CHAPTER1 Introduction
1.1Timeseries
Manyphenomenanaturallyhavevariationwithtime;thesephenomenaencompassa widevarietyoffieldsofstudy.Onesuchexampleiswaterqualitydatafromastream. Thewaterqualityparameters(alkalinity,turbidity,organiccontent,etc.)maychange throughouttheyearandinterannually.Theapproachusedtostudythesephenomena ofinterestistocollectdataregardingtheparametersthathaveaffectedtheminthepast andthosethatwillinfluencetheminthefuture.Followingthisapproach,timeseries maybeconsideredthebesttoolsforanalyzingthecollectedpastandpresentdatato beabletomakefuturedecisions(Akhbarietal.,2019).Infact,timeseriesarevery importantinthedevelopmentofplanningandmanagementpolicies.Withthehelpof timeseries,youcanseethetrendofchangesinphenomenafromthepasttothepresent alongwiththedifferencesbetweentheobservedandexpectedvaluesduetofluctuations inthephenomena.Aclearpictureofthebehaviorofphenomenaofinterestcanbe developedthroughtimeseriesmodeling.Periodicfluctuationsandseasonalchangescan beobservedinphenomena,allowingtheirbehaviortobeunderstoodandrelatedto otherinfluencingphenomena.Ifweconsidertheexampleofwaterqualitydataonce more,well-developedtimeseriesmodelsmayallowonetounderstandhowseasonal differencesinfluencewaterqualityindicators,suchasturbidity.Notonlytimeseriesallow ustoexplaintheinfluenceofseasonalchangesonwaterqualityindicators,buttheyalso allowustounderstandinterannualchangesforthesameseason.Thisinformationcan allowmunicipalofficialstodevelopwatershedmanagementpoliciesorallowforthe optimizationofdrinkingwaterproductionforexample.Themanagementandplanning decisionsthataremadearebasedonthepredictionoffutureconditionsfrompastand presenttimeseriesdata.Forecastsareconstantlyneeded,andovertime,theeffectsof thesepredictionsonactualperformancearemeasured.Fromtheconstantmeasurement ofperformance,thepredictionsareregularlyupdated,andthedecisionscorrected.This cyclecontinuesinaniterativefashioninordertoachievethedesiredconclusion(Azari, Soori,andBonakdari,2017; Langridge,Gharabaghi,McBean,Bonakdari,andWalton, 2020).
Overtherecentyears,vastimprovementsintechnologyhavemaderecordingdata fortimeseriesmodelingmorepracticalandreliable.Asaresult,timeseriesmodelingis oneofthemostpracticaltoolsforinvestigatingavarietyphenomenoninscience,engineering,andeconomics(Azimi,Bonakdari,Ebtehaj,Gharabaghi,andKhoshbin,2018;
StochasticModeling:AThoroughGuidetoEvaluate,Pre-Process,ModelandCompare TimeSerieswithMATLABSoftware.
Copyright c 2022ElsevierInc. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-91748-3.00001-X Allrightsreserved. 1
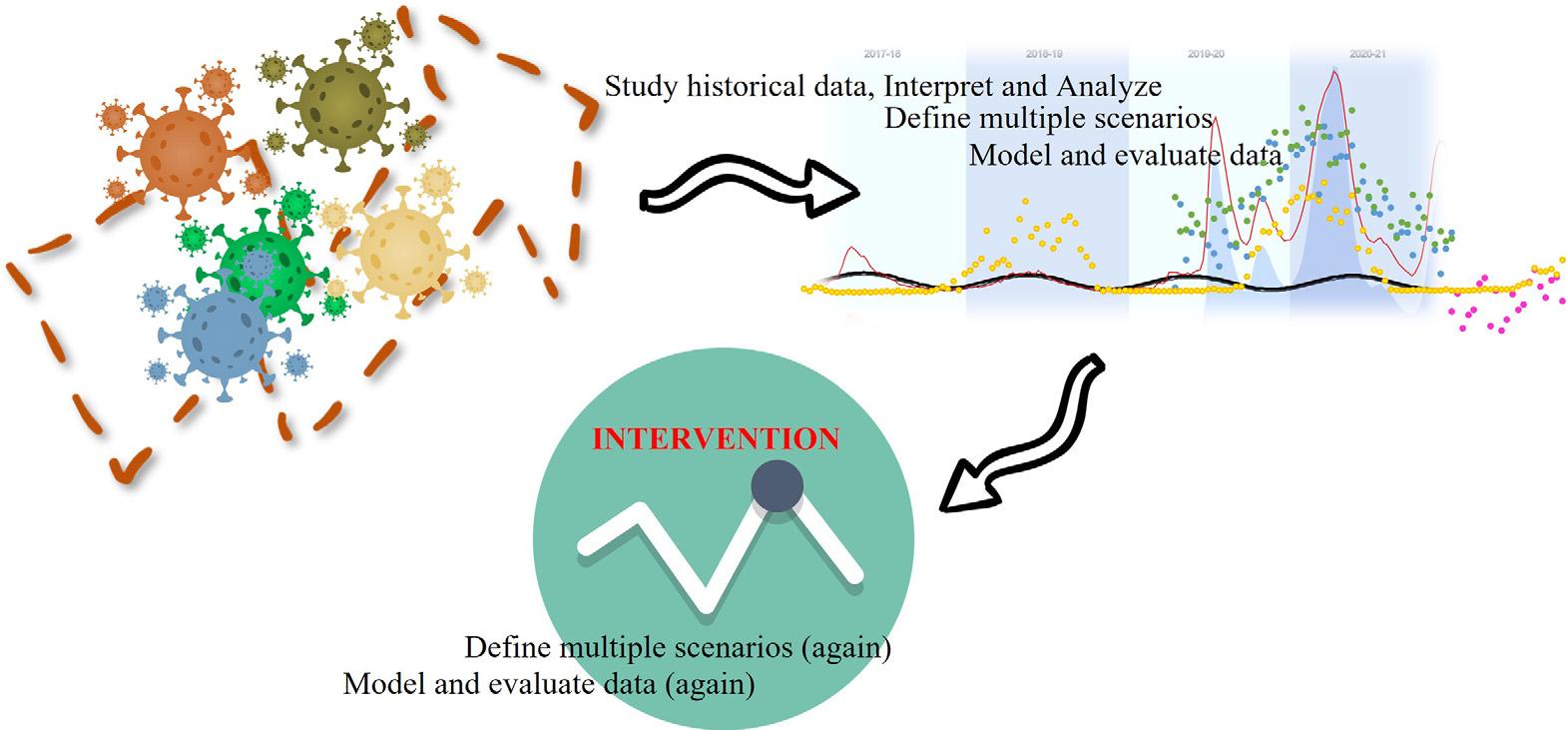
Figure1.1 Schematicofenvironmentalepidemiology.
