TitaniumAlloysforBiomedicalDevelopmentand Applications:Design,Microstructure,Properties, andApplicationZhentaoYu
https://ebookmass.com/product/titanium-alloys-forbiomedical-development-and-applications-designmicrostructure-properties-and-application-zhentao-yu/
Instant digital products (PDF, ePub, MOBI) ready for you
Download now and discover formats that fit your needs...
Titanium for Consumer Applications: Real-World Use of Titanium Francis Froes
https://ebookmass.com/product/titanium-for-consumer-applications-realworld-use-of-titanium-francis-froes/
ebookmass.com
Nickel-Titanium Smart Hybrid Materials: From Micro- to Nano-structured Alloys for Emerging Applications (Micro and Nano Technologies) 1st Edition Sabu Thomas (Editor)
https://ebookmass.com/product/nickel-titanium-smart-hybrid-materialsfrom-micro-to-nano-structured-alloys-for-emerging-applications-microand-nano-technologies-1st-edition-sabu-thomas-editor/
ebookmass.com
Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) and Its Applications Francesco Parrino
https://ebookmass.com/product/titanium-dioxide-tio2-and-itsapplications-francesco-parrino/
ebookmass.com
Highland Gladiator Kathryn Le Veque [Veque
https://ebookmass.com/product/highland-gladiator-kathryn-le-vequeveque-3/
ebookmass.com
Beginning Spring Data: Data Access and Persistence for Spring Framework 6 and Boot 3 Andres Sacco
https://ebookmass.com/product/beginning-spring-data-data-access-andpersistence-for-spring-framework-6-and-boot-3-andres-sacco/
ebookmass.com
How Much For The Whole Night? (Shadow Team Book 1) Rj Scott
https://ebookmass.com/product/how-much-for-the-whole-night-shadowteam-book-1-rj-scott/
ebookmass.com
Knowledge Management in Innovative Companies 1 Ermine
https://ebookmass.com/product/knowledge-management-in-innovativecompanies-1-ermine/
ebookmass.com
Biopolymer Nanostructures for Food Encapsulation Purposes
Seid Mahdi Jafari
https://ebookmass.com/product/biopolymer-nanostructures-for-foodencapsulation-purposes-seid-mahdi-jafari/
ebookmass.com
The Bilateral Mind as the Mirror of Nature: A Metaphilosophy James Blachowicz
https://ebookmass.com/product/the-bilateral-mind-as-the-mirror-ofnature-a-metaphilosophy-james-blachowicz/
ebookmass.com
https://ebookmass.com/product/herod-the-great-martin-goodman/ ebookmass.com
TITANIUMALLOYSFOR BIOMEDICALDEVELOPMENT ANDAPPLICATIONS Thispageintentionallyleftblank
TITANIUMALLOYS FORBIOMEDICAL DEVELOPMENTAND APPLICATIONS DESIGN,MICROSTRUCTURE, PROPERTIES,ANDAPPLICATION JinanUniversity,Guangzhou,P.R.China
ZHENTAO YU
Elsevier
Radarweg29,POBox211,1000AEAmsterdam,Netherlands
TheBoulevard,LangfordLane,Kidlington,OxfordOX51GB,UnitedKingdom 50HampshireStreet,5thFloor,Cambridge,MA02139,UnitedStates
Copyright©2022ElsevierInc.Allrightsreserved.
Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproducedortransmittedinanyformorbyanymeans, electronicormechanical,includingphotocopying,recording,oranyinformationstorageand retrievalsystem,withoutpermissioninwritingfromthepublisher.Detailsonhowtoseek permission,furtherinformationaboutthePublisher’spermissionspoliciesandourarrangements withorganizationssuchastheCopyrightClearanceCenterandtheCopyrightLicensingAgency, canbefoundatourwebsite: www.elsevier.com/permissions
Thisbookandtheindividualcontributionscontainedinitareprotectedundercopyrightbythe Publisher(otherthanasmaybenotedherein).
Notices Knowledgeandbestpracticeinthisfieldareconstantlychanging.Asnewresearchandexperience broadenourunderstanding,changesinresearchmethods,professionalpractices,ormedical treatmentmaybecomenecessary.
Practitionersandresearchersmustalwaysrelyontheirownexperienceandknowledgein evaluatingandusinganyinformation,methods,compounds,orexperimentsdescribedherein.In usingsuchinformationormethodstheyshouldbemindfuloftheirownsafetyandthesafetyof others,includingpartiesforwhomtheyhaveaprofessionalresponsibility.
Tothefullestextentofthelaw,neitherthePublishernortheauthors,contributors,oreditors, assumeanyliabilityforanyinjuryand/ordamagetopersonsorpropertyasamatterofproducts liability,negligenceorotherwise,orfromanyuseoroperationofanymethods,products, instructions,orideascontainedinthematerialherein.
