

YEAR 10
TABLE OF CONTENTS

INTRODUCTION TO THE YEAR 10 CURRICULUM GUIDE
We are pleased to provide you an overview of Learning Pathways intended to allow students to plan their own learning directions with the goal of achieving their individual potential.
The principles we have used to construct our curriculum at Caboolture are as follows:



Foundations
Grace implements the mandatory aspects of the three-dimensional Australian Curriculum from Year 7 and innovatively designs this curriculum to transition students into the QCAA Senior School model of the QCE.
Holistic Education
Grace prioritises an education for the whole person – spiritual, academic, physical, social-emotional, technological and cultural. As a result, mandatory aspects of the curriculum include Christian Studies/Religion and Ethics, Chapel, GEL, Sport and Outdoor Education (including the Googa program).
Personalised Pathways
Grace recognises the importance of student agency and creating their own personalised pathways based on the College’s offerings. The College aims to offer a wide range of learning opportunities for students and will enact innovative methods to facilitate these where practicable.
Connections
Grace incorporates authentic learning experiences through connections within local, national, or global communities. This includes but is not limited to intentional focuses on service-learning experiences and considering the ‘real world’ in problem-based learning experiences.
Empowered Learners
Grace encourages learning environments that nurture, mentor and facilitate learning allowing students to take control of their learning journey empowering them to unlock their potential and celebrate individual mastery.
We trust Grace students will enter the world having developed the skills and attitudes to live a life of faith and service so that God will be glorified in the world.
Yours in Christ
David Radke
Jason Miles Monique Atwell Head of College Head of Campus Deputy Head of Campus
THE YEAR 10 CURRICULUM AT GRACE
Grace is proud of encouraging a culture of personalised learning at the College. As part of the subject selection process, we achieve this by offering an extensive range of subject choices. This allows for a timetable to be constructed that in the main addresses the needs of the individual student.
Grace is committed to encouraging students to develop their gifts and talents. This is achieved through the carefully constructed ‘Grace Curriculum Journey’.
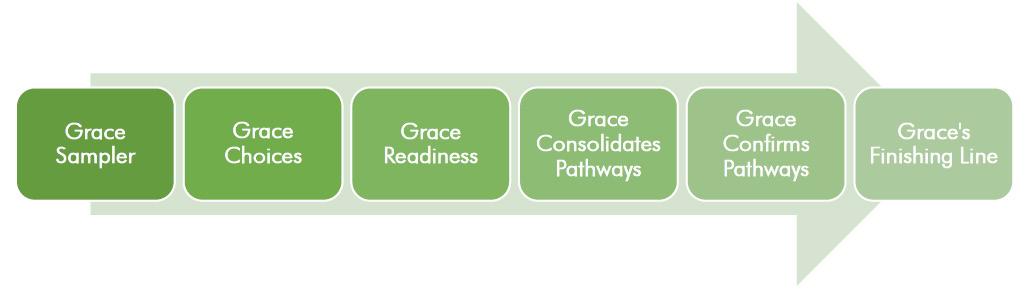
The Year 10 curriculum is named GRACE CONSOLIDATES PATHWAYS due to its core and elective curriculum design that has careful alignment to Year 11/12 directions. This allows students to consolidate pathways and subject appropriateness for senior studies.
Languages must be studied in Year 9 to be studied in Year 10 and it is recommended that they have been studied in earlier years.
DIVERSE LEARNING – Independent Learning (By Invitation only)
Independent Learning will be offered to students that meet the criteria as determined by Diverse Learning. This support program will be in lieu of an elective. Please contact Diverse Learning Lead at diverselearningcc@glc.qld.edu.au for further information.
ACADEMIC ENRICHMENT
Students who are identified as gifted and talented in the Senior School are case managed by the Academic Enrichment Coordinator. Academic Enrichment students will have meetings with their case manager and can make additional appointments as necessary by visiting the Cave. The Senior School focus is ensuring students are maximising their potential and striving towards their pathways beyond Grace. Contact academicenrichmentcc@glc.qld.edu.au
Career Guidance staff are available to support your child in their subject selection process. In addition, the College has a structured approach to ensure that all students in the Senior School are assigned a Careers Guidance Officer who manages their academic progress and supports their pathway choices beyond Grace.
Year 10
Year 11
Year 12
• Each student has a scheduled Careers Appointment in Semester 1
• Students who participate in the Career Profiling program will have an additional careers appointment to reflect on the program
• Each student has a scheduled Careers Appointment in Semester 2
• Each student has a scheduled Careers Appointment in Semester 1
• Each student has a second scheduled Careers Appointment in Semester 2 (focused on QTAC Applications)
Students can make Careers Appointments at any time by requesting this at the Pathways Centre.

There is a dedicated Grace Careers website page which provides information and support for students and for students once they have graduated. For more information on Grace Careers click here or email pathwayscc@glc.qld.edu.au
VOCATIONAL EDUCATION AND TRAINING (VET)
The College allows students to integrate Vocational Education and Training (VET) into their senior studies.
SCHOOL BASED CERTIFICATE QUALIFICATIONS OFF-CAMPUS QUALIFICATIONS
• Other qualifications are offered off-line or off campus at TAFE or a private provider and may include on-the-job training.
• Offered as part of the students’ timetables.
• Some students may choose to complete a school-based traineeship or commence a school-based apprenticeship in Year 10, 11 and 12.
The Registered Training Organisation (RTO) issues a Statement of Attainment for successfully completed VET units. These courses can lead to higher levels in vocational training or traineeships and apprenticeships.
STRATEGIES FOR CHOOSING SUBJECTS
It is suggested that subjects be chosen based on the following:
Subjects which may be prerequisites for further study
Keep your options open
Subjects which a student enjoys
Explore subjects offered at Grace
Personalised Pathways - Make decisions about a range of subjects
Be prepared to seek guidance
Subjects in which a student has already experienced some success
Subjects which provide an appropriate challenge to the student
Subjects which will help a student reach a chosen career or keep a wide range of options open
• Many students have thought about their future but are still uncertain
Subjects which will develop skills, knowledge and attitudes useful throughout the student’s life.
• It is therefore wise to keep options open. This makes it possible for students to develop their interests and abilities, which will then help them to decide on a study pathway or career choice
• Read the subject descriptions in this Curriculum Guide
• Refer to the Points of Contact page in this Curriculum Guide to discuss subjects
• Refer to the videos on the Subject Selection website
• Look at books and materials used by students in the subjects
• Ask questions about content and assessment types
• All students are individuals, and that their particular needs and requirements in subject selection will be quite different from those of other students.
• This means that it is unwise to either take or avoid a subject because:
o Someone told them that they will like or dislike it
o Their friends are or are not taking it
o They like or dislike the teacher
o Prejudice or Bias
• Students should be honest about their abilities and realistic with their career goals. There is little to be gained by continuing with or taking advanced levels of subjects that have proved difficult, even after students have put in their best efforts. Similarly, if career goals require the study of certain subjects, students must consider if they have the ability and determination to work hard enough to achieve the necessary level of results in those subjects.
• If students need more help, they should try to seek it. Refer to the Points of Contact page in this Curriculum Guide.
• Download the Tertiary Prerequisites guides, which are listed by tertiary institution and are designed to help students select their Senior subjects.
• Check tertiary prerequisites or recommended subjects by clicking here
Grace Careers
TAFE QLD
QLD Tertiary Admissions Centre (QTAC)
Myfuture Your Career
The Good Careers Guide Study Assist Graduate Careers
School-based apprenticeships and traineeships
Queensland Training Information Service
Queensland Training Subsidies List
www.gracecareers.com/ www.tafeqld.edu.au www.qtac.edu.au/ www.myfuture.edu.au www.yourcareer.gov.au www.goodcareersguide.com.au/ www.gooduniversitiesguide.com.au www.studyassist.gov.au/ GradAustralia
www.desbt.qld.gov.au/training/apprentices www.qtis.training.qld.gov.au/ www.desbt.qld.gov.au/training/training-careers/incentives
ALTERNATIVE DELIVERY MODES
Alternative Delivery modes are supported by the College where possible with the following focuses:
• Provide students with their subject choices as they continue their academic pathways.
• Focus on the quality of the education rather than the quantity of lessons.
• Personalised learning opportunities.
Alternative Delivery is at the discretion of the College. Subjects that do not meet the minimum number of student subscription per the class sizes guidelines are required to follow the alternative delivery guidelines.
The College acknowledges that Alternative Delivery best suits self-motivated and dedicated learners who are driven to succeed in the subject area. It may not be the preferred mode of learning for all students hence another subject choice may need to be considered. The College also notes that students can perform and achieve at a very high level when completing a subject using an alternative delivery mode.
Alternative Delivery may take the form of:
• Completing the subject at the same time as students completing the subject in another year level. (Traditionally referred to as composite classes)
Concurrent Delivery
Alternative Sequence
Alternative Delivery
• Each year level is studying their year levels content and completes their year levels assessment
• Completing the subject at the same time as students completing the subject in another year level
• The same content is delivered to each year level with year level appropriate assessment
• QCAA determines which subjects can be run using an Alternative sequence
• Reduced number of teacher contact lessons with the remainder of lessons supported in an online format such as TEAMS
• After school delivery in a once per week session eg 3.20 – 5.00pm
• Lunchtime lessons to avoid any other curriculum clashes
• Completely online delivery through TEAMS with a weekly teacher check-in
Online Learning
• The teacher could be based at either the Rothwell or Caboolture Campus
Subjects that have a history of using an Alternative Delivery mode of delivery, will be identified on their subject page in the Curriculum Guide. This does not confirm that this is their pre-determined delivery model for the year your child is selecting their subjects.
STUDY LESSONS
The Year 10 Curriculum at Grace is designed to be the junction point of the completion of the Australian Curriculum and the transition to the Senior System framework.
Based on student’s having the opportunities to experience as much of the curriculum as possible in preparation for Year 11 and 12, Year 10 students are not granted a Study Lesson. Where student’s meet the requirements of the College’s Flexible Learning Pathway guidelines, they may be granted a Study Lesson.
SUBJECT CHANGES
At times students may feel it is necessary to change their elective subjects for various reasons. A meeting with one of our Career Guidance staff is recommended. Students who want to change electives will need their parent/guardian to complete the “Application to Change a Subject” form accessible on Parent Lounge (click School Links then Curriculum Information).
Students cannot start attending the new elective subject until they have received an updated timetable (on eGrace). The deadline for subject changes can be found on the eGrace and Parent Lounge calendar, any requests received after this time will be held until the following term.
