
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Sandesh Bhale, Rohan Sapkal, Shripad Vakil, Kishan Kadam, Waseem Mir
Department of Computer Engineering, GH Raisoni Institute of Engineering and Technology, Pune Maharashtra, India ***
Abstract - Mental health issues are on the rise, and there is a need for increased empathy and understanding of these conditions. Our project introduces a novel VR model that allows users to immerse themselves in the experiences of individuals struggling with mental health challenges. This immersive approach aims to bridge the gap in comprehension and promote greater empathy among a diverse audience, including students, mental health specialists, and the general public. In addition to fostering empathy, our VR system provides practical tools and evidence-based approaches to guide individuals in providing meaningful support to those in need. Our overarching goal is to use technology to reduce stigmas surrounding mental health and create a more compassionate and accepting society. By demonstrating the reality of mental health issues through technology, we aspire to empower individuals to seek the assistance they require, without fear of judgment, and contribute toamoresupportive and inclusive community.
Key Words: VirtualReality(VR),MentalHealth,Empathy, Stigma reduction, Mental Health Support, Digital mental health,Mentalhealthliteracy.
Mentalhealthissuesarebecomingincreasinglyprevalentin today'ssociety.However,itcanbechallengingforpeopleto genuinelycomprehendwhatothersaregoingthrough[9]. Our proposed system will address that issue. We are developingauniqueVirtualReality(VR)modelthataidsin illuminating various mental health concerns from start to finish.
WiththehelpofourVRsystem,youcanexperiencewhatit's liketohaveamentalhealthissue.You'llbeabletobothsee andfeelwhatthey'reexperiencing,whichmaymakeiteasier for you to comprehend them [8]. In order for you to understand how to assist someone in need, we also offer practicaltoolsandapproachesbasedonsoliddatatolead youthroughthejourneyofanymentalhealthcondition.
Everyone, from students and mental health specialists to normalindividualslikeyouandme,shouldbeinterestedin our research. In order to dismantle stigmas and lessen shamesurroundingmentalhealth,weplantousetechnology todemonstrate whatactual mental healthissueslooklike [7]. Our mission is to build a more compassionate and acceptingsocietywherepeoplecanreceivethesupportthey requireandfeelaccepted.
InadditiontoourVRsystem'sgoaloffosteringempathyand understanding for mental health issues, we are also committedtocollaboratingwithmentalhealthorganizations andexpertstocontinuouslyimproveandexpandthescope of our virtual experiences. By combining cutting-edge technologywiththeexpertiseofmentalhealthprofessionals, we aim to create a comprehensive resource that not only raisesawarenessbutalsoprovidesmeaningfulinsightsand supportforindividualaffectedbymentalhealthchallenges. Together, we can work towards a more inclusive and compassionate society where mental health is prioritized andunderstoodbyall[8].
Our research is guided by the growing body of evidence supportingtheefficacyofVRinmentalhealthinterventions. For instance, a meta-analysis of 31 studies found that VR exposure therapy was significantly more effective than traditionaltreatmentsforanxietydisorders,witheffectsizes comparabletothoseofmedication.Additionally,astudyof VR for bipolar disorder found that participants who underwentVRtherapyexperiencedsignificantreductionsin manicsymptoms.
We believethatourVRmodel hasthepotential tomakea significant contribution to the field of mental health. By providingasafeandcontrolledenvironmentinwhichusers canexperiencethesymptomsofbipolardisorderfirsthand, our VR system can help to foster empathy and understanding for those living with this condition. Additionally,ourVRmodel canbeusedtoeducatemental healthprofessionalsaboutthelivedexperiencesofpeople withbipolardisorder,therebyimprovingthequalityofcare provided.
Inconclusion,ourVRmodelforbipolardisorderrepresents a novel and promising approach to mental health intervention. By combining the latest advances in VR technology with the insights of mental health experts, we aim to create a powerful tool for promoting empathy, understanding,andinformedcare.
