
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
P. R. Peshwe1 , V. N. Wankhade2
1Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering and Technology, Akola
2Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering and Technology, Akola ***
Abstract
The investigation presented in this paper aimed at predicting the seismic response of RC buildings with different configuration on sloping & plain ground. A seismic analysis performed on G+6 story RC structural & steel structural building. 3-D Analysis including seismic effect have been analysis method by using STAAD PRO. Here we have four configuration rectangular RCstructure on plainandsloping ground and Rectangular steel structure on plain and sloping ground building were considered for analysis and they are rested on 0 & 10 slope From the analysis of dynamic parameters obtained and has been discussed in terms of Horizontal moments, Seismic base shear, Axial forces and Displacement.
Keywords: SlopingandPlainground,SeismicAnalysisMethod,STAADPRO,Displacement,BaseShear
1. Introduction
Insomepartsofworld,hillyarea ismorepronetoseismicactivity;e.g.northeastregionofIndia. TheTourism andrapid urbanizationinhillyregionhasacceleratedtherealestatedevelopment.Duetothis,populationdensityinthehillyregion hasincreasedcontinuously.Therefore,thereisdemand fortheconstructionofmulti-storeybuildingsonhillslopeinand aroundthecities.Hillbuildingsaredifferentfromthoseinplains;theyareveryirregularandunsymmetricalinhorizontal andverticalplanes,andtorsionallycoupled.
1.1 Aim
TostudythebehaviorofRCCandsteelbuildingrestingonPlainandslopingground.
1.2 Objectives
Theobjectivesofprojectareasfollows:-
Tocomparevariousstructuralparametersforbuildingsrestingonplainground.
TostudybehaviorofRCCandSteelframeinvariousseismiczones.
Tostudythevariationinmaterialrequirementforframingmaterial.
Tofindthemostvulnerableframingsystemamongstallframesconditions.
To find various parameters for all frames Such as, Axial forces, Bending Moments, Displacementsand compare them.
1.3
Hill buildings are different from those in plains; they are very irregular and unsymmetrical in horizontal and vertical planes,andtorsionallycoupled.Hence,theyaresusceptibletoseveredamagewhenaffectedbyearthquakegroundmotion. Pastearthquakes[e.g.Kangra (1905),Bihar- Nepal (1934&1980),Assam(1950), Tokachi-Oki-Japan(1968), UttarkashiIndia(1991)][1],haveprovedthat buildings located near the edge of stretch of hills or sloping ground suffered severe damages
Suchbuildingshave massandstiffnessvaryingalongtheverticalandhorizontalplanes, resultingthecenterofmassand centerofrigiditydonotcoincideonvariousfloors.Thisrequirestorsional analysis;inadditiontolateralforcesunderthe action of earthquakes. Little information is available in the literature about the analysis of buildings on sloping ground. The investigation presented in this paper aimed at predicting the seismic response of RC buildings with different configurationonslopingandplainground

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
2. Configuration of Building on Plane and slopping ground.
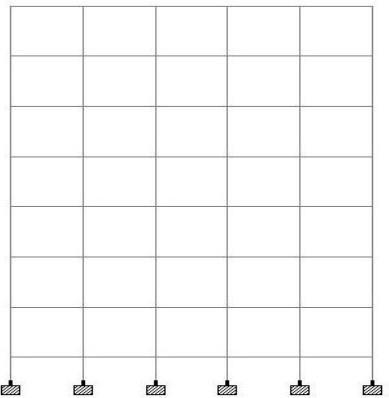
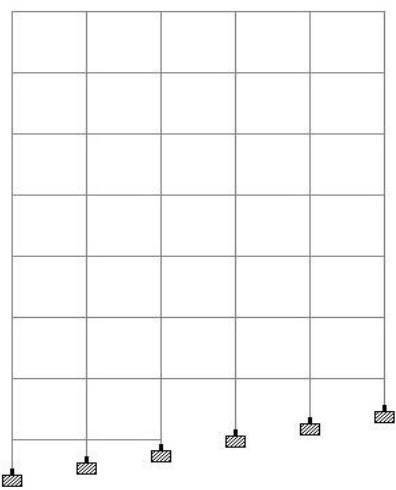
i) Regularbuildingonleveledground (ii)slopinggroundbuilding
3.1 Work Process
Themethodologyforpresentworkisasmentionedbelow:-
1) InthefirstphasegeneralparametersofprojectwillbefinalizedSuchas,Aim,Objectivesandneedofthiswork.
2) ThenVariousLiteratureswillbestudiedregardingtheprocessofwork.
3) Detailstepbystepprocedurewillbethendecideforeasygoingofwork
4)Detailinformationwillbecollected regarding sloping groundtypes offraming materialand loading and their combinations.
5) Allgeneralparametersregardingmaterial,theirconstants,andloadingintensitieswillbedecidedatthisstep.
6) NowafterdoingallabovestepsNoofmodelsandtheirshapespatternswillbenowfixed.
7) Suitablemethodofanalysis(SeismicCo-efficientMethod)willnowbeselected.
8) Suitabletypeofsoftware(STAADPRO.)WillbeselectedforAnalysis.
9) AfterAnalyzingallmodelscomparativeresultswillbeplotted.
10) Basedonobtainedresultsfinalconclusionswillbedrafted.
11) Atlastallreferenceswillbemadeavailableforfuturework.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
3.2 Design Data:-
Live load : 3.0kN/m2at
Typical floor : 1.5kN/m2onterrace
Floor finish : 0.50kN/m2
Location : ZoneIIandZoneV
Earthquake load : AsperIS-1893(Part1)-2002
Depth of foundation below ground : 1.5m(RegularCase)
Type of soil : TypeII,MediumasperIS:1893
Storey height : Typicalfloor:3.05m,
Floors : G.F.+6upperfloors
Walls : 230mmthickbrickmasonrywalls.
Beam size :- 230mmx300mm, Column size :- 300mmx400mm,Slab thickness :- 130mm
Unit weight of concrete :- 25Kn/m3
Unit weight of brick masonry :- 19Kn/m3
4. Model Nomenclature
Inthepresentworkthemodelcombinationwillbedoneasfollow:-
Total08 models will be analyzed 04 ofRCC and 04 ofSteelFrame. Labeling of models will be doneas:-
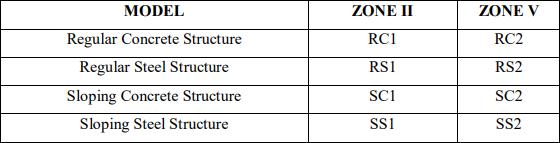
Theangleforslopinggroundwillbetakenas10

