Techniquesin Ophthalmic PlasticSurgery
APersonalTutorial
SECONDEDITION
JeffreyA.Nerad,MD,FACS
CincinnatiEyeInstitute ProfessorofOphthalmology UniversityofCincinnati Cincinnati,Ohio
ELSEVIER
1600JohnF.KennedyBlvd. Ste.1600
Philadelphia,PA19103-2899
TECHNIQUESINOPHTHALMICPLASTICSURGERY
APERSONALTUTORIALISBN:978-0-323-39316-4 SECONDEDITION
Copyright © 2021byElsevierInc.
Allrightsreserved. Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproducedortransmittedinany formorbyanymeans,electronicormechanical,includingphotocopying,recording,orany informationstorageandretrievalsystem,withoutpermissioninwritingfromthepublisher. Detailsonhowtoseekpermission,furtherinformationaboutthePublisher’spermissions policies,andourarrangementswithorganizationssuchastheCopyrightClearanceCenterand theCopyrightLicensingAgencycanbefoundatourwebsite: www.elsevier.com/permissions Thisbookandtheindividualcontributionscontainedinitareprotectedundercopyrightbythe Publisher(otherthanasmaybenotedherein).
Previouseditioncopyrighted2010
Notices
Knowledgeandbestpracticeinthisfieldareconstantlychanging.Asnewresearchand experiencebroadenourunderstanding,changesinresearchmethods,professional practices,ormedicaltreatmentmaybecomenecessary.Practitionersandresearchersmust alwaysrelyontheirownexperienceandknowledgeinevaluatingandusingany information,methods,compounds,orexperimentsdescribedherein.Inusingsuch informationormethodstheyshouldbemindfuloftheirownsafetyandthesafetyofothers, includingpartiesforwhomtheyhaveaprofessionalresponsibility.Withrespecttoany drugorpharmaceuticalproductsidentified,readersareadvisedtocheckthemostcurrent informationprovided(i)onproceduresfeaturedor(ii)bythemanufacturerofeachproduct tobeadministered,toverifytherecommendeddoseorformula,themethodandduration ofadministration,andcontraindications.Itistheresponsibilityofpractitioners,relyingon theirownexperienceandknowledgeoftheirpatients,tomakediagnoses,todetermine dosagesandthebesttreatmentforeachindividualpatient,andtotakeallappropriate safetyprecautions.Tothefullestextentofthelaw,neitherthePublishernortheauthors, contributors,oreditors,assumeanyliabilityforanyinjuryand/ordamagetopersonsor propertyasamatterofproductsliability,negligenceorotherwise,orfromanyuseor operationofanymethods,products,instructions,orideascontainedinthematerial herein. ThePublisher
LibraryofCongressControlNumber: 2020944491
SeniorContentStrategist: KaylaWolfe
SeniorContentDevelopmentSpecialist: RaeRobertson
PublishingServicesManager: CatherineJackson
SeniorProjectManager: JohnCasey
SeniorDesigner: MilesHitchen
Thankyouforyourinterestinthesecondeditionof TechniquesinOculoplasticSurgery APersonalTutorial. This textisforyouifyouwanttolearntheprinciplesandtechniquesofoculoplasticsurgerythatyoucanputintousein yourpracticeeveryday.Althoughthebookiswrittenfrom myperspectiveasanoculoplasticsurgeon,Iamcertainthat mycolleaguesinplasticsurgery,ENT,anddermatologywill findthebookusefulaswell.
ThecontentisupdatedfromtextsthatIwrotein2001 and2010.Thesebookswerewritteninaconversational toneasthoughIwereatyoursidetohelpyouthrougheach stepoftheevaluationandtreatment.Ifollowthesameformatherewithupdatesandnewmaterialwhereappropriate.Mostcommondisordersandproceduresareincluded andsomelesscommonones,too.Mygreatestcompliment fromaformerfelloworresidentisthattheycanhearmy voiceremindingthemoftheimportantstepstodowhile actuallydoingtheoperation.Asyourvirtualpreceptor,I hopethatyouwillfindthisapproachequallyhelpful. Becausethereissomuchinformationpresented,Isuggest thatyoustartbyflippingthroughthechapterstogetfamiliarwiththecontentandthelayout,thenyoucandetermine whereyourinterestsare.
Thebookbeginswithanintroductiontosurgicaltechnique.Beingwellpreparedbeforeenteringtheoperating roomiskeytoyourresultsandefficiency.Youwillfindthat yourpreparednesswillgiveyoutherespectandreadyhelp ofalltheORstaff.Thesecondchapterissurgicalanatomy.I havetriedtokeeptheanatomyverypracticalandhave placedclinicalexamplesthroughout.Thesefirsttwochaptersareimportant bereadytoreadthemmorethan once.Yoursuccessasasurgeonisbasedonyourexpert technicalmanipulationofnormalandabnormalanatomy. Mygoalisthatthesechapterswillstartyouonyourwayto understandandperfectyouroperativetechnique.
Theremainingchaptersaretopicoriented:ectropion, entropion,ptosis,andthelike.Allchaptersbeginwithanoutlineofwhatiscovered,followedbyaformalintroductionto thechaptertopic.Wemovethroughareviewofpertinent anatomy,principlesofevaluationandtreatment,andfinally surgicaltechniqueswithpracticaltips.Thechaptersarewritteninahierarchalfashionthatshouldmakeiteasytogetthe basicsandthendivemoredeeplyintodetailsonasecond read.Eachchapterhasalargeamountofredundancy this isintentional.Lookatthesummaryboxesandusethecheckpointstomakesureyouactuallyrememberwhatyoujust read.Youwillfindover500diagramsandasimilarnumber
ofphotographstohelpyouunderstandandputtheprinciples intopractice.Checkoutthesuggestedreadinglistforanother pointofview.Therearemanygoodtextsout.
Forthesecondedition,therearemanyupdatesandadditions.Thereisanexpandedaestheticsurgerychapter. Manyoftheseproceduresformalargepartofmanyof today'soculoplasticpractices.Youwillgetanewappreciationoftheagingprocessandlearnthebasicsofskincare, resurfacing,peeling,andmanysurgicaltechniques.Ihave includedtheimportantconceptsofaestheticforeheadlifting,midface,andfullfaceandneckrhytidectomy.Thisisan areawhereanexperiencedmentorishelpful.Ihaveadded manyneweyelidlesionexamples,updatesonthereconstructivetechniquesforeyelidrepair,andasectiondevoted totheposteriorapproachtoptosisrepair,amongmany otherchanges.Ihopethatyouwillfindtheseadditions excitingandhelpful.Thevideosectionisgreatlyimproved withalmost100videosdealingwiththeevaluationand managementofthewiderangeofproblemsintheperiocularregionandface.Don’tneglecttolookatthevideosthat introduceyoutothebookandalsoacknowledgeallthose thathavemadecontributionstomylifeandwork.
Forme,learningworksbestina “layered” fashion.Start withthebigpicture.Don’ttrytolearnitallatonce.Read andstudytheprinciples.Readagainandagainasmany timesasittakestogetthedetails.Afteryougainconfidence intheprinciplesandtechniques,startwithsomeeasyprocedures.Someoftheprocedurescangetquitecomplicated. Ideally,youwillhaveamentortohelpputwhatyoulearn intopractice.Don’tforgettocollaboratewithcolleagues outsideyourspecialty.Youwilllearnagooddealandmake somegreatfriendshipsalongtheway.
Thetechniquesdescribedarenotmyownideas,but ratherreflect35yearsofpracticeandlearningfrommyteachers,colleagues,andstudents.Thesearecommon approachestotheproblemsthatyouwillseeinyourpractice.Theconceptsandtheteachingstylearemyownand thetechniquesdescribedworkforme.Ofcourse,thesetechniquesarenottheonlywaystodealwithparticularproblems definitelynottheonlywaysthatwork butthey arewaysthatdoworkforme.Trythetechniquesaswritten. Asyougetcomfortablefeelfreetomodifyanypartofthe operationthatseemstobeanimprovementforyou.Always keepanopenmindtolearning,askquestions,understand whysomethingworks,don’tbeafraidtoimplementnew techniques.Putintheworkandtimetobeasuperlativesurgeon,themasterofunderstandingandtechnique.
Acouplewordsofpersonaladvice.AlthoughIam emphasizingthetechniqueaspectsofourpractice,don’tforgettoenjoyyourpatients,aswellastheworkyoudointhe operatingroom.Itiseasytotakeforgrantedthehuge respectandgratitudethatyourpatientswillshowyou.My adviceistoslowdownabitandletitsoakin.Youwillenjoy yourpracticemore.Youcanbethebesttechnicianever, butwithoutappreciatingthat takingcareofyourpatients meanscaringforyourpatients,youwon ’tbethebestdoctor youcanbe.Don’tmisstheopportunitytofeeltheimportant contributionsthatyoumaketoyourpatients’ lives.Ifeel veryfortunatetohavehadagreatacademiccareeratthe UniversityofIowaandaterrificprivatepracticecareerat theCincinnatiEyeInstitute.Mywishisthatthistexthelps
youinsomewaytoenjoyyourpracticeasmuchasIhave enjoyedmine.
Thanksagainforreadingthis.Ifyouhavecommentsor questions,feelfreetowriteoremailmeattheaddresses below.Youareonyourwaytoasuccessfulandrewarding surgicalpractice.
Jeff JeffreyA.Nerad,MD,FACS
CincinnatiEyeInstitute 1945CEIDrive Cincinnati,OH45242 jnerad@cvphealth.com
Iwouldliketothankthemanypeoplethathelpedmakethis bookpossible.
Thanksgofirsttomyfamily.Myparents,Frankand BlancheNerad,madelearningfunformysiblingsandme. Mydaughters,KristenandElizabeth,andmywife,Jodi, offeredsupportandencouragementthroughoutthewhole process.Thankyouverymuch.