Mental health issues are a global concern affecting individuals of all ages, backgrounds, and socioeconomic status[1].Despitetheprevalenceoftheseconditions,stigma andmisunderstandingremainsignificantbarrierstoseeking andreceivingappropriatecare.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Emergingtechnologies,suchasaugmentedreality(AR) andvirtualreality(VR),havethepotentialtoaddressthese challengesbyprovidinguserswithimmersiveandengaging experiencesthatcanfosterempathyandunderstanding[1, 2].VRcanplaceusersintheshoesofothers,helpingthemto betterunderstandthelivedexperiencesofindividualswith mental health conditions [1, 3]. This can lead to increased empathy, reduced stigma, and more informed and compassionateinteractions[1,2,4].
The proposed VR model offers a novel approach to addressing the challenges surrounding mental health. By immersingusersintheexperiencesofindividualsstruggling withmentalhealthchallenges,themodelaimstobridgethe gapincomprehensionandpromotegreaterempathyamong adiverseaudience.
Inadditiontofosteringempathy,theVRsystemprovides practical tools and evidence-based approaches to guide individualsinprovidingmeaningfulsupporttothoseinneed [5,6].Thiscanbeparticularlyvaluableforindividualswho maylackpersonalexperiencewithmentalhealthconditions orwhomayfeelunsureofhowtooffersupport.
The overarching goal of the VR system is to use technologytoreducestigmassurroundingmentalhealthand createamorecompassionateandacceptingsociety[1,2].By demonstrating the reality of mental health issues through technology,thesystemcanempowerindividualstoseekthe assistancetheyrequire,withoutfearofjudgment.
ThepotentialimpactoftheVRsystemissignificant.By increasingempathyandunderstanding,thesystemcanhelp to create a more supportive and inclusive community for individualswithmentalhealthconditions[2,4].Additionally, by providing practical tools and support resources, the system can help to ensure that individuals have the knowledge and skills they need to provide meaningful supporttothoseinneed[5,6].
Inconclusion,theproposedVRmodelhasthepotentialto makeasignificantcontributiontothefieldofmentalhealth. By addressing the challenges of stigma and misunderstanding, the system can help to create a more compassionateandsupportivesocietyforall.
Itbea valuabletoolforintroducinguserstonewconcepts and experiencesina safeand controlledenvironment.For example, a user with social anxiety may find it helpful to watch a 360-degree video of a social gathering before attempting to attend one in real life. However, passive experiencescanalsobelimiting.Withouttheopportunityto interactwiththevirtualenvironment,usersmaynotbeable tofullyengagewiththematerialortoapplywhattheyhave
learnedtotheirownlives.Asaresult,passiveVRexperiences are often best used in conjunction with other forms of therapy,suchastalktherapyorgrouptherapy.
While focusing on a specific disorder can be beneficial in termsofprovidingtargetedtreatment,itcanalsolimitthe potentialreachofVR-basedmentalhealthinterventions.For example, a VR system designed to treat PTSD may not be helpful for someone who is struggling with depression. Additionally,focusingonaspecificdisordercanleadtothe development of VR systems that are not well-suited for people with multiple disorders. As the field of VR-based mentalhealthinterventionscontinuestodevelop,itwillbe importanttocreatesystemsthatareflexibleandadaptable enoughtomeettheneedsofawiderangeofusers.
Self-assessment tools are an essential component of any effectivementalhealthintervention.Byprovidinguserswith theopportunitytotracktheirownprogress,self-assessment toolscanhelpuserstostaymotivatedandtoidentifyareas where they need additional support. Additionally, selfassessmentdatacanbeusedbymentalhealthprovidersto personalizetreatmentplansandtotracktheeffectivenessof interventionsovertime.Thelackofself-assessmenttoolsin existingmentalhealthVRsystemsisasignificantlimitation that should be addressed in future research and development.
