Pearson Foundation Series Biology 10 CLASS
Trishna Knowledge Systems
Photo Credits
Chapter 1 Opener: Andrea Danti. Shutterstock
Chapter 2 Opener: MedicalRF.com / Alamy Stock Photo
Chapter 3 Opener: Greg Brave. Shutterstock
Chapter 4 Opener: flynt. 123rf.com
Chapter 5 Opener: nobeastsofierce. Shutterstock
Chapter 6 Opener: lightwise. 123rf.com
Chapter 7 Opener: Lukiyanova Natalia frenta. Shutterstock
Chapter 8 Opener: Eraxion. 123rf.com
Chapter 9 Opener: nobeastsofierce. 123rf.com
Chapter 10 Opener: Macrovector. Shutterstock.com
Chapter 11 Opener: divedog. Shutterstock
Icons of Practice Questions: graphixmania. Shutterstock
Icons of Answer Keys: Viktor88. Shutterstock
Icons of Hints and Explanation: graphixmania. Shutterstock
Copyright © 2019 Trishna Knowledge Systems
Published by Pearson India Education Services Pvt. Ltd, CIN: U72200TN2005PTC057128.
No part of this eBook may be used or reproduced in any manner whatsoever without the publisher’s prior written consent.
This eBook may or may not include all assets that were part of the print version. The publisher reserves the right to remove any material in this eBook at any time.
ISBN 978-93-530-6208-8 eISBN 9789353065010
First Impression
Published by Pearson India Education Services Pvt. Ltd, CIN: U72200TN2005PTC057128.
Head Office: 15th Floor, Tower-B, World Trade Tower, Plot No. 1, Block-C, Sector-16, Noida 201 301, Uttar Pradesh, India.
Registered Office: 4th Floor, Software Block, Elnet Software City, TS-140, Block 2 & 9, Rajiv Gandhi Salai, Taramani, Chennai 600 113, Tamil Nadu, India. Fax: 080-30461003, Phone: 080-30461060
Website: in.pearson.com, Email: companysecretary.india@pearson.com
This page is intentionally left blank.
Chapter Insights Cell-the Basic Unit of Life Cell—The Basic Unit of Life
and functions of membranes covering the cell
Characteristic Features
Functions:
• Provides a framework to the cell
• Provides definite shape to the cells
REMEMBER
Before beginning this chapter, you should be able
• Gives rigidity and support to the tissues in plants
• Gives mechanical strength to the cell to facilitate the plant to support its long and tall body
Before beginning this chapter, you should be able to:
• Protects protoplasm against infections
• Recall the basic structure and functions of major cell organelles
Recall the basic structure and functions of major
• Helps in balancing and maintaining osmotic pressure and prevents bursting of cells
Remember section will help them to memorize and review the previous learning on a particular topic
• Helps in the transport of water and minerals over long distances
• Remember the structure and important components of nucleus
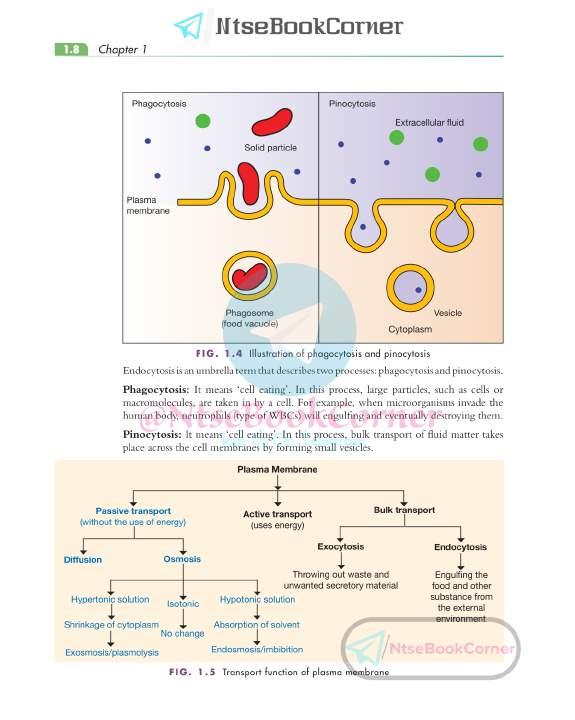
Transport of Substances through the Plasma Membrane
Remember the structure and important components
The passage of substances across the cell membrane takes place by three modes, which are listed as follows listed as follows.
