Techno-economicsandLifeCycleAssessmentof Bioreactors:Post-COVID-19WasteManagement ApproachPuranjanMishra
https://ebookmass.com/product/techno-economics-and-lifecycle-assessment-of-bioreactors-post-covid-19-wastemanagement-approach-puranjan-mishra/
Instant digital products (PDF, ePub, MOBI) ready for you
Download now and discover formats that fit your needs...
Reinforced polymer composites processing, characterization and post life cycle assessment Wiley-Vch
https://ebookmass.com/product/reinforced-polymer-compositesprocessing-characterization-and-post-life-cycle-assessment-wiley-vch/
ebookmass.com
Project Management for Engineering and Construction: A Life-Cycle Approach Fourth Edition Garold Oberlender
https://ebookmass.com/product/project-management-for-engineering-andconstruction-a-life-cycle-approach-fourth-edition-garold-oberlender/
ebookmass.com
Sustainable Construction Technologies: Life-Cycle Assessment Vivian W.Y. Tam
https://ebookmass.com/product/sustainable-construction-technologieslife-cycle-assessment-vivian-w-y-tam/
ebookmass.com
Complete Solutions Manual for Calculus of a Single Variable, Early Transcendental Functions 7th Edition Ron Larson
https://ebookmass.com/product/complete-solutions-manual-for-calculusof-a-single-variable-early-transcendental-functions-7th-edition-ronlarson/
ebookmass.com
Building Java Programs - A Back to Basics Approach 5th Edition Stuart Reges
https://ebookmass.com/product/building-java-programs-a-back-to-basicsapproach-5th-edition-stuart-reges/
ebookmass.com
The Duchess Gamble (All's Fair in Love and Racing Book 2) Sofie Darling
https://ebookmass.com/product/the-duchess-gamble-alls-fair-in-loveand-racing-book-2-sofie-darling/
ebookmass.com
The Bourgeois and the Savage: A Marxian Critique of the Image of the Isolated Individual in Defoe, Turgot and Smith Iacono Alfonso Maurizio
https://ebookmass.com/product/the-bourgeois-and-the-savage-a-marxiancritique-of-the-image-of-the-isolated-individual-in-defoe-turgot-andsmith-iacono-alfonso-maurizio/ ebookmass.com
Natural Fiber-Reinforced Composites: Thermal Properties and Applications Senthilkumar Krishnasamy
https://ebookmass.com/product/natural-fiber-reinforced-compositesthermal-properties-and-applications-senthilkumar-krishnasamy/ ebookmass.com
La casa de Foster Hill Jaime Jo Wright
https://ebookmass.com/product/la-casa-de-foster-hill-jaime-jowright-2/
ebookmass.com
The Art and Science of Thread Lifting: Based on Pinch Anatomy 1st ed. 2019 Edition, (Ebook PDF)
https://ebookmass.com/product/the-art-and-science-of-thread-liftingbased-on-pinch-anatomy-1st-ed-2019-edition-ebook-pdf/
ebookmass.com
Techno-economicsand LifeCycleAssessment ofBioreactors
Thispageintentionallyleftblank
Techno-economicsand LifeCycleAssessment ofBioreactors
Post-Covid19WasteManagement Approach
Editedby
PURANJANMISHRA
FacultyofCivilEngineeringTechnology,Universiti MalaysiaPahang(UMP),Gambang,Pahang,Malaysia
LAKHVEERSINGH
DepartmentofEnvironmentScience,SRM-University-AP, Amaravati,India
POOJAGHOSH
CentreforRuralDevelopmentandTechnology,Indian InstituteofTechnologyDelhi,NewDelhi,India
Elsevier
Radarweg29,POBox211,1000AEAmsterdam,Netherlands
TheBoulevard,LangfordLane,Kidlington,OxfordOX51GB,UnitedKingdom 50HampshireStreet,5thFloor,Cambridge,MA02139,UnitedStates
Copyright©2022ElsevierInc.Allrightsreserved.
Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproducedortransmittedinanyformorbyanymeans, electronicormechanical,includingphotocopying,recording,oranyinformationstorageand retrievalsystem,withoutpermissioninwritingfromthepublisher.Detailsonhowtoseek permission,furtherinformationaboutthePublisher’spermissionspoliciesandour arrangementswithorganizationssuchastheCopyrightClearanceCenterandtheCopyright LicensingAgency,canbefoundatourwebsite: www.elsevier.com/permissions
Thisbookandtheindividualcontributionscontainedinitareprotectedundercopyrightby thePublisher(otherthanasmaybenotedherein).
Notices
Knowledgeandbestpracticeinthisfieldareconstantlychanging.Asnewresearchand experiencebroadenourunderstanding,changesinresearchmethods,professionalpractices, ormedicaltreatmentmaybecomenecessary.
