
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Duckki Lee
Associate Professor, Department of Smart Software, Yonam Institute of Technology, Jinju, South Korea
Abstract -
The Internet of Behavior (IoB) represents a convergence of data analytics, behavioral science, and advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to collect, analyze, and influence human behavior. By leveraging data from wearable devices, social media,sensors,andIoT networks,IoBprovides deep insights into user behavior patterns, enabling targeted interventions across diverse sectors. This paper explores the core concepts of IoB, its technological framework, and its broad range of applications, including healthcare, smart cities, marketing, and education. Additionally, it addresses the ethical and privacy challenges associated with handling sensitive behavioral data and outlines strategies for mitigating these concerns. The study further examines future prospects for IoB, including integration with emerging technologies like 5G/6G networks and the Metaverse, and discusses the potential societal and legal implications. By presenting a comprehensive overview, this paper aims to contribute to the growing body of research on IoB and highlight its transformative potential in shaping behavior-driven servicesandsolutions.
Key Words: Internet of Behavior, IoT, Behavioral Analytics, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Data Privacy,SmartCities,PersonalizedServices
With the advancement of digital technology, data-driven decision-making has become increasingly crucial. The Internet of Behavior (IoB) has emerged within this trend asaconceptthatdiffersfromthe InternetofThings(IoT) While IoT focuses on data exchange between physical objects, IoB encompasses technologies that collect and analyze human behavioral data to influence specific actions[1,2].
IoB integrates behavioral science, data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML), enabling its application across various industries[2]. For instance, in the healthcare sector, IoB is utilized to monitor and improve patient health behaviors, while in marketing, it helps analyze consumer behavioral patterns to provide personalizedadvertising[3].
In particular, following the COVID-19 pandemic, the expansion of remote environments has led to increased attention to IoBtechnologies.Businessesandgovernment
institutions leverage behavioral data to maintain public safety, enhance productivity, and optimize work and educational environments[4]. According to a Gartner study,by2025,morethan50%oftheglobalpopulationis expected to be exposed to at least one IoB system, indicating that both corporations and governments will increasinglyutilizeIoBtechnologiesto optimizebehaviorbaseddecision-making[5].
IoB was identified by Gartner in 2020 as one of the key emerging technology trends. It refers to internet-based technologies that collect, analyze, and leverage human behavioral data to induce or modify behaviors[5]. Unlike traditional IoT, which focuses on sensor-based data collection and automated inter-device processes, IoB is characterized by its ability to intervene in human decision-makingbyutilizingthecollecteddata[6].
The concept of IoB was first introduced by Gote Nyman (2012), who described it as a technological approach to digitizing human intent, allowing for behavior prediction and improvement[1]. Building on Kevin Ashton’s (2009) IoT concept, IoB has evolved beyond simple data collection to include behavioral analysis and modification technologies[5].
Data Collection: Collecting real-time behavioral data from wearable devices, smartphones, CCTV, socialmedia,andIoTsensors[1].
Data Analysis: Utilizing AI and ML to analyze collecteddataandpredictbehavioralpatterns[3].
Behavior Modification: Implementing systems that provide personalized feedback or encourage specific behaviors based on the analysis results[8].
This study aims to systematically define the concept of IoB, explore key applications, and analyze challenges, therebysuggestingpotentialdirectionsforfutureresearch andindustrialapplications.Thecontributionsofthisstudy areasfollows:
1. Establishing a conceptual framework: Clearly definingIoBanditscharacteristicsincomparison toIoTandInternetofEverything(IoE)

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
2. Analyzing key technological components: Examining the fundamental elements that comprise IoB, such as data collection, analysis, andbehaviormodification
3. Exploring industry applications: Investigating practical IoBusecases inhealthcare,smartcities, marketing, and education to assess its real-world applicability
4. Discussing challenges and proposing solutions: Addressing ethical concerns, data privacy issues, and technological limitations, while suggesting potentialcountermeasures.
