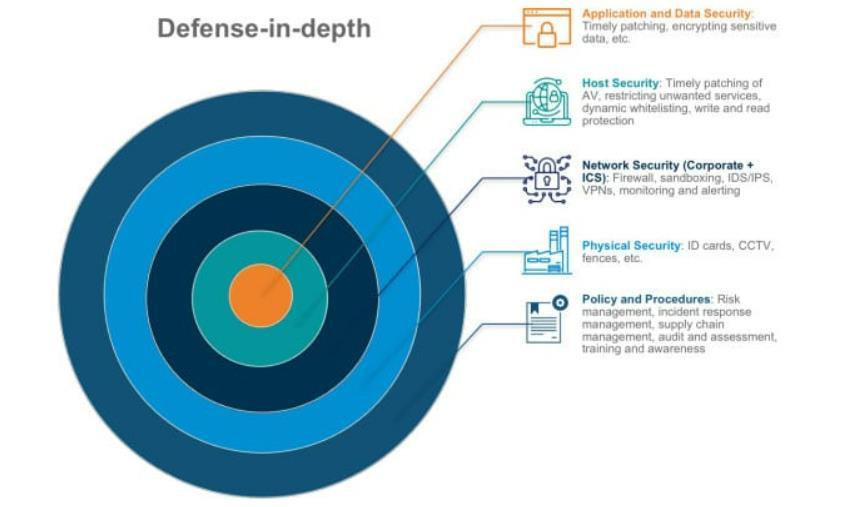
b) NetworkSecurity: Cloudprovidersimplement robust network security measures to protect againstunauthorizedaccess,databreaches,and maliciousattacks.Thesemeasuresinclude:
o Firewalls: Deploying firewalls to filter incoming and outgoing network traffic, blocking unauthorized access attempts [11]
o Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Monitoring network traffic for suspicious activity and actively preventingintrusions[22]

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04| Apr2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
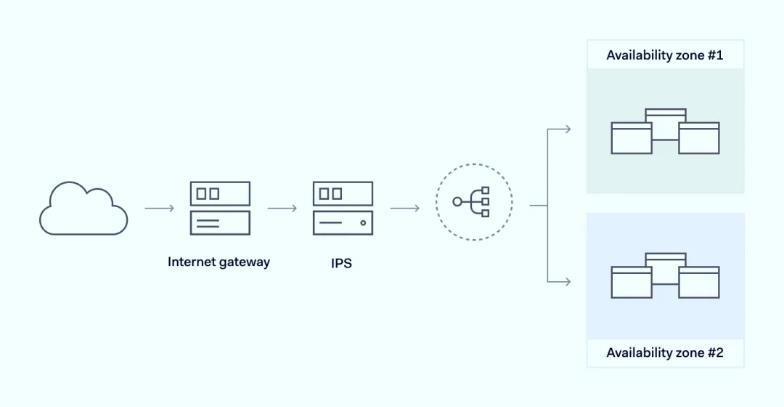
3.1:NetworkSecurity[21]
o Network segmentation: Segmenting the cloudnetworkintologicaldivisionstolimit the potential impact of a security breach [23].
c) Virtualization Technologies: Cloud providers leverage virtualization technologies to create multiplevirtualmachines(VMs)onasinglephysical server. Security measures within virtualization environmentsinclude:
o Secure hypervisor: Utilizing a secure hypervisortoisolatevirtualmachinesfrom each other and the underlying hardware [3].
o Virtual machine security controls: Implementing access controls, encryption,andothersecuritymeasuresat thevirtualmachinelevel[24]
d) BaselineSecurityFeatures: Cloudprovidersoffer varioussecurityfeaturespre-configuredwithintheir platforms.Thesefeaturesempowerorganizationsto further secure their cloud resources. Examples include:
o Data encryption: Offering encryption options for data at rest and in transit to protectsensitiveinformation.
o Identity and Access Management (IAM): Providing tools for managing user access and permissions within the cloud environment.
o Security logging and monitoring: Enabling organizations to monitor security events and activities withintheircloudresources.
Organization Responsibility: Organizations are responsibleforsecuringtheirdata,applications,and accesscontrolswithinthecloudenvironment.This includesuseraccessmanagement,dataencryption atrestandintransit,configurationmanagementof cloud resources, and implementing security best practicesforapplicationsdeployedinthecloud[11].
