
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Shejal Devkar1 , Jagruti Patil2 , Akhil Naskar3 , Rakesh Singh4
B.E.StudentsDepartmentofComputerEngineering
G. V. Acharya Institute of Engineering and Technology, Shelu, Dist-Raigad, Maharashtra, India-410201
Abstract - This desktop voice assistant initiative leverages Python’s AI capabilities to offer an interactive experience through vocal interactions. The endeavor encompasses crafting a voice assistant rootedinPythonthatisadeptatexecutinganarrayof functions such as activating alarms, providing meteorological updates, dispatching electronic mails, streaming melodies, among others. Engineered for optimal intuitiveness and accessibility, the assistant boastsastreamlinedinterfacethatfacilitatesseamless communication via spoken language instructions. The project harnesses AI-driven voice recognition technologies, ensuring precise comprehension and executionofuserdirectives.
To actualize the voice assistant’s capabilities, the project employs a suite of Python libraries. Speech Recognition is deployed for translating spoken words into written text, while PyAudio handles the auditory inputs and outputs. Text-to-speech conversion is managed by gTTS, and audio file playback is orchestratedusingtheplaysoundlibrary.
Key Words: Voice,Assistant,Static,Text,Speech
1.INTRODUCTION
In an era where efficiency is paramount, the advent of intelligent home automation and IoT devices has sparked ademandforsolutionsthatstreamlineeverydayactivities. Addressing this need, virtual assistants have emerged as AI-driven facilitators, enabling users to orchestrate their tasks and manage smart devices through conversational language.Thisprojectintroducesadesktopvoiceassistant builtonPython,designedtoenhanceuserinteractionwith theircomputersinafrictionlessandeffectivemanner.
The system is crafted using a variety of Python libraries, encompassing speech recognition, natural language processing, and text-to-speech modules, to forge a virtual assistant that is both reactive and approachable. Interactionwiththeassistantisvoice-driven,empowering users to accomplish tasks such as scheduling reminders, web searching, audio playback, and email composition effortlessly. The software serves as a digital aide, streamlining tasks like weather forecasts, reminder
settings, and to-do list creation through voice or text commands. It requires activation phrases to engage its listening feature, followed by the user’s instructions. This voice assistant is tailored for optimal use across all user demographics,enhancingproductivitybyhandlingroutine tasksandfetchingonlineinformation.Historically,‘virtual assistants’ referred to web-based service providers; however, today’s voice assistants are distinct, focusing on three core functions: converting text to speech, interpreting text for intent, and translating intent into action. Our voice assistant is under continuous development to expand its capabilities. Unlike virtual assistantswhoarehumancontractors,voiceassistantsare automated systems that proactively fulfill our needs, all thankstoadvancementsinAI-drivenvoicetechnology.
Themanuscriptcommenceswithanexpositiononvoice assistants, charting their ascent to prominence in the digital age. It traces the lineage of these systems from the nascent IBM Shoebox to contemporary incarnations like Siri,GoogleAssistant,andAlexa.
Subsequently, the document delves into the architectureofvoiceassistantsystems,dissectingelements such as speech recognition, natural language processing, dialogueorchestration,andspeechgeneration.Itelucidates thearrayofmethodologiesandcomputationalframeworks that underpin each component, appraising their efficacies andconstraints.
Thediscourseculminatesinthepresentationofavoice assistant, conceived through Python and AI, capable of interpreting and executing user-issued directives. Employing NLP, the assistant translates vocal or textual inputs into operative commands, thereby streamlining processesandconservingtime.
In recent years, AI-based voice assistant systems have garnered significant attention due to their potential to revolutionizehuman-computerinteraction.Thesesystems utilize artificial intelligence techniques to understand and respond to user queries and commands via natural language. This literature survey aims to explore the advancements, challenges, and future directions in the fieldofAI-basedvoiceassistantsystems.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
FundamentalComponents:
Speech Recognition: Empowers the voice assistant with the ability to discern and processverbalinstructions.