Through this research, we aim to systematically organize the theoretical background of IoB and propose future research directions, providing valuable guidance for researchersandindustryprofessionals
2.1 Definition and Conceptual Framework of IoB
2.1.1 Definition of IoB
The Internet of Behavior (IoB) refers to the concept of collecting, analyzing, and utilizing human behavioral data to induce specific behavioral changes. IoB has evolved from the Internet of Things (IoT) and is defined as a technologythatpromotesdecision-makingandbehavioral changes by analyzing human behavioral data collected through social media, wearable devices, smart sensors, andotherdigitalsources[1-5].
IoB extends the data collection and connectivity capabilities provided by traditional IoT by integrating behavioral science and data analytics to drive behavioral changes for specific purposes[4]. This transformation enablespersonalizedexperiencesandcreatesnewvaluein various fields, including healthcare, security, marketing, andeducation[4].
2.1.2 Conceptual Framework of IoB
The conceptual framework of IoB consists of three primary stages: data collection, data analysis, and behaviormodification
Data Collection
IoB collects user behavioral data from multiple sources. Themaindatacollectionmethodsinclude:
IoTDevicesandSensors:Dataisgatheredthrough smartwatches, smartphones, and IoT sensors, including biometric information (e.g., heart rate, step count), location data, and environmental information[17].
Social Media and Web Activities: User activity patterns, search history, and click data are analyzed from social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter to understand userinterests[18].
Smart Home and Smart City Systems: Data collected from smart home devices (e.g., smart refrigerators, smart lighting systems) can be utilizedtoanalyzeuserhabits[19].
IoB leverages machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to process large volumes of data and extract patterns. The primary analytical approaches include:
Behavioral Pattern Analysis: Analyzing repetitive user behaviors to identify specific habits and correlations[20].
Predictive Modeling: Utilizing machine learning algorithmstoforecastfutureuserbehaviors[21].
Real-time Data Processing: Implementing cloud computing and edge computing to provide realtimedataanalysisandfeedback[22].
The ultimate goal of IoB is to alter user behavior through targetedinterventions.Somekeyapplicationsinclude:
Healthcare Management: Smart healthcare systemsnotifyuserswhentheiractivitylevelsare insufficient and recommend appropriate health managementstrategies[12,13].
Personalized Advertising: Ads are optimized based on user search history and interests to improvemarketingeffectiveness[14].
Security System Enhancements: AI-driven security systems detect unusual activities and issue immediate security alerts to prevent fraud andhackingattempts[15].

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
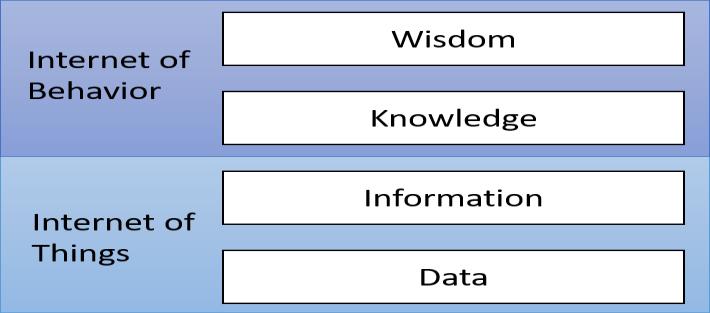
Fig-1: IoTandIoBHierarchy:FromDatatoWisdom
Figure 1 illustrates the hierarchical relationship between IoT and IoB, depicting the flow of data and how IoB leveragesIoTdatatotransformrawdataintoinformation, knowledge,andultimatelywisdom[16].
The Internet of Behavior (IoB) is closely related to both the Internet of Things (IoT) and the Internet of Everything (IoE).Eachconceptrepresentsanevolutionin data collection, analysis, and application, with distinct rolesinthedigitalecosystem.
Thedifferencesbetweentheseconceptsareoutlinedinthe tablebelow:
Technology
Concept Description
IoT (Internet of Things) Atechnologythatconnectsphysicaldevices to the internet to exchange and process data.
IoB (Internet of Behavior) A technology that analyzes data collected from IoT devices to influence and modify humanbehavior.
