https://ebookmass.com/product/the-earth-through-time-10thedition/
Instant digital products (PDF, ePub, MOBI) ready for you
Download now and discover formats that fit your needs...
Eleanor (Omegas Through
Time Book 2) Calliope Stewart https://ebookmass.com/product/eleanor-omegas-through-timebook-2-calliope-stewart/
ebookmass.com
Burning Planet: The Story of Fire Through Time Andrew C. Scott
https://ebookmass.com/product/burning-planet-the-story-of-firethrough-time-andrew-c-scott/
ebookmass.com
Earth Science (15th Edition)
https://ebookmass.com/product/earth-science-15th-edition/
ebookmass.com
Freed James
https://ebookmass.com/product/freed-james-4/
ebookmass.com
Sams Teach yourself Java in 24 Hours [8th Ed] 8th Edition Rogers Cadenhead
https://ebookmass.com/product/sams-teach-yourself-javain-24-hours-8th-ed-8th-edition-rogers-cadenhead/
ebookmass.com
Big Data Mining for Climate Change Zhihua Zhang
https://ebookmass.com/product/big-data-mining-for-climate-changezhihua-zhang/
ebookmass.com
Handbook of Clinical Psychopharmacology for Therapists (Ebook PDF)
https://ebookmass.com/product/handbook-of-clinical-psychopharmacologyfor-therapists-ebook-pdf/
ebookmass.com
Textbook of Lifestyle Medicine (Feb 10, 2022)_(1119704421)_(Wiley-Blackwell) Labros S. Sidossis
https://ebookmass.com/product/textbook-of-lifestyle-medicinefeb-10-2022_1119704421_wiley-blackwell-labros-s-sidossis/
ebookmass.com
Management: A Practical Introduction 7th Edition Angelo Kinicki
https://ebookmass.com/product/management-a-practical-introduction-7thedition-angelo-kinicki/
ebookmass.com
Das Herz des irischen Löwen (Love, Books & Magic 1)
(German Edition) C. Shamrock & Dagny Fisher
https://ebookmass.com/product/das-herz-des-irischen-lowen-love-booksmagic-1-german-edition-c-shamrock-dagny-fisher/
ebookmass.com
Harold(“Hal”)Levin beganhiscareerasapetroleum geologistin1956afterreceivingbachelor’sandmaster’s degreesfromtheUniversityofMissouriandadoctorate fromWashingtonUniversity.Hisfondnessforteaching broughthimbacktoWashingtonUniversityin1962,where heiscurrentlyprofessoremeritusofgeologyand paleontologyintheDepartmentofEarthandPlanetary Sciences.Hiswritingeffortsincludeauthorshipoften editionsof TheEarthThroughTime;foureditionsof ContemporaryPhysicalGeology; LifeThroughTime;EssentialsofEarthScience;andco-authorshipof Earth: PastandPresent,aswellasnineeditionsof LaboratoryStudiesinHistoricalGeology;and Ancient InvertebratesandTheirLivingRelatives
Forhiscoursesinphysicalgeology,historicalgeology,paleontology,sedimentology,and stratigraphy,Halhasreceivedseveralawardsforexcellenceinteaching.Theaccompanying photographwastakenduringalectureonlifeoftheCenozoicEra.Thehorseskullservestoillustrate changesintheteethandjawsofgrazinganimalsinresponsetothespreadofprairiesandsavannahs duringtheMioceneandsubsequentepochs.
StudentsenrolinanEarthHistorycourseformany reasons.Oftenitissimplytosatisfyacollegescience requirement.Thoseofuswhoteachthecourse,however,strivetoprovideabetterreason.Wehopeto instillinourstudentsknowledgeabouthowourplanet becameahavenforlife;how change hasdominated Earthhistory;andhowchangewillcontinuetochallengeusinthefuture.Inthegeologicpast,changehas beendrivenbynaturalforces.Nowwehumans,only recentlyarrivedonEarth,areanadditionalcauseof change.Moreoftenthannot,wecausechangethatis harmful.Thesearereasonswhyourstudentsneedto morefullyunderstandthissmallandovercrowded planet.Theyneedtolearnfromitshistory,itscatastrophes,anditssuccesses.
ThistextbookchroniclestheEarth’sstoryfromthe timetheSunbegantoradiateitslight,tothebeginning ofcivilization.Itisahistorythatbegan4,600million yearsagoafterourplanethadgatheredmostofitsmass fromarotatingcloudofdust,gases,andmeteorites. Fromthattimetothepresent,theEarthhasexperiencedclimaticshiftsfromwidespreadwarmthtoice ages.Thefloorsoftheoceanshavealternately expandedandcontracted.Continentshavedrifted thousandsofmiles,coalescedorsplinteredapart. Rockshavebeenthrustskywardtoformloftymountains,andplacidlandscapeshavebeendisruptedby earthquakesorburiedinfloodsoffierylava.
Atleastforthepast300millionyears,lifehasexisted onourplanet.Fossilremainsofthatlifeattesttobiologicalachievementsandfailuresincopingwithchanging conditions.Therearelessonstobelearnedfromour biologicalhistory—lessonsthatwillhelpusanticipate andactwiselytodangerswemayfaceinthefuture.
LearningwhathashappenedonEarthinthepastis sufficientreasontostudyEarthHistory.Acoursein HistoricalGeology,however,hasvalueinmanyother waysaswell.Asascience,itinformsusaboutawayto answerquestions,howdiscoveriesaremade,andhow totellthedifferencebetweenvalidandfaultyassumptions.Allofthiscomesbywayoftheso-calledscientificmethod.Theterm“scientificmethod”maysound abitformidabletostudents,butitisonlytherational wayweaskquestions,makeeducatedguessesabout theanswers,andtestthoseanswersbyobservationor experimentation.Asoneexample,wemightinferthat thedemiseofaparticulargroupofancientanimals resultedfromcoolingoftheplanet.Thisleadsustoask
whycoolingoccurred.Wasittheresultofchangesin theamountofradiationreceivedfromtheSun,ashift intheEarth’saxisofrotation,changesinthecompositionoftheatmosphere,ormajorchangesinthe distributionofcontinents?TheEarthscientiststest eachoftheseideasinthelaboratoryandexaminerocks oftheappropriateagetofindthebestanswer.That answerisalwaystentativeandsubjecttonewdiscoveries.Usually,theanswerrelatestoreciprocalactions ofalltheEarth’s systems: theatmosphere,biosphere, andsolidEarth.Studentswillreadofsuchanintegratedapproachtoansweringquestionsaboutthe geologicpastinthepagesahead.
TheEarthThroughTime isdesignedfortheundergraduatestudentwhohaslittlepreviousacquaintance withgeology.Studentsexploringthepossibilityofan academicmajoringeology,however,canbeconfident thatthetextwillprovidethenecessarybackgroundfor advancedcourses.Ihaveincludedbasicinformation aboutminerals,igneous,andmetamorphicrocksso thatthetextcanbeusedeitherforasingle,selfcontainedfirstcourse,orforthesecondcourseina two-semestersequenceofPhysicalGeologyfollowed byHistoricalGeology.
cTHETENTHEDITION Thegoalof TheEarthThroughTime istopresentthe historyoftheEarth,andthesciencebehindthat history,assimplyandclearlyaspossible.Wehave strivedtomakethenarrativemoreengaging,toconvey theuniqueperspectiveandvalueofhistoricalgeology, andtoimprovethepresentationsoastostimulate interestandenhancethestudent’sabilitytoretain essentialconcepts,hopefully,longafterthefinalexam.
Inthistenthedition,wehavegreatlyimprovedthe illustrationprogramwithabout140newphotographs. Alsoincludedaredrawingspreparedbytheauthor. Theseareoftenmoreinstructivethanaphotographof thefossilitself.Thereislittledoubtthatgoodillustrationshelpstudentslearnandretaininformation. AstheRussianwriterIvanTurgenevwrotein1862, “Apictureshowsmeataglancewhatittakesdozensof pagesofabooktoexpound.”
Theseventeenchaptersinthetentheditionhave beenorganizedintothreemajordivisions.PartI, DiscoveringTimeandDecipheringEarth’sAmazingHistory,explainsthemethodsusedinreconstructingEarth
history,andtheimportantcontributionsofearlygeologists.Studentswilllearnhowrocksaredatedand thenusedtoconstructageologictimescaleinthethird chapterofPartI.PartII, RocksandFossilsandWhat TheyTellUsaboutEarthHistory,describesthenature andoriginofEarthmaterials,andhowrocksand fossilsrevealeventsofthegeologicpast.InPartIII, TheHistoryofPlanetEarthandItsInhabitants, we examinetheactualhistoryofourplanet,fromitsfiery birthtotheunfoldingofthemodernworld.New informationhasbeenprovidedrelatingtohowscientifichypothesesarevalidated,thehistoryofdiscoveries relatingtoradioactivedating,howvolcanicactivity relatestoatmosphericchangeandextinctions,the “snowballEarth”controversy,laggerstatten,new energysources,theroleofHOXgenesinevolution, theGreatOrdovicianBiodiversityEvent,andanimaginativewalkthroughaCarboniferousrainforest.We thoroughlyreviewedthepreviousedition,updated information,addednewdiscussions,andobjectively deletedmaterialrarelyusedintoday’shistoricalgeologycourses.
cHOWDOES THEEARTHTHROUGH TIME HELPSTUDENTSLEARN? TheEarthThroughTime hasanumberoffeaturesto engagethestudentandpromotelearning.
QuestionsforReview allowsstudentstotesttheir understandingofmaterialinachapterandtofurther processwhattheyhavelearned.Inthiseditionwe haveaddedoverseventy-fivenewquestions.