3.2ChallengesoftheShared ResponsibilityModel:
Thesharedresponsibilitymodelpresentsseveralchallenges fororganizationsmigratingtothecloud:
Complexity: Organizationsneedtounderstandthe specificsecurityboundarieswithinachosencloud provider's model. This complexity can be further amplified with hybrid cloud deployments that combine on-premise infrastructure with public cloudservices[18].
Visibility and Control: Organizations may have limitedvisibilityintotheinnerworkingsofthecloud provider's security infrastructure. This lack of controlcanmakeitdifficulttoensurethesecurity posturealignswiththeorganization'sspecificneeds.
Misconfiguration: Accidental misconfiguration of cloud resources is a common security risk. Organizationsneedtoestablishrobustconfiguration managementpracticestoensurecloudresourcesare setupsecurelyandremaincompliantwithsecurity policies.
InsiderThreats: Insiderthreats,whethermalicious orunintentional,canposeasignificantrisktocloud security.Organizationsneedtoimplementsecurity measureslikedatalossprevention(DLP)anduser activitymonitoringtomitigatetheserisks.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04| Apr2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
4. Why Network Security Matters in the Cloud: The Backbone of Data Protection
Networksecurityplaysacriticalroleinsafeguardingthe cloudenvironment.Itencompassesacomprehensivesetof strategies and technologies designed to secure the communication channels between users, applications, and cloudresources.Robustnetworksecurityisfundamentalfor ensuring the CIA triad (Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability)ofdatainthecloud:
a. Confidentiality:ProtectingSensitiveInformation
Inthecloud,datatravelsacrossnetworks,makingit vulnerable to potential interception. Network security measureslike:
Firewalls: Actasgatewaysthatfilterincoming and outgoing traffic, blocking unauthorized access attempts and preventing sensitive data fromleakingout.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Create secure encrypted tunnels over public internet connections,ensuringconfidentialityofdatain transit.
Data Encryption: Encryptsdataatrest(stored in the cloud) and in transit, rendering it unreadable even if intercepted by malicious actors.
Byimplementingthesemeasures,networksecurity safeguardssensitiveinformationlikefinancialdata, customer records, and intellectual property from unauthorizedaccess.
b. Integrity:MaintainingDataAccuracyandTrust
Data integrity ensures that information remains unaltered during transmission and storage in the cloud.Networksecuritymeasureslike:
IntrusionDetectionandPreventionSystems (IDS/IPS): Monitornetworktrafficformalicious activity that could attempt to modify data in transit.
Checksums and Hashing: These techniques generate unique digital fingerprints for data, allowing for verification and detection of any unauthorizedmodifications.
Secure protocols: Implementing secure protocolslikeHTTPS(encryptedHTTP)during datatransferensuresdataintegrityandprevents man-in-the-middleattacks.
Networksecurityplaysavitalroleinmaintainingthe accuracy and trustworthiness of data within the cloud environment.
c. Availability:EnsuringAccesstoCloudResources
Availabilityreferstotheabilityofauthorizedusersto access cloud resources and applications reliably. Networksecuritymeasureslike:
Networkredundancy: Implementingredundant networkpathsandfailovermechanismsensures that even if one network path experiences an outage,userscanstillaccesscloudresources.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) mitigation strategies: ThesetechniquesprotectagainstDoS attacksthataimtooverwhelmthenetworkwith traffic, preventing legitimate users from accessingresources.
Capacityplanningandscaling: Cloudproviders implement network capacity planning and scalingtohandlefluctuatingtrafficvolumesand maintainoptimalperformanceforuseraccess.
By ensuring network availability, cloud providers and organizations alike can guarantee that authorized users have reliable access to the resources they need, minimizing downtime and disruptions.
