
https://ebookmass.com/product/workbook-for-diagnostic-

Instant digital products (PDF, ePub, MOBI) ready for you
Download now and discover formats that fit your needs...
Abdomen and Superficial Structures (Diagnostic Medical Sonography Series)
https://ebookmass.com/product/abdomen-and-superficial-structuresdiagnostic-medical-sonography-series/
ebookmass.com
Workbook for Diagnostic Medical Sonography: A Guide to Clinical Practice Obstetrics and Gynecology (Diagnostic Medical Sonography Series) 4th Edition, (Ebook PDF)
https://ebookmass.com/product/workbook-for-diagnostic-medicalsonography-a-guide-to-clinical-practice-obstetrics-and-gynecologydiagnostic-medical-sonography-series-4th-edition-ebook-pdf/ ebookmass.com
Obstetrics & Gynecology (Diagnostic Medical Sonography Series) 4th Edition, (Ebook PDF)
https://ebookmass.com/product/obstetrics-gynecology-diagnosticmedical-sonography-series-4th-edition-ebook-pdf/
ebookmass.com
Principles and Practice of Sleep Medicine - 2 Volume Set 7th Edition Meir H. Kryger Md. Frcpc
https://ebookmass.com/product/principles-and-practice-of-sleepmedicine-2-volume-set-7th-edition-meir-h-kryger-md-frcpc/
ebookmass.com




Second Chance At Love (Love And Devotion Book 4) Jr
https://ebookmass.com/product/second-chance-at-love-love-and-devotionbook-4-jr-salisbury/
ebookmass.com
An Introduction to PHP: Learn PHP 8 to Create Dynamic Websites 1st Edition Mark Simon
https://ebookmass.com/product/an-introduction-to-php-learn-php-8-tocreate-dynamic-websites-1st-edition-mark-simon/
ebookmass.com
Maladie de Lyme et co-infections Daniel Christmann [Christmann
https://ebookmass.com/product/maladie-de-lyme-et-co-infections-danielchristmann-christmann/
ebookmass.com
Break You Hard (Rebel Hearts, Book 1) Michelle Hercules



https://ebookmass.com/product/break-you-hard-rebel-heartsbook-1-michelle-hercules/
ebookmass.com
LUST: A Vampire and Werewolf Power-Couple Romance (Out of the Fire Book 5) Candace Blevins
https://ebookmass.com/product/lust-a-vampire-and-werewolf-powercouple-romance-out-of-the-fire-book-5-candace-blevins/
ebookmass.com


Instructional Design, 3rd Edition 3rd Edition, (Ebook PDF)
https://ebookmass.com/product/instructional-design-3rd-edition-3rdedition-ebook-pdf/
ebookmass.com


The Pediatric Abdomen
The Pediatric Urinary System and Adrenal Glands
The Neonatal Brain
The Infant Spine
The Infant Hip Joint
PART FOUR | SPECIAL STUDY SONOGRAPHY
Organ Transplantation
Point-of-Care Sonography
Foreign Bodies
Sonography-Guided Interventional Procedures

REVIEW OF GLOSSARY TERMS
Matching
Match the terms with their definitions.
KEY TERMS anechoic echogenic echopenic isoechoic heterogeneous homogeneous hyperechoic hypoechoic specificity sensitivity accuracy
1. 2. 3. 4.
DEFINITIONS
Describes regions or portions on the sonogram where the echoes are not as bright as surrounding tissues or are less bright than normal Defines how well an examination documents whatever disease or
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
j.
k. pathology is present
Describes tissues or organ structures on the sonogram having several different echo characteristics
Describes the sonographic appearance where the echoes are less echogenic or where a tissue or organ has few internal echoes
Describes a region or portion on the sonogram that appears echo-free
Defines the ability of the examination to find a disease that is present and not find a disease that is not present
Describes image echoes brighter than surrounding tissues or those brighter than what is normal for that tissue or organ
Describes where imaged echoes are of equal intensity
Describes structures of equal echo density
Defines how well an examination documents normal findings or excludes patients without disease
Describes an organ or tissue capable of producing echoes by reflecting the acoustic beam
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY REVIEW
Image Labeling
Complete the labels in the images that follow.


