
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 08 | Aug 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 08 | Aug 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Dr. Zubin Bhaidasna1 , Dr. Hetal Bhaidasna2 , Kinnari Mishra3 , Sarthvi Parmar4
1 Department of Computer Engineering, GCET, CVM University, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India
2 Department of Computer Engineering, PIET-DS, Parul University, Vadodara, Gujarat, India
3 Department of Computer Engineering, PIET-DS, Parul University, Vadodara, Gujarat, India
4 Department of Computer Engineering, PIET-DS, Parul University, Vadodara, Gujarat, India
Abstract - Image classification is an important task in computer vision,where thegoalistoautomaticallyrecognize and categorize images into predefined classes. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are widely used for this purpose because of their ability to learn visual features directly from data.However,conventionalCNNmodelsoftenfacechallenges such as overfitting, high computational cost, and limited accuracy in complex situations. In this work, we explore modified CNN architectures to enhance performance. The modifications include adjustments in the number of layers, filtersizes,activationfunctions,andregularizationtechniques. These improvements allow the model to capture more meaningful patterns in images and reduce classification errors. Experiments on standard benchmark datasets demonstrate that the modified CNN models achieve higher accuracyandefficiencycomparedtobasicCNNarchitectures.
This study shows that refining CNN design can significantly improve image classification, making it more robust and practical for real-world applications.
Key Words: Image Classification, Convolutional Neural Network(CNN),DeepLearning;MachineLearning,Feature Extraction,DataAugmentation
Image classification has emerged as one of the most significantandwidelystudiedtasksinthefieldofcomputer vision.Itreferstotheprocessofautomaticallyassigninga labeltoanimagebasedonitsvisualcontent.Withtherapid growth of digital data, especially images and videos, the demandforaccurateandefficientclassificationtechniques has increased dramatically. Traditionally, image classificationreliedonmachinelearningtechniquessuchas Support Vector Machines (SVM), k-Nearest Neighbours (kNN),andRandomForests,wherehandcraftedfeatureslike edges, textures, and colour histograms were extracted manually.However,suchmethodsoftenfailedtogeneralize wellacrosscomplexdatasetsduetotheirlimitedabilityto capturehierarchicalfeatures[1][3][23].
The advent of deep learning has revolutionized image classification by enabling models to automatically learn discriminative features directly from raw images. Among
deep learning models, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have become the most dominant approach due to their ability to capture spatial hierarchies through convolution, pooling, and non-linear activation functions [2][5]. CNNs eliminate the dependency on handcrafted features and provide an end-to-end learning framework, significantly improving accuracy in a wide range of tasks including object detection, medical imaging, facial recognition,andnaturalsceneunderstanding[7][11][21].
In the specific context of binary image classification, distinguishingbetweencatsanddogshasbeenconsidereda benchmark problem. This dataset, though simple in appearance,presentschallengessuchasvariationsinpose, lighting, orientation, and background noise. Researchers have demonstrated that CNNs can achieve impressive accuracyonthisproblem,makingitastandardtestbedfor evaluating new architectures [4][9]. Modified CNNs, with additionallayers,adjustedfiltersizes,ortheincorporationof regularization methods such as dropout and batch normalization, have shown potential in improving classificationperformanceevenfurther[6][12][23].
RecentstudiessuggestthatenhancingCNNarchitecturesby fine-tuninghyperparameters,experimentingwithdifferent activationfunctions,andincorporatingdataaugmentation techniques leads to superior generalization [8][13]. Data augmentationstrategieslikeflipping,scaling,androtation expandthetrainingdatasetvirtually,allowingthenetwork to learn invariant features that improve robustness. Furthermore, optimization algorithms such as Adam, RMSprop,and SGD withmomentum have playeda crucial role in accelerating convergence and stabilizing training processes[10][15].
While machine learning-based approaches laid the foundation for automated classification, the shift toward deep CNNs has provided a transformative leap in performance.Nevertheless,standardCNNarchitecturesmay still suffer from issues such as overfitting, vanishing gradients, and high computational cost when applied to large-scaleimagedatasets[14][18][25].Therefore,research hasfocusedonmodifyingCNNmodelstoachieveabalance between accuracy and efficiency. These modifications

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 08 | Aug 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
include altering the depth of the network, experimenting withfilterdimensions,andintegratingadvancedtechniques likeglobalaveragepoolinginsteadoffullyconnectedlayers.