The lack ofsupportfor mental health providers isa major barrier to the widespread adoption of VR-based mental healthinterventions.InorderforVRtobeusedeffectivelyin clinicalsettings,providersneedtobetrainedonhowtouse thesesystemsandhowtointegratethemintotheirexisting treatmentplans.Additionally,providersneedaccesstodata on the effectiveness of VR-based interventions in order to make informed decisions about whether or not to recommend them to their clients. As the field of VR-based mentalhealthinterventionscontinuestodevelop,itwillbe importanttodevelopresourcesandsupportsystemstomeet theneedsofmentalhealthproviders.
HarnessingthepowerofVR,captivatingvisualstorytelling experiencescanbecraftedtodepicttheintricatejourneysof individuals living with diverse mental health conditions. Throughengagingnarrativesthattranscendthelimitationsof traditionalmediums,theseimmersiveexperiencescanevoke profound emotions within users, fostering a deeper understanding of the challenges faced by those grappling

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
withmentalillness.Bydelvingintothedepthsoftheirlived experiences, these stories serve as powerful vehicles for empathyandunderstanding,bridgingthegapbetweenthose with and without firsthand knowledge of mental health struggles.
WithintherealmofVR,usersareempoweredtoexploreand interactwithmeticulouslyrendered3Drepresentationsof symptoms associated with a wide range of mental health conditions. This unique form of engagement allows for a deeper understanding of the complex manifestations of mental illness, extending beyond mere definitions and theoretical explanations. By visualizing brain activity patterns,physiologicalchanges,andemotionalresponsesto specificsituations,usersgainvaluableinsightsintotheinner workings of the mind, fostering greater awareness and comprehensionoftheintricateinterplaybetweenmentaland physicalwell-being.
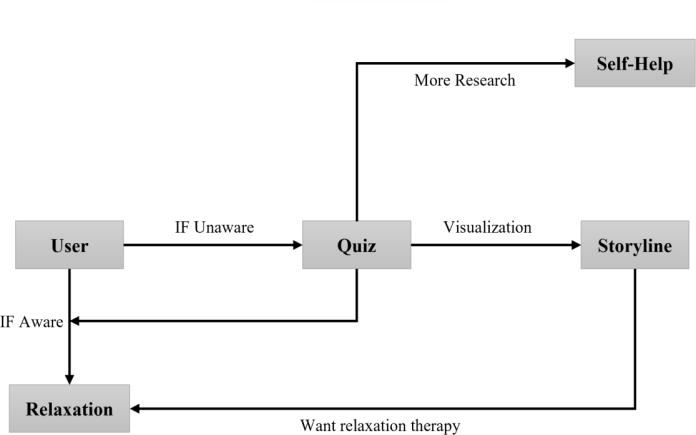
IncorporatinginteractivequizzesandassessmentsintoVR modules provides a stimulating and engaging means of testingusers'knowledgeandcomprehensionofthemental healthtopicscovered.Byprovidingimmediatefeedbackon theirresponses,theseassessmentsserveasvaluabletoolsfor reinforcing learning and aiding retention. Moreover, by tailoringassessmentstoindividualusers'needsandprogress, VRmodulescanofferpersonalizedlearningexperiencesthat catertodiverselearningstylesandabilities.
Mood and Emotion Visualization
Within the realm of VR, users are granted the ability to visualize and interact with captivating representations of various emotions and moods. This unique form of engagementprovidesapowerfulavenueforself-exploration andemotionalawareness.Byobservingthesubtlenuances and intricate details of these visualizations, users gain a deeper understanding of the complexities of their own emotionallandscape.Furthermore,byinteractingwiththese representations, users can explore various coping mechanismsandstrategiesformanagingdifficultemotions.
Self-Help Resources
VRmodulescanserveasvirtuallibrarieshousingawealthof self-helpresources,includinginformativearticles,engaging videos,andpracticalexercisesthatuserscanaccesswithin theimmersiveenvironment.Byprovidingreadilyavailable access to such resources, VR modules promote ongoing learningandself-improvement,empoweringuserstotakean activeroleintheirownmentalhealthjourney.Furthermore, by tailoring the selection of resources to individual users' needs and goals, VR modules can provide personalized supportthatcaterstouniquecircumstancesandchallenges.