ChapterSummaries.Eachchapterendswitha summaryofessentialconcepts,affordingstudents thecondensed“meat”ofatopic.Ifthesummary statementisnotfullyunderstood,itisacuetorevisit thetopicinthechapter.
Technicalterms areprintedin boldface thefirst timetheyareused.AlistofKeyTermsisprovidedat theendofthechapter,alongwiththepagenumber onwhichtheyaredefined.Ifencounteredlaterin thetext,thestudentcanseethetermdefinedagain inthebook’s Glossary. Sothatstudentscananticipatewhatliesahead,each chapterbeginswithalistof KeyChapter Concepts.
Captionquestions occurbeneathmanytextfigures. Thesedrawattentiontogeologicorfossilfeatures andhelpclarifyinformationprovidedinthetext. Appendices includea ClassificationofLiving Things thathelpsstudentsplacefossilsdescribed inthetextinthetextwithintheirtaxonomicgroup. Theappendicesalsoincludetheaforementioned Glossary,amapofthePhysiographic Provinces oftheUnitedStates, a WorldPoliticalMap
(whichstudentscanrefertowhentheyread aboutgeologiceventsatparticularlocalities),a PeriodicTableandSymbolsforChemical Elements(usefulasasareferencewhenreadingthe sectionsonmineralcompositionandradioactive elements), ConvenientConversionFactors, ExponentialScientificNotation,RockSymbols, asimplified BedrockGeologyofNorthAmerica, anda TableofCommonRock-FormingSilicate Minerals
Mostchaptersincludeoneormoregeneralinterest “boxes.” Enrichment boxesbrieflyexamineatopicof generalinterestthatisrelatedtomaterialinthechapters. GeologyofNationalParksandMonuments boxesprovideinformationaboutwherethegeology describedinthechaptercanactuallybevisited.
cPEDAGOGICALSUPPLEMENTS Tohelpstudentsunderstand,retain,andappreciate theinformationintheirHistoricalGeologycourse, TheEarthThroughTime isaccompaniedbyanextensivesetofsupportingmaterials.Thesesupplements include:
LecturePowerPoints,TestBanks preparedby MarcWillis. StudentStudyGuide,ChapterQuizzes, WebLinks,ChapterTutorials,Instructors’Manual preparedbyDavidKing.
OverheadTransparencies foruseinthelaboratoryandlecturehallareavailabletoinstructorson request. (JohnWileyandSons,Inc.,mayprovidecomplementaryinstructionalaidsandsupplementarypackagesto thoseadoptersqualifiedunderouradoptionpolicy.Please contactyoursalesrepresentativeformoreinformation.)
Student Companion Website (www.wiley .com/college/levin). This website features simple-touseandhighlyeffectivestudytoolsthatwillhelp studentsisolateandretainkeyinformationfromthe text,prepareefficientlyforexams.Thewebsite includes:
StudentStudyGuide preparesstudentsfortests andquizewsbyprovidingaconcisechaptersummary,keyterms,andself-quizwithanswerkey.
ChapterQuizzes withimmediateresultsoncompletionofeachquiz.
WebLinks allowstudentstoexploreexternal resourcesfortopicsexaminedineachchapter.
ChapterTutorials permittingthestudenttodissecteachchapterwithathoroughlynotated outline.
Flashcards permitthestudenttodisplayeither termordefinitiontolockininformationfor examinations.
GeographyReferenceSites providegeographic sitestosupplementinformationinthetext.
cACKNOWLEDGMENTS Mostofthechangesinthiseditionresultedfromthe suggestionsofaninsightfulanddiligentgroup thoughtfulanddedicatedprofessorswhoreviewed thetextandwhosenamesarebelow.Inparticular, mysincerethanksmustincludethoseatJohnWiley andSons.
RyanFlahiveprovidedthestimulusandencouragementtomovetheprojectforwardonschedule.Whateverproblemarose,Ryanalwayshadaninstant solution.Thecountlessdetailsassociatedwithchannelingthebookintoproductionwereefficiently handledbyEditorialAssistantJuliaNollen.Forassistanceinbringingthebooktothepublic,theauthoris indebtedtoMarketingManagerMargaretBarrett. TheskillandunflaggingassistanceofSeniorPhoto EditorJenniferMacMillanwasindispensibletothis
edition.Nomatterhowdifficult,Jenniferalwaysmanagedtofindjusttherightimageofafossilorsignificant rockoutcrop.Astheprojectmovedthroughpreparationoffinalpages,AssociateProductionManager JoycePohcoordinatedvariousaspectsofproduction fromfar-awaySingapore.Finally,theauthorisgratefulfortheopportunitytoworkwithsofineapublisher asJohnWileyandSons,Inc.
Manychangesinthiseditionaretheresultof incisivecommentsandsuggestionsofthediligent groupofreviewerslistedbelow:
ToddFeeley
TorreyNyborg
BruceRobertson
KerryWorkmanFord JaneMatheney-Rood
PARTI DiscoveringTimeand DecipheringEarth’sAmazingHistory
CHAPTER1
TheScienceofHistoricalGeology 1
WhyStudyEarthHistory? 2
GeologyLivesinthePresentandthePast 2
AWaytoSolveProblems:TheScientific Method 3
ENRICHMENT ScientificDiscoveriesMustbeTested 5
ThreeGreatThemesinEarthHistory 7
WhatLiesAhead? 9
CHAPTER2
EarlyGeologistsTackleHistory’s Mysteries 13
TheIntrigueofFossils 14
AnEarlyScientistDiscoversSome BasicRules 15
EuropeanResearchersUnraveltheSuccessionof Strata 17
NeptunistsandPlutonistsClash 18
Uniformitarianism:JamesHuttonRecognizesthat thePresentisKeytothePast 18
ThePrincipleofFossilSuccession 20
TheGreatUniformitarianism–Catastrophism Controversy 21
ThePrincipleofCross-Cutting Relationships 21
Evolution:HowOrganismsChangeThrough Time 23
EarthHistoryinAmerica 24
CHAPTER3
TimeandGeology 29
FindingtheAgeofRocks:RelativeVersusActual Time 29
AScaleofGeologicTime 30
ActualGeologicTime:ClocksintheRocks 34
RadioactivityProvidesaWaytoDateRocks 36
WhatOccursWhenAtomsDecay? 37
ThePrincipalRadioactiveTimekeepers 41 HowOldisEarth? 45
PARTII RocksandFossilsandWhat TheyTellUsAboutEarthHistory
CHAPTER4
RocksandMinerals:DocumentsThat RecordEarth’sHistory 49
MineralsasDocumentsofEarthHistory 50 MineralsandTheirProperties 50 CommonMineralsthatFormRocks 52 Earth’sThreeGreatRockFamiliesandHowThey Formed 57
IgneousRocks:“Fire-Formed” 58
SedimentaryRocks:LayeredPagesofHistory 67 MetamorphicRocks:ChangedwithoutMelting 72
CHAPTER5
TheSedimentaryArchives 81
TectonicSettingistheBiggestFactorinSediment Deposition 82 EnvironmentsWhereDepositionOccurs 83 WhatRockColorTellsUs 89 WhatRockTextureTellsUs 91
ENRICHMENT YouAretheGeologist 93 WhatSedimentaryStructuresTellUs 94 WhatFourSandstoneTypesRevealAboutTectonic Setting 98
LimestonesandHowTheyForm 99
OrganizingStratatoSolveGeologicProblems 103 Sea-LevelChangeMeansDramaticEnvironmental Change 106
StratigraphyandtheCorrelatingofRock Bodies 107
Unconformities:SomethingisMissing 109 DepictingthePast 112
GEOLOGYOFNATIONALPARKSANDMONUMENTS GrandCanyonNationalPark,Arizona 118
CHAPTER6
LifeonEarth:WhatDoFossilsReveal? 125
Fossils:SurvivingRecordsofPastLife 126
ENRICHMENT Amber,theGoldenPreservative 129
ENRICHMENT TheMazonCreekLagerstatte 131
FiguringOutHowLifeisOrganized 132
Evolution:ContinuousChangesinLife 133
TheCaseforEvolution 141
ENRICHMENT EarbonesThroughtheAges 142
FossilsandStratigraphy 144
FossilsIndicatePastEnvironments 151
HowFossilsIndicatePaleogeography 155
HowFossilsIndicatePastClimates 158
AnOverviewoftheHistoryofLife 159
LifeonOtherPlanets:AreWeAlone? 163
CHAPTER7
PlateTectonicsUnderliesAllEarth History 169
EarthquakeWavesRevealEarth’sMysterious Interior 170
Earth’sInternalZones 172
Earth’sTwoTypesofCrust 175
PlateTectonicsTiesItAllTogether 177
DriftingContinents 178
EvidenceforContinentalDrift 179
Paleomagnetism:AncientMagnetismLockedInto Rocks 182
Today’sPlateTectonicsTheory 184
WhatHappensatPlateMargins? 189
WhatDrivesPlateTectonics? 194
VerifyingPlateTectonicsTheory 195
ENRICHMENT RatesofPlateMovement 201
ThermalPlumes,Hotspots,andHawaii 202
ExoticTerranes 202
Broken,Squeezed,orStretchedRocksProduce GeologicStructures 205