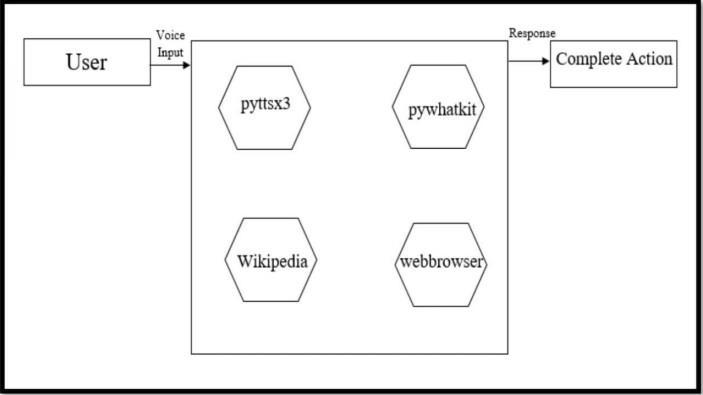
pyttsx3: Endows the assistant with the capability to vocalize responses to user interactions.
PyAudio: Facilitates the assistant’s engagement with the system’s audio hardwareforinputandoutputoperations.
date time: Equips the assistant with functionalities to manage temporal information,enablingittoschedulealertsand providecurrentdateandtimeinsights.
web browser: Grants the assistant the proficiency to navigate the internet, allowing ittoconductsearchesandaccesswebpages.
os: Enhances the assistant with a suite of toolstointeractwiththeoperatingsystemfor tasks like launching programs and managing files.
json: Allows the assistant to handle JSON data, which is instrumental in maintaining usersettings,commandstructures,andother pertinentinformation.
These modules represent a selection from the extensive library available for augmenting a Python-based desktop voice assistant. The project’s unique demands and desired features willdictatetheinclusionofadditionalmodules.
Thesystemisdesignedwiththefollowingcapabilities:
Adaptive Listening: It continuously listens for instructions,withacustomizablelisteningdurationtosuit individualuserpreferences.
Persistent Querying:Shoulditencounterambiguityin userinput,thesystemwillpersistentlyrequestclarification until it receives the necessary information, up to a userdefinedlimit.
Voice Customization: It offers a choice between male and female vocalizations, catering to the user’s personal preference.
Interactive Modules: Utilizing the speech-recognition and pyttsx modules, the system is equipped to engage in bidirectional communication, processing spoken language andarticulatingresponses.
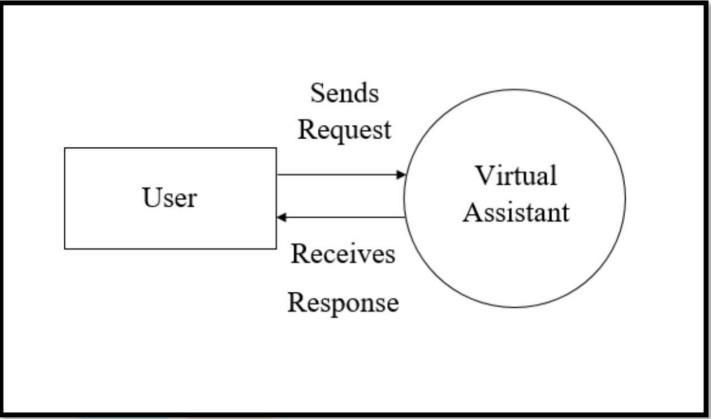
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Serving as the AI’s linguistic conduit, NLP enables the voice assistant to interpret and respondtospokencommands.
Machine Learning: These algorithms are honed on extensive speech datasets, enhancing the system’s proficiency in voice detectionandlinguisticinterpretation.
Speech Recognition: This technology transcribes spoken words into textual data, readyforPythonprocessing.Python’sSpeech Recognition library is among the tools availableforthispurpose.
Text-to-Speech: This function translates the assistant’s textual responses into audible speech.Python’spyttsx3libraryisoneoption forimplementingthisfeature.
