SCIENCE

4
ANDALUcíA
GLO BAL THINKERS
DIGITAL PROjEcT
PRIMARY sample
We present all the tools used by people involved in science that will be used throughout the learning experiences.





Let’s analyse our habits and propose new ways to live a healthy life.



Let’s imagine you are an animal and create a presentation about the ecosystem to which you belong to.
Let’s gather your holiday photos and make an album with fun facts about landscapes.
TERM REVIEW 1
Let’s investigate the powers given to us by the machines around us and organise a small exhibition.
Let’s report on the increase in the number of fires and record a video on ways to prevent them.
Let’s create a poster explaining how sustainable development or rural and maritime trade is necessary and important to put an end to hunger.
TERM REVIEW 2
Let’s write an email to the Ministry of Industry, Trade and Tourism explaining the need to reform the sector to allow for a sustainable present and future.
Let’s campaign to promote a healthy lifestyle.
Let’s provide information and ideas to educate and inform others about the importance of the culture of peace.
TERM REVIEW 3

PAGE LEARNING EXPERIENCE TAKE ACTION SDG INTERDISCIPLINARY 1
16
Good health and well-being
WE IN GOOD SHAPE?
MY STEAM TOOLBOX 38
ARE
8
Life on land
TAkING CARE OF NATURE! 62
2
Life on land
DISCOVERING ROCkS AND LANDFORMS 86
3
Industry, innovation and infrastructure
MACHINES,
108
4
OUR SUPERPOWERS!
Life on land
WHERE
THE MOST DAMAGE? 130
5
DO FIRES DO
Zero hunger
WHAT
gIvE US? 154
6
DOES NATURE
Industry,
and
INDUSTRY 4.0
innovation
infrastructure 7
Peace, justice
192 9 UNDERSTANDING HISTORY, A PATH TO PEACE
and solid instruments
174 8 HOW
CHANGED? Good health and well-being
HAVE OUR HAbITS
What are we GOING to learN?
2
• The scientific method
• ICT Plan
• Programming by blocks
• Health and illness
• Habits and prevention
• Hygiene
• Ecosystems and components
• Biodiversity and classification of living things
• Diversity of animals and plants
• Layers of the Earth
• Rocks
• Rocks and uses
KNOW HOW TO: LEARN, APPLY AND RESEARCH
• Computational thinking
• The project-based method
• Physical activity and rest
• A balanced diet
• Food pyramid
• Food chains
• Types of ecosystems
• Ecosystems as resources
• Damage to ecosystems
• Looking for rocks in the landscape
• Landforms and landscapes change
• Erosion of rocks
INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT · Magazine : Eco-Action!
• Avoiding risks
• Emotions management
Competence-based activities
• Human impact on ecosystems
• Protecting ecosystems
Competence-based activities
Competence-based activities
STEAM: Margaret Mee and Mary Anning
• Physical and chemical changes
• Heat and its effects
• Forces
• The atmosphere and atmospheric phenomena
• Climate
• Climate in Spain
• Natural and processed products
• Rural work
• Sea and river work
• Types of forces
• Machines
• Machines in our lives
• Climate and landscapes
• Climate in Andalucía
• The hydrosphere
• Rural and maritime work in Spain
• Primary sector in Andalucía
• How industries can take care of nature
• Designing a machine
• How to program a video game
Competence-based activities
• Climate change
• Earth and relief
Competence-based activities
Competence-based activities
STEAM: Elena García Armada
INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT · Plastic-free mission : Now or never
• Jobs in the Earth’s interior
• Jobs in workshops and factories
• Jobs in transport
• Time and history
• The Palaeolithic period
• The Neolithic period
• The first colonisers
• The pre-Roman peoples
• The Roman Empire and the conquest
• Jobs in commerce
• Jobs in tourism
• Economic activity
• The Metal Age
• Prehistory in the Iberian Peninsula
• Prehistory in Andalucía
of Hispania
• The Romanisation of Hispania
• Society and life in Roman Hispania
INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT · Water pollution : Eco-soap
• Andalusian economic activity
Competence-based activities
Competence-based activities
• The community in the Ancient Times
Competence-based activities
3
how have our habits changed?
It is known that a nomadic and survivalist lifestyle meant a lot of physical activity, but how did our ancestors rest or cook? What about their diet? Was it very different from our diet today?

WHAT DO YOU THINK?
What physical activities were performed in prehistoric times? Were they for leisure or for survival? Do you lead an active or sedentary lifestyle?

