49 minute read
Global Initi ati ve for Asthma (GINA) – What’s new in 2020
Global initiative for asthma (GINA) – What’s new in 2020
AUTHORS: Dr Dermot Nolan, ICGP/HSE Clinical Lead for Asthma; and Dr Emer Glanville, GP Registrar, SE Training Scheme
The Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA, https://ginasthma.org) is a medical guidelines organisation which works with public health officials and healthcare professionals globally to reduce asthma prevalence and mortality.
The 2020 report of the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention sets out new scientific information about asthma and is a review of the most recent scientific literature by an international panel of experts on the GINA Science Committee.
Since 2007, GINA has been actively seeking interventions for mild asthma in order to reduce the risk of exacerbations and death and also to set out goals of treatment and preventing exacerbations, as well as guidelines on the use and reliance of short-acting beta-agonists (SABA) in early disease.
In 2019, GINA published landmark changes in the management of asthma: ● SABA monotherapy – no longer recommended for Step 1. The background to this change was that frequent use of SABA is associated with adverse clinical outcomes – dispensing of >three canisters per year was associated with increased risk of emergency department presentations and dispensing of >12 canisters per year was associated with higher risk of death. ● In children under five years, the evidence is still unclear – a trial of ICS should be used in those not responding to as-needed SABA. ● ICS (inhaled corticosteroids) recommended for all adults and adolescents with asthma to reduce risk of serious exacerbations (regular daily treatment or as-required low-dose ICS-formoterol).
GINA recommendations on Covid-19 and asthma 2020: ▶ Advise patients to continue taking
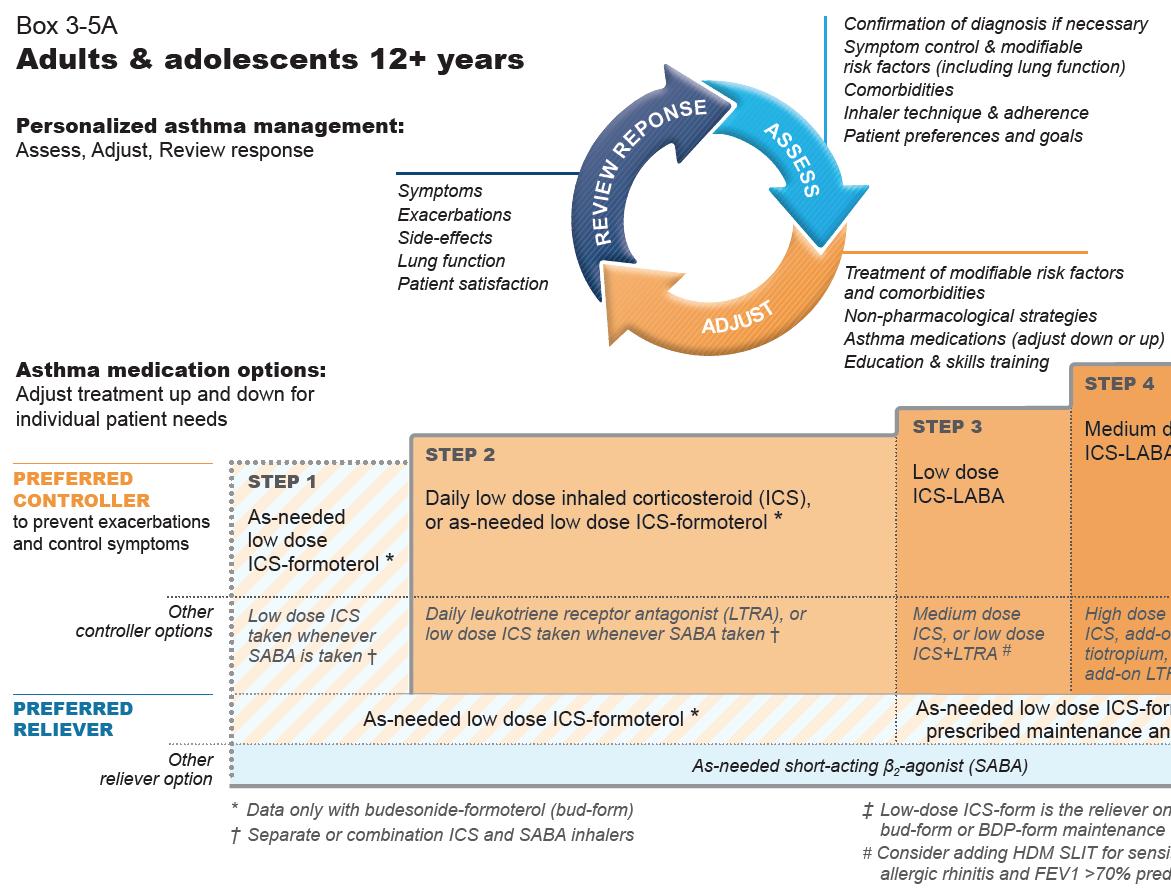
FIGURE 1A: GINA 2020 report steps 1-5 in management of adults and adolescents over 12 years
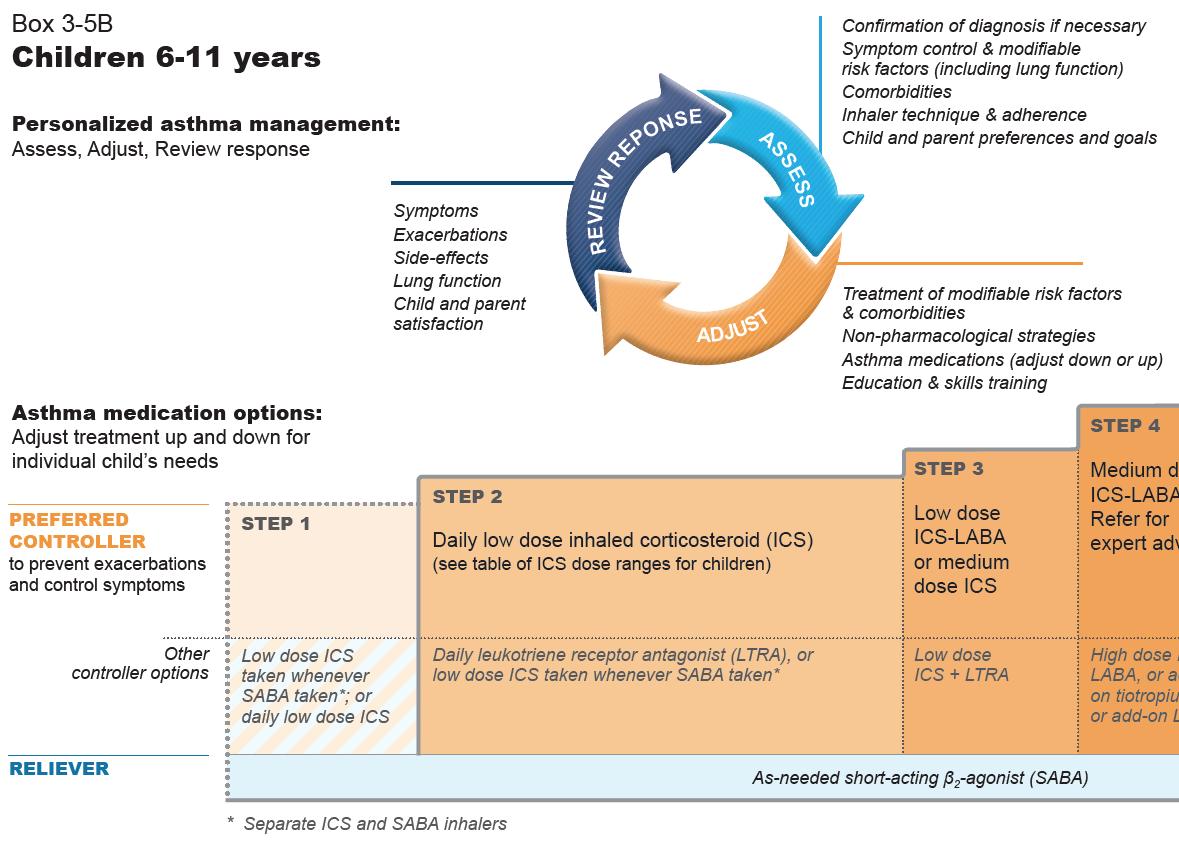
FIGURE 1B: GINA 2020 report Steps 1-5 in management of Adults and adolescents over 12
their prescribed asthma medications, particularly ICS and OCS (oral corticosteroids) if prescribed. ▶ Patient on biological therapy for severe asthma should continue and not stop if prescribed OCS. ▶ All patients should have a written asthma action plan that should be followed and this action plan should include instructions about increasing controller and reliever when required, taking a short course of OCS for severe exacerbations if needed and outlining when to seek medical help. ▶ Nebuliser therapy should be avoided where possible due to the risk of disseminating virus to other patients and to healthcare staff. Use of a pressurised metered dose inhaler via a spacer is the preferred treatment during severe exacerbations. ▶ Spirometry and peak flow tests should be avoided, again due to the risk of dissemination and should only be carried out if there is an urgent need.
