Michael Grimwade
Visit to download the full and correct content document: https://ebookmeta.com/product/ten-laws-of-operational-risk-understanding-its-behavio urs-to-improve-its-management-1st-edition-michael-grimwade/

More products digital (pdf, epub, mobi) instant download maybe you interests ...

Risky Strategy Understanding Risk to Improve Strategic Decisions 1st Edition Jamie Macalister
https://ebookmeta.com/product/risky-strategy-understanding-riskto-improve-strategic-decisions-1st-edition-jamie-macalister/

Fundamentals of Risk Management: Understanding, Evaluating and Implementing Effective Enterprise Risk Management 6th Edition Clive Thompson
https://ebookmeta.com/product/fundamentals-of-risk-managementunderstanding-evaluating-and-implementing-effective-enterpriserisk-management-6th-edition-clive-thompson/

Understanding Risk Management and Hedging in Oil Trading: A Practitioner's Guide to Managing Risk 1st Edition Chris Heilpern
https://ebookmeta.com/product/understanding-risk-management-andhedging-in-oil-trading-a-practitioners-guide-to-managingrisk-1st-edition-chris-heilpern/

Battery Management System and its Applications 1st Edition Xiaojun Tan
https://ebookmeta.com/product/battery-management-system-and-itsapplications-1st-edition-xiaojun-tan/

The Sharing Economy Its Pitfalls and Promises 1st Edition Michael C
Munger
https://ebookmeta.com/product/the-sharing-economy-its-pitfallsand-promises-1st-edition-michael-c-munger/

Integer Optimization and its Computation in Emergency Management 1st Edition Zhengtian Wu
https://ebookmeta.com/product/integer-optimization-and-itscomputation-in-emergency-management-1st-edition-zhengtian-wu/

Nigeria a Country under Siege Issues of Conflict and Its Management 1st Edition Dele Babalola
https://ebookmeta.com/product/nigeria-a-country-under-siegeissues-of-conflict-and-its-management-1st-edition-dele-babalola/

Azure Kubernetes Services with Microservices: Understanding Its Patterns and Architecture Kasam Ahmed Shaikh
https://ebookmeta.com/product/azure-kubernetes-services-withmicroservices-understanding-its-patterns-and-architecture-kasamahmed-shaikh/

Internet of Things and Its Applications
https://ebookmeta.com/product/internet-of-things-and-itsapplications/

Table of Contents
Cover Title Page
Copyright
Dedication
About the Author Introduction
NOTES
PART One: Ten Laws of Operational Risk (Grimwade, 2020)
CHAPTER 1: Patterns in the Behaviour of Operational Risk
PATTERNS IN THE FREQUENCY AND SEVERITY OF OPERATIONAL RISK LOSSES
PATTERNS IN THE RELATIVE SIGNIFICANCE OF DIFFERENT RISKS FOR DIFFERENT BUSINESS
LINES
PATTERNS IN THE CONCENTRATION OF LOSSES WITHIN INDIVIDUAL FIRMS
CONCLUSIONS
NOTES
CHAPTER 2: The Occurrence and Severity of Loss Events
1ST LAW OF OPERATIONAL RISK: OCCURRENCE
EXPLANATION OF THE COMPONENTS OF THIS FORMULA
ILLUSTRATIONS & OBSERVATIONS
IMPLICATIONS
2ND LAW OF OPERATIONAL RISK: DETECTION
EXPLANATION OF THE COMPONENTS OF THIS FORMULA
ILLUSTRATIONS & OBSERVATIONS