BineshandBonakdari,2014; Bonakdari,Ebtehaj,Gharabaghi,Vafaeifard,andAkhbari, 2019; HuiPu,Bonakdari,Lassabatère,Joannis,andLarrarte,2010).Theconceptoftime seriesmodelingallowsresearcherstoassesstheoutcomesofavarietyofphenomenaat anytimewithminimumcostsandefforts.Usingforecasteddata,theycanplanpossible solutionstoproblems,makedecisions,andimplementcontrolmeasures.
1.1.1Timeseriesinenvironmentalepidemiology
Oneoffieldthathaswidelybenefitedfromtimeseriesconceptisenvironmental epidemiology(Bhaskaran,Gasparrini,Hajat,Smeeth,andArmstrong,2013; Bonakdari, Pelletier,andMartel-Pelletier,2020a, 2020b; CorcueraHotzandHajat,2020; Tejasvini, Amith,andShilpa,2020).Environmentalepidemiology(Fig.1.1)allowsresearchersto forecasttheoutcomesofanyphenomenonlikehealthfieldorassesstheimpactof environmentalexposuressuchasweather,airpollutants,andothercontributingfactors impactinghealthcondition.Usingstudydatatoforecastfutureeventsenablesdecision makerstoplansolutionsandimplementcontrolmeasuresinawaythatismuchsimpler andmuchmorecost-effectivewhencomparedtoothermethods,suchasrandomized controltests(Bonakdarietal.,2021; Bonakdari,Pelletier,andMartel-Pelletier,2020c; Bonakdari,Tardif,Abram,Pelletier,andMartel-Pelletier,2020).
1.1.2Engineeringandsequentialdata
Anotherdomainofapplicationoftimeseriesisinengineering.Oneexampleofan emergingapplicationoftimeseriesmodelingisinwatermanagement.Ascommunities
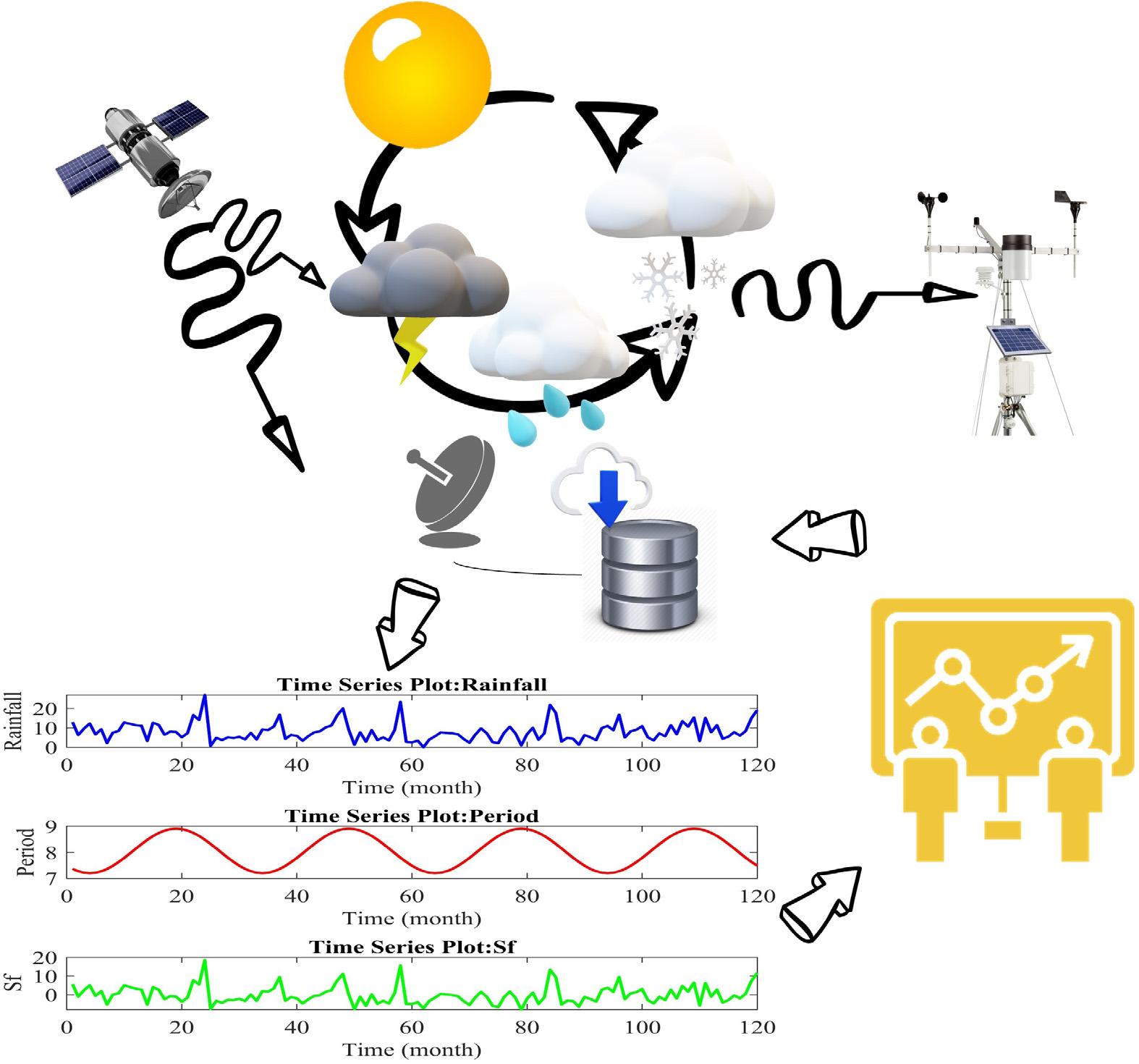
Figure1.2 Cycleofdatacuring,analyzing,anddecisionmaking.