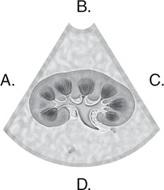

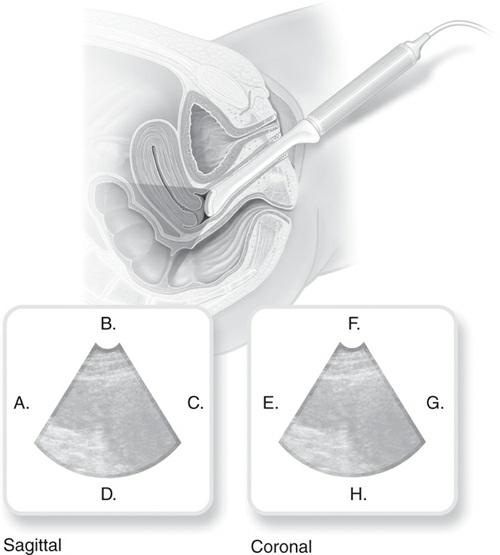
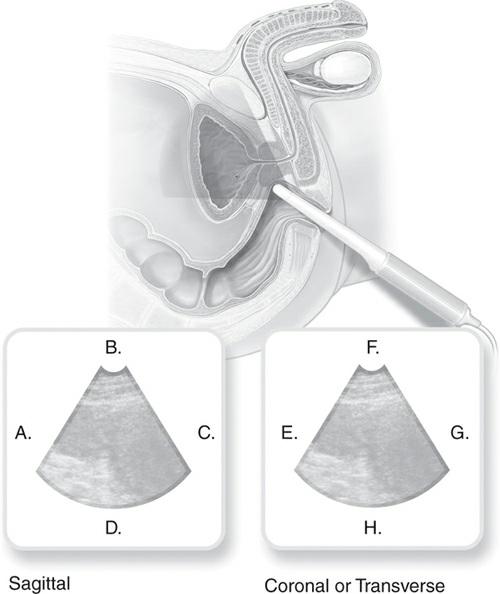

CHAPTER REVIEW
Multiple Choice
Complete each question by circling the best answer.
1.
a.
b.
c. d.
When performing a neurosonography examination, the top of the image represents which scanning surface? anterior posterior superior inferior
2. a. b. c.
When scanning in the longitudinal, sagittal plane, where is the transducer indicator located in relation to the organ of interest? at the 12:00 position at the 3:00 position at the 6:00 position
d.
3. a. b.
c. d.
4. a.
b.
When scanning in the transverse plane, where is the transducer indicator located in relation to the organ of interest? at the 12:00 position at the 3:00 position at the 6:00 position at the 9:00 position
c. d.
5. a. b. c. d.
When performing a neonatal brain examination, where is the transducer indicator located in the sagittal plane? at the 12:00 position at the 3:00 position at the 6:00 position at the 9:00 position
When performing a neonatal brain examination, where is the transducer indicator located in the coronal plane? at the 12:00 position at the 3:00 position at the 6:00 position at the 9:00 position
6. a. b. c. d.
When scanning in the longitudinal, sagittal plane, which of the following is NOT demonstrated in the image presentation? anterior cephalic right caudal
7. a. b.
When scanning in the transverse plane on the anterior surface, which of the following is NOT demonstrated in the image presentation? posterior superior right
c. at the 9:00 position
8. a. b.
9.
Which of the following structures would NOT normally produce acoustic enhancement? urinary bladder
c.
d.
simple kidney cyst gallbladder gallstone
Which of the following is NOT a sonographic criterion of a simple cyst?
10. a. b.
c.
d.
11. a. b.
posterior acoustic shadowing anechoic center well-defined posterior wall edge-shadowing artifact
If a kidney stone is diagnosed with an abdominal sonogram but further testing reveals that the kidney is normal, what is this result called?
a true-positive result
a true-negative result
a false-positive result
a false-negative result
If a kidney stone is diagnosed with an abdominal sonogram and further testing also finds a kidney stone, what is this result called?
c. d.
12. a. b.
c. left
a true-positive result
a true-negative result
a false-positive result
a false-negative result
If the abdominal sonogram appears normal but a CT examination reveals a mass in the liver, what is this result called?
a true-positive result
a true-negative result
a false-positive result
a false-negative result
If the number of false-negative examinations increases, what happens to the sensitivity of the examination? The sensitivity will increase. False-negative results do not affect the sensitivity. The sensitivity will decrease. The sensitivity will remain the same.
What describes the likelihood of disease actually being present if the sonogram is positive? the negative predictive value the positive predictive value sensitivity specificity
Which term describes the ability of the examination to find diseases that are present and not find diseases that are not truly present?
sensitivity specificity efficacy accuracy
Fill-in-the-Blank
The liver and spleen are located on opposite sides of the body and are therefore .
In directional terms, the lungs are to the liver.
The plane is a vertical plane that runs through the body and divides it into right and left sections.
The vertical plane that divides the body into equal right and left halves is called the plane.
In the position, the patient is lying supine on the
examination table with his or her head lower than his or her feet.
The plane is a horizontal plane that is perpendicular to the sagittal plane and divides the body into superior and inferior portions.
The plane is a vertical plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior portions.
When performing an endovaginal examination in both the sagittal and coronal planes, the anatomy is located at the apex of the image.
An organ may appear to have an abnormal echogenicity if disease is present or a poor examination technique is used, such as incorrect settings.
Fluid-filled structures, such as the gallbladder, urinary bladder, or simple cysts, appear
A normal testicle is described as , whereas a normal kidney appears .
The reduced echo amplitude found beyond a highly attenuating object such as a kidney stone is called an acoustic .
An artifact called may be seen at the near wall of a simple cyst.
A structure contains both solid and fluid components and will usually exhibit both anechoic and echogenic areas on the sonogram.
The preliminary report, which is also referred to as the , should include the sonographic findings but should not include a diagnosis.
Short Answer
List the sonographic criteria that define a simple cyst.
What terminology can be used to describe a solid mass?
IMAGE EVALUATION/PATHOLOGY
Review the images and answer the following questions.
3. 1. What information should the sonographer include in his or her preliminary report? What information should be avoided?