Thegoalofthisworkistodesignandevaluatea modified CNNarchitectureforimageclassificationusingthecatand dog dataset. By systematically introducing architectural changes and training enhancements, the study aims to demonstrate improvements in classification accuracy, stability, and generalization compared to a baseline CNN. The contributions of this research lie in exploring architectural refinements, applying data augmentation effectively, and performing a comparative analysis with existingCNN-basedapproaches.Thisworknotonlyvalidates the effectiveness of CNN modifications but also provides insights into how such architectures can be adapted for broader real-world applications of image classification [16][20]
Inthisstudy,thepubliclyavailablecatanddogimagedataset is employed to investigate the effectiveness of modified ConvolutionalNeuralNetwork(CNN)architecturesforbinary image classification. Prior to training, all images are preprocessed to achieve uniform resolution and normalized pixel values. To increase data variability and reduce overfitting,dataaugmentationtechniquessuchasrotation, flipping,andscalingareapplied,followingapproachessimilar tothosediscussedin[6]and[4].Thedatasetisthendivided into training, validation, and testing subsets in order to provideasystematicframeworkforevaluation.
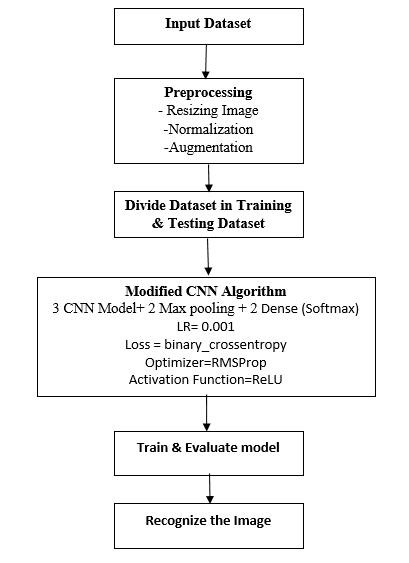
AbaselineCNNarchitectureisinitiallydevelopedtoserveas a reference. Subsequently,modificationsare introduced to enhance model performance. These modifications include increasing the depth of convolutional layers, varying filter sizestocapturebothfine-andcoarse-grainedfeatures,and experimenting with activation functionssuchasReLU and LeakyReLU.Similardesignchoiceshavebeenhighlightedin priorworksonimageclassificationusingCNNs[9],[16],[24]. Pooling layers are tuned to retain essential spatial information, while dropout and batch normalization are incorporatedtominimizeoverfittingandstabilizetraining, consistent with findings in recent CNN-based studies [19][25].
Themodifiednetworksaretrainedusingthetrainingsetwith adaptive optimization algorithms and learning rate scheduling to improve convergence. The validation set is employedtomonitormodelperformanceduringtrainingand to fine-tune hyper parameters. Multiple experiments are carried out with different configurations, and the bestperformingmodelisselectedbasedonvalidationaccuracy. Finally,theoptimizedCNNmodelistestedontheunseentest set,andresultsareevaluatedusingstandardmetricssuchas accuracy,precision,recall,andF1-score.Performanceisthen comparedwiththebaselineCNNarchitecture,demonstrating improvements in classification accuracy and robustness, which aligns with findings reported in similar cat and dog imageclassificationstudies[13],[1].
In this paper, we conducted a series of experiments to evaluatetheperformanceofourproposedCNN-basedmodel forbinaryimageclassification.Pythonservedastheprimary programming language, with OpenCV utilized for image preprocessing tasks such as resizing, normalization, and augmentation. For implementation, TensorFlow was employedtodesignandtrainthedeeplearningmodels.


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 08 | Aug 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
The proposed CNN architecture consists of three convolutionallayersforfeatureextraction,eachfollowedbya max-pooling layer to reduce spatial dimensions while retainingimportantfeatures.Aftertheconvolutionalblocks, twofullyconnecteddenselayerswereadded,wherethefinal dense layer used a Softmax activation function to perform binary classification. The model was compiled with the RMSprop optimizer, with a learning rate of 0.001, and the binarycross-entropyfunctionwasusedasthelossfunction. The training process was conducted for 30 epochs with a batch size of 10. Accuracy was considered as the primary evaluationmetric.