Practitionersandresearchersmustalwaysrelyontheirownexperienceandknowledgein evaluatingandusinganyinformation,methods,compounds,orexperimentsdescribed herein.Inusingsuchinformationormethodstheyshouldbemindfuloftheirownsafety andthesafetyofothers,includingpartiesforwhomtheyhaveaprofessionalresponsibility.
Tothefullestextentofthelaw,neitherthePublishernortheauthors,contributors,or editors,assumeanyliabilityforanyinjuryand/ordamagetopersonsorpropertyasamatter ofproductsliability,negligenceorotherwise,orfromanyuseoroperationofanymethods, products,instructions,orideascontainedinthematerialherein.
ISBN:978-0-323-89848-5
ForInformationonallElsevierpublications visitourwebsiteat https://www.elsevier.com/books-and-journals
Publisher: SusanDennis
EditorialProjectManager: LenaSparks
ProductionProjectManager: BharatwajVaratharajan
CoverDesigner: MarkRogers
TypesetbyMPSLimited,Chennai,India
Part1Bioreactors:Currentstatus,recenttrends andchallenges1
1.ImpactofCOVID-19onwasteandresource managementpractices3 VikramThakur
1.1 Introduction3
1.2 Typesofwaste4
1.2.1 WastegenerationduringCOVID-19pandemic4
1.3 ImpactofCOVID-19onwastemanagement5
1.4 TheuniquechallengewithSARSCoV-2andwastemanagement6
1.4.1 Wastemanagementstrategies7
1.5 Policyandregulatoryapproaches9
1.6 WHOguidelinesonwastemanagement10
1.7 Conclusionandfutureperspective10 References11
2.Aerobicandanaerobicbioreactorsystemsfor wastewatertreatment13 MonikaJain,SmitaS.KumarandLalitGoswami
2.1 Introduction13
2.2 Bioreactoranddifferentconfigurations15
2.3 Continuousstirredtankbioreactor15
2.4 Airliftbioreactors16
2.5 Anaerobicfluidizedbedbioreactors16
2.6 Packedbed(fixedbed)bioreactors17
2.7 Membranebioreactors18
2.8 Upflowanaerobicsludgeblanketreactor19
2.9 Conclusion20 Acknowledgment21 References21
3.Emergingtrendsinbioreactorsystemsforanimproved wastesvalorization23
OlusegunAbayomiOlalere,Chee-YuenGan,AbiolaEzekielTaiwo, HamoudAlenezi,OladayoAdeyiandAbiolaJohnAdeyi
3.1 Introduction23
3.1.1 Stirredtanksystem23
3.1.2 Fluidized-bedreactor25
3.1.3 Fixedbedbioreactor26
3.2 Thetheoryofbioreactoranditsgeometry27
3.3 Bioreactordevelopmentforimprovedwastevalorization29
3.4 Currenttrendsinthebioreactorsystem30
3.5 Conclusion32 References33
4.Developmentofbioreactors:currentscenarioand futurechallenges37
PragyaPrakash,SupriyaPandey,SantoshKumarJha andHareRamSingh
4.1 Introduction37
4.2 Stirredtankbioreactors38
4.2.1 Stirredtankbioreactorsinwastemanagement38
4.3 Bubblecolumnreactors39
4.3.1 Advancesinbubblecolumnbioreactors39
4.3.2 Bubblecolumnreactorinwastemanagement:recentadvances41
4.4 Membranebioreactors42
4.4.1 Anaerobicmembranebioreactor43
4.4.2 Membranefouling45
4.5 Somemoderntypesofbioreactorsandtheirapplications46
4.5.1 Fixedbedbioreactors46
4.5.2 Integratedmembraneandhangingspongebioreactor46
4.5.3 Disposablebioreactors48
4.5.4 Denitrificationbioreactors48
4.6 COVIDwastemanagementinthepandemictimes48
4.6.1 Membranebio-reactorsintheremovalofCOVIDviralload50
4.7 Conclusion50 References51 Furtherreading53
5.Economicaspectsofbioreactors:currenttrendsand futureperspective55
MamtaDeviSharma,SwatiSharma,PuranjanMishra andSaurabhKulshrestha
5.1 Introduction55
5.2 Directivesofeconomicanalysis56
5.3 Costanalysis56
5.3.1 Capitalcosts57
5.3.2 Productioncosts57
5.3.3 Materialsandutilities58
5.4 Costanalysisforbioreactorsappliedforwastemanagement58
5.5 Costevaluationofsubmergedanaerobicmembranebioreactorfor municipalsecondarywastewatertreatment60
5.6 MonteCarlocostestimationmethodforwastewatertreatment membranebioreactors61
5.7 Costanalysisforaerobicfermenters63
5.7.1 Stirredtankreactorandbubblecolumnreactorcostanalysis64
5.8 Futureperspectives65 References67 Furtherreading68