IMPLICATIONS
3RD LAW OF OPERATIONAL RISK: VELOCITY
EXPLANATION OF THE COMPONENTS OF THIS FORMULA
ILLUSTRATIONS & OBSERVATIONS – THE NATURE OF IMPACTS
ILLUSTRATIONS & OBSERVATIONS – THE QUANTUM OF FAILURES
ILLUSTRATIONS & OBSERVATIONS – VELOCITIES
IMPLICATIONS
4TH LAW OF OPERATIONAL RISK: DURATION AND SEVERITY
EXPLANATION OF THE COMPONENTS OF THIS FORMULA
ILLUSTRATIONS & OBSERVATIONS
IMPLICATIONS
5TH LAW OF OPERATIONAL RISK: LAGS IN SETTLEMENT
EXPLANATION OF THE COMPONENTS OF THIS FORMULA
ILLUSTRATIONS & OBSERVATIONS
IMPLICATIONS
CONCLUSIONS
NOTES
CHAPTER 3: Concentration and Systemic Operational Risk Events (SOREs)
6TH LAW OF OPERATIONAL RISK: CONCENTRATION DUE TO INTERNAL DRIVERS
EXPLANATION OF FORMULA
ILLUSTRATIONS & OBSERVATIONS
IMPLICATIONS
7TH LAW OF OPERATIONAL RISK: CONCENTRATION DUE TO EXTERNAL DRIVERS
ILLUSTRATION & OBSERVATIONS
IMPLICATIONS
CONCLUSIONS
NOTES
CHAPTER 4: Homeostasis, Risk Transference, Transformation and Conservation, and Active Risk Taking
8TH LAW OF OPERATIONAL RISK: RISK HOMEOSTASIS
EXPLANATION OF THE COMPONENTS OF THIS FORMULA
ILLUSTRATION & OBSERVATIONS
IMPLICATIONS
9TH LAW OF OPERATIONAL RISK: RISK TRANSFERENCE, TRANSFORMATION AND CONSERVATION
EXPLANATION OF THE COMPONENTS OF THESE FORMULAE
ILLUSTRATIONS & OBSERVATIONS
IMPLICATIONS
10TH LAW OF OPERATIONAL RISK: ACTIVE AND PASSIVE RISK TAKING
EXPLANATION OF THE FORMULA
ILLUSTRATION & OBSERVATIONS
IMPLICATIONS
CONCLUSIONS
NOTES
CHAPTER 5: Three Taxonomies: Inadequacies or Failures, Impacts and Causes
1. TAXONOMIES OF INADEQUACIES OR FAILURES COVERING BOTH EVENTS AND CONTROL FAILURES
2. IMPACT TAXONOMY
3. CAUSAL TAXONOMY
CONCLUSIONS
NOTES
CHAPTER 6: Conclusions – How and Why THE NATURE OF THE TEN LAWS
HOW DO THE TEN LAWS EXPLAIN THE PATTERNS IN THE BEHAVIOUR OF OPERATIONAL RISK
WHY DO THESE LAWS EXPLAIN PATTERNS IN THE BEHAVIOUR OF OPERATIONAL RISK?
APPLICATION OF THESE TEN LAWS OF OPERATIONAL RISK
NOTES
PART Two: Operational Risk Management Tools Designed for Success
CHAPTER 7: Defining and Cascading Operational Risk Appetites
THE CHALLENGES OF DEVELOPING AN OPERATIONAL RISK APPETITE STATEMENT
POTENTIAL SOLUTIONS
CONCLUSIONS
NOTES
CHAPTER 8: Risk & Control Self-Assessments
REDESIGNING RCSAS BASED UPON THE TEN LAWS
CONCLUSIONS
NOTES
CHAPTER 9: Scenario Analysis
CHALLENGES – BIASES AND LANGUAGE
IDENTIFYING A PORTFOLIO OF SCENARIOS
ESTIMATING THE IMPACTS OF RARE EVENTS
ESTIMATING THE LIKELIHOODS OF RARE EVENTS – TOP-DOWN AND BOTTOM-UP
VALIDATING THE OUTPUTS OF SCENARIO ANALYSIS
CONCLUSIONS
NOTES
CHAPTER 10: Operational Risk Capital Modelling
BASEL II'S ADVANCED MEASUREMENT
APPROACH – ACTUARIAL MODEL
BASEL III'S NEW STANDARDISED APPROACH – A PROXY FOR RISK PROFILE, SCALED FOR ACTUAL LOSSES
MODEL VALIDATION
A MORE HOLISTIC APPROACH TO OPERATIONAL RISK CAPITAL MODELLING – AN “HOURGLASS”
CONCLUSIONS
NOTES
CHAPTER 11: Stress Testing
THE HISTORICAL PROFILE OF OPERATIONAL RISK LOSSES
OVERVIEW OF THE REGULATORY APPROACHES TO STRESS TESTING