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
5.1 Results for all models in Zone-2
5.1.1 Reactions for all models in zone-2
From below graph it can be observed that RCC structure has maximum values of forces inalldirectionon slopinggroundmeanwhileithaslowestvaluesincaseofplaneground.
Maximum Reactions forall models of Zone-2



International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
5.1.2 Mode Frequency and Time Period for all models in zone-2

The graph shows that frequency requirement for steel structures on sloping ground andon planeground requireslesswhereasRCCstructurehasvaluesonhighersides.
MODE FREQUENCY FOR ALLTHE MODES IN ZONE -2



Fig. 5.1.2(a) Comparison of mode of frequency for all models of zone 2
BelowgraphshowsthattimeperiodrequiredforRCCstructureislessthanallothersandalsoshowsalineardecrementin requirementoftimeperiodfrommode1to6.Thegraphalsoshows that steelstructuresonplaneandslopinggroundhas thehightimeperiodthanRCCstructures.


Fig. 5.1.2(b) Comparison of Time Period for all models of zone 2
5.1.3 Displacement for all models in zone-2
Graph shows that steel structures has less displacement in X direction but shows maximum values in Z direction and resultant values. Whereas steel structures on sloping ground has higher values of displacement in but direction but minimizes in Z direction from all this discussion it can be conclude that steel structures are better than RCC structure fromdisplacement pointofview. Time Period for all models of zone 2
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072 © 2024, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.226 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page72

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Maximum Displacementfor All Models Of Zone 2

5.1.3 Comparison of Maximum Displacement for all models of zone 2
5.1.4 Beam End Forces for all models in zone-2


Maximum Moment for all models of Zone 2




Fig. 5.1.4 Comparison of Maximum Moment for all models of zone 2
Above graph shows that Steel Structures on plane ground and Concrete structures on sloping ground attains maximum values of moment in X, Y, and Z direction all models have negligible values ofMxcaused byMx moment at a particular point.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
5.1.5 Base Shear and Storey Shear for all models of Zone-2

Storey Shear for all models of zone 2


5.1.5 Comparison of Storey Shear for all models of zone 2
Though there is variation in Base shear values of all models but Graph of storey shear represents the similar pattern of storeyshearandforbottom3storey’stheyarealmostcoincidingwitheachothers.Itcanalsobeseenthatbaseshearare storeyshearvaluesarelessforsteelstructureonbothplaneandslopingground.
5.1.6 Reactions for all models in zone-5
While comparing reactions in severe zone RCC structures shows higher values of reactions onsloping ground whereasonplanegroundSteelstructuresshowslowervalues.