KEY IDEAS
1. Passive transport
2. Active transport
After completing this chapter, you should be able to:
After completing this chapter, you should be able
Some Interesting Facts about Vitamins
3. Bulk transport
• Explain the structure and function cell membranes
Key points will help the students to identify the essential points in a chapter
Explain the structure and function cell membranes
Passive Transport
• Vitamin D is called sunshine vitamin as human skin can produce large amounts of Vitamin D when exposed to the Sun.
• Understand transport of substances through plasma membrane
• Vitamins B and C are most sensitive to heat. They may get destroyed by excessive cooking.
• Understand transport of substances through plasma membrane
Balanced diet
Info boxes are some add-on information on related topics
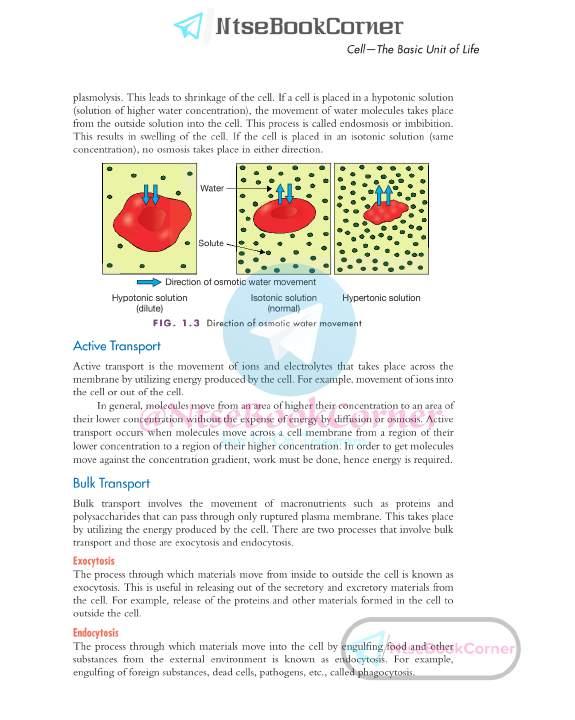
Passive transport is a mode of transport that takes place without the expenditure of energy. It takes place by either diffusion or osmosis.
Diffusion
• Describe the structures and functions of different cell organelles
• Describe the structures and functions of different cell organelles
• Know the structure and function of DNA
We have studied that we require nutrients in certain required amounts to maintain an overall health of the body. We require carbohydrates in the largest amount followed by proteins and fats. Vitamins and minerals are required in minute quantities. Overconsumption and deficiency of them can be harmful to us. Hence, we need to maintain a balanced intake of the nutrients we obtain from dietary sources.
• Know the structure and function of DNA
• Understand the significance of chromosome number and their function
• Understand the significance of chromosome number and their function
A balanced diet is one that contains all the essential nutrients required by us in definite and necessary proportions. Balanced diet helps maintaining the overall physical and mental health of our body. Every food item does not contain all the nutrients that are required for a balanced diet. Some of them may be rich in proteins and some may be in fats. Depending on the type of nutrients present, food items can be categorized into: cereals; fruits and vegetables; milk and cheese; meat; and fats and oil group.
(Continued) Concepts are explained in a well structured and lucid manner
Diffusion is the process in which movement of molecules takes place from higher to lower concentrations until the concentrations become equal. It is generally applicable to the movement of gaseous substances. With diffusion, the plants take in carbon dioxide from the air and release oxygen during the process of photosynthesis. The taking in of oxygen into the blood from lungs and the release of carbon dioxide from the lungs into the blood also take place by diffusion.