5.Strategies forSecuring CloudNetworks:Buildinga Robust Defense
Securingcloudnetworksrequiresamulti-layeredapproach. Herearekeystrategiesorganizationscanleveragetobuilda robustdefense:

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04| Apr2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
a. Identity and Access Management (IAM): The CornerstoneofAccessControl
Description: Identity and Access Management (IAM) establishes a clear framework for who can access cloud resources and what actions they can perform.Itencompassesthefollowingelements:
o UserIdentityManagement: Creatingand managinguseridentitieswithinthecloud environment.
o AccessControls: Defininggranularaccess permissionsforusersandgroups,ensuring theycanonlyaccessauthorizedresources andfunctionalities.
o Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing an additional layer of securitybeyondpasswords.MFArequires users to provide a second authentication factor, such as a code from a mobile authenticatorapp,togainaccess[18]
Benefits: IAM safeguards cloud resources by preventingunauthorizedaccessandminimizingthe impactofcompromisedcredentials.
b. Data Encryption: Securing Data at Rest and In Transit
Description: Dataencryptionscramblesdatausing cryptographic algorithms,renderingitunreadable withoutadecryptionkey.Cloudsecuritystrategies shouldinclude:
o DataEncryptionatRest: Encryptingdata stored within the cloud environment, protectingitfromunauthorizedaccesseven ifaserverbreachoccurs.
o Data Encryption in Transit: Encrypting data during transmission between users, applications, and cloud resources, safeguarding it from interception on the network.
Benefits: Data encryption ensures confidentiality and minimizes the risk of sensitive information exposureintheeventofasecuritybreach.
c.NetworkSegmentation:LimitingtheBlastRadiusof Threats(Yu etal.,2017)
Description: Network segmentation divides the cloudnetworkintologicallyisolatedsegments.This strategycanbeimplementedinvariousways:
o Public vs. Private Subnets: Separating public-facingresources(e.g.,webservers) frominternalresources(e.g.,databases)on differentnetworksegments.
o Workload Segmentation: Segmenting workloads based on security sensitivity, isolating critical applications from less sensitiveones.
Benefits: Network segmentation minimizes the potentialimpactofasecuritybreach.Ifamalicious actor gains access to one segment, the damage is contained,andothersegmentsremainprotected.
d. Firewalls and Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems(IDS/IPS):ActiveNetworkDefense
Description: Thesenetworksecuritytoolsprovide activedefensesagainstmaliciousactivity:
o Firewalls: Act as gateways that filter incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined security rules, blocking unauthorizedaccessattempts.
o IntrusionDetection/PreventionSystems (IDS/IPS): Continuouslymonitornetwork traffic for suspicious behavior and can either alert security teams or take automated actions to block potential threats.
Benefits: Firewalls and IDS/IPS offer real-time protection against network attacks, preventing unauthorizedaccessandmitigatingtheriskofdata breaches[27].
6. Innovations in Cloud Security: Forging a Path Towards Enhanced Protection
Thelandscapeofcloudsecurityisundergoingacontinuous transformation. Emerging technologies offer promising avenuesforstrengtheningnetworkdefensesandmitigating security risks. Let's explore some of these innovative approaches:
a. Machine Learning (ML): Automated Threat DetectionandResponse [6]
Description: Machinelearning(ML)algorithmscan be trained on historical network traffic data to identifypatternsandanomalies.Thisallowsfor:
o Real-timeThreatDetection:MLmodelscan continuously analyze network traffic, flagging suspicious activity that may indicateapotentialcyberattack.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04| Apr2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
o Automated Response:Advanced ML systems can be configured to take automatedactionsinresponsetodetected threats,suchasblockingmalicioustrafficor quarantininginfecteddevices.
Benefits: ML automates threat detection and response, reducing the burden on security teams and improving the overall efficiency of cloud securityoperations.
b. Blockchain: Immutable Audit Trails and Secure DataProvenance
Description: Blockchaintechnology,knownforits applicationincryptocurrencies,canbeleveragedin cloudsecurityfor:
o Tamper-proof Audit Logs:Blockchain can createanimmutablerecordofdataaccess and transactions, providing a transparent andsecureaudittrail.
o Enhanced Data Provenance:By tracking data origin and changes throughout its lifecycle, blockchain can ensure data integrity and facilitate forensic investigationsincaseofsecurityincidents.
Benefits:Blockchainoffersasecureandtransparent way to track data access and modifications, improving accountability and reducing the risk of datatampering.
c. Zero-Trust Security: Least Privilege Access and ContinuousVerification [23]
Description: Zero-trustsecurityisasecuritymodel that departs from the traditional perimeter-based approach. It assumes no user or device, whether inside or outside the network, is inherently trustworthy.Thismodelenforces:
o Least Privilege Access:Users and devices are granted only the minimum level of accessrequiredtoperformtheirtasks.
o Continuous Verification:Continuous authenticationandauthorizationprocesses areimplementedtoverifyuseranddevice identity before granting access to cloud resources.