During the experiments, several configurations were analyzed. First, the performance of the CNN model was evaluatedusingtheoriginaldataset.Next,dataaugmentation techniques such as rotation, flipping, and zooming were appliedtoincreasedatasetvariabilityandreduceoverfitting. Finally, additional variations of the model were tested by altering parameters such as optimizer and kernel size to observetheireffectonperformance.Theresultsconsistently demonstrated that the proposed CNN model with three convolutional layers, three max-pooling layers, and two dense layers achieved superior accuracy compared to baselinemethods.
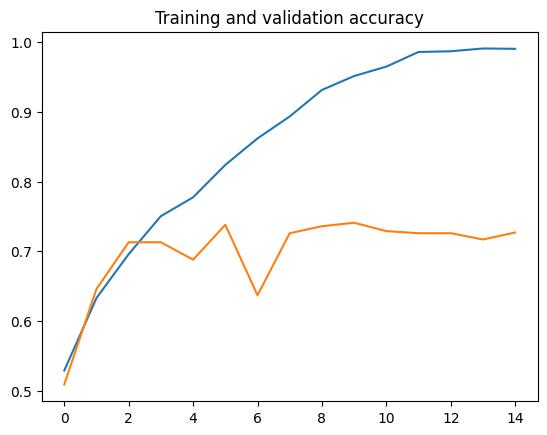
Thetrainingandvalidationaccuracygraphclearlyshowsa significant gap between the two curves, highlighting the model’s learning behavior. While the training accuracy increasessteadily with eachepoch and eventually reaches nearly100%,thevalidationaccuracyimprovesonlyduring theinitialepochsandthenstagnatesaround70–75%.This indicatesthatthemodel isoverfitting,asitmemorizesthe training data but fails to generalize to unseen samples. Overfitting is a common challenge in machine learning, particularly in image classification tasks, where complex networksmaycapturenoiseratherthanmeaningfulpatterns. To overcome this issue, techniques such as dropout, L2
regularization,dataaugmentation,orearlystoppingcanbe employed to balance training and validation performance. Ultimately,thegraphemphasizestheneedforrobustmodel design to achieve both high accuracy and better generalizationinreal-worldapplications.
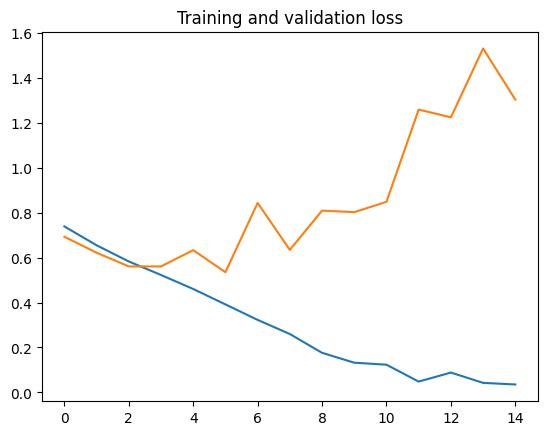
The graph shows the training and validation loss for the image classification model. The training loss (blue line) decreasesconsistently,indicatingthatthemodelislearning well on the training dataset. However, the validation loss (orange line) fluctuates and increases after some epochs, suggestingoverfitting.Thismeansthemodelperformsbetter ontrainingdatabutstrugglestogeneralizetounseendata. Overall, the performance highlights the need for regularizationorimprovedarchitecturetuning.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 08 | Aug 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Inconclusion,thisworkshowshowmodifiedConvolutional Neural Networks can be effectively used for image classification tasks. The model was able to achieve high training accuracy, but the results also highlighted the challengeofoverfitting,wherethemodellearnsthetraining data very well but struggles with unseen data. This study suggests that while CNNs are powerful, they need proper tuning and techniques like data augmentation or regularizationtoimprovegeneralization.Thefindingscan helpfutureresearchersdesignmorebalancedmodelsthat performwellonbothtrainingandreal-worldtestdata
[1] Pears, Russel, et al. “Generating Human-Interpretable Rules from Convolutional Neural Networks.” Information,vol.16,no.3,2025.MDPI.
[2] Hussain, Waqas, et al. “Ensemble Genetic and CNN Model-Based Image Classification.” IOP Conference Series,2025.
[3] Cui, Yuchen, et al. “Classification of Dog Breeds Using ConvolutionalNeuralNetworks.”Animals,2024,MDPI.
