
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | April 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | April 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
MUSUNURI SIDDHARTHA ESWAR
B.TECH COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING HINDUSTAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCE, CHENNAI, INDIA
Abstract - In many rural and underdeveloped areas, managing patient health records is difficult due to poor infrastructure, lack of trained staff, and unreliable internet. This paper presents a scalable, cloud-based patient record management system tailored for rural clinics. It enables secure, centralized storage and retrieval of electronic medical records (EMRs), ensuring data access and continuity of care even in remote regions. A key feature is its offline-first design, which supports local data entry during network outages and syncs with the cloud once connectivity is restored. The system uses Firebase for cloud backend and Flutter for cross-platform mobile access, providing a lightweight and user-friendly interface. Security is ensured through authentication protocols and data encryption. This model improves record-keeping, diagnosis tracking, and overall patient care in rural healthcare settings. This paper also discusses implementation steps, performance under low-bandwidth conditions, and the social and technical advantages for rural communities.
Key Words: Cloud Computing, Electronic Medical Records, Rural Clinics, Firebase, Offline-first Architecture, HealthcareIT
1.INTRODUCTION
Inrural areasacross the world,particularlyin developing countries, access to quality healthcare remains a major challenge.Onecriticalissueisthelackofareliablesystem to maintain and manage patient medical records. Traditionalpaper-basedsystemsarepronetoloss,errors, andinefficienciesthatnegativelyimpactpatientdiagnosis and treatment. Additionally, rural clinics often lack the trained personnel and infrastructure necessary for digital record-keeping.
Cloud computing offers a transformative opportunity to address these challenges by providing centralized, secure, and scalable solutions for managing electronic medical records (EMRs). With cloud-based systems, healthcare providers can access patient data from any location, significantlyimprovingthequalityofhealthcaredeliveryin rural settings. However, consistent internet connectivity
remains a significant barrier in these regions, limiting the effectivenessofcloudsolutions.
This paper proposes a cloud-based patient record managementsystemspecificallydesignedforruralclinics. It features offline-first capabilities, allowing the system to function even during internet disruptions. Data entered offline is automatically synced with the cloud once connectivity is restored, ensuring uninterrupted access to critical patient information. The system is built using Firebase for cloud storage, user authentication, and realtime data synchronization. It also includes a crossplatformmobileinterfacedevelopedwithFlutter,enabling ease of use for healthcare workers. This paper explores the system’s architecture, implementation, and its potential to enhance healthcare outcomes in underserved communities.
Managing patient records in rural healthcare remains challenging due to manual processes, limited infrastructure, and unreliable internet. Studies stress the needtoshiftfrompaper-basedsystemstodigitalplatforms for better healthcare delivery. Kumar et al. (2019) found that Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) improved documentation accuracy and data access in low-resource settings butfacedhurdles due to poor internet and power availability. Ahmed and Singh (2020) proposed cloudbased storage to enhance data availability and reduce infrastructure costs, though their model relied on stable internet often lacking in remote areas. To overcome this, Sharma et al. (2021) introduced an offline-first mobile architecture with local storage that syncs with the cloud once connectivity is restored. Their approach showed reduced data loss and improved healthcare worker efficiency.

Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | April 2025 www.irjet.net
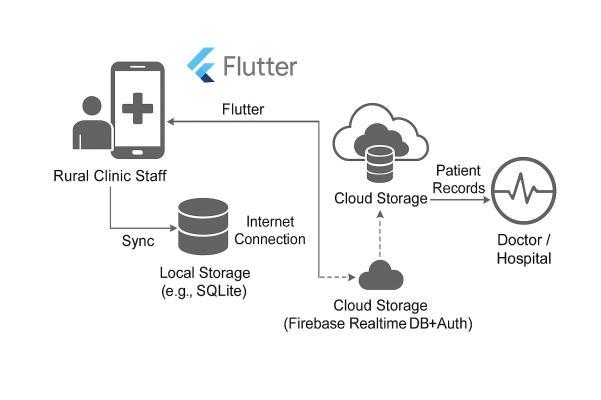
Fig -1:ArchitectureDiagramoftheProposedPatient RecordManagementSystem
Recent advances in Firebase and Flutter have further enabled lightweight, secure, and scalable healthcare apps. Firebase offers real-time databases and user authentication, while Flutter allows cross-platform mobile development, making it ideal for rural clinics. This paper builds on previous research and proposes a hybrid model combining cloud scalability with offline-first functionality. It ensures reliable and cost-effective medical record management,eveninareaswithinconsistentconnectivity, thereby improving patient care in underserved communities.