ASSESSMENT OF THE RECENT RESULTS OF INDUSTRY EXERCISES
CONCLUSIONS
AN APPROACH BASED UPON THE TEN LAWS OF OPERATIONAL RISK
CONCLUSIONS
NOTES
CHAPTER 12: Reverse Stress Testing and the Transfer of Risks via Insurance
REVERSE STRESS TESTING
REGULATORY GUIDANCE
IDENTIFYING REVERSE STRESS TESTING SCENARIOS
ASSESSING REVERSE STRESS TESTING
SCENARIOS
CONCLUSIONS
THE TRANSFER OF RISKS VIA INSURANCE
DETERMINANTS OF INSURABILITY
EFFECTIVENESS OF INSURANCE POLICIES AS AN OPERATIONAL RISK MITIGANT
MAPPING OF INSURANCE COVERAGE TO EVENTS AND IMPACTS
DEDUCTIONS FROM OPERATIONAL RISK CAPITAL
REQUIREMENTS
CONCLUSIONS
NOTES
CHAPTER 13: Day-to-Day Operational Risk Management
1. INCIDENT MANAGEMENT AND ROOT CAUSE ANALYSIS
2. CONTROL ASSURANCE AND THE NATURE OF CONTROL FAILURES
3. PREDICTIVE METRICS
4. CHANGE MANAGEMENT
5. REPUTATIONAL RISK QUANTIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT
QUANTIFICATION OF REPUTATIONAL DAMAGE
ARISING FROM OPERATIONAL RISK EVENTS
CONCLUSIONS
OVERALL CONCLUSIONS
NOTES
CHAPTER 14: Conclusions
CONCLUSIONS
NOTES
PART Three: Predictions of the Future Behaviours of Operational Risk
CHAPTER 15: Identifying Emerging Risks
NOTES
CHAPTER 16: Predictions of the Future Behaviours of Operational Risk in Response to Four Emerging Threats
1. PANDEMICS
2. CLIMATE CHANGE
3. CYBERCRIME
4. TECHNOLOGICAL ADVANCES, INCLUDING ALGOS, AI AND MACHINE LEARNING
CONCLUSIONS
NOTES
PART Four: Conclusions
CHAPTER 17: Conclusions and Operational Risk Strategy
1. SUMMARY OF THE BEHAVIOURS OF OPERATIONAL RISK
2. OVERVIEW OF THE TEN LAWS OF OPERATIONAL RISK
3. THE UNDERLYING DRIVERS OF THE BEHAVIOURS OF OPERATIONAL RISK
4. SUMMARY OF KEY ENHANCEMENTS TO OPERATIONAL RISK MANAGEMENT TOOLS
5. ALTERNATIVE STRATEGIES TO MEET THE OBJECTIVES OF OPERATIONAL RISK MANAGERS IN CONCLUSION
NOTES
APPENDIX I: Taxonomy of Inadequacies or Failures: Events and Control Failures
APPENDIX I.1 MAPPING THE NATURE OF INADEQUACIES OR FAILURES (EVENTS) TO BASEL II
APPENDIX I.2: TAXONOMY OF INADEQUACIES OR FAILURES: THE NATURE OF EVENTS
APPENDIX I.3: TAXONOMY OF INADEQUACIES OR FAILURES: THE NATURE OF THE CONTROL FAILURES
SOURCES FOR APPENDIX I.3
NOTE
APPENDIX II: Impact Taxonomy and Their Relative Scales and Velocities
NOTE
APPENDIX III: Causal Taxonomy Based Upon a Review of Large, Well-Documented Events
SOURCES FOR APPENDIX III
NOTES
APPENDIX IV: Risk Taxonomies for Cybercrime and IT
Operational Risks Based on Analysis of Actual Loss Events
APPENDIX IV.1 RISK TAXONOMY FOR CYBERCRIME BASED ON AN ANALYSIS OF ACTUAL LOSS EVENTS
APPENDIX IV.2: RISK TAXONOMY FOR IT
OPERATIONAL RISK EVENTS BASED ON AN ANALYSIS OF ACTUAL LOSSES
NOTE
Glossary
Bibliography
Index
End User License Agreement
List of Tables
Introduction
TABLE I.1 The coverage of the Ten Laws of Operational Risk and their units
Chapter 1
TABLE 1.1 Changes in average frequency and severity of losses ≥€10 million
Chapter 2
TABLE 2.1 Author's view of the mapping of inadequacies or failures to the Ba...