6.Landfillmanagementandefficacyofanaerobicreactorsinthe treatmentoflandfillleachate69
ImranAhmad,AidaBatrisyiaJasni,NorhayatiAbdullah,SanthanaKrishnan, IwamotoKoji,ShreeshivadasanChelliapan,AliYuzirandMohdNasrullah
6.1 Introduction69
6.2 Advantagesofbiologicaltreatmentoverphysicalandchemicaltreatment73
6.3 Advantagesofanaerobicprocessoveraerobicprocess77
6.4 Latestdevelopmentofanaerobicreactorstreatinglandfillleachate78
6.4.1 Anaerobicmembranebioreactor79
6.4.2 Upflowanaerobicsludgeblanketreactor79
6.4.3 Anaerobicfixedbedreactor81
6.4.4 Anaerobiccontactreactor81
6.4.5 Anaerobicbaffledreactor82
6.4.6 Anaerobicammoniumqxidation(anammox)83
6.5 Combinedanaerobictechnologies83
6.6 Conclusion86 Acknowledgement87 Conflictofinterest87 References87
Part2Techno-economicassessment ofbioreactors93
7.Technoeconomicsandlifecycleassessmentofbioreactors: wastewatertreatmentplantmanagement95
TarnimaWardaAndalib,ZaiedBinKhalidandPuranjanMishra
7.1 Introduction95
7.2 Conceptsoftechno-economyanalyses97
7.3 Methodologyoftechno-economicanalysis99
7.3.1 Staticcost benefitassessment99
7.3.2 Annuitymethod99
7.3.3 Netcashflow101
7.3.4 Netpresentvalue101
7.3.5 Internalrateofreturn102
7.4 Techno-economicanalysismodels102
7.5 Techno-economicparadigm102
7.6 Techno-economicinnovations105
7.7 Environmentalimpactassessment106
7.8 Environmentalimpactassessmentmethodology107
7.9 Bioreactors,categorization,andsustainablefactors108
7.10 Typesofbioreactor109
7.10.1 Osmoticmembranebioreactors110
7.10.2 Integratedtwo-phasefixed-filmbaffledbioreactor110
7.10.3 High-solidanaerobicmembranebioreactor111
7.10.4 Solarassistedbioreactor112
7.10.5 Anaerobiclandfillbioreactors112
7.10.6 Microbialfuelcells113
7.11 TechnologicalimpactassessmentofbioreactorsonWWTP114
7.12 EconomicalimpactassessmentofbioreactorsonWWTP115
7.13 Challengesindealingwithwastewatertreatmentplant115
7.13.1 Upgradedbiocrude-HTLconfigurationprocessandtheory117
7.14 Feedstockandplantscale117
7.15 Hydrothermalliquefaction119
7.16 Hydrothermalliquefactionaqueousphasetreatmentbycatalytic hydrothermalliquefaction/gasification119
7.17 Sludgehydrothermalliquefactionoilupgrading119
7.18 Conclusion120
7.19 Contributionofauthors121 Acknowledgment122 References122
8.Strategiestowardsustainablemanagementoforganicwaste131
RenuandPuranjanMishra
8.1 Introduction131
8.2 Activitiesforsolidwastemanagement134
8.3 Strategiesforwastemanagement135
8.3.1 Preventionofwastegeneration136
8.3.2 Minimization136
8.3.3 Reuse137
8.3.4 Recycling137
8.3.5 Biologicaltreatment138
8.3.6 Incineration139
8.3.7 Landfilldisposal139
8.3.8 Sanitarylandfill140
8.3.9 Municipalsolidwastelandfills140
8.3.10 Constructionanddemolitionwastelandfills140
8.3.11 Industrialwastelandfills140
8.3.12 Hazardouswastelandfills141
8.4 Conclusion141 Acknowledgment142 References142
9.Applicationofmatricesforthedevelopmentofnext-gen bioreactorsfromCOVID-19wastemanagementprospects145
SnehiSoy,BishwajitSinghKapoor,ShubhaRaniSharma andVinodKumarNigam
9.1 Introduction145
9.2 Emergingtrendsinbioreactorswithrespecttomatrix andapplications146
9.2.1 Monoclonalantibodiesproduction146
9.2.2 Wastewatertreatment150
9.2.3 Applicationoffixed-filmmicrobialreactorsforthetreatment ofeffluents152
9.2.4 Abatementofairpollutants154
9.2.5 Matrixdesignanddevelopmentforcellcultivation154
9.2.6 Advancementinthedevelopmentofphotobioreactor155
9.2.7 Immobilizationandtheroleofmatricesintheimprovement ofbioreactorfunction156
9.2.8 Otherapplications158
9.3 Applicationofmatrices-basedbioreactorsinCOVID-19 wastemanagement158
9.4 Conclusion158 References161 Furtherreading165
10.Sustainableengineeringoffoodwasteintohigh-quality animalfeedusingadryingtechnology167