DISCLAIMERS

1. Staffing and/or resource constraints oblige the College to remove subjects which are not sufficiently supported by student subject selection. All students impacted, their lower preference choice will be selected, or they will be asked to reselect from the subjects available.
2. If an insufficient number of students choose a given subject, it will be withdrawn or offered as alternative delivery.
3. If a subject is oversubscribed class allocation will be based on the students’ preference order of the subject. (E.g. Students with the subject listed as a higher preference will be given priority in the subject).
4. If a subject is oversubscribed at the time of subject changes, class allocation and the associate waiting list, will be based on the date order of the subject change requests.
5. The electives in the curriculum each year will be arranged on timetable lines that optimises student choices.
6. It is possible that two subjects that a student wishes to study, may end up occurring on the same timetable line (therefore at the same time on the timetable). A choice will then have to be made between the two subjects.
POINTS OF CONTACT
If you or your child have questions about subjects or would like further information, the table below will guide you to the best point of contact.
Subject
Agents of Change
Business
Legal Studies
Digital Solutions
Dance Drama
Film TV & New Media
Music
Visual Art
English Essential English Literature
Japanese
Design
Food Studies
Practical Technology Skills*
Modern History
Health
Physical Education Health and Physical Education (Core)
Essential Mathematics
General Mathematics
Mathematical Methods
Specialist Mathematics
Religion & Ethics
General Science
Natural Science
Physical Science
STEM
Teacher Contact
Mrs Price caroline_price@glc.qld.edu.au
Mr Grieve shayne_grieve@glc.qld.edu.au
Ms Green penny_green@glc.qld.edu.au
Mrs Ledden nicole_ledden@gld.qld.edu.au
Miss Cronin lydia_cronin@glc.qld.edu.au
Mrs Brady rosemary_brady@glc.qld.edu.au
Mr Maunders peter_maunders@glc.qld.edu.au
Mrs Babey monique_babey@glc.qld.edu.au
Dr Ganendran billie_ganendran@glc.qld.edu.au
Role Teacher Email
Teaching & Learning
Diverse Learning Lead
Academic Enrichment Coordinator
Pathways Coordinator
Ms Atwell
Dr Ganendran teachingandlearningcc@glc.qld.edu.au
Ms Weatherill diverselearningcc@glc.qld.edu.au
Mrs McGucken academicenrichmentcc@glc.qld.edu.au
Mrs Barnes pathwayscc@glc.qld.edu.au
QUEENSLAND CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION (QCE)
Queensland’s senior secondary schooling qualification referred to as the QCE is internationally recognised and provides evidence of senior schooling achievements and is awarded when the specific requirements are met.
REQUIREMENTS FOR THE QCE
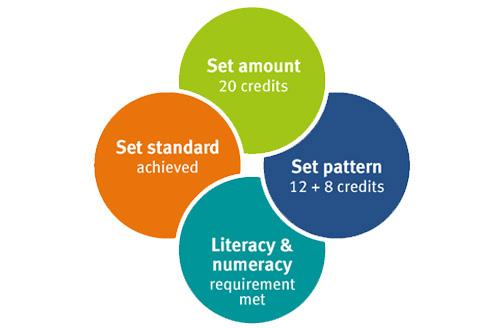
To receive a QCE, students must achieve the set amount of learning, at the set standard, in a set pattern, while meeting literacy and numeracy requirements.
The set amount is 20 credits from contributing courses of study, including:
• QCAA-developed subjects or courses
• Vocational education and training (VET) qualifications
• Non-Queensland studies
• Recognised studies.
Students must meet literacy and numeracy requirements.
A credit is the minimum amount of learning at the set standard that can contribute towards the QCE:
• A pass or ‘C’ grade for one semester of a school subject.
• Certificate I - Competent in all of the units
• Certificate II, III or IV - Competence in at least one quarter of the units.
• The number of credits allocated, depends on whether the VET qualification is Certificate II or higher; as not all vocational qualifications are given the same value.

To read more information about the QCE requirements and see fact sheets click here
MYQCE - LEARNING ACOUNT
The College assists students to track their progress/credits towards achieving a QCE during their senior school. Each student will have a learning account they can access using a Learner Unique Identifier (LUI) and a password.

To read more information and to access your child’s learning account click here
QUEENSLAND CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION (QCE)
Academic Monitoring is a holistic process where progress is monitored on a regular basis to:
REQUIREMENTS FOR THE QCE
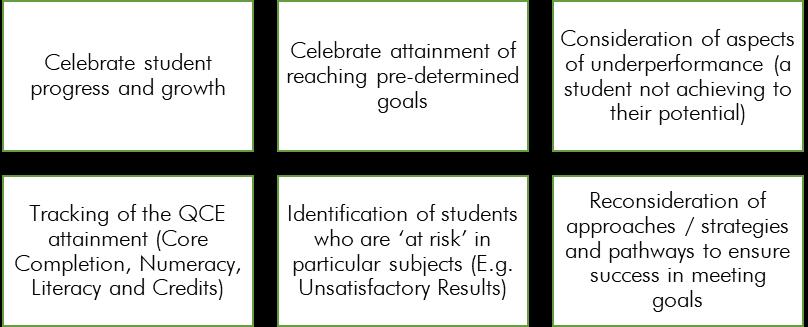
The Academic Monitoring process begins with the GEL Teacher from a holistic perspective, at regular intervals throughout the year. During this time in GEL, students review their own performance and self-reflect. Academic Monitoring is also conducted from a subject based lens, where the class teacher may refer a student’s under performance or risk in a particular subject to the Learning Lead.
POSSIBLE ACTIONS FROM ACADEMIC MONITORING:
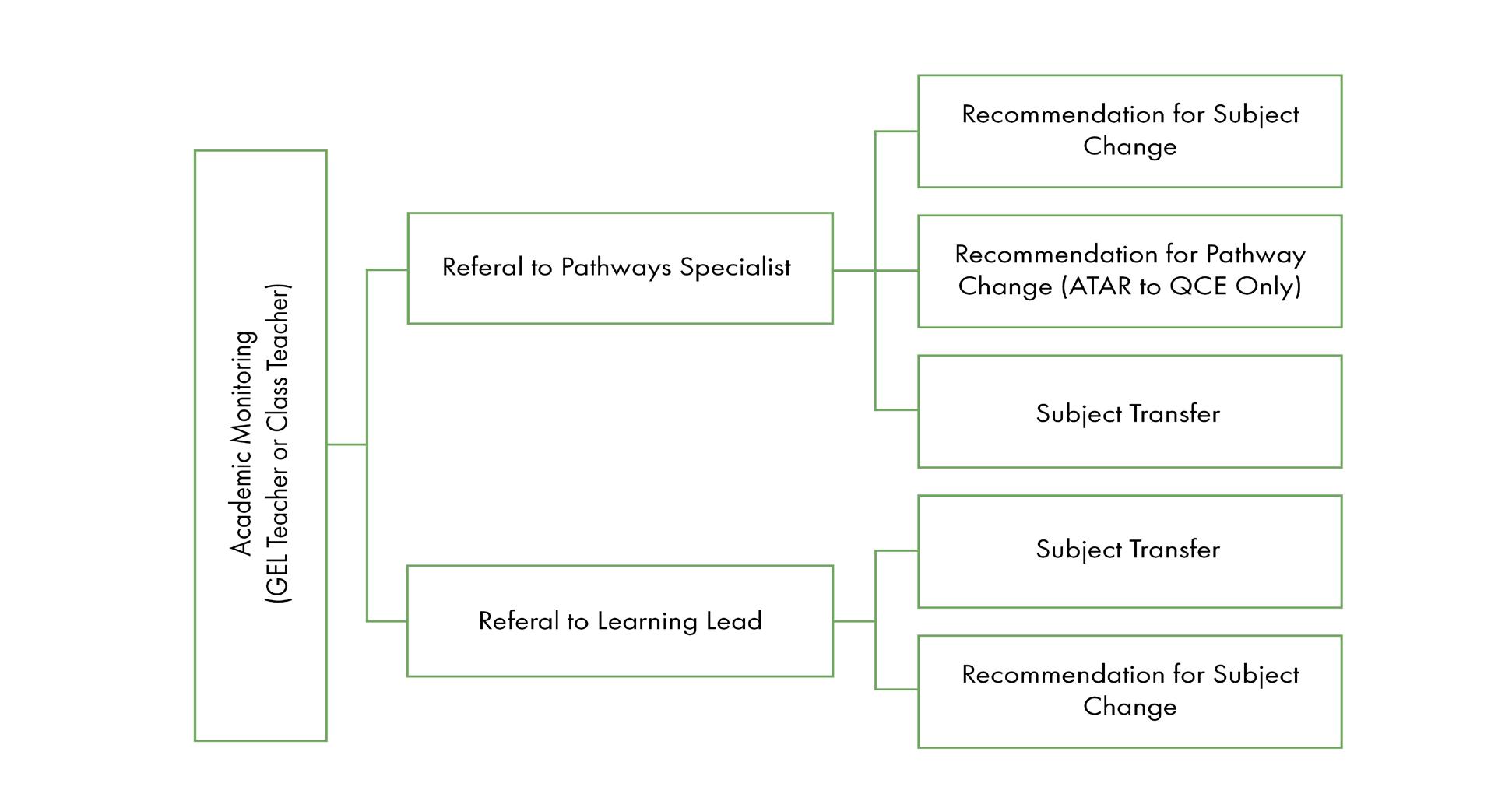
Recommendation for Subject Change
Subject Transfer
Recommendation for Pathway Change
College staff will contact the parent/guardian to recommend that the parent/ guardian submit a subject change via Parent Lounge for their child.
College staff will enact a subject change on behalf of the parent/guardian/student due to the child being at academic risk. The parent/guardian is advised after the transfer is enacted.
College staff will contact the parent/guardian to recommend that the student changes from an ATAR and QCE pathway to a QCE only pathway, generally due to academic performance or subject combinations taking into consideration a student’s pathway directions.
GENERAL SUBJECTS SUBJECT TRANSFER ACTION
• The student will meet with their Pathway specialist.
Receives an ‘Unsatisfactory’ result in Unit 1
Receives an ‘Unsatisfactory’ result across Unit 1 and 2
• A subject change will be recommended.
• Parents/guardians will be emailed to recommend that a subject change is submitted on Parent Lounge. (This may impact a student’s pathway changing from ATAR & QCE to QCE only)
• The student will meet with their Pathway specialist.
• A subject transfer will be enacted (where possible in the timetable design).
