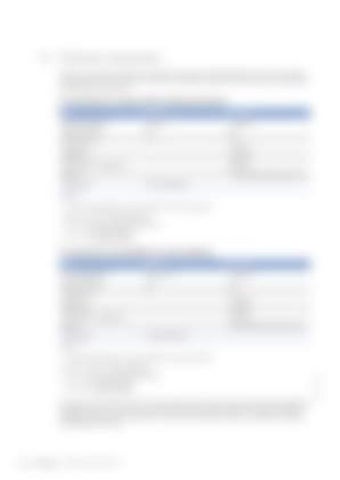
5.3 Freshwater requirements Only clean, clear water with values in accordance with those in the following table must be used for preparing the coolant. If the limit values for the water are exceeded, hardness or mineral content can be decreased by adding demineralized water.
For preparation of coolant without antifreeze protection: Item
Minimum
Maximum
Total earth alkalines (Water hardness)
0 mmol/l 0°d
2.7 mmol/l 15°d
pH value at 20 °C
5.5
8.0
1)
Chloride ions
100 mg/l
Sulfate ions
100 mg/l
Total chloride + sulfate ions
200 mg/l
Bacteria
103CFU (colony forming unit )/ml
Fungi, yeasts
are not permitted!
Table 13: 1)
= Common designations for water hardness in various countries:
1 mmol/l = 5.6°d = 100 mg/kg CaCO³ • 1°d = 17.9 mg/kg CaCO³, USA hardness • 1°d = 1.79° French hardness • 1°d = 1.25° English hardness
For preparation of emulsifiable corrosion inhibitors: Item
Minimum
Maximum
Total earth alkalines1) (Water hardness)
0.36 mmol/l 2°d
1.8 mmol/l 10°d
pH value at 20 °C
7.0
8.0
Chloride ions
100 mg/l
Sulfate ions
100 mg/l
Total chloride + sulfate ions
200 mg/l
Bacteria
103CFU (colony forming unit )/ml
Fungi, yeasts
are not permitted!
Table 14: = Common designations for water hardness in various countries:
1 mmol/l = 5.6°d = 100 mg/kg CaCO³ • 1°d = 17.9 mg/kg CaCO³, USA hardness • 1°d = 1.79° French hardness • 1°d = 1.25° English hardness If the water is too soft, this can result in foam formation and the water has to be hardened before application by adding hard water. If the water is too hard, this impairs the emulsion stability. This causes increased oil separation and the formation of deposits in the system. Excessively hard water must therefore be softened by blending with soft water.
26 | Coolants | A001061/37E 2016-12
TIM-ID: 0000018571 - 006
1)