GEOLOGYOFNATIONALPARKSANDMONUMENTS HawaiiVolcanoesNationalPark 210
PARTIII TheHistoryofPlanetEarthand ItsInhabitants
CHAPTER8
TheEarth’sFormativeStagesandthe ArcheanEon 215
EarthinContext:ALittleAstronomy 216
ENRICHMENT TheOriginoftheUniverse 221
ASolarSystemTour,fromCentertoFringe 221
FollowingAccretion,Earth Differentiates 228
ThePrimitiveAtmosphere—VirtuallyNo Oxygen 229
ThePrimitiveOceanandthe HydrologicCycle 232 OriginofPrecambrian“Basement”Rocks 232 TheOriginofLife 238
GEOLOGYOFNATIONALPARKSANDMONUMENTS VoyageursNationalPark 246 InRetrospect 247
CHAPTER9
TheProterozoic:DawnofaMoreModern World 251
HighlightsofthePaleoproterozoic (2.5to1.6billionyearsago) 253
ENRICHMENT The18.2-HourProterozoicDay 255 HighlightsoftheMesoproterozoic (1.6to1.0billionyearsago) 257
ENRICHMENT BIF:Civilization’sIndispensable Treasure 258
HighlightsoftheNeoproterozoic (1.0to542millionyearsago) 259
ProterozoicRocksSouthoftheCanadian Shield 260
ENRICHMENT HeliotropicStromatolites 262 ProterozoicLife 263
CHAPTER10
EarlyPaleozoicEvents 275
DanceoftheContinents 277 SomeRegionsTranquil,Others Active 277
IdentifyingtheBaseoftheCambrian 281 EarlyPaleozoicEvents 281 CratonicSequences:TheSeasComein,the SeasGoOut 282
TheSaukandTippecanoeSequences 284 WayOutWest:EventsintheCordillera 287 DepositionintheFarNorth 288 DynamicEventsintheEast 289
GEOLOGYOFNATIONALPARKSANDMONUMENTS JasperNationalPark 290
ENRICHMENT AColossalOrdovicianAshFall:Wasita Killer? 292
TheCaledonianOrogenicBelt 296
ENRICHMENT TheBigFreezeinNorthAfrica 297
AspectsofEarlyPaleozoic Climate 299
CHAPTER11
LatePaleozoicEvents 303
TheSeasComein,theSeasGoOut 306 UnrestAlongtheWesternMarginof theCraton 309
ENRICHMENT TheWealthofReefs 312
TotheEast,AClashofContinents 315 SedimentationandOrogenyin theWest 323
EuropeDuringtheLatePaleozoic 326
GondwanaDuringtheLatePaleozoic 327
ClimatesoftheLatePaleozoic 327
MineralProductsoftheLate Paleozoic 328
GEOLOGYOFNATIONALPARKSANDMONUMENTS
AcadiaNationalPark 329
CHAPTER12
LifeofthePaleozoic 335
AnimalswithShellsProliferate—andSoDoes Preservation 337
TheCambrianExplosionofLife:AmazingFossil SitesinCanadaandChina 338
TheGreatOrdovicianBiodiversification Event 343
AVarietyofLivingStrategies 343 Protistans:CreaturesofaSingleCell 343
MarineInvertebratesPopulatetheSeas 344
ENRICHMENT TheEyesofTrilobites 360 AdventoftheVertebrates 361 TheRiseofFishes 363 Conodonts:ValuableButEnigmatic Fossils 370 AdventofTetrapods 370
PlantsofthePaleozoic 374
ENRICHMENT AWalkThroughanAncientRainforest 377 MassExtinctions 377
CHAPTER13
MesozoicEvents 385
TheBreakupofPangea 386
TheMesozoicinEasternNorthAmerica 387
TheMesozoicinWesternNorthAmerica 390
GEOLOGYOFNATIONALPARKSANDMONUMENTS
ZionNationalPark 394
ENRICHMENT DidSeafloorSpreadingCauseCretaceous EpicontinentalSeas? 401
TheTethysSeainEurope 406
GEOLOGYOFNATIONALPARKSANDMONUMENTS
GrandStaircase–EscalanteNational Monument 407
GondwanaEvents 410
ENRICHMENT ChunnelingThroughtheCretaceous 411
CHAPTER14
LifeoftheMesozoic 417
ClimateControlsItAll 418
MesozoicInvertebrates 421
MesozoicVertebrates 426
Dinosaurs:“TerrifyingLizards” 429
GEOLOGYOFNATIONALPARKSANDMONUMENTS
DinosaurNationalMonument 430
Dinosaurs:Cold-blooded,Warm-blooded,or Both? 444
DinosaurParenting 445
ENRICHMENT CanWeBringBacktheDinosaurs? 445
FlyingReptiles 446
DragonsoftheSeas 448
TheRiseofModernBirds 449
ENRICHMENT The Archaeopteryx Controversy 450
TheMammalianVanguard 451
SeaPlantsandPhytoplankton 455
LandPlants 457
LateCretaceousCatastrophe 459
ENRICHMENT BolidesandModernDay Catastrophism 463
CHAPTER15
CenozoicEvents 469
TheTectonics–ClimateConnection 470
StabilityandErosionAlongtheNorthAmerican EasternMargin 472
GulfCoast:TransgressingandRegressingSea 473
TheMightyCordillera 473
ENRICHMENT OilShale 477
CreatingtheBasinandRangeProvince 478
GEOLOGYOFNATIONALPARKSANDMONUMENTS
BadlandsNationalPark,SouthDakota 479
ENRICHMENT HellishConditionsintheBasinandRange Province 482
ColoradoPlateauUplift 482
ColumbiaPlateauandCascades Volcanism 482
SierraNevadaandCalifornia 485
TheNewWestCoastTectonics 487
Meanwhile,DramaOverseas... 488
BigFreeze:ThePleistoceneIceAge 491
WhatCausedtheIceAge? 497
CenozoicClimates:GlobalWarmingThen Cooling 501
CHAPTER16
LifeoftheCenozoic 505
GrasslandsExpand,MammalsRespond 507
Plankton 508
MarineInvertebrates 509
Vertebrates 512
Mammals 517
Monotremes 519
Marsupials 519
PlacentalMammals 520
ENRICHMENT HowtheElephantGotItsTrunk 536
DemiseofthePleistoceneGiants 539
CHAPTER17
HumanOrigins 543
Primates 544
ModernPrimates 546
PrimateBeginnings 547
TheEarlyAnthropoids 550
TheAustralopithecineStageandtheEmergenceof Hominins 552
ASpeciesinTransition: Australopithecus Sediba 554
The HomoErectus Stage 556
FinalStagesofHumanEvolution 557
ENRICHMENT BeingUpright:GoodNews,BadNews 558
ENRICHMENT NeandertalorNeanderthal? 559
ENRICHMENT NeandertalRitual 560
HumansArriveintheAmericas 563
HumanPopulation:7BillionandGrowing 565
WhatLiesAhead? 566
APPENDIXA
ClassificationofLivingThings A1
APPENDIXB
PhysiographicProvincesoftheUnitedStates A5
APPENDIXC
PeriodicTableandSymbolsforChemical Elements A6
APPENDIXD
ConvenientConversionFactors A9
APPENDIXE
ExponentialorScientificNotation A10
APPENDIXF
RockSymbols A10
APPENDIXG
BedrockGeologyofNorthAmerica A11
APPENDIXH
CommonRock-formingSilicateMinerals A12
GLOSSARY G1
INDEX I1
Orange,brown,andwhitecross-beddedNavajoSandstone exposedinCheckerboardMesa,ZionNationalPark, Utah.Thecriss-crosspatternistheresultofdepositionby wind. (GlenR.Osburn)
TheScienceof HistoricalGeology Amillionyearsisnothing.Thisplanetlivesand breathesonamuchvasterscale.
—MichaelCrichton,JurassicPark
KeyChapterConcepts ThestudyofeventsintheEarth’spastcanoftenbe usedtopredictfutureevents.
TheEarthanditsinhabitantshaveundergone continuouschangeduringthepast4.56billion years.(4,560,000,000years).
Physicalgeologyexaminesthestructure, composition,andprocessesthataffecttheEarth today.Historicalgeologyconsidersallpastevents onEarth.
Thescientificmethodisawaytofindanswersto questionsandsolveproblems.Itinvolves collectionofinformationthroughobservation andexperimentation,formulationofanswers, andvalidationbytesting.
Thethreemostpervasivethemesinthehistoryof Eartharetheimmensityofgeologictime,plate tectonics,andbiologicevolution.
Welcometotheamazinghistoryofourplanet!Here youwilldiscovermanyastonishingeventsofthe pastandlearnhowwecametounderstandthem. YouwilllearntheintriguingstoryofhowlifedevelopedonEarthandhowanextraordinaryspecies evolvedthatistheonlyonecapableofreadingbooks likethis: us
OUTLINE c PARTI—DISCOVERINGTIMEAND DECIPHERINGEARTH’SAMAZINGHISTORY
c WHYSTUDYEARTHHISTORY?
c GEOLOGYLIVESINTHEPRESENTAND THEPAST
c AWAYTOSOLVEPROBLEMS: THESCIENTIFICMETHOD
c THREEGREATTHEMESINEARTHHISTORY
c WHATLIESAHEAD?
c SUMMARY
c KEYTERMS
c QUESTIONSFORREVIEWANDDISCUSSION
Ourplanetformedabout4.56billionyearsago.Since thattime,ithascircledthesunlikeasmallspacecraft observingaratheraveragestar.Betweenabout300,000 and150,000yearsago,aspeciesofprimatewecall Homo sapiens (Latin: wisehuman)evolvedonEarth.Unlike earlieranimals,thesecreatureswithoversizedbrainsand nimblefingersaskedquestionsaboutthemselvesand theirsurroundings.Theirquestioninghascontinuedto thepresentday: HowdidEarthform?Whydoearthquakes occur?Howdoweunlockthehistorythatliesbeneaththeland andbelowtheoceanfloor?