Somanycolleagueshavecontributedtomyeducation.In manycases,Iremembertheexactmomentthataparticular persontaughtmesomethingthatIusetoday.Myformal teachers,RickAnderson,DavidTse,JohnWright,Richard Collins,andDickWelham,weregenerousinshowingme the “ way ” earlyinmycareerandcontinuetobevalued friendsandcolleagues.Manyothershavetaughtme throughoutmycareer.Specialthankstomycolleagues RobertKersten,JackRootman,JeffCarithers,andKeith Carter.Thankstoalltheresidentsandfellowsthathave taughtmesomuchoverthepastthreedecades.Andthanks to “toomanytoname” colleaguesaroundtheworldthat havetaughtmeandbecomelong-timefriends.
Manypeoplehelpedwiththeproductionandtechnical aspectsofthecurrenttextandpasteditions.Specialthanksto someofmyrecentfellows(JillMelicher,RobPeralta,Blake Fausett,andCarolineVargason)andvideographers(Randy VerdickandEricRedder)fortheworkonthenewandoldsurgicalvideos.Thankyoutomyofficeteamformanagingmy dailydutiesandcorrespondence.ThanksgotoSusanGilbert whomadetheillustrationsfortheoriginaltext,andthanksto theartteamsatElsevierforcolorizationsandnewillustrations.ThankstotheeditorialandproductionteamsatElsevier includingKaylaWolfe,RaeRobertson,andJohnCaseyforall thedirectionandhardworkthroughouttheprocessofgetting thiseditiontoyou.Ihaveincludedavideothankingmanyof youwhohavehelpedmethroughmycareeraswell.
Importantly,thankstothoseofyouthatarereadingthis newtext.Iamhappyandgratefultobeadistantpreceptor toyou!Ihopethatthistextwillplayaroleinyourfuture successes.Mybestwishesforalongandfulfillingcareer.
P1 Introductionto TechniquesinOphthalmic PlasticSurgery,2ndedition
1.1 SurgicalInstruments:UsingtheToolsofYour TradeEffectively
1.2 SuturesandSuturingTechnique
2.1 Eyelid,Nasolacrimal,andOrbitalAnatomy
3.1 TheLateralTarsalStripProcedure
3.2 EctropionRepair:LateralTarsalStripand MedialSpindle
3.3 FloppyEyelidSyndrome:PentagonalWedge Resection
3.4 FullThicknessSkinGraftingforCicatricial EctropionRepair
4.1 EntropionRepair,RetractorReinsertion,and LateralTarsalStrip
4.2 SpasticEntropionRepair:QuickertSutures
4.3 TarsalFractureProcedure
4.4 CicatricialEntropionMucousMembraneGraft
5.1 MisdirectedEyelashes:WedgeResectionUpper Eyelid
6.1 UpperBlepharoplasty:ColoradoNeedle
6.2 UpperBlepharoplasty:CO2 Laser
6.3 DirectBrowplasty:TemporalDirectand CompleteDirect
6.4 MidforeheadBrowplasty
7.1 CosmeticBotoxInjection
7.2 FillerInjectionforFacialRejuvenation
7.3 CO2LaserResurfacing
7.4 LowerTranscutaneousBlepharoplasty Technique
7.5 UpperBlepharoplastyandLower TransconjunctivalBlepharoplasty
1 TheArtofSurgicalTechnique
CHAPTEROUTLINE Introduction 1
PreparationfortheOperation 1
FirmPlanwithContingencies 1
SkinMarkingandLocalAnesthesia 2
PreparingandDrapingthePatient 4 Instruments 4
CuttingtheSkin 5
HandPosition 5
ScalpelBlades 6
OtherCuttingTools 6
PlacementofSkinIncisions 7
AnxietyandTremor 7
CuttingTissuewithScissors 8
HowDoScissorsCut? 8
TypesofScissors 8
CuttingwithScissors(YouLearned ThisasaChild) 10
RetractionandExposure 11
FingersasRetractors 11
SkinHooks 12
Forceps 12
DissectionTechnique 13
Retractors 13
Hemostasis 15
PreoperativeConsiderations 15
Tamponade 15
Cautery 15
BoneWax 17
Drugs 17
Drains 17
Suction 17
Suturing 18
TypesofSutureMaterial 18
TypesofNeedles 19
NeedleHolders 20
SuturingTechnique 21
TheSurgicalAssistant 24
MajorPoints 27
SuggestedReading 28
VIDEOS ’ 1.1SurgicalInstruments:UsingtheToolsofYourTradeEffectively ’ 1.2SuturesandSuturingTechnique
VisitExpertConsult(expertconsult.inkling.com)forvideosontopicsdiscussedthroughoutthetext.
Introduction
Welcome!Ihopethatthisbookwilladdtoyoursuccessin theclinicandoperatingroom.Itismypleasureandhonor tomakeanycontributionIcantoyourlearning!Forme, threedecadesofpracticehavebeenmorefunthanwork, andevenafteralltheseyearsIamstilllearningandimprovingmytechnique.Mywishisthatyoudothesame.
Thischapterservesasyourintroductiontosomeofthe theoreticalandpracticaltechnicalaspectsofactuallyperformingsurgery.Asuccessfuloperationstartswithplanningbeforeyouentertheoperatingroom.Tobeeffective, youmusthaveaplanandlettheoperatingroomteam knowwhatitis.Ifyouareprepared,youwillinspirethe teamtofollowyourleadership.Youwillcoordinatethe setupoftheoperatingroomandequipmentnecessaryfor yourprocedure.
Tobeeffective,youneedtoknowthetoolsofthetrade andhowtousethem.Inthischapter,wediscussdifferent typesofinstrumentsandtheirgeneralandspecialuses.We
stresssomefundamentaltechniques,includingholdingand cuttingoftheskin.Wedescribetheimportantinstruments usedinretraction,hemostasis,suctioning,andsuturing.In thelastsection,wetalkabouttheroleoftheassistant,who hasanunderestimatedandimportantjob.
Asyoureadthischapterandtheothers,lookatthebigpicturefirst.Isuggestthatyoureadthechapterthreetimes,going intomoredeptheachtime.Scanthechapterinitiallytogetthe flowofthematerial,andthengobackandperusethecontent casually.Don’tlaboroverthedetailsofeachsection;rather, readthetextseveraltimesasyourabilitiesandinterests increase,eachtimetakinginmoredetail.Ifyouarelikeme, youhavereadatextandcarefullyunderlinedpassagesinit, andthenrealizedthatyoudon’trememberathing!Thereisa lotofinformationhere.Learninghappensinlayersovertime.
PreparationfortheOperation FIRMPLANWITHCONTINGENCIES
Whenyouentertheoperatingroom,youshouldhavea firmplaninmind.Earlyinyourcareer,itishelpfultohavea
setofcontingencyplansifthingsdon’tgoasexpected.As yoursurgicalexpertiseincreases,yourneedtomakeformal contingencyplanswilldisappear.Attheearlystage,orlater whenyouareplanninganewprocedure,itishelpfulto writedownthestepsoftheoperationandlistthenecessary equipmentandthenbringthelisttotheoperatingroom. Thenursingstaffwillappreciateyourpreparationandbe confidentinyourabilities.
Youaretheteamleaderintheoperatingroom.Your behaviorsetsthestageforhowtheoperationgoes.Youset thepaceandthequalityoftheentireeffort.Ifyouareoperatinginanewsetting,besuretointroduceyourselftothe nursingstaff.Discussyourplansforsurgerywiththeteam. Yourpreparationandwillingnesstoincludetheminyour planswillimprovetheoveralleffortandgivetheteamconfidenceinyourabilitytogetthejobdone.Thisapproach appliestoeverysurgeon,fromnewresidentstoexperienced surgeonsinpracticeformanyyears.
RoomSetup
Partofyourplanshouldbetoknowwheretheoperating equipmentisplaced.Generally,thesetupisasshownin Figure1.1 .Inmostcases,thepositionandorientationwill bethesameforeachprocedureinaparticularoperating room.Forexample,usuallytheheadisawayfromthe doorandawayfromtheflowoftrafficintheroom.In somecases,theoperatedeyewillbeplacedawayfromthe anesthesiaequipment.You,asthesurgeon,willsitat theheadofthebed.Yourassistantwillsitatthesideofthe bedcorrespondingtotheoperatedeye.Forsomeprocedures,youmayfinditeasiertositatthepatient ’ sside (e.g.,forlateraltarsalstripandlateralorbitotomyprocedures).Feelfreetomovethroughouttheoperationandbe comfortable.Thenursingtableisplacedonthesideofthe operatingtable,oppositeanyanesthesiaequipmentand staff.
EquipmentSetup
Formostoperations,youwillbeinthesittingposition.If youareplanningtomovearoundthepatientduringthe operation,asinanorbitalfloorexplorationforablowout fracture,youmaywanttostand.Ifso,considerstepstools tomaketheassistantandsurgeonrelativelythesame height.
Onceyouhavedecidedwhethertositorstand,you shouldpositiontheoperatingroomtable.Oftenitishelpful toangletheheadofthetableawayfromtheanesthesia equipment.Remembertoconsiderwheretheoperating roomoverheadlightsarewhenpositioningthetable.Adjust yourchairtoanappropriateheightwithyourfeetflaton theground.Adjustthetableheightsothatyourelbowsare bentslightlymorethan90degrees.Makesurethatthe patient’sheadisatthetopedgeoftheoperatingtableand theplaneofthefaceisparalleltothefloorsoyouwillnot havetoleanoverthepatient.Takethepatient’spillowand placeitunderthepatient’sknees.