Benefits: Zero-trust security minimizes the potential impact of a security breach by limiting access privilegesand continuously validatinguser identity.
Byembracingtheseinnovativesolutions,organizations canbolstertheircloudsecurityposture,improvethreat detection capabilities, and adapt to the ever-evolving landscapeofcyberthreats
Securingthecloudrequiresacomprehensiveapproachthat combinesestablishedstrategieswithinnovativetechnologies. Byunderstandingthesecuritychallenges,implementingthe right security measures, and staying informed about advancements in the field, organizations can ensure their cloud environments remain safe and reliable for modern computingneeds.
7. Securing the Cloud: Strategies and Innovations in Network Security for Modern Computing Environments:
The ever-increasing reliance on cloud computing necessitates robust security measures to safeguard data, applications,andinfrastructure.Thistablesummarizeskey strategies and emerging innovations in cloud network security,alongwiththeirlimitations:
Table4.1SecuringtheCloud:
SecurityArea Description Advantages Limitations
Cloud Provider Responsibility
Physical Security: Restricting access, environme ntal controls, video surveillance
Network Security: Firewalls, IDS/IPS, network segmentati on.
Baseline Security Features: Encryption , IAM, security logging.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Establishesclear user identities, defines access controls, and implements multi-factor authentication.
Protects underlying infrastruct ure.
Provides baseline security for cloud resources.
Reliance on cloud provider' ssecurity posture.
Limited control over physical security measures
Prevents unauthoriz edaccess.
Minimizes impact of compromis ed credentials
Complexi ty in managing user identities and access across multiple cloud

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04| Apr2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
environm ents.
Potential for human error in access control configura tion.
Data Encryption Encryptsdataat rest (stored) and in transit (transmitted).
Ensures data confidentia lity.
Mitigates risk of exposure in a security breach.
Blockchain
Performa nce overhead associate d with encryptio n and decryptio n.
Potential key managem ent challenge s.
Network Segmentation
Divides the cloud network into isolated segments.
Firewalls and Intrusion Detection/Pre vention Systems (IDS/IPS)
Firewalls filter traffic, IDS/IPS monitor for suspicious activity.
Limits blast radius of security threats. * Protects critical resources.
Zero-Trust Security
Createstamperproofrecordsof dataaccessand transactions.
Provides real-time protection against network attacks.
Prevents unauthoriz ed access and data breaches.
Increased complexit y in network managem ent.
Requires careful planning and configura tion.
False positives from IDS/IPS can generate alertsand require investigat ion.
Firewalls may not beableto detectall types of attacks.
Assumes no userordeviceis inherently trustworthyand requires continuous verification.
Improves data provenanc eandaudit trails.
Enhances data security and accountabi lity.
Scalabilit y challenge s for largescale deployme nts.
Relatively new technolog y with evolving standards
Minimizes impact of breaches bylimiting access privileges.
Enforces continuous user and device identity validation.
Can be complex to impleme nt and manage.
May impact user experienc e due to frequent authentic ation challenge s.
The world of cloud computing necessitates navigating a complex web of compliance requirements and regulatory frameworks. Organizationsleveragingcloud services must ensure their practices align with relevant regulations to safeguard data privacy, security, and integrity. Here's a breakdownofsomekeycomplianceconsiderations:
a.General DataProtectionRegulation(GDPR):
Description: The General Data Protection Regulation(GDPR)isa regulationenforcedbythe European Union (EU) that governs the processing and protection of personal data for individuals residingwithintheEU.
Machine Learning(ML) Analyzes network traffic patterns to detect anomalies and identify potential threats.
Enables real-time threat detection.
Automates response tosecurity incidents.
Requires large volumes of training data for effective threat detection.
Potential forbiasin ML algorithm s.
Compliance Requirements for Cloud Security: Organizations storing or processing the personal data of EU residents, regardless of their location, must comply with GDPR. This includes implementing robust cloud security measures to protectthisdataandensuring:
o Data Subject Rights: Individualshavethe right to access, rectify, erase, and restrict processingoftheirpersonaldata.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04| Apr2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
o Data Breach Notification: Organizations must notify regulators and affected individualsintheeventofadatabreach.
o Security Measures: Implementing appropriate technical and organizational security measures to safeguard personal data[28]
b. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA):
Description: TheHealthInsurancePortabilityand AccountabilityAct(HIPAA)isa USregulationthat sets standards for protecting the privacy and security of protected health information (PHI) of patients.