What is the name of the artifact that the large white arrows are pointing to?

2. What type of artifact are the large white arrows pointing to? The small arrows are pointing to a cyst in the kidney. What term could be used to describe this structure?

3. What term could you use to describe the echotexture of the kidney cortex (K) to the liver parenchyma (L)? What about the echotexture of the mass (M) to the kidney cortex? Would you describe the mass as heterogeneous or homogeneous?

4. What one term would you use to describe the internal echo pattern of this mass?
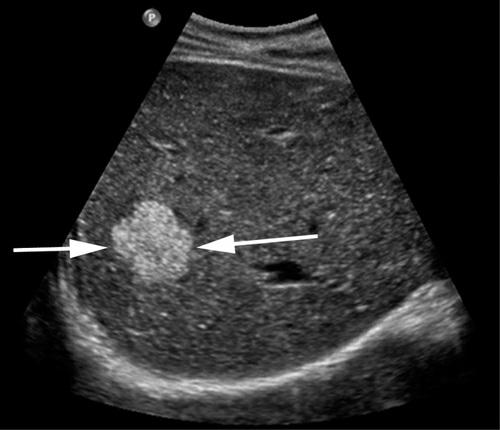
What term would be used to describe the echotexture of the mass (arrows) in comparison to the surrounding liver parenchyma?
CASE STUDY
A 38-year-old woman with right upper quadrant pain presents for an abdominal sonogram. What steps must the sonographer take prior to starting the examination that will enable him or her to provide the best possible examination?
You have been working on a research study. You have scanned 73 patients. Out of the 73 patients, 35 had a true-positive result and 31 had a true-negative result. There were 6 false-negative results and 1 false-positive result. From these statistics, calculate the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the examination.
ANSWERS: CHAPTER 1
Matching e
f
Image Labeling
1A. supine
1B. lateral
1C. prone
1D. left anterior oblique
2A. cephalic/superior
2B. anterior
2C. caudal/inferior
2D. posterior
3A. cephalic/superior
3B. left
3C. caudal/inferior
3D. right
4A. right
4B. anterior
4C. left
4D. posterior
5A. anterior
5B. caudal/inferior
5C. posterior
5D. cephalic/superior
5E. right
5F. caudal/inferior
5G. left
5H. cephalic/superior
6A. cephalic/superior
6B. posterior/rectum
6C. caudal/inferior
6D. anterior
6E. right
6F. posterior/rectum
6G. left
6H. anterior
7A. anterior
7B. caudal/inferior
7C. posterior
7D. cephalic/superior
7E. right
7F. caudal/inferior
7G. left
7H. cephalic/superior
Multiple Choice
Short Answer
In order to be classified as a simple cyst, the structure must meet the following criteria: (1) anechoic center; (2) well-defined mass with a well-defined posterior wall; (3) increased through transmission; (4) possible reverberation artifact behind the near wall; and (5) possible edge-shadowing artifact.
The preliminary report or technical impression should describe the findings from the sonographic examination by using descriptive terminology such as the scan plan, tissue textures, and measurements. Although the sonographer should describe what he or she sees as completely and accurately as possible, he or she should refrain from recording a diagnosis.
When describing a solid mass, the location of the mass should be described, and the mass should also be described in reference to the surrounding tissues. Terms such as “hyperechoic,” “hypoechoic,” “or isoechoic” to the surrounding tissues can be used to describe a solid mass. The echo intensity can also be described with the terms homogeneous or heterogeneous. The attenuation properties of the mass can be described if there is acoustic shadowing or increased through transmission posterior to the mass.
Image Evaluation/Pathology
Shadowing
3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. sagittal mid-sagittal Trendelenburg transverse coronal inferior/caudal gain anechoic homogeneous; heterogeneous shadow reverberation complex technical impression
Acoustic enhancement or increased through transmission; anechoic
The kidney cortex is isoechoic to the liver parenchyma; the mass is hypoechoic to the kidney cortex; homogeneous Complex
Hyperechoic
Case Study
Prior to starting any examination, the sonographer should obtain as much pertinent information as possible. Having a complete clinical picture can enable the sonographer to tailor the exam to the patient’s needs. The sonographer should know the indication for the examination and relevant information such as laboratory values, surgical history, results of prior examinations, and related imaging examinations. This information could be obtained from the physician’s order, from the patient’s chart, or from the patient directly. The examination procedures should be explained to the patient, and any questions or concerns should be addressed.
2.
Sensitivity = 85%, Specificity = 97%, Accuracy = 90%