BritishLibraryCataloguing-in-PublicationData AcataloguerecordforthisbookisavailablefromtheBritishLibrary LibraryofCongressCataloging-in-PublicationData AcatalogrecordforthisbookisavailablefromtheLibraryofCongress
ISBN:978-0-12-823927-8
ForInformationonallElsevierpublications visitourwebsiteat https://www.elsevier.com/books-and-journals
Publisher: MatthewDeans
AcquisitionsEditor: ChristinaGifford
EditorialProjectManager: JohnLeonard
ProductionProjectManager: PrasannaKalyanaraman
CoverDesigner: VictoriaPearson
TypesetbyMPSLimited,Chennai,India
Listofcontributorsvii Prefaceix
1. Overviewofthedevelopmentandapplicationof biomedicalmetalmaterials1
1.1Biomedicalstainlesssteels1
1.2BiomedicalCoCralloys5
1.3Biomedicalshapememoryalloys9
1.4Biomedicalnoblemetals11
1.5Biomedicalrefractorymetals13
1.6Tianditsalloys17
1.7Degradablemetals19 References24
2. Designandphysicalmetallurgyofbiomedical β-Tialloys27
2.1OverviewofdesignmethodsofbiomedicalTialloys27
2.2OverviewofcompositiondesignofbiomedicalTialloys32
2.3Overviewofthedesignanddevelopmentoftypicalbiomedical β-Tialloys34
2.4Smeltingandphysicalmetallurgicalpropertiesoftypical β-Tialloys39
2.5DesignandphysicalmetallurgicalpropertiesofnovelTLMalloy45 References51
3. Processing,heattreatment,microstructure,andproperty evolutionofTLMalloy55
3.1Overviewofprocessingandheattreatmentof β-Tialloys55
3.2BilletsandsemifinishedproductsofTLMalloy56
3.3PlatesandstripsofTLMalloy58
3.4BarsandrodsofTLMalloy65
3.5TubesofTLMalloy71
3.6TLMalloyproductswithspecialspecifications77
3.7TLMalloyfoils83 References88
4. BiologicalandmechanicalevaluationofTLMalloy91
4.1BiologicalevaluationofTLMalloy91
4.2BiomechanicalcompatibilityofTLMalloy109 References123
5. SurfacemodificationandfunctionalizationofTLMalloy125
5.1SurfacemodificationofTialloys125
5.2SurfacefunctionalizationofTialloys128
5.3SurfacedealloyingofTLMalloy134
5.4BioactivecoatingsonTLMalloy137
5.5Wear-resistantcoatingsonTLMalloy144
5.6AnticoagulantcoatingsonTLMalloy148
5.7AntimicrobialcoatingsonTLMalloy153 References159
6. DevelopmentandapplicationofTLMalloyforthe replacementandrepairofsurgicalimplants163
6.1DevelopmentandapplicationoftraditionalTiimplants163
6.2DesignandnovelmanufactureofTiimplants165
6.3Implantsfororthopedicsandtraumarepair170
6.4Implantsforjointrepairandreplacement174
6.5ImplantsfororalandmaxillofacialrepairandreplacementofTLMalloy185
6.6MedicaldevicesofTLMalloyforspinerepair195 References196
7. DevelopmentandapplicationofTLMalloyfor treatmentofsofttissuewithminimallyinvasivesurgery199
7.1Developmentandapplicationsurveyofminimallyinvasivedevices199
7.2Designandmanufacturesurveyofinterventionaldevices201
7.3CoronarystentsofTLMalloy204
7.4NonvascularstentsandrelateddevicesofTLMalloy212
7.5ShellofbrainandheartactivedevicesofTLMalloy216
7.6OtherminimallyinvasiveandinterventionaldevicesofTLMalloy222 Reference223
Listofcontributors LeiJing NorthwestInstituteforNon-FerrousMetalResearch,Xi’an, P.R.China
XiqunMa NorthwestInstituteforNon-FerrousMetalResearch,Xi’an, P.R.China
SenYu NorthwestInstituteforNon-FerrousMetalResearch,Xi’an,P.R.China
ZhentaoYu JinanUniversity,Guangzhou,P.R.China
Thispageintentionallyleftblank
Preface Newmaterialsarethebasisandforerunnerofnewtechnological revolutions,andthedevelopmentandapplicationofthesematerialsare importantmilestonesofhumansocialcivilizationandmaterialprogress. Biomedicalmaterialsareusedmainlytodiagnose,treat,orreplace humantissuesandorgansortoimprovetheirfunctions.Theyarehightechmaterialswithadvancedstructuresorfunctionsthatarewidely applicableandhavehigheconomicvalue.Theycannotbereplacedby drugsandhavebecomeoneofthemostvigorousresearchfieldsin materialsscience.
Epoch-makingmedicaldevices,suchastitaniumhipjoints,titanium dentalimplants,CoCrvascularstents,andtitaniumartificialhearts, havesavedthelivesofpatientsandimprovedtheirqualityoflife. Amongallthebiomedicalmetalmaterials,suchasTialloys,CoCr alloys,TiNialloys,and316Land317Lstainlesssteels,theadvancedbiomedicaltitaniumanditsalloyshavebeenorarebecomingthemainand keyrawmaterialsforsurgicalimplantsandminimallyinvasiveinterventionaldevices.
Sincethebeginningofthe21stcentury,inordertocontinuously improveandenhancethefunctionaldiversity,biologicalsafety,biomechanicalcompatibility,andlong-termapplicationofbiomedicaltitaniumalloymaterials,researchonthealloydesign,novelmaterial development,processingandpreparation,microstructureandproperty evaluation,andproductapplicationofthesematerialshasbeendeepeningandbecomingaresearchhotspotinthefieldofnewbiomaterialsin theworld.Thisbookconsistsofsevenchapters,focusingprimarilyon alloydesign,physicalmetallurgy,materialsprocessing,microstructure andmechanicalproperties,surfacemodification,advancedmanufacturing,andclinicalresearchofnovelbiomedicalbeta-typeTLMtitanium alloy.Thebookalsooffersacomprehensiveandsystematicintroduction intotheresearchanddevelopmentachievementsoftheauthor’s researchgroupinthepast18years.
Thefirstchapterdescribesthelatestresearchprogressofalloy design,typicalmicrostructure,mechanicalproperties,andclinicalapplicationsofcommonlyusedmedicalmetals(stainlesssteels,cobalt chromiumalloys,titaniumalloys,shapememoryalloys,etc.)and degradablemetals(magnesiumalloys,zincalloys,etc.).
Inthesecondchapterthealloydesign,selectionofalloyelements, processandpreparation,andphysicalmetallurgyofthenewgeneration ofmetastablebeta-typeTLMtitaniumalloysareintroduced,andthe mainmechanicalpropertiesofthetypicalbeta-typetitaniumalloysthat havebeendevelopedathomeandabroadaresummarized.