TABLE 2.2 Identification of the explicit causes of 16 welldocumented Operat...
TABLE 2.3 Average lags (days) by event types for losses >€20k for ORX member...
TABLE 2.4 The relative significance of different categories of financial ...
TABLE 2.5 Analysis of PPI settlements as at 31st December, 2018
TABLE 2.6 An extract from an US Securities & Exchange Commission (SEC) lawsu...
Chapter 3
TABLE 3.1 Differing Operational Risk profiles of 31 G-SIBs for 1996 to 2006 ...
TABLE 3.2 Drivers for Operational Risks events rising during an economic slo...
Chapter 4
TABLE 4.1 Ratio of average large losses (≥$0.1 billion) for 2007 to 2017 rev...
Chapter 5
TABLE 5.1 Basel definitions of the subcategories of Operational Risk and the...
TABLE 5.2 Taxonomy of inadequacies or failures – the nature of the events
TABLE 5.3 Taxonomy of inadequacies or failures – the nature of the control f...
TABLE 5.4 The nature of impacts and their relative velocity (Appendix II)
TABLE 5.5 Causal taxonomy based upon a review of large, well-documented even...
Chapter 6
TABLE 6.1 Coverage of the Ten Laws and their units
TABLE 6.2 Key drivers of the scale of five very large loss events up to Dece...
Chapter 7
TABLE 7.1 Assessment of potential quantitative Operational Risk appetite mea...
Chapter 8
TABLE 8.1 Likelihood Matrix
TABLE 8.2 Impact Matrix
Chapter 9
TABLE 9.1 FCA's methodology for setting fines
Chapter 11
TABLE 11.1 Key variables used in the Federal Reserve's regression model
TABLE 11.2 Mapping of the impacts of Operational Risk events (Table 5.4) to ...
TABLE 11.3 Examples of the mapping of the nature of events (Table 5.2) to ec...
TABLE 11.4 Examples of sensitivities of scenarios to economic factors and du...
Chapter 12
TABLE 12.1 Percentage of individual loss events with nonzero reported recov...
TABLE 12.2 Mapping of insurance coverage to events and impacts
Chapter 13
TABLE 13.1 Taxonomy of inadequacies or failures – the nature of the control ...
TABLE 13.2 Illustration of the monitoring of the operating effectiveness of ...
TABLE 13.3 Illustration of rogue trading Red Flags –detective rather than p...
TABLE 13.4 The applicability of metrics based upon the nature of events and ...