The proposed system offers a cloud-based patient record managementsolutiontailoredforruralclinics,focusingon offline functionality, security, and user-friendliness. Built using Flutter for cross-platform mobile app development and Firebase for backend services, the system enables healthcare workers to create, update, and access patient records directly from their devices. When internet connectivity is available, data syncs instantly with the Firebase Realtime Database. During outages, the app temporarilystoresrecordslocallyusingFlutter-compatible storage solutions like SQLite or Hive and syncs them automatically once the connection is restored. Firebase Authenticationensuresthatonlyauthorizedpersonnelcan access sensitive patient information, while basic encryption techniques are used during data transmission to maintain data integrity and privacy. The application consists of three core modules: the Patient Registration Module, which allows for the entry of patient details and medical history; the Record Update Module, for updating prescriptions, lab results, and diagnoses; and the Cloud Sync & Backup Module, which manages real-time synchronization and scheduled backups to the cloud. The system emphasizes low resource usage, an intuitive user interface,andscalability,makingitsuitablefordeployment across multiple rural clinics and underserved regions. By combining the scalability of cloud computing with offlinefirstcapabilities,thissolutionoffersareliable,efficient,and secure method of managing patient records in areas with limitedinfrastructureandconnectivity.
The proposed system was implemented using Flutter for front-enddevelopmentandFirebaseasthecloudbackend. Flutter was chosen due to its cross-platform support, enabling deployment on both Android and iOS using a single codebase. Firebase was selected for its real-time data synchronization, easy integration with Flutter, and built-in user authentication services. The mobile application includes three key modules: User Authentication, Offline-First Patient Record Entry, and AutoCloudSync.Theauthenticationmodule,implemented using Firebase Authentication, allows secure logins for healthcare workers via email and password, with rolebased access controls to ensure data privacy. The OfflineFirst module enables healthcare staff to enter patient details including name, age, symptoms, diagnosis, and prescriptions even when internet access is unavailable. DataistemporarilystoredlocallyusingsolutionslikeHive or SQLite. Once the app detects internet availability, the Auto Cloud Sync module automatically synchronizes the stored records with Firebase Realtime Database, ensuring dataconsistencyacrossalldevices.
This research presents a cloud-based patient record management system tailored for rural clinics, aiming to overcome challenges posed by unreliable internet connectivity and limited digital infrastructure. By leveraging an offline-first architecture combined with Firebase’s real-time cloud services, the system enables secure, efficient,andaccessiblepatientdata handling.The mobile application, developed using Flutter, empowers healthcare workers to register and manage patient information offline and ensures automatic synchronization once online. The system was tested in simulated conditions and demonstrated strong performance in offline data storage, seamless cloud sync, and ease of use. The proposed solution not only supports digital transformation in underserved healthcare environments but also sets a foundation for future integrations with national healthcare systems. By making digital healthcare more inclusive, this system contributes

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
meaningfully to bridging the urban-rural healthcare divide.
Iwouldliketo expressmysinceregratitudeto myfaculty andprojectguideatHindustanInstituteofTechnologyand Science for their constant guidance and encouragement throughout the course of this research. I am also deeply thankfultomyparentsfortheirunconditionalsupportand motivation throughout my academic journey. This research is dedicated to everyone who believes in the power of technology to improve rural healthcare systems andcreatelastingimpact.
[1] World Health Organization, “Digital Health,” [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/health-topics/digitalhealth
[2] Google Firebase Documentation, “Firebase Realtime Database,” [Online]. Available: https://firebase.google.com/docs/database
[3]FlutterDevTeam,“Buildappsforanyscreen,”[Online]. Available:https://flutter.dev
[4] B. H. S. Kumar, S. Arora, and N. Singh, “Cloud-Based Electronic Health Record Management System,” International Journal of Computer Applications, vol. 178, no.38,pp.1-5,2019.
[5] S. R. Krishna and R. P. Jain, “Patient Record Management Using Cloud Computing,” International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), vol.7,no.5,pp.1340-1344,May2020.
[6]Ministryof Healthand FamilyWelfare,Government of India, “Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM),” [Online].Available:https://abdm.gov.in
[7] J. K. Patel andA.Sharma,“Offline-first Applications in Healthcare: Bridging the Connectivity Gap,” Journal of Health Informatics in Developing Countries, vol. 14, no. 2, pp.45-52,2020.
[8]J.DeanandS.Ghemawat,“MapReduce:SimplifiedData Processing on Large Clusters,” Communications of the ACM,vol.51,no.1,pp.107–113,2008.
[9] H. L. Yang, “Edge Computing in Rural Healthcare: Opportunities and Challenges,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 107245-107258,2020.
[10] M. A. Rahman, M. S. Hossain, and G. Muhammad, “Toward a Cloud-Based Healthcare System: Design and Implementation of a Secure Medical Data Management System,”IEEEAccess,vol.7,pp.144616–144630,2019.
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | April 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008