SanthanaKrishnan,NurShahidah,MohdFadhilBinMdDin, PuranjanMishra,MohdNasrullah,AbudukeremuKadier, ShazwinMatTaib,MohdHafizBinPuteh,NorahimbinIbrahim, NurfarhainMdRusli,FadzlinMdSairanandLakhveerSingh
10.1 Introduction167
10.2 Appliedprocessingforfoodwasteintoanimalfeed169
10.2.1 Dryingtechnology170
10.2.2 Solardrying172
10.2.3 Oven172
10.3 Resultsanddiscussion173
10.3.1 Effectivenessofconventionalfan173
10.3.2 Effectivenessofsolardrying173
10.3.3 Effectivenessofovendrying174
10.3.4 Improvementofthedryingprocess175
10.3.5 Moisturecontent175
10.3.6 Analysisofproteincontent177
10.3.7 Analysisof Escherichiacoli 179
10.4 Conclusions181 Acknowledgments182 References183
11.Environmentalandeconomiclifecycleassessmentofbiochar useinanaerobicdigestionforbiogasproduction185 ZaiedBinKhalid,AhasanulKarim,PramodJadhav,PuranjanMishra, ZularisamBinAbdWahidandMohdNasrullah
11.1 Introduction185
11.2 Lifecycleassessmenttechnology187
11.2.1 Lifecycleassessment basedmethodology188
11.2.2 Lifecycleassessmentevaluationmeasures192
11.2.3 Lifecyclecostassessment194
11.3 Lifecycleassessmentstudiesinanaerobicdigestionfor biogasproduction196
11.4 Challengesforlifecycleassessmenttechnology199
11.5 Concludingremarksandrecommendations200
11.6 Acknowledgment202
11.7 Declarationofcompetinginterest202 References203
12.Challengesandemergingapproachesinlifecycleassessment ofengineerednanomaterialsusageinanaerobicbioreactor207 PramodJadhav,ZaiedBinKhalid,PuranjanMishra, ZularisamBinAbdWahidandMohdNasrullah
12.1 Introduction207
12.2 Anaerobicdigestionprocessinthebioreactor208
12.2.1 Hydrolysis208
12.2.2 Acidogenesis208
12.2.3 Acetogenesis209
12.2.4 Methanogenesis209
12.3 Engineerednanoparticlesintheanaerobicdigestionprocess210
12.3.1 Interactionofnanoparticlesintheanaerobic digestionprocess210
12.3.2 Engineerednanoparticlesinbioreactor211
12.4 Challengesandassessmentofengineerednanoparticlesinbioreactor214
12.4.1 Techno-economicanalysisofengineerednanoparticles intheanaerobicdigestionprocess214
12.4.2 Challengesofengineerednanoparticles215
12.5 Conclusion216 Acknowledgment216 Declarationofcompetinginterest217 References217
Index 223
Thispageintentionallyleftblank
Listofcontributors
NorhayatiAbdullah
Malaysia-JapanInternationalInstituteofTechnology(MJIIT),UniversitiTeknologi Malaysia,KualaLumpur,Malaysia
AbiolaJohnAdeyi
DepartmentofMechanicalEngineering,LadokeAkintolaUniversityofTechnology, Ogbomoso,OyoState,Nigeria
OladayoAdeyi
DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,MichaelOkparaUniversityofAgriculture, Umudike,AbiaState,Nigeria
ImranAhmad
Malaysia-JapanInternationalInstituteofTechnology(MJIIT),UniversitiTeknologi Malaysia,KualaLumpur,Malaysia
HamoudAlenezi
ProcessSystemsEngineeringCentre(PROSPECT),ResearchInstituteforSustainable Environment,SchoolofChemicalandEnergyEngineering,UniversitiTeknologi,Kuala Lumpur,Malaysia
TarnimaWardaAndalib
BRACBusinessSchool,BRACUniversity,Dhaka,Bangladesh
ShreeshivadasanChelliapan
RazakFacultyofTechnologyandInformatics,UniversitiTeknologiMalaysia,Kuala Lumpur,Malaysia
MohdFadhilBinMdDin
DepartmentofWaterandEnvironmental,CentreforEnvironmentalSustainabilityand WaterSecurity(IPASA),ResearchInstituteofSustainableEnvironment(RISE),Schoolof CivilEngineering,FacultyofEngineering,UniversitiTeknologiMalaysia(UTM),Skudai, Malaysia;DepartmentofWaterandEnvironmentalEngineering,SchoolofCivil Engineering,FacultyofEngineering,UniversitiTeknologiMalaysia(UTM),Skudai, Malaysia
Chee-YuenGan
AnalyticalBiochemistryResearchCenter(ABrC),UniversitiSainsMalaysia,University InnovationIncubatorBuilding,Sains@USM,BayanLepas,Penang,Malaysia
LalitGoswami