• Parents/guardians will be made aware that the change has occurred via email from the Pathway Specialist/Head of Department. (This may impact a student’s pathway changing from ATAR & QCE to QCE only)
Core Subjects
An English Subject
A Mathematics Subject
General Subjects
Elective Subjects
Applied Subjects
Course of study is based on a syllabus that has been issued by the Queensland Curriculum and Assessment Authority (QCAA) and involves an external exam.
Results count in the calculation of a student’s final school-based mark as well as their ATAR.
Course of study is based on a syllabus that has been issued by the QCAA but does not have an external exam.
Designed for students who may be exploring pathways after high school that do not involve university study.
Results count in the calculation of a student’s final school-based mark as well as their ATAR.
Vocational Certificate Subjects
Course of study results in competency in modules of work leading to the achievement of a certificate.
Queensland Tertiary Admission Centre (QTAC) is responsible for ATAR calculations and in turn determines the weighting of subjects (referred to as ‘inter-subject scaling’). Scaling is fluid year to year and can only ever be used as a guide.
A student can do a combination of subject types when determining their pathway, it is important to be aware that all subjects have different scaling when it comes to calculating the ATAR.


For more information and fact sheets from QTAC about the ATAR click here
For more information from Qtac about Scaling click here
STRUCTURE OF YEAR 11 AND 12
Unit 1 is typically started in Term 4 Year 10. All senior subjects are organised into 4 units of work. UNIT 1
FORMATIVE
Designed to prepare students for Unit 3 and 4 Unit 1 (Satisfactory Achievement) contributes 1 credit towards the QCE Unit 2 (Satisfactory Achievement) contributes 1 credit towards the QCE
UNITS 3 AND 4
3 Internal (schoolbased) Assessments
1 External Assessment
SUMMATIVE
Contributes towards a student’s ATAR Calculation Unit 3 and 4 (Satisfactory Achievement) must both be completed and collectively contribute 2 credits towards for the QCE
• Contributes to 75% of the subject’s overall result, except for Science and Mathematics subjects where it contributes 50%
• Instruments are endorsed for use by the QCAA with results confirmed by the QCAA
• Contributes to 25% of the subject’s overall result, except for Science and Mathematics subjects where it contributes 50%
• Exams are set and marked externally by the QCAA but facilitated by the College
AUSTRALIAN TERTIARY ADMISSION RANK (ATAR)
The Queensland Tertiary Admissions Centre (QTAC) is responsible for calculating ATARs. QTAC will calculate ATARs based on either:
A student’s best five General subject results OR
A student’s best results in a combination of four General subject results, plus one Applied learning subject result. (Eligible Applied learning subjects are a QCAA Applied subject, or Certificate III, or Certificate IV, or Diploma, or Advanced diploma)
If a student is eligible for an ATAR in both categories, QTAC will use their highest ATAR.
ATAR Eligibility requires students to attain a satisfactory result (equivalent to a Pass or ‘C’) of:
• A QCAA English subject - English, Essential English, Literature, English and Literature Extension.
While students must meet this standard to be eligible to receive an ATAR, it doesn’t mean a student’s English result to be included in the calculation of their ATAR.

For more information and fact sheets from QTAC about the ATAR click here
AUSTRALIAN TERTIARY ADMISSION RANK (ATAR)
In Year 11 and 12, students will have two pathways available to them:
University Entry
Work Readiness and Further Training
Students who wish to study at university to acquire degree level qualifications should select subjects that ensure ATAR eligibility. Applied subjects or Certificate III or IV courses will contribute to an ATAR but will not be scaled as highly as a General Subject in their contribution to the ATAR.
Students who are seeking to move to work or an apprenticeship and further training (through TAFE or other providers) after senior school are advised to select subjects and courses with embedded skills to prepare for this pathway.
The recommended study plan is:
• A minimum of five General subjects
• The sixth subject could be:
о A General Subject
о An Applied Subject
о A Certificate Course
The recommended study plan is:
• Any combination of Applied, Certificate and General Subjects to the equivalent of 6 Subjects.
• The program in Senior School could also include a School Based Apprenticeship or Traineeship.
Regardless of pathway, it is a College decision that students are required to study:
• An English subject.
• A Mathematics subject.
• Religion and Ethics. (Year 11 only)
• Health and Wellness (Year 11 only)
• Four other subjects according to one of the above pathways.
SUBJECT CHOICES FOR YEAR 10 2026
In Year 10 students are required to study all Core Subjects and 3 of the Elective Subjects listed below.
Religion and Ethics
English (English, Literature or Essential English)
Mathematics (General Mathematics, Mathematical Methods, or Essential Mathematics)
Core Subjects
Science (Science Natural and / or Science Physical or General Science)
Health and Physical Education
Agents of Change
Sport
Business
Dance
Design
Digital Solutions
Drama
Film, Television & New Media
Food Studies
Health
Japanese
Legal Studies
ELECTIVE SUBJECTS
(Choose Three of the Below)
Modern History
Music
Physical Education Practical Technology Skills*
Science Natural
Science Physical
Specialist Mathematics
STEM
Visual Art
Applied Subject marked *
Special requirements of VET qualifications are outlined at the back of this guide.
RELIGION AND ETHICS
APPLIED CORE
Religion and Ethics focuses on the personal, relational and spiritual perspectives of human experience. Students investigate and critically reflect on the role and function of religion and ethics in society.
Students investigate topics such as the meaning of life, spirituality, purpose and destiny, life choices, moral and ethical issues and justice and explore how these are dealt with in various religious, spiritual and ethical traditions. They examine how personal beliefs, values and spiritual identity are shaped and influenced by factors such as family, culture, gender, race, class and economic issues. Students gain knowledge and understanding and develop the ability to think critically and communicate concepts relevant to their lives and the world in which they live.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
In Year 10 students will complete Units 1 and 2 of the Senior QCAA RE applied course. They will then complete Units 3 and 4 in Year 11. Then in Year 12 students will undertake Service Learning Projects as three immersion days across Terms 1-3.
Semester 1
Term 1 - Unit 1 Sacred Stories - Sacred Story
Term 2 - Unit 1 Sacred Stories - What makes a story sacred?
Semester 2
Term 3 and 4 - Unit 2 World Religions and Spiritualities – Religious and Spiritual Diversity ASSESSMENT
There are three pieces of assessment in Year 10. These consist of an Investigation (written) and two Projects (product and evaluation).
- FIA1 – Project (product & evaluation) – Sacred Story Reimaging/ Recreation
- FIA2 – Investigation (Written) - What makes a story sacred?
- FIA3 – Project (product & evaluation) - Religious and Spiritual Diversity
Five dimensions are used to determine student achievement:
- Explain
- Examine
- Apply
- Communicate
- Evaluate
PREREQUISITES
There are no prerequisites for the subject.
PATHWAYS
In Year 10 RE students complete Unit 1 and 2 of the RE Applied subject. Units 3 and 4 will be completed in Year 11. Successful completion of the 4 Units can contribute towards a student’s ATAR score and QCE. A course of study in Religion and Ethics can establish a basis for further education in any field, as it helps students develop the skills and personal attributes necessary for engaging efficiently, effectively, and positively in future life roles. It helps students develop an understanding of themselves in the context of their family, their community, and the workplace.
ENGLISH (GENERAL) CORE
PRE-REQUISITES
Achieved a C or higher in Year 9 English
CO-REQUISITES Nil
The Year 10 English Course is underpinned by the fundamental requirements of Australian Curriculum in terms of General Capabilities and the three strands – Language, Literature and Literacy. This course prepares students for the rigours of Senior English by further developing the essential learnings including:
• An ability to shape texts that achieve a variety of cultural purposes.
• An understanding of a variety of texts in contexts.
• An ability to use language with accuracy and mastery.
• An understanding of the construction of a wide range of literary and non-literary texts.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Semester 1
Units of work undertaken in this semester accommodate the Googa experience. The units will include:
• Journey into Asia – Literary Essay
• Classic Stories – Imaginative text; writing a short story based on a poem
Semester 2
The units will include:
• Classic Novel – Analytical Essay (mock external exam)
• The World of Shakespeare: Persuasive Oral
Students will need to obtain a “C” average across written assessment to enter 11 English (General) or 11 Literature.
ASSESSMENT
The feature article is completed under open conditions.
• The imaginative persuasive script is written under supervised conditions.
• The analytical essay and the short story are written under exam conditions.
PREREQUISITES
English from Years 7-9.
PATHWAYS
Year 10 English is preparation for the rigorous demands of English and/or Literature in Years 11 and 12.
A course of study in English promotes open-mindedness, imagination, critical awareness, and intellectual flexibility — skills that can establish a basis for further education and employment and prepare students for local and global citizenship, and for lifelong learning across a wide range of contexts.
LITERATURE CORE
PRE-REQUISITES
Achieved a B or higher in Year 9 English
CO-REQUISITES Nil
Students in Literature will complete the same task types and units of study as English but with a focus solely on literary texts. This program is aimed at students who might be interested in studying Literature in Years 11 and 12. Some of the novels and text types do have increased difficulty compared with English. This subject prepares students for Senior English (General), Literature and English and Literature Extension.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Semester 1
• Literature of the Shoah – This unit explores the events of the holocaust through a range of literature including novels, film, poetry and art. Is asks the question, “how does literature create empathy?”
• Science Fiction Short Stories – Students explore a wide range of Bradburian narratives and create a similar narrative, in theme, genre and style.
Semester 2
• Study of a Classic Novel; Unseen Exam: write an analytical essay
• The World of Drama – The Taming of the Shrew: Write and perform a monologue, reimagining an aspect of the play.
The course is designed for entry into both Senior Literature or English
ASSESSMENT
The assessment for the year is designed to mirror Senior Literature and will consist of:
• Written literary essay (assignment)
• Written Creative task (assignment)
• Written analytical task (practice for external exams)
• Spoken creative (oral presentation)
ESSENTIAL ENGLISH CORE
PRE-REQUISITES
CO-REQUISITES
Nil
Nil
Essential English is a subject for students looking at a post school pathway that does not require an English (General) prerequisite. It has a greater focus on the practical uses of language. It has less focus on analysis and explores the function of language to create meaning across different mediums and contexts. The subject offers an alternative and promotes language efficiency especially as it relates to workplace communication.
In Semester One student’s study and write about Invasion Narratives and the Language of Protest. In Semester Two students complete the Literacy Short Course.