Evenancientpeoplesoughtanswerstothesequestions.Infrailwoodenships,theyprobedthelimitsof theknownworld,fearingthattheymighttumblefrom itsedgeorbeconsumedbydragons.Theirdescendantscametoknowtheplanetasanimperfectsphere, andtheybegantoexamineeveryobscurerecessofits surface.Inharsherregions,explorationproceeded slowly.Ithasbeenonlywithinthelast100years
thathumanshavepenetratedthedeepinteriorof Antarctica.Today,exceptforafewareasofgreat coldordensetropicalforest,thecontinentsarewell charted.Newfrontiersforexplorationnowliebeneath theoceanandoutwardintospace.
cWHYSTUDYEARTHHISTORY? Earth’sspectacularhistorydeservestobeclosely examined,foritpermitsustoseethefuture.We expectthatmanyeventsofthepastwillhappenagain. Weoweittoourselvesandtoourhomeplanettolook carefullyatthoseeventsandattempttounderstand them.
Fromthetimeofitsorigintothepresentday,Earth hasundergonecontinuousmodification.Continents havebeenfloodedbyvastinlandseas.Theyalsohave ponderouslydriftedacrossthefaceoftheglobeand slowlycollidedwithotherlandmassestoformlofty mountainranges(Fig.1-1).Massiveglaciershave buriedvasttractsofforestandprairie.Earthhas witnessedrecurrentearthquakes,rampantvolcanism, catastrophicimpactsofmeteoritesandasteroids,and majorchangesinthechemistryoftheoceanand atmosphere.Alongwiththesephysicalchanges,life onEarthhasalsoundergonechange;sometimesslow, butoccasionallyswiftanddeadly.
Alloftheseeventsofthegeologicpasthaverelevancetoourlivestoday.Bydiscoveringwhythey occur,wecanbetterpredictthefuture.Forexample, wearecarefullyexaminingclimatictrendsofthepast sowecanbetterunderstandtoday’sclimaticchanges. WithknowledgeofEarth’shistory,wecanplanahead. Wecanavoidfurtherdamagetothisplanetaryhaven inspacethatisourhome.Asidefromtheseconcerns, animportantreasontostudyEarthhistoryissimplyto betterunderstandourfavoriteanduniqueplanetand itsamazingformsoflife.
cGEOLOGYLIVESINTHEPRESENT ANDTHEPAST Forconvenience,wedividethebodyofknowledge called geology into physicalgeology and historical geology.Theword“convenience”isappropriatehere. Thisisbecausemanyaspectsofphysicalgeologyare necessarytounderstandtheEarth’shistory. Conversely,manyeventsinourplanet’s4.6billionyearhistorydeterminetheEarth’sphysicalcharacteristics.Topicssuchasweatheringandsoils,mass wasting,geologicresources,thebehaviorofstreams, glaciers,winds,groundwater,oceanwavesandcurrents,andgeologicresourcesaretypicalsubjectsfound inphysicalgeologytextbooks.Historicalgeology addressesEarth’soriginandevolution,distribution oflandsandseasthroughtime,thegrowthandreductionofmountains,andthesuccessionofanimalsand plantsthatlivedintheoceanandoncontinentsdown throughtheages.Thehistoricalgeologistseesthe results ofpastgeologiceventsandworksbackwardin timetofindtheir cause. Theprocessratherremindsus ofthe“CrimeSceneInvestigator”whoarrivesonthe sceneofamurderandmustreconstructwhathappenedfromwhatevercluesheorshecanfind.
GeologyprimarilystudiesEarth,butitsviewhas broadenedtoincludeotherplanets.Thisincreasein scopeisappropriate,becausegeologicknowledgeis employedininterpretingtheimagesofthesurfacesof otherplanetsandtheirmoons,inestimatingthepower ofvolcanoesonVenus,andinidentifyingrocksand mineralsfromEarth’smoon.
Geologistsexaminethemineralsinmeteorites (Fig.1-2)todiscoverhowEarthformed.Withsophisticatedinstruments,theyscrutinizeimagesofplanets orinterpretdatatransmittedbyspaceprobesand planetaryexplorationrovers(Fig.1-3).Othergeologistsunravelthestructureofmountainranges,attempt
FIGURE1-1 Themagnificent CanadianRockyMountainsviewed fromMalignLake,BritishColumbia Thesemountainswereinitiallyraised over80millionyearsago.Theirpresent appearanceresultsfromfurtheruplift anderosionalsculptingduring subsequentgeologicperiodsdownto thepresentday.(HaroldLevin)
FIGURE1-2 Stonymeteoriterestingonsnowofthe AntarcticIceCap.Thecontrastofdarkmeteoritesonwhite snowmakesAntarcticaagoodplaceforcollectingmeteorites. Themeteoriteiscomposedofironandmagnesiumsilicates.It isabout8cm.indiameter.(HaroldLevin)
topredicthazardslikeearthquakesandvolcaniceruptions(Fig.1-4),orstudythebehaviorofglaciers, streams,orundergroundwater.
Many“explorationgeologists”searchforfossilfuels andthemetallicoresvitaltoourstandardofliving. Thisrequiresknowledgeofbothphysicalandhistoricalgeology.Tounderstandwheretofindresources, explorationgeologistsdrawontheirknowledge ofEarthhistory,astronomy,physics,chemistry,
mathematics,andbiology.Forexample,apetroleum geologistmustunderstandthephysicsofmoving fluids,thechemistryofoilandgas,andthebiology ofthefossils(Fig.1-5)thatareusedtotracesubsurface rocklayers.
Becausegeologyincorporatesinformationfromso manyotherscientificdisciplines,itisan“eclectic” science;itdrawsoninformationfrommanysources. Allsciencesareeclectictosomedegree,butgeologyis decidedlymoreso.
cAWAYTOSOLVEPROBLEMS: THESCIENTIFICMETHOD Geologists,bothphysicalandhistorical,employthe sameproceduresusedbyscientistsinotherdisciplines. Thoseproceduresarecalledthe scientificmethod. Thescientificmethodisasystematicwaytouncover answerstoquestions,solutionstoproblems,andevidencetoproveordisproveideasandbeliefs.
Ascientificinvestigationoftenbeginswitha question (Fig.1-6).Itproceedstothecollectionof data (facts fromobservationsandexperiments),andisfollowed bythedevelopmentofa hypothesis thatfitsallthe dataandislikelytoaccountforobservationsinthe futureaswellasthepresent.Ahypothesisthenistested andcriticallyexaminedbyotherscientists,soitsubsequentlymaybeconfirmed,modified,ordiscarded.In somecases,severalhypothesesmaybeproposedto explainthesamesetofdata,andeachistesteduntil the“best”oneemerges.Forexample,theoriginofthe universeandtheoriginoflifehaveeachbeenthe subjectofseveralhypotheses.
Ahypothesisthatsurvivesrepeatedchallengesand issupportedbyaccumulatingfavorableevidencemay beelevatedtoa theory.Atheoryhassurvivedsuch
FIGURE1-3 (A)NASA’sroboticrover Opportunity onMarsin2004.Itsinstrumentsphotographedrock outcropsandfoundevidencefortheformerpresenceofwaterontheredplanet. (B)The Phoenix landeron thearcticplainsofMarsin2008.Thesoilsamplerintheforegroundisdiggingatrenchandwillpasssoil samplestosmallchemicallaboratoriesforanalysis.(RenditionsbyartistCorbyWasteoftheJetPropulsion Laboratory.CourtesyofNASAandtheJetPropulsionLaboratory)
FIGURE1-4 Geologiststudiesa disastrousmudflowresultingfrom theeruptionofMountSt.Helens, WashingtonState,in1980.Mount St.Helensisinthebackground.The eruptiondevastatednearly600square kilometersandkilled57people. (USGS/CVO)
FIGURE1-5 Fossilshellsofsingle-celledmarineanimals Thesedistinctiveshellsofforaminiferaarewidelyusedto identifyrockformationswhendrillingforoilandnaturalgas. (Theshellsaverageabout.10mm.)(HaroldLevin)
SCIENTIFIC LAW
Understanding of how things happen
THEORY
Consistent confirmation from further testing
Further testing
HYPOTHESIS
Explanation of data
What do we want to know? Is a belief correct? Data collection, observations, and experiments
QUESTIONS
FIGURE1-6 Typicalstepsinthescientificmethod.An initialquestionstimulatesthecollectionofdata.Scientists thenstudythedataandbuildahypothesistoanswerthe question.Throughexhaustivetesting,thehypothesisis accepted,revised,orrejected.Ahypothesisthatconsistently answersquestionsrisestothelevelofascientifictheory.If thetheory“works”ineveryknowncaseoveralongperiod, itcanattainthestatusofascientificlaworprinciple.
ENRICHMENT ScientificDiscoveriesMustbeTested Thescientificmethodtellsusthatany findingorhypothesis madebyscientistsmuststandthetestofadditionalexperimentationorobservation.Anexampleofhowscienceis continuouslytestedbeganinSeptember2010whenastronomersfromtheUnitedStatesmadeheadlineswiththe announcementthattheyhaddetectedthe firstplanetoutsideofthesolarsystemwithconditionssuitableforlife.They calledthebodya “GoldilocksPlanet” because,likethe porridgeinthechildren’sstory,itwas “nottoohotand nottoocold.” Thepresumedplanetorbitedadwarfstar namedGliese581andwascalledGliese581g.Likemany planetstoofarawaytobeseendirectlybytelescope,the evidencethatGliese581gactuallyexistedwasbasedlargely
intensescrutinythatitcanbeacceptedwithmore confidencethanahypothesis.Examplesarethetheory ofrelativity,platetectonicstheory,evolutionarytheory,andatomictheory.