CentreforEnvironment,IndianInstituteofTechnology,Guwahati,Assam,India
NorahimbinIbrahim
DepartmentofBiosciencesandHealthSciences,FacultyofBiosciencesandMedical Engineering,UniversitiTeknologiMalaysia(UTM),Skudai,Malaysia
PramodJadhav
FacultyofCivilEngineeringTechnology,UniversitiMalaysiaPahang(UMP),Pahang, Malaysia
MonikaJain
DepartmentofNaturalResourceManagement,CollegeofForestry,BandaUniversityof Agriculture&Technology,Banda,UttarPradesh,India
AidaBatrisyiaJasni
SchoolofEngineering,FacultyofEngineering,UniversitiTeknologiMalaysia,Skudai, Johor,Malaysia
SantoshKumarJha
DepartmentofBio-EngineeringandBiotechnology,BirlaInstituteofTechnology, Ranchi,Jharkhand,India
AbudukeremuKadier
LaboratoryofEnvironmentalScienceandTechnology,TheXinjiangTechnicalInstitute ofPhysicsandChemistry,KeyLaboratoryofFunctionalMaterialsandDevicesforSpecial Environments,ChineseAcademyofSciences,Urumqi,PRChina
BishwajitSinghKapoor
DepartmentofBiotechnology,NationalInstituteofTechnology,Durgapur,WestBengal, India
AhasanulKarim
DepartmentofSoilSciencesandAgri-foodEngineering,UniversitéLaval,Quebec,QC, Canada
ZaiedBinKhalid
FacultyofCivilEngineeringTechnology,UniversitiMalaysiaPahang(UMP),Pahang, Malaysia
IwamotoKoji
Malaysia-JapanInternationalInstituteofTechnology(MJIIT),UniversitiTeknologi Malaysia,KualaLumpur,Malaysia
SanthanaKrishnan
DepartmentofWaterandEnvironmental,CentreforEnvironmentalSustainabilityand WaterSecurity(IPASA),ResearchInstituteofSustainableEnvironment(RISE),Schoolof CivilEngineering,FacultyofEngineering,UniversitiTeknologiMalaysia(UTM),Skudai, Malaysia;PSUEnergySystemsResearchInstitute,DepartmentofEnvironmental Engineering,FacultyofEngineering,PrinceofSongklaUniversity,Songkhla,Thailand; CenterofEnvironmentalSustainabilityandWaterSecurity(IPASA),ResearchInstituteof SustainableEnvironment(RISE),FacultyofEngineering,UniversitiTeknologiMalaysia, JohorBahru,Malaysia;PSUEnergySystemsResearchInstitute(PERIN),Departmentof EnvironmentalEngineering,FacultyofEngineering,PrinceofSongklaUniversity,Hat Yai,Thailand
SaurabhKulshrestha
FacultyofAppliedSciencesandBiotechnology,ShooliniUniversityofBiotechnologyand ManagementSciences,Solan,HimachalPradesh,India;CenterforOmicsandBiodiversity Research,ShooliniUniversityofBiotechnologyandManagementSciences,Solan, HimachalPradesh,India
SmitaS.Kumar
DepartmentofEnvironmentalSciences,J.C.BoseUniversityofScience&Technology, YMCA,Faridabad,Haryana,India
PuranjanMishra
FacultyofCivilEngineeringTechnology,UniversitiMalaysiaPahang(UMP),Pahang, Malaysia;InstituteofBioresourceandAgriculture,HongKongBaptistUniversity, KowloonTong,HongKong
MohdNasrullah
FacultyofCivilEngineeringTechnology,UniversitiMalaysiaPahang(UMP),Pahang, Malaysia
VinodKumarNigam
DepartmentofBioengineering&Biotechnology,BirlaInstituteofTechnology,Ranchi, Jharkhand,India
OlusegunAbayomiOlalere
AnalyticalBiochemistryResearchCenter(ABrC),UniversitiSainsMalaysia,University InnovationIncubatorBuilding,Sains@USM,BayanLepas,Penang,Malaysia
SupriyaPandey
DepartmentofBiotechnology,ManipalInstituteofTechnology,ManipalAcademyof HigherEducation(MAHE),Udupi,Karnataka,India
PragyaPrakash
DepartmentofBio-EngineeringandBiotechnology,BirlaInstituteofTechnology, Ranchi,Jharkhand,India;CentreforBiopharmaceuticalTechnology,Departmentof ChemicalEngineering,IndianInstituteofTechnology,NewDelhi,India
MohdHafizBinPuteh
DepartmentofEnvironmentalEngineering,FacultyofCivilEngineering,Universiti TeknologiMalaysia(UTM),Skudai,Malaysia
Renu
DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,MalaviyaNationalInstituteofTechnology,Jaipur, Rajasthan,India
NurfarhainMdRusli