API Integration: By incorporating APIs, the voice assistant gains the ability to execute tasks like fetching weather forecasts, initiatingcalls,andsendingtexts.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Contextual Awareness: This capability allows the assistant to grasp the nuances of user requests, yielding more tailored and precise responses. It’s bolstered by machine learningandNLPtechniques.
Modular Design: The voice assistant’s structureiscompartmentalized, with distinct modules dedicated to specific functions like voice recognition, language processing, or speech output. This modular approach enhances the system’s expandability and maintainability.
4.2 Implementations
Project Planning and Research:
Definethescopeandobjectivesofyourvoiceassistant.
Researchexistingvoiceassistanttechnologiesandtheir capabilities.
Analyzethetargetuserbaseandtheirneeds.
Design:
Design the user interaction flow, including how the assistant will be invoked, how it will understand commands,andhowitwillrespond.
Createadesignfortheuserinterface,ifapplicable.
Data Collection and Management:
Collect diverse datasets for training the voice recognition models, including different languages, accents,anddialects1.
Ensure proper data management practices, including dataprivacyandsecuritymeasures.
AI Model Training:
Use deep learning techniques to train models that can processandinterpretspeechsignals1.
Implement natural language processing (NLP) algorithms to understand and interpret user commandsaccurately1.
Testing and Validation:
Conduct thorough testing with various user groups to ensure the assistant understands different accents, dialects,andlanguages.
Validate the performance ofthe assistant in real-world scenarios.
User Experience (UX):
Focus on creating a seamless and intuitive user experience.
Implement contextual understanding to provide personalizedandaccurateresponses1.
Continuous Improvement:
Design the system for continuous learning, allowing it toimproveovertimebasedonuserinteractions1.
Regularly update the system with new data and features.
Ethical Considerations and Compliance:
AddressethicalconcernsrelatedtoAI,suchasbiasand transparency.
Ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations regardingdataprotectionandprivacy.
Deployment and Maintenance:
Planforthedeploymentofthevoiceassistant,including integrationwithexistingsystems.
Set upa maintenanceschedule for system updatesand performancemonitoring.
Documentation and Reporting:
Document the entire process, including design decisions, system architecture, and training methodologies.
Prepare reports on the performance metrics and user feedbackforstakeholders.
The project delivers a dynamic voice assistant proficient in fundamental operations like scheduling reminders, streaming tunes, fielding inquiries, and offering meteorological forecasts. Enhanced precision in voice command interpretation and responses is achieved through advanced machine learning algorithms and analytical techniques. The assistant’s functionality is broadened byintegratingwithexternalAPIsandservices, including those from Google and Spotify. It also features customization options, allowing users to tailor the assistanttotheiruniquevoicecommandsandpreferences. Thedevelopmentofalifelikevocalizationisrealizedusing sophisticated text-to-speech technology. Lastly, the user interface is designed to be both instinctive and usercentric,augmentingtheoveralluserexperience.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Improved User Experience: Voice commands provide aseamlessandintuitivewayforuserstointeractwiththeir devices. Opening applications and websites via voice reduces the need for manual navigation, streamlining the userexperienceandsavingtime.
Increased Productivity: Voice-activated opening of applications and websites enhances productivity by enabling users to quickly access the tools and information they need without interrupting their workflow. This is especially valuable in professional settings where efficiencyisparamount.
Integration with Smart Devices: AI-based voice assistants are integrated into a wide range of smart devices, including smartphones, tablets, smart speakers, and wearables. This integration allows users to open applications and websites across different devices, providing a consistent experience regardless of the platform.
Customization and Personalization: Voice assistant systems can be customized to recognize individual users' voices and preferences, allowing for personalized interactions.Userscanopentheirfavoriteapplicationsand websites with simple voice commands tailored to their specificneedsandpreferences.
Multi-lingual Support: AI-based voice assistants support multiple languages, allowing users to open applicationsandwebsitesintheirpreferredlanguage.This feature enhances accessibility for users worldwide and accommodatesdiverselinguisticpreferences.