Itisimportanttounderstandthattheterm“theory” hasverydifferentmeaningstoscientistsandtothe public.Toascientist,atheoryrepresentsknowledge thathasaveryhighprobabilityofbeingcorrect. Theterm“theory”doesnotimplyalackofknowledge oraguess.
Thesearchforscientifictruthdoesnotendwiththe formulationofatheory.Evenafteratheoryhasbeen firmlyestablished,itmustcontinuetosurviverigorous testingderivedfromadvancesinscienceandtechnologythatitsauthorcouldnothaveforeseen.Ifatheory continuestotriumphovereverychallenge,itcanbe raisedtothelevelofa scientificlaw,suchasthelawof gravitationalattraction.
AnExampleoftheScientificMethod
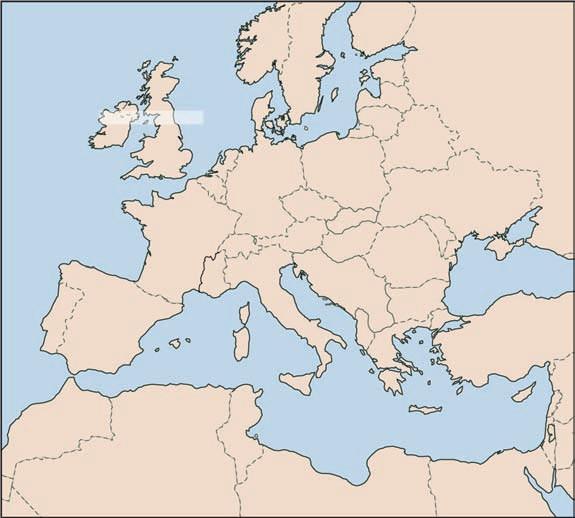
Applyingthescientificmethodinhistoricalgeology, considerthefollowingresearchintosomecurious featuresoftheMediterraneanseafloor.
TheQuestions.SeveralobservationsraisedquestionsabouttheMediterraneanSea’shistory:
1.Microscopicsingle-celledplantsandanimals livingintheMediterraneanchangedabruptly about6millionyearsago.Mostoftheolder organismswerenearlywipedout.Afewsurvived bymigratingintotheAtlantic.Somewhatlater, themigrantsreturned,bringingnewspecieswith them. Whatdramaticeventhappened?Whydidthe nearextinctionoccur?Whydidthemigrantssubsequentlyreturn?
2.Anenormousburiedgorgeextendsseaward fromthepresentcourseoftheRhoneRiver (Fig.1-7).Similarburiedgorgeshadbeen
onthewobbledetectedinthedwarfstarbelievedtobe causedbytheattractionofGliese581gasitorbiteditsdwarf star.Anothercluewasaslightdimmingofthelightfromthe parentstarcausedwhentheplanetpassesinfrontofit.
Excitingnews,butthecalculationsusedtoidentifyGliese 581gweresoontobetestedbySwissscientists.They analyzedalltheoldandnewdataandannouncedtheycould notconfirmthepresenceofGliese581g.Wouldthisbethe endofthestory?Notatall,forotherscientistsarecontinuing toanalyzethedata.Newtechnologyisbeingemployedthat mayrefinethedata.Ultimately,additionaldiscoverieswill eitherrefuteorsupporttheoriginalscientificreport.Thatis thewayscienceworks.
foundoffthecoastofNorthAfrica. Whatgave astreamsufficientpowertoerodesuchcanyon-like features?
3.Ahardlayerofsedimentaryrock,detectedby seismicinstruments,lies100metersorso belowthepresentseafloor. Whatistheoriginof thishardlayer?
4.Domelikerockstructuresexistdeepbeneaththe Mediterraneanseafloor.Theyweredetected yearsearlierbyecho-soundinginstruments, buttheyhadneverbeeninvestigatedbydrilling. Aretheyhugeplumesofsalt(calledsaltdomes) liketheonesthatarecommonalongtheU.S.Gulf Coast?Ifso,whatcausedtheprecipitationofsomuch rocksalt?
In1970,geologistsKennethJ.HsuandWilliamB.F. Ryanboardedtheoceanographicresearchvessel GlomarChallenger tosearchforanswers(Fig.1-8). TheydrilledtheMediterraneanseafloortoobtain samples.Asdrillingprogressed,theyrecoveredasamplefromthesurfaceofthehardlayer.Itconsistedof pebblesofhardenedsedimentthathadoncebeensoft, deep-seamud,plusgranulesofgypsum(amineral commonlyformedbytheevaporationofseawater). However,notasinglepebblewasfoundtoindicate thatthesedimenthadbeencarriedtotheseafrom surroundinglandareas.
Inthedaysfollowing,samplesofsolidgypsumwere repeatedlybroughtondeckasdrillingpenetrated thehardlayer—clearly,itwasabedofgypsum.The compositionandtextureofthegypsumsuggestedit hadformedbyevaporationondesertflats.Butsedimentaboveandbelowthegypsumlayercontainedtiny marinefossils,indicatingnotadesert-likeenvironment,butnormalopen-oceanconditions.
TheHypothesis.Thetimehadcometo formulatea hypothesisthattheMediterraneanSeawasonceadesert.
HsuandRyanproposedthatabout20millionyears ago,theMediterraneanwasabroadseawaylinkedto theAtlanticbynarrowstraits,likethepresentStraitof Gibraltar.TectonicmovementsofEarth’scrustclosed thestraits.Turnedintoagiantsaltlake,theMediterraneanbegantoevaporateandshrink.Evaporation concentratedthevarioussaltsthatweredissolvedin thewater,andthisincreasingsalinityexterminated scoresofmarinespecies.
Asevaporationcontinued,theremainingbrine becamesosaturatedthatmineralsdissolvedinit wereforcedtoprecipitate—thatis,theywereforced toseparatefromthesolution.Thisformedthehard layerofgypsum.Differentsaltsprecipitateatdifferent rates,andtheremainingbrineinthecentral,deeper partofthebasinwasrichinsodiumandchlorineions,
FIGURE1-7 Mediterraneanregion.Whenthe Mediterraneanwasadesert,theRhoneRiverno longerenteredatsealevel,butfloweddownasteep slope,erodingagorgeoverakilometerdeepthatis nowburiedbeneathsediment.
sothewaterevaporatedtoprecipitatesodiumchloride (tablesalt).
Thedried-upMediterraneanhadbecomeavast “DeathValley”3000metersdeep.Streamsentering thebasinfromEuropeandAfricanowhadsteep gradients,enablingthemtoerodespectaculargorges. Then,about5.5millionyearsago,newcrustalmovementscausedtheStraitofGibraltartoopen.AgigantictorrentofwaterpouredintotheMediterranean basinatavelocityof140kilometersperhour(87miles perhour).Thedelugequicklyerodedarapidlydeepeninggorgethatwasoversevenkilometerswide(four andahalfmileswide).Itwouldhavebeenanastonishingspectacletoobserve,buthumanswerenotyet onthescene.AsthesillthatoncebarredAtlantic watersfromflowingintotheMediterraneanbasin
FIGURE1-8 TheDeepSeaDrilling Vessel GlomarChallenger. Theprominent derrickatmidshipallowsroughnecksonthe drillingfloortohoistlengthsofpipeupward, andthenaddthatnewlengthofpipetothe pipealready“inthehole.”In1970,while operatingintheMediterranean,the Glomar Challenger broughtupdrillcoresindicating theMediterraneanwasonceadesert.)
(# Corbis)
ALGERIA SPAIN PORTUGAL
TURKEY
Sea
Strait of Gibraltar
LIBYA EGYPT
MOROCCO BRITISH ISLES
wasbeingeroded,therateofwaterflowincreased enormously.TheMediterraneanwouldhavebeen filledinonlyabouttwoyears.Inthatsameperiod oftime,theglobalsealevelwouldhavedroppedabout 9.5meters(35feet).
Evidencefortheerosionofthesillthathadbarred AtlanticwatersfromenteringtheMediterraneanbasin wasfoundincoresdrilledintheseafloorinpreparation fortheproposedAfrica–Europetunnelproject.The coresrevealadeep,200kilometerlongchannelfilled withtheloosesediment.
Theturbulentcurrentsracingdowntheslopetore intothehardenedsaltflats,grindingtheminto thepebblesobservedinthefirstsampletakenbythe GlomarChallenger.Asthebasinrefilled,marineorganismsreturned,mostlymigrantsfromtheAtlantic. Soonlayersofoceanicoozeweredepositedabovethe oldhardlayer.
LongaftertheMediterraneanBasinwasrefilled, pressurefromtheweightofoverlyingsediments forcedthesalttoflowplasticallyupwardtoform saltdomeslikethoseontheU.S.GulfCoast.
Thequestionsaboutthefaunalchanges,thesaltand gypsumdeposits,theunusualpebblysediment,and thedeeplyburiedgorgeswerenowanswered.The scientificmethodhadworkedwell,and thehypothesis thattheMediterraneanSeawasonceadesert couldnowbe criticallyexaminedbyothergeologists.Thisexample ofhowquestionscanbesolvedbythescientific methoddemonstrateshowgeologistsarelikedetectivesprobingtherocksforcluestothecomplexpastof ourplanet.
TheTheory.Thehypothesishassurvivedcritical examinationandisonitswaytobeingacceptedasa theory.Itisimportanttounderstandthattheterm theory, asusedinscience,doesnotmeanaguessorhunch.As spelledoutbytheNationalAcademyofSciences,a scientifictheoryisawell-establishedexplanationof someaspectofthenaturalworldthatisbasedona bodyoffactsthathavebeenrepeatedlyconfirmed.
cTHREEGREATTHEMES INEARTHHISTORY Earth’shistoryislikeanovel,withgrand,sweeping themes.Thethreemajorthemes—intenselyinteractingthemes—aredeeptime,platetectonics,andthe evolutionoflife.