IoE (Internet of Everything)
An extended concept integrating IoT, IoB, and AI, enabling broader connectivity and automateddecision-making
While IoT primarily focuses on data collection and exchange, IoBgoesastepfurtherbyinterpretingcollected data to induce behavioral changes. IoE incorporates both IoT and IoB, creating a more comprehensive system that integrates AI-driven automation and intelligent decisionmaking[23].
3.1 Data Collection Technologies (Wearable Devices, Sensors, IoT)
The first stage of IoB involves collecting data from a varietyofsources.Wearabledevices,sensors,andInternet of Things (IoT) technologies serve as the foundation for datacollection.
Wearable Devices: Devices such as smartwatches and fitness bands continuously monitor users' biometric signals, movement patterns, and sleep states to track health conditions. For example, researchers at UC San Diego have developed an electronic fingertip wrap that can monitor glucose, vitamins, and drug levels in sweat[9].
Thisdeviceallowsforreal-timetrackingofhealth indicatorsusingsweatanalysis.
Sensor Technology: Various sensors, including accelerometers, gyroscopes, and GPS, collect location, movement, and environmental information. These sensors are embedded in IoT devices, enabling real-time data collection. For example, smart home temperature control systems and security systems detect environmental changes, providing alerts or automatically adjusting conditions accordingly[24].
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT refers to a network of interconnected physical devices that exchange data via the internet. Within an IoT environment, numerous devices and sensors collect vast amounts of data, which can be analyzed to understand user behaviors. For instance, smart home ecosystems learn users' daily routines and optimizeenergyefficiencyandconvenience[25].
The data collected through IoB is analyzed using artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and behavioral science to extract meaningful insights and develop behavioralmodels.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): These technologies process large datasets and identify patterns. ML algorithms learn user behavior patterns and use them to predict future actions or provide personalized recommendations. For example, streaming services analyze viewing history to recommend contentthatalignswithauser'spreferences[26].
BehavioralScience:Behavioralsciencefocuseson understanding human decision-making processes and applying this knowledge to data analysis for moreaccuratebehavioralmodeling.Byleveraging behavioral science principles, user motivations and preferences can be better understood, allowing for strategic behavior modification. For instance, health applications analyze users' exercise habits and provide motivational notifications or rewards to promote sustained healthmanagement[27].
Integratingandvisualizingdatafrommultiplesourcesisa crucial aspect of IoB, as it facilitates better understanding andusabilityofthecollectedinformation.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Data Integration: Combining heterogeneous data sourcestocreateaconsistentdatasetisessential. For example, biometric data collected from wearable devices can be integrated with environmental data from smart home devices to provide a comprehensive analysis of a user's healthandlifestylepatterns[28].
Data Visualization: Presenting analytical results through graphs, charts, and dashboards enables users to easily interpret and utilize information. Effective visualization helps identify patterns and trends at a glance. For instance, fitness applications display a user's daily and weekly physicalactivitylevelsandcalorieconsumptionin a graphical format, providing an intuitive understanding of progress toward fitness goals[29].
Since IoB involves handling sensitive personal data, ensuringprivacyprotectionandsecurityisparamount.
DataEncryption:Encryptingcollecteddataduring storage and transmission prevents unauthorized access. This is a fundamental measure for protecting personal information from data breaches or hacking attempts. For example, medical data is secured using strong encryption protocols during transmission to ensure patient privacy[30].
User Consent and Transparency: Clear communicationaboutdatacollectionandusageis necessary, and obtaining explicit user consent is essential. This is not only a legal requirement for privacyprotectionbutalsoakeyfactorinbuilding user trust. For instance, during app installation, users should be provided with a transparent explanation of data collection policies and a consentprocessfordatausage.
Privacy by Design: Integrating privacy protection measuresinto system architecture from the early stages of development minimizes the risk of privacy violations. This approach includes principles such as data minimization, anonymization,andaccesscontrol[31].
By employing these technologies, IoB ensures that while harnessing behavioral data for insights, it also safeguards user privacy and security in compliance with ethical and regulatorystandards.
IoB utilizes wearable devices and sensors to collect individuals'healthdata,analyzeit,andusetheinsightsfor health monitoring and improvement. For example, smartwatchesandfitnessbandsgatherdataonheartrate, sleeppatterns,andphysicalactivitylevels,whicharethen used to provide personalized health management programs[32]. This approach contributes to chronic disease management, preventive healthcare, and increasedpatientengagement.