Chapter 16
TABLE 16.1 The mapping of Pandemic Risks to Basel II
TABLE 16.2 The mapping of Transition and Physical Risks to Basel II
TABLE 16.3 Mapping these emerging risks to the impact taxonomy (Appendix II)
Chapter 17
TABLE 17.1 The coverage of the Ten Laws of Operational Risk and their units
TABLE 17.2 Alternative strategies
List of Illustrations
Introduction
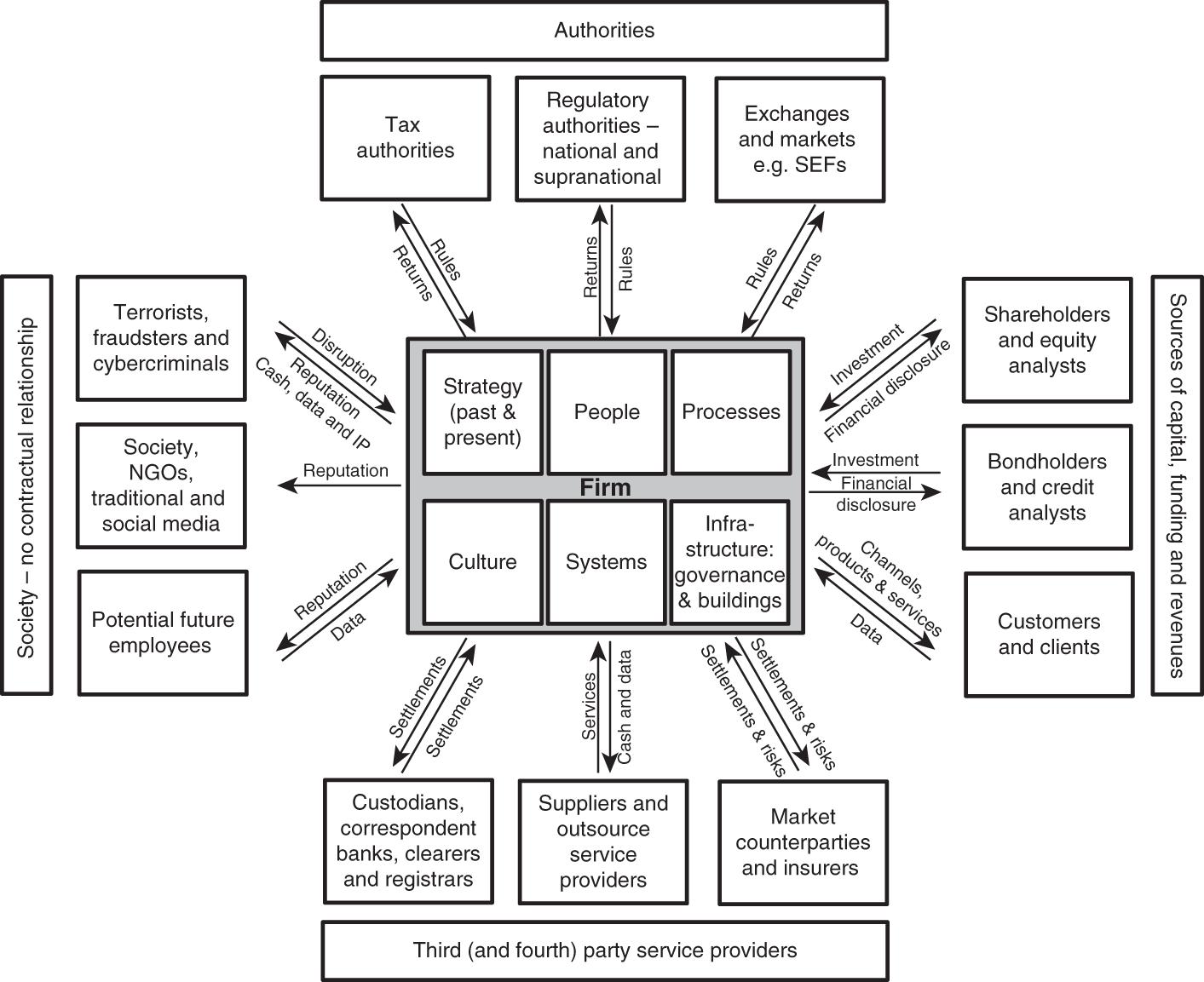
FIGURE I.1 The business profile of a firm (Grimwade, 2020)
FIGURE I.2 The revised butterfly/bow-tie diagram (Grimwade, 2020)
FIGURE I.3 An overarching formula for Operational Risk
Chapter 1
FIGURE 1.1 Distribution of total value of gross losses by size of individual...