Thethirdchapterintroducestheresearchonthecoldandhotprocessing,heattreatment,relatedtypicalmicrostructure,andmechanical propertiesoftherawmaterialsofplates,rods,andtubesmadeofnovel TLMalloysandintroducestheadvancedmanufacturingmethodsand typicalmicrostructureandmechanicalpropertiesofthetubesinsmalldiameterandthin-wall-thicknessfoilsandstripsandextrafinewiresof TLMtitaniumalloy.
Thefourthchapterintroducesthebiologicalevaluation(hemocompatibility,cytotoxicity,genetictoxicity,skinandoralstimulation,bone implantation,etc.)ofthenovelTLMalloymaterial,andtheresultsof researchintobiomechanicalcompatibilityofTLMalloy,including superelasticityandshapememoryeffects,high-andlow-cyclefatigue behavior,andwearresistance.
Thefifthchapterintroducestheresearchandevaluationonsurface processingandmodificationtreatments,surfacefunctionalcoatings, andtheirbiocompatibilitywithbodytissues(cells)ofnovelTLMtitaniumalloy,whichaimstoimprovethebiologicalactivity,wearresistance,andanticoagulantabilityoftitaniumalloy,inordertoendowthe surfacemultifunctioningoftitaniumalloymaterials.
Thesixthchapterintroducestheresearchanddevelopmentofnovel TLMtitaniumalloymaterialsinthefieldofsurgicalimplants,focusing onthestructuraldesign,finiteelementnumericalsimulation,advanced manufacturing,andperformanceevaluationofsometypicaldevices forrepairinghumanhardtissue,suchasdentalimplantsandartificial hipjoints.
Theseventhchapterintroducestheresearchanddevelopmentof TLMtitaniumalloyspecialmaterialsthatareusedintypicalminimally invasiveinterventionalproductsandactivemedicaldevices,focusing onthestructuraldesign,processing,andmanufacturingprocessof sometypicaldevices,suchasvascularstentsandcardiacpacemakers, andtheirrelatedperformanceevaluation.
Thebookshouldbehelpfultoresearchers,teachers,technicians,and graduatestudents,whoareengagedinbasicandappliedresearch, development,andeducationwithregardtobiomedicalmetalsbyintroducingsomenewmaterials,newtechnologies,newmethods,andnew productsofmedicaltitaniumalloys.Thebookisalsoexpectedtocontributetoourunderstandingoftheresearchanddevelopmentofnew biomaterialsandmedicaldevices,especiallytoachievethefollowing purposes:
1. Todeepentheunderstandingofalloydesignmethodsandphysical metallurgicalpropertiescontrolofnewmedicalmetalmaterialssuch astitaniumalloys.
2. Tograspthebasicprinciplesandkeytechnologiesofprocessing, preparation,heattreatment,microstructureandmechanical properties,andadjustmentandcontrolofbasicrawmaterialsand specialmaterialsofmedicaltitaniumalloys.
3. Bycomprehensivelyintroducingthebiologicalandbiomechanical properties,functionalcoating,andnewsurfacemodification technologyofthenovelTLMtitaniumalloymaterials,tostrengthen theunderstandingoftheapplicationofthisnewtypeoftitanium alloymaterialincustomdesignfunctionalityandthelong-term effectsofvariousimplantableandinterventionalmedicaldevices.
4. Byintroducingthesimulationdesign,advancedmanufacturing process,andapplicationperformanceofsometypicalmedical devicesofthenovelTLMtitaniumalloy,topromotetheapplication ofthesehigh-endproductsinavarietyofbiomedicalengineering fields.
TheliteraturereferredtointhisbookisderivedmainlyfromthepreviousresearchresultsofmygroupfromNorthwestInstitutefor NonferrousMetalResearch(NIN).Themajorcontributorsinvolvedin thecompilationofthisbookareProfessorSenYu(Chapters5 7), ProfessorXiqunMa(Chapters2 and 3).Engineer,andDr.LeiJing (Chapters1 and 4).Theothercolleagueswhoparticipatedinthesurvey andcollationofthepublishedliteratureareSeniorEngineerYafeng Zhang(Sections3.5,3.6,7.3,and7.4),SeniorEngineerJunCheng (Sections1.6,2.5,2.6,and3.1),SeniorEngineerBinbinWen(Sections 6.3,6.4,6.5,and7.5),ProfessorJinlongNiu(Sections2.3and2.7), EngineerHanyuanLiu(Sections1.2and1.3),EngineerChangWang (Sections1.7and7.1),ProfessorYushengZhang(Section5.5),Senior EngineerWangtuHuo(Section5.5),EngineerQiShen(Section7.2), EngineerXiZhao(Section2.1),andEngineerWeiZhang(Section5.5). Theothercolleagueswhoparticipatedinthesurveyandcollationofthe publishedliteratureandwhoworkinXi’anJiuzhouBiomaterialsCo., Ltd.areProfessorJianyeHan(Sections6.4and6.5),SeniorEngineer QiangHuangFu(Sections3.5,3.6,7.1,and7.3),SeniorEngineerSibo Yuan(Section6.5),EngineerHuiLiu(Sections6.3and6.4),and EngineerXiaoyanShi(Sections6.1and7.1).
ThestudyofsurfacebioactivitymodificationofnovelTLMtitanium alloymaterialsinthisbook(Section5.4)hasbeensupportedby ProfessorYongHanfromXi’anJiaotongUniversity.ThebiosafetyevaluationofnovelTLMtitaniumalloymaterialsinthisbookhasalsobeen supportedbyProfessorYumeiZhang(Sections4.1.6,4.1.7,and4.1.8)
andProfessorMinghuaZhang(Section4.1.9)fromPLAAirForce MilitaryMedicalUniversityandProfessorXiaohongLi(Sections4.1.2, 4.1.3,and4.1.4)andProfessorKunzhengWang(Sections4.1.5and4.1.9) fromXi’anJiaotongUniversity.