Doyourbesttopositionthepatientforthecomfortof boththepatientandyourself.Whenoperatingonchildren,yourviewwillimproveifyouplaceatowelroll underthepatient ’ sshoulderstohyperextendtheneck, bringingthefaceintothesameplaneasthetable.Older
patientswithneckarthritismayrequirearollunderthe headforcomfort.Markedlykyphoticpatientsmayneeda pillowundertheneckandshouldersforcomfort.You mayhavetooperatestandingatthispatient ’ ssidewith theheadofthebedelevated.Insomecases,youcanraise thefootofthebedsothatakyphoticpatientisflatter onthetable. Doyourbesttomaintainreasonableposture. Manyoldersurgeonshavetoalterorstoptheirsurgical practicesbecauseoftheneckachesandbackpainsthat resultfromyearsofpoorbodymechanics.Learntopreserveyourspineandneckfromthebeginningofyoursurgicalcareer!
Ifyouexpectsignificantvenousbleeding,asinnasalsurgery,putthepatientinabouta10%reverseTrendelenburg position(headup,feetdown)beforeadjustingthe tableheight.Oncethetableisatthechosenpositionand height,makesurethatitislockedintoposition.
Ifyouareusinganoperatingmicroscope,thisisthetime tomakeadjustmentstothescopeandyourchair.Thereare severalpossiblepositionsforthescopebase,butthemost commonisofftheshoulderofthepatientoppositetotheeye onwhichyouareoperating.Setthebaseofthescopeto allowforthefullrangeofthemicroscope’sarm.Makegross adjustmentstothemicroscopeheight.Settheinterpupillary distanceofthemicroscopeheadsforthesurgeonandthe assistant.Setthefocusofthemicroscope.Ifyouaredoinga conjunctivalorcanalicularprocedure,setthefocusofthe microscopeinthemiddleoftherange.Ifyouaredoingdeep orbitalsurgery,setthefocusatthetopofthefocustravelso thatyouareabletoadjustthefocuswiththefootpedalto seedeepertissuewithoutrepositioningtheoperatingscope asthedissectioncontinuesintotheorbit.Mostprocedures areperformedwithoutawristrest,butdon’thesitatetouse oneifitincreasesyoursteadiness.Ifyouplantodrapethe scope,swingthemicroscopearmawaywithoutaltering yourmicroscopebasepositionandhavethescrubnurse drapethescopeawayfromtheoperatingfield.Consider usingsterilehandlesorsterilebaggiesoverthehandles ratherthandrapingthewholescopetosavetimeand money.Positionthemicroscopeandcauteryfootpedalsin theappropriatespotunderneaththeheadofthetable.If youdon’tdothis,youmaybesurprisedathowmanytimes youstarttheoperationandreachforthecauterypedalbut findthatitisnotyetreadytouse.Doallthisbeforeyouleave toscrub.
SKINMARKINGANDLOCALANESTHESIA
Manyoculoplasticproceduresrequireskinmarkingasa guidetoincisionplacement.Mostincisionsare placedinnaturalskincreases,suchastheupperlidskincreaseforptosis andblepharoplastyoperations.Otherskinincisionsare placedadjacenttoanatomicstructures sothescarwillbehidden.Youshouldmarktheskinbeforeanylocalanestheticis injected.Twogoodchoicesformarkingeyelidskinareavailable:(1)gentianvioletsolutionand(2)thesurgicalmarkingpen.Gentianvioletcanbeappliedwiththesharpendof abrokenapplicatorusedasaquill.Withexperience, youcandrawafinelinethatdoesnoteasilywashoffwith prepping,butthistakessomeexperiencetokeepfrom makingamess.Usually,weuseathin-tippedsurgical
marker(Blephmarker1424GentianVioletTwinUltra FineTipRulerSterile, Viscot.com ,reference1424SR-100). Besuretodegreasetheskinwithanalcoholwipebefore marking.
Youshouldusealocalanestheticwithepinephrinefor allprocedurestoprovidesomehemostasis(duetothevasoconstriction).Themostcommonlocalanestheticmixture is2%lidocainewith1/100,000epinephrineincombinationwith0.5%bupivacaine.Somesurgeonschoosetoadd hyaluronidasetothemix,butIhavenotfoundthisnecessary.Forlargerscalpandfaceprocedures,youmaywant toconsider “ tumescent ” anesthesia.Withthistechnique,a largeamountofverydilutelocalanestheticwithepinephrineisinjectedintothesubcutaneoustissues.Thistechniquefirmsupthetissuesandmakesiteasiertodevelop flapsandperformliposuction.Thisisnotneededforperiocularprocedures.
Localanestheticsstingbadly(ifyouarenotfeelingsympathetic,haveacolleagueinject1mLoflocalanesthetic
intoyoureyelid;youwillnotsoonforgethowitfeels).Two factorsarethoughttoberesponsible:(1)adifferenceinpH and(2)thedistentionofthetissuesduringrapidinjection. Tominimizethepain,tryinjectingatinyamount about 0.1mL intotwoorthreeplacesandthenmassagethe localanestheticintothetissues.Afterafewseconds,inject moreanesthetic veryslowly. Thisgreatlyminimizesthe pain.Somesurgeonsbufferthelocalanestheticusingone part7.5%sodiumbicarbonateinnineparts2%lidocaine withepinephrine(2mLofbicarbonatein20mLoflidocaine).Ihavenotfoundthisworththetrouble,butmany surgeonsswearbyit.Ifyouoperatewithananesthesiologist,usingappropriatesedatingagents,thepatientistotally unawareofanylocalinjections.
Remembertoinjectjustbeneaththeeyelidskin.Avoid placingtheneedleintothemuscletopreventahematoma, whichmaymakeintraoperativeadjustmentsoftheeyelid difficult;thisisespeciallytruewithanteriorptosiscorrection.Avoidputtingtheneedleinthecreaseatthejunction
Anesthesiologist
Anesthesia equipment
Surgeon
Assistant
Mayo stand
Scrubnurse
Circnurse
"Back" instrument table
Patient
Figure1.1 Typicaloperatingroomsetupforanoperationontherighteye.
ofthelateralonethirdandmedialtwothirdsoftheeyelid. Thereisavesselthat,iftorn,willguaranteeahematoma beforeyoustarttheprocedure!Foranuppereyelidprocedure,suchasablepharoplastyorptosisrepair,youshould inject1to1.5mLoflocalanestheticmix.
ThetopicalsolutionsthatprovideanesthesiaareEMLA creamandBetacainegel.EMLAcreamshouldbeapplied inathickcoating1to2hoursaheadoftheprocedureand coveredwithanocclusivedressing(topicallidocaine2.5% andprilocaine2.5%).BLTcream(20%benzocaine,6% lidocaine,and4%tetracaine)isanalternative.Betacaine gel(topicallidocaine5%, http://www.sanofi.com )canbe appliedfor20to30minutesaheadoftheprocedurewithoutanocclusivedressing.Thesepreparationsprovide someanesthesiabutdonotcausevasoconstriction,soan additionallocalinjectionwithepinephrineisrequiredfor surgicalprocedures.Topicalagentsarealsousefulpriorto Botoxorfillerinjectionsandcanbehelpfulinchildren. Overdosingwithasystemicreactionisunlikelybutpossible.Mostofthetime,Idonotusethesepreparations,but youmightfindthemhelpfulinsomesituations.Youmay beabletoavoidtakingachildtotheoperatingroomfor suturingifyouapplytopicalcreambeforeinjectionofany localanesthesia.
Mosteyelidandlacrimaloperationscanbeperformed underlocalanesthesia.Ifyouchoosetooperatewithout thebenefitofananesthesiologist,youshouldconsider intravenous(IV)sedationtominimizethepatient ’ sanxiety.Dosesofmidazolamin0.5-to1.0-mgincrementsare reasonabletoachievesomerelaxation.Ifindithelpfulto haveamidazolamdriprunning(1to3mg/hour)rather thangiveintermittentdosesofthemedication.Somesurgeonspreferpreoperativeoralsedationwith2to10mg oforaldiazepam.Additionalpainreliefcanbegiven intraoperativelyusingsmalldosesofanarcotic,suchas morphine(1to2mgIV).Intravenousfentanylisuseful becauseofitsshortduration,butkeepinmindthatthisis averypotentopiatenarcoticandahighlyabuseddrug. Surgicalcentersoftendonotpermitthesurgeonto administerthiswithoutanesthesiastaffoversight.Avoid oversedationtothepointthatthepatienthaslostinhibitionsandgetsrestlessoristoosleepytofollowyour instructions.Asupportiveattitudefromyouandthe nursingstaff(sometimescalledtalk-esthesiaorvocal local)ishelpful.Iamalwaysimpressedbyhowmany postoperativepatientscommentonhowhelpfulitwasto havethecirculatingnurseoffertoholdhandsduringthe procedure.Thenursecanalsoalertyouwhenthepatient isfeelingdiscomfort.
Ifyouroperatingsituationallowsfortheefficientuseof monitoredanesthesiacare,youranesthesiologistcanmedicateyourpatienttothepointatwhichthereisnomemory ofanypainfromtheinjectionandoftennomemoryofthe entireoperation.Thedownsideofthisismorestaffingand anincreasedcost.Themajorityofmyeyelidandlacrimal proceduresaredonewithmonitoredanesthesiacareinour practice-ownedambulatorysurgerycenter.Ifyouplanto askforanyintraoperativepatientcooperation,suchaseyelidopeningforaptosisadjustmentoperation,makesure thatnoIVmidazolamisadministereduntilyouhavecompletedtheadjustment.Asyouwouldexpect,workingwith thesameanesthesiaandnursingteamonaregularbasis
increasesyourefficiencygreatlyandcanmakeyourlifein theoperatingroommuchbetter.