Summary of GINA 2020 recommendations
▶ Covid-19 and asthma recommendations as outlined above. ▶ All patients with asthma should be treated with ICS regularly or as required, but trialled in children under fi ve years to be reviewed after three months of therapy. ▶ GINA no longer recommends SABA alone for fi rst-line. ▶ For adults and adolescents over 12 years old GINA recommends ICS in combination with formoterol for asneeded symptom relief. ▶ ICS with SABA recommended in children aged six-to-11 years. ▶ Mild asthma – where reliever is required no more than twice per month. The preferred treatment is asneeded ICS-formoterol combination. ▶ All patients should be regularly reviewed and this should include assessment (1), adjustment (2), and (3) review of any response to adjustments. (1) Assessments to include confi rmation of diagnosis, symptom control and modifi able risk factors, inhaler technique and adherence, and patient preferences and goals. (2) Adjustments should involve treatment of modifi able risk factors and comorbidities, nonpharmacological strategies, adjustments of asthma medications and education and skills training. (3) Response review should look at symptoms, exacerbations, side e ects, lung function and patient or parent satisfaction.
Recommended options below – based on symptom prevalence – remember Assess, Adjust, and Review.
The guidelines recommend as-needed low-dose budesonide-formoterol to be prescribed in maintenance and reliever
Should all pa*ents start at Step 1 of management?
Recommended opFons below – based on symptom prevalence – remember Assess, Adjust and SHOULD ALL PATIENTS START AT STEP 1 OF MANAGEMENT? Review. Recommended options below – based on symptom prevalence – remember Assess, Adjust, and Review.
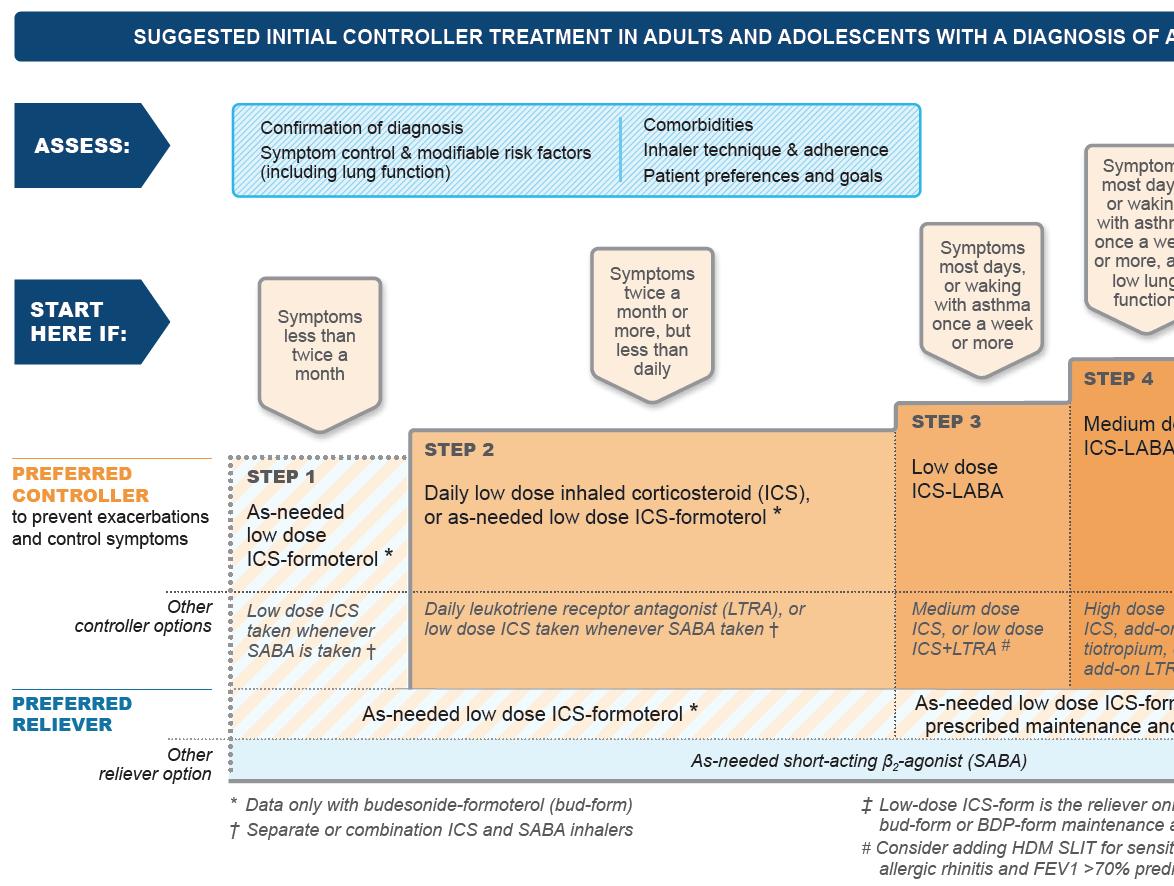
therapy (Steps 3-5) above or as-needed and reliever therapy max daily Further data is awaited on assessing only therapy (Step 1). dose is 48mcg (six inhalations of whether ICS use should be included in The guidelines recommend as needed low-dose budesonide-formoterol to be prescribed in Max daily dose recommended is 72mcg beclomethasone-formoterol 100/6mcg). the symptom control assessment.maintenance and reliever therapy (Steps 3-5) above or as needed only therapy (Step 1). (12 inhalations of budesonide-formoterol Turbohaler 200/6mcg). In assessing symptom control and frequency of SABA use, GINA recommends Low-dose ICS is all that is required for most patients, however, some patients may Max daily dose recommended is 72mcg total daily dose (12 inhalaFons of budesonide-formoterol
Turbohaler 200/6mcg). asking the following questions in the box require medium dosing if their asthma For as-needed low-dose beclomethasone- below (Box 2-2) and categorising them symptoms are uncontrolled despite formoterol prescribed in maintenance according to level of control. following correct techniques and usage. For as needed low dose beclomethasone-formoterol prescribed in maintenance and reliever therapy max daily dose is 48mcg (six inhalaFons of beclomethasone-formoterol 100/6mcg).