DeepTime Recognitionoftheimmensityofgeologictimeisthesingle mostimportantcontributiontohumanknowledgemadeby geology.Geologistslookbackacross4.56billionyears ofEarthhistory,fromourplanet’schaoticbirthtothe present.Comparedtotheaveragedurationofahuman life,itisaspanoftimesohugeastobedifficultto
comprehend.Itisnotsurprising,therefore,thatour ancestorsbelievedhillsandvalleyswerechangeless andeternalandthattheplanetoriginatedonlyafew thousandyearsago.
Eventually,wecametorealizethattheslowand relentlessworkoferosionreducesmountainstoplains, thatvalleysaretheresultoflongperiodsoferosion, andthatsandsandgravelsproducedbyerosionhave beenturnedtorock.Thesechangesclearlyrequired vastamountsoftime.
Buthowmuchtime?Andwhicheventpreceded— orfollowed—another?Toanswerthesequestions,it wasnecessarytofindthe absoluteage (actualage)of rocksinyears.Awaytodosowasenabledbythe discoveryof radioactivity in1896.
Certainatomsareunstable,causingthemtobe radioactive.Thismeanstheydecaybyexpellingparticlesoftheirnuclei,convertingthemselvesintostable “daughter”atoms,mostlyofdifferentelements.A well-knownexampleisuranium,whichisradioactive andcontinuallyexpelsparticles.Therateofthisdecay canbeaccuratelymeasured.Theterm half-life expressestherateofdecay.Half-lifeisthetime requiredforone-halfoftheoriginalquantityofradioactiveatomstodecay.
Asanexample,theradioactiveelementuranium235hasahalf-lifeofapproximately704millionyears. Thismeansthatafter704millionyearspass,onlyhalf (50%)oftheuranium-235inamineralwillremain. Afterasecond704millionyearspass,halfofthathalf (25%)willhavedecayed.Thus,arockthatcontains only25%uranium-235and75%ofthedaughter atomsmustbe1,408millionyearsold(704 þ 704). Usingthismethod,someEarthrockshavebeencalculatedtobe4.03billionyearsold(Fig.1-9),andsome mineralsareasoldas4.38billionyears.
FIGURE1-9 GeologistSamuelBowringstandsbefore Earth’soldestknownrocks.NamedtheAcastaGneiss (pronounced“nice”),thismostancientofrocksoutcropsin Canada’sNorthwestTerritories.Radioactivedating methodsindicateitis4.03billionyearsold,havingsurvived 87%ofEarth’s4.56-billion-yearhistory.(CourtesySamuel Bowring)
Beforethediscoveryofradioactivity,geologists wereabletodetermineonlyifparticularlayersor bodiesofrockwere older or younger thanothers. Thisdeterminedarock’s relativeage.Relativeage determinationsprovidedaframeworkinwhichto placeeventsofthegeologicpast.Throughrelative dating,geologistsdevelopeda geologictimescale,and withdatingthroughradioactivedecay,thattimescale wascalibratedinactualyears.Wewillexaminehow thiswasaccomplishedinChapter3.
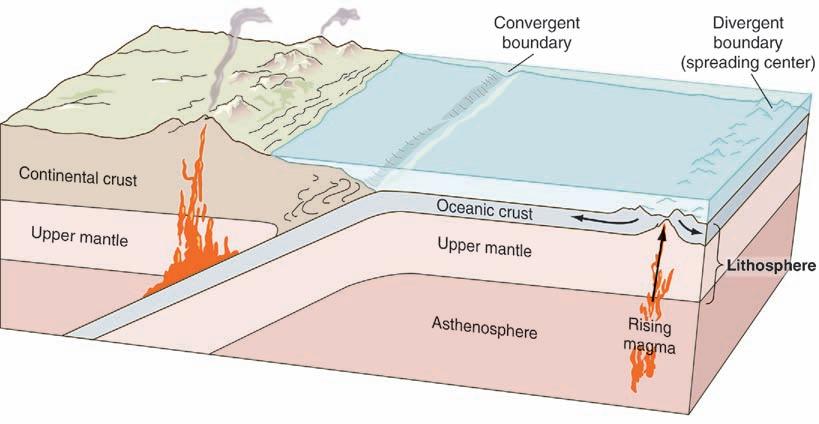
PlateTectonics Asignificantnumberofeventsinbothphysicaland historicalgeologyarerelatedtoagrandunifying concepttermed platetectonics.“Tectonics,”from thesameGreekwordas“architecture,”referstolargescaledeformationofrocksinEarth’souterlayers. Theterm“plate”isgiventolargeslabsofEarth’s lithosphere.The lithosphere istherigidouterlayerof Earth(roughly100kmthick)thatincludesthe crust as wellastheuppermostpartofthe mantle (Fig.1-10).
Earth’ssurfaceconsistsofsevenlargelithospheric platesandabouttwentysmallerones.Theplatesrest onaplastic,easilydeformedlayerofthemantlecalled the asthenosphere.Probablybecauseofheat-driven convectionalflowintheasthenosphere,theplates move.Theymovealmostimperceptibly,onlymillimetersperyear.
Tectonicplateshavewell-definededgesor “margins.”Wheretwoormoreplatesmoveapart (diverge)fromoneanother,theplatemarginsform divergentboundaries.Whereplatesconverge,
convergentboundaries occur.Whereplatesgrind pastoneanother, transformboundaries occur.You willmeetthesetermsagaininChapter7,wherewe examineplatetectonicsinmoredetail.
EvolutionofLife(BiologicEvolution) Platetectonicsisthe“greatunifyingtheory”that explainsmanyphysicalphenomenaingeology.In biology,evolutionisthe“greatunifyingtheory”for understandingthehistoryoflife.Becauseofevolution, animalsandplantslivingtodayaredifferentfrom theirancestors.Theyhavechangedinappearance, ingeneticcharacteristics,inthewaytheyfunction, andintheirbodychemistry,apparentlyinresponseto changesintheenvironmentandcompetitionforfood. Fortunately,fossilsrecordthesechangesforusto study.Fossilsarealsovaluableindicatorsoftheage ofrocks.
AlthoughCharlesDarwiniscreditedfortheconceptofevolution,theideabeganasearlyas2600 yearsago,intheseventhcentury BCE.Wefinditin thewritingsoftheGreekphilosopherAnaximander. ButDarwinandhiscolleagueAlfredR.Wallacewere thefirstscientiststoproposeahypothesiswith convincingevidence.Theyalsoproposedaworking mechanismforevolution,whichDarwincalled naturalselection
Naturalselection isbasedonseveralimportant observations:thatanygivenspeciesproducesmore organismsthancansurvivetomaturity;thatvariations existamongoffspring;thatoffspringmustcompetefor foodandhabitat;andthatthoseindividualswiththe
FIGURE1-10 ThelithosphereisEarth’srigidoutershell.Itliesabovetheasthenosphere, anditincludestheupperpartofthemantleandbothtypesofcrust:continentalandoceanic.
mostfavorablevariationsaremostlikelytosurviveand passtheirbeneficialtraitstothenextgeneration. Scientistseventuallycametounderstandgeneticsas thecauseofthesevariations.
Darwinprovidedmanylinesofevidenceforevolution.Hecitedthedirectevidenceofchangesseen infossilsinsuccessivelyyoungerstrata.Henoted thatcertainorganswerefundamentallysimilarfrom speciestospecies,butbecamemodifiedtofunction differently,apparently tomakethespeciesmore competitive.Therewerealsouselessorgansin modernanimalsthatclearlyhadausefulfunction inancestralspeciesbutwere“evolvingout.”(Human examplesincludetheappendixandtailbone.)He furthernotedthatanimalsthatlookedquitedifferent asadultsneverthelesshadverysimilar-looking embryos.
Thereweremanyotherlinesofevidenceaswell, butnoneascompellingassubsequentworkingenetics,biochemistry,andmolecularbiology.Wenow knowthatthebiochemistryofcloselyrelatedorganismsissimilarto,butdistinctlyunlike,thatoftheir distantrelatives.Thesequenceofaminoacidsin proteinsandthecharacteristicsofthefamousDNA moleculearealsomostsimilarincloselyrelatedorganisms.Discoveriessuchastheseclearlyindicatethat animalsandplantsofeachgeologiceraarosefrom earlierspeciesbytheprocesswecallbiologicevolution.(“Biologic”referstothewayorganismschange throughtime,asopposedtothephysicalevolutionof Earthrocks.)Wewillexaminethisimportantconcept inChapter5.
cWHATLIESAHEAD? Yourbookisdividedintothreeparts:
PartI—DiscoveringTimeandDecipheringEarth’s AmazingHistory givesyouabroadperspectiveonour subject,introducingthepioneersofhistoricalgeology whosecarefuldetectiveworkandbrilliantinsights enabledthemtounravelthegeologicrecord.
PartII—RocksandWhatTheyTellUsabout EarthHistory illustrateshowrocksandfossils haverecordedeventsingeologichistoryandhow wehavelearnedtoreadthiswonderfularchive.We examinesedimentaryrocks,becausetheyoftencontaintheancientanimalandplantdebriswecall fossils.Westudyfossilsbecausewithoutthem,nothingwouldbeknownaboutourplanet’searlierinhabitants.Youwilllearnabouttheevidenceforplate tectonicsandhowthisdynamicprocesshasshaped Earthandinfluencedlifethroughoutgeologictime.