In smart cities, IoB helps analyze residents' behavioral patternstooptimize traffic flowand energy consumption. For example, real-time traffic data and driver behavior analysis can be used to reduce congestion and improve public transportation efficiency[33]. Additionally, energy consumption patterns in buildings can be analyzed to implement automated systems for energy conservation, reducingoverallurbanenergywaste.
IoB is widely used in marketing to collect and analyze consumer behavior data from both online and offline activities, enabling the development of personalized marketing strategies. Data from social media interactions, purchase history, and website browsing patterns helps businesses understand consumer preferences and deliver tailored advertisements and promotions[34]. This approach enhances customer satisfaction and brand loyaltybyofferinghighlyrelevantmarketingcontent.
Intheeducationsector,IoBenablespersonalizedlearning experiences by analyzing students' learning patterns and behaviors. Data collected from online learning platforms helps identify students' strengths and weaknesses, allowing for customized content recommendations and adaptivelearningpaths[35].Additionally,IoBsupportsthe design of interventions that enhance student engagement andmotivation.
IoB is also used in public policy and social campaigns to influence and guide societal behavior changes. For example, in environmental conservation campaigns,

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
individuals'energyconsumptionpatternscanbeanalyzed to develop programs that encourage energy-saving behaviors[36].Furthermore,IoBcanassistinpublicsafety policy development by analyzing citizens' mobility patterns and social interactions, helping policymakers designeffectivesolutionsforurbansafetyandsecurity.
TheInternetofBehavior(IoB)isatechnologythatcollects and analyzes human behavioral data to influence or modify specific actions. While it has applications across various domains, its implementation presents several challenges.
Since IoB deals with sensitive personal data, data privacy and ethical issues are significant concerns. The European Data Protection Supervisor (EDPS) has pointed out that the proliferation of IoB could increase personal data collection and profiling, potentially violating individuals' privacy rights[37]. IoB relies on data gathered from variousIoT devices totrack andanalyze human behavior, raising concerns about potential misuse or abuse of such data. Ensuring that IoB systems comply with stringent data protection regulations and ethical standards is criticaltoaddressingthesechallenges.
The effectiveness of IoB systems depends on the quality and accuracy of the collected data. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to erroneous analysis, resulting in inappropriate behavioral interventions or flawed decision-making[23]. Therefore, ensuring data accuracy during the collection process and implementing rigorous data-cleaning procedures are essential to maintaining the reliabilityofIoBsystems.
The implementation of IoB involves several technical challenges. Processing vast amounts of data in real time requiressignificantcomputationalpowerandastabledata communication infrastructure[38]. Additionally, issues such as compatibility between various IoT devices, efficient data storage, and data management must be considered. Overcoming these technical challenges necessitates high-performance computing resources and effectivedatamanagementstrategies.
The successful adoption of IoB technologies depends on social acceptance and the degree of psychological resistance among individuals[39]. Concerns about data collectionandusagecanleadtodistrustandreluctanceto
embrace IoB applications. To mitigate these concerns, transparent data processing practices and robust privacy policies must be implemented. Furthermore, clearly communicating the benefits and security measures of IoB tousersiscrucialinfosteringtrustandacceptance.
TheInternetofBehavior(IoB)isatechnologythatcollects and analyzes human behavioral data to influence or modify specific actions. As IoB continues to develop and expand its applications, several future directions and researchopportunitiesemerge.
IoBisevolvingalongsidethedevelopmentof6Gnetworks, allowing for more sophisticated and real-time behavioral analysis. 6G networks utilize terahertz (THz) ultrabroadband communication, enabling high-capacity data transmission and ultra-low latency communication to enhance real-time data processing[40]. With these advancements, IoB systems will be able to analyze and predictbehaviorwithgreaterspeedandaccuracy.