PREPARINGANDDRAPINGTHEPATIENT
Inmostoperatingrooms,thepatientcanbepreppedwhile youscrub.Thisgivestimeforthelocalanesthetictotake effect.Atraditionalpovidone-iodinescrubappliedinconcentricringsawayfromtheplannedsurgicalexcisions, repeatedthreetimes,providesadequatecleaningofthe skin.Asurgicalbonnetandadrapewithasinglesticky edge(bardrape)acrosstheforeheadkeepthepatient ’ s hairoutoftheoperatingfield.Ifthehairlineisparticularly loworclosetotheoperatingfield,tapecanbeusedtopull thehairawayfromthefield.Formostproceduresfor whichthepatientisawake,theentirefaceisprepped underlocalanesthesia.Ifthepatientisasleep,prepboth eyeswheneverthereisaneedtoobtainsymmetry betweenthetwosidesorifforcedductiontestingmaybe required.Agoodgeneralruleistoprepalargerareathan youthinkyouwillneed.Mostofmypatientsaredraped withasinglesplitsheet(U-drape)spreadovertheface.It isworthconsideringplacin gatoweloveranyendotrachealtubebeforeplacingtheU-drapesothattheadhesive onthedrapedoesnotsticktothetube(anditisalwaysa goodideanottopullthetubeoutwhentearingthedrapes offthepatient!).
Instruments
Inthenextsectionsofthechapter,wewilldiscussseveral typesofsurgicalinstruments.Theseinstrumentsinclude:
’ Scalpelbladesandothercuttingtools
’ Scissors
’ Forceps
’ Retractors
’ Cauterytools
’ Suctionimplements
’ Needleholders
’ Sutures
Youareundoubtedlyfamiliarwithseveralvariationsof eachoftheseinstruments.IamgoingtoexplaintheinstrumentsthatIhavefoundmostusefulinmypractice.You mayalreadyhaveyourownfavoritetoolsforspecificjobs, oryoumaychoosetousetheinstrumentsthatIhave suggested.
Particularinstrumentsareavailableindifferentlengths andcalibers.Ingeneral,thelengthoftheinstrumentis relatedtothedepthofthesurgicalincisioninwhichthe instrumentisused.Mostoftheeyeinstrumentsareonly 4incheslong.Theseinstrumentsarenotusedindeepincisionsandarerarelyusedforincisionsdeeperthantheeyelid.Thedelicateinstrumentsusedforneurosurgeryare muchlonger,oftenmeasuring12inches.Anexampleisthe curvedYasargilscissorsusedinopticnervesheathfenestration.Theseinstrumentsare9incheslongandhaveafiner tipthanthefamiliarWestcottscissorsusedforeyeandcardiacsurgery.Ideally,foranopticnerveprocedure,Iusea 6-inchinstrument,butnoneiscurrentlyavailableinthis
scissortypesoImakedowiththelongerinstrument.The caliberorstrengthoftheinstrumentvaries,dependingon thetypeoftissuetobemanipulatedorcut.Conceptually, youwanttopickthecorrectinstrumentbasedonlength andcaliber.Wetalkmoreabouttheindividualvariationsof eachoftheseinstrumenttypeslaterinthischapter.
CuttingtheSkin HANDPOSITION
Onceyouareproperlypositionedattheheadofthebedofa patientwhohasbeenpreppedanddraped,yournextjobis tomakeaskinincision.Rememberyouarepositionedwith your feetflatonthegroundandyourelbowsatyoursideinflexionslightlymorethan90degrees.Holdyourhandsinthe functionalposition (likeholdingapencil),withyourhandin slightflexionatthewrist.Thisimprovesyourdexterityand strength.
Therearethreetoolsusedforcuttingtheskin:
’ No.15scalpelblade
’ Microdissectionneedle(Coloradoneedle)
’ CO2 laser
Mostofmycommentsnotonlypertaintothetraditional scalpelbutalsotothecuttingcauteryneedleandCO2 laser. Itisworthlearningthetraditionalsurgicaltechniqueswith thescalpelandscissors.Asyourskillincreases,youwill likelyfindthatusingthemicrodissectionneedleorlaser shortenstheoperatingtime.Althoughsomesurgeonsusea bladeandscissorsthroughoutalloperations,Iuseamicrodissectionneedleformostsurgeries.
Asyouholdthescalpelwiththe pencilgrip,younotice that,onthescalpelhandle,thereisagrooveorflatarea whereyourindexfingerrests.Thescalpelissupported betweenyourthumb,indexfinger,andmiddlefinger (Figure1.2).
Theeyelidskinismobile.Precisioncuttingrequires immobilizationoftheskinwiththehelpofyourfingersor theassistant’sfingers.Letyourringfingerrestonthe
handisinthefunctionalpositioninslightflexion.
patient,stabilizingtheskinorguidingyourhand.Learnto usetheringfingeronyourdominanthandandthethumb andforefingeronyournondominanthandtostabilizethe skin(Figure1.3).Ifthetissueisslippery,usingagauzepad forsometractionwillbehelpful.
Itisbesttostarttheskinincisionwiththetipofthescalpel blade.Asyoumoveacrosstheincision,laythescalpeldown sothatyouarecuttingwiththecurvedpartofano.15 blade.Asthewoundedgesstarttoseparate,observethe depthofthewound.Ideally,youwanttocuttheeyelidskin onlyandnotextendthecutdeepintotheorbicularis.Thisis difficulttodobut,nevertheless,worthwhile.Controllingthe depthofanyeyelidincisioniscritical.Rememberthatthe eyelidisonlyslightlymorethan1mmthickattheskin crease,andyoudonotwanttoextendyourincisionintothe cornea!Youmightfindinitiallythatusingacornealprotectorisausefulsafeguard.Withexperience,youwillprobably finditeasiernottouseacornealprotectorforscalpelcutting orcuttingcauteryincisions,butsurgeonsvaryonthisopinion.Adjustthepressuretomaintaintheproperdepthofthe wound.Asifyouweredrivingacar,lookdowntheroadas youpullthescalpelacrosstheskin.Allofthisishappening asyouoryourassistantholdssteadytensionontheskin. Remember,tightskinismoreeasilyandaccuratelycut thanmoremobileskin.Likemostinstrumentsforeyeand eyelidsurgery,thescalpelisafingertool.Asyoubringyour fingerstowardyourpalmwiththescalpeltip,youmayneed torepositionyourhandandrepeatthecuttingprocessin lengthsofthewound(Figure1.4).Asyougetmoreexperienced,youwillbeabletoflexyourfingersandmoveyour handatthesametime.
Thisisagoodtimetoremindyouabouthavinga good bodyposition.Youshouldfeelrelaxedandateaseasyoucut.
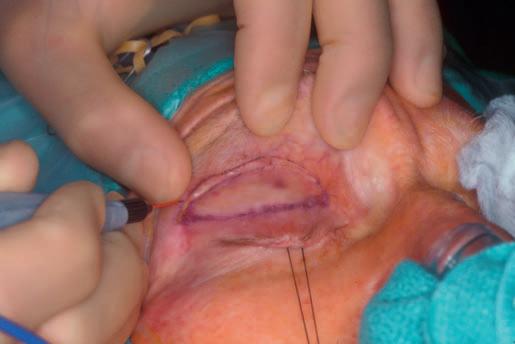
Figure1.3 Skinstabilization.Duringuppereyelidblepharoplasty,the skinfoldisstabilizedandstretchedwiththesurgeon’sfingerswhile theuppereyelidisdrawndownwardusingalidmargintraction suture.NotethataColoradomicrodissectionneedle isbeingused fortheincision.Withexperience,thetractionsuturecanbe eliminatedandthesurgeoncanusefingerstostretchtheskintightly. ( Theoriginalmicropointelectrocauteryneedlewascalledthe Coloradoneedle.Otherbrandsoftruemicrodissectionneedlesare nowavailable.Inthistext,thetermsColoradoneedleand microdissectionneedleareusedsynonymously.However,thisfine tungstenmicrotippedneedleshouldnotbeconfusedwiththeolder needlepointmonopolarcauterytoolavailableinmanyoperating rooms.)
Figure1.2 Holdingthescalpelwiththepencilgrip.Notethatthe
Makesureyourelbowsremainclosetoyoursiderather thanuphigh;havingthemuphighconvertsthescalpelto anarmtoolratherthanafingertool.Youwillbemaking manyincisionsinyourlife,solearntocutawayfromimportantstructuressuchasyourfingersandtheeye.Familiarize yourselfwiththeseveraltypesofscalpelbladesavailable.
SCALPELBLADES
’ No.11blade:Thisbladehasasharppointthatisgood fortightanglesandcurves.Itisagood “stabbing” knife fordraininganabscessorachalazion.Itisnotuseful forlongerincisions.
’ No.15blade:Thisisthebestall-purposescalpelblade foreyelidandfacialskin;99%ofyoureyelidsurgery withascalpelwillbedoneusingano.15blade.
’ No.10blade:Theno.10bladeisshapedlikeano.15 bladeexceptitisbigger.Thisbladeisusedprimarilyfor thickerskinincisions.Itisnotusedforperiorbital incisionsbutcanbehelpfulinfacialflaps.
’ Beaverblades(www.bvimedical.com):Theno.66 Beaverblade(376600)isaspecial-purposeright-angled blade.Itsprimaryuseisformakingcutsintightspaces. Itisespeciallyusefulfornasalmucosalincisionsin dacryocystorhinostomyprocedures.Angledkeratomes designedforanteriorsegmentsurgeryworkinasimilar fashion(Figure1.5).Otherusefulbladesaretheno.64 blade(376400roundedtip,sharpononeside)andthe no.76blade(376700,aminino.15blade),bothof whichareusefulforthedelicateshavingoftissueoff thescleraorcornea.Theneedleblade375910isgood whenyouneedtomakeamicroincision.Beaver handlescomeinavarietyoflengths,themostcommon being10cm.Longer-lengthhandles(13and15.5cm) areusefulfordeeporbitotomiesorcraniotomies.