Compliance Requirements for Cloud Security: Healthcareorganizationsleveragingcloudservices to store or process PHI must comply with HIPAA. Thisincludesimplementingcloudsecuritymeasures that meet the HIPAA Security Rule, which focuses on:
o AdministrativeSafeguards: Implementing policies and procedures to manage PHI securityrisks.
o Physical Safeguards: Protecting physical accesstoPHIwithinthecloudenvironment.
o Technical Safeguards: Utilizingtechnical security measures like encryption and accesscontrolstosecurePHIinthecloud [29]
c. Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS):
Description: The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of security requirementsdesignedtoprotectcardholderdata.It applies to organizations that store, process, or transmitcardholderdata.
Compliance Requirements for Cloud Security: Organizations accepting online payments and utilizing cloud services to store or process cardholder data must comply with PCI DSS. This includes implementing security measures as outlinedinthePCIDSS,suchas:
o Building and Maintaining a Secure Network: Segmenting the network to isolatecardholderdataandimplementing firewalls to protect against unauthorized access.
o Protecting Cardholder Data: Encrypting cardholderdataatrestandintransit.
o Implementing Strong Access Control Measures: Restrictingaccesstocardholder datatoauthorizedpersonnel[30]
d.Industry-SpecificRegulations:
Inadditiontothesebroadregulations,manyindustrieshave theirownspecificdatasecurityandprivacyregulationsthat may apply to cloud environments. These regulations can address areas such as financial data, intellectual property, andgovernmentinformation.Organizationsshouldbeaware of and comply with any industry-specific regulations that applytotheirclouddeployments.
Understanding and adhering to relevant compliance requirementsiscrucial for organizationsleveraging cloud services. By implementing robust cloud security practices and staying informed about evolving regulations, organizations can ensure they are meeting their legal obligations and protecting sensitive data in the cloud environment.
In conclusion, securing cloud networks demands a multifacetedapproachthatintegratesrobustIAMpractices, dataencryption,andcutting-edgesolutionssuchasmachine learningandzero-trustsecurity.Whilethesestrategiesoffer significantadvancementsinfortifyingcloudenvironments, it's imperative to recognize their inherent limitations and ensurecompliancewithregulatorystandards.Byfosteringa shared security model, prioritizing user education, and maintainingvigilantoversight,organizationscanconfidently navigate the complexities of the cloud landscape while safeguardingtheconfidentiality,integrity,andavailabilityof their data. This holistic approach enables organizations to leverage the full potential of cloud computing while mitigating security risks in today's rapidly evolving technologicalera.
References
[1] Mell,P.,&Grance,T.(2011).TheNISTDefinitionof Cloud Computing. National Institute of Standards andTechnology(NIST)SpecialPublication800-145. https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/legacy/sp/nists pecialpublication800-145.pdf
[2] National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).SpecialPublication800-63B:DigitalIdentity Guidelines. https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/specialpublicatio ns/nist.sp.800-63b.pdf

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04| Apr2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[3] Chen, X., Li, J., Weng, J., & Lou, W. (2010). On the Security and Performance of Encrypted Data StorageinCloudComputing.IEEETransactionson Parallel and Distributed Systems, 21(12), 17081717.
[4] Yu, C., Gong, L., Xu, K., & Liu, G. (2017). MultigranularityNetworkSegmentationforCloudData Security.IEEETransactionsonNetworkandService Management, 14(3), 872-885. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8740923
[5] Scarfone, K., & Souppaya, M. (2015). Guide to IntrusionDetectionandPreventionSystems(IDPS). National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)SpecialPublication800-94.