Success in Essential English in Year 11 and 12 does allow a student to be eligible for a QCE. The aim of this subject is to improve preparedness for work, apprenticeships, traineeships, or further study by increasing literacy skills.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Semester 1
• Invasion Narratives: Written Journal
• The Language of Protest: Seen and Unseen Response, Exam
Semester 2 - Literacy Short Course
• Unit One – Personal Identity: Create a website exploring Personal Identity
• Unit Two – Workplace Contexts; An oral identifying importance of 21st Century skills in modern workplaces
PATHWAYS
A course of study in Essential English develops and refines students’ understanding of language, literature, and literacy to enable them to interact confidently and effectively with others in everyday, community and social contexts and prepare students for further education and employment.
GENERAL MATHEMATICS CORE
PRE-REQUISITES
Achieved a C or higher in Year 9 Mathematics Or by consultation with the Learning Lead of Mathematics
CO-REQUISITES Nil
The mathematical concepts and processes in General Mathematics provide students with opportunities to make meaning of their world. It aims to give direction for students as lifelong learners who have knowledge of mathematics and when and where to apply their learned mathematics.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
• Number and Algebra – indices, scientific notation, fractions, financial transactions, variables, equations, manipulation of algebraic expressions, graphs.
• Measurement and Geometry – length, formulae for area, surface area and volume, capacity, tangent ratios, 2D & 3D shapes, cross section, properties of plane figures, latitude and longitude
• Statistics and Probability – samples, surveys, displaying data, experimental probability.
ASSESSMENT
Assessments include supervised Exams and Problem Solving and Modelling Tasks.
PREREQUISITES
Students must have completed and passed the course work at Year 9 level.
Approximately two hours of homework/study per week are expected in order to progress in the subject. Students are expected to bring the necessary equipment to each lesson which includes textbook, scientific calculator, black and red pens, pencil, ruler and notebook. Any necessary software will be supplied by the College being covered by the technology levy.
PATHWAYS
Year 10 General Mathematics is a prerequisite for Year 11 and 12 General Mathematics. Students studying Year 10 General Mathematics are NOT eligible to enrol in Year 11 Mathematical Methods. A course of study in General Mathematics can establish a basis for further education in the fields of business, commerce, education, finance, IT, social science, and the arts. General Mathematics is also a requirement for Biology in Year 11/12.
MATHEMATICAL METHODS CORE
PRE-REQUISITES
Achieved a B or higher in Year 9 Mathematics Or by consultation with the Learning Lead of Mathematics
CO-REQUISITES Nil
The mathematical concepts and processes studied in Year 10 Mathematical Methods prepare students for the high demands in Year 11 Mathematical Methods by providing them a solid foundation.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
• Number and Algebra – indices, scientific notation, surds, irrational numbers, financial transactions; equations, manipulation of algebraic expressions, graphs, quadratic and nonlinear functions, distributive law, factorisation, function notation, simultaneous equations
• Measurement and Geometry – length, area, surface area and volume, nets, capacity, trigonometric ratios, and their applications; 2D & 3D shapes, properties of plane figures, distance and mid-point formulae, similarity and congruence, latitude and longitude
• Statistics and Probability – samples, surveys, displaying data, experimental and theoretical probability
ASSESSMENT
Assessments include supervised Exams and Problem Solving and Modelling Tasks.
PREREQUISITES
Students must have completed the mainstream course work at Year 9 level. Experience shows that students who experience success in Year 10 Mathematical Methods have achieved a grade of B or better in Year 9 Mathematics.
Mathematical Methods is a developmental subject, and students need to maintain the knowledge and skills developed over the course. Homework is therefore essential to support and consolidate work done in class. Approximately two to three hours of homework/study per week are expected to progress in the subject. A graphing calculator is essential.
PATHWAYS
Year 10 Mathematical Methods is the prerequisite for Mathematical Methods in Year 11and 12. Students who have not studied Mathematical Methods in Year 10 should not expect to be enrolled in Year 11 Mathematical Methods.
A course of study in Mathematical Methods can establish a basis for further education in the fields of:
• Natural and physical sciences (especially physics and chemistry),
• Mathematics and science education, medical and health sciences (including human biology, biomedical science, nanoscience, and forensics),
• Engineering (including chemical, civil, electrical, and mechanical engineering, avionics, communications and mining),
• Computer science (including electronics and software design), psychology and business
ESSENTIAL MATHEMATICS CORE
PRE-REQUISITES Nil
PRE-REQUISITES Nil
Essential Mathematics is a subject into which students will be invited. It caters for students who have a history of difficulty and poor performance with the Core Maths topics. The subject concentrates on the basic concepts and skills and less on the applications.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Semester 1
• Number and Algebra – indices, scientific notation, fractions, financial transactions, variables, equations, manipulation of algebraic expressions, graphs
• Measurement and Geometry – length, formulae for area, surface area and volume, capacity, tangent ratios, 2D & 3D shapes, cross section, properties of plane figures, latitude and longitude
• Statistics and Probability – samples, surveys, displaying data, experimental probability.
Semester 2
QCAA Numeracy Short Course
The course is designed based on the needs of the students with a goal of ensuring students are ready for Senior Essential Mathematics. Upon successful completion, students will receive their Numeracy tick and one QCE point.
PATHWAYS
Students completing year 10 Essential Mathematics are primarily enrolled in Essential Mathematics in Year 11. Students who have done well in Essential Mathematics may ask to be enrolled in General Mathematics.
The aim of this subject is to improve preparedness for work, apprenticeships, traineeships, or further study by increasing basic numeracy skills.
A course of study in Essential Mathematics can establish a basis for further education in the fields of trade, industry, business, and community services.
SCIENCE (GENERAL) CORE
ELECTIVE
If Science General is chosen, then students will not be intending to take Science in Year 11. Students need to ensure this does not impact their pathway options in the future and a Pathways appointment would be recommended.
PRE-REQUISITES Nil
CO-REQUISITES Nil
This course follows the Australian curriculum and covers the content in Earth Science and Biology in Semester 1 and Physics and Chemistry in Semester 2. This course has practical focus and aims to engage students in finding solutions to real world problems.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Semester 1
Earth and Environmental Science – An exploration of the features of the universe. Students will investigate galaxies, stars and the solar system. They will explore the Big Bang Theory and how this can be used to explain the origins of Earth. They will also examine large scale cyclic processes of Earth and these processes can affect our day to day lives.
Biology – Students will explore how our genes influence the way our body functions. They will use models to understand patterns of inheritance. Students will investigate how natural selection causes changes to the gene pool. They will consider the use of genetic testing for genetic counselling, embryo selection and medical treatments. They will also explore ethical considerations around the release of our genetic information to industry via at home testing kits.
Semester 2
Chemistry – Students will investigate different types of chemical reactions and how they are used to produce a variety of products. They will explore how factors such as temperature and catalysts can influence the rate of these reactions. Students will be asked to make predictions about chemical reactions and gather data.
Physics - Students will explore how our understanding of energy transfers and transformations can be used to make our life easier. Students will perform a range of investigations to gather information on speed, acceleration, and forces. They will use the data they have collected to draw conclusions and evaluate claims made by others.
ASSESSMENT
The assessment is aimed at providing students the opportunity to demonstrate their understanding of the concepts covered throughout each term. Assessment includes:
• Written Tests
• Student Experiments
• Group Based Presentations
• Models and Prototypes
PATHWAYS
This course is designed for students who have an interest in science however are not intending to do Science in Year 11 and 12.
SCIENCE (NATURAL) CORE
PRE-REQUISITES
CO-REQUISITES
ELECTIVE
Nil
Nil
This course covers the content in Biology based on the Australian Curriculum in Semester 1. In Semester 2 the focus is on Psychology and Forensic Science. Psychology aims to engage with concepts that explain behaviours and underlying conditions. Biology aims to investigate natural systems of the living world and the diversity of organisms within it.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Semester 1
Biology – Natural Selection and Genetics. Investigating the mechanics of the transmission of genetic information from generation to generation and how changes accumulate over time to produce an evolutionary effect. Students are confronted with some of the ethical issues surrounding human manipulation of natural selection processes.
Biology – Cell Biology. Examining the parts and processes within plant and animal cells that allow life to flourish in a wide range of environments, experimentally investigating the actions of enzymes and how cells transport materials across the cell membrane.
Semester 2
Psychology – Sampling Methods, Experimental Design and Memory. Exploring the scientific method, experimental design, data collection and research within Psychology. Students will examine cognitive psychology with a minor focus on memory.
Forensic Science – Investigating the scientific techniques used to solve crimes, including fingerprint analysis, DNA profiling, and crime scene investigation. Through hands-on experiments and case studies, students develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills while uncovering the real science behind criminal investigations.
ASSESSMENT
The assessment to model the types of assessment experienced in Year 11 and 12 to prepare students for the rigours of senior science. Assessment includes:
• Data Tests and Written Exams
• Research Investigations and
• Student Experiments (incorporating research, modifying, and conducting experiments).
PATHWAYS
Natural Science leads to Year 11 and 12 Biology and/or Psychology.
A course of study in Biology can establish a basis for further education in the fields of medicine, forensics, veterinary, food and marine sciences, agriculture, biotechnology, environmental rehabilitation, biosecurity, quarantine, conservation, and sustainability.
A course of study in Psychology can establish a basis for further education in the fields of psychology, sales, human resourcing, training, social work, health, law, business, marketing and education.
SCIENCE (PHYSICAL)
PRE-REQUISITES
CO-REQUISITES
CORE
ELECTIVE
Passing grade in Year 9 Science
It is strongly recommended that students are enrolled for Mathematical Methods as the underpinning theory of mathematics will support students in achieving success in this course.
This course covers the content in Physics and Chemistry in the Australian Curriculum. The subject provides a foundation of knowledge combined with investigative, analytical, and experimental skills that will support students in their study of the Year 11 and 12 Physics and Chemistry.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
The universe can be divided into two aspects: matter and energy.
• Chemistry is the study of the matter in the universe.
• Physics is the study of energy and its relationship with matter.
Chemistry-focused units. The relationships and trends of the elements that make up the Period Table are studied and students apply this knowledge to predict and use the characteristics of elements. Influences on reaction rates are explored and skills in writing chemical formulas and balanced chemical equations are developed.
Physics-focused units. The concepts of motion, force and energy are investigated. Students investigate Kinematics and Forces, including friction, through experimental investigations and Electrical Circuits through building and testing circuits.
ASSESSMENT
The assessment to model the types of assessment experienced in Year 11 and 12 to prepare students for the rigours of senior science. Assessment includes:
• Data Tests and Written Exams
• Research Investigations and
• Student Experiments (incorporating research, modifying, and conducting experiments).
PATHWAYS
Physical Science leads to Year 11 and 12 Chemistry and/or Physics.