In assessing symptom control and frequency of SABA use, GINA recommends asking the following quesFons and categorising them according to level of control:

NOW AVAILABLENOW AVAILABLE CONFIRMED DOSE WITH TRANSPARENT CAPSULE3 ONCE-DAILY DOSING3 PROVEN EFFICACY* & INFLAMMATION CONTROL1,2,3 IND/GLY/MF 114/46/136μg 1x daily ONCE-DAILY ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® the first LABA/LAMA/ICS combination for asthma3,4 UNLOCK THE POTENTIAL OF INHALED ASTHMA CARE1,2 CONFIRMED DOSE WITH TRANSPARENT CAPSULE PROVEN EFFICACY* & INFLAMMATION CONTROL1,2,3 ONCE-DAILY ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® the first LABA/LAMA/ICS combination for asthma3,4 UNLOCK THE POTENTIAL OF INHALED ASTHMA CARE1,2 CONFIRMED DOSE WITH TRANSPARENT ONCE-DAILY DOSING3 IND/GLY/MF 114/46/136μg 1x daily IND/GLY/MF 114/46/136μg 1x daily ONCE-DAILY UNLOCK THE POTENTIAL OF INHALED ASTHMA CARE1,2 NOW AVAILABLE UNLOCK THE POTENTIAL OF INHALED ASTHMA CARE1,2 NOW AVAILABLE ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® ONCE-DAILY ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® is indicated as a ONCE DAILY ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® is indicated as a ONCE DAILY the first LABA/LAMA/ICS ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® maintenance treatment of asthma in adult patients not adequately controlled with a maintenance combination of a long-acting beta2-agonist and maintenance treatment of asthma in adult patients not adequately controlled with a maintenance combination of a long-acting beta2-agonist and combination for asthma3,4 the first LABA/LAMA/ICS a high dose of an inhaled corticosteroid who experienced one or more asthma exacerbations in the previous year.3 Indacaterol acetate / glycopyrronium bromide / mometasone furoate inhalation powder a high dose of an inhaled corticosteroid who experienced one or more asthma exacerbations in the previous year.3 Indacaterol acetate / glycopyrronium bromide / mometasone furoate inhalation powder combination for asthma3,4









Abbreviated Prescribing Information with caution in patients being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, or Abbreviated Prescribing Information with caution in patients being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, or Please refer to Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) before prescribing. medicinal products known to prolong the QT-interval. Hypokalaemic treatment: Concomitant treatment Please refer to Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) before prescribing. medicinal products known to prolong the QT-interval. Hypokalaemic treatment: Concomitant treatment Enerzair® Breezhaler® (indacaterol (as acetate), glycopyrronium bromide, mometasone furoate) inhalation powder, hard capsules. Presentation: Hard capsules for inhalation each containing 150 mcg of indacaterol (as acetate), 63 mcg of glycopyrronium bromide equivalent to 50 mcg of glycopyrronium and 160 mcg of mometasone furoate. Each delivered dose contains 114 mcg of indacaterol acetate, 46 mcg of glycopyrronium and 136 mcg of mometasone furoate. Indications: Maintenance treatment of asthma in adult patients not adequately controlled with a maintenance combination of a long-acting beta2-agonist and a high dose of an inhaled corticosteroid who experienced one or more asthma exacerbations in the previous year. Dosage and Administration: One capsule once daily, administered at the same time of the day each day, using the Enerzair Breezhaler inhaler. No dose adjustment is required in elderly patients, in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment, or in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. Caution should be observed in patients with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease requiring dialysis. No data available for patients with severe hepatic impairment, only use in these patients if the expected benefit outweighs the potential risk. The safety and efficacy in paediatric with methylxanthine derivatives, steroids, or non-potassium sparing diuretics may potentiate the possible hypokalaemic effect of beta2-adrenergic agonists. Beta-adrenergic blockers: Should not be given together with beta-adrenergic blockers unless there are compelling reasons for their use. Where required, cardioselective beta-adrenergic blockers should be preferred, although they should be administered with caution. CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein inhibitors: Inhibition of CYP3A4 and P-gp has no impact on the safety of therapeutic doses of Enerzair Breezhaler. Cimetidine and inhibitors of organic cation transport: No clinically relevant drug interaction is expected when glycopyrronium is co-administered with cimetidine or other inhibitors of the organic cation transport. Other long-acting antimuscarinics and LABAs: Co-administration with other medicinal products containing long-acting antimuscarinics or LABAs is not recommended. Fertility, Pregnancy and Lactation: Should only be used during pregnancy if the expected benefit to the patient justifies the potential risk to the foetus. No information available on the presence of indacaterol, glycopyrronium or mometasone furoate in human milk, on the effects on a breast-fed infant, or on the effects on milk production. A decision must be made whether to discontinue breast-feeding or to discontinue/abstain from therapy, taking into account the benefit Enerzair® Breezhaler® (indacaterol (as acetate), glycopyrronium bromide, mometasone furoate) inhalation powder, hard capsules. Presentation: Hard capsules for inhalation each containing 150 mcg of indacaterol (as acetate), 63 mcg of glycopyrronium bromide equivalent to 50 mcg of glycopyrronium and 160 mcg of mometasone furoate. Each delivered dose contains 114 mcg of indacaterol acetate, 46 mcg of glycopyrronium and 136 mcg of mometasone furoate. Indications: Maintenance treatment of asthma in adult patients not adequately controlled with a maintenance combination of a long-acting beta2-agonist and a high dose of an inhaled corticosteroid who experienced one or more asthma exacerbations in the previous year. Dosage and Administration: One capsule once daily, administered at the same time of the day each day, using the Enerzair Breezhaler inhaler. No dose adjustment is required in elderly patients, in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment, or in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. Caution should be observed in patients with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease requiring dialysis. No data available for patients with severe hepatic impairment, only use in these patients if the expected benefit outweighs the potential risk. The safety and efficacy in paediatric with methylxanthine derivatives, steroids, or non-potassium sparing diuretics may potentiate the possible hypokalaemic effect of beta2-adrenergic agonists. Beta-adrenergic blockers: Should not be given together with beta-adrenergic blockers unless there are compelling reasons for their use. Where required, cardioselective beta-adrenergic blockers should be preferred, although they should be administered with caution. CYP3A4 and Inhibition of CYP3A4 and P-gp has no impact on the safety of therapeutic doses of Cimetidine and inhibitors of organic cation transport: No clinically relevant drug interaction is expected when glycopyrronium is co-administered with cimetidine or other inhibitors of the organic cation Other long-acting antimuscarinics and LABAs: Co-administration with other medicinal products containing long-acting antimuscarinics or LABAs is not recommended. Fertility, Pregnancy and Lactation: Should only be used during pregnancy if the expected benefit to the patient justifies the potential risk to the foetus. No information available on the presence of indacaterol, glycopyrronium or mometasone furoate in human milk, on the effects on a breast-fed infant, or on the effects on milk production. A decision must be made whether to discontinue breast-feeding or to discontinue/abstain from therapy, taking into account the benefit CONFIRMED DOSE WITH TRANSPARENT CAPSULE3 ONCE-DAILY DOSING3 PROVEN EFFICACY* & INFLAMMATION CONTROL1,2,3 CONFIRMED DOSE PROVEN EFFICACY* patients below 18 years of age have not been established. Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to the active substances, lactose monohydrate or magnesium stearate. Warnings/Precautions: Deterioration of disease: Should not be used to treat acute asthma symptoms, including acute episodes of bronchospasm. Treatment should not be stopped abruptly. Hypersensitivity: Immediate hypersensitivity reactions have been observed of breast-feeding for the child and the benefit of therapy for the woman. Studies do not indicate a concern regarding fertility in either males or females. Undesirable Effects: Very common (≥1/10): nasopharyngitis, asthma (exacerbation). Common (≥1/100 to <1/10): upper respiratory tract infection, candidiasis, urinary tract infection, hypersensitivity, headache, tachycardia, oropharyngeal pain, cough, dysphonia, gastroenteritis, patients below 18 years of age have not been established. Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to the active substances, lactose monohydrate or magnesium stearate. Warnings/Precautions: Deterioration of disease: Should not be used to treat acute asthma symptoms, including acute episodes of bronchospasm. Treatment should not be stopped abruptly. Hypersensitivity: Immediate hypersensitivity reactions have been observed of breast-feeding for the child and the benefit of therapy for the woman. Studies do not indicate a concern regarding fertility in either males or females. Undesirable Effects: Very common (≥1/10): nasopharyngitis, Common (≥1/100 to <1/10): upper respiratory tract infection, candidiasis, urinary tract infection, hypersensitivity, headache, tachycardia, oropharyngeal pain, cough, dysphonia, gastroenteritis, WITH TRANSPARENT & INFLAMMATION after administration. If signs suggesting allergic reactions occur, in particular angioedema, urticaria or skin rash, treatment should be discontinued immediately and alternative therapy instituted. Paradoxical bronchospasm: If paradoxical bronchospasm occurs, treatment should be discontinued immediately and alternative therapy instituted. Cardiovascular effects: Like other medicinal products containing beta2-adrenergic agonists, may musculoskeletal pain, muscle spasms, pyrexia. Uncommon (≥1/1,000 to <1/100): hyperglycaemia, cataract, dry mouth, rash, pruritus, dysuria. Please consult the Summary of Product Characteristics for a detailed listing of all adverse events before prescribing. Pack Size(s): Single pack containing 30 x 1 hard capsules, together with one inhaler. Pack containing 30 x 1 hard capsules, together with 1 inhaler and 1 sensor. The after administration. If signs suggesting allergic reactions occur, in particular angioedema, urticaria or skin rash, treatment should be discontinued immediately and alternative therapy instituted. Paradoxical bronchospasm: If paradoxical bronchospasm occurs, treatment should be discontinued immediately and