REVIEW OF GLOSSARY TERMS
Matching
Match the key terms with their definitions.
KEY
TERMS
abscess ascites aponeurosis ecchymosis erythema fascia linea alba omphalocele peristalsis pleural effusion pneumothorax rectus abdominis
DEFINITIONS
b.
Redness of the skin due to inflammation
Long, vertical, paired abdominal muscles that run from the xiphoid process to the symphysis pubis
c.
Skin discoloration caused by the leakage of blood into the subcutaneous tissues
d.
Cavity containing dead tissue and pus that forms due to an infectious process
e.
Fibrous tissue network that is richly supplied by blood vessels and nerves located between the skin and the underlying structures
f.
g.
h.
i.
j.
k.
l.
Accumulation of serous fluid in the peritoneal cavity
Rhythmic contraction of the GI tract that propels food through it
Fibrous structure that runs down the midline of the abdomen from the xiphoid process to the symphysis pubis
Fluid accumulation in the pleural cavity
Collapsed lung that occurs when air leaks into the space between the chest wall and lung
Layers of flat fibrous sheets composed of strong connective tissue, which serve as tendons to attach muscles to fixed points
Congenital defect in the midline abdominal wall that allows abdominal organs to protrude through the wall into the base of the umbilical cord
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY REVIEW
Image Labeling
Complete the labels in the images that follow.


CHAPTER REVIEW
Multiple Choice
Complete each question by circling the best answer.
1. a. b.
Which of the following has the primary function of attaching muscles to fixed points?
superficial fascia
deep fascia
c.
d.
2. a. b.
subcutaneous tissue
aponeuroses
Which of the following muscles is not a paired muscle?
pyramidalis muscle
external oblique
c.
d.
3. a. b.
rectus abdominis
transverse abdominis
Which of the following is an anatomical area, where vessels can enter and exit the abdominal cavity, and is a potential site for hernias?
linea alba
inguinal canal
c.
d.
4. a. b. c. d.
umbilicus
rectus sheath
Which of the following is a true statement about the right crus of the diaphragm?
It can be seen sonographically anterior to the abdominal aorta. It is shorter than the left crus of the diaphragm.
It can be seen anterior to the IVC.
It appears anterior to the caudate lobe.
5. a. b.
Which of the following muscles is not part of the anterolateral abdominal wall?
pyramidalis muscle
psoas muscle
c.
d.
rectus abdominis
external oblique
Which statement regarding the diaphragm is FALSE?
The right dome of the diaphragm is slightly higher than the left. The diaphragmatic apertures allow the esophagus, blood vessels, and nerves to pass between the chest and abdomen.
The central portion of the diaphragm descends during inspiration and ascends during expiration.
Due to diaphragmatic contraction, the IVC dilates during inspiration.
Which transducer is best suited for a sonographic examination of the superficial abdominal wall?
12 MHz linear array
4 MHz curved array
3 MHz phased array
4 MHz linear array
Which of the following is an inflammatory response? hematoma hernia abscess lipoma
9. a. b. c. d.
In order to determine if an abscess is intraperitoneal or extraperitoneal, what structure must the sonographer demonstrate? linea alba peritoneal line rectus abdominus diaphragm
10. a. b. c.
d.
Which of the following may be a contraindication to sonographyguided aspiration? septations within the abscess particulate debris floating within the abscess an anechoic abscess with increased through transmission an echogenic abscess