DepartmentofWaterandEnvironmental,CentreforEnvironmentalSustainabilityand WaterSecurity(IPASA),ResearchInstituteofSustainableEnvironment(RISE),Schoolof CivilEngineering,FacultyofEngineering,UniversitiTeknologiMalaysia(UTM),Skudai, Malaysia;DepartmentofWaterandEnvironmentalEngineering,SchoolofCivil Engineering,FacultyofEngineering,UniversitiTeknologiMalaysia(UTM),Skudai, Malaysia
FadzlinMdSairan
DepartmentofWaterandEnvironmental,CentreforEnvironmentalSustainabilityand WaterSecurity(IPASA),ResearchInstituteofSustainableEnvironment(RISE),Schoolof CivilEngineering,FacultyofEngineering,UniversitiTeknologiMalaysia(UTM),Skudai, Malaysia;DepartmentofWaterandEnvironmentalEngineering,SchoolofCivil Engineering,FacultyofEngineering,UniversitiTeknologiMalaysia(UTM),Skudai, Malaysia
NurShahidah
DepartmentofWaterandEnvironmental,CentreforEnvironmentalSustainabilityand WaterSecurity(IPASA),ResearchInstituteofSustainableEnvironment(RISE),Schoolof CivilEngineering,FacultyofEngineering,UniversitiTeknologiMalaysia(UTM),Skudai, Malaysia;DepartmentofWaterandEnvironmentalEngineering,SchoolofCivil Engineering,FacultyofEngineering,UniversitiTeknologiMalaysia(UTM),Skudai, Malaysia
MamtaDeviSharma
FacultyofAppliedSciencesandBiotechnology,ShooliniUniversityofBiotechnologyand ManagementSciences,Solan,HimachalPradesh,India;CenterforOmicsandBiodiversity Research,ShooliniUniversityofBiotechnologyandManagementSciences,Solan, HimachalPradesh,India
ShubhaRaniSharma
DepartmentofBioengineering&Biotechnology,BirlaInstituteofTechnology,Ranchi, Jharkhand,India
SwatiSharma
ShooliniInstituteofLifeSciencesandBusinessManagement,Solan,HimachalPradesh, India
HareRamSingh
DepartmentofBio-EngineeringandBiotechnology,BirlaInstituteofTechnology, Ranchi,Jharkhand,India
LakhveerSingh
DepartmentofEnvironmentalScience,SRMUniversity-AP,Amaravati,AndhraPradesh, India
SnehiSoy
DepartmentofBioengineering&Biotechnology,BirlaInstituteofTechnology,Ranchi, Jharkhand,India
ShazwinMatTaib
DepartmentofWaterandEnvironmental,CentreforEnvironmentalSustainabilityand WaterSecurity(IPASA),ResearchInstituteofSustainableEnvironment(RISE),Schoolof CivilEngineering,FacultyofEngineering,UniversitiTeknologiMalaysia(UTM),Skudai, Malaysia;DepartmentofWaterandEnvironmentalEngineering,SchoolofCivil Engineering,FacultyofEngineering,UniversitiTeknologiMalaysia(UTM),Skudai, Malaysia
AbiolaEzekielTaiwo
DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,LandmarkUniversity,Omu-Aran,KwaraState, Nigeria
VikramThakur
DepartmentofVirology,PostgraduateInstituteofMedicalEducationandResearch, PGIMER,Chandigarh,India
ZularisamBinAbdWahid
FacultyofCivilEngineeringTechnology,UniversitiMalaysiaPahang(UMP),Pahang, Malaysia
AliYuzir
Malaysia-JapanInternationalInstituteofTechnology(MJIIT),UniversitiTeknologi Malaysia,KualaLumpur,Malaysia
Thispageintentionallyleftblank
PART1 Bioreactors:Current status,recenttrends
andchallenges
Thispageintentionallyleftblank
CHAPTER1
ImpactofCOVID-19onwaste andresourcemanagement practices
VikramThakur DepartmentofVirology,PostgraduateInstituteofMedicalEducationandResearch,PGIMER, Chandigarh,India
1.1Introduction
AsofOctober4,2021,therehavebeenmorethan234millionconfirmed casesofCOVID-19,including4,800,375deathsreportedgloballytothe WorldHealthOrganization(WHOCoronavirus.,2021).Pandemicnot onlyaffectedthesocioeconomicpoorcountries,butmiddleandhigherincomecountrieslikeUnitedStates,Brazil,Russia,andtheUnited Kingdomwerearealsoworseaffected.Theeffectofthesecondwaveand thesuspicionoftheemergenceofthird-wavewithnewSARS-CoV-2 deadlyvariantsincomingmonthsisamatterofgreatconcernnotonlyin termsoflossoflifebutalsointermsoftheeconomicstructure,geopoliticalrelations,changeinsocialbehaviorandpersonalhabits,andtheattitudetowardlifeandenvironment.