A course of study in Chemistry can establish a basis for further education in the fields of forensic science, environmental science, engineering, medicine, pharmacy, and sports science.
A course of study in Physics can establish a basis for further education and employment in the fields of science, engineering, medicine, and technology.
HEALTH AND PHYSICAL EDUCATION
PRE-REQUISITES Nil
CO-REQUISITES Nil
Students will investigate dietary recommendations and guidelines as well as establishing the skills to identify and establish healthy eating habits for a range of contexts throughout life. Students learn how to develop behaviours and attitudes that promote healthy, safe, and respectful relationships. Additionally, students will be involved in a range of physical activities that cover essential physical movements across different age groups. They will learn to engage through and about physical activity and be exposed to a range of activities they may be able to continue after leaving Grace Lutheran College.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
• Food and Nutrition
• Respectful Relationships
• Games theory and coaching session activities
• Rhythmic Activities
• Racquet sports
ASSESSMENT
Assessment of progress in Physical Education will follow these criteria:
• Progressive and ongoing assessment of skills, application of these, and evaluation of game play situations
• In-class written skills in the form of essays, reflections and portfolios of work.
PREREQUISITES
Health and Physical Education is a subject all students are required to complete. There are no prerequisites for this subject.
AGENTS OF CHANGE CORE
PRE-REQUISITES
CO-REQUISITES
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Nil
Nil
In this dynamic subject Agents of Change (AOC), students are encouraged to initiate transformations within their communities, whether on a local, national, or global scale, by utilising social-entrepreneurial skills developed through a college design thinking process.
Students set forth on a path of empathy, investigation, idea generation, prototyping, and refinement, under the guidance of design thinking principles. Emphasising social entrepreneurship, students acquire the skills to craft enduring solutions that tackle societal issues. Through promoting teamwork, analytical reasoning, and innovation, this the AOC program nurtures a cohort of forward-thinking individuals ready to enact substantial positive changes.
This educational program empowers students with a diverse array of transferable skills crucial for thriving beyond their academic journey. The collaborative environment encourages effective communication and teamwork, equipping students for success in varied professional settings. Students emerge from this experience with a sense of empowerment and a dedication to social responsibility, ready to lead purposeful lives and catalyse positive change within their communities and beyond.
PRESENTATION OF LEARNING
At the conclusion of this unit, students will exhibit their innovative real-world solutions in an interactive showcase for the community. By effectively communicating their concepts to a diverse audience, students enhance their public speaking and presentation skills, building confidence in expressing their perspectives and advocating for their innovations.
The community showcase not only celebrates the students’ accomplishments but also encourages dialogue and collaboration between students and community members, nurturing a sense of shared responsibility and investment in addressing critical societal issues. Ultimately, this culminating event applauds the students’ creativity and dedication to effecting meaningful change in the world, inspiring others to join them in their quest for positive transformation.
PRE-REQUISITES
Nil. However, studying Business in Years 8 and 9 would be advantageous.
CO-REQUISITES Nil
The study of Business is relevant to all individuals in a rapidly changing, technology-focused and innovation-driven world. Through studying Business, students are challenged academically and exposed to authentic and real-life practices. The knowledge and skills developed in Business will allow students to contribute meaningfully to society, the workforce and the marketplace and prepare them as potential employees, employers, leaders, managers and entrepreneurs of the future.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
The Economy, government Policy and You: - Students analyse how economic indicators influence Australian Government decision-making. They explain ways that government intervenes to improve economic performance and living standards.
Australia’s Superannuation System - Students explain the importance of Australia’s superannuation system and its effect on consumer and financial decision-making. They interpret and analyse information and data to evaluate trends and economic cause-and effect relationships and make predictions about consumer and financial impacts.
Managing People– They explain processes that businesses use to manage the workforce and improve productivity. They develop an evidence-based response to an economic and business issue. They evaluate a response, using appropriate criteria to decide on a course of action.
Financial Decision Making– Students analyse how economic indicators influence Australian Government decisionmaking. They explain ways that government intervenes to improve economic performance and living standards.
ASSESSMENT
Assessment techniques include:
• Combination Response Examinations
• Feasibility Report
• Investigation Business Report
PATHWAYS
• Year 11 and 12 Business
• Year 11 and 12 Legal Studies
• University degrees, TAFE certificates and diplomas in Business as well as Law and Justice Studies
• Business employment opportunities - management opportunities, entrepreneur, small business owner, marketing research, foreign trade and investment, education, real estate and finance.
DANCE ELECTIVE
PRE-REQUISITES
Middle School Dance is highly recommended
CO-REQUISITES Nil
Dance is made available for students from a wide range of abilities and experiences. The program seeks to provide a foundation for performance, choreography and appreciation as well as offers those students who are already skilled practitioners, opportunities to extend themselves. Dance aims to foster creative and expressive communication. It uses the body as an instrument for expression and communication of ideas. It provides opportunities for students to critically examine and reflect on their world through higher order thinking and movement. It encourages the holistic development of a person, providing a way of knowing about oneself, others and the world. Students apply critical thinking and literacy skills to create, demonstrate, express and reflect on meaning made through movement. Exploring dance through the lens of making and responding, students learn to pose and solve problems, and work independently and collaboratively. They develop aesthetic and kinaesthetic intelligence, and personal and social skills.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Students study dance in various genres and styles, embracing a variety of cultural, societal and historical viewpoints integrating new technologies in all facets of the subject. Historical, current and emerging dance practices, works and artists are explored in global contexts and Australian contexts, including the dance of Aboriginal peoples and Torres Strait Islander peoples. Students learn about dance as it is now and explore its origins across time and cultures.
POSSIBLE UNITS OF STUDY
• Narrative Connections // Fusion Dance: Students explore a fusion of dance genres including Contemporary, Jazz, Hip Hop and Lyrical. They discover how key choreographers can influence their own hybrid choreographic and performance style.
• Cultural Connections // World Dance: Asian forms, Classical Indian and Bollywood. Students explore the technical and expressive skills of performing in the Bollywood style.
• Urban Connections // Stomp and Film: Stomp, Body Percussion and Hip Hop. Students explore the use of alternate spaces in which to choreograph and film their work.
• 21st Century Connections // Dance on Film: Students appreciate the technical and artistic choreographic works of filmed Contemporary performance.
ASSESSMENT
• Choreographing: Students use dance components to create movement and to structure and organise dance into a cohesive whole that reflects an intent.
• Performing: Performance is concerned with the development of physical, expressive, and technical skills in both informal and formal settings. Through engaging in, and reflecting on performance, students realise the body’s potential as an instrument of expression, developing positive self-esteem and building confidence in personal physicality.
• Responding: Dance Appreciation involves students analysing their own and others’ dance across a range of contexts. Through dance appreciation, students develop an understanding that dance is a recognised and popular form of social interaction and is a living expression of culture, spirituality, and history.
• Project: Students will complete a project that integrates performing, choreography and responding.
PATHWAYS
Dance is a course that assists students in developing a variety of skills in choreographing, performing and appreciation of Dance, which are widely transferrable and highly relevant to the study of the senior subject, tertiary study and beyond. Collaboration, communication, creativity, and critical reflection are all highly relevant 21st century workplace requirements gained in study of this subject.
A course of study in Dance can establish a basis for further education in the field of dance, and to broader areas and careers such as, Physiotherapy, education, arts administration and communication, sports science, director etc.
DESIGN ELECTIVE
PRE-REQUISITES Nil
CO-REQUISITES Nil
Design focuses on the practical application of problem solving, design thinking, visual communication, and prototyping skills. The program explores design fundamentals with a view to creating designs for the future. Students will develop higher order thinking skills and learn a variety of design presentation and communication techniques. This subject has been designed to extend concepts commenced in Middle School Design, further developing skills and techniques for real world application in design. Design is a critical part of solving some of the major issues facing our planet in the 21st century through innovative and visionary thinking.
• To develop the fundamentals of Graphical communication
• Promote literacy in the language of Design.
• Foster the ability to produce drawings of real articles.
• Equip students with problem solving skills.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Design principles.
• Design Thinking
• Design style.
• Prototyping
• Collaborative Design
• Evaluation and refinements of design ideas.
Students have the opportunity to design and make projects from a design brief based on a set project with clear guidelines. Students will make wood, metal, plastics, and electronics projects, with personal touches being added to individualise their projects.
ASSESSMENT
Design Folios
Design Challenge exams
PREREQUISITES
This course is designed to further develop students’ knowledge and understanding of materials, equipment and techniques within the practical area, building on their experiences of Year 8 and Year 9, however, there is no prerequisite for Design in Year 10.
PATHWAYS
Design gives students an invaluable set of skills for many careers including but not limited to: Architecture, Engineering, Drafting, Interior Design, Fashion Design or trades like Building, Landscaping, Manufacturing and Jewellery making.
DIGITAL SOLUTIONS
PRE-REQUISITES
CO-REQUISITES
ELECTIVE
Achieved a B or higher in Year 9 Mathematics
English, General Mathematics
In Digital Solutions, students learn about algorithms, computer languages and user interfaces through generating digital solutions to problems. They engage with data, information and applications to create digital solutions that filter and present data in timely and efficient ways while understanding the need to encrypt and protect data. They understand computing’s personal, local, and global impact, and the issues associated with the ethical integration of technology into our daily lives.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Students engage in problem-based learning that enables them to explore and develop ideas, generate digital solutions, and evaluate impacts, components, and solutions. Learning in Digital Solutions provides students with opportunities to create, construct and repurpose solutions that are relevant in a world where data and digital realms are transforming entertainment, education, business, manufacturing, and many other industries.
Digital Solutions develops the 21st century skills of critical and creative thinking, communication, collaboration and teamwork, personal and social skills, and information and communication technologies (ICT) skills that are critical to students’ success in senior Digital Solutions, further education, and life. Students will study units including: Visual Basic, SQL, Databases and Web design.
Students will delve into comprehending real-life challenges, pinpointing areas for enhancement, and devising creative solutions.
ASSESSMENT
Assessment techniques include:
• Short Response Examinations
• Investigation – Project
• Project – Digital Solution
REQUIREMENTS
All the software used in Digital Solutions is Windows based and as such students must have a device that supports this.
PATHWAYS
This subject prepares students for Year 11/12 Digital Solutions. Digital Solutions prepares students for education in a variety of digital contexts. It develops thinking skills that are relevant for digital and non-digital real-world challenges. A course of study in Digital Solutions can establish a basis for further education in the fields of science, technologies, engineering and mathematics.