OTHERCUTTINGTOOLS
Twootherusefulcuttingtoolsareavailableforeyelidsurgery:themicrodissectionneedleandtheCO2 laser.The microdissectionneedlehasbeenmychoiceformostperiocularsurgicalproceduresinrecentyears.Thisunipolarcauterydevicedoesanexcellentjobofcuttingandcauterizing thethineyelidtissues.Theneedleismadeoftungstenand hasanextremelyfinetip.Tissueincontactwiththetipis vaporized.Gettingusedtothisinstrumenttakessomepractice.Cuttingthetissueshouldbedonewithsuperficiallight passingoverthetissueina “painting” motionandtheneedleslightlyangledasifyouareusingapaintbrush.Ifyou
findthatcarbonisbuildinguponthetipoftheinstrument, youaremovingtoofast,cuttingtoodeep,orhavethepower turneduptoohigh.Thetrickofusingthistooliscutting onlyattheverytipsothatthereislittlethermaldamageto thesurroundingtissues.Youlearnthat “pulling” thelayers oftissueapartis essential forthistoolandgivesaveryclean dissectionwithlittlecollateraldamagetotheadjacenttissues.Usinga “blend” modesettingonthecauterymachine providescuttingandcautery.Trythisforthedissectionof anuppereyelidblepharoplastyskinmuscleflap.Onceyou getusedtothis “bloodless” field,youwillhavetroublegoing backtoscissors.Youshoulduseasmokeevacuatortoeliminatethehazardoussmokeproducedbythistool.Thepatient requiresgrounding,aswiththeuseofanyunipolarcautery equipment.Theuseofthisunipolarcuttingtoolissometimeslimitedtotissuesanteriortotheorbitalseptum, becausetheelectriccurrentiscarriedintotheorbitand causespainformanypatientsunderlocalanesthesia.The tipworksonthedryeyelidskinbutworksbestontissues deeptotheskin.Forthisreason,somesurgeonspreferusing abladefortheinitialskinincisionbecausetheedgesofthe woundarecleaner.Theyswitchtotheneedleforanydeeper work.YoumayfindtheColoradoneedlewithafootpedal useful,butIpreferthehandswitchonthecauteryhandle itself.Severalcompaniesmakeamicrodissectionneedle (e.g.,StrykermakestheColoradomicrodissectionneedle, www.stryker.com,andMedtronicmakestheValleylab tungstenmicrosurgicalneedleE1650, www.medtronic. com).Theshortest-lengthneedleistheeasiesttoworkwith onperioculartissues.Thequalityandpricevaryfrommanufacturertomanufacturer.
TheCO2 laserisalsoausefultoolforcuttingeyelidskin. Likethemicrodissectionneedle,tissuesarevaporized,with excellentcauteryofcapillariesandsmallveins.The UltraPulseCO2 laserwasintroducedyearsagoandremains aworkhorseinmypractice.Thecurrentmodelisthe UltraPulseEncoremadebyLumenis(www.lumenis.com). Theselasersremainthegoldstandardforlaserincisional andresurfacingwork.Aswhenusingamicrodissection needle,largevesselsareoftencutwiththelaserratherthan cauterized,soyouneedabipolarcauterytoolontheoperatingroomtable,aswell.Bothofthesecuttingandcauterizingtoolscanshortenoperatingtimesconsiderably.Ifyou haveaCO2 laseravailable,youshouldtryitasacutting tool.Youmustemphasizethepullingapartofthetissues withyourforceps,eventoagreaterdegreethanwitha microdissectionneedle.Thereisnotouchorfeelinvolvedin thecutting.Itisallvisual,sotechniqueisveryimportant. Onceyoulearnit,youloveit.Patientshavelessdiscomfort withtheCO2 laserthanwiththeColoradomicrodissection
Figure1.4 Flexionofthefingerswiththescalpelbladefollowedbymovementofthehand.
Figure1.5 Surgicalcuttinginstruments.(A)Coloradomicrodissection needles.Blueneedleisshorter(preferred);redneedleislonger.(B) Beaverblades376400,376600,376700,375910.(C)(Topdown) scalpelbladesno.15,no.11,andno.10.
needle.Someprecautionsarenecessary.Youneedsandblastedinstrumentstopreventreflectionofthelaserenergy. Metalcornealshieldsareamust.Surgeonsandstaffmust wearprotectivegoggles.Smokeevacuationisnecessary. Carewithoxygenandtheuseofwetdrapesareimportant topreventfire.Mostproceduresinthistextusethemicrodissectionneedle,butIsuggestyoutrythelaser,especiallyfor upperblepharoplasty.Theskillsthatyoulearnusingthe microdissectionneedleandthelaserarecomplementary; learningtouseonehelpsyouwiththeother.
PLACEMENTOFSKININCISIONS
Mostskinincisionsarehiddeninnaturalcreasesorwrinkle lines(Figure1.6).The upperlidskincrease isanaturalplace tomakeincisionsintheupperlid.Theupperlidskincrease isoftencarriedlaterallyintoalaughline.Ifyouarenot familiarwiththewrinklelinesofacertainarea,askthe
patienttocontractthefacialmusclesinthatarea.Seeing thewrinklesandfoldsintheskinshowsyouwheretoplace yourincisions.Youcananticipatetheselines.Thenatural skincreasesoccurperpendiculartothedirectionofthemusclefiberscausingthecreases.Bycontractingyourfrontalis muscleyouareabletoseethefurrowsoftheforeheadperpendiculartothefrontalismusclefibers.
Otherskinincisionscanbecamouflagedbyplacingthem nearanatomicstructuressuchastheeyelashesoreyebrow. Adultsgenerallyhavenolowerlidskincrease.Skinincisionsinthelowerlidareusuallyplaced 2to3mminferiorto thelowerlidlashes (subciliaryincision).Thisincisioncan alsobecarriedlaterallyintoalaughline.Similarly,aneyebrowincisioncanbehiddenbyplacingit adjacenttothe upperorlowermarginoftheeyebrowhairs.Incisionscanbe placedwithinthebrowitselfbutcancausepermanentvisiblescarringasaresultofthelossofciliaroots.Otherexamplesofcamouflagingscarsnearfacialstructuresinclude pretrichialhairlineincisions,preauricularskinincisions, andincisionsalongthealaeofthenose.Older-styleincisions suchastheStallard-Wrightlateralorbitotomyincisionand theLynchincisionhavebeenlargelyreplacedbyincisions thatleaveabetterscar.
ANXIETYANDTREMOR
Everysurgeonhasatremortosomedegreeoranother.This tremorisworsewhenyouareanxious,aretired,orhave drunktoomuchcoffee.Ifyoufindthatyourtremorisbothersome,trytoeliminatethesefactors.Ioccasionallyhearof aresidentwhotakesabeta-blockerbeforeperformingan operation.Thiscanserveasaconfidenceboosterbutis likelynotnecessaryonceyoulearntorelaxduringsurgery, althoughIdoknowexperiencedsurgeonsthatfeeltheir handsbecome “silkier” whentheyhavetakenabetablocker.Abigpartofbeinganxiouswhenlearningsurgery isthefeelingthatyouwilllookbadtoyourteacherorothers observing.Consequently,yougetmorenervousandyour tremorincreases.Don’tforget,everyoneintheoperating roomisonyourside,doingeverythingtheycantohelpyou doyourbestforyourpatient.Ifyouarefeelingalittleshaky, youmightwanttoexplaintoyourmentorthatyouarenervous.Usually,thisconfessionwillbringsomedeserved empathy,andyourtremorwillsettledownabit.Takeafew deepbreaths.Makesurethatyourchairandthe tableheightareappropriate.Trytorelaxyourforearmsand loosenyourgripontheinstruments.Ifthisdoesnotwork, considerawristrest. Ihaveyettoseeastudentwhohada tremorthatkepthimorherfrombeingasuccessfulsurgeon.
CHECKPOINT
• Remembertohaveaplanwhenyouenterthe operatingroom.Letthestaffknowwhattheplanis. Knowhowtheroomissetup.Knowtheinstruments. Yourpreparednessinspiresconfidenceandsetsthepace fortheoperation.
• Youmusthaveaplanfortheoperationandsome contingenciesifthingsdon’tgoasplanned.Youwould besurprisedhowmanyresidentscometotheoperating roomexpectingtobe “shown” whattodo.Asa resident,themoreyoupreparebeforeenteringthe
B
Figure1.6 Facialincisionsaretypicallyhiddeninnaturalskincreasesorplacednexttoanatomicstructuresforcamouflage. A,Upperlidcrease incisionextendedintolateralcanthallaughlineforlateralorbitotomy. B,TraditionalStallard Wrightlateralorbitotomyincision(rarelyused). C, ModifiedBerkelateralcanthotomyincision. D,Transcaruncularincision. E,Frontoethmoidal(Lynch)incision(rarelyused). F,Upperlidcreaseincision. G,Verticallidsplitincision. H,Subciliaryincision. I,Transconjunctivalincisionformedialorbitotomy. J,Inferiortransconjunctivalincision. K,Gingival upperbuccalincision. L,Foreheadfurrowincision. M,Suprabrowincision. N,Pretrichialincision. O,Transcoronalforeheadincision. P,Endoscopic browplastyincisions.
operatingroom,themoreyouwillgettodoandthe fasteryouwilllearn.
• Getthepatient,operatingtable,yourstool,andyour bodyinacomfortablepositionbeforestarting.Haveall theequipmentpreparedbeforeyoumakeaskin incision.