continuetoexpandandgrow,sodotheirwaterrequirements,whetheritbeforenergy production,drinkingwatersupply,oragriculturalpractice(Fig.1.2).Hydrologicaltime seriesdataarecriticalinordertoallowpolicymakerstomakeeffectivedecisionsregarding watermanagementandresourcesustainability(Kazemian-Kale-Kaleetal.,2020; Lotfi etal.,2019; Lotfietal.,2020; Zaji,Bonakdari,andGharabaghi,2019).Withthehelpof thesetimeseries,costsassociatedwiththeimplementationofwatermanagementpolicies (includingoperationandmaintenanceofwaterutilities)canbegreatlyreduced,andthe managementofwaterresourcesefficientlyconducted(Soltanietal.,2021; Zinatizadeh, Pirsaheb,Bonakdari,andYounesi,2010).Theexampleofwaterresourcesisoneof severalapplicationsoftimeseriesinengineering,whichismoreexorbitantthanother

Figure1.3 Preprocessing,analyzing,andmodelingdataineconomy. examplesduetotheglobalwatercrisis.Timeseriesarealsousedinotherengineering sections,forinstance,estimatingandforecastingtheamountofenergyconsumedby industriesandhomeconsumers,surveyingnaturalcyclesintheseusesandmanaging energyconsumption,modelingtheamountoftrafficinacorridorandforecastfuture needs,studytheproductionandharvestofagriculturalproductsandcomparewiththe needsofsocietyandmanyotherexamples.
1.1.3Historicaldataforforecastingfutureeconomy
Furtherapplicationoftimeseriesmodelingcanbefoundinthestudyofeconomics (Fig.1.3).Withthistool,producers,sellers,andindustryownerscanobserveandinterpret marketsinordertoidentifysupplyanddemandrequirements(LarssonandNossman, 2011; Qiu,Ren,Suganthan,andAmaratunga,2017).Moreover,byusingtheappropriate methods,theycanforecastfuturedemandsinordertopreparethemselvesforpotential downturnsorperiodsofsustainedeconomicgrowth.Fromtheabovediscussion,we canseethattimeseriesplayasignificantroleinalmostallscientificandmanagement fields.Therefore,anintimateknowledgeofhowtoimplementtimeseriesmodeling
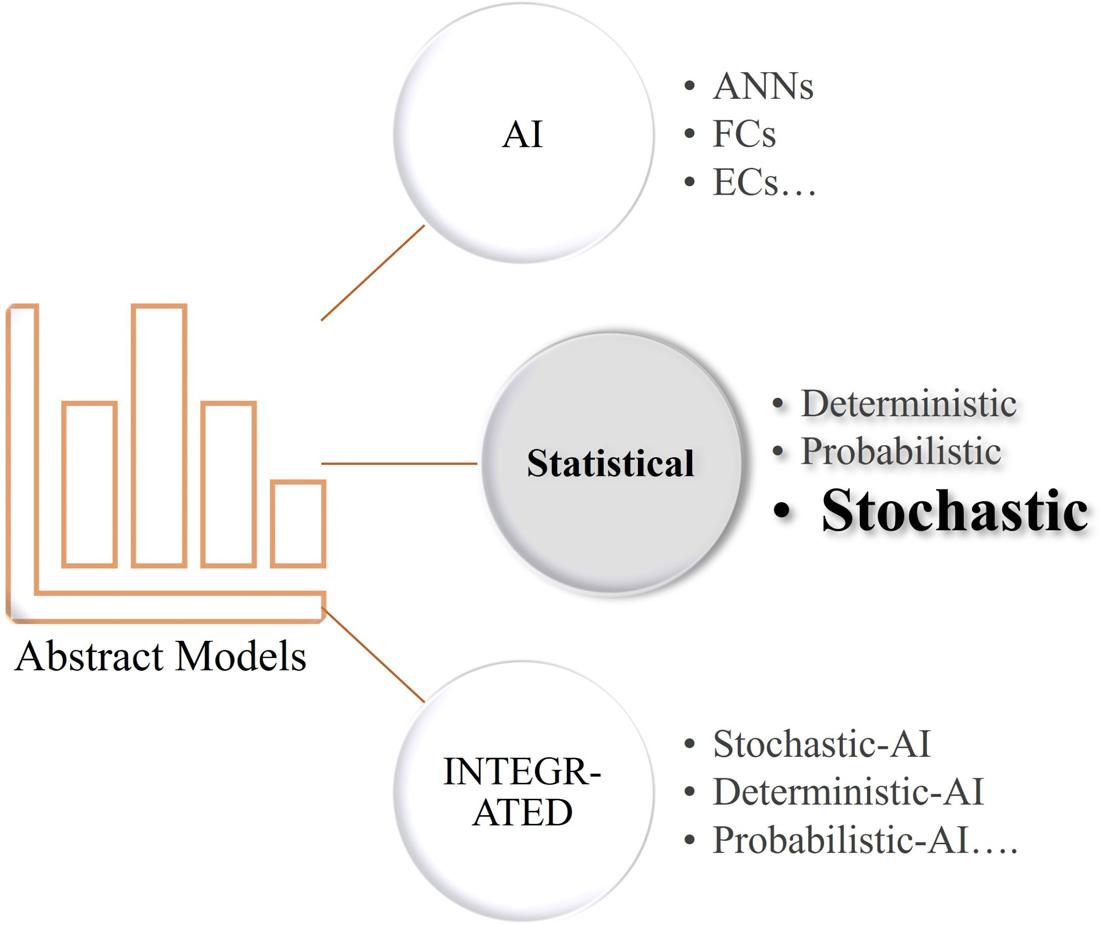
Figure1.4 Abstractmodelcategorization.
andtherequiredpre-andpost-processingstepsisvitallyimportant(Ebtehaj,Zeynoddin, andBonakdari,2020; Moeeni,Bonakdari,andFatemi,2017; Zeynoddin,Ebtehaj,and Bonakdari,2020).