PartIII—HistoryofEarthandItsInhabitants gives youourbestchronologyofphysicalandbiological eventsonEarthsinceitsorigin4.56billionyearsago. Wedescribetheplanet’sbirthasaprimordialballof cosmicdebrisandexplainhowourcontinents,oceans, andtheatmosphereevolvedandinteractedovertime. Hereyoucansurveythevastpanoramaofanimalsand plantsthatpopulatedbygoneeras.Mostrecently, humansappearedonthescene,thefirstcreatures weknowtodiscoverEarth’samazinghistory.
SUMMARY Earthisnotastaticballofrockorbitingthesun.Fromthe timeofitsorigin4.56billionyearsagotothepresent,ithas beenundergoingcontinuouschange.
Knowledgeofeventsinthegeologicpasthaverelevanceto conditionsonEarthtodayandcanbeusedtosolvecurrent andfutureproblems.
GeologyisasciencedevotedtothestudyofEarth—its origin,history,composition,andproperties.Geologyhas twointerrelatedbranches.Physicalgeologyfocuseson processeswithinandonthesurfaceofEarth,aswellas Earth’schemicalandphysicalfeatures.Historicalgeology isthebranchconcernedwithdecodingtherockandfossil recordoftheplanet’slonghistory.
Thescientificmethodisaprocedurebywhichscientists studyproblemsandanswerquestions.Themethodusually beginswithoneormorequestions,thencollectionofdata. Fromthis,scientistsformulateahypothesisthatissupportedbythedata.Itcanthenbetestedforitsvalidity.
Withsufficienttesting,ahypothesiscanbecomeelevated toatheoryorevenalaw.
Threegreatthemesinhistoricalgeologyaredeeptime, platetectonics,andorganicevolution.
Geology’smostimportantcontributiontoknowledgeis recognitionoftheimmensityofgeologictime.Realization ofdeeptimeisfundamentaltoourunderstandingofEarth andourplacewithintheuniverse.
Platetectonicsdescribeslarge-scalemovementsandinteractionsofrigidplatesofEarth’slithosphere.Thesemovementsandinteractionscontrolmajorgeologicevents, includingmountainbuilding,earthquakes,volcanism, andtheconfigurationofcontinentsandoceanbasins. Biologicevolutionreferstochangesthathaveoccurredin organismswiththepassageoftime.Itisfundamentally importantforunderstandinghumanity’srelationshipto Earth’sbiologicalrealm,anditprovidesabasisfordeterminingtherelativeageofrocks.
absoluteage,p.7
asthenosphere,p.8
convergentboundary,p.8 crust,p.8
divergentboundary,p.8 half-life,p.7
historicalgeology,p.2 hypothesis,p.3 lithosphere,p.8
KEYTERMS mantle,p.8 naturalselection,p.8 physicalgeology,p.2 platetectonics,p.8 relativeage,p.8 scientificlaw,p.5 scientificmethod,p.3 theory,p.3 transformboundary,p.8
QUESTIONSFORREVIEWANDDISCUSSION 1. Applicationofthescientificmethodmayleadtothe developmentofahypothesis.Thehypothesismayatalater stagebeelevatedtoatheory(likethetheoryofplate tectonics).Whatmustoccurtovalidateahypothesisin thisway?
2. Whatisthelithosphere?Howdoesitdifferfromthe crust?
3. Defineplatetectonics.Differentiateamongconvergent, divergent,andtransformplateboundaries.Whatisthe significanceofplatetectonicsinourlivestoday?
4. Whatistheimportanceoffossilstohistoricalgeology?
5. Whyarefossilsusefulasevidenceforevolution?
6. Howoldisourplanet?Whatistheageoftheoldest rocksfoundsofar?Whyisitunlikelythatgeologistswillfind rocksatEarth’ssurfacethatareasoldasEarthitself?
7. Throughoutgeologictime,theclimateandtopography ofparticularregionshavechanged.Wouldthesechanges affectthecourseofevolution?Provideanexample.
8. IndeterminingtheageofEarth,whyisitimportantto determinetheageofmeteorites?
9. Howmightknowledgeofthecauseandeffectsofancient episodesofglobalwarminghelpinestimatinghazardswe mayfaceinthefuture?
10. WhatarethethreegreatthemesofEarthhistory?
11. Howistheabsoluteageofarockbodyexpressed?How doesthatdifferfromthewayweexpressrelativeage?
12. Whichofthefollowingis not anexampleofthe scientificmethod?
a. Aprocedureforconductingresearchthatstatesthat atestablehypothesisshouldbeverifiableandtheresults repeatable.
b. Asystematicapproachtoobservingphenomena, drawingconclusions,andrepeatedlytestinghypothesis.
c. Aprocedureforthesystematicpursuitofknowledge involvingtherecognitionandformulationofaproblem,
thecollectionofdatathroughobservationand experimentation,andtheformulationandtestingof hypotheses.
d. Amethodwhichseekstounderstandthenatural worldfromaccountsofmysticalrevelations,mythology, orfrominformationembeddedinone’straditions, language,orculture.
13. TheEarthformed:
a. 65millionyearsago
b. 4.56billionyearsago
c. About4,000yearsago
d. 2.5billionyearsago
e. 542 million yearsago
14. Whichofthestatementsbelowis notvalid?
a. Atheoryisacommonlyacceptedguess.
b. Atheoryissubjectedtocontinuoustesting.
c. Atheoryhassurvivedmorescientifictestingthana hypothesis.
d. Atheorymaybebasedonexperimentation,observation,orboth.
15. WithregardtothehistoryoftheMediterraneanBasin, whichofthestatementsbeloware notvalid?
a. Theburiedgorgesbeneaththeseafloorwhere majorriverscouldhaveformedwhensealevelwaseither verylowintheMediterraneanorwhenthebasinwas emptyofseawater.
b. Thelayerofhardenedsedimentrichingypsumand saltbeneaththeflooroftheMediterraneansuggestthe Basinwasoncedry.
c. About6millionyearsago,fossilsofmarineplankton intheMediterraneandifferedfromthoseintheadjoiningAtlantic,indicatingtheMediterraneanwasnot connectedtotheAtlantic.
d. Pebblesrecoveredbythe GlomarChallenger fromthe hardlayer100metersbelowtheseafloorweredropped byglaciersastheyenteredtheseaandbegantomelt.
StrataatSiccarPointonthesoutheastcoastof Scotlandrevealanangularunconformity.Atthis location,JamesHuttonperceivedthatthesteeplytilted layerswereformedwhenoriginallyhorizontalbedswere deformedbymountainbuilding.Theseolderstratawere theneroded,andweresubsequentlycoveredbyyounger, flat-lyingrocks.Huttonhadclearlyrecognizedthe significanceofunconformitiesinEarthhistory.
(# MarliBryantMiller)
EarlyGeologistsTackle History’sMysteries Andsomerinuphillanddowndale,knappingthe chunkystanestopieceswi’hammers,likesaemany roadmakersrundaft.Theysayitistoseehowthe worldwasmade.
—SirWalterScott, St.Ronan’sWell
KeyChapterConcepts Fossilsareintriguingremnantsofformerlife, withoutwhichahistoryofEarthwouldbe incomplete.
NicholasStenoprovidesthebasicprinciplesof superposition,originalhorizontality,andoriginal lateralcontinuity.
JohnStrachey,GiovanniArduino,Johann Lehmann,GeorgFuchsel,andPeterSimonPallas recognizethegeneralagerelationshipsandnature ofmajorgroupsofrockassemblagesinEurope.
AbrahamG.Wernerpublishesthefirstgreat textbookofmineralogy,buterrsinhisbelief thatbasaltwasanoceanicdeposit.
JamesHuttonperceivestheimmensityofgeologic timeandunderstandstherelationbetween processesofthepresentandofthegeologicpast.
WilliamSmithdemonstratestheuseoffossilsfor correlatingstrata.
OUTLINE
c THEINTRIGUEOFFOSSILS
c ANEARLYSCIENTISTDISCOVERSSOME BASICRULES
c EUROPEANRESEARCHERSUNRAVELTHE SUCCESSIONOFSTRATA
c NEPTUNISTSANDPLUTONISTSCLASH
c UNIFORMITARIANISM:JAMESHUTTON RECOGNIZESTHATTHEPRESENTIS KEYTOTHEPAST
c THEPRINCIPLEOFFOSSILSUCCESSION
c THEGREATUNIFORMITARIANISM–CATASTROPHISMCONTROVERSY
c THEPRINCIPLEOFCROSS-CUTTING RELATIONSHIPS
c EVOLUTION:HOWORGANISMSCHANGE THROUGHTIME
c EARTHHISTORYINAMERICA
c SUMMARY
c KEYTERMS
c QUESTIONSFORREVIEWANDDISCUSSION
GeorgesCuvierconceivesthetheoryof catastrophismandstipulatesthatlifeonEarth underwentperiodicextermination,followedby reappearanceofentirelynewlifeforms.
CharlesLyellexplainstherelativeageofinclusions ofonerockinanother,andhowrocksthatcutinto andacrossotherrockscanalsobeusedto determinerelativegeologicage.
CharlesDarwinandAlfredR.Wallaceconceive ofnaturalselectionasamechanismforevolution.
PioneersofAmericangeology:
LouisAgassizrecognizesevidenceforthe greatPleistoceneIceAge
JamesHallunderstandsthedepositionaland mountain-buildinghistoryoftheAppalachian Mountains
FerdinandHayden,JohnPowell,andClarence Kingcompletegeologicandtopographic surveysoftheAmericanWest OthnielC.MarshandEdwinD.Copecollect anddescribeextinctvertebrateanimalsthat oncepopulatedNorthAmerica
In1795,WilliamSmith,asurveyorinEngland,was hiredtodeterminethebestrouteforacanalforcoal barges.Butbeforebeginningwork,Smithaskedsome preliminaryquestions:Whatkindofrockswouldhave tobeexcavated?Couldhepredictwhatrockswould beencounteredalongtheroute?Wherewouldthe diggingbeeasyandwheredifficult?