Security and Privacy Measures: Voice assistant systems implement robust security measures to protect users' data and privacy. Biometric authentication, encryption, and user permission settings ensure that only authorized individuals can open applications and access sensitiveinformationviavoicecommands.
The future trajectory of voice assistant technology is poisedforthefollowingenhancements:
Broader Capabilities: With technological evolution, voice assistants are expected to gain sophistication, managing a wider array of devices, offering tailored suggestions,andachievingdeeperintegrationwithdiverse softwareecosystems.
Enhanced Accessibility: Voiceassistantsserveas powerful accessibility tools, allowing users to open applications and websites hands-free. This feature is particularly beneficial for individuals with mobility impairmentsorthosewhopreferhands-freeinteraction.
Refined Language Processing: The core of a voice assistant’s comprehension capabilities, natural language processing, is anticipated to advance, leading to a more nuancedunderstandingofhumanspeech.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Superior Voice Recognition: Ongoing improvements in voice recognition are projected toyieldhigheraccuracy and dependability, facilitating clearercommunication with voiceassistants,evenamidstdisturbances.
Expanded Linguistic Support: The global adoption of voice assistants suggests a future where they will support an extensive variety of languages and dialects, broadening theirreach.
AI Progressions: As the backbone of voice assistants, advancements in AI are expected to endow these systems with heightened intelligence, enhancing their predictive andinterpretativefaculties.
AR Integration: Theriseofaugmentedrealityheraldsa potential convergence with voice assistant technology, offeringusersenrichedandengaginginteractions.
To encapsulate, the desktop voice assistant initiative stands as a pivotal innovation for users, offering a handsfreeinterfacetoaccessinformationandmanagecomputer functionalities.Despitecurrentconstraintslikevocabulary breadth and the precision of voice recognition, the progressive strides in natural language processing and AI herald a new era for voice assistant capabilities. In essence, the desktop voice assistant project harbors immense promise to elevate userinteractionand simplify daily operations, thereby representing a significant asset forbothcommercialentitiesandpersonalusers.
In summation, the desktop voice assistant project is not merely a technological convenience but a trans formative tool that reshapes how users interact with digital environments. It stands as a testament to human ingenuity,harnessingthepowerofAItosimplifycomplex tasksandenhanceproductivity.
[1] Allen,A.A.,Shane,H.C.,&Schlosser,R.W.TM(2018). The echo as a speaker- independent speech recognition device to support children with autism: An ex ploratory Study. Advances in Neurodevelopmental Disorders, 2(1), 6974. doi:10. 1007/s41252-017-0041-5.
[2] Angelini,L.,Caon,M.,Carrino,S.,Bergeron,L.,Nyffeler, N., Jean-Mairet, M., & Mugellini,E. (2013). Designing a desirablesmartbraceletfor older adults. In Proceedingsofthe2013ACMconferenceonpervasive andubiquitouscomputing adjunct publicationUbiComp '13 Adjunct. In UbiComp '13 Adjunct (pp. 425–434). New York, New York, USA: ACM Press. doi:10.1145/2494091.2495974.
[3] Azvine, B., Djian, D., Tsui, K. C., & Wobcke, W. (2000). In B. Azvine, D. D. Nauck, & N. Azarmi (Eds.), The intelligent assistant: An overview (pp. 215–238)). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. doi:10.1007/10720181_9.
[4] Bellegarda, J. R. (2014). Spoken language understanding for natural interaction: The Siri experience.InJ.Mariani,S.Rosset,M.GarnierRizet,& L. Devillers (Eds.), Natural interaction with robots, knowbotsandsmartphones(pp.3–14).NewYork,NY: Springer New York. doi:10.1007/978- 1- 4614-82802_1.
[5] Biolchini, J., Gomes Mian, P., Candida, A., Natali, C.,& Travassos,G.H.(2005).Systematicreviewinsoftware engineering.TechnicalReport.Cin.ufpe