alternative therapy instituted. Cardiovascular effects: Like other medicinal products containing beta2-adrenergic agonists, may musculoskeletal pain, muscle spasms, pyrexia. Uncommon (≥1/1,000 to <1/100): hyperglycaemia, cataract, dry mouth, rash, pruritus, dysuria. Please consult the Summary of Product Characteristics for a detailed listing of all adverse events before prescribing. Pack Size(s): Single pack containing 30 x 1 hard capsules, together with one inhaler. Pack containing 30 x 1 hard capsules, together with 1 inhaler and 1 sensor. The CAPSULECONTROL1,2,3 produce a clinically significant cardiovascular effect in some patients as measured by increases in pulse rate, sensor and App are not required for administration to the patient. The sensor and App do not control or produce a clinically significant cardiovascular effect in some patients as measured by increases in pulse rate, sensor and App are not required for administration to the patient. The sensor and App do not control or blood pressure, and/or symptoms. Use with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders (coronary artery interfere with delivery of the medicinal product using the inhaler. Legal Category: POM. Product (Marketing) blood pressure, and/or symptoms. Use with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders (coronary artery interfere with delivery of the medicinal product using the inhaler. Legal Category: POM. Product (Marketing) disease, acute myocardial infarction, cardiac arrhythmias, hypertension), convulsive disorders, thyrotoxicosis, and in patients who are unusually responsive to beta2-adrenergic agonists. Long acting beta2-adrenergic agonists (LABA) or LABA containing combination products such as Enerzair Breezhaler should be used with caution in patients with known or suspected prolongation of the QT interval or who are being treated with medicinal products affecting the QT interval. Hypokalaemia: Beta2-adrenergic agonists may produce significant hypokalaemia in some patients, which has the potential to produce adverse cardiovascular effects. The Authorisation Number(s): EU/1/20/1438/002 & 003. Product (Marketing) Authorisation Holder: Novartis Europharm Limited, Vista Building, Elm Park, Merrion Road, Dublin 4, Ireland. Full prescribing information is available upon request from: Novartis Ireland Limited, Vista Building, Elm Park Business Park, Elm Park, Dublin 4. Tel: 01-2601255 or at www.medicines.ie. Detailed information on this product is also available on the website of the European Medicines Agency http://www.ema.europa.eu Prescribing Information last revised: July 2020. disease, acute myocardial infarction, cardiac arrhythmias, hypertension), convulsive disorders, thyrotoxicosis, and in patients who are unusually responsive to beta2-adrenergic agonists. Long acting beta2-adrenergic agonists (LABA) or LABA containing combination products such as Enerzair Breezhaler should be used with caution in patients with known or suspected prolongation of the QT interval or who are being treated with medicinal products affecting the QT interval. Hypokalaemia: Beta2-adrenergic agonists may produce significant hypokalaemia in some patients, which has the potential to produce adverse cardiovascular effects. The EU/1/20/1438/002 & 003. Product (Marketing) Authorisation Holder: Novartis Europharm Limited, Vista Building, Elm Park, Merrion Road, Dublin 4, Ireland. Full prescribing information is available upon request from: Novartis Ireland Limited, Vista Building, Elm Park Business Park, Elm Park, Dublin 4. Tel: 01-2601255 or at www.medicines.ie. Detailed information on this product is also available on the website of the European Medicines Agency http://www.ema.europa.eu Prescribing Information last ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® is indicated as a ONCE DAILY decrease in serum potassium is usually transient, not requiring supplementation. In patients with severe asthma hypokalaemia may be potentiated by hypoxia and concomitant treatment, which may increase the susceptibility to cardiac arrhythmias. Hyperglycaemia: Inhalation of high dose of beta2-adrenergic agonists and corticosteroids may produce increases in plasma glucose. Upon initiation of treatment, plasma glucose should Reporting suspected adverse reactions of the medicinal product is important to Novartis and the HPRA. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk profile of the medicinal product. All decrease in serum potassium is usually transient, not requiring supplementation. In patients with severe asthma hypokalaemia may be potentiated by hypoxia and concomitant treatment, which may increase the susceptibility to cardiac arrhythmias. Hyperglycaemia: Inhalation of high dose of beta2-adrenergic agonists and corticosteroids may produce increases in plasma glucose. Upon initiation of treatment, plasma glucose should Reporting suspected adverse reactions of the medicinal product is important to Novartis and the HPRA. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk profile of the medicinal product. All maintenance treatment of asthma in adult patients be monitored more closely in diabetic patients. Anticholinergic effect related to glycopyrronium: use with caution in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma or urinary retention. Prevention of oropharyngeal infections: In order to reduce the risk of oropharyngeal candida infection, patients should be advised to rinse their mouth suspected adverse reactions should be reported via HPRA Pharmacovigilance, website www.hpra.ie. Adverse events could also be reported to Novartis preferably via www.report.novartis.com or by email: drugsafety.dublin@novartis.com or by calling 01 2080 612. be monitored more closely in diabetic patients. Anticholinergic effect related to glycopyrronium: use with caution in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma or urinary retention. Prevention of oropharyngeal infections: In order to reduce the risk of oropharyngeal candida infection, patients should be advised to rinse their mouth suspected adverse reactions should be reported via HPRA Pharmacovigilance, website www.hpra.ie. Adverse events could also be reported to Novartis preferably via www.report.novartis.com or by email: drugsafety.dublin@novartis.com or by calling 01 2080 612.not adequately controlled with a maintenance or gargle with water without swallowing it or brush their teeth after inhaling the prescribed dose. Systemic effects of corticosteroids: Systemic effects of inhaled corticosteroids may occur, particularly at high doses prescribed for prolonged periods. Should be administered with caution in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis or in patients with chronic or untreated infections. Excipients: Contains lactose. Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, total lactase deficiency or glucose galactose malabsorption should not take this medicinal product. Interactions: No specific interaction studies were conducted with indacaterol/ glycopyrronium/mometasone furoate. Information on the potential for interactions is based on the potential for References: 1. Kerstjens H, et al. Lancet Respir Med 2020; https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30190-9. 2. Gessner C, et al. Respiratory Medicine 2020; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2020.106021. 3. ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER®. Summary of Product Characteristics. Available at www.medicines.ie Date accessed: October 2020. 4. European Medicines Agency CHMP Press Release. Available at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ news/meeting-highlights-committee-medicinal-products-human-use-chmp-28-30-april-2020 Date accessed: or gargle with water without swallowing it or brush their teeth after inhaling the prescribed dose. Systemic effects of corticosteroids: Systemic effects of inhaled corticosteroids may occur, particularly at high doses prescribed for prolonged periods. Should be administered with caution in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis or in patients with chronic or untreated infections. Excipients: Contains lactose. Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, total lactase deficiency or glucose galactose malabsorption should not take this medicinal product. Interactions: No specific interaction studies were conducted with indacaterol/ glycopyrronium/mometasone furoate. Information on the potential for interactions is based on the potential for Kerstjens H, et al. Lancet Respir Med 2020; https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30190-9. Gessner C, et al. Respiratory Medicine 2020; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2020.106021. 3. ENERZAIR® . Summary of Product Characteristics. Available at www.medicines.ie Date accessed: October European Medicines Agency CHMP Press Release. Available at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ news/meeting-highlights-committee-medicinal-products-human-use-chmp-28-30-april-2020 Date accessed: combination of a long-acting beta2-agonist and a high dose of an inhaled corticosteroid who ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® is indicated as a maintenance treatment of asthma in adult patients *In symptomatic asthma patients despite treatment with medium- or high-dose LABA/ICS.2 Date of preparation: October 2020 IE02/ENE20-025 each of the monotherapy components. Medicinal products that prolong QTc interval: Should be administered October 2020. *In symptomatic asthma patients despite treatment with medium- or high-dose LABA/ICS.2 Date of preparation: October 2020 IE02/ENE20-025 each of the monotherapy components. Medicinal products that prolong QTc interval: Should be administered experienced one or more asthma exacerbations in the previous year.3 Indacaterol acetate / glycopyrronium bromide / mometasone furoate inhalation powder not adequately controlled with a maintenance combination of a long-acting beta2-agonist and
a high dose of an inhaled corticosteroid who
High-dose ICS is required for a very small cohort of patients due to the increased risk of systemic side effects with this use.
In Step 2 of management, the daily use of a leukotriene receptor antagonist such as montelukast is recommended, however, GINA recommends that its use must be closely monitored and its benefits and risks considered by the clinician prescribing, given the US FDA warning that was issued in March 2020. The FDA warns that there is a serious risk of neuropsychiatric events including suicidality, nightmares, and behavioural problems among adolescents and adults prescribed this.
Children five years and younger
A diagnosis of asthma in young children with a history of wheezing is much more likely if: ▶ It is wheezing that is associated with exercise, laughing or crying, or in absence of any respiratory infection ▶ There is the presence of another allergic disease such as eczema or allergic rhinitis, allergen sensitisation or asthma in a first-degree relative. ▶ There is worsening of symptoms with cessation of controller treatment and clinical improvement during two-tothree months of treatment.