MycolleaguesandgraduatestudentsfromNINandJinanUniversity assistedmeintheEnglishtranslationandproofreadingofthisbook. ProfessorZengXiangFufromNorthwesternPolytechnicalUniversity andAssociateProfessorWeihongJinandDr.BaisongGuofromJinan UniversityputinalotofeffortintotheEnglishreviewandproofreadingofthisbook.Mydoctoralandmasterstudents,LanWang,Xiaojun Dai,LongchaoHe,andYunhaoXufromNINandQingyunFu, MingchengFeng,WenqiLiang,JiaxinHuang,andYueWufromJinan UniversitytookpartintheEnglishtranslationofthisbook.
Finally,Iamgratefultotheabovepeoplefortheirstrongsupport duringthebookeditingandpublishing.Inaddition,asaresultofmy limitedknowledgeandwritingability,theremightbesomeerrorsand omissionsinthebook.Isincerelywelcomecriticism,guidance,andcorrectionbyreaders.
ZhentaoYu1,2
1BiomedicalMaterialsTechnologyResearchCenter, InstituteofAdvancedWear&CorrosionResistantandFunctionalMaterials, JinanUniversity,Guangzhou,P.R.China 2BiomaterialsResearchCenter, NorthwestInstituteforNon-FerrousMetalResearch, Xi’an,P.R.China
metalmaterials 1.1Biomedicalstainlesssteels
1.1.1Overviewofbiomedicalstainlesssteels
Biomedicalstainlesssteelhasgoodbiocompatibility,mechanicalproperties,andcorrosionresistanceaswell asexcellentprocessingandforming capabilities,andithasalowcost.Thereforeitisaclassofmetalmaterials thathavebeenwidelyusedinmedicaldevicesandequipment.
Becauseofthelackofintergranularcorrosionresistanceandstress corrosionresistanceoftraditionalindustrialstainlesssteel,biomedical stainlesssteelmaterialsmainlyincorporateausteniticstainlesssteel withthebestcorrosionresistancetoreducethedissolutionofpotentiallyharmfulmetalionsinthealloy,suchasnickelandchromium ions.Thisputsforwardhigherrequirementsforthecompositionregulationofmedicalstainlesssteel.Medicalstainlesssteelusuallyrequires strictcontrolofNiandCrcontentandlowimpurityelementcontent, andthesizeofnonmetallicinclusionsshouldnotexceedgrade1.5(fine series)andgrade1(coarseseries).Inaddition,thecarboncontentinthe alloymustnotexceed0.03%toimproveitsintergranularcorrosionresistance [1].Thedetailedchemicalcompositionsarelistedin Table1.1
However,theNielementthatisusedtostabilizetheaustenitephase instainlesssteeltendstocausesometissuereactionsandotherproblemswhenitdissolves,suchascontactdermatitisandeczema,andit maycausecancerandmayevencauserestenosisafterthecardiovascularstenttosomeextent,whichislifethreatening.Thereforedomestic
TABLE1.1 Comparisonofchemicalcompositionsoftypicalmedicalstainlesssteelmaterials(wt.%).
022Cr19Ni13Mo3(S31703)317L
Source:datafromGB/T1220 2007StainlessSteelBars,StandardizationAdministrationofChina.
andforeignresearchinstitutionshavebeguntodevelopaseriesofnew biomedicalstainlesssteelssuchaslow-nickelornickel-freeaustenitic stainlesssteelandantibacterialstainlesssteeltomeettheincreasing requirementsofthemedicalandhealthfield.
1.1.2Nickel-freeausteniticstainlesssteels Nimainlyplaysaroleinstabilizingtheaustenitephaseinaustenitic stainlesssteel.Thereforeitisnecessarytoaddanewnontoxicaustenite stableelementtoreplaceNitodevelopNi-freeausteniticstainlesssteel. Nitrogenisanidealaustenitestabilizingelementwithalowcost.Ithas astrongstrengtheningeffectasaninterstitialatom,whichcansignificantlyincreasethestrengthofstainlesssteelwithoutreducingitsplasticity.BecausetheNielementwasreplacedwitharelativelyhigh contentofNtostabilizetheausteniticstructureofstainlesssteel,nickelfreestainlesssteelhasalsobeencalledhigh-nitrogennickel-free (HNNF)stainlesssteel [2],whichhasbeenthemostwidelyused. Forexample,0.9wt.%NelementinBIOSSNstainlesssteelcangiveit theplasticityandtwofoldstrengthof316Lstainlesssteel [1,3].The Fe21Cr22Mn1Mo1NHNNFstainlesssteeldevelopedintheUnitedStates hasbeenputintotheUSmedicalmarkettoreplaceCrNiseriesstainless steel.Chinahasalsomadeimportant achievementsinthisregardandhas developedFel7Cr14Mn2Mo(0.45 0.7)NbiomedicalHNNFausteniticstainlesssteelwithexcellentcomprehensiveproperties,suchashighstrength, fatigueresistanceandexcellentwearresistance [3].Themechanicalproperties,suchastensilestrength(Rm),yieldstrength(Rp),elongation(A),and areareduction(Z),ofHNNFstainlesssteelareshownin Table1.2.
TABLE1.2 MechanicalpropertiesofHNNFstainlesssteel.
Material
316L(solution)2255556472290164
Co62Cr28Mo6(solution)4921013192433318
HNNFstainlesssteel(solution)5378845271193262
HNNFstainlesssteel(10%cold deformation) 85710083673 316
HNNFstainlesssteel(20%cold deformation) 104111053070
HNNFstainlesssteel(30%cold deformation) 117512152468
Source:datafromGB/T1220 2007StainlessSteelBars,StandardizationAdministrationofChina.
1.1.3Antibacterialstainlesssteels Withthedevelopmentofsocietyandtheimprovementofpeople’s healthawareness,thethreatfromthespreadofbacteriahasattracted increasingattention.Accordingly,peoplehaveputforwardhigher requirementsfortheantibacterialpropertiesofbiomedicalstainless steel.Humanshavelongrealizedthatmetalionssuchassilverandcopperionshavestrongantibacterialeffects [4,5].Theantibacterialeffects ofmetalionsareasfollows:Hg . Ag . Cd . Cu . Zn . Fe . Ni.The antibacterialeffectofthespecificalloydependsonwhetherthereare enoughactiveparticlesoftheelementonthealloysurface.Forexample, FeandNihavecertainantibacterialfunctions;however,itisdifficultto showtheirantibacterialfunctionsbecausethepassivationlayeroroxide layerformseasilyonthemetalsurface.