Integration with Emerging Technologies (5G/6G, Metaverse)
The integration of IoB with next-generation communication technologiessuchas5Gand6G pavesthe way for new applications in virtual environments like the Metaverse[41]. 5G technology provides high-speed data transmission and low latency, allowing IoB systems to collect and analyze data in real time. Furthermore, the combination of IoB and the Metaverse can enable user behavior analysis within virtual environments, leading to the creation of personalized experiences and services tailoredtoindividualneeds.
The widespread adoption of IoB introduces new challenges related to data privacy and security. Research on privacy protection in IoT environments explores legal and technological approaches to safeguarding personal information collected through various devices and sensors[42].Additionally,theutilizationofIoBdataraises concernsregardingsocialtrustandethicalconsiderations, necessitating in-depth studies on these topics. Legal frameworksand industry regulationsmust be established toensurethatIoBsystemsoperatewithinethicalandlegal boundaries.
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
To ensure the sustainability of the IoB ecosystem, businesses must adopt environmentally and socially responsible models. Companies should avoid greenwashing and instead pursue genuine eco-friendly business practices[43]. Establishing clear legal foundations and standardized evaluation metrics is essential to ensuring sustainable economic activities withintheIoBlandscape.
The advancement of IoB must be accompanied by both technological progress and societal and ethical considerations. A balanced approach is necessary to achieve personalized services, data security, privacy protection,andsustainabledevelopment.
TheInternetofBehavior(IoB)isatechnologythatcollects and analyzes human behavioral data to influence or modifyspecificactions.ByintegratingwiththeInternetof Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML), IoB plays a key role in developing personalizedservicesandoptimizingvarioussystems.
Key application areas of IoB include healthcare, smart cities,marketing,andeducation,whereuserbehaviordata isleveragedtoprovidetailoredservicesandsolutions.
In healthcare, IoB utilizes data from wearable devices tomonitorandimprove individual health conditions.
In smart cities, IoB analyzes citizens’ mobility patternsand energyusagedatato enhancetraffic managementandenergyefficiency.
In marketing, IoB processes consumer behavioral data to deliver personalized advertisements and promotions,increasingcustomersatisfaction.
In education, IoB enables customized learning experiences by analyzing students’ learning patterns and providing adaptive content recommendations.
Despite its potential, the implementation of IoB faces several challenges. Data privacy, ethical concerns, data accuracy, technical limitations, and social acceptance are majorissuesthatmustbeaddressed.SinceIoBdealswith sensitive personal data, clear guidelines and legal regulations are necessary to ensure ethical data usage. Additionally, ensuring the accuracy and quality of collected data is crucial for effective decision-making. Public awareness and education on IoB technology can also help improve social acceptance and mitigate psychologicalresistance.
Looking ahead, the integration of IoB with 5G/6Gand the Metaverseisexpectedtoexpanditsapplications,allowing for more precise and real-time behavioral analysis. These advancements will facilitate innovative services and solutions across industries. However, continued research and discussions on data privacy, ethics, and social acceptance are essential to building a sustainable IoB ecosystem.
IoB requires a harmonized approach that balances technological advancements with ethical and societal considerations. By addressing these challenges, IoB can provide personalized services while ensuring privacy protection,datasecurity,andlong-termsustainability.
[1] G. Nyman, "Internet of behaviors (IoB)," https://gotepoem.wordpress.com/2012/03/,2012.
[2] A Complete Guide to the Internet of Behaviors (IoB), https://www.cprime.com/resources/blog/acomplete-guide-to-the-internet-of-behaviors-iob/
[3] Mohd Javaid, Abid Haleem, Ravi Pratap Singh, Shanay Rab, Rajiv Suman. "Internet of Behaviours (IoB) and its role in customer services." Sensors International, 2021.
[4] JiayiSun,WenshengGan,Han-ChiehChao,PhilipS.Yu, WeipingDing."InternetofBehaviors:ASurvey."IEEE Xplore,2021.
[5] Gartner. "Top Strategic Technology Trends for 2021." https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/gartn er-top-strategictechnology-trends-for-2021/ (accessedAug.17,2021).
[6] Aayush Halgekar, Jay Bhatia, Aryan Chouhan, Nemil Shah, Ishaan Khetan. "Internet of Behavior (IoB): A Survey."IEEEISCON,2021.