1.2Stochasticandstochasticwithexogenousvariables
1.2.1Stochasticmodels
Theabilitytomodel,implementthosemodels,andanalyzemodeloutcomesarefundamentalskillsthatarerequiredofmanyreal-worldapplications.Theseapplicationsspana diverserangeofsectorsfrommedicaltocivilandmilitary(MoazamniaandBonakdari, 2014; Mojtahedi,Ebtehaj,Hasanipanah,Bonakdari,andAmnieh,2019; Momplotetal., 2012).Inpractice,inordertoachieveaneffectiveplan,appropriatemodelingshouldbe donewithintelligibleanalysisandreview,atthelowestcost.
Differentapproachesareneededtomodelphenomenaandpredictparameters. Oneoftheapproachesusedtomodelphenomenaandanalyzetimeseriesistouse models,which,basedonmathematicalconceptsandrelationshipsdescribesystemsand makeitpossibletopredictfutureparametersandconditions.Thesemodelscanbe classifiedintothreecategories:(1)statisticalmodels;(2)artificialintelligence(AI)models; (3)andintegratedmodels(Fig.1.4).Integratedmodelsareformedbycombination
ofstatisticalandAImodels(Azimi,Bonakdari,andEbtehaj,2017; Bonakdari,2011; Moeeni,Bonakdari,andEbtehaj,2017b; Moeeni,Bonakdari,Fatemi,andZaji,2017; Wang,Hu,Ma,andZhang,2015).Eachcategoryofmodelsmaybefurthersub-divided intoseveralcategories,eachofwhichmaybeemployedintheresolutionofdifferent typesofproblems.Inthistext,stochasticmodeling,asub-classofstatisticalmethods, ispresented.Thesemodelsarelaudedamongstindustrymembersandtheacademic communityalikeastheyhaveaneasilycomprehensiblestructure,canbereadilyapplied toavarietyofproblems,andhavehighprecisioninshort-termforecasts(Zeynoddin, Bonakdari,Ebtehaj,Azari,andGharabaghi,2020).
1.2.2Stochasticmodelstructure
Stochasticmodelsaretoolsforestimatingtheprobabilisticdistributionsofresultsusing randomvariablesbyoneormoreinputs.Theserandomvariablesarebasedonthe fluctuations,observedinhistoricaldataforagivenperiodusingdatastandardization techniques.Thesemodelscanbeusedtopredicttimeseries,suchastheamountof precipitation,numberofpatients,customers,oranyotherparameteratagiventime inthefuture.Inthesemodels,itisassumedthatthedataarestationaryandnormal (BrockwellandDavis,2016; ZeynoddinandBonakdari,2019).Therefore,thedatasets usedformodelingmustbepreparedandpreprocessedbeforemodeling.
1.2.3Modelclassifications
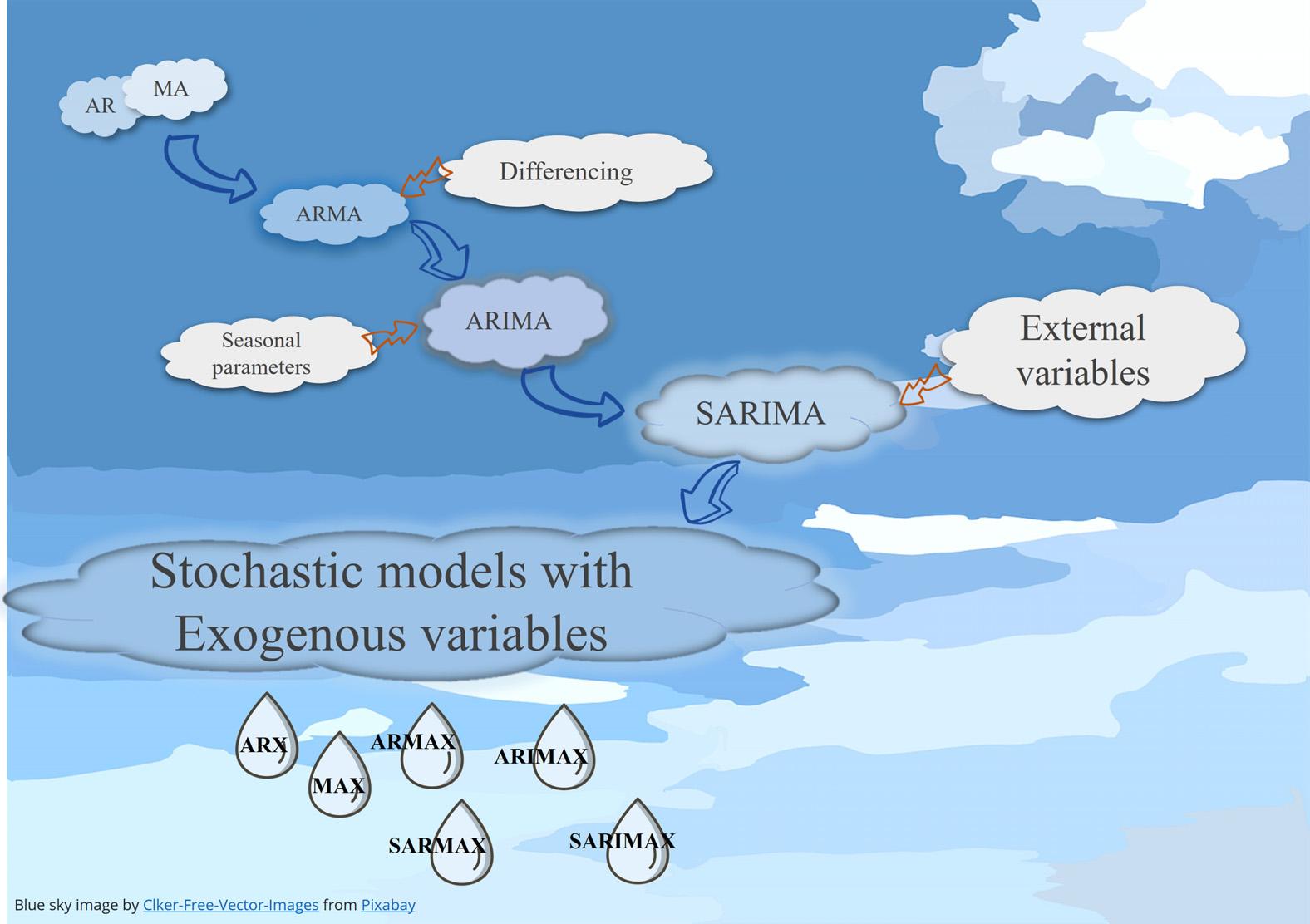
Thefirststatisticalstochasticmodeltobeintroducedwastheauto-regressive(AR)model, whichwasabletoestablishacorrelationbetweencurrentandpreviousvaluesintheseries. Thismodelquicklygainedpopularityduetothesimplicityofitsstructureandisstill usedinmanyannualorseasonalmodelingapplications.TheARmodelworkswellfor modelingphenomenawhoseparametersarerelativelystableandexhibitrelativelysmall changeswithoutdramaticfluctuation.Iftheserieschangesexhibitsdramaticfluctuations undercertainconditions,suchasanoutbreakofadisease,asuddengrowthinmarket share,orfloodconditionsinariver,theARmodelwillnotperformwell.Inorder toaddressthisdeficiencyoftheARmodel,anewmodelwasdevelopedthrough theadditionofmovingaveragealgorithmcreatingtheauto-regressivemovingaverage (ARMA)model.Iftherearesignificantseasonalfluctuations,seasonalARMAmodels canbecreated.