WHAT Is GOING On arOUND you?
Access to healthcare and well-being is a right. The Sustainable Development Agenda aims to make sure that all people have access to it. Do you think there are countries where this right is not able to be accessed by all people?

WHAT cAN you do To HElp?
Campaign to promote a healthy lifestyle.

174 3 8
TAKE ACTIon
WhAT WErE ThE TrACES oF EArLY hUMAn LIFE LIKE?

whaT do you NEeD To knOW To TAkE aCTIOn?
hoW Do WE MEASUrE AnD InVESTIGATE TIME?
WhAT nEW ChAnGES oCCUrrED In ThE
LAST pErIoD oF prEhISTorY?
The Neolithic period

2 The Palaeolithic period
3
WhAT IMporTAnT ChAnGES hAppEnED In ThIS pErIoD?
4 The Metal Age
WhAT DID prEhISTorY LooK LIKE In ThE CoMMUnITY?



6 Prehistory in Andalucía
WhAT rEMAInS DID prEhISTorY LEAVE In ThE IBErIAn pEnInSULA?

175
Time and
history 1
Prehistory in the Iberian
Peninsula 5
hoW Do WE MEASUrE AnD InVESTIGATE TIME?
When did we start talking about Prehistory?

Look, listen and read.
When we study history, ordering events according to the date they occurred is very important. It is known as dating. Dating uses different units of time measurement.
Old events
A lustrum = 5 years
A decade = 10 years
A century = 100 years

A millennium = 1000 years
Recent events
A year = 12 months
A month = 4 or 5 weeks
A week = 7 days
A day = 24 hours
An hour = 60 minutes
A minute = 60 seconds
To order historical events in chronological order (dated by time), we use the birth of Christ as a reference point, which is considered to be the beginning of year 1.
The stages of History
Prehistory
Ancient Times
Middle Ages

Modern Age
BC (Before Christ)
Birth of Chist
AD (Anno Domini, After Christ)
Contemporary Age
The beginning of human beings. 2 000 000 BC.

Invention of writing. 3 000 BC.

Fall of the Roman Empire. 476 AD.
Discovery of America. 1492 AD.
Historical sources

Everything that contains important information about past events, people and ways of life.

Written sources. Diaries, letters, legal documents, press, inscriptions, books, etc.
Start of French Revolution. 1789 AD.
Unwritten sources. Graphics (drawings, maps, films), oral (songs, legends or tales) and material such as tools or objects.
176 1
1 Time and history
t HINK
2 How many years are represented by the following labels?
2 centuries
6 millennia

36 months
3 Look at the pictures. To which historical period do they refer to?
Two centuries
4 Decide which type of historical sources are listed below.
a) My grandmother’s photographs.
b) Roman coins.
c) A magazine from the 20th century.
d) A traditional song sang by my father.
Your turn!
FEMALES I n h ISTorY
1 In groups of four, choose the name of a street or school that has a woman’s name.
Step 1. Use the Internet to find out information about this person.
Step 2. Make a fact sheet following the example given. Present it to your classmates.
NOW I KNOW…
• What is her name?
• What is her profession?
• Which historical period did she live in?


• Why is she so important today?
History is divided into different stages: from Prehistory to Contemporary Age. We learn things about history from written and unwritten sources.

177
ChECK WhAT YoU LEArnED
1 3 2 4 1 2 3 4
The Palaeolithic period
WhAT WErE ThE TrACES oF EArLY hUMAn LIFE LIKE?
t HINK
How did our Palaeolithic ancestors survive?

1 Look, listen and read.
The first period of Prehistory is the Palaeolithic period. It began when the first hominids appeared in Africa.
They were nomads as they travelled from place to place looking for food to survive.
The first hominids
Cave paintings. They drew scenes of their daily life with engravings on the cave walls.
Early humans lived in small groups.
Palaeolithic
Fire control made it possible to eat much more food and to favour group relationships around the light and warmth of the campfire.
They made their tools from stones, wood and bones.
They formed tribes (clans) and lived in caves.
They left Africa and travelled to other continents.
They hunted, fished and gathered fruit and vegetables to live on.
They made clothes from animal skins and plant fibres.
178
2
Prehistory
2 When did Prehistory begin? How did humans get food?
3 Read the sentences and decide if they are true or false.
a) Palaeolithic people stayed in one place.
b) The first humans hunted and gathered their food.
c) The first humans moved to Africa from Asia.
d) The discovery of fire is very important in the Palaeolithic period.