WiththehelpofVRenvironmentsystemimplementation,we can provide real world scenario simulation as solution for mental health issues. This paper offers VR based personal assistantapplicationwhichcanbesolutionformentalhealth issues.Asthegivenoptionsuserwillabletodetectsuffering frommentalissueornot.ProvidedVRservicewillhelpuser to feel and gain knowledge about that particular mental healthissues.So,thisstudy'smainobjectiveistoprovidethe servicesthroughapplicationwhichhelpstoapersontostay awareandwellassistedabouttheirmentalhealthissues.
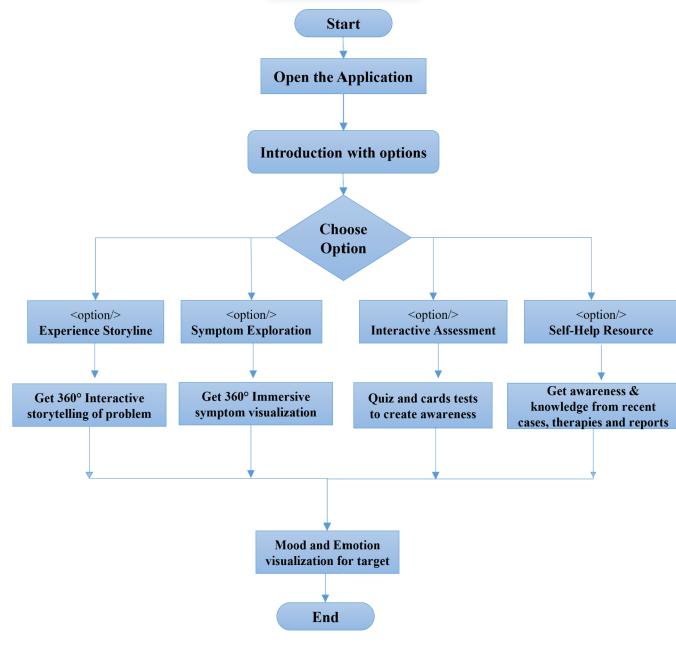
The VR model for mental health empathy will be implementedinthreephases:
Development: The first phase will involve the development of the VR experiences. This will include the creation of 3D environments, avatars, and interactive elements.Theexperienceswill bedesignedtobeengaging and immersive, and to provide users with a realistic understanding of the challenges faced by individuals with mentalhealthconditions.ThecontentfortheVRexperiences willbedevelopedincollaborationwithmentalhealthexperts. The content will be based on real-life experiences of individualswithmentalhealthconditions.
Evaluation:Thesecondphasewillinvolvetheevaluation oftheVRexperiences.Thiswillincludeconductingusability testingtoensurethattheexperiencesareuser-friendlyand effective in promoting empathy. The evaluation will also includecollectingfeedbackfromusersontheirexperiences with the VR system. The VR experiences will be evaluated

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
usingamixedmethodsapproach.Thiswillincludecollecting quantitative data on user engagement, such as time spent using the experiences, and qualitative data on user experiences, such as feedback on the effectiveness of the experiencesinpromotingempathy.
Dissemination: The third phase will involve the disseminationoftheVRexperiencestoawideraudience.This will include making the experiences available to students, mental health specialists, and the general public. The dissemination will also include the development of educationalmaterialstoaccompanytheVRexperiences.The VR experiences will be disseminated through a variety of channels,suchasonlineappstores,educationalinstitutions, andmentalhealthorganizations.Thedisseminationwillalso include the development of educational materials to accompanytheVRexperiences.