[6] Meng,W.,Zhu,Q.,Lv,Z.,&Wang,X.(2018).ASurvey onMobileCloudComputingNetworkSecurity.IEEE CommunicationsSurveys&Tutorials,20(1),161
[7] CenterforInternetSecurity(CIS).(2023,April4). Zero Trust Security Model. https://www.cisecurity.org/insights/blog/wheredoes-zero-trust-begin-and-why-is-it-important
[8] https://cloudacademy.com/blog/what-is-cloudcomputing/
[9] Armbrust,M.,Fox,A.,Griffith,R.,Joseph,A.D.,Katz, R.,Konwinski,A.,...&Zaharia,M.(2010).Aviewof cloud computing. Communications of the ACM, 53(4),50-58.
[10] Mather, T., Kumaraswamy, S., & Latif, S. (2009).Cloudsecurityandprivacy:Anenterprise perspective on risks and compliance. " O'Reilly Media,Inc.".
[11] Amazon Web Services. (2021). Shared Responsibility Model. Retrieved from https://aws.amazon.com/compliance/sharedresponsibility-model/
[12] Wang,C.,Wang,Q.,Li,J.,Ren,K.,&Lou,W. (2010). Enabling Efficient and Scalable Integrity CheckingforCloudDataStorage.Proceedingsofthe 19th ACM conference on Computer and communications security (CCS '10), 345-356. https://dl.acm.org/doi/proceedings/10.1145/3560 810
[13] Ristenbatt, M., Wolford, T., & Shankar, U. (2009). Security Considerations for Cloud Computing.2009IEEEInternationalConferenceon Services Computing (SERVICES), 90-93. doi:10.1109/SERVICES.2009.53
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/iel7/6287639/651489 9/08726303.pdf
[14] Cloud Security Alliance (CSA). (2023). Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.1. https://cloudsecurityalliance.org/
[15] Li,S.,Wang,L.,Zhang,X.,&Zou,Z.(2011).A Comparative Study of Cloud Computing Security Issues. 2011 4th International Conference on ComputerScienceandInformationTechnology(Vol. 1, pp. 501-504). IEEE. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5284165/
[16] Buyya,R.,Yeo,C.S.,&Venugopal,S.(2010). Market-Oriented Cloud Computing: Economy, Technology,andOptimization.Springer.
[17] Microsoft Azure. (2023). Security Responsibility Shared Model. https://learn.microsoft.com/enus/azure/security/fundamentals/sharedresponsibility
[18] National Institute of Standards and Technology(NIST).(2020).SpecialPublication800165: Guide for Applying the Risk Management FrameworktoInformationSystems:ASecurityLife Cycle Approach. [https://doi.org/10.6028/NIST.SP.800-165]
[19] https://www.coresite.com/blog/datacenter-security-when-security-gets-physical
[20] https://www.trendmicro.com/vinfo/us/se curity/news/virtualization-and-cloud/cloudsecurity-key-concepts-threats-and-solutions
[21] https://nordlayer.com/blog/what-is-cloudnetwork-security/
[22] International Organization for Standardization(ISO).(2014).ISO/IEC27018:2014 - Information technology - Security techniquesInformation technology for cloud service useProtection of personally identifiable information (PII).https://www.iso.org/standard/56820.html
[23] CenterforInternetSecurity(CIS).(2023). CISControlsv8:ImplementationGroups.
[24] Cloud Security Alliance (CSA). (2013). Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V1.0. https://cloudsecurityalliance.org/artifacts/security -guidance-for-critical-areas-of-focus-in-cloudcomputing-v1-0/
2024, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.226 | ISO

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04| Apr2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[25] https://www.pingidentity.com/en/resourc es/blog/post/everything-you-need-to-know-aboutcloud-iam.html
[26] Nikander,J.,Manninen,O.,&Laajalahti,M. (2020). Requirements for cybersecurity in agricultural communication networks.Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 179, 105776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2020.105776
[27] Scarfone,K.,&Souppaya,M.(2015).Guide to Cloud Computing Security (NIST Special Publication 800-165). National Institute of Standards and Technology. https://doi.org/10.6028/NIST.SP.800-165
[28] Regulation(EU)2016/679oftheEuropean ParliamentandoftheCouncilof27April2016on theprotectionofnaturalpersonswithregardtothe processing of personal data and on the free movement of such data, and repealing Directive 95/46/EC (General Data Protection Regulation) https://gdpr-info.eu/
[29] Health Insurance Portability and AccountabilityActof1996, Pub.L.No.104-191,§ 117(1996)
[30] PCISecurityStandardsCouncil.(2023).PCI DataSecurityStandard(DSS)v4.0.