Watch the ‘Kima in the Palaeolithic period’ at anayaeducacion.es and learn more about life in this period.
1 Atapuerca is one of Europe’s most important archaeological sites. Traces of hominid life from a million years ago have been found in this area.

a) Where is Atapuerca located in Spain?
b) What is its most famous cave called? Why is it important?

2 In pairs, choose a clan: the Northern clan own tools and objects and the Southern clan owns food. Someone has mixed up the belongings and now you need to ask questions to find out what items belong to which clan.


Whose are these oranges? Whose is that fish? These are mine.

That is yours!
NOW I KNOW…
Palaeolithic people started to gather fruits and vegetables. They contain vitamins, calcium, iron, etc. which help to strengthen the immune system and protect us against diseases.

179
ChECK WhAT YoU LEArnED
turn!
ATA p UE rCA A n D ITS IM porTA n CE
Your
Southern clan
Northern clan
WhAT IMporTAnT ChAnGES hAppEnED In ThIS pErIoD?
Was there a transition from nomadic to sedentary life? t HINK

1 Look, listen and read.
They grew cereal and vegetables crops and improved agriculture. They discovered seeds.
Livestock farming began with the domestication of animals by early humans.
Neolitithic
Techniques and tools for hunting and fishing are improved.
The first ceramic utensils are used to transport, store and preserve food.
The first settlements are built near rivers or natural water sources.
Watch the ‘Nala in the Palaeolithic period’ at anayaeducacion.es and learn more about life in this period.
Clothes are made from skins or vegetable fibres such as hemp and esparto grass using looms.

180
3
The Neolithic period
Prehistory
2
What were the main discoveries made during the Neolithic period? What were the consequences of them?
3 Read the text and complete using the following words.
constructions
food
discovery livestock
The Neolithic period started with the development of ••• and agriculture thanks to the ••• of seeds.
Now it was not necessary to move from one place to another because humans produced their own •••
The first ••• and villages appeared.
4 In pairs, look at the picture on the previous page and ask and answer questions about what is happening.
What is he doing?
He is painting using his hands!
Your turn!
1 Neolithic people started growing cereals and vegetables. Did the discovery of agriculture make their diet richer and more varied? How did their lives change? Use the following diagram to compare and contrast the two periods.
The Palaeolithic period The Neolithic period
2
Some historians agree that the introduction of cultivated products in the Neolithic period, especially cereals, led to the appearance of tooth decay.
a) Do you regularly go for check-ups at a dental clinic? How often?
b) Do you brush your teeth correctly?
NOW I KNOW…
Consumed refined starchy carbohydrates such as white sugar, soft drinks, pastries, sweets and candies contributes to tooth decay.
181
ChECK WhAT YoU LEArnED
AG r ICULTU r E A n D or AL h EALT h CA r E
WhAT nEW ChAnGES oCCUrrED In ThE LAST pErIoD oF prEhISTorY?

t HINK
What was the main reason for trade to happen?
1 Look, listen and read.
The Metal Age started with the discovery of metallurgy (the art of obtaining and working with metals).
Economic differences also appeared so not everyone had the same social status.
A minority of chiefs and warriors lived side by side with a majority of peasants and craftsmen.
The first cities are built.
Irrigation, the plough, the wheel, and the sail are invented.
Funerary monuments (megaliths) made of stones are built.
Besides everyday objects and work tools, weapons are made. Attacks and insecurity increased.
Woollen cloth is made. Trade or exchange of goods between cities began.
Early navigation encouraged trade and contact between places and cultures.
182
4 The Metal Age
Prehistory Metal Age
2
What discovery led to the transition from the Neolithic to the Metal Age? Name two changes in the human way of life that began in the the Metal Age.
3 Read the following historical events and match them to the correct label.
a) Hunter-gathered society.
b) The discovery of fire.
c) Megalithic monuments are built.
d) First settlements.
e) Metal weapons and tools.
The Palaeolithic period
The Neolithic period
The Metal Age
4 In pairs, you are a time traveller. You have met a person from the Metal Age. What plans does he or she have for tomorrow? Think about it and ask questions.
What are you going to do tomorrow?askre you going to build a wall?
Yes, I am. / No, I’m not.
Watch the ‘Megalithic monuments’ at anayaeducacion.es for better understanding of religious monuments in the Metal Age.

1 During Prehistory, humans travelled long distances on foot and had to be physically fit to survive the dangers they faced.
a) What physical activity do you do every day?
b) Do you have a sedentary lifestyle? What is causing sedentary lifestyles to occur today?
2 Your local and surrounding areas are sure to have a wide range of physical and sporting activities on offer. Investigate and make a list of the activities, locations, schedules, target audience. Take some photographs if you want!
NOW I KNOW…
The WHO recommends children should do at least three days a week of physical activity that strengthens our locomotor and cardiorespiratory systems.