DRAMA ELECTIVE
PRE-REQUISITES
Nil. However previous study of Drama is advantageous
CO-REQUISITES Nil
Year 10 Drama is a natural progression from the Year 9 subject and provides an opportunity for students to further develop their skills in the areas of performance, creation of dramatic material and analysis of dramatic works, as well as advancing their grasp of the dramatic languages and performance technologies. Students continue to work independently and collaboratively as innovative, imaginative and resourceful problem solvers. Direct links are made with current and emerging practices to encourage students to connect with a range of career possibilities. Drama fosters creative and expressive communication: investigating, communicating and embodying stories, experiences, emotions and ideas that reflect the human experience across time and various cultural contexts, allowing students to discover different perspectives of themselves, others and the world in which they live.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Units for study may include:
• Shakespearean performance transformed through Cinematic Theatre and a comic ‘She’s the Man’ revision of ‘Twelfth Night’. Students will polish their performance skills and engage with stagecraft such as lighting, sound, costume, props, set and industry standard technologies.
• Students experiment with the components of Physical Theatre to create dynamic and meaningful movement pieces, whilst honing and extending their energy, focus, control and ensemble awareness.
• A fusion study of ancient Greek Tragedy, compelling Indigenous stories and empowering Theatre of the Oppressed processes culminating in a Contemporary Performance.
• Beginning AS Unit 1 or 3: bringing our stories to life in linear and non-linear forms.
ASSESSMENT
Assessment instruments include:
• Scripted Performance
• Devised Performance
• Analytical response
REQUIREMENTS
There are no prerequisites for this subject. However, study of Drama in Years 8 and 9 is of great benefit. Students are encouraged to attend live dramatic performances and participate in school-based and cocurricular drama activities. Students are required to have black performance clothes: plain black shirt and plain black pants that allow movement.
PATHWAYS
Drama is a course, which provides opportunities for a wide variety of career ambitions. The ability to speak and act confidently is a universally useful skill. Collaboration, communication, creativity, and critical reflection are all highly relevant 21st century workplace requirements gained in study of this subject, as well as the range of skills developed in the making and presenting of Drama works and responding to them. Students considering careers in the fields of communication, entertainment, social media, advertising, education, politics, law, psychology, journalism, and social justice, amongst others, will benefit from this course. The course directly links to and is of great benefit to those looking to study the Drama course in Year 11 and 12.
FILM, TELEVISION AND NEW MEDIA
PRE-REQUISITES Nil
CO-REQUISITES Nil
Film, Television & New Media are our primary sources of information and entertainment. They are important channels for educational and cultural exchange and are fundamental to our self expression and representation as individuals and as communities. Through making and responding to moving-image media products, students will develop a respect for diverse perspectives and develop knowledge and skills in creative thinking, communication, collaboration, and planning, critical analysis, digital and ethical citizenship. Students will develop the necessary critical and creative skills to reflect on and appreciate Australian and global cultures and make sense of what they see and experience. Film, Television & New Media will equip students for a future of unimagined possibilities with highly transferable and flexible thinking and communication skill.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Documentaries
Construct pre-production proposals to communicate a documentary concept or idea
• Synthesis media sequences that communicate the real or a satirical representation of the real
• Research and explore notions of “the real”
Music Videos
• Compare and critique the distribution methods used in music videos to sell the artist
• Critically discuss the evolution of old to new technology and how this has changed the music industry
• Design their own music video using a range of pre-production formats
• Create a music video through use a diverse range of production technologies. Foundations for Film, Television and New Media (Senior Syllabus Unit 1)
Develop understanding of foundational concepts and processes used in Film, Television and New Media.
ASSESSMENT
Students’ complete assignments in two different strands: MAKING and RESPONDING.
• Technologies (use of cameras, lighting, and sound equipment, editing and use of other software)
• Representations (designing a stereotyped character, analysing the representation in a media text)
• Institutions (analysing the companies and organisations that produce the media)
• Audiences (designing a piece with a particular audience in mind, analysing a target audience)
• Languages (analysing the film techniques used in a sequence, designing a film with a range of techniques).
REQUIREMENTS
This subject might involve filming outside of school hours and on weekends. Students need earphones for when editing and a USB/external Hard drive for backing up their production work.
PATHWAYS
This subject prepares students for and gives a pathway into leads to Film, Television & New Media (General Subject) or Media Arts in Practice (Applied) in Year 11 & 12. A course of study in Film, Television & New Media can establish a basis for further education in fields that are experiencing unprecedented growth, such as Film and Television Production, Marketing, Journalism, Web Design, App Design, Animation, Online Publishing and Game Design.
FOOD, FASHION AND HOSPITALITY
ELECTIVE
PRE-REQUISITES Nil
CO-REQUISITES Nil
Food, Fashion and Hospitality is an introduction to Food and Nutrition, Fashion and Hospitality Practices. It provides students an introduction to the design process of textiles and the fashion industry, the study of food in the context of food science, nutrition, and food technologies, and delivers an understanding of hospitality and the structure, scope and operation of related activities in the food and beverage sector.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Students will explore Food and Nutrition at an introductory level:
• The food system – the role of nutrients
• The role of nutrients
• The chemical, physical and functional properties of food
• The use of food experiments to understand the chemical properties of protein, fats and carbohydrates
• Taste Testing of a variety of food products for sensory evaluation purposes
• Investigate and develop food prototypes
• Application of scientific concepts in practical cookery
Students will explore Hospitality at an introductory level:
• Basic Hospitality skills, food service and preparation
• Responsible Service of Alcohol RSA (optional and additional cost)
Students will explore Fashion and Design at an introductory level:
• What is design?
• Using a design process
• Designing for individuals or groups using the Principles of Good Design
• Building on already developed textile skills
• An introduction to the Fashion Industry ~ Designers and Merchandising
ASSESSMENT
Project Folio, Multimodal Presentations and Products, Functions
PREREQUISITES
There is no prerequisite for Food, Fashion and Hospitality. Students need not have done Food Studies in Years 8 and/or 9.
PATHWAYS
This subject prepares students for and gives a pathway into Yr 11 and 12 Food & Nutrition, Design (General Subject) and Hospitality and Fashion (Applied Subject).
A course of study in Design can establish a basis for further education in the fields of architecture, digital media design, fashion design, graphic design, industrial design, interior design, landscape architecture, personal styling, costume design, production manufacture, merchandising, and retail. While a course of study in food & Nutrition and Hospitality can establish a basis for further education food technology; science, majoring in food, or majoring in both food and nutrition; exercise and nutrition science; nutrition science; nutrition; dietetics.
PRE-REQUISITES Nil
CO-REQUISITES Nil
Health is a quality of life that is influenced by the interaction between individuals and their socio-cultural, physical, political, and economic environments. Students who study this subject investigate content that focuses on how health can be promoted so that individuals and groups can achieve better health outcomes. Students use an inquiry approach to investigate sustainable health change at personal, peer, family and community levels from a Salutogenic perspective. Students will cover a broad range of health topics and plan, implement, evaluate, and reflect on action strategies that promote health.
By completing this course students will develop the skills required to recognise health issues, use health frameworks, investigate, and develop strategies to improve health, and evaluate strategies in a range of settings. Please Note: There are distinct differences between the subjects Health and Physical Education. Health is a theoretical social science subject that does not contain any practical components. Students should consult the Health & Physical Education Head of Department for further clarification.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Personal Health: Nutrition
This INSPIRE unit explores the role of nutrition in promoting health and examines the current health status of Australians, including members of the Grace community. Students will develop a targeted healthy eating strategy to address the specific nutritional needs of a chosen audience.
Peer Health: Alcohol
This unit examines how social and community resources influence teenagers’ perceptions of alcohol. Students investigate the role of schools in educating young people about alcohol prevention and actively engage in evaluating the effectiveness of various prevention programs. Community Health: Communicable diseases Students will review the health inequities the people of the Mentawai Islands face, specially focussing on malaria. They will analyse the contributing factors and use research to work as a group to plan suitable strategies to support the health of the Mentawai peoples. The unit has a Service-Learning focus, with students also contributing to the planning and execution of a fundraiser for the Mentawai people.
Personal and Peer health: Resilience
Term 4 will see the commencement of content, not assessment, for the General Health subject for Year 11 and 12. Students will be introduced to the topics of resilience as a personal health resource and investigate Positive Psychology concepts.
ASSESSMENT
Students are shown how to research and use reliable sources, as well as how to write academic reports. Assessment tools utilised will include Action Research report writing, analytical essays and essays under exam conditions. Term 4 will see students begin learning some content relevant to the first unit of the Senior Health subject.
PATHWAYS
Year 10 Health leads into the subject of Health in Year 11 and 12. A course of study in Health can establish a basis for further education in the fields of health science, public health, health education, allied health, nursing, and medical professions.
JAPANESE ELECTIVE
PRE-REQUISITES
Achieved a C or higher in Year 9 Japanese
CO-REQUISITES Nil
Japanese provides students with the opportunity to reflect on their understanding of the language and the communities that use it. It supports students in effectively navigating experiences and interpreting meaning across different cultures and languages. Students participate in a variety of interactions where they exchange ideas, develop intercultural understanding, and actively engage with written, spoken, and visual texts. Through communication with people from Japanese-speaking communities, students explore the purpose and nature of language and gain insight into its linguistic structures.
They acquire language in social and cultural contexts and use it in a range of situations for different purposes. Students experience and evaluate a variety of text types. Students learn to adjust their thinking to incorporate different linguistic and cultural perspectives and to create texts suited to various contexts, audience, and purposes.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Year 10 Japanese builds on students’ existing language skills and prepares them for the senior secondary Japanese program in Years 11 and 12. The course aims to develop students’ confidence in using Japanese to communicate in a range of everyday and unfamiliar contexts, as well as deepen their understanding of Japanese culture and society.
Students will:
• Learn and use plain verb and adjective forms in present, past, and negative tenses
• Apply grammar and sentence structures to express daily routines, personal experiences, and opinions
• Explore topics such as school life, extracurricular activities, families, homes, and social life
• Compare cultural elements of Japanese and Australian school and daily life
• Reflect on how language and culture influence identity and communication
• Use Japanese to interpret texts, respond to information, and create a range of spoken and written texts
Students will engage in activities such as diary writing, multimodal presentations, and conversations that require them to apply language in meaningful ways. They will also use strategies to maintain communication, interpret messages, and reflect on their learning progress.
This course supports the development of the four macro skills: listening, speaking, reading, and writing. It also focuses on building students’ ability to think critically, express opinions, and understand different perspectives through language.
ASSESSMENT
Students will experience a range of assessment and examination types, including short response items, extended response items and combination response items. These occur across the range of skills - Reading, Listening, Speaking and Writing.