• Whyshouldyoumarktheskinandinjectthelocal anestheticbeforescrubbing?
• Doyouneedtowritedownthenamesofthespecial instruments,sutures,orequipmentyouwillbeusing?
• Lettheoperatingroomnursesknowwhatyouare planning,especiallyifyouanticipateanychangefrom theroutine.
• Practicestabilizingandcuttingtheskinonpiecesof chickenathome.Itisnottheperfectmodel,butitcan behelpful.Practiceeverythingyoucanathome, includingcutting,suturing,andtying.Operatingroom timeisveryvaluable.
• Learntobecomfortableandrelaxedintheoperating room.Asasurgeon,itisyourhomeandworkplacefor abigpartofyourcareer.
CuttingTissuewithScissors
HOWDOSCISSORSCUT?
Scissorscutbythe shearingaction ofthebladescrossingso closetogetherthattissuebetweenthebladesisseparatedin acontrolledfashion.Themajorityofskinincisions,especiallyonthickerskin,shouldnotbemadewithscissors, becauseofthiscrushingactionofthescissorsblades.Some surgeonsdo,however,usescissorstocutthethinskinofthe eyelid.Mostsurgeonsreservescissorsforthedissectionof deepertissueplanes.
TYPESOFSCISSORS
IntheStorzinstrumentcatalog(storzeye.com,nowapartof BauschandLomb),therearemorethan50pagesshowing over200typesofscissors.ForaviewofENTandplasticsurgeryinstrumentscheckout www.bauschinstruments.com Ihopethatafterreadingthenextseveralparagraphsyou canmakeasensiblechoiceinselectingtherightscissorsfor
thesurgicalstepyouaredoing.Scissorsvaryinthefollowingcharacteristics:
’ Length
’ Caliber
’ Tipsharpness
’ Bladedesign
’ Cuttingmotion
Let’slookateachofthesecharacteristicsbriefly.
ScissorsLength
Choosescissorsoftheproperlengthforthedepthofthe woundinwhichyouareworking.Mostoftheinstruments ontheeyetrayare4incheslong.Thissizegoeswiththe scaleanddepthoftheusualocularprocedures.Longer instrumentswouldbeless steadyandbumpintothe microscope.Youwillusemany4-inchinstrumentsin oculoplasticsurgery.Plasticsurgeryinstrumentsareusually6incheslongandfitthenormalhandsizebetter,for instance,aMetzenbaumscissors.Inmostcases,thelonger neurosurgicalinstrumentsarenotuseful.Fororbitsurgery,onoccasion,youmayusealongerneurosurgical scissorsfortheparticulartipratherthanthelength (Yasargilscissors).
ScissorsCaliber
Ingeneral,thickerscissorsbladesareusedfortoughertissues.Thisisfairlyintuitive.Youwouldnotuseadelicate Westcottscissorstocutthroughthethickdermisofthe cheek.Similarly,youwouldnotusethetoughMayoscissors tocuteyelidskin.Rememberitisthebladetipsize,not thelengthoftheinstrument,thatyoushouldconsiderfor thedelicacyofthetissueyouwanttocut.Manylongerdelicateinstrumentsarealsoavailable.
ScissorsTips
Thetipofapairofscissorsmaybebluntorsharp.Blunttippedscissorsareusuallyusedfordissectionintissue planes.Sharpscissorsareusedtocutthroughtoughtissuessuchasscartissue.Asharp-tippedWestcottscissors worksbetterthanablunt-tipp edWestcottscissorstoopen aneyelidcyst.Faceliftscissorshaveslightlysharpened roundedtipstofacilitateflapdissectioninthesubcutaneousplane.
ScissorsBladeDesign
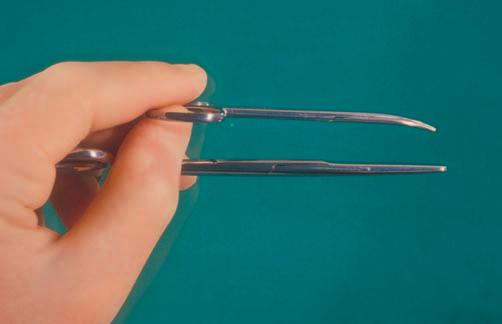
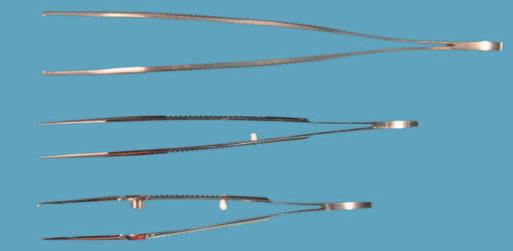
Scissorsbladesare straight or curved ( Figure1.7 ).Most straightscissorsareusedfor cuttingsuturesandbandages andaresometimescalledsuturescissors.Itiseasiertocut astraightlinewithstraightscissorsthanwithcurvedscissors,andviceversa.Remembertousethecurveofthe scissorsbladetoyouradvantage(thecurveofthescissors shouldfollowthecurveoftheeyelidcrease,forexample). Curvedscissorsareusefulfortissuedissections.The curvedangleofthebladeliftsthetissueplanesapartasthe tipcutsthereflectedtissue,whichisplacedonstretch. Thecurveofascissorsbladeiseasytopalpatethroughtissues.Youwilllearntoprotecttissuesagainsttheconvex surfaceofthecurve.AnexampleofthistechniqueisseparatingthelevatoraponeurosismusclefromtheunderlyingMüller ’ smuscle.Asthetwolayersare pulledapart ,fine
Figure1.7 BladesofthestraightMayoscissorscomparedwiththose ofthecurvedStevenstenotomyscissors.Noticethatthelengthand caliberofthescissorsarealsodifferent.
Figure1.8 DissectionoflevatoraponeurosisfromMüller’smuscle usingcurvedWestcottscissors.Notehowpullingthetissuesapart createsbandsoftissuethatareeasytoseeandcut.Theconvexside ofthescissorsbladesshouldbeagainstthetissuethatisthe strongest,inthiscase,theaponeurosis.
tissuebandsareseenstretchingbetweenthetissueplanes (learningto “ pull ” thelayersapartisthemostimportant surgicaltechnicaltipIcangiveyou;moreonthislater). Theconvexsurfaceofthescissorscanslideupthefibrous bandsandrestagainsttheaponeurosis.Cuttingcanbe performedwithoutbuttonholingtheaponeurosis ( Figure1.8 ).Thistechniqueisusefulforseparatingany tissueplanes.Anothergoodexampleisseparating Müller ’ smusclefromtheconjunctiva.
ScissorsCuttingMotion
Scissorsarecomposedofopposingbladesheldtogetherbya centralpin.Mostscissorscloseandopenwithoppositehand motions,stabilizedbyoneormorefingersintheringholes (oftencalledringscissors).Youcancontroltheforcewhen openingtheblades,aswellastheforcewhenclosingthe
blades,withyourhands.Thisallowsyoutousethescissorstipsasadissectingtoolasyouspreadopenthetissue planesbyopeningthescissors. Springscissors openwith therecoilofaspringmechanisminthehandleofthescissors.Westcottscissorsareanexampleofthistype.These scissorsaregenerallyusedforfinetissueswhereminimal handmotionisimportant(fingertools).Thespring actiondeterminestheforceoftheopeningoftheblades. Stevenstenotomyscissorsar eringscissorswithslender curvedblades;theyarecommon4-inchscissorsusedfrequentlyinophthalmicprocedures(see Figure1.7 ).Iris scissorsareatypeofdelicate,sharp-tippedringscissors designedwithshortbladesthatareeithercurvedor straight.Althoughtheusageistechnicallyincorrect,the term irisscissors hasalmostbecomegenericandhasbeen appliedtoanypairofstraightscissorsusedassuturecuttingscissors.
Westcottscissorscanbeusedasaspreadingtooluseful forseparatingdelicatelayers,forexample,separatingthe conjunctivafromTenon’scapsule,orbitalseptumfromorbicularismuscle,Müller’smusclefromlevatoraponeurosis, conjunctivafromlowereyelidretractors,oranyadjacent delicatetissuesfromeachother.Rememberthatdissection ismoreaboutpullinglayersapartandusingtheconvexside ofthebladestoteasethetissuesawayfromeachotherthan itisaboutcuttingthetissues.
Scissorscutbyashearingaction.Mostringscissorsare designedasright-handedcuttingtools.Imagineholdinga pairofscissorsinyourhand.Pushyourthumbawayfrom thepalmandpullyourfingerstowardyourpalm.This actionsqueezesthebladesofthescissorsmoretightly together,increasingthecu ttingpower.Youmayrecall doingthisasachildplayingwithdullscissors.Youquickly learnthatsqueezingthebladestogetherincreasesthecuttingpower.Trydoingthiswithyourlefthand;there ismuchlessshearingaction.Thisiswhyleft-handed children(andtechsandsurgeons,aswell)sometimes havetroublecuttingwithright-handedscissors.Try squeezingthebladestogetherthenexttimeyouuseapair ofscissors.Comparecuttingsuturesortissueswithyour lefthandinsteadofyourrighthand;youwillappreciate thedifference.
CUTTINGWITHSCISSORS(YOULEARNEDTHISASA CHILD)
Springscissors,orWestcottscissors,areheldasfingertools, likeapencil.Aswithanyscissors,youshouldgentlysqueeze thebladestogetherinacontinuousaction.Asthescissors cut, watchthetissueseparate Avoidclickingorsnippingthe scissorsclosedinonequickmotion (closethescissorslikeyou mayhavebeentaughttoslowlysqueezethetriggerofagun oracamerashutterreleasebutton).Quickmotionsdonot allowyoutoevaluatethedepthorlengthofthescissors’ cut asyouproceed.Observinghowthetissuesspreadapartas youcutthemistheverybestwaytostayinthecorrectsurgicalplane.