Althoughmanymetalshaveantibacterialfunctions,notallelements aresuitableforuseasantibacterialelementsforcomprehensivesafety andantibacterialpropertiesreasons.Atpresent,themostcommonly usedantibacterialelementsareCuandAg.Ithasbeenfoundthatthat afteraddingCuelementtostainlesssteel,auniformlydispersedand stable ε-Cuphasewillbeformedinthestainlesssteelmatrix,whichcan providealong-lastingandstableantibacterialeffect.
Hongetal. [6] studiedtheeffectofcoppercontentandagingtreatment onSUS304austeniticstainlesssteelandfoundthattheresidualferrite contentinas-castSUS304steeldecreasedwiththeincreaseofCucontent andthattheadditionofCuinhibitedtheformationofmartensiteinduced bystrain.Corrosiontestsshowthatthepittingpotentialdecreaseswith theincreaseofCucontentinSUS304steel.Theresultsoftheantibacterial testshowthattheadditionofanappropriateamountofCu(2wt.%)can giveSUS304stainlesssteelexcellentantibacterialproperties.Whenthe addedamountofCuexceeds3.5wt.%,eveniftheagingtimeisasshort as30minutes,theantibacterialratecanreach99.99%.However,the amountofaddedCushouldnotexceed3.5wt.%toensurethattheCucontainingSUS304steelcanachieveabalancebetweenformability,corrosionresistance,andantibacterialproperties.ChenandThouas [7] foundthatdissolvedCu21 playsamajorantibacterialroleinantibacterial stainlesssteel,whichledtothecollapseofsomelipopolysaccharide patchesonthecellsurface,thuschangingthepermeabilityandphysiologicalfunctionoftheextracellularmembrane,providingastructural basisfortheantibacterialeffectofCu21 onmicroorganisms.
1.1.4Application Accordingtoapreviousstudy [1],whentheNicontentexceeds 12wt.%,single-phaseaustenitecanbeobtained,andCrcanforma
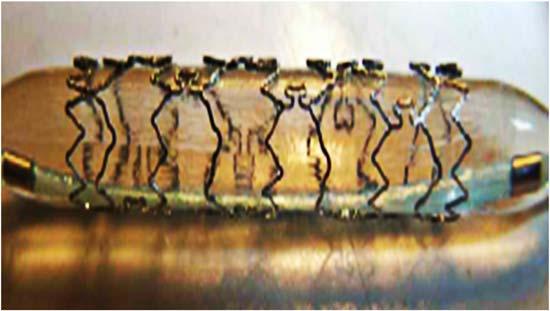
chromiumoxidepassivationfilmtoimprovecorrosionresistance.As theNcontentincreases,theHNNFausteniticstainlesssteelhasbetter anticoagulantperformance.Thereforethenewbiomedicalstainlesssteel notonlycanbeusedtomakeartificialjoints,spinalinternalfixationsystems,andfractureinternalfixationdevices,suchasboneplates,bone screws,andsurgicaltools,butalsocanbeutilizedincardiovascularsystems,suchasinartificialheartvalvesandintravascularstents.Atypical coronarystentmadefromHNNFausteniticstainlesssteelisshownin Fig.1.1.Itcanalsobeusedfordentalcrowns,dentalorthopedicwires, ophthalmicsutures,artificialeyewires,orbitalfillings,andothermedicaldevices.
1.2BiomedicalCoCralloys 1.2.1OverviewofCoCralloys ThefirstapplicationresearchofCoCralloysinsurgicalimplantcan bedatedtothe1930s,whentheyweremadeascastpartsandthen forgedalloys.Thecasting,extrusion,andforgingconditionshaveasignificanteffectonthecorrosionresistanceandmechanicalpropertiesof thealloy.Generallyspeaking,castingtendtoproducecoarsegrains, grainboundaryseparation,porosity,andshrinkageinCoCralloys. Althoughcastingalloysaresuperiortononcastingalloysintermsof wearresistance,pittingresistance,andcrevicecorrosionresistance,they areinferiortoforgedalloysintermsoffatiguestrengthandfracture toughness.Thereforetheuseofprecisioncastingcaneliminatethe structuraldefectsofthealloysandalsoimprovetheirmechanicalproperties.Theuseofforging,extrusion,rolling,drawing,andotherhot
FIGURE1.1 CoronarystentofHNNFstainlesssteel.
pressureprocessingmethodscanfurtheramelioratetheas-caststructure ofthematerialandachievebettermechanicalproperties [7].Inaddition, withthedevelopmentofthree-dimensional(3D)printingtechnology, theuseof3DtoprepareCoCralloyproductsisanewmethodthathas highprocessingspeedandstrongcustomizationandcanbeeffectively appliedintreatingbonedefectsanddentistry.
Co-basedalloysaregenerallyCoCralloys,ofwhichtherearetwo basictypes:CoCrMoalloyandCoNiCrMoalloy.Sixtypesofalloys havebeenincludedinmedicalstandards.TheCoCrMoalloyhasan austeniticstructure,whichcanbeproducedbyforgingorcasting,butit isverydifficultbycolddeformation.Itsmechanicalpropertiesandcorrosionresistancearebetterthanthoseofstainlesssteel,makingitarelativelygoodbiomedicalmetalmaterial.ForgedCo-basedalloysareused mainlytomakereplacementprosthesesforkneeandhipjoints.The AmericanSocietyforTestingandMaterialsrecommendsfourCoCr alloysthatcanbeusedinsurgicalimplants:forgedCoCrMo(F76), forgedCoCrWNi(F90),forgedCoNiCrMo(F562),andforged CoNiCrMoWFe(F563),inwhichF76,F90,andF562havebeenwidely usedinthemanufactureofsurgicalimplants.Acomparisonofthe mechanicalpropertiesofdifferentmetalimplantmaterialsisshownin Table1.3.