FIGURE 1.2 Distribution of total number of losses by size of individual loss...
FIGURE 1.3 Comparison of the frequency of seven subcategories of Operational...
FIGURE 1.4 Comparison of the number and value of events 1998 to 2018
FIGURE 1.5 Number of individual loss events reported by banks (Basel Committ...
Chapter 2
FIGURE 2.1 The business profile of a firm (Grimwade, 2020)
FIGURE 2.2 The duration of large losses (≥$0.1 billion) by time bucket as a ...
FIGURE 2.3 Differing rates of velocity of five significant Operational Risks...
FIGURE 2.4 Duration and average value of losses and velocity, pre & post cri...
FIGURE 2.5 Historical lags between detection and settlement for losses ≥$0.1...
FIGURE 2.6 Profile of the accretion of the parent bank's exposure to litigat...
FIGURE 2.7 Relationship between value of MBS issued and penalties and settle...
FIGURE 2.8 Charges (and releases) from the parent bank's litigation provisio...
Chapter 3
FIGURE 3.1 Composition of large loss events suffered by the 11 current and f...
FIGURE 3.2 Operational Risk losses as a % of annual revenues for 2004 to 201...
FIGURE 3.3 The occurrence of large losses (≥$0.1 billion) discovered at the ...
FIGURE 3.4 Triggering an Operational Risk Real Option: US MBS litigation and...
FIGURE 3.5 Profile of trading losses (Market Risk), impairments (Credit Risk...
Chapter 4
FIGURE 4.1 Gross and net losses from public SWIFT cyberpayments frauds over...
FIGURE 4.2 Value of new record FSA & FCA fines over the last 19 years
FIGURE 4.3 The differing risk profiles and income streams of originators, ar...
FIGURE 4.4 The relationship between large losses and income streams (Grimwad...
Chapter 5
FIGURE 5.1 Representation of the discontinuous risk profile of Damage to Phy...
FIGURE 5.2 Correlations between causal factors associated with individual la...
Chapter 6
FIGURE 6.1 The contribution of 38 very large loss events to the total losses...
FIGURE 6.2 The business profile of a firm annotated for factors driving the ...
FIGURE 6.3 A revised butterfly/bow-tie diagram (Grimwade, 2020)
FIGURE 6.4 Illustration of the interactions between the three pillars drivin...
Chapter 7
FIGURE 7.1 Potential approaches for defining Operational Risk appetite (Revi...
FIGURE 7.2 Efficient frontier between risk/losses and control expenditure
FIGURE 7.3 Representation of the impact of fat-finger limits and the link to...
FIGURE 7.4 Cascade of Board-level Operational Risk appetite statements into ...
Chapter 8
FIGURE 8.1 The drivers of the occurrence of Operational Risk events (Repeat ...
FIGURE 8.2 Spectrum diagrams can represent different Operational Risk distri...
Chapter 9
FIGURE 9.1 Three rogue trader events that occurred over a three-month period...
FIGURE 9.2 Estimating the impacts and likelihoods for fatfingered typing us...
FIGURE 9.3 An example of using Fault Tree Analysis to estimate the likelihoo...
FIGURE 9.4 Estimating to likelihood of a successful cyberattack (Grimwade, 2...
FIGURE 9.5 Back-testing a portfolio of scenarios against both historical int...
FIGURE 9.6 Observed frequencies and ranges of impacts of common and/or indus...
Chapter 10
FIGURE 10.1 Overview of Operational Risk capital models
Figure 10.2 Analysis of losses and RWAs for nine AMA banks 2008 to 2016 (Gr...
FIGURE 10.3 Average losses ≥$0.1 billion over ten years vs average recent re...
FIGURE 10.4 Operational Risk capital requirements should look like an hourgl...
Chapter 11
Figure 11.1 Analysis of large losses ≥$0.1 billion for 31 current and former...
FIGURE 11.2 Profile of Market, Credit and Operational Risk losses from the E...
FIGURE 11.3 Frauds reported to CIFAS before, during and after the Global Fin...