[7] KevinAshton. "That ‘Internet of Things’ Thing." RFID Journal,2009.
[8] Elayan, Haya, et al. "Internet of behavior and explainable ai systems for influencing iot behavior."IEEENetwork37.1(2022):62-68.
[9] Ding, S., Saha, T., Yin, L.et al.A fingertip-wearable microgrid system for autonomous energy management and metabolic monitoring.Nat Electron7, 788–799 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-024-01236-7
[10] Zhao, Qinglin, et al. "A tutorial on internet of behaviors: Concept, architecture, technology, applications, and challenges."IEEE Communications Surveys&Tutorials25.2(2023):1227-1260.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[11] Romeo, Nzanzu Katasohire, et al. "Transforming Data into Behavioral Insights: A Review of the Internet of Behavior (IoB)."2024 11th International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom).IEEE,2024.
[12] MohdJavaid,AbidHaleem,RaviPratapSingh,Shahbaz Khan, Rajiv Suman. "An extensive study on IoB enabled Healthcare-Systems: Features, facilitators, and challenges." BenchCouncil Transactions on Benchmarks,StandardsandEvaluations,2022.
[13] P. K. Gupta, B. T. Maharaj, and R. Malekian, “A novel and secure IoT based cloud centric architecture to perform predictive analysis of users activities in sustainable health centres,” Multimedia Tools and Applications,vol.76,no.18,pp.18489–18512,2017.
[14] K. Varnali, “Online behavioral advertising: An integrative review,” Journal of Marketing Communications,vol.27,no.1,pp.93–114,2021.
[15] D. Vikram, N. Jeyakkannan, S. Santhoshkumar, R. Karthika, P. Punitha and H. Ajina, "Securing IoT: Anomaly Detection and Behavioral Analysis for Data Integrity," 2024 5th International Conference on Intelligent Communication Technologies and Virtual Mobile Networks (ICICV), Tirunelveli, India, 2024, pp. 892-896
[16] C. Kidd, “What is the internet of behaviors? IoB explained,” https://www.bmc.com/blogs/iobinternet-of-behavior/,2019.
[17] Abdulmalek S, Nasir A, Jabbar WA, Almuhaya MAM, Bairagi AK, Khan MA, Kee SH. IoT-Based HealthcareMonitoringSystemtowardsImprovingQualityofLife: A Review. Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Oct 11;10(10):1993. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10101993. PMID:36292441;PMCID:PMC9601552.
[18] W. Alswiti, J. Alqatawna, B. Al-Shboul, H. Faris and H. Hakh, "Users Profiling Using Clickstream Data Analysis and Classification," 2016 Cybersecurity and Cyberforensics Conference (CCC), Amman, Jordan, 2016,pp.96-99
[19] D. Vavilov, A. Melezhik and I. Platonov, "Smart home user's behavior prediction,"2013 IEEE Third International Conference on Consumer Electronics ¿ Berlin(ICCE-Berlin),Berlin,Germany,2013,pp.1-4
[20] G. Martín, A., Fernández-Isabel, A., Martín de Diego, I.et al.A survey for user behavior analysis based on machine learning techniques: current models and applications.ApplIntell51,6029–6055(2021)
[21] F. Tan et al., "A Blended Deep Learning Approach for Predicting User Intended Actions," 2018 IEEE
International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), Singapore,2018,pp.487-496
[22] S. K. Sharma and X. Wang, "Live Data Analytics With Collaborative Edge and Cloud Processing in Wireless IoT Networks," in IEEE Access, vol. 5, pp. 4621-4635, 2017
[23] I. Moustati, N. Gherabi, H. E. Massari and M. Saadi, "FromThe Internet of Things(IoT) to The Internet of Behaviors (IoB) for Data Analysis," 2023 7th IEEE Congress onInformationScience andTechnology (CiSt), Agadir-Essaouira,Morocco,2023,pp.634-639
[24] Özgür, Levent, et al. "An IoT based smart thermostat."2018 5th International Conference on Electrical and Electronic Engineering (ICEEE). IEEE, 2018.
[25] Atzori, Luigi, Antonio Iera, and Giacomo Morabito. "The internet of things: A survey."Computer networks54.15(2010):2787-2805.