Ifyouwatchless-skilledsurgeonsornursescutyour suturesyouseethattheyoftensnipawayatthem.Thistype ofcuttingistooinaccuratefortissues.
Asyouproceedwithcuttingtissue,donotclosethe bladescompletelytothetips.Youloseyourplaceinthe
Figure1.9 Holdingscissors. Left,Ringscissors(afinger-and-hand tool). Right,Westcottscissors,themostcommonspringscissorsused ineyelidsurgery(afingertool).
woundifyouclosethescissors.Again,rememberwhenyou firstlearnedtousescissorsasachild.Initially,everytime youcutapieceofpaper,youwouldclosethescissorsblades completely.Itwasdifficulttomakeastraight,continuous smoothline.Youhadtostartovereachtimeyoucut.As youlearnedtousethescissorsbetter,youfoundthatyou couldmoreeffectivelycutacontinuouslinebyclosingthe scissorshalfwaytotwothirdsofthewayandthenadvancingthebladesforward.Thisisthesametechniquethatyou shoulduseincuttingtissue. Asthebladescutapproximately halfwayclosed,pushthebladeforwardinthesameplaneandcut again.Donotcutwiththefullclosureofthebladeuntilthe endoftheincision.
Rememberwhencuttingwithcurvedscissorstoposition thecurveofthescissorsalongthecurveoftheincision. Manyoftheincisionsthatyoumake,suchastheskincrease incision,arecurved.
Whenusingaringscissors,restyourmiddlefingerinone ringandyourthumbin,oron,theotherring .Usethisgrip withtheindexfingerprovidingthree-pointfixationofthe scissors( Figure1.9 ).Theselargerscissorsareusefulasa finger-and-handtool.Youwillfindacomfortablethumb andfingerposition,oftennottotallywithinthering.The samecuttingmotionthatisdescribedaboveshouldbe usedwiththistypeofscissors.Youmightwanttopractice thistechniqueonapieceofpapertomakesurethatyou havetheidea.Youmaybeusingscissorsinmorethanone wayalready.Dr.Edgerton ’ sbooknicelydescribesthe functionofscissors.Scissorscanbeusedforcutting suturesandtissue,functioningasshearingcutters. Scissorscanbeusedtospreadopenplanesaspushcutters ( Figure1.10 ).Planesmaybedissectedusinglateral sweepsorpullwedges.Smallvesselsmaybesqueezed closedwiththeshearingactionofscissors.Palpationof thecurvedbladeofscissorscanbeusedtohelpguidea deeptissuedissection.
CHECKPOINT
• Comparetwotypesofscissorsthatyoumaybefamiliar with:straightMayoscissorsandStevenstenotomyscissors (see Figure1.7).Mayoscissorscomeinmanyvariations,
Figure1.10 Usesofscissors.(A)Shearingcutters.ThenormalcuttingactionofthescissorsisshownwithWestcottscissorstrimmingredundantskin andmuscleoffalowerblepharoplastyflap.(B)Pushcutters.Thebladesareopenhalfway(top),andthetissueiscutbypushingthescissorsagainst thetissue(bottom).AgoodexampleisthedissectingofMüller’smuscleoffthelevatormuscleasshownin Figure1.8.(C)Lateralsweepsorpull wedges.Thebladesareinsertedclosedandopenedinthewoundorastheyarepulledout.Theactioniswiththeoutsideofthescissorblade(dull side).Thiscanbeusedtocreateadissectionplane,forexample,betweentheorbicularismuscleandtheorbitalseptum.Scissorsaretypicallyused inthisfashiontoopenanabscesspocket.
solookatthescissorspictured.Thisvariationisalmost 7incheslongandhasthickstraightbladeswithfairly pointedtips.TheStevensscissorsarejustover4inches longandhavethinnercurvedbladeswithblunttips. Whichscissorswouldbebestforcuttingsuturesina deepabdominalwound?TheMayoscissors,ofcourse. Thestraight,thick,pointedbladesarenotwellsuitedfor tissueplanedissection.Theshorter,curved,blunt-tipped bladesoftheStevensscissorsareideallysuitedforthe tissueplanedissectionoftherelativelysuperficiallayers oftheeyelid.
• Thinkofwhichlayersoftheeyeoreyelidwouldbe appropriateforWestcottscissors.Wouldyouchoose sharporbluntWestcottscissorsforaconjunctival peritomy?Thesoftconjunctivalandepiscleraltissues wouldtearifsharp-tippedscissorswereused.
• Remindyourselfhowtocuttissueusingaplainpieceof paper.Drawastraightandacurvedline.Trycuttingthe linein “snips.” Nowtrycuttingthelinewithsmooth
continuousstrokes,notclosingthebladescompletely. Whichiseasier,moreaccurate,andfaster?Cutthe straightlinewithacurvedscissors.Cutthecurvedline withthecurvedscissorsusingthecurveoftheblades with thecurveoftheline.Nowcutthecurvedlinewith thescissorsbladesturned against thecurve.Youshould begettingtheideathatlearninghowtouseyourtools correctlyproducesabetterandfasterresult.
RetractionandExposure
FINGERSASRETRACTORS
Oneofthemajordifferencesbetweenlearningocularsurgeryandoculoplasticsurgeryislearninghowtomanipulateandretracttissues.Mostoftheretractiondonein
ocularsurgeryisdonewithalidspeculum.Youwilllearn touseavarietyoftoolstoholdthetissues.Youarealready familiarwiththebestandgentlestretractorofall, yourfingers .Allofthefingersonyournondominanthandcanbe usedtosupportorstretchthetissues.Asyouareworking, youcanholdacuttingtoolinyourdominanthandwith yourthumbandfirstandsecondfingersand,atthesame time,usetheringandsmallfingersasretractors(visualize holdingabladewiththepencilgripandstretchingthetissueswithyourotherfingers,andthentrytodothis).A fingercoveredwithagauzespongehelpstostabilizeslipperytissues.
SKINHOOKS
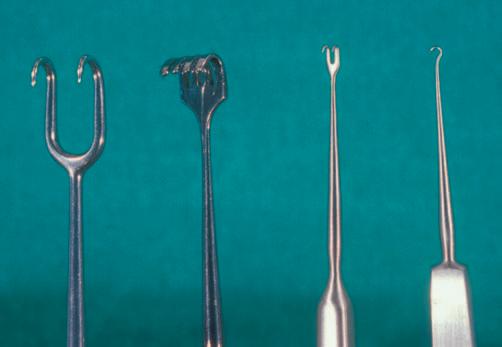
Youmaynotbefamiliarwiththeuseofa skinhook .Thisis oneoftheoldestsurgicalinstrumentsand,whenusedcorrectly,oneofthe gentlestretractors .Skinhooksareavailableindifferentsizesandwithvaryingnumbersofprongs. Themostusefulskinhookforeyelidsurgeryisthe Storz doublefixationhook ,asmalldouble-prongedhook(Storz E0533; Figure1.11 ).Therearealso smallsingle-pronged hooks thatcanbeusedforverydelicatetissues(Tyrelliris hook,StorzE0548)and rake-typeskinhooks withmultiple prongsthatareusedforlacrimalsurgery(Knapplacrimal sacretractor,StorzE4538).A largedouble-prongedskin hook ,knownastheJosephdoublehook(StorzN4730),is usefulforretractionoflargetissueflaps.TheSennretractor(StorzN3553)haslargehooksononeendandarightanglednarrowbladeretractorontheotherend.Thisisa goodall-purpose,softtissueretractorforfacialprocedures.Obviously,youmustbequitecarefulnottopullthe hooktowardtheeyewhereinadvertentpunctureofthe globecouldoccur.
FORCEPS
Themostcommontypeofinstrumentforholdingtissueisa forceps.Allforcepsworkthesame,usingapinchingaction ofthefingerstograsptissue.Forcepsdifferinlength,caliber, andtip.Lengthandcaliberdifferforthesamereasonsasall instrumentsingeneral.Thetipsofforcepscaneitherbe smooth orhave teeth
Smoothforcepsgenerallycausemoretraumathanforcepswithteeth.Becausethereislowfrictiononthetipof smoothforceps,morepressureisrequiredtoholdtissue. Consequently,thetissuetendstobe crushed.Smoothforceps (Figure1.12)areusedmainlyfortyingsutures.Onoccasion forcepswithoutteethmaybeusedondelicatetissuesifconcernexistsabouttearingthetissueusingforcepswithteeth. Variationsofsmoothforcepsincludediamonddustingand smallserrationsontheinnersurfaceoftheblades.These variationsincreasethefrictionoftheforcepsandreducethe pressurerequiredtograspthetissue.
Jeweler-typeforcepsarethesmoothpointedforceps thatyouareprobablyalreadyusingtoremovedelicate sutures(StorzE19471).Jewelerforcepsdonotgrasp tissuewell.
Forcepswithteethofferabettergripwith lesscrushingof tissue.Youshoulduseforcepswithteethwheneverpossible. Severaltypesofforcepswithteethareavailable.Themost commonformhastwoteethononebladeopposingasingle
Figure1.11 Skinhooks(lefttoright):Largedouble-pronged(Joseph) skinhook,lacrimalrake,smalldouble-prongedskinhook,small single-prongedhook(Tyrell).
Figure1.12 Forceps.(A) Fromtopdown:Adsonforceps(largeforceps withteeth,forcheekandscalp),forcepswithoutteeth(smooth),and Paufiqueforcepswithteeth(themostcommonforcepsthatyouwill use).(B)Forcepstips. Lefttoright:Adsonforceps,smoothforceps, andPaufiqueforceps.
toothontheotherblade.Ingeneral,forcepswithmultiple smallteetharemoredelicatethanforcepswithfewerand largerteeth.Asyougraspthetissuewithforcepsyoushould usegentlepressuretoclosethetips.Theteethshouldnot leavemarksinthetissue.