PATHWAYS
A course of study in Japanese can establish a basis for further education in many professions and industries, particularly those where the knowledge of an additional language and the intercultural understanding it encompasses could be of value, such as business, hospitality & tourism, defence force, law, science, technology, sociology, and education.
LEGAL STUDIES
PRE-REQUISITES
ELECTIVE
Nil. However, studying Business in Years 8 and 9 would be advantageous.
CO-REQUISITES Nil
In Legal Studies, students compare the key features and values of Australia’s system of government and describe role and responsibilities at a regional and global level. They explain the role of the High Court of Australia and how Australia’s international legal obligations influence the law and government policy. They identify and explain challenges to a resilient democracy and a cohesive society in Australia.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Topic 1: Australia in the World – Students compare the key features and values of Australia’s system of government to those of another system of government, describing the Australian Government’s role and responsibilities at a regional and global level.
Topic 2: Human Rights and International Law - Students explore various human rights laws in Australia as well as major international laws. This topic gives students a great introduction to relevant human rights laws that could impact them as well as expanding their knowledge of Australia’s relationship with other countries.
Topic 3: Introduction to Civil Law - Students gain insight into the foundations of the Australian and Queensland legal systems in the context of Civil Law. They consider the importance of Civil Law in their lives and distinguish between Civil and Criminal Law matters.
Topic 4: Introduction to Criminal Law – Students will develop an appreciation of criminal law by investigating the principles that underpin the law process in Queensland. Students will consider how criminal law attempts to safeguard individuals’ right to freedom from interference, with society’s need for order.
ASSESSMENT
Assessment techniques include:
• Combination response examinations
• Investigation Inquiry Report
• Analytical Essay
PATHWAYS
Year 11 and 12 Legal Studies
• University degrees, TAFE certificates and diplomas in Law and Justice Studies
• Legal Studies employment opportunities - in legal firms, law enforcement, criminology, forensics, justice studies, social work, government, corrective services, business, education, economics, and politics.
MODERN HISTORY
ELECTIVE
PRE-REQUISITES Nil
CO-REQUISITES Nil
Understanding modern and ancient historical events, people, places, and cultures assists students in a plethora of knowledge and skills which inform many areas of study. In the current Core History Course (Years 7-9) students study historical periods up to the end of World War II (1945). Elective History gives students the opportunity to study more modern and recent events and contextualise their world today.
Students develop research skills which assist them to locate information that is specialised and unique to their own investigations. Throughout the course students are taught the value of evaluating the origins of historical documents, their reliability and usefulness. This course is designed to directly feed into the Senior Modern History Courses. Students will develop key literacy skills and come to evaluate and analyse historical sources to give opinion and arguments regarding historical events, people, and changes over time.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Popular Culture: Historical Events and Trends from the 1950s-2000s.
Slavery and Race Relations: Trans-Saharan slave trade, trans-Atlantic slave trade, slavery in the US, the
US Civil War and impacts on race relations in modern USA.
The Cold War: Korea, Vietnam, Space Race, Berlin Wall, Cuban Missile Crisis, and Collapse of the Soviet Union.
History Goes to Hollywood: Students select a historical time period or historical event that is depicted in film and assess the question ‘does accuracy matter?
ASSESSMENT
Independent Source Investigation
• Research Essay Assignment
• Response to Stimulus Short Response Exam.
PATHWAYS
• Year 11 and 12. Modern History
• A course of study in History can establish a basis for further education in the fields of archaeology, history, education, psychology, sociology, law, business, economics, politics, journalism, the media, health and social sciences, writing, academia, and research.
MUSIC ELECTIVE
PRE-REQUISITES
Nil. However Middle School Music would be advantageous.
CO-REQUISITES Nil
This subject has a history of running as an Alternative Delivery subject
The Year 10 Music Course is a natural progression from the Year 9 subjects of Music and Music Game On! and provides an opportunity to further develop music skills framed in the three areas of study as set down in the Senior Music Syllabus: Making (Performance, Composition) and Responding (Musicology). Music aims to foster creative and expressive communication allowing students to develop musicianship through engaging in performing, composing and musicology-based activities and study.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
The Music subject is based around two areas, Making and Responding which branches into three broad areas: Composition, Musicology and Performance. Underpinning these three areas is knowledge and understanding of music elements and concepts, and the skills to interpret and apply these within a range of music activities. Students will have the opportunity to become adept in using music-related technologies.
Students use essential literacy skills to engage in a multimodal world. They demonstrate practical music skills and analyse and evaluate music in a variety of contexts, styles and genres.
Units for study in Year 10 are:
• Jazz
• Art Music Through the Eras
• Rock Since 2000
• Film Music
The most memorable and eagerly awaited learning experience in Year 10 Music is the opportunity to record a cover or original in a professional recording studio. Computers and recording hardware are used for composition and aural training.
ASSESSMENT
Assessment in Music gives students opportunities to demonstrate their musicianship and apply their knowledge and understanding.
• Performance Tasks (demonstrating, interpreting music elements and concepts through playing, singing and/or conducting)
• Composition Tasks
• Extended Response Written Examination (Musicology Focus: read, listen, interpret/analyse scores and recordings)
• Integrated Task - combination of Musicology and Composing or Performance into a multi modal presentation. This mirrors requirements in the senior syllabus.
PREREQUISITES
Students are encouraged to attend live music performances and participate in school-based and cocurricular music activities. Private tuition (instrument and/or voice) is not necessary but could be an advantage in some circumstances.
PATHWAYS
The subject assists the students in developing a variety of skills in performing, composing and musicology, which directly articulates into the study of the senior subjects, Year 11 and 12 Music and Year 12 Music Extension (offered only in Year 12).
PHYSICAL EDUCATION
ELECTIVE
PRE-REQUISITES Nil
CO-REQUISITES Nil
Physical Education is based on the relationship between learning about, through and in physical activity. Students engage in a range of concepts theoretically and practically to develop a deep understanding of principles relevant to their engagement in physical activity.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Students engage in physical activity as a means of learning in and about the subject areas being studied. They engage in learning experiences that will develop their movement sequences and strategies in a range of physical contexts. This subject matter occurs across a range of different disciplines such as sociology and exercise science areas and includes the following units:
Theory:
• Training and fitness
• Equity in accessing physical activity and sport
• Anatomy, Physiology and Biomechanics
• Motor Learning and Physical Activity.
Practical:
• Touch Football, Futsal, Taekwondo, Australian Rules Football (subject to change).
ASSESSMENT
Students will be assessed through performance in physical activity (acquisition of skill, use of tactics and strategies, evaluation, and initiation of changes to personal and team performance) and written assessment. Theory units are assessed through examinations or written/oral assignments and video reels of physical performance.
PATHWAYS
This subject is designed to allow the first three terms for students to sample the subject to ensure that they are equipped to handle the demands and have a clear direction of the subject’s objectives, assessment instruments and structure. The Year 10 Physical Education Elective subject leads into Year 11 and 12 Physical Education (General).
A course of study in Physical Education can establish a basis for further education in the fields of exercise science, biomechanics, the allied health professions, psychology, teaching, sport journalism, sport marketing and management, sport promotion, sport development and coaching.
PRACTICAL TECHNOLOGY SKILLS
PRE-REQUISITES
Nil
CO-REQUISITES Nil
Practical Technology in Year 10 aims to provide students with a greater understanding of material and equipment in a world of change, equip students with problem solving skills, which can be used in all facets of life. promote the expressions and communication of ideas in written and graphical and practical forms, promote workplace health and safety awareness and enhance students’ knowledge and use of machines and power tools in the production of practical items.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
A course of study in Practical Technology Skills comprises:
• Workshop and tool safety training
• Woodworking skills
• Metalworking skills
Students have the opportunity to design and make projects from a design brief based on a set project with clear guidelines. Students will make wood, metal, plastics, and electronics projects, with personal touches being added to individualise their projects.
ASSESSMENT
Assessment methods are Practical Projects
PREREQUISITES
This course is designed to further develop students’ knowledge and understanding of materials, equipment, and techniques within the practical area, building on their experiences of Year 8 and Year 9, however, there is no prerequisite for Practical Technology in Year 10.
PATHWAYS
Practical Technology is an ideal course for students considering taking senior subjects like Industrial Technology Skills or any of the Certificate courses in Engineering, Construction or Furnishing in the College’s Trades Skills Centre. Career pathways are endless from this direction of study.
SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS
PRE-REQUISITES
ELECTIVE
Achieved a B or higher in Year 9 Mathematics
CO-REQUISITES Mathematical Methods
Specialist Mathematics is an elective subject providing enrichment opportunities and should be taken by interested and motivated mathematics students. The aim of the subject is to give students a wider experience of mathematics and problem solving. Students can expect to become familiar with topics not seen in the Mathematical Methods course.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Students who undertake Specialist Mathematics will develop confidence in their mathematical knowledge and ability, and gain a positive view of themselves as mathematics learners. They will gain an appreciation of the true nature of mathematics, its beauty and its power.
The topics covered over the year are:
Number Theory (primes and GCD), Number Theory (divisibility and modular arithmetic), Set Notation, Axioms, Matrices, Cryptography, Inductive and deductive reasoning, Geometric Proofs, Permutations and Combinations, and Vectors.
ASSESSMENT
Assessment will be supervised examinations and Problem Solving and Modelling Tasks. Student experiences include an excursion to Mathema - the mathematics museum.
PATHWAYS
Year 10 Specialist Mathematics is not a prerequisite to Year 11and 12 Specialist Mathematics but does provide students with a broader and deeper mathematical base for further study. A course of study in Specialist Mathematics can establish a basis for further education in the fields of science, all branches of mathematics and statistics, computer science, medicine, engineering, finance and economics.
PRE-REQUISITES
CO-REQUISITES NIL
In this subject, students focus on the practical application of science, technology, engineering and mathematics knowledge to problem-solve and develop solutions for real-world problems in a variety of situations. Students will recognise and describe complex problems, determine solution success criteria, develop, and communicate ideas and predict, generate, evaluate and refine prototype solutions within a science context. The problem-based learning framework in STEM encourages students to become self-directed learners and develop beneficial collaboration and management skills. Students will enter competitions, such as the Queensland Science Teachers Competition, which will become the basis for their assessment.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
This subject will investigate a range of disciplines based on STEM principles, including Biomedical Science, Construction, and Flight. Students are challenged to design novel solutions to real world challenges.
Biomedical Engineering: Students learn about human anatomy and the mechanics of human tissue. They are then given the challenge to design novel and prototype improved medical treatments and devices.