Furtherinvestigationrevealedthattheseries,whichwerenotstationaryonaverage, canbecomestationarybyconsideringthedifferentialchange.Therefore,byintegrating thedifferenceoperatorintheARMAmodel,anewmodelcalledtheauto-regressive integratedmovingaverage(ARIMA)wasdeveloped.Comparedtopreviousmodels,this modelrequiresfewerparameters,whichleadstoreducedmodelingcostsandthecreation ofaparsimoniousmodel(Moeeni,Bonakdari,andEbtehaj,2017a).Ifseasonalparameters
Figure1.5 Stochasticmodelingmethods.
areusedinthismodel,seasonalARIMAorSARIMAoralsoknownasmultiplicative ARIMAisproduced(Zeynoddinetal.,2019).Stochasticmodelsusingextrainputs (StochasticX:ARX,ARMAX,ARIMAX,andSARIMAX)areanadditionalformof modelthatutilizesexogenousinputsinordertoforecastaspecificvariable(Fig.1.5). Inthistypeofstochasticmodel,severaltimeserieswhichhavemutualimpactsoneach other,suchasprecipitation,airtemperature,andmoistureareusedasinputstoescalatethe accuracyofthemodels(Box,Jenkins,Reinsel,andLjung,2015; MoeeniandBonakdari, 2018).
1.3Datapreprocessing
1.3.1Definitionofpreprocessing
Intheanalysisoftimeseries,therearetwomaingoals.Thefirstgoalistoidentifythe patternofthephenomenonpresentedbyasequenceofobservations,andthesecondgoal istopredictfuturevalues.Toachievethesetwogoals,itisnecessarytounderstandthe structureandpatternofchangesintheobservedtimeseriesandtobeabletointerpret them.Oncethesestructuresandthepatternsofchangehavebeenidentified,thenecessary
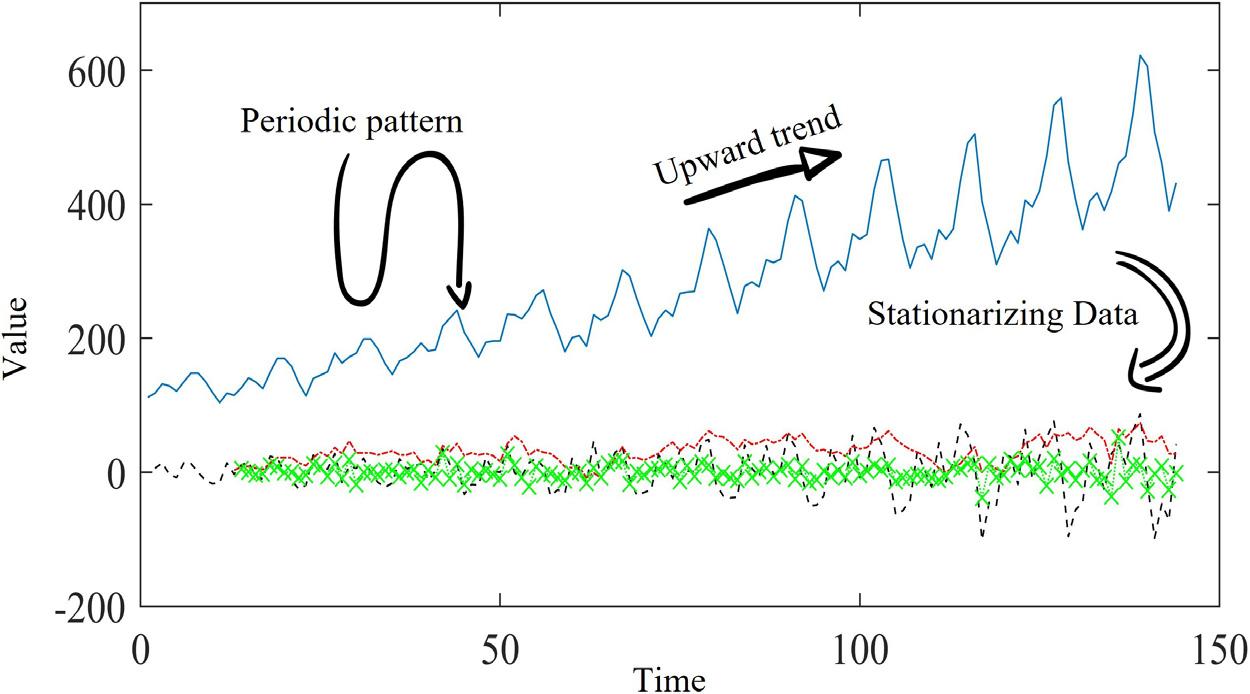
Figure1.6 Stationarizingtimeseries.
datacanbeinterpretedandanalyzed.Afteranalyzingthedata,itispossibletopredict futurephenomenabyextractingtheidentifiedpatterns.
