
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF A MULTI-STORIED BUILDING FOR DIFFERENT SEISMIC ZONES BY PROVIDING SHEAR WALLS
Dr. Prasenkumar Saklecha1 , Yashwanthkumar S S2 ,Bhosale Vivek Ganpat3 , Birvatkar Omkar Deepak4 , Gole Rohit Rajendra5, Saha Narayan Deglal6
1Head of Department , Department Of Civil Engineering , New Horizon Institute Of Technology And Management , Maharashtra , India
2Asst Professor, Department Of Civil Engineering, New Horizon Institute Of Technology And Management, Maharashtra, India
3B.E Student , Department Of Civil Engineering , New Horizon Institute Of Technology And Management , Maharashtra , India
4B.E Student , Department Of Civil Engineering , New Horizon Institute Of Technology And Management , Maharashtra , India
5B.E Student , Department Of Civil Engineering , New Horizon Institute Of Technology And Management , Maharashtra , India
6B.E Student , Department Of Civil Engineering , New Horizon Institute Of Technology And Management , Maharashtra , India ***
Abstract – This Study Presents The Design And Analysis Of AG+17Multi-Storied BuildingIncorporatingShearWalls To Withstand Seismic Forces In Different Seismic Zones. The AnalysisIsPerformedUsingETABSSoftware,WhichIsWidely Recognized for Its Capability In Structural Analysis And Design. The Seismic Zones Considered In The Study Represent Varying Levels Of Seismic Activities, Ranging From Low To High. The Inclusion Of Shear Walls In The Building Design Is Crucial For Enhancing Its Seismic Resistance And Insuring Structural Integrity During Earthquakes. Through Comprehensive Analysis And Design Iterations, The Effectiveness Of Shear Walls In Mitigating Seismic Loads Is Evaluated, Considering Factors Such As Building Materials, Geometry, And Load Distribution. Finding Of This Study Provide Valuable Insights Into The Optimization Building DesignsForSeismicResilienceAcrossDifferentSeismicZones, Contributing To Safer And More Sustainable Construction Practices.
Key Words: analysisanddesign,manual, zonecomparisons zoneIIIzoneIV
1.INTRODUCTION
SeismicDesignAndAnalysisOfMulti-StoryBuildingPlayA CriticalRoleInsuringTheStructuralIntegrityAndSafetyOf Structures Located In Different Seismic Zones. In This Comparative Analysis, We Will Explore The Use Of Shear WallInTheDesignOfMuti-StoryBuildingsInSeismicZone III And Seismic Zone IV Using The ETABS Software. ETAB Widely Use Structural Analysis And Design, Provides EngineersWithPowerfulToolsForModeling,AnalyzingAnd DesigningBuildingsSubjectedToSeismicForces.TheUseOf ETABSoftwareInBothSeismicZoneIiiAndSeismicZoneIv
Allows Engineers To Conduct Comprehensive Structural AnalysisAndDesign,ConsideringFactorsSuchAsSeismic Load Combinations, Material Property And Geometric Constraints. ETABS Provides The Necessary Tools For ModellingShearWalls,AnalyzingTheirPerformance Under SeismicLoadsAndEnsuringComplianceWithLocalBuilding AndRegulationsSpecificToEachSeismicZones.
TheComparativeAnalysisWillDelveIntoSpecificsOfUsing ETABSSoftwareToDesignMulti-StoryBuildingsWithShear WallsInSeismicZoneIiiAndSeismicZoneIv,Highlighting TheSoftware’sCapability’s.
1.1 EARTHQUAKE
Earthquake Can Be Understood As Earth-Surface Shaking BecauseOfEnergyWhichIsSuddenlyReleasedByReasonOf Earth’sMovement.ThisEarth’sMovementIsConsequence OfPlatesAreTermedAsTectonic-Plates.TheCrustOfThe Earth Is Surrounded By Large-Number Of Very Big Size Bodies Called Tectonic-Plates, They Are Constantly Under Motion With Respect To One Another, Due To Their UnexpectedCollisionWithOneAnother-LeadingToRelease OfEnergyWhichTravelsTowardsTheEarth-SurfaceInThe FormOfWaves
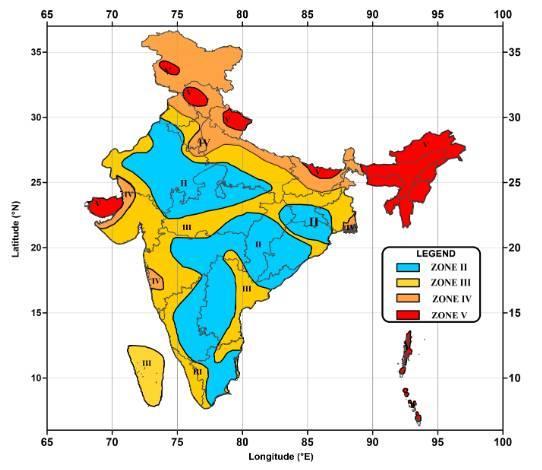
1.2 DIFFERENT SEISMIC ZONES IN INDIA
Indian Plate Is Responsible For Earthquakes Of High IntensitiesAndFrequencyReadingIndianSubcontinentTo CatastrophicEarthquakesAround53%IndianLandMassIs VulnerableToEarthquakes,BasedOnIndianGeographical Statistics. According To Estimations Based on Report Of WorldBankAndUnitedNations,Around200MillionIndian