5.1.7 Mode Frequency and Time Period
ThoughfrequencyrequirementforRCCstructureissameforstructuresonplaneandsloping grounditchangesitvalues forsteelstructuresonplaneandslopinggrounds.InbothcasesteelstructureshaslowerfrequencythanRCCstructures.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
In above comparative graph time period for steel structures and RCC structures in respective cases are same. RCC structure shows less time period than steel structures. This is might be because of material properties of steel and concrete. Frequency for all models of zone 5




Fig. 5.1.7(a) Comparison of Frequency for all models of zone 5






Fig. 5.1.7(b) Comparison of Time Period for all models of zone 5

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
5.1.8 Displacement for all models of Zone-5
Displacement for all models of zone 5




Fig. 5.1.8 Comparison of Displacement for all models of zone 5
Incaseofdisplacementvaluesforzone5steelstructuresshowcomparativelylowervaluesthan RCCstructuresfromthis itcanbeconcludedthatsteelstructuresbehavesgoodinseverezonesthan RCCstructures.
5.1.9 Beam End Forces for all models of Zone-5





Fig. 5.1.9 Comparison of Beam Moments for all models of zone 5

Moment comparison in severe zone represents higher values of Mx, My for concrete structures on sloping ground while lowervaluesMzonplaneground. Whilesteel structureshaslowestvalueson plane groundand highest values for Mzon Slopingground.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
5.1.10
Base Shear and Storey Shear
Base ShearForAll Models Of Zone 5






Fig. 5.1.10 Comparison of Base Shear for all models of zone 5
While RCC structure on plane ground shows highest values of Base shear and because of this it is the highest curve amongst all models. So that it can be conclude that steel structures behaves goodin both plane and sloping ground in severezone.
6. CONCLUSION
(a) In low intensity zone and in very severe seismic zone steel structure reduces axial forces than RCC structures on planegroundandalsoonslopingground.
(b) Inconcernwithmodal frequencyandtime periodRCC structurebehave betterthansteel structureson both plane and sloping ground in low seismic zone but in severe seismic zones steel structure behaves excellent than RCC structure.
(c) In both low and very severe seismic zones steel structures have less displacement values thanRCC structureson bothplaneandslopingground.
(d) In both low and very severe seismic zones steel structure reduces the intensity of vertical moments than RCC structuresbuthashighvaluesofHorizontalmoments.
(e) In both low and very severe seismic zones for the same structural configurations and load- ing conditions steel structurecanbedesignedefficientlyandhascomparativelylowervalueofSeismicbaseshear.
(f) Atlastfromall aboveconclusionsit can be concludedthatsteel structuresare efficientand better inboth low and verysevereseismiczonesinanytypeofgroundconditions.
1. Analytical Study on Performance of Steel and RCC Frame Structure by Non-linear Static Analysis International Journal of Engineering Technology Science and Research IJETSRISSN2394 – 3386 Volume 5, Issue3March2018,AnujDomale,KalurkarL.G.
2. COMPARATIVESTUDYOFANALYSISANDDESIGN OFR.C.ANDSTEELSTRUC- TURESInternational Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 2, February-2015 ISSN 2229-5518Prof. Prakarsh Sangave,Mr.NikhilMadur,Mr.Sagar

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 03 | Mar 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
3. SEISMICANALYSISOFRCCANDSTEELFRAMESTRUCTUREBYUSINGETABSIOSRJournalofMechanicaland Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-ISSN: 2278- 1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. II (Mar. - Apr. 2018), PP 38-42AnujDomale,L.G.Kalurkar.
4. COMPARATIVE STUDY OF SEISMIC PARAMETERS IN STEEL AND RCC FRAMES WITH ANDWITHOUT MASONRY INFILL WALLS International Journal of Sci- entific Development and Research (IJSDR), Dr. S.A. Halkude,C.G.Konapure,F.R.Hirapuri.
5. SEISMICANALYSISOFBUILDINGSRESTINGONSLOPINGGROUND13thWorldConfer- enceonEarthquake EngineeringVancouver,B.C.,CanadaAugust1-6,2004PaperNo.1472B.G.Birajdar,S.S.Nalawade.
6. ANALYSISOFAMULTISTOREYBUILDINGFRAMEFORLATERALFORCESATSLOPINGSTRATAUNDERTHE EFFECT SEISMIC FORCES USING STAAD.PRO. Inter- national Journal Of Engineering Sciences & Research Technology,DeependraSinghRaghuvanshi,RashmiSakalle &Dr.RajeevArya.
7. SEISMIC PERFORMANCE OF STEEL FRAME STRUCTURE OVER RCC FRAME STRUC- TURE ,International Journal of Engineering Technology Science and ResearchIJETSR ISSN 2394 –3386 Volume 5, Issue 3 March 2018,SudarshanBhutekar,MohammedIshtiyaque.
8. A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN RCC AND STEEL DESIGN FOR INDUSTRIAL AND COMMERCIAL STRUCTURES,InternationalJournal of Civil and Structural Engineering Research ISSN 2348-7607(Online) Vol.4,Issue2,pp:(22-42),Month:October2016-March2017,M.SatyanarayanaReddy.
9. SEISMIC ANALYSIS PERFORMED ON RCC AND STEEL FRAME IN VARIOUSZONESUSINGSTADDPRO, InternationalJournalOfInformationAndComputingScienceVolume 5, Issue 11,November2018 ISSNNO: 0972-1347,MonaliBhakare,MeghnaPatankar.