Eventhe5sustainabledevelopmentgoals(SDSs)likecleanwaterand sanitation(WorldHealthOrganization,2018),climateaction(VanFan etal.,2021),lifebelowwater[WastemanagementanessentialpublicserviceinthefighttobeatCOVID-19.,2021],andlifeonland(Liangetal., 2021)arefacingchallengestosustainduetotheCOVID-19pandemic (THE17GOALS,2021).Theseareessentialforthesustenanceofthe humanraceincloseassociationwithnatureandbiodiversity.Alreadythe worldisfacingdevastatingissueslikeglobalclimatechange,air,and marinepollution,plasticandmicroplasticsasapollutant,explodingpopulationcreatingenormousbiodegradableandnonbiodegradablewaste.Due totheemergenceoftheCOVID-19pandemic,ahugeincreaseinamedicalandhazardouswastegenerationhasputaburdenontheexisting remedialresources.Additionally,ensuringthesafehandlingandproper disposalofhazardousCOVID-19associatedwasteisvitalforprotecting humanhealthandtheenvironmentforfuturegenerations.
Techno-economicsandLifeCycleAssessmentofBioreactors DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-89848-5.00010-X ©2022ElsevierInc. Allrightsreserved.
DuringtheinitialnationwidelockdowntocurtailCOVID-19,the worldhadwitnessedtherejuvenatingimpactontheenvironmentand ecosystemsuchaslowpollution,clearerskies,andcleanerrivers(National Geographic.,2020).ButsimultaneouslyCOVID-19preventivemeasures generatedandalteredthedynamicsofsolidandmedicalwastegenerated, creatingwoesamongpolicymakers.
1.2Typesofwaste
Withtheriseinlivingstandardsandurbanization,thereisahikeinthe complexityandvolumeofthewastegenerated.Industrializationand advancementsinmedicalfacilitieshaveaddedsubstantialquantitiesof infectiouswasteintotheenvironmentwhichhaveadversehumanhealth consequences.Usually,thereare6typesofwastegeneratedintheenvironment,thatis,municipalwaste(household),industrialwaste,agriculturalwaste,biomedicalwaste(BMW),e-waste,andhazardouswaste.
1.2.1WastegenerationduringCOVID-19pandemic
Municipalwaste,thatis,solidwasteisgeneratedfromhouseholdsand othercommercialorresidentialspaceswherefoodwaste,plastic,etc.,are themaincomponent.Duringtheworldwidelockdown,thereisasurge inthegenerationofcommonpackingplasticwasteforgroceriespurposes addingthepoolofalreadyexistingnonbiodegradablewaste(TheAmount OfPlasticWasteIsSurgingBecauseOfTheCoronavirusPandemic., 2020).Thismenaceisfurtherenhancedbytheuseofsingle-useplastic (SUP).Themainconcernisthesurvivalofthevirusforaprolongedtime onthesematerials.However,thechangeinthebehavioralpatternand lifestyleduringCOVID-19certainlyforcedtheconsumerstopreferplastic packagingforhygienereasonsdominatingtheplasticwaste’senvironmentalimpacts(Grodzi ´ nska-Jurczaketal.,2020).
BMW,thatis,wastegeneratedbyhospitals,medicallaboratories,and researchinstitutionsincludeswastesofsharps,infectious,pathological, chemical,andradioactivenature(WorldHealthOrganization).Broadly categorizedasinfectiouswaste,hazardouschemicalwaste,radioactive waste,andpharmaceuticalwaste.Itiscomposedofnonhazardouswaste (85%)andhazardouswaste(15%)ofwhichinfectiouswasteis10%and chemicalwasteis5%.
AmidtheCOVID-19pandemic,medicalwasteincludesinfected masks,gloves,andprotectiveequipmentgeneratedduetoasuddensurge
inthedemandandmandatoryuseofprotectiveitems.AsperWHO,89 millionmasksand76millionglovesarethemonthlyrequirementstodeal withthisvirus(Shortageofpersonalprotectiveequipmentendangering healthworkersworldwide.,2020).Inadditiontotheinfectedmasksand gloves,theviruscansurviveoncardboard,plastic,andmetalsforhoursto days,endangeringthelivesofwastemanagementworkerswhilecollecting ormanagingsuchwaste(Kampfetal.,2020).Safehandlinganddisposal ofsuchwasteareimportanttoavoidcontaminationofmunicipalsolid wastewiththevirus,soil,andundergroundwatercontaminationwhich couldposeariskoftransmission(Dattaetal.,2018).