[26] Gomez-Uribe, Carlos A., and Neil Hunt. "The netflix recommendersystem:Algorithms,businessvalue,and innovation."ACM Transactions on Management InformationSystems(TMIS)6.4(2015):1-19.
[27] Yang Y, Koenigstorfer J. Determinants of Fitness App Usage and Moderating Impacts of Education-, Motivation-, and Gamification-Related App Features onPhysicalActivityIntentions:Cross-sectionalSurvey Study.JMedInternetRes.2021Jul13;23(7):e26063.
[28] Khan,Samiya,andMansafAlam."WearableInternetof Things for personalized healthcare: Study of trends and latent research."Health informatics: a computational perspective in healthcare(2021): 4360.
[29] Banal, Mary Grace, et al. "MyFitnessPal smartphone application: relative validity and intercoder reliability among dietitians in assessing energy and macronutrient intakes of selected Filipinoadults with obesity."BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health7.1 (2024):54.
[30] Saif, Sohail, et al. "A secure data transmission frameworkforIoTenabledhealthcare."Heliyon10.16 (2024).
[31] Frik,Alisa,etal."Users’expectationsaboutanduseof smartphone privacy and security settings."Proceedings of the 2022 CHI Conference on HumanFactorsinComputingSystems.2022.
[32] JaflehEA,AlnaqbiFA,AlmaeeniHA,Faqeeh S,Alzaabi MA, Al Zaman K. The Role of Wearable Devices in Chronic Disease Monitoring and Patient Care: A
2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Comprehensive Review. Cureus. 2024 Sep 8;16(9):e68921.
[33] Z. Abbas, P. Sottovia, M. A. Hajj Hassan, D. Foroni and S. Bortoli, "Real-time Traffic Jam Detection and Congestion Reduction Using Streaming Graph Analytics," 2020 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Atlanta, GA, USA, 2020, pp. 31093118
[34] Dibak,M.etal.(2025).UNICON:AUnifiedFramework forBehavior-Based Consumer Segmentation inECommerce. In: Dokoohaki, N., Laserre, J., Shirvany, R. (eds) Revolutionizing Fashion and Retail. RECSYS 2023. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 1299.Springer
[35] Embarak, Ossama H. "Internet of Behaviour (IoB)based AI models for personalized smart education systems."Procedia Computer Science203 (2022): 103-110.
[36] Allcott,Hunt,andSendhilMullainathan."Behaviorand energypolicy."Science327.5970(2010):1204-1205.
[37] European Data Protection Supervisor, https://www.edps.europa.eu/dataprotection/technologymonitoring/techsonar/internet-behaviours_fr
[38] Dolgui,Alexandre,andDmitryIvanov.2024.“Internet of Behaviors: Conceptual Model, Practical and Theoretical Implications for Supply Chain and Operations Management.”International Journal of ProductionResearch63(1):1–8.
[39] Kim, Jina, and Eunil Park. "Understanding social resistance to determine the future of Internet of Things (IoT) services."Behaviour & Information Technology41.3(2022):547-557.
[40] Shamsabadi, Afsoon Alidadi, et al. "Exploring the 6G Potentials: Immersive, Hyper Reliable, and LowLatency Communication."arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.11051(2024).
[41] Adil, Muhammad, et al. "5G/6G-enabled metaverse technologies: Taxonomy, applications, and open security challenges with future research directions."Journal of Network and Computer Applications223(2024):103828.
[42] Kitkowska, Agnieszka, Farzaneh Karegar, and Erik Wästlund. "Share or protect: Understanding the interplay of trust, privacy concerns, and data sharing purposes in health and well-being apps."Proceedings of the 15th biannual conference of the Italian SIGCHI chapter.2023.
[43] Shirvani, Ghazaleh, and Saeid Ghasemshirazi. "Towards Sustainable IoT: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Directions for Device Longevity."arXiv preprintarXiv:2405.16421(2024).

Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO
Duckki Lee is currently an Associate Professor in the Department of Smart Software at Yonam Institute of Technology in South Korea. His research interestsincludeIoTandIoB