Asyougetmoreadeptatusingsurgicalinstruments, youmayusethesingletoothofatoothedforcepsasaskin hooktoliftandsometimesunrollaskinedge.Thisbladeis knownasa liftingjaw.Whengraspingtissue,selectthe layeroftissuethatistheleastsusceptibletoinjury.Itis bettertograspthedermisorsubcutaneousfatthanthe skinedgedirectly.
A
B
Figure1.13 Thesurgeonandassistantworktogethertopullthe tissuesapart.Noticethatthebandsoftissuestretchedbetweenthe orbicularismuscleandtheorbitalseptumareeasytocut.
ThePaufiqueforcepsaregreatformostperiocularwork. Theyhavesmallteeththatgraspdelicatetissues,butthe bladesandgriparestoutenoughtoworkwithheaviertissues.ManhattanforcepsaresimilartoPaufiqueforceps; theyhavethesamebladesbutsmoothgripsonthehandle. Youshouldbefamiliarwithlighterandheavierforcepswith teeth.UsefulmoredelicateforcepsincludetheCastroviejo suturingforceps,morefamiliarlyknownaspoint1 2,point 3,orpoint5forceps,referringtothecaliberoftheteeth (CastroviejosuturingforcepsE1796,E1797,andE1798, respectively).Theseforcepshaveatyingplatformproximal totheteethsothesuturewillnotslipwithtying.Heavier forcepsusefulinthecheek,scalp,andlowerfaceinclude AdsonandBrown Adsonforceps(StorzN5405and N5420).
ItisworthwhiletopagethroughtheBauschandLomb StorzophthalmicandENT/plasticsurgerycatalogs(www. bauschinstruments.com).Youwillbeamazedatthevariety ofinstrumentsavailable.
DISSECTIONTECHNIQUE
Mostsurgeryisnotcuttingbutratherseparatingtissue planes.Thisconceptmaybethemostimportantinthistext. Thesurgeonandassistantshouldpullthetissuesapartas thesurgeonseparatesthetissueswiththecuttingtool.For example,toseparatetheorbicularismusclefromtheorbital septum,thesurgeonshouldholdthescissorsinthedominanthandandgraspthemusclewiththeforcepsinthe nondominanthand.Theassistantshouldgrasptheseptum withanotherforceps.Workingtogether,thetwopairsof forcepspulltheorbicularismuscleofftheseptum.Youwill seesmallfibrousbandsthatareeasytoseparatewiththe scissors,Coloradoneedle,orlaser(Figure1.13).Inasense, yournondominanthandshowsyourdominanthandwhat todo.Itiseasytooperatewithanexperiencedsurgeonas yourassistantbecausethelayersarepulledapartforyou. Usethistechniquewheneverpossible.Thereareafew planesinwhichusingthistechniqueisnotpossible.For example,inthesubcutaneousplaneofthecheek,youhave
Box1.1 DissectionTechniqueThatYouMustKnow
’ Mostsurgeryisnotcutting;rather,itisseparatingtissue planes.
’ Graspthetissuelayersthatyouwanttoseparate(don’thold theskinwhenyouareseparatingthemusclefromthe septum).
’ Graspthetissuesclosetowhereyouwanttoworkonthem.
’ Learntopullthetissuesapartasyoucutwiththescissorsor Coloradoneedle.
’ Lookforthefibrousbandsthatshowupasyoupullthe tissuesapart.
’ Separatethelayerswithcontrolledclosureofthescissors ratherthanshort “snips.” Watchthetissuesopenasyouclose theblades.
Figure1.14 Jaffeeyelidspeculuminplace.Thespeculumcanbe usedtoopenthesurgicalwound(asshownhereforalacrimalgland biopsy),oritcanbeusedtoelevateaneyelidawayfromthe operatingsite.Itisausefultoolinalmosteveryeyelidprocedure.
tosharplyincisethetissues.Haveanexperiencedsurgeon checkyourdissectiontechniquetoconfirmthatyouarecorrectlypullingthetissuesapartandseparatingtheplanes withthecuttingtool.Thisconceptofdissectionissoimportant.Readthisparagraphagainandmakesurethatyou understandtheprinciple.Consciouslytryitnexttimeyou areintheoperatingroom.
Remembertoavoid “snips,”;closethescissorsslowly. Watchhowthetissuesopen.Thiscanbeoneofthemost elegantandrewardingofsurgicaltechniques(Box1.1).
RETRACTORS
Therearethreetypesofretractors:
’ Self-retainingretractors
’ Handheldretractors
’ Sutureretractors
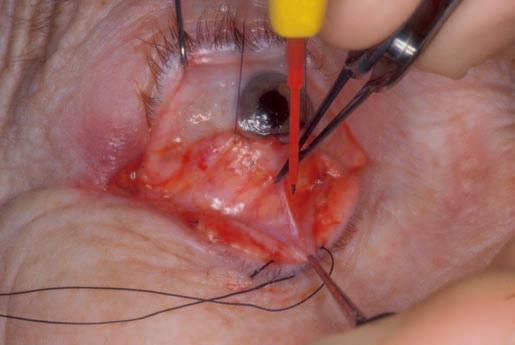
The Jaffeeyelidspeculum isanexcellentself-retaining retractorforeyelidsurgery(Figure1.14).Thisspeculum
Figure1.15 TheDesmarreslidretractorisusedsimilarlytotheJaffe lidspeculumbutmustbehandheld.Thisretractorcanbeplacedover aJaffelidspeculumforextraretraction,ausefulcombination.Here, theDesmarreslidretractorisopeningaskincreaseincisiontodraina superiororbitalabscess.
wasoriginallydesignedforcataractsurgerytoretractthe eyelidsindependentlywithoutanypressureontheglobe.I usethisretractorinalmosteverylidprocedure(www.katena. com,K1 8000,soldasapair).Self-retainingretractorsare rarelyusedinorbitalsurgerybecauseitisdifficulttoposition theretractorsadequatelyintheorbit.Theconstantpressure onthetissuewithaself-retainingretractorcanlimitcirculationtotheeye.Thereareself-retainingretractorsmadefor lacrimalsurgery,butIhavenotfoundtheseinstrumentsto besatisfactory.
Handheldretractors areusefulbutrequireagoodassistant.Thewell-trainedassistantwillmovetheretractors asthesurgeryproceedsfromoneareatoanother(good assistants “ dance ” withthesurgeonastheymoveacross thesurgicalfield).Whenmaximumretractionisnotnecessary,theassistanteasesthepressureontheretractorto improvethecirculation.Themostcommonlyusedhandheldretractorforeyelidsurgeryisthe Desmarreslidretractor (size1:13mm;StorzE0981)( Figure1.15 ).Theshape oftheDesmarreslidretractorishelpfulforatraumatically retractingthetissues.Usefulorbitalhandheldretractors arethemalleableretractorsandtheSewallorbitalretractors.The flat-bladedmallea bleretractors areavailable throughanumberofcompaniesandcomeinstraightand taperedvarieties(symmetrysurgical.com andsurgicalinstruments.comaregoodsources).Taperedmalleableretractors arehelpfulindeepwoundsbutrequirespecialordering. Sewallretractors arecommonlyusedtoretractorbitaltissues. AdisadvantageofbothmalleableretractorsandSewall retractorsisthattowing-inoftheretractormaydamagetissues,especiallythosedeepintheorbit(experiencedorbital surgeonsfearthetowed-inretractorasacauseofblindness morethananycuttinginstrument).Youwillfindthat orbitalexposureisimprovedbyliningthewoundwith neurosurgicalcottonoids (similartothelapspongesyouused topackoffthebowelasageneralsurgerystudent) (Figure1.16).Iprefercottonoidsof 1/2-inchwidthand3-inch
Figure1.16 Orbitalretractors(top,lefttoright):malleableretractors andSewallretractors.(Below)Neurosurgicalcottonoids.
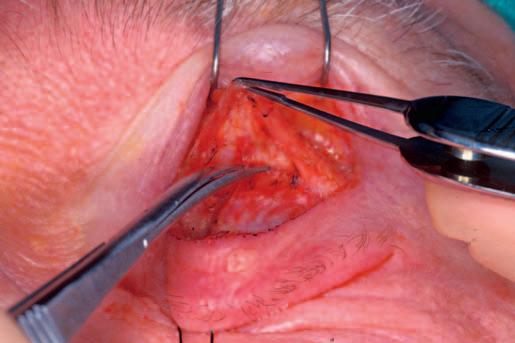
Useof4-0silksutureretractorsforexposureofan externaldacryocystorhinostomywound.
lengthfordeeporbitcases.Thefamiliar nasalspeculum isa typeofhandheldretractor.
Sutures canbeusedasretractors.Nomanipulationbya surgicalassistantisnecessary.Asmanysuturesasnecessarycanbeplacedtoprovidegoodtissueexposure(4-0 silk).Handheldretractorscanbeplacedontopofthesuture retractorstogiveextraretractionwhennecessary.Aswith anyotherstaticorself-retainingretractor,ifproblemswith circulationareanticipated,sutureretractorsshouldbe avoidedorfrequentlyreleased(Figure1.17).Smallhooks onelasticbandscanbeusedasretractors,aswell.The hookscanbeeasilyrepositionedastheneedforadifferent exposurecomesup(http://www.medline.com/product/LoneStar-Retractor-Hooks-by-Cooper-Surgical/Z05-PF65677). Thesehooksarebestforlargerfacialorneurosurgical dissections.Youneedtobeextracarefulwithhookedinstrumentsaroundtheeye.
Figure1.17