1.3ImpactofCOVID-19onwastemanagement
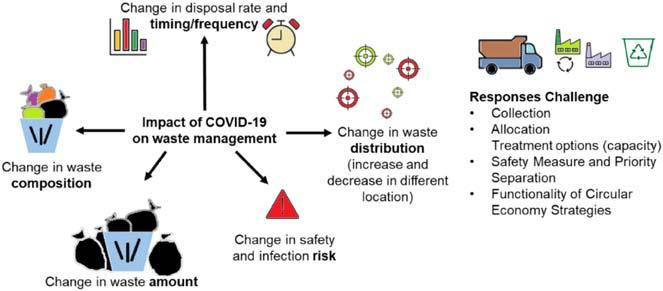
Inthepre-COVIDera,approximately3billionpeopleworldwideare devoidofcontrolledwastecollectionandwastedisposalfacilities(Global WasteManagementOutlook,2015).Additionally,lackoftechnicaland scientificknowledgeisthecontributingfactorworseningwastemanagementinthelowsocioeconomicdevelopingcountries.Inadequatemedical wastemanagementcanbeverydetrimentaltothehumansandecosystem. However,withtheemergenceoftheCOVID-19,thequantity,composition,disposalfrequencyandtiming(temporal),anddistribution(spatial)of wastechanges.TheproblemofBMWandwastewaterdisposalhascaused widespreadpublicconcern(InternationalWater,2020).Thepresenceof SARS-CoV-2insewagewasteindicatesthepotentialriskofwaterborne transmissionofthecoronavirus(Quilliametal.,2020)(Fig.1.1).
Marineplasticpollutionhasincreasedduetotherapiduseand improperdisposaloffacemasks.Approximately0.15milliontonsto0.39 milliontonsofplasticdebriscouldendupinglobaloceanswithinayear. Thedocumentationof “moremasksthanjellyfish” alongtheFrench Mediterraneancoastisanalarmingconcernforriverandmarinepollution. Asasourceofmicroplastic,facemaskscontributenegativeimpactsonthe ecosystemduetothebreakupoftheirconstituentslikepolypropyleneand polyethylene.ThehealthcarewastegenerationduringtheCOVID-19 pandemicisincreasedto3.4kg/person/day.Suchchangeinthewaste dynamicsfortifiestheneedforspecialattentionasevidencedbyBasel, Rotterdam,andStockholmConvention(BRS)wheretreatmentofmedical,household,aswellashazardouswaste,isevaluatedasanessentialpublicserviceduringwithCOVID-19[Wastemanagementanessential publicserviceinthefighttobeatCOVID-19.,2021].Thereforethe
foremostcriteriashouldbeanaccurateassessmentandstatisticalprediction ofCOVID-19wasteflowthroughgovernmentalorpublicagencies. However,multisectorialeffortsincludinglocal,andNGOsarealso requiredtocopewithsuchpandemicchallenges(Liangetal.,2021).
1.4TheuniquechallengewithSARSCoV-2andwaste management
Duringthispandemic,themajorchallengesarecollectingandtreating wasteseffectively.Thequantityofsolidwastehasincreasedwhereasthe recyclingofwastehasreduced(Zambrano-Monserrateetal.,2020). Virus-contaminatedwastesarealsogeneratedbyinfectedpeoplequarantinedathome,thereforemayberesponsibleforthefurtherspreadingof thevirus.
TheSARS-CoV-2remainsviableandinfectiousforupto72hon plasticandmetalsurfacesandformorethan9daysoninanimatesurfaces. EvidencesuggestedsheddingofvirusinthestoolofCOVID-19patients thatcanleadtocontaminationofdrinkingwateralongwithotherenvironmentalimplications.Solidwastewhencontaminatedwithbodyfluids andsecretionsofCOVID-19patientsisconsideredinfectiousand canbedisinfectedwith0.5%hypochlorite,0.5%hydrogenperoxide,and 2%glutaraldehyde.However,thefateofcoronavirusinwastewatertreatmentplantsorthewaterenvironmentisyettobeelucidated(Nghiem etal.,2020).
Figure1.1 ImpactsandchallengesofCOVID-19onwastemanagement(VanFan etal.,2021).
1.4.1Wastemanagementstrategies
Thewastemanagementstrategydependsonthequantity,characteristics, andseasonalvariationsofwastegeneration.Identification,collection,separation,storage,transportation,treatment,anddisposalarethecrucialsteps involvedintheeffectivemanagementofBMW(Fig.1.2).
Storageandcollection:Wastesegregationisveryimportantbeforeproceedingtowastetreatment.Differentcategoriesofwastesarecollectedin separatecolor-codedbagsasinfectiousandnoninfectiouswastesareseparated.Whilecollectingwaste,themanagementstaffshouldbeequipped withproperPPEtoavoidcontactwithcoronavirus(Cohen,2020). Effortsshouldbedonetotransportthewasteasearliestaspossibletothe treatmentsite.
Wastetransport:Thecontaminatedwastematerialshouldbetransported inaproperlybar-codedsealedcontainer.Dedicatedtrolleyscarryingthe infectedwastematerialshouldbedisinfectedwith1%sodiumhypochlorite.Separatevehicleswithtraineddriversshouldbearrangedfortransportationofwastethroughthelesscrowdedornonresidentialarea.The vehiclecontainershouldbeclosedtoavoidanyaccidentortransport glitch(Central,2021).
Wastetreatment:TheCOVID-19wastesareusuallytreatedbychemical methods,autoclaving,andincineration.Highlyinfectiouswastecannotbe
Figure1.2 Schematicrepresentationofdifferentstagesofwastemanagement.