GINA recommends a probability approach and following symptom pattern in diagnosing asthma under the age of five.
Estimated probability of asthma diagnosis in under five-year-olds
▶ Symptoms (cough, wheeze and heavy breathing) for <10days during an upper respiratory tract infection with two-to-three episodes of this per year and no symptoms in between – few have asthma. ▶ Symptoms (cough, wheeze and heavy breathing) for >10 days during an upper respiratory tract infection, occurring three or more times per year and/or worsening at night-time, with often wheezy episodes in between – some have asthma. The goals of asthma management in young children are similar to adult management, with the objective being to achieve good control and maintain normal activity levels as well as minimising the risk of flare-ups, impaired lung development and side effects of medications
▶ Symptoms (cough, wheeze, and heavy breathing) for >10 days during upper respiratory tract infections with >three episodes per year, worsening of symptoms at night and a history of allergic sensitisation, atopic dermatitis, food allergy or positive family history – most have asthma.
The goals of asthma management in young children are similar to adult management, with the objective being to achieve good control and maintain normal activity levels as well as minimising the risk of flare-ups, impaired lung development, and side effects of medications.
GINA recommends that all wheezy episodes in children should be treated initially with inhaled SABA, regardless of a diagnosis of asthma being present.
Asthma management in general practice
The Asthma Society of Ireland has developed resources and training programmes aimed at GPs. These are up-to-date to reflect the new GINA 2020 guidelines.
Goals of long-term management remains to achieve and maintain symptom control and prevent any further exacerbations or mortality.
Regular review, assessment and adjustment where required will remain to ensure good adequate control of symptoms. The key to this is guiding self-management in the patient through education and training and ensuring formulation of an action plan to follow.
Uncertainty about disease severity, implications for quality-of-life and management can often lead to nonadherence and poor control.
Some barriers in general practice include the cost of devices, particularly some of the combined agents, and the unlicensed use of some of those recommended.
Summary
This article sets out the key changes in the GINA 2020 recommendations.
SABA use alone is no longer recommended for first-line.
For adults and adolescents over 12 years old, GINA recommends ICS in combination with formoterol for asneeded symptom relief .
Covid-19 presence does not change asthma management, but care must be taken with use of nebulisers and aerosol equipment due to risk of disseminating virus to others. n
FLEXIBILITY TO ADJUST TREATMENT AS NEEDED1,2
ONCE-DAILY ATECTURA® BREEZHALER®2

NEW LABA/ICS therapy option for your patients ≥12 years*2
Available in 3 doses:2
LOW IND/MF
125/62.5μg
MEDIUM IND/MF
125/127.5μg
HIGH IND/MF 125/260μg
1x daily
ATECTURA® BREEZHALER® is indicated as a maintenance treatment of asthma in adults maintenance treatment of asthma in adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older not and adolescents 12 years of age and older not adequately controlled with inhaled corticosteroids adequately controlled with inhaled corticosteroids and inhaled short-acting beta2-agonists.2

ONCE DAILY
ONCE-DAILY DOSING2
Abbreviated Prescribing Information Please refer to Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) before prescribing. Please refer to Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) before prescribing. Atectura® Breezhaler® (indacaterol (as acetate), mometasone furoate) inhalation powder, hard capsules.
Presentation: Hard capsules for inhalation available in three strengths: (indacaterol acetate/mometasone Hard capsules for inhalation available in three strengths: (indacaterol acetate/mometasone furoate) 150/80 mcg; 150/160 mcg; 150/320 mcg. Each delivered dose contains (indacaterol acetate/ furoate) 150/80 mcg; 150/160 mcg; 150/320 mcg. Each delivered dose contains (indacaterol acetate/ mometasone furoate): 125/62.5 mcg; 125/127.5 mcg; 125/260 mcg respectively. Indications: Indications: Maintenance Maintenance treatment of asthma in adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older not adequately controlled with inhaled treatment of asthma in adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older not adequately controlled with inhaled corticosteroids and inhaled short-acting beta2-agonists. Dosage and Administration: Dosage and Administration: Adults and adolescents Adults and adolescents aged 12 years and over: one capsule once daily, administered at the same time of the day each day, using the one capsule once daily, administered at the same time of the day each day, using the Atectura Breezhaler inhaler. The appropriate mometasone furoate dosage for the severity of disease should be Atectura Breezhaler inhaler. The appropriate mometasone furoate dosage for the severity of disease should be given and regularly reassessed. The maximum recommended dose is 125 mcg/260 mcg once daily. Capsules given and regularly reassessed. The maximum recommended dose is 125 mcg/260 mcg once daily. Capsules must not be swallowed. After inhalation, patients should rinse their mouth with water without swallowing. No must not be swallowed. After inhalation, patients should rinse their mouth with water without swallowing. No dose adjustment is required in elderly patients, in patients with renal impairment, or in patients with mild or dose adjustment is required in elderly patients, in patients with renal impairment, or in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. No data available for patients with severe hepatic impairment, only use in these moderate hepatic impairment. No data available for patients with severe hepatic impairment, only use in these patients if the expected benefit outweighs the potential risk. The safety and efficacy in paediatric patients below patients if the expected benefit outweighs the potential risk. The safety and efficacy in paediatric patients below 12 years of age have not been established. Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to the active substances or lactose monohydrate. Warnings/Precautions: Should not be used to treat acute asthma symptoms, including acute episodes of bronchospasm. Hypersensitivity: Immediate hypersensitivity reactions have been observed after administration. If signs suggesting allergic reactions occur, in particular angioedema, urticaria or skin rash, treatment should be discontinued immediately and alternative therapy instituted. Paradoxical bronchospasm: If paradoxical bronchospasm occurs, treatment should be discontinued immediately and alternative therapy instituted. Cardiovascular effects: Like other medicinal products containing beta2-adrenergic agonists, may produce a clinically significant cardiovascular effect in some patients as measured by increases in pulse rate, blood pressure, and/or symptoms. Use with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders (coronary artery disease, acute myocardial infarction, cardiac arrhythmias, hypertension), convulsive disorders, thyrotoxicosis, and in patients who are unusually responsive to beta2-adrenergic agonists. Long acting beta2-adrenergic agonists (LABA) or LABA containing combination products such as Atectura Breezhaler should be used with caution in patients with known or suspected prolongation of the QT interval or who are being treated with medicinal products affecting the QT interval. Hypokalemia: Beta2-adrenergic agonists may produce significant hypokalemia in some patients, which has the potential to produce adverse cardiovascular effects. The decrease in serum potassium is usually transient, not requiring supplementation. In patients with severe asthma hypokalemia may be potentiated by hypoxia and concomitant treatment, which may increase the susceptibility to cardiac arrhythmias. Hyperglycaemia: Inhalation of high dose of beta2-adrenergic agonists and corticosteroids may produce increases in plasma glucose. Upon initiation of treatment, plasma glucose should be monitored more closely in diabetic patients. Prevention of oropharyngeal infections: In order to reduce the risk of oropharyngeal candida infection, patients should be advised to rinse their mouth or gargle with water without swallowing it or brush their teeth after inhaling the prescribed dose. Systemic effects of corticosteroids: Systemic effects of inhaled corticosteroids may occur, particularly at high doses prescribed for prolonged periods. Should be administered with caution in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis or in patients with chronic or untreated infections. Excipients: Contains lactose. Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, total lactase deficiency or glucose galactose malabsorption should not take this medicinal product. Interactions: No specific interaction studies were conducted with indacaterol/mometasone medicinal product. Interactions: No specific interaction studies were conducted with indacaterol/mometasone furoate. Information on the potential for interactions is based on the potential for each of the monotherapy furoate. Information on the potential for interactions is based on the potential for each of the monotherapy components. components. Medicinal products that prolong QTc interval: Medicinal products that prolong QTc interval: Should be administered with caution in patients Should be administered with caution in patients being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, or medicinal products known to being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, or medicinal products known to prolong the QT-interval. prolong the QT-interval. Hypokalemic treatment: Hypokalemic treatment: Concomitant treatment with methylxanthine derivatives, Concomitant treatment with methylxanthine derivatives, steroids, or non-potassium sparing diuretics may potentiate the possible hypokalemic effect of beta steroids, or non-potassium sparing diuretics may potentiate the possible hypokalemic effect of beta2 adrenergic agonists. adrenergic agonists. Beta-adrenergic blockers: Beta-adrenergic blockers: Should not be given together with beta-adrenergic blockers Should not be given together with beta-adrenergic blockers unless there are compelling reasons for their use. CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein inhibitors: Inhibition of CYP3A4 unless there are compelling reasons for their use. CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein inhibitors: Inhibition of CYP3A4 and P-gp has no impact on the safety of therapeutic doses of Atectura Breezhaler. and P-gp has no impact on the safety of therapeutic doses of Atectura Breezhaler. Other long acting beta Other long acting beta2 adrenergic agonists: adrenergic agonists: Co-administration with other medicinal products containing LABA is not recommended. Co-administration with other medicinal products containing LABA is not recommended. Fertility, Pregnancy and Lactation: Fertility, Pregnancy and Lactation: Should only be used during pregnancy if the expected benefit to the Should only be used during pregnancy if the expected benefit to the patient justifies the potential risk to the foetus. No information available on the presence of indacaterol or patient justifies the potential risk to the foetus. No information available on the presence of indacaterol or mometasone furoate in human milk, on the effects on a breast-fed infant, or on the effects on milk production. mometasone furoate in human milk, on the effects on a breast-fed infant, or on the effects on milk production. A decision must be made whether to discontinue breast-feeding or to discontinue/abstain from therapy, taking A decision must be made whether to discontinue breast-feeding or to discontinue/abstain from therapy, taking into account the benefit of breast-feeding for the child and the benefit of therapy for the woman. Studies into account the benefit of breast-feeding for the child and the benefit of therapy for the woman. Studies do not indicate a concern regarding fertility in either males or females. Undesirable Effects: Very common (≥1/10): nasopharyngitis, asthma (exacerbation). Common (≥1/100 to <1/10): upper respiratory tract infection, hypersensitivity, headache, oropharyngeal pain, dysphonia, musculoskeletal pain. Uncommon (≥1/1,000 to <1/100): candidiasis, angioedema, hyperglycaemia, vision blurred, cataract, tachycardia, rash, pruritus, muscle spasms. Please consult the Summary of Product Characteristics for a detailed listing of all adverse events before prescribing. Pack Size(s): Single pack containing 10 x 1 or 30 x 1 hard capsules, together with one inhaler. Legal Category: POM. Product (Marketing) Authorisation Number(s): EU/1/20/1439/002, -006 & -010. Product (Marketing) Authorisation Holder: Novartis Europharm Limited, Vista Building, Elm Park, Merrion Road, Dublin 4, Ireland. Full prescribing information is available upon request from: Novartis Ireland Limited, Vista Building, Elm Park Business Park, Elm Park, Dublin 4. Tel: 01-2601255 or at www.medicines.ie. Detailed information on this product is also available on the website of the European Medicines Agency http://www.ema.europa.eu Prescribing Information last revised: May 2020.