183
ChECK WhAT YoU LEArnED
ph YSICAL ACTIVITY I n T h E METAL AGE Your turn!
5 Prehistory in the Iberian Peninsula

Can we create a timeline about Prehistory in the Iberian Peninsula? t
1 Look, listen and read.
The Palaeolithic period
• Homo Antecessor, Homo Neanderthalensis and Homo Sapiens coexisted.
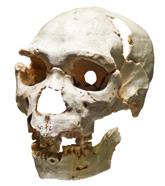
• Evolution in weapons and tools.
The Neolithic period


• Agricultural and livestock knowledge.
• The first settlements appeared to the north of the Ebro river.
• Discovery of pottery.
The Metal Age
• Development of techniques for metal work and the manufacture of objects, ornaments, and weapons.
• First major population movements in Europe.
• Social differences took place.
The Copper Age
In Almería and Murcia there were large copper deposits. The culture of Los Millares and its campaniform pottery appeared.


The Bronze Age
Bronze began to be used with the mixture of copper and other metals. El Argar culture emerged in the area of Murcia.


The Iron Age
The Greeks, the Phoenicians and the Celts introduced iron metallurgy.
184
rEMAInS
prEhISTorY LEAVE In ThE IBErIAn pEnInSULA?
WhAT
DID
HINK
2.5 million 3 000 BC 10 000 BC
Los Millares in Almería.
El Argar in Murcia.
2
Which period of Prehistory do these human species belong to? Put them in chronological order. Find out information on the Internet if necessary.
3 Order the letters to find out the three periods or stages of the Metal Age. Then, put them in chronological order.
Watch the ‘Evolution’ at anayaeducacion.es for better understanding of human evolution.

1 In Prehistory many people worshipped female statues. The most famous of the Palaeolithic female statues is the Venus of Willendorf. Look for information on the Internet and complete the following sheet.

Material: .......................................................
Where was it found? .............................
Finding date: .............................................
Where is it located today? .................
What is its importance? .......................
2 In the Iberian Peninsula, a famous female statue is the Dama of Elche. What similarities and differences are there between Dama of Elche and Venus of Willendorf?

NOW I KNOW…
The Prehistory in the Iberian Peninsula made a number of advances thanks to the different cultures and settlements that coexisted at this time.
185
ChECK WhAT YoU LEArnED
Your turn!
NIOR
Homo Antecessor Homo Sapiens Homo Neanderthalensis 1 2 3
FEMALE SCUL p TU r ES
The BZERON Age The
Age The PRECOP Age
The Dama of Elche has more details on her head.
WhAT DID prEhISTorY LooK LIKE In ThE CoMMUnITY?


What remains of Prehistory can we find in our community? t HINK
1 Look, listen and read.
The Palaeolithic period
During the Palaeolithic period, the first people to inhabit the land of Andalucía settled on the banks of the Guadalquivir river and lived in the caves they found in the nearby mountain areas. Important cave paintings are found there.
The Prehistory in Andalucía
The Neolithic period
The Neolithic period began with the arrival of people from the eastern Mediterranean who settled in Almería. They developed agriculture, lumbering, new polished stone techniques and ceramics. Large stone dolmens were built.
The Metal Age
The most important settlements in the Metal Age are Los Millares, El Gracel and El Argar. They were walled settlements, inhabited by many people and well organised. Important megaliths are found in La Giganta (Málaga) and the Megalithic Park of Gorafe (Granada).

186
6 Prehistory in Andalucía
La Pileta cave in Benaoján, Málaga.
The Menga Dolmen in Antequera, Málaga.
2
What areas did the first humans inhabit in Andalucía? What evidence is there of this?
3 In pairs, look at the following picture and describe it briefly.
What are you going to visit tomorrow?
Watch the ‘Megaliths at anayaeducacion.es for better understanding of this structure.

I am going to visit a dolmen in Granada. It has...

Your turn!
I n VE n TI on S o F T h E pr E h ISTorY
1 Let’s make a Prehistory object!
Step 1. In groups of four, choose a stage of the Prehistory and an important invention of that period.
Step 2. Use plasticine and your hands to create it.