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Population To Be Affected From Storms And Earthquakes Around2050.AccordingToLatestDesignPracticeCode(Is: 1893:Part-1;2016),IndiaIsDividedInto4ZonesBased OnSeismicityObservedOfIndianLandMaskThisZonesAre NamelyZoneIi,Iii,Iv,VWhichCoversEntireCountry.Before ThePresentCodeThisDivisionsOfZonesIsOf5To6Types For Entire Country Which Is Now Reduce Two Only Four RangingBetweenZoneVToZoneIiAssociatedWithHighest ToLowestSeismicityRespectively.
ZoneV:-
This Zones Attracts Earthquake Of High Intensity With Highest Risk Involved Attributed With Very High-Risk Damaged. Zone Factor Indicates Effective Level Of EarthquakeI.E.ForZeroPeriodWhichIsUsedForDesigning Of Earthquakes Resistance Structures By Structural Engineers. Earthquake Prone Areas Generally Consists of Trap And Basalt Rocks, Regions Under This Zones Are Kashmir And Himalayan Regions, North East States, NorthernAreasOfBiharAndRegionOfGujratStateMainly Kutch.
ZoneIV:-
ThisZoneAttributedWithHighRiskDamageWithFactorOf 0.24AsPerIsCode.TheZoneIncomePassesGangeticPlains, NationalCapitalDelhi,StateOfJammuAndKashmir,Faltan AreaOfMaharashtra,NorthernRegionsOfBiharAndBorder OfNepalAndIndia.
ZoneIII:-
This Zone Classified As Moderate Damage Risk Zone With FactorOf0.16AsPerIs Code.RegionsIncludedAre Some PartsOfHimalayasAndKashmir,AndamanAndNicobar.
ZoneII:-
This Zone Attracts Less Intensities Of Earthquakes And Classified Under Low Damage Risk Zone, As Per Is Code Assigned Factor Of 0.10 As Only 10% Of Gravitational Acceleration Is Experienced By Structure As Maximum HorizontalAcceleration.
1.3 SHEAR WALL
WhatIsAShearWall?
Shear Wall Is Structural Member In A Reinforce Concrete Framed Structure To Assist Lateral Forces Such As Wind Forces. Shear Walls Are Generally Used In Multi-Storied Buildings Subject To Lateral Wind And Seismic Forces. In ReinforcedConcreteFramedStructuresTheEffectOfWind Forces Increased In Height. Codes Of Practice Imposed Limits On Horizontal Movement Or Sway. Shear Wall Are TypicallyVerticalComponentsMadeOfReinforcedConcrete Strategically Placed In The Building’s Layout To Provide StiffnessAndStability.
ShearWallsWorkByTransferringLateralForcesActingOn StructureToTheFoundation,ThusReducingTheBuildings
VulnerabilityToSideWaysMovementAndPotentialCollabs DuringEarthquakesOrHigh-Winds.TheyAreEssentialFor Ensuring The Safety And Stability Of Buildings In Areas ProneToSeismicActivityOrStrongWinds.