1.3.2Relationshipbetweenforecastingandtimeseriesstructure
Whenstudyingmostnaturalphenomena,however,complextimeseriesstructuresare formedthatmakeitdifficulttoanalyze,interpret,model,andpredictvariables(Fig.1.6). Thesecomplexstructurescanoccurinserieswithascendinganddescendingtrends, seasonalalternations,drasticjumpsthatemergeasaresultofsuddenchangesinphenomena,andthesynergyofthesefactorsmakeanalysisevenmoresophisticated(Ebtehaj, Bonakdari,Zeynoddin,Gharabaghi,andAzari,2020).Broadly,thepurposeofusing timeseriesistofacilitatetheinterpretationofeventsandpredictfutureconditions withoptimalaccuracy.However,manymodelsusedinpredictingtimeserieshavebeen formedbasedonsimplisticinitialassumptionswhicharerequiredtomakemodelingand predictionoftimeseriespossible.Anexampleofonesuchsimplisticassumptionisthe developmentofstatisticalmodelsbasedonnormaldatadistributionandstationarity.
1.3.3Distributionanditsimpactontimeseriesforecasting
Asaresultoftheinherentstructuralcomplexityinvolvedinmostnaturalphenomena, methodsareneededthatprovidethepossibilitytoeliminateorreducethemodel complexityoftimeseries,aswellastomakethemeasiertoanalyzeandinterpret.Furthermore,thesemethodsshouldaimtoincreasethemodelprecisionwhilemaintainingthe validityoftheproducedmodels.Toaccomplishthisgoal,preprocessingisrequired,and isconsideredanonseparablecomponenttoanymodelingexercise.Thesepreprocesses canincludeestimatingmissingdata;identifyinganddeletingoutliers;normalizingdata
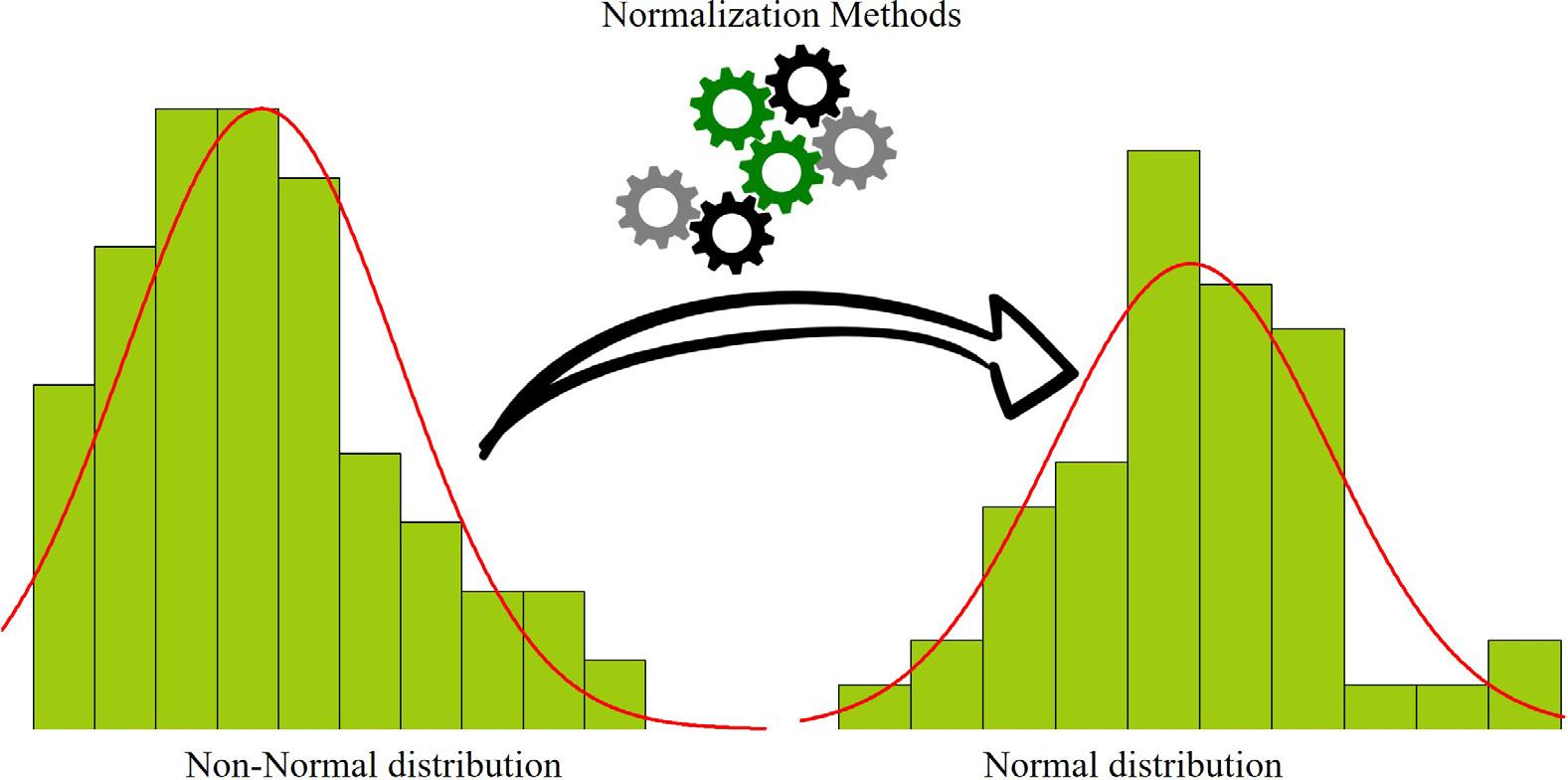
Figure1.7 Normalizationofnon-normaltimeseries.
bylogarithmic,BoxCox,John-Draper,Manly,Johnson,andYeo-Johnsontransformsand manyotherconversions(Fig.1.7)(ZeynoddinandBonakdari,2019; Zeynoddinetal., 2018);stationarizingbyeliminatingperiodicpatternsinseriesusingspectralanalysis; jumpelimination;trendanalysis;anddatastandardization(MoeeniandBonakdari,2017; Moeeni,Bonakdari,andFatemi,2017).Eachoneoftheabovemethodsisusedinspecial circumstancesandaccordingtotheunderlyingnatureoftheexistingstructuresinthe seriesbeingstudied.
References
Akhbari,A.,Ibrahim,S.,Zinatizadeh,A.A.,Bonakdari,H.,Ebtehaj,I.,Khozani,Z.S.,Gharabaghi,B.,2019. Evolutionarypredictionofbiohydrogenproductionbydarkfermentation.CLEAN-Soil,Air,Water,47 (1),1700494.