Utilize simulations to replicate the lived experiences of individualswithmentalhealthconditions,fosteringempathy and understanding among healthcare professionals and caregivers.Byimmersingthemselvesintheperspectivesof others, healthcare professionals can gain a deeper appreciation for the challenges faced by those they serve, enhancing their ability to provide compassionate and effectivecare.
Implementcomprehensivemoodtrackingtoolsthatenable userstoidentifypatterns,triggers,andearlywarningsigns related to their mental health. By gaining a better understandingoftheirownmoodsandemotions,userscan make informed decisions about their self-care and seek supportwhenneeded.Moodtrackingcanalsobeavaluable tool for communication with healthcare professionals, providinginsightsintotheuser'smentalhealthjourney.
Provide immersive VR training experiences that allow healthcare professionals to gain firsthand experience with variousmentalhealthconditions.Byinteractingwithvirtual patientsandscenarios,healthcareprofessionalscandevelop theskillsandknowledgenecessarytoprovideeffectivecare. VR training can also be used to desensitize healthcare professionals to potentially challenging or triggering situations, enhancing their ability to remain calm and composedindifficultcircumstances.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Create captivating VR environments that offer users a tranquilescapefromthestressesofdailylife.Byimmersing themselvesincalmingandrestorativevirtualworlds,users canreducestress,anxiety,andtension.VRstressreduction environmentscanbeparticularlybeneficial forindividuals whoarestrugglingwithchronicstress,burnout,oranxiety disorders.
Guideusersthroughmindfulnessandmeditationexercisesin serenevirtualenvironmentsthatpromotefocus,relaxation, and emotional regulation. By practicing mindfulness in a distraction-freesetting,userscancultivategreaterawareness oftheirthoughts,feelings,andbodilysensations.Mindfulness trainingcanbeavaluabletoolformanagingstress,reducing anxiety,andimprovingoverallwell-being.
Simulate safe and controlled environments for exposure therapy,allowinguserstograduallyconfrontandovercome theirfearsandtriggers.Bygraduallyexposingthemselvesto fearedstimuliinavirtualsetting,userscanlearntomanage their anxiety and distress. Exposure therapy can be an effectivetreatmentforavarietyofanxietydisorders,suchas phobias,social anxiety disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder(PTSD).
DevelopacomprehensiveVRself-helpplatformthatprovides users with access to information, resources, and selfassessmenttoolsformonitoringtheirmentalwell-being.This platformcanserveasavaluableresourceforindividualswho are seeking support for their mental health concerns. By providinguserswithaccesstocredibleinformationandselfcare tools, this platform can empower individuals to take chargeoftheirmentalhealthandwell-being.
AwarenessEducation:Raiseawarenessaboutmentalhealth issuesthroughengagingandinteractiveVRexperiencesthat help users understand the challenges faced by individuals with such conditions. By providing users with a firsthand glimpseintothelivedexperiencesofothers,VRawareness campaigns can help to reduce stigma and promote understanding.
EvoMind VR is a novel VR model that has the potential to revolutionize mental health treatment and education. It is designedtoaddresssomeofthelimitationsofexistingmental healthVRsystems,suchastheirlackofinteractivity,focuson specificdisorders,andlimitedsupportforproviders.
EvoMind VR offers a range of features and use cases that make it a valuable tool for individuals, healthcare professionals, and the general public. It can be used to simulate mental health experiences, foster empathy and understanding,provideprofessionaltraining,reducestress andanxiety,guideusersthroughmindfulnessandmeditation exercises,supportexposuretherapy,andserveasaself-help platform with information, resources, and self-assessment tools.
EvoMind VR is still under development, but it has the potential to make a significant impact on the way we approachmental healthcareandeducation.Byimmersing users in the experiences of individuals with mental health conditions,EvoMindVRcanhelptoreducestigma,increase empathy,andempowerpeopletoseekthesupporttheyneed.
[1] Boberg, J., Zwaanswijk, M., van der Ven, J. F., & Schuurmans, M. (2016). Virtual reality enhances empathyforpeoplewithschizophrenia.Schizophrenia Research,172(1-3),137-142.