Reporting suspected adverse reactions of the medicinal product is important to Novartis and the HPRA. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk profile of the medicinal product. All suspected adverse reactions should be reported via HPRA Pharmacovigilance, website www.hpra.ie. Adverse events could also be reported to Novartis preferably via www.report.novartis.com or by email: drugsafety.dublin@novartis.com or by calling 01 2080 612.
References: 1. Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention, 2020. Available at: https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/GINA-2020-full-report_-final-_wms.pdf. Date accessed: October 2020. 2. ATECTURA® BREEZHALER®. Summary of Product Characteristics. Available at www.medicines.ie Date access: October 2020. 3. van Zyl-Smit RN et al. Lancet Respir Med 2020; https://doi. org/10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30178-8.
azelastine hydrochloride / fluticasone propionate azelastine hydrochloride / fluticasone propionate
Treating allergic rhinitis patients all year round Treating allergic rhinitis patients all year round
Fast and effective treatment of allergic rhinitis symptoms1 Fast and effective treatment of allergic rhinitis symptoms1
2019 ARIA Guidelines 2019 ARIA Guidelines
recommends: a combination recommends: a combination therapy for moderate/severe therapy for moderate/severe allergic rhinitis patients allergic rhinitis patients uncontrolled on INAHuncontrolled on INAH or INS monotherapy or INS monotherapy8 8
Ef cacy con rmed Ef cacy con rmed in real life in real life6 6 Onset of action Onset of action within 30 minutes in within 30 minutes in clinical practice1 clinical practice1
Nasal & ocular Nasal & ocular symptom relief1, 2, 3symptom relief1, 2, 3
Well tolerated2, 7 Well tolerated2, 7 Suitable for long-term use4Suitable for long-term use4
Combination approach leads to clinical improvement days earlier Combination approach leads to than with FP or AZ alone5 clinical improvement days earlier
INS - Intranasal steroid INAH - Intranasal antihistamine AZ - Azelastine FP - Fluticasone Propionate than with FP or AZ alone5 ARIA - Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma ABBREVIATED PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: DYMISTA (AZELASTINE HYDROCHLORIDE / FLUTICASONE PROPIONATE) 137 MICROGRAMS / 50 MICROGRAMS PER ACTUATION, NASAL SPRAY, SUSPENSION.INS - Intranasal steroid INAH - Intranasal antihistamine AZ - Azelastine FP - Fluticasone Propionate Please refer to Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) before prescribing. Indications: Relief of symptoms of moderate to severe seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis if monotherapy with either intranasal antihistamine or glucocorticoid is not considered sufficient. ARIA - Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma Presentation: Nasal Spray, suspension. Dosage and administration: Posology For full therapeutic benefit regular usage is essential. Contact with the eyes should be avoided. Adults and adolescents (12 years and older) One actuation in each nostril twice daily (morning and evening). Children below 12 years Dymista Nasal Spray is not recommended for use ABBREVIATED PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: DYMISTA (AZELASTINE HYDROCHLORIDE / FLUTICASONE PROPIONATE) 137 MICROGRAMS / 50 MICROGRAMS PER ACTUATION, NASAL SPRAY, SUSPENSION. in children below 12 years of age as safety and efficacy has not been established in this age group. Elderly No dose adjustment is required in this population. Renal and hepatic impairment There are no data in patients with renal and hepatic impairment. Duration of treatment Dymista Nasal Spray is suitable for long-term use. The duration of treatment should correspond to the period of allergenic exposure. Method of administration Dymista Nasal Spray is for nasal use only. Instruction for use Preparing the spray: The bottle should be shaken gently before use for about 5 seconds by tilting it upwards and downwards and the protective cap be removed afterwards. Prior to first use Dymista Nasal Spray must be primed by pressing down and releasing the pump 6 times. If Dymista Nasal Spray has not been used for more than 7 days it must be reprimed once by pressing down and releasing the pump. Using the spray: The bottle should be shaken gently before use for about 5 seconds by tilting it upwards and downwards and the protective cap be removed afterwards. After blowing the nose the suspension is to be sprayed once into each nostril keeping the head tilted downward (see figure in section 4.2 of the SmPC). After use the spray tip is to be wiped and the protective cap to be replaced. Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to the active substances or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1 of the SmPC. Warnings and precautions: During post-marketing use, there have been reports of clinically significant drug interactions in patients receiving fluticasone propionate and ritonavir, resulting in systemic corticosteroid effects including Cushing’s syndrome and adrenal suppression. Therefore, concomitant use of fluticasone propionate and ritonavir should be avoided, unless the potential benefit to the patient outweighs the risk of systemic corticosteroid side-effects (see section 4.5 of the SmPC). Systemic Please refer to Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) before prescribing. Indications: Relief of symptoms of moderate to severe seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis if monotherapy with either intranasal antihistamine or glucocorticoid is not considered sufficient. Presentation: Nasal Spray, suspension. Dosage and administration: Posology For full therapeutic benefit regular usage is essential. Contact with the eyes should be avoided. Adults and adolescents (12 years and older) One actuation in each nostril twice daily (morning and evening). Children below 12 years Dymista Nasal Spray is not recommended for use in children below 12 years of age as safety and efficacy has not been established in this age group. Elderly No dose adjustment is required in this population. Renal and hepatic impairment There are no data in patients with renal and hepatic impairment. Duration of treatment Dymista Nasal Spray is suitable for long-term use. The duration of treatment should correspond to the period of allergenic exposure. Method of administration Dymista Nasal Spray is for nasal use only. Instruction for use Preparing the spray: The bottle should be shaken gently before use for about 5 seconds by tilting it upwards and downwards and the protective cap be removed afterwards. Prior to first use Dymista Nasal Spray must be primed by pressing down and releasing the pump 6 times. If Dymista Nasal Spray has not been used for more than effects of nasal corticosteroids may occur, particularly when prescribed at high doses for prolonged periods. These effects are much less likely to occur than with oral corticosteroids and may vary in individual patients and between different corticosteroid preparations. Potential 7 days it must be reprimed once by pressing down and releasing the pump. Using the spray: The bottle should be shaken gently before use for about 5 seconds by tilting it upwards and downwards and the protective cap be removed afterwards. After blowing the nose the systemic effects may include Cushing’s syndrome, Cushingoid features, adrenal suppression, growth retardation in children and adolescents, cataract, glaucoma and more rarely, a range of psychological or behavioural effects including psychomotor hyperactivity, sleep suspension is to be sprayed once into each nostril keeping the head tilted downward (see figure in section 4.2 of the SmPC). After use the spray tip is to be wiped and the protective cap to be replaced. Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to the active substances or to any of disorders, anxiety, depression or aggression (particularly in children). Dymista Nasal Spray undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism, therefore the systemic exposure of intranasal fluticasone propionate in patients with severe liver disease is likely to be increased. This may the excipients listed in section 6.1 of the SmPC. Warnings and precautions: During post-marketing use, there have been reports of clinically significant drug interactions in patients receiving fluticasone propionate and ritonavir, resulting in systemic corticosteroid effects including result in a higher frequency of systemic adverse events. Caution is advised when treating these patients. Treatment with higher than recommended doses of nasal corticosteroids may result in clinically significant adrenal suppression. If there is evidence for higher than Cushing’s syndrome and adrenal suppression. Therefore, concomitant use of fluticasone propionate and ritonavir should be avoided, unless the potential benefit to the patient outweighs the risk of systemic corticosteroid side-effects (see section 4.5 of the SmPC). Systemic recommended doses being used, then additional systemic corticosteroid cover should be considered during periods of stress or elective surgery. In general, the dose of intranasal fluticasone formulations should be reduced to the lowest dose at which effective control of the effects of nasal corticosteroids may occur, particularly when prescribed at high doses for prolonged periods. These effects are much less likely to occur than with oral corticosteroids and may vary in individual patients and between different corticosteroid preparations. Potential symptoms of rhinitis is maintained. Higher doses than the recommended one (see section 4.2 of the SmPC) have not been tested for Dymista. As with all intranasal corticosteroids, the total systemic burden of corticosteroids should be considered whenever other forms of systemic effects may include Cushing’s syndrome, Cushingoid features, adrenal suppression, growth retardation in children and adolescents, cataract, glaucoma and more rarely, a range of psychological or behavioural effects including psychomotor hyperactivity, sleep corticosteroid treatment are prescribed concurrently. Growth retardation has been reported in children receiving nasal corticosteroids at licensed doses. Since Dymista is also given to adolescents, it is recommended that the growth of adolescents receiving prolonged treatment disorders, anxiety, depression or aggression (particularly in children). Dymista Nasal Spray undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism, therefore the systemic exposure of intranasal fluticasone propionate in patients with severe liver disease is likely to be increased. This may with nasal corticosteroids is regularly monitored, too. If growth is slowed, therapy should be reviewed with the aim of reducing the dose of nasal corticosteroid if possible, to the lowest dose at which effective control of symptoms is maintained. Visual disturbance may be reported result in a higher frequency of systemic adverse events. Caution is advised when treating these patients. Treatment with higher than recommended doses of nasal corticosteroids may result in clinically significant adrenal suppression. If there is evidence for higher than with systemic and topical corticosteroid use. If a patient presents with symptoms such as blurred vision or other visual disturbances, the patient should be considered for referral to an ophthalmologist for evaluation of possible causes which may include cataract, glaucoma or recommended doses being used, then additional systemic corticosteroid cover should be considered during periods of stress or elective surgery. In general, the dose of intranasal fluticasone formulations should be reduced to the lowest dose at which effective control of the rare diseases such as central serous chorioretinopathy (CSCR) which have been reported after use of systemic and topical corticosteroids. Close monitoring is warranted in patients with a change in vision or with a history of increased ocular pressure, glaucoma and/or cataracts. If there is any reason to believe that adrenal function is impaired, care must be taken when transferring patients from systemic steroid treatment to Dymista Nasal Spray. In patients who have tuberculosis, any type of untreated infection, or have had a recent surgical operation or injury to the nose or mouth, the possible benefits of the treatment with Dymista Nasal Spray should be weighed against possible risk. Infections of the nasal airways should be treated with antibacterial or antimycotical therapy, but do not constitute a specific contraindication to treatment with Dymista Nasal Spray. Dymista contains benzalkonium chloride. It may cause irritation of the nasal mucosa and bronchospasm. Interactions with other medicinal products and other forms of interactions: Fluticasone propionate Under normal circumstances, low plasma concentrations of fluticasone propionate are achieved after intranasal dosing, due to extensive first pass metabolism and high systemic clearance mediated by cytochrome P450 3A4 in the gut and liver. Hence, clinically significant drug interactions mediated by fluticasone propionate are unlikely. A drug interaction study in healthy subjects has shown that ritonavir (a highly potent cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitor) can greatly increase fluticasone propionate plasma concentrations, resulting in markedly reduced serum cortisol concentrations. During postmarketing use, there have been reports of clinically significant drug interactions in patients receiving intranasal or inhaled fluticasone propionate and ritonavir, resulting in systemic corticosteroid effects. Co-treatment with other CYP 3A4 inhibitors, including cobicistat-containing products is also expected to increase the risk of systemic side-effects. The combination should be avoided unless the benefit outweighs the increased risk of systemic corticosteroid side-effects, in which case patients should be monitored for systemic corticosteroid side-effects. Studies have shown that other inhibitors of cytochrome P450 3A4 produce negligible (erythromycin) and minor (ketoconazole) increases in systemic exposure to fluticasone propionate without notable reductions in serum cortisol symptoms of rhinitis is maintained. Higher doses than the recommended one (see section 4.2 of the SmPC) have not been tested for Dymista. As with all intranasal corticosteroids, the total systemic burden of corticosteroids should be considered whenever other forms of corticosteroid treatment are prescribed concurrently. Growth retardation has been reported in children receiving nasal corticosteroids at licensed doses. Since Dymista is also given to adolescents, it is recommended that the growth of adolescents receiving prolonged treatment with nasal corticosteroids is regularly monitored, too. If growth is slowed, therapy should be reviewed with the aim of reducing the dose of nasal corticosteroid if possible, to the lowest dose at which effective control of symptoms is maintained. Visual disturbance may be reported with systemic and topical corticosteroid use. If a patient presents with symptoms such as blurred vision or other visual disturbances, the patient should be considered for referral to an ophthalmologist for evaluation of possible causes which may include cataract, glaucoma or rare diseases such as central serous chorioretinopathy (CSCR) which have been reported after use of systemic and topical corticosteroids. Close monitoring is warranted in patients with a change in vision or with a history of increased ocular pressure, glaucoma and/or cataracts. If there is any reason to believe that adrenal function is impaired, care must be taken when transferring patients from systemic steroid treatment to Dymista Nasal Spray. In patients who have tuberculosis, any type of untreated infection, or have had a recent surgical operation or injury to the nose or mouth, the possible benefits of the treatment with Dymista Nasal Spray should be weighed against possible risk. Infections of the nasal airways should be treated with antibacterial or antimycotical therapy, but do not constitute a specific contraindication to treatment with Dymista Nasal Spray. Dymista contains benzalkonium chloride. It may cause irritation of the nasal mucosa and bronchospasm. Interactions with other medicinal products and other forms of interactions: Fluticasone propionate Under normal concentrations. Nevertheless, care is advised when co-administering potent cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors (e.g. ketoconazole), as there is potential for increased systemic exposure to fluticasone propionate. Azelastine hydrochloride No specific interaction studies with circumstances, low plasma concentrations of fluticasone propionate are achieved after intranasal dosing, due to extensive first pass metabolism and high systemic clearance mediated by cytochrome P450 3A4 in the gut and liver. Hence, clinically significant drug interactions azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray have been performed. Interaction studies at high oral doses have been performed. However, they bear no relevance to azelastine nasal spray as given recommended nasal doses result in much lower systemic exposure. Nevertheless, care mediated by fluticasone propionate are unlikely. A drug interaction study in healthy subjects has shown that ritonavir (a highly potent cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitor) can greatly increase fluticasone propionate plasma concentrations, resulting in markedly reduced serum should be taken when administering azelastine hydrochloride in patients taking concurrent sedative or central nervous medications because sedative effect may be enhanced. Alcohol may also enhance this effect (see section 4.7 of the SmPC). Fertility, pregnancy and cortisol concentrations. During postmarketing use, there have been reports of clinically significant drug interactions in patients receiving intranasal or inhaled fluticasone propionate and ritonavir, resulting in systemic corticosteroid effects. Co-treatment with other CYP 3A4 lactation: Fertility There are only limited data with regard to fertility (see section 5.3 of the SmPC). Pregnancy There are no or limited amount of data from the use of azelastine hydrochloride and fluticasone propionate in pregnant