Azari,A.,Soori,S.,Bonakdari,H.,2017.Theapplicationofimperialistcompetitivealgorithmindetermining theoptimalparametersofempiricalareareductionmethodtopredictthesedimentationprocessinDez Dam.GeographyandSustainabilityofEnvironment7(3),1–14.
Azimi,H.,Bonakdari,H.,Ebtehaj,I.,2017.Sensitivityanalysisofthefactorsaffectingthedischarge capacityofsideweirsintrapezoidalchannelsusingextremelearningmachines.FlowMeasurement andInstrumentation,54,216–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2017.02.005
Azimi,H.,Bonakdari,H.,Ebtehaj,I.,Gharabaghi,B.,Khoshbin,F.,2018.Evolutionarydesignofgeneralized groupmethodofdatahandling-typeneuralnetworkforestimatingthehydraulicjumprollerlength. ActaMechanica,229(3),1197–1214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-017-2043-9
Bhaskaran,K.,Gasparrini,A.,Hajat,S.,Smeeth,L.,Armstrong,B.,2013.Timeseriesregressionstudiesin environmentalepidemiology.InternationalJournalofEpidemiology,42(4),1187–1195.
Binesh,N.,Bonakdari,H.,2014.Investigatingdifferentmodelsforestimationoflongitudinalvelocity distributioninrectangularopenchannels.AppliedMathematicsinEngineering,Managementand Technology1,19–27.
Bonakdari,H.,2011.Entropyanditsapplicationincomputationofvelocitydistributioninsewers.In:World EnvironmentalandWaterResourcesCongress2011:BearingKnowledgeforSustainability.
Bonakdari,H.,Ebtehaj,I.,Gharabaghi,B.,Vafaeifard,M.,Akhbari,A.,2019.Calculatingtheenergyconsumptionofelectrocoagulationusingageneralizedstructuregroupmethodofdatahandlingintegratedwith ageneticalgorithmandsingularvaluedecomposition.CleanTechnologiesandEnvironmentalPolicy, 21(2),379–393.
Bonakdari,H.,Jamshidi,A.,Pelletier,J.-P.,Abram,F.,Tardif,G.,Martel-Pelletier,J.,2021.Awarningmachine learningalgorithmforearlykneeosteoarthritisstructuralprogressorpatientscreening.Therapeutic AdvancesinMusculoskeletalDisease,13.1759720X21993254.
Bonakdari,H.,Pelletier,J.-P.,Martel-Pelletier,J.,2020a.Acontinuousdatadriventranslationalmodelto evaluateeffectivenessofpopulation-levelhealthinterventions:Casestudy,smokingbaninpublicplaces onhospitaladmissionsforacutecoronaryevents.JournalofTranslationalMedicine,18(1),1–21.
Bonakdari,H.,Pelletier,J.-P.,Martel-Pelletier,J.,2020b.Areliabletime-seriesmethodforpredictingarthritic diseaseoutcomes:Newstepfromregressiontowardanonlinearartificialintelligencemethod.Computer MethodsandProgramsinBiomedicine,189,105315.
Bonakdari,H.,Pelletier,J.-P.,Martel-Pelletier,J.,2020c.Viewpointontimeseriesandinterruptedtimeseries optimummodelingforpredictingarthriticdiseaseoutcomes.CurrentRheumatologyReports,22,1–11.
Bonakdari,H.,Tardif,G.,Abram,F.,Pelletier,J.-P.,Martel-Pelletier,J.,2020.Serumadipokines/related inflammatoryfactorsandratiosaspredictorsofinfrapatellarfatpadvolumeinosteoarthritis:Applying comprehensivemachinelearningapproaches.ScientificReports,10(1),1–12.
Box,G.E.P.,Jenkins,G.M.,Reinsel,G.C.,Ljung,G.M.,2015.Timeseriesanalysis:Forecastingandcontrol (WileySeriesinProbabilityandStatistics),5thed.Wiley,Hoboken,NJ. http://gbv.eblib.com/patron/ FullRecord.aspx?p=2064681
Brockwell,P.J.,Davis,R.A.,2016.Introductiontotimeseriesandforecasting.©SpringerInternational PublishingSwitzerland.
CorcueraHotz,I.,Hajat,S.,2020.Theeffectsoftemperatureonaccidentandemergencydepartment attendancesinLondon:Atime-seriesregressionanalysis.InternationalJournalofEnvironmental ResearchandPublicHealth,17(6),1957.
Ebtehaj,I.,Bonakdari,H.,Zeynoddin,M.,Gharabaghi,B.,Azari,A.,2020.Evaluationofpreprocessing techniquesforimprovingtheaccuracyofstochasticrainfallforecastmodels.InternationalJournalof EnvironmentalScienceandTechnology,17(1),505–524.
Ebtehaj,I.,Zeynoddin,M.,Bonakdari,H.,2020.Discussionof“Comparativeassessmentoftimeseries andartificialintelligencemodelstoestimatemonthlystreamflow:Alocalandexternaldataanalysis approach”.JournalofHydrology,583,124614.
HuiPu,J.,Bonakdari,H.,Lassabatère,L.,Joannis,C.,Larrarte,F.,2010.Profildevitessesturbulent:Unenouvelle loipourlescanauxétroits.LaHouilleBlanche96(3),65–70.
Kazemian-Kale-Kale,A.,Gholami,A.,Rezaie-Balf,M.,Mosavi,A.,Sattar,A.A.,Azimi,A.H.,Gharabaghi, B.,Bonakdari,H.,2021.Uncertaintyassessmentofentropy-basedcircularchannelshearstressprediction modelsusinganovelmethod,Geosciences(Switzerland)11,308.
Langridge,M.,Gharabaghi,B.,McBean,E.,Bonakdari,H.,Walton,R.,2020.Understandingthedynamic natureoftime-to-peakinUKstreams.JournalofHydrology,583,124630.
Larsson,K.,Nossman,M.,2011.Jumpsandstochasticvolatilityinoilprices:timeseriesevidence.Energy Economics33(3),504–514.