FIGURE 11.4 The triggering of claims of mis-sale of interest rate swaps and ...
FIGURE 11.5 Trends in UK unemployment and employment tribunal claims (Grimwa...
FIGURE 11.6 Stressing Fault Tree Analysis to estimate the likelihood of a po...
FIGURE 11.7 Estimating the impacts and likelihoods for fatfingered typing u...
FIGURE 11.8 Comparison of UK GDP during the Global Financial Crisis (2007 to...
FIGURE 11.9 Average lags (in years) between occurrence and detection (4th La...
FIGURE 11.10 Operational Risk capital requirements should look like an hourg...
FIGURE 11.11 Analysis of the risk categories involved when an individual ban...
Chapter 12
FIGURE 12.1 Potential points of business plan failure (Revision of Figure 2....
FIGURE 12.2 Comparison of capital with a reverse stress scenario and histori...
FIGURE 12.3 Comparison of revenues and operating expenses with a reverse str...
FIGURE 12.4 Operational Risk capital models can be rerun for insurable impac...
Chapter 13
FIGURE 13.1 Fishbone diagram reflecting the first four Laws of Operational R...
FIGURE 13.2 Swiss Cheese Model annotated for the nature of control failure
FIGURE 13.3 Butterfly diagram annotated for what KRIs and KCIs may predict (...
FIGURE 13.4 Illustration of the alteration of business and Operational Risk ...
FIGURE 13.5 Open bugs on TSB's 2018 banking system migration
FIGURE 13.6 Varying Market Risk profiles of products
FIGURE 13.7 Different scenarios for equity release products
FIGURE 13.8 Internal and external stakeholders with whom firms have reputati...
FIGURE 13.9 The differing impacts of Operational Risk events on share prices...
FIGURE 13.10 “A heavy two-year outflow of funds from its wealthy clients” ...
FIGURE 13.11 Impacts of unexpected Operational Risk events on credit ratings...
Chapter 14
FIGURE 14.1 Integrating the Operational Risk management tools with other spe...
Chapter 15
FIGURE 15.1 An illustration of the interrelationships between emerging threa...
FIGURE 15.2 The differing time horizons of a sample of past and present emer...
Chapter 16
FIGURE 16.1 Applying the Ten Laws to the COVID-19 pandemic
FIGURE 16.2 How the movement of the oil price drove derivative litigation
FIGURE 16.3 The interrelationships between the physical and economic consequ...
FIGURE 16.4 A brief history cybercrime firsts and some of the most notorious...
FIGURE 16.5 Gross and net losses from public SWIFT cyber-payments frauds (Gr...
FIGURE 16.6 Scale and severity of data hacks >50 million records over the la...
FIGURE 16.7 Visualisation of the application of Optimal Foraging Theory to c...
FIGURE 16.8 Duration of inappropriate outcomes of decision-making models, co...
FIGURE 16.9 Drivers of the impacts of individual malfunctioning trading algo...
Chapter 17
FIGURE 17.1 A revised butterfly/bow-tie diagram (Repeat of Figure 6.3)
FIGURE 17.2 The business profile of a firm annotated for factors driving the...
FIGURE 17.3 Correlations between causal factors associated with individual l...
FIGURE 17.4 Illustration of the interactions between the three pillars drivi...
FIGURE 17.5 Linking Operational Risk management tools to objectives (Revisio...
Part 2
FIGURE P2.1 SOREs that coincided with the implementation of Basel II (Grimwa...
Founded in 1807, John Wiley & Sons is the oldest independent publishing company in the United States. With offices in North America, Europe, Australia and Asia, Wiley is globally committed to developing and marketing print and electronic products and services for our customers’ professional and personal knowledge and understanding.
The Wiley Finance series contains books written specifically for finance and investment professionals as well as sophisticated individual investors and their financial advisors. Book topics range from portfolio management to e-commerce, risk management, financial engineering, valuation and financial instrument analysis, as well as much more.
For a list of available titles, visit our Web site at www.WileyFinance.com.