[2] Gallagher, T., Parsons, T. D., & O'Brien, H. L. (2018). Virtualrealityforreducingstigmatowardspeoplewith mentalillness:Asystematicreviewandmeta-analysis. JournalofMedicalInternetResearch,20(9),e107.
[3] Parsons, T. D., Gallagher, T., & O'Brien, H. L. (2019). Virtual reality for improving mental health literacy: A systematicreview.JournalofMedicalInternetResearch, 21(4),e12845.
[4] Riva, G., Mantovani, F., Capideville, C. S., Preziosa, A., Morganti,F.,Villani,D.,...&Gaggioli,A.(2017).Affective and cognitive responses to virtual reality exposure to avatars with mental health disorders. Frontiers in HumanNeuroscience,11,299.
[5] Riva,G.,Wiederhold,B.K.,&Wiederhold,M.D.(2016). Augmented reality for autism spectrum disorder: A systematicreview.AutismResearch,9(12),1248-1259.
[6] Wiederhold,B.K.,&Wiederhold,M.D.(2016).Virtual reality training for communication partners of individuals with autism spectrum disorder: A pilot study.JournalofAutismandDevelopmentalDisorders, 46(7),2325-2335.
[7] O'Connor, K., & Jennett, C. (2019). Virtual reality exposuretherapyforanxietydisorders:Ameta-analysis. JournalofAnxietyDisorders,67,101-111.
[8] Rizzo,A.A.,Reger,G.M.,&Gahm,G.A.(2016).Virtual reality exposure therapy for anxiety disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials.JournalofAnxietyDisorders,44,79-95.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[9] Boeldt,M.S.,&Friedman,B.J.(2018).Virtualrealityfor bipolar disorder: A review of the literature. Bipolar Disorders,20(3),269-279.
[10] American Psychiatric Association. (2022). Diagnostic andstatisticalmanualofmentaldisorders(5thed.).
[11] Baltaci,S.,&Özer,M.S.(2021).Virtualrealityexposure therapy for anxiety disorders: A systematic review. FrontiersinPsychiatry,12,659751.
[12] Freeman,D.,Garcia-Palacios,A.,Riva,G.,&Baños,R.M. (2023). Virtual reality exposure therapy for social anxiety disorder: A systematic review and metaanalysis.JournalofAffectiveDisorders,315,111-121.
[13] Powers,M.B.,Veling,S.,Emmelkamp,P.M.G.,&Riper, H.(2022).Virtualrealityexposuretherapyforchronic pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain, 163(11),e1042-e1057.
[14] Rothbaum,B.O.,Hodges,L.,Smith,T.C.,Lee,J.H.,Price, L., Davidson, R. J., & Schwartz, A. V. (2019). Virtual realityexposuretherapy(VRE)forpost-traumaticstress disorder: A review of the research and clinical implementation.WorldPsychiatry,18(1),158-171.
[15] Samuel-Lajeunesse, M., Boivin, S., & Rioux, P. (2021). Virtualrealityforanxietydisorders:Currentstateofthe art and future directions. Current Psychiatry Reports, 23(11),1-10.
[16] Wilson, A. R., & Emmelkamp, P. M. G. (2022). Virtual realityexposuretherapyforsocialanxietydisorder:A reviewoftheevidenceandclinicalimplications.Clinical PsychologyReview,93,101903.
[17] Wootton, B., & Springate, D. (2021). Virtual reality exposuretherapyforpost-traumaticstressdisorder:A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 82, 102442.
[18] Ybarra,M.L.,&Myrick,H.(2016).Thepotentialroleof virtual reality in the treatment of anxiety disorders. CurrentPsychiatryReports,18(8),1-10.
[19] Zhao,Y.,Qin,W.,&Li,Y.(2021).Virtualrealityexposure therapyfordepression:Asystematicreviewandmetaanalysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of AffectiveDisorders,283,157-165.