Lotfi,K.,Bonakdari,H.,Ebtehaj,I.,Delatolla,R.,Zinatizadeh,A.A.,Gharabaghi,B.,2020.Anovelstochastic wastewaterqualitymodelingbasedonfuzzytechniques.JournalofEnvironmentalHealthScienceand Engineering18(2),1099–1120.
Lotfi,K.,Bonakdari,H.,Ebtehaj,I.,Mjalli,F.S.,Zeynoddin,M.,Delatolla,R.,Gharabaghi,B.,2019.Predicting wastewatertreatmentplantqualityparametersusinganovelhybridlinear-nonlinearmethodology. JournalofEnvironmentalManagement,240,463–474.
Moazamnia,M.,Bonakdari,H.,2014.VelocitydistributionandestimationofdischargeinsewersbyShannon entropyconcept.JournalofWaterandWastewater;AbVaFazilab(inPersian)25(2),26–35.
Moeeni,H.,Bonakdari,H.,2017.Forecastingmonthlyinflowwithextremeseasonalvariationusingthe hybridSARIMA-ANNmodel.StochasticEnvironmentalResearchandRiskAssessment31(8),1997–2010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-016-1273-z
Moeeni,H.,Bonakdari,H.,2018.ImpactofnormalizationandinputonARMAX-ANNmodelperformance insuspendedsedimentloadprediction.WaterResourcesManagement,32(3),845–863.
Moeeni,H.,Bonakdari,H.,Ebtehaj,I.,2017a.IntegratedSARIMAwithneuro-fuzzysystemsandneural networksformonthlyinflowprediction.WaterResour.Manage.31(7),2141–2156. https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s11269-017-1632-7
Moeeni,H.,Bonakdari,H.,Ebtehaj,I.,2017b.Monthlyreservoirinflowforecastingusinganewhybrid SARIMAgeneticprogrammingapproach.JournalofEarthSystemScience,126(2),2. https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s12040-017-0798-y
Moeeni,H.,Bonakdari,H.,Fatemi,S.E.,2017.Stochasticmodelstationarizationbyeliminatingtheperiodic termanditseffectontimeseriesprediction.JournalofHydrology,547,348–364. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.02.012.
Moeeni,H.,Bonakdari,H.,Fatemi,S.E.,Zaji,A.H.,2017.Assessmentofstochasticmodelsandahybrid artificialneuralnetwork-geneticalgorithmmethodinforecastingmonthlyreservoirinflow.INAE Letters2(1),13–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41403-017-0017-9.
Mojtahedi,S.F.F.,Ebtehaj,I.,Hasanipanah,M.,Bonakdari,H.,Amnieh,H.B.,2019.Proposinganovelhybrid intelligentmodelforthesimulationofparticlesizedistributionresultingfromblasting.Engineeringwith Computers35(1),47–56.
Momplot,A.,Bonakdari,H.,Mignot,E.,LipemeKouyi,G.,Rivière,N.,Bertrand-Krajewski,J.-L.,2012.Effects ofcomputationalmeshesonhydrodynamicsofanopenchanneljunctionflowusingCFDtechnique. In:Proceedingsofthe9thInternationalConferenceonUrbanDrainageModelling.Belgrade.
Qiu,X.,Ren,Y.,Suganthan,P.N.,Amaratunga,G.A.J.,2017.Empiricalmodedecompositionbasedensemble deeplearningforloaddemandtimeseriesforecasting.AppliedSoftComputing54,246–255.
Soltani,K.,Amiri,A.,Zeynoddin,M.,Ebtehaj,I.,Gharabaghi,B.,Bonakdari,H.,2021.Forecastingmonthly fluctuationsoflakesurfaceareasusingremotesensingtechniquesandnovelmachinelearningmethods. TheoreticalandAppliedClimatology143(1),713–735.
TejasviniK.N.,AmithG.R.,Akhtharunnisa,ShilpaH.,2020.Airpollutionforecastingusingmultipletime seriesapproach.In:MandalJ.,MukhopadhyayS.(Eds.)ProceedingsoftheGlobalAICongress2019. AdvancesinIntelligentSystemsandComputing,vol1112.Springer,Singapore.
Wang,J.,Hu,J.,Ma,K.,Zhang,Y.,2015.Aself-adaptivehybridapproachforwindspeedforecasting.Renewable Energy78,374–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2014.12.074
Zaji,A.H.,Bonakdari,H.,Gharabaghi,B.,2019.AdvancingfreshwaterlakelevelforecastusingKingâscastle optimizationwithtrainingsampleadaptionandadaptiveneuro-fuzzyinferencesystem.WaterResources Management33(12),4215–4230.
Zeynoddin,M.,Bonakdari,H.,2019.Investigatingmethodsindatapreparationforstochasticrainfall modeling:AcasestudyforKermanshahsynopticstationrainfalldata,Iran.JournalofAppliedResearch inWaterandWastewater6(1),32–38.
Zeynoddin,M.,Bonakdari,H.,Azari,A.,Ebtehaj,I.,Gharabaghi,B.,Madavar,H.R.,2018.Novelhybridlinear stochasticwithnon-linearextremelearningmachinemethodsforforecastingmonthlyrainfallatropical climate.JournalofEnvironmentalManagement222,190–206.
Zeynoddin,M.,Bonakdari,H.,Ebtehaj,I.,Azari,A.,Gharabaghi,B.,2020.Ageneralizedlinearstochastic modelforlakelevelprediction.ScienceoftheTotalEnvironment,723,138015.
Zeynoddin,M.,Bonakdari,H.,Ebtehaj,I.,Esmaeilbeiki,F.,Gharabaghi,B.,Haghi,D.Z.,2019.Areliablelinear stochasticdailysoiltemperatureforecastmodel.SoilandTillageResearch,189,73–87.
Zeynoddin,M.,Ebtehaj,I.,Bonakdari,H.,2020.Developmentofalinearbasedstochasticmodelfordaily soiltemperatureprediction:Onestepforwardtosustainableagriculture.ComputersandElectronicsin Agriculture176,105636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2020.105636
Zinatizadeh,A.A.L.,Pirsaheb,M.,Bonakdari,H.,Younesi,H.,2010.Responsesurfaceanalysisofeffectsof hydraulicretentiontimeandinfluentfeedconcentrationonperformanceofanUASFFbioreactor.Waste Management.(Oxford)30(10),1798–1807.