women. Therefore, Dymista Nasal Spray should inhibitors, including cobicistat-containing products is also expected to increase the risk of systemic side-effects. The combination should be avoided unless the benefit outweighs the increased risk of systemic corticosteroid side-effects, in which case patients should be monitored be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the foetus (see section 5.3 of the SmPC) Lactation It is unknown whether nasally administered azelastine hydrochloride/metabolites or fluticasone propionate/metabolites are excreted in human for systemic corticosteroid side-effects. Studies have shown that other inhibitors of cytochrome P450 3A4 produce negligible (erythromycin) and minor (ketoconazole) increases in systemic exposure to fluticasone propionate without notable reductions in serum cortisol breast milk. Dymista Nasal Spray should be used during lactation only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the newborns/ infant (see section 5.3 of the SmPC). Effects on ability to drive and use machines: Dymista Nasal Spray has minor influence on the ability to concentrations. Nevertheless, care is advised when co-administering potent cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors (e.g. ketoconazole), as there is potential for increased systemic exposure to fluticasone propionate. Azelastine hydrochloride No specific interaction studies with drive and use machines. In isolated cases fatigue, weariness, exhaustion, dizziness or weakness that may also be caused by the disease itself, may occur when using Dymista Nasal Spray. In these cases, the ability to drive and use machines may be impaired. Alcohol may azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray have been performed. Interaction studies at high oral doses have been performed. However, they bear no relevance to azelastine nasal spray as given recommended nasal doses result in much lower systemic exposure. Nevertheless, care enhance this effect. Undesirable effects: Very common (≥1/10): Epistaxis. Common (>1/100, <1/10): Headache, dysgeusia (unpleasant taste), unpleasant smell. Uncommon (>1/1000, <1/100): Nasal discomfort (including nasal irritation, stinging, itching), sneezing, nasal should be taken when administering azelastine hydrochloride in patients taking concurrent sedative or central nervous medications because sedative effect may be enhanced. Alcohol may also enhance this effect (see section 4.7 of the SmPC). Fertility, pregnancy and dryness, cough, dry throat, throat irritation. For details of rare and very rarely reported adverse events see SmPC.lactation: Fertility There are only limited data with regard to fertility (see section 5.3 of the SmPC). Pregnancy There are no or limited amount of data from the use of azelastine hydrochloride and fluticasone propionate in pregnant women. Therefore, Dymista Nasal Spray should Reporting of suspected adverse reactions: Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via HPRA Pharmacovigilance, Earlsfort Terrace, IRL – Dublin 2; Tel: +353 1 6764971; Fax: + 353 1 6762517. Website: www.hpra.ie. E-mail: medsafety@hpra.ie. Adverse events should also be reported to Pharmacovigilance, Mylan, Building 4 – Trident Place, Hatfield Business Park, Mosquito Way, Hatfield, Hertfordshire, AL10 9BW, phone no: +44 (0) 800 121 8267, Email: UKPharmacovigilance@mylan.com. Legal Category: Product subject to prescription which may be renewed (B) Marketing Authorisation Number: PA2010/059/001 Marketing Authorisation Holder: Mylan IRE Healthcare Limited, Unit 35/36, Grange Parade, Baldoyle Industrial Estate, Dublin 13, Ireland. Full Prescribing Information available on request from: Mylan Dublin, Dublin 17. Phone 01 8322250. Date of revision of Abbreviated Prescribing Information: 20 Dec 2018 Item Code: IE-PI-Dymista-001 be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the foetus (see section 5.3 of the SmPC) Lactation It is unknown whether nasally administered azelastine hydrochloride/metabolites or fluticasone propionate/metabolites are excreted in human breast milk. Dymista Nasal Spray should be used during lactation only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the newborns/ infant (see section 5.3 of the SmPC). Effects on ability to drive and use machines: Dymista Nasal Spray has minor influence on the ability to drive and use machines. In isolated cases fatigue, weariness, exhaustion, dizziness or weakness that may also be caused by the disease itself, may occur when using Dymista Nasal Spray. In these cases, the ability to drive and use machines may be impaired. Alcohol may enhance this effect. Undesirable effects: Very common (≥1/10): Epistaxis. Common (>1/100, <1/10): Headache, dysgeusia (unpleasant taste), unpleasant smell. Uncommon (>1/1000, <1/100): Nasal discomfort (including nasal irritation, stinging, itching), sneezing, nasal dryness, cough, dry throat, throat irritation. For details of rare and very rarely reported adverse events see SmPC. References: Reporting of suspected adverse reactions: Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any 1. Meltzer E et al. MP29-02 (a novel intranasal formulation of azelastine hydrochloride and uticasone propionate) in the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ef cacy and safety. Allergy Asthma suspected adverse reactions via HPRA Pharmacovigilance, Earlsfort Terrace, IRL – Dublin 2; Tel: +353 1 6764971; Fax: + 353 1 6762517. Website: www.hpra.ie. E-mail: medsafety@hpra.ie. Adverse events should also be reported to Pharmacovigilance, Mylan, Building 4 – Trident Proc. 2012; 33(4):324–32. 2. Carr W, et al. A novel intranasal therapy of azelastine with uticasone for the treatment of allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012 May; 129(5): 1282-9 3. Hampel FC, et al. Double-blind placebo-controlled study of azelastine Place, Hatfield Business Park, Mosquito Way, Hatfield, Hertfordshire, AL10 9BW, phone no: +44 (0) 800 121 8267, Email: UKPharmacovigilance@mylan.com. Legal Category: Product subject to prescription which may be renewed (B) Marketing Authorisation Number: and uticazone in a single nasal spray delivery device. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2010; (105): 168-173 4. Dymista® Summary of Product Characteristics 5. Scadding GK, et al. BSACI guideline for the diagnosis and management of allergic rhinitis (Revised Edition 2017. First edition 2007). Clin Exp Allergy 2017. 47(7): 856-889. 6. Klimek L et al. Effectiveness of MP20-02 for the treatment of allergic rhinitis in real-life: Results from a non interventional study. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2015; 36:40-47 7. Berger PA2010/059/001 Marketing Authorisation Holder: Mylan IRE Healthcare Limited, Unit 35/36, Grange Parade, Baldoyle Industrial Estate, Dublin 13, Ireland. Full Prescribing Information available on request from: Mylan Dublin, Dublin 17. Phone 01 8322250. Date of revision of Abbreviated Prescribing Information: 20 Dec 2018 Item Code: IE-PI-Dymista-001 WE, et al. References: Long-term, Randomized Safety Study of MP29-02 (a Novel Intranasal Formulation of Azelastine Hydrochloride and Fluticazone Propionate in an Advanced Delivery System) in Subjects With Chronic Rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2014; 2:179-85. 8. Bousquet J, et al. Next-generation Allergic Rhinitis and Its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) guidelines for allergic rhinitis based on Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) and real-world evidence. J Allergy 1. Meltzer E et al. MP29-02 (a novel intranasal formulation of azelastine hydrochloride and uticasone propionate) in the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ef cacy and safety. Allergy Asthma Proc. Clin Immunol. 2019 2012; 33(4):324–32. 2. Carr W, et al. A novel intranasal therapy of azelastine with uticasone for the treatment of allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012 May; 129(5): 1282-9 3. Hampel FC, et al. Double-blind placebo-controlled study of azelastine and uticazone in a single nasal spray delivery device. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2010; (105): 168-173 4. Dymista® Summary of Product Characteristics 5. Scadding GK, et al. BSACI guideline for the diagnosis and management of allergic rhinitis (Revised Edition 2017. First edition 2007). Clin Exp Allergy 2017. 47(7): 856-889. 6. Klimek L et al. Effectiveness of MP20-02 for the treatment of allergic rhinitis in real-life: Results from a non interventional study. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2015; 36:40-47 7. Berger WE, et al. Long-term, Randomized Safety Study of MP29-02 (a Novel Intranasal Formulation of Azelastine Hydrochloride and Fluticazone Propionate in an Advanced Delivery System) in Subjects With Chronic Rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2014; 2:179-85. 8. Bousquet J, et al. Next-generation Allergic Rhinitis and Its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) guidelines for allergic rhinitis based on Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) and real-world evidence. J Allergy Item code: DYM-2020-0138Clin Immunol. 2019
Date of Preparation: May 2020