Ashewalkedalongacreek,Smithstudiedevery exposededgeofthelayeredrocks.Atonepoint,he climbeddownanembankmenttocloselyexaminea protrudingledgeofrock.Heranhishandacrossthe rocksurface.Theshellofanancientsnailcaughthis eye.Withhammerandchisel,Smithchippedhisdiscoveryfromtherockandplaceditinacanvasbag.
Herecognizedthisrockwithitssignaturefossil.He knewwhatrockstratumhewouldfindbelowitand whatlayaboveit.Onlyyesterday,hehadseenthis samelayertwomilestothenorth.Therewasremarkableconsistencyhere.Smithperceivedthateachstratum,knownbyitsfossilsandrocktype,notonly extendedinvisiblybeneaththefarmsinthedistance, butalsomaintaineditsplaceintheverticalsuccession ofrocklayers.
WilliamSmith’sdiscoveryisjustoneofthegreat contributionstoearlygeologythatyouwilldiscoverin thischapter.
cTHEINTRIGUEOFFOSSILS Theremainsandtracesofprehistoriclifewecallfossils havesparkedtheinterestandimaginationofpeople frombeforetheadventofcivilizationtothepresent day.Wethinkthatfossilswereprizedpossessionsof Neandertalsover30,000yearsago,forfossilshave beenfoundamongtheartifactsoftheseheavy-browed cavedwellers.
WesuspectthatNeandertalsbelievedthatfossils heldmagicalpowers.Butamorescientificinter-
pretationwasofferedabout450 BCE bytheGreek philosopherHerodotus.WhiletravelinginEgypt andLibya,Herodotussawfossilseashellsinoutcrops ofsedimentaryrockfarfromtheseaandhighabove sealevel.Theyweresimilartothosehehadseen alongtheshoresoftheMediterranean.Fromthis, heconcludedthatthelandhestoodonwasonce beneaththesea.
Inthecenturiesthatfollowed,fossilsofall kindswereobservedandcollectedacrossEurope. Somewerebonesofancientlandanimals,butthe majoritywerefossilshellsofmarinecreaturessimilar tothoseobservedbyHerodotus(Fig.2-1).They indicatedthatseashadoncecoveredthecontinent. Buthowcouldsuchagreatfloodingbereconciledwith religiousdoctrineoftheday?Tomanytheanswer seemedobvious.Thefossilseashellsandtherocksin whichtheywereembeddedwereanaffirmationofthe biblicalstoryofagreatfloodandNoah’sArk.
Butwhywouldocean-dwellingcreaturesbeexterminatedbyafloodofwater,theverymediuminwhich theylived?Andhowmightweexplaintheevidenceof manyfloodsatdifferenttimesandindifferentplaces? Bythebeginningofthe1800s,geologistshad acquiredabetterunderstandingoftheimmensity ofgeologictimeandwereabletousemethodsof relativedatingtoderiveamorevalidinterpretationof fossils.Theynowrealizedthatfossilsweretherecord ofentiredynastiesoflivingcreaturesthatpreceded thearrivalofhumans.
HowDoFossilsForm? Worldwide,sedimentiscontinuallydeposited. Sedimentincludesmudandsiltfromstreams,debris settlingfromoceanwaterontotheseafloor,dustor volcanicashdepositedbythewind,andchemical precipitates.Countlesstimesinthegeologicpast,
FIGURE2-1 Limestonecontaining 200-million-year-oldfossil ammonites.Ammonitesareanextinct groupofcephalopodsrelatedtothe livingchamberednautilus.(# Biophoto Associates/PhotoResearchers,Inc.)
PrincipleofSuperposition The principleofsuperposition statesthatinany sequenceofundisturbedstrata,theoldestlayerisatthe bottom,andsuccessivelyyoungerlayersaresuccessively higher.Thisseemsobvious,easilydemonstratedby tossingsheetsofpaperonthefloor:theoneonthe bottomwas“deposited”firstandthereforeistheoldest.YetSteno,basedonhisobservationsofstratain northernItaly,wasthefirsttoformallydescribethe conceptappliedtorocklayers.Herecognizedthat,as hewentdownwardinexaminingapileofstrata,hewas goingdeeperintothepast,andasheclimbedupward, hewasseeingrocksofincreasinglyyoungerage.
plantsandanimals—deadorliving—havebeencoveredbysedimentandpreservedasfossils.
Forpreservation,quickburialisneeded.Inthecase ofanimals,ifthecreaturehasahardskeletonorshell, allthebetter.Afterdeath,softtissuewillrotawayas flesh,andothersofttissueareconsumedbybacteria andscavengers.Butshellandbonewillbeleftto petrifyinthegraduallyhardeningmatrixofsediment. Thisiswhytheyareplentifulasfossils.
However,occasionallywearerewardedwithevidenceofsoftparts.Smallanimals,especiallyinsects, arepreservedinthehardenedresin(“amber”)of conifers(Fig.2-2).Carbonizedimprintsofjellyfish andwormscanbeseeninX-raysofrocks.Skin,hair, andstomachcontentsofIceAgemastodonshave beenpickledintarfromoilseepsorfrozeninto glacialice.
Allofthesepreservations—aswellasfoottracks, trails,andevenholesdugbysomeanimals—permitus todiscernthehistoryoflife.Thestoryisnotcomplete, fornewfossildiscoveriesaremadedaily.Oftenonlya fragmentofboneorshellremains,butthereinliesthe fascination.Webecomedetectives,usingourreason, imagination,andintuitiontorecreatetheformand habitsofaonce-livingthing.
cANEARLYSCIENTISTDISCOVERS SOMEBASICRULES NielsStensen(1638–1687),aDanishphysician,was widelyrecognizedforhisstudiesinanatomy.He movedtoItaly,LatinizedhisnametoNicolausSteno, andbecamephysiciantotheGrandDukeofTuscany. Thedukewasagenerousemployer,givingSteno ampletimetotrampthecountryside,visitquarries, andexaminestrata.Hisobservationsofsedimentary rocksledhimtoformulatethreebasicprinciplesof historicalgeology:superposition,originalhorizontality,andoriginallateralcontinuity.Allthreearecommonsensebutvaluable,andaredescribedbelow.
Thefactthatsuperpositionisself-evidentdoesnot diminishtheprinciple’simportanceindeterminingthe relativeageofstrata,oldesttoyoungest.Thesuperpositionalrelationshipofstrataisnotalwaysclearwhere layersaresteeplytiltedorevenoverturned(Fig.2-3).In suchinstances,thegeologistmustexaminethestratafor cluesusefulinrecognizingtheirlowermostanduppermostlayers.Usefulcluesindetermining“whichway wasup”atthetimeofdepositionarethewayfossilsliein therockandtheevidenceofmudcracksandripple marks,whichformonasurface.
PrincipleofOriginalHorizontality The principleoforiginalhorizontality statesthat sedimentisdepositedinlayersthatareoriginallyhorizontal Stenoreasonedthistobesobecausemostsedimentary particlessettleoutofwaterorairstraightdown,under theinfluenceofgravity(Fig.2-4).Thisisobviouswhen youpouracupofsandintoanaquariumfilledwith water;theresultisahorizontallayerofsand.Today,if weseeflat-lyingstrata,itisprobablyinitsoriginal horizontalposition,untiltedandunfolded.Butifwesee steeplyinclinedstratalikethoseinFigure2-3B,this indicatescrustaldisturbancethatoccurred after deposition,alteringtheoriginalhorizontality(Fig.2-5).
PrincipleofOriginalLateralContinuity The principleoforiginallateralcontinuity statesthat arocklayerextendscontinuouslyinalldirectionsuntilit thinsoutorencountersabarrier.Steno’sthirdprinciple recognizesthat,whensedimentisdepositedonthe floorofanoceanoralake,itextendscontinuouslyin alldirectionsuntilthinningatthemarginofthebasin. Again,pouracupofsandintoanaquarium,andthisis howitbehaves.Thelayermayendabruptlyagainst somebarriertodeposition,orgradelaterallyintoa differentkindofsediment(Fig.2-6).
Thesignificanceofthisingeologyisthat,ifyou observeanexposedcross-sectionofstrataonavalley wall,youknowthatthestrata,asoriginallydeposited, willcontinuelaterallyontheothervalleywall.Further,
FIGURE2-2 Spiderpreservedinamber.(Courtesy W.BruceSaunders)
FIGURE2-3 Principleof superposition.(A)Exampleofa superpositionalsequenceof undisturbedTriassicandJurassic stratainCapitalReefNational Monument,Utah. ? Isthegreen shalerelativelyyoungerorolderthan thegrayrocklayerbeneathit? (B) Stronglyfoldedstratainthe HimalayanMountainsofTibet.It isoftendifficulttorecognizethe originaltopsandbottomsofrock layers.Geologistslookforbedding featurestohelpthemmakethe distinction. ? Ifageologistwas unabletotellthetopfromthebottomof bedsinanoutcropofseveralbeds,how mightthataffecthisinterpretationof theageofthestratafrombottomto top?(Answerstoquestionsabout figurescanbefoundintheStudent StudyGuide).((A)USGS,(B)Peter L.KresanPhotography)
FIGURE2-4 Undisturbedhorizontalstrata ErosionbytheColoradoRiverinthe foregroundhascarvedthecanyonandexposed thestratainthisnaturalgeologiclaboratory. ? Drawanarrowonthephotographtoindicatewhere youwouldfindtheyoungeststrata.(FarleyLewis/ PhotoResearchers,Inc.)