OwingtotherelativelyhighcontentofCrinCoCralloys,Crspontaneouslyformsaninertoxidelayer(Cr2O3)inthehumanenvironment, sothecorrosionresistanceofCoCralloysisbetterthanthatofstainless steel.Asinstainlesssteel,Cr,Mo,andNiallhavecorrosionresistance. Tungsten(W)isaddedtoincreasesolidsolutionstrengtheningandcontrolthedistributionandsizeofcarbides,butitwillalsoreducethecorrosionresistanceandcorrosionfatiguestrengthofCoCr-basedalloys. ThedissolutionofCoandNifromCoCralloyswillcausecellandtissue necrosis.Co,Ni,andCrcanalsocauseallergicskinreactions,ofwhich Cohasthegreatestimpact.Thereforeitisoftheutmostimportanceto strictlycontrolthephasestructure,grainsize,andiondissolutionlimit ofCoCralloys.
1.2.2TypicalmicrostructureandpropertiesofCoCralloys
CoCralloysaregenerallycomposedofsolidsolution strengthenedaustenitematrixandcarbidesdistributed inthematrix.Thetypeandcontentof precipitatedphasesarecontrolledbyregulatingtheheattreatmentprocesses tostrengthenthematrix.CoCralloyshavelowstackingfaultenergy,leading totheformationofalargenumberofannealingtwinsafterannealing [8].Li etal. [9] studiedthemicrostructureevolutionofbiomedicalL605alloyduringtheprocessofmultipassthermomechanicalprocessing(TMP),indicating
TABLE1.3 ComparisonofmechanicalpropertiesamongdifferentCoCralloys.
MaterialsBrandISOASTM Rm (MPa) Rp (MPa) A (%)Condition
Co28Cr6MoCoCrMo5832 4F756554508Cast
Co20Cr15W10NiL6055832 5F90125076015Hard
Co19Cr17Ni14Fe7Mo1.5MnGrade2 Phynox 5823 7F10581170 2240690 17251 17Hard 1 age
Co20Cr20Ni5Fe3.5Mo3.5W2TiSyncoben5832 8F6531310117212Hard
Co28Cr6MoWroughtCoCrMo Alloy2 5832 12F1537100070012Hard
Co28Cr6MoWroughtCoCrMo Alloy1 5823 12F153789751720Annealed
Co20Cr15Ni15Fe7Mo2MnGrade1 Elgiloy 5823 7F10581860 22751240 1450 Hard 1 age
Co35Ni20Cr10MoMP35N5832 6F5621207100010Hard
18Cr14Ni2.5MoWroughtstainlessSteel5832 1F138/490 80019040Annealedhard 139860 110069012
8 1.Overviewofthedevelopmentandapplicationofbiomedicalmetalmaterials
thatafter5passesofTMPtreatment,thegrainscanberemarkablyrefined, andabimodalgrainmicrostructurecomposedoffinegrains(3 μm)and coarsegrains(4 16 μm)canbeformed.Suchabimodalgrainmicrostructureprovidessuperiormechanicalpropertieswithatensilestrengthof 1197 1304MPa,ayieldstrengthof593 738MPa,andauniformelongation of54.7% 61.1%.
StudieshaveshownthatwhentheconcentrationofCu21 islower than500mm,Cuionscanpromotetheproliferationofhumanvenous endothelialcellsbuthaveaninhibitoryeffectontheproliferationof arterialsmoothmusclecells.Wangetal. [10] andothershavestudied theeffectoftheadditionofCu(1 4wt.%)onthestructure,corrosion, mechanicalproperties,andcytotoxicityofL-605alloy,aimingto developanewtypeofbiologicalfunctionalalloy.Theresultsshown thatdendritesegregationoccursinallL-605alloyswithdifferentCu contentsduringthecastingprocess,andtheadditionofcopperreduces thecorrosionresistanceofthealloy,slightlyreducesthemicrohardness ofthematerial,andhasalimitedeffectsonthecompressionperformanceofthematerial.CCK8resultsshownthatL-605Cualloyhas goodcellviability,andtheadditionofCudoesnotcausecytotoxicity.
1.2.3TypicalapplicationofCoCralloys AlthoughtheNicontentofL-605islowerthanthatof316Lstainless steel,sensitivereactionsinducedbyNimayalsooccur.Althoughits mechanicalpropertiesaresimilartothatofCoCrMoalloy,itsmechanicalpropertiesaretwiceashighasthatofCoCrMoalloyundertheconditionofcoldworkingdeformationof44%,andthestresscorrosion crackingresistanceinaqueoussolutionisalsoimproved.Intheworkhardenedstate,L-605alloyisstillnonmagnetic.ThereforeL-605alloyis commonlyusedforcardiovascularstents,anditsannealedstatecanbe usedasasurgicalfixationsuture.MP35Nalloyhasveryhightensile propertiesinthework-hardenedstateandthework-hardenedaging state,whichhasalmostthehighestmechanicalpropertiesamongall implantedmetalmaterials.ThereforeMP35Niswidelyusedtoproduce artificialjoints,pacemakerelectrodewires,stylets,urinarycatheters, andorthopedicwires.
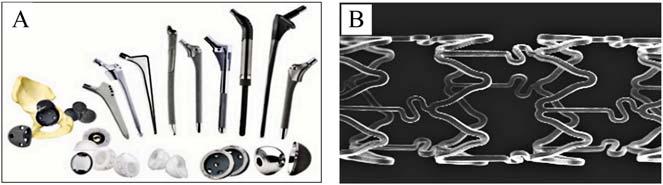
Ingeneral,comparedwithstainlesssteel,CoCr-basedalloyshave higherstrength,morestablepassivationfilm,andbettercorrosionresistanceandwearresistance.Thereforetheyaremoresuitablefor manufacturingsurgicalimplantsinthebodyforlong-termservicethat needtobearhighloadsandhavehighwearandcorrosionresistance, suchasartificialjoints,vascularstents,anddentalcrowns.TypicalmedicaldevicesmadefromCrCo-basedalloysareshownin Fig.1.2.