Step 3. Discuss and describe your tool to the rest of your classmates.
Step 4. Prepare an exhibition for your school!
2 Prepare an oral presentation about the object made and describe all the things you know about its history, its importance, etc.
NOW I KNOW…
Since the beginning of human history, human beings have lived together in society. Our purpose to educate ourselves on positive values for living together, helps to build healthy social relationships.
187 ChECK WhAT YoU LEArnED
A dolmen in Gorafe, Granada.
How have your habits changed?




Date measurements



Ages of history




188 MY VisuaL suMMaRY
Historical sources Old events Recent events Lustrum (5 years) Minutes Hours Days Weeks Months Years Decade (10 years) Century (100 years) Millenium (1000 years) Use of fire 1 million years BC Invention of writing 3000 BC Columbus discovered America 1492 AD French Revolucion 1789 AD First human species 25 million years BC Agriculture begins 10000 BC Fall of western Roman Empire 476 AD Prehistory 3 million years to 3000 BC Written Non-written History 3000 BC to nowadays Palaeolithic Neolithic Ancient Times Middle Ages Modern Age Contemporary Age 3 million years to 10000 BC 10000 BC to 3000 BC 3000 BC to 476 AD 476 AD to 1492 BC 1492 BC to 1789 AD 1789 AD to 2023 AD Year 0 BC AD
Prehistory

Palaeolithic
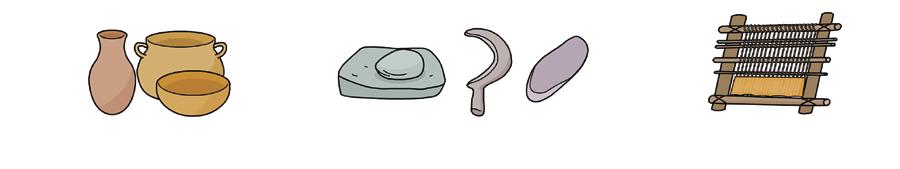

Neolithic
Metal Age

189
Cave paintings
Stone – Wood –Bones tools
Nomadism
Fire
Small groups
Caves and shelters
Agriculture
Pottery
Livestock farming
Polished Stone tools
Small villages
Weaving looms
Cooper – Bronze – Iron – Tools and weapons
Chiefs and social status
Trade Megaliths
Fortified towns
Sailing
PoRTFoLio
WhAT hAVE I LEArnED?
1 What are the main dating units?
2 Decide if it is a written or unwritten historical source.
a) A cave painting.
b) Megalithic monuments.
c) Trade agreement in an exchange of goods.
3 Copy and complete the table comparing the stages of Prehistory. Where they lived Developments
Palaeolithic period



Neolithic period

Metal Age
4 Look at the pictures and sort them according to the historical period to which they belong to. Name the event each of them corresponds to.
5 Why do you think humans lived nomadically
9 What three ages are the Metal Age divided into?
10 Read the sentences and decide if they are true or false.
a) The Palaeolithic period begins with the appearance of the first hominids.
b) Our first ancestors arrived on the Peninsula a million years ago.
c) Learning to produce their own food with the discovery of agriculture and livestock farming meant the transition from a sedentary life to a nomadic lifestyle.
d) In the Neolithic period, metal production and trade brought major changes to life in the first cities.



Traffic lights. Apply this colour code to each activity in your notebook.
If you knew the answer.
If you needed help.
If you couldn’t answer the question.
190
1 3 5 2 4 6
Campaign to promote a healthy lifestyle.
Reflect on the investigations carried out throughout these last pages using the ‘What makes you say that?’ technique. These reflections will provide you with ideas to encourage people to lead a healthy lifestyle.
Eating three to four pieces of fruit and vegetables is a healthy habit. Justification and evidence
What makes you say that?
Healthy habits are one of the reasons for increased life expectancy. Justification and evidence
What makes you say that?
We can improve our oral hygiene. Justification and evidence
hoW hAVE I LEArnED?
What makes you say that?
There are physical activities for everyone in our town. Justification and evidence
Think about this!
What makes you say that?
1 Have you learned anything new? What images do you remember? What did you like most about what you learned? How useful is what you have learned? How will it help you in your everyday life? 2
Reflect on what you can improve in the future and ask your classmates what they can improve.
How can you spread the word and raise awareness, through historical research, about the need to understand and adopt a healthy lifestyle?
Make healthy habits part of your daily life!
Share what you have learned with your family and friends.
Do a healthy living campaign in your educational community.
191
1
TAKE
ACTIon
© GRUPO ANAYA, S.A., 2023 - C/ Valentín Beato, 21 - 28037 Madrid.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior permission of the publishers.








































