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
2 METHODLOGY
CreateTheAuto CadPlan
Assignbeam column,slabs
CreateThe Model In ETABS
DefineMaterial andsection Properties
3. SPECIFICATIONS OF BUILDING
DefineLoadCases
UsingIs456: 2000AndIs 1893-2016
Defineshearwall anddrawshear wallsanddefine thepierlabelsfor eachwall
Selectslabsand assignliveload, floorfinishand roofliveloadfor theterracefloor
Definezone factor,importance factor,response reductionfactor
Checkthemodel andrunanalysis iscarriedout
Comparisonof zoneIIIand zoneIV
Checkresults, conclusion

3.1 DEVELOPMENT OF PLAN IN AUTOCAD Fig 3:- AutoCAD Plan
3.2 BUILDING PROPERTIES
Particulars Values
TypesOfBuilding Residential
HeightOfStructure(M) 55.4
NumberOfStories G+17
HeightOfEachFloorIn(M) 3.1
GradeOfConcreteUsed M40
SteelGradeUsed HYSD500
BeamDimension 230X700
ColumnDimension 450X600
ConcreteDensity 24KN/M
DensityOfSteel 78.5KN/M
TypeOfSoil Medium
SeismicZoneFactor 0.16,0.24
LiveLoad 4kN/M^2
DeadLoad 11.04kN/M^2
FloorFinishLoad 1.5KN/M^2
ShearwallThickness 23mm
SlabThickness 200

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072



5 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
5.1BaseShear
Base Shear Is The Fundamental Concept In Structural EngineeringAndEarthquakeEngineering.ItRefersToThe TotalLateralForcesExertedOnABuilding’sFoundationBy TheGroundDuringAnEarthquakeThisForceIsCalculated BasedOnTheSeismicDesignParametersOfTheStructures, SuchAsItsMass, Stiffness, And The CharcatersticsOf The GroundMotion.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

7.BaseShearGraph
5.2DisplacementOfEarthquakeLoad
The Maximum displacement in the building along the x direction is obtained for seismic load combination. ( 1.2 DL+LL+EQX) and along Y- direction is obtained for the seismicloadcombination (1.2DL+LL+EQY).
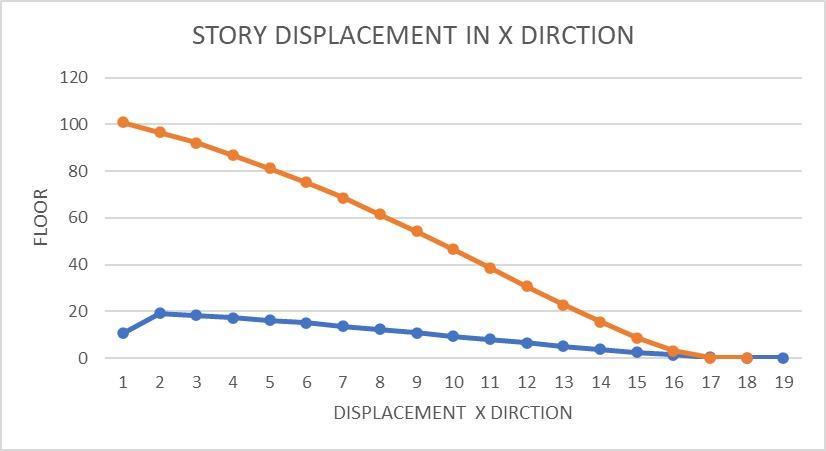
Fig:-8StoryDisplacementInXDirection
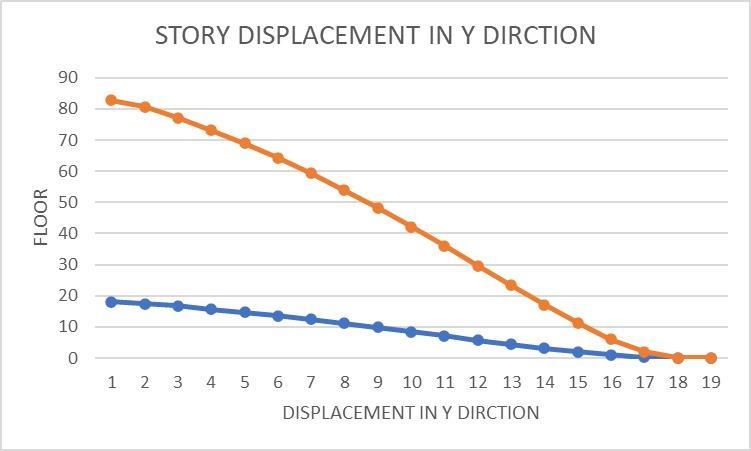
Fig:-9StoryDisplacementInYDirection
5.3storydriftforearthquakeload
Thestorydriftinthebuildingalongxdirectionisobtained fortheseismicloadcombination(1.2DL+LL+EQX)Andalong y direction is obtained for the seismic load combination (1.2DL+LL+EQY).