1.3.1Overviewofshapememoryalloys
Shapememoryalloyreferstoatypeofmetalmaterialthatcanbe restoredtoitsoriginalshapeandsizeafteraproperthermodynamic process,thatis,atypeofmetalmaterialdevelopedbytheprincipleof reversiblemartensiticphasetransformation.Sincethediscoveryof shapememoryphenomenoninthe1960s,morethan20kindsofmemoryalloyshavebeenstudiedaroundtheworldandhavebeenwidely used.Atpresent,themostwidelyusedmemoryalloyisTiNi(orNiTi) shapememoryalloy [11].
NiTishapememoryalloyhasshapememorycharacteristicsand superelasticityinthephasetransitionzone.Atlowtemperatures (around0 C)ithasamonocliniccrystalphase,whichissoftand deformable.Whenthealloyisheatedtoahightemperature,itbecomes acubiccrystalphaseandimmediatelyreturnstoitsoriginalshapeand produceacontinuoussoftrestoringforce.Atthistime,thematerialis hardandelastic,whichcanbeusefulinorthopedicsorsupport.The memoryrecoverytemperatureofthealloyisclosetothetemperatureof humanbody(36 C 6 2 C),Becauseitexhibitsgoodbiocompatibility, corrosionresistance,andabrasionresistance,thismetalmaterialis calledanewfunctionalmaterialinthe21stcentury [12].
1.3.2Typicalcompositionandbrandofshapememoryalloys
NiTishapememoryalloyisanalloywith54.5 57.0wt.%Ni.The chemicalcompositionofNiTishapememoryalloyhasasignificant effectonthephasetransitiontemperature(PTT).ForNiTibinarysystem shapememoryalloys,thePTTwilldecreasebyabout10 Cforevery 0.1%increaseinNicontent,whichcanbecontrolledbyadjustingtheNi content.However,whentheNicontentistoohigh( . 51%,atomicfraction),thealloyprecipitatesNi-richcompoundssuchasTiNi2 andTiNi3,
FIGURE1.2 TypicalmedicaldevicesofCrCoalloys.(A)Jointprostheses.(B)Stent.
TABLE1.4 Thetypicalplate,rod,andwireproductsofNiTimemoryalloy.
MaterialtypesGradePTT(Af/ C)Standard
Rod,wireNiTi 01/NiTi 0220 40ASTMF2063 12/GB24627 2009
NiTi ss45 90
TN3/TNC5 15
NiTi ss/NiTi yy 30to20
NiTiCu33 6 3
NiTiNbAs Ms # 5
NiTi ssAs Ms , 150
PlateNiTi 01/NiTi 0220 40
NiTi ss45 90
NiTi yy5 15
whichreducesNicontentinmatrix,resultinginanincreaseinthePTT andbrittlenessofthealloy.TheadditionofathirdelementtotheTiNi alloywillalsosignificantlyaffectthePTT.Forexample,addingV,Cr, Mn,orAltoreplaceTioraddingCoorFetoreplaceNicanlowerthe PTT.ThedetailedPTTsofdifferentNiTimemoryalloysareshownin Table1.4.
1.3.3TypicalapplicationofNiTishapememoryalloys Atpresent,NiTishapememoryalloysareusedmainlyforcardiovascularandcerebrovascularandnerveinterventionaltreatments,suchascardiovascularstents,cerebrovascularstents,andperipheralvascularstents forlaryngotracheal,esophageal,andurethralstenosis,aswellaspercutaneoustransluminalcoronaryangioplastycathetershafts,nerveterminalarea stentcatheters,internalandmirrorinspectiondeliverysystems.Inthe fieldsofartificialjointreplacement,spinalrepair,traumasurgery,and sportsmedicine,NiTishapememoryalloyscanbeusedforartificialjoints, spinalcorrectiondevices,patellaclaws,patellarcollectors,boneplates,sternumfixators,embracingdevices,andtensionhooks.Inthefieldoforal cavityanddentistry,thesealloyscanbeusedfordentalorthopedicsand dentalsurgicaltreatmenttools,suchasdentalarchwires,dentalmemory fixators,androotcanalfiles.Inthefieldsofcardiovascularsurgery,general surgery,urology,gastroenterology,gastrointestinalotolaryngology,and otherfields,thealloyscanbeusedforsurgicalaccessoriesforendoscopic examinationandlaparoscopicsurgery,suchasvalveregulators,tissue retractors,surgicaltools,andcatheters.
Noblemetalshavegoodcorrosionresistanceandductilityaswellas goodbiocompatibilityandphysiologicalnontoxicity.Thereforetheyare widelyusedinthemedicalfieldandhavebroadapplicationprospects indentistry,acupuncture,implantableelectronicdevices,preciousmetal drugs,andmedicalbiosensors [13].
1.4.1Dentalmaterials Goldisthefirstmetaltobeusedindentalmaterials.Asearlyas2000 yearsago,ancientpeopleusedgoldtofixorfillteeth.Sincethedental goldalloysareusedmostlytomakejewelryorgoldcoins,suchas AuAgCu,Au10Cu,andAuPtPd,thesealloysareeasytoformrough segregatedgrainsduringcastingandsolidification.Sometimesthealloy loseslusterintheenvironment,sopeopletrytoimproveitscorrosion resistancebyaddingotheralloyingelements.Forexample,addinga smallamountofRu,Os,orIrtotheAu Pt Pdalloycanrefinetheascaststructureandincreaseitsstrength.AddingacertainamountofPt, Pd,Zn,andotherelementstoAu10Cualloycangiveitbetteranticorrosionandantidarknessabilitiesandcanpresentdifferentcolors,providingmorechoicesforpatientswithdifferentoralestheticneeds [13 15].