Flight: Students will investigate the forces caused by moving air and apply them to designs of aircraft and other vehicles so they may function correctly, efficiently and safely.
Independent research and design: In this unit, students will develop their own design challenge that explores a chosen scientific context and engages them in the engineering design process to explore, develop, Generate, and evaluate and refine.
ASSESSMENT
Assessment is based on competition entries, prototype models, portfolios of work and presentations.
• Scientific reports and data analysis
• Project – folio
• Prototype models.
PATHWAYS
Studying STEM maintains a broad range of options available to students for future subject and career choices. A course of study in STEM can establish a basis for further education in the fields of applied science, engineering, medicine, technology, forensic science, environmental science, medicine, pharmacy, and sports science.
VISUAL ART ELECTIVE
PRE-REQUISITES Nil
CO-REQUISITES Nil
Visual Art prepares young people for participation in the 21st century by fostering curiosity and imagination, and teaching students how to generate and apply new and creative solutions. This learnt ability to think in divergent ways and produce creative and expressive responses enables future artists, designers, and craftspeople to innovate and collaborate with the fields of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics to design and manufacture images and objects that enhance and contribute significantly to our daily lives.
The processes and practices of Visual Art, such as self-directed learning and creative problem-solving, develop transferable 21st century skills that are highly valued in many areas of employment. Organisations increasingly seek employees who demonstrate work-related creativity, innovative thinking, and diversity.
SUBJECT OUTLINE
Unit Overview
Portraiture (Applied): Drawing, evaluation
Wearable Art (Applied): Drawing, weaving, found materials sculptures, photography, performance
Visions of the Future (General): Drawing, oil painting.
Evaluating and Analysing: Evaluation and analysis of artworks of self and others
ASSESSMENT
Projects (Making artworks) Essays under exam conditions
Written Report (incorporating practical tasks)
Multimodal Presentation
Essays under exam conditions
PATHWAYS
This subject is the prequel to Visual Art studies in Year 11 and 12. This course is highly recommended for Year 11 and 12 Visual Art (General)
Further studies in the area of visual arts can lead to and benefit careers in diverse fields such as; Fine Arts, Electronic Imaging, Digital Photography, Graphic/Game/Interior/Fashion/Textile/Urban Design, Cartooning, Advertising, Art Teaching, Illustration, Architecture and Animation.

VET ON CAMPUS
VOCATIONAL EDUCATION & TRAINING (VET)
VET QUALIFICATIONS

Competency-based qualifications rely on a practical focus to all assessment to ensure all skills are relevant to the workplace and can be demonstrated to industry standards. Assessment types will include short written responses, practical tasks and projects, presentations, and case studies. Students will need to be able to provide evidence that they meet the performance and knowledge requirements of each unit under the assessment conditions outlined in each qualification’s training package. Students will not be given a level of achievement in school reports but will always receive an effort mark and at the end of each semester, a list of units of competency achieved.
VET OFFERED ON ROTHWELL CAMPUS FOR CABOOLTURE STUDENTS
Students from Caboolture Campus are able to access some vocational qualifications offered at the Rothwell campus which are delivered in blocks of training or one day a week. Please contact the VET Department to enquire about dropping an elective subject and replacing it with a VET qualification on the Rothwell campus. Some of these programs are covered by VETiS funding (Qld Govt) and some are fee-for-service.
Qualifications Available:
• Certificate III in Music (CUA30920) offered one afternoon per week for 2 years (commencement Yr 10 or Yr 11 Semester 1)
• Certificate II Health Support Services (HLT23215) & Certificate III Health Services Assistance (HLT33115) offered one day a week for 3 terms. (commencement varies)
RESOURCES/REQUIREMENTS
If any resources are required for particular qualifications, it will be available from the RTO offering the qualification. This will include fees, subject levies for consumables, required equipment, work placement requirements or other legislative requirements.
VET HANDBOOKS
Each subject delivering a VET qualification will provide students with a Handbook explaining the special requirements of the training package. These handbooks will be available in hardcopy or through eGrace.
RELEVANCE TO FURTHER STUDIES
• Most VET qualifications offered have TAFE or university pathways available after Year 12 through external providers.
• Some VET qualifications may lead directly into employment opportunities in private and government sectors.
• Students will be able to participate more effectively and responsibly in a changing working environment.
• Each qualification’s pathway into further education will be outlined by each Department.
PREREQUISITES
Each Department will state if their VET qualifications have any prerequisite school subjects or levels of achievement, units of competency or qualifications.
RECOGNITION OF PRIOR LEARNING
When assessing students in VET qualifications, assessors need to offer a process of recognising prior learning. This process is to determine if students may receive credit for a unit of competency or advanced standing based on previous experience or training. This will affect the way the student is trained as they may just require “gap training” to cover specific performance criteria or may not require any training at all in a particular unit. Recognition of Prior Learning Forms are available on the College ERM and will be made available to students on application, once their teachers have been notified.
DIRECT CREDIT FOR COMMON UNITS
Some of the units of competency are common to several qualifications offered at Grace Lutheran College, (e.g. WHS units) and may also be part of qualifications studied at TAFE, through an apprenticeship or traineeship. If this Is the case than the student will be obliged to notify the trainer, as it may result in a direct credit for this unit or a direct credit off future qualifications undertaken at the College.
FURTHER VET INFORMATION
VET qualifications at Grace Lutheran College generally commence in Year 10 or 11 and run throughout the senior years to complete by the end of Year 12. The school guarantees that the student will be provided with multiple opportunities to demonstrate competency, as per the rights and obligations outlined in the enrolment process and VET information provided in the Student Handbook for the course.
ISSUING QUALIFICATIONS
Students successfully achieving all requirements of a qualification will be provided with an official Certificate and Record of Results. Students who achieve at least one unit (but not the full qualification) will receive a Statement of Attainment. Should students misplace their original documents, another certificate can be issued by Grace Lutheran College for a small fee.
PARTIAL COMPLETION
Students who receive a Statement of Attainment may be awarded a portion of the allocated QCE credits gained through completing qualifications higher than a Certificate I. At least one quarter of the units of a Certificate II or higher qualification must be successfully completed before attracting any QCE credits.
LATE ENTRY
Should a student enter the subject after the start of the course they will be expected to catch up on units covered prior to their entry into the course if they expect to achieve the full qualification.
TRANSITIONING INTO NEW VERSIONS OF VET QUALIFICATIONS
Where possible, all students in expiring qualifications will be “transitioned” to the new versions of those qualifications as soon as they have been added to the scope of registration and approved by the registering body. When this is not possible, no new students will be enrolled in the expiring qualification from the publication date of the new training package.
VET DELIVERY REQUIREMENTS
The college retains the right to suspend/cancel part of the course if it is unable to meet the Training Package requirements. The school must have industry experienced teachers and specific equipment to run these courses. If the school loses access to these resources, the school will attempt to provide students with alternative opportunities to complete the courses and the related qualifications.
USI (UNIQUE STUDENT IDENTIFIER)
Students undertaking a Vocational Qualification will need to apply for a Unique Student Identifier (USI) to keep track of all vocational training. https://www.usi.gov.au/students/create-your-usi
FURTHER INFORMATION
Please contact the Learning Lead of the relevant Department via College Reception on 5495 2444 for Caboolture and 3203 0066 for Rothwell.
• VET Department – Judith Barnes (Caboolture) or Leisa Jones (Rothwell)
• Grace Academy – Nathan Poetschka
• Trade Skills Centre – Dwayne Blair (Rothwell)
VET OFF CAMPUS
TAFE Colleges and private Registered Training Organisations (RTOs) in the Brisbane area offer secondary school students’ access to their certificate courses through the VET in Schools Program (Certificate I, II, III, IV and Diploma). On successful completion of these qualifications, credit points are awarded towards the students’ QCE and banked into their Learning Accounts.
Students enrolled in these courses will either attend a TAFE or other Training campus one day a week, complete their qualification on-line or use a combination of on-line and tutorial methods.
VETIS FUNDING
Some qualifications are fully government-funded under the VET in Schools (VETis) funding initiative. This initiative allows school students to access one fully subsidised course from a list of qualifications identified as being on the National Skills Shortage List. http://www.skillsgateway.training.qld.gov.au/content/user/subsidy/SUBSIDIES-LIST.pdf
Qualifications on this list can be accessed through TAFE, Private Registered Training Organisations (RTOs) or at school through partnerships with TAFE or private providers. However, only one fully funded qualification is accessible by school students, after that a fee will apply.
SCHOOL BASED APPRENTICESHIPS AND TRAINEESHIPS
School based apprenticeships and traineeships (SATs) allow students in Years 10, 11 & 12 to enter into paid employment and undergo training both on-and-off the job whilst undertaking their senior studies. Students wishing to undertake a school-based apprenticeship or traineeship (SAT) must first consult with the VET Department. For a student to undertake a school-based traineeship or apprenticeship, it must feature in his/her Senior Education & Training (SET) Plan and lead towards a legitimate career pathway.
Please note: Changes to Government legislation may affect student eligibility to access any further funding for an apprenticeship or traineeship after school, so advice should be sought from the VET Department prior to sign up.
Industry release days are determined by the individual student’s timetable as well as the needs of industry. However, a College/subject activity scheduled for this allocated day, will take priority (e.g. subject excursion, exams). Students undertaking a school-based traineeship or apprenticeship are expected to complete all the classroom and assessment requirements of their academic studies and also maintain an acceptable level of behaviour.
A consultant from the supervising Registered Training Organisation will monitor the apprentice/trainee’s progress towards the completion of their qualification in the workplace while the head of VET and the Head of Teaching and Learning will monitor academic progress.
The Queensland Certificate of Education (QCE) allows for students to have their apprenticeship recognised as a part of the credits towards the QCE. The number of credits depends on whether the traineeship or apprenticeship is Certificate II, III or IV. On completion of Certificate II, students gain 4 credit points. Successful completion of Certificate III generates 5-8 credit points, depending on the qualification as not all vocational qualifications are given the same value.
QCAA will only allow 8 credits from any one training package to be counted as credits for the QCE. This means that students doing several qualifications from the same training package will only receive a maximum of 8 QCE credits.
ATAR
One vocational qualification (Certificate III and above) can be used in the ATAR calculation, but they do not scale well when compared with more academic subjects.
CHOOSING THE VET PATHWAY
Students choosing to undertake a school-based apprenticeship or to enrol in a nationally recognised qualification will be eligible to drop a subject. Students will then be expected to catch up on work missed in the study periods allocated on their timetables or to use the study spares to complete training for their qualifications.