Fig-9 storydriftinXdirection

Fig-10StoryDriftInYDirection
6 CONCLUSION
BasedOnTheAnalysisConductUsingETABSSoftware,The Comparison Between Zone III And Zone IV Reveals Significant Insights Into Structural Behavior And Performance. The Conclusions Drawn From The Projects Are:
1. Seismic Performance: Zone IV Structures Demonstrate Higher Resistance and Resilience Against Seismic Forces Compared To Zone III Structures. This Is Evident In The Reduced Structural Damage And Lower Displacement ObservedInZoneIVBuildingsUnderSeismicLoading.
2.designconsiderations:engineeringdesignanddetailing for zone IV structures should prioritize stricter seismic design criteria, including stronger materials, enhanced reinforcementdetailing,andmorerobuststructuralsystems toensuresafetyandfunctionalityduringseismicevents.
3.economicimplications:whilezoneIVconstructionsmight involve higher initial costs due to stricter design requirementsandmaterialspecifications,thelongtermsof reduced damaged and maintenance expenses justify the investment,especiallyinhighseismicriskregions.
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2024, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.226 | ISO 9001:2008

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
7. REFERENCE
1. Mohammed Affan, Md. Imtiyaz Qureshi Syed Farooq Anwar(Nov2018)
2.Ravikumar,PRaghava,Dr.T.SureshBabu(April2017)
3.SivaNaeenE,NimmyMariamAbrahamEtAl(2018)
4.RakshithG.M,PangenderNaikG,EtAl(2019)
5.MvNaveenKjBrahmaChari(2016)
6.A.Fathia<ShahiKumarNv
7.VishalYadavAndSandeepSingla(2019)
8.M.Pavanig.Nageshkumaretal(jan2015)
BIOGRAPHIES






Prasenkumarsaklecha
(Head Of Department Department Of Civil Engineering, New Horizon Institute Of Technology And Management, Maharashtra, India)
Yashwantkumar S S
(Asst.Professor,DepartmentOfCivil Engineering,NewHorizonInstitute Of Technology And Management, Maharashtra, India)
BhosaleVivekGanpat
(B E Student, Department Of Civil Engineering,NewHorizonInstitute Of Technology And Management, Maharashtra, India)
BirvatkarOmkarDeepak
(B E Student, Department Of Civil Engineering,NewHorizonInstitute Of Technology And Management, Maharashtra India)
GoleRohitRajendra
(B.E Student, Department Of Civil Engineering,NewHorizonInstitute Of Technology And Management, Maharashtra, India)
SahaNarayandeglal
(B.E Student, Department Of Civil Engineering,NewHorizonInstitute Of Technology And Management, Maharashtra, India)