Since1968,toreducethecostofmaterials,aseriesofdentalgold alloyswithlowgoldcontenthavebeenstudied,includingprecious metalcastingalloysandporcelainfusedtometalalloys.Inaddition, owingtotheirpriceadvantage,nonpreciousmetalsalsooccupyaplace inthedentalmarket,graduallyformingthethreepillarsofgoldalloys, palladium-basedalloys,andnonpreciousmetalalloys.Thecommon compositionsofnoblealloysareshownin Table1.5.
1.4.2Acupuncturematerials Acupunctureandmoxibustionareimportantpracticesintraditional Chinesemedicine.Theyarenotonlyuniqueintheirmethods,butalso haveremarkablecurativeeffects.Acupuncturehasbeendevelopedand appliedinmorethan100countries,suchastheUnitedStates,France, andGermany.Acupunctureneedlesmainlyincludegoldneedles,silver needles,andhardneedles.Thehardneedlesaremainlymadeofstainlesssteel.Becauseofthelowhardnessofpuregoldandsilver,theseelementsnotsuitabletobeusedasaneedle,sothehardnessmustbe improvedbyalloying.Atpresent,thecommonlyusedgoldneedlesare madeof10K,12K,14K,and18Kgold,ofwhich14Kgoldisthemost widelyused.Becauseofthediscolorationofsilverneedles,itis
TABLE1.5 AuAgCualloycomposition.
Source:datafromY.Wang,Q.Cao,Z.Jia,J.Zheng,Applicationanddevelopmentofpreciousmetalsinthefield ofmedicine,RareMetalMaterialsandEngineering43(2014)165 170. 12 1.Overviewofthedevelopmentandapplicationofbiomedicalmetalmaterials
necessarytosimultaneouslyimprovetheircorrosionresistanceduring alloying.Amongthecommonlyusedsilverneedles,Ag Pdsilverneedleshavethebestcorrosionresistance,buttheircostishigher.AgSn andAgSnInalloyshavelowercostbutpoorductility,whileAgCuZn haslowercostandbetteroverallperformance.
1.4.3Medicinalpreciousmetals Becauseofthespecialpropertiesofpreciousmetals,suchasantiinflammatoryandsterilization,theyarewidelyusedinthepharmaceutical industry.Thepreciousmetalsthathavebeenusedtomakemedicines includegold,silver,platinum,andosmium.InChinatheuseofgold medicinetotreatdiseaseshasalonghistory,whichcanbetracedbackto 2500BCE.Europeanshavealsousedgoldmedicinetotreatdepression, fainting,fever,epilepsy,andotherdiseases.Theorganiccompoundsof goldhaveantiinflammatoryeffects,andtheoralmedicineanuranofin, whichwasdevelopedin1985,peakedthedevelopmentofgoldmedicine [16].Asanoralmedicinefortreatingarthritis,ithasmanyexcellentpropertiesthatoutcompetetheinjectiontype.Italsohasaninhibitoryeffect onlymphomaandisexpectedtobeapotentialanticancerdrug.
Silverisabactericidalmetalthatisinferioronlytomercury.Ag1 has astrongbactericidaleffectwithverylittleconsumption.Generally,it cansterilizeatalevelof1 3 10 6molL 1.Inancienttimes,people
discoveredthatsilverwarehasacertainanticorrosiveandfresh-keeping function.Sincethe1990sresearchanddevelopmentofsilversterilizationmaterialshavedrawngreatattention.Peopletakeadvantageofthe bactericidalandantibacterialpropertiesofAg1 topreparematerials withbactericidalfunctions,suchasmedicaldevicecleaningfluids,bactericidalbandages,thegauze.Someorganicsilvercompoundantibacterialagentscanalsobeusedtotreatlocalinfections,syphilis,andother diseases.
Platinumdrugsarealsocommonlyusedpreciousmetaldrugs.Inthe middleofthe18thcentury,platinummedicinewasusedtotreatsyphilisandrheumatism,whicharousedpeople’sinterestinplatinummedicine.Inthe1970s,ProfessorLuxembourgintheUnitedStatesfirst reportedthatcisplatinhasbroad-spectrumanticanceractivity,opening upanewfieldofanticancerdrugresearch [17].
1.4.4Surgicalmaterials Becauseoftheirexcellentcorrosionresistanceandbiocompatibility, preciousmetalssuchasgoldandsilverarewidelyusedassurgical implantmaterials.Forexample,Agalloycanbeusedasacraniomaxillofacialsubstitutematerialinbrainsurgery.Silveramalgamcementcan beusedfororthopedicrepairsurgery,andhigh-purityAumembraneis usedaseartympanicmembranerepairmaterial.Incancerradiotherapy, implantingPt-coatedIrwireorwiremeshcanshieldhealthytissues fromradiationdamage.
1.5Biomedicalrefractorymetals
1.5.1Overviewofbiomedicalrefractorymetals
Biomedicalrefractorymetalsmainlyincludetantalum(Ta),zirconium (Zr),hafnium(Hf),niobium(Nb),tungsten(W),molybdenum(Mo), andvanadium(V).Thecommoncharacteristicsofthesemetalsarehigh density,highmeltingpoint,highhardness,strongcorrosionresistance, goodchemicalstability,andrelativelyhighprice.Thereforetheyare usedmainlyasalloyadditionelementsofstainlesssteel,cobalt chromiumalloyandtitanium(Ti)alloyandthusareusuallynotusedalone asbiomedicalmetalmaterials.Ti(1 60wt.%)Zrisanewtypeofmedicalalloythatissuitableforthedesignanddevelopmentofdental implants,denturebrackets,andotherdentalproducts.TheTiNb (1 45wt.%)andTiTa(1 45wt.%)alloyscanbeusedfororthopedic implants,suchasartificialjoints [18]