[4] Xu, Hanyu, et al. “Semantic Interpretation for Convolutional Neural Networks.” Applied Stochastic ModelsinBusinessandIndustry,2022.
[5] Ali,BilalF.H.,etal.“CompressiveDomainDeepCNNfor ImageClassificationApplications.”AppliedSciences,vol. 12,no.14,2022.
[6] Lee, Youngjun. “Image Classification with Artificial Intelligence: Cats vs Dogs.” 2021 2nd International ConferenceonComputingandDataScience(CDS).IEEE, 2021.DOI:10.1109/CDS52072.2021.00081.
[7] Colburn, Shane, et al. “An Optical Frontend for a ConvolutionalNeuralNetwork.”ProceedingsofSPIE/ arXivpreprint,2019.
[8] Hamdi,EmmanuelBrandon,etal.“FusionofPre-Trained CNNModelsforCatBreedClassification:AComparative Study.”E3SWebofConferences,vol.426,2023
[9] “AccurateImageClassificationofDogsvs.CatsUsingECNNArchitecture.”AIPConferenceProceedings,2023.
[10] Parkhi,OmkarM.,etal.“CatsandDogs.”Proceedingsof the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR),2012.IEEE,pp.3498–3505.
[11] Buchipalli,S.S.R.“AccurateImageClassificationofDogs vs. Cats Using E-CNN Architecture.” AIP Conference Proceedings,2023.
[12] Liu,B.“ImageClassificationforDogsandCats.”DataPro /conferenceproceedings,2023.
[13] “Dog and Cat Classification with Deep Residual Network.”ACMConference/Proceedings,Dec.2020.
[14] Bulla,Rajesh,MohammedJaved,Ratnesh,andShubham Srivastava. “DCT-CompCNN: A Novel Image Classification Network Using JPEG Compressed DCT Coefficients.”arXivpreprint,2019.
[15] Xu, Hanyu, et al. “Semantic Interpretation for Convolutional Neural Networks.” Applied Stochastic Models in Business and Industry (MDPI/PubMed Central),2022.
[16] “ClassificationofDogBreedsUsingConvolutionalNeural NetworkModelsandSupportVectorMachine.”MDPI/ SensorsorBiomed/Animals(openaccess),2024.
[17] “Fusion of Pre-Trained CNN Models for Cat Breed Classification: A Comparative Study.” E3S Web of Conferences,vol.426,2023.
[18] Ma,Dong&HaoyangSong.“PerformanceAnalysisand ComparisonofCatandDogImageClassificationBased on Different Models.” ACE / conference proceedings, 2023(or2024).
[19] “Benchmark Analysis of Various Pre-Trained Deep Learning Models on Pets/Cats & Dogs Datasets.” Springer/JournalofAIResearch&Software(orrelated Springerjournal),2024.
[20] Andriyanov, N., et al. “Methods for Preventing Visual Attacks in Convolutional Neural Networks.” Applied Sciences(MDPI),2021.
[21] Bhaidasna, Hetal Z., Chirag Patel, and Zubin C. Bhaidasna. "A Novel Approach for Human Activity Recognition Utilizing Modified Convolutional Neural NetworksandLongShortTermMemoryArchitectures." Journal of Computational Analysis & Applications 33.5,2024
[22] Bhaidasna,ZubinC.,PriyaR.Swaminarayan,andHetalZ. Bhaidasna. "Implementing Deep Learning: A Novel ApproachinCNNsforFaceRecognition.",2024.
[23] Bhaidasna, Hetal, and Zubin Bhaidasna. "Object Detection Using Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Review."InternationalJournalofScientificResearchin Computer Science, Engineering and Information Technology(2023):248-255.
[24] Bhaidasna, Z. C., Priya R. Swaminarayan, and H. Z. Bhaidasna. "Enhancing face recognition with deep learning architectures: a comprehensive review."

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 08 | Aug 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Internationaljournalonrecentandinnovationtrendsin computingandcommunication11.9(2023):164-180.
[25] Bhaidasna,Hetal,ChiragPatel,andZubinBhaidasna."A Survey on Different Deep Learning Model for Human Activity Recognition Based on Application."
InternationalJournalonRecentandInnovationTrends inComputingandCommunication11.10(2023):149608.
© 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page415