Osmosis
Osmosis is vital to many body processes, including the workings of the kidney and the nerves
groups
Cell—The Basic Unit of Life 1.23
The movement of solvent (water) molecules from a solution of higher water concentration to a solution of lower water concentration through a semipermeable membrane is called ‘osmosis’. In living systems, the process of osmosis is affected by the external environment. If a cell is in an environment of a hypertonic solution (solution of lower water concentration), the movement of water molecules takes place from the cell into the outside solution. This process is called exosmosis or
1. What are the morphological and physiological features that distinguish ‘Rough ER’ and ‘Smooth ER’? Why are they named so?
Rough ER
Ribosomes are present on the surface
Rough appearance and looks like sheets
Found attached to the nuclear membrane with closely situated Golgi apparatus
Involved in the synthesis of proteins
Smooth ER
Ribosomes are absent
Smooth appearance and looks like tubes
Found dispersed throughout the cytoplasm of the cell
Involved in the synthesis of lipids
2. DNA has a double helical structure. What purpose does this structure serve?
• The nitrogen bases are hydrophobic. This means that they lack affinity for water.
• The sugar molecule and the phosphate group are hydrophilic. This means that they have affinity for water.
• The cytosol (liquid matrix of cytoplasm) contains water-based liquids.
QUICK RECAP
Quick Recap section will help to review all important concepts, discussed in that particular chapter
Info Box!
Nutrition in Plants and Animals 2.5
Cell Organelle
Mitochondria
Ribosomes Matrix Outer membrane Inner membrane
Each section contains detailed diagrams, images, real life microscopic views for better understanding and conceptual clarity. Cell—The Basic Unit of Life 1.25
TEST YOUR CONCEPTS
Directions for questions from 1 to 11: Fill in the blanks in each question.
1. _________ is a group of the basic entities of living organisms that are specialized to perform specific functions.
2. All the activities of a cell are performed by a single cell in an _________ organism.
TEST YOUR CONCEPTS
3. _________ is the main characteristic phenomenon taking place in living cells which is responsible for growth of an individual.
1. Tissue
2. Unicellular
4. _________ are the structures that are found floating in cytoplasm of a cell.
3. Cell division
13. Identify the cell organelles that are responsible for intercellular transport system.
(a) Mitochondria
(b) Ribosome
(c) Endoplasmic reticulum
(d) Golgi complex
14. Identify the cell organelle in which respiration in a living cell takes place.
(a) Mitochondria
14. (a)
(b) Ribosome
(c) Endoplasmic reticulum
Different levels of questions have been included in the Test Your Concepts as well as on Mastering the Concept which will help students to develop the problem-solving skill Table 1.2
Structure
• Present
• Continuous on the membrane • Rod-shaped double • Outer • Inner membrane like projections
The
• Site for releasing
Energy
• Synthesis
• Regulation concentration
5. In a plant cell, _________ protects protoplasm against infections.
4. Cell organelles
5. Cell wall
6. Homeostasis
‘Test Your Concepts’ at the end of the chapter for classroom preparation
15. (c)
(d) Golgi complex
16. (a)
MASTERING THE CONCEPTS
6. The stable condition of an organism and its internal structure as regulated by a plasma membrane is known as _________.
7. Water constitutes
15. Which of the following components help maintain the osmotic pressure in a plant cell?
(c)
Knowledge and Understanding
(a) Plasma membrane
(a)
(b) Cytoplasm
1. What are the functions of a cell wall?
7. About 90% of the cytoplasm is occupied by _________.
8. Known as a chromoplast.
9. Nuclear membrane
Respiration in Plants and Animals 4.15
(c) Cell wall
(d)
tEst Your concEpts
1. Respiration
8. The cell organelle that imparts colours to fruits and flowers is __________.
2. Breathing
(d) Cell organelle
2. What are the major components of a cell nucleus?
(b)
(a)
3. What are the basic units of deoxyribose nucleic acid? What are they composed of?
7. Mention the types of chromosomes based on the position of centromere.
8. What is the significance of chromosomes?
16. Which of the following cell organelles contain a green pigment that contributes to greenery around us?
(d)
9. What is the difference between cytoplasm and cytosol?
3. Glucose
9. _________ separates nucleus from the cytoplasm.
10. Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid and Ribose Nucleic Acid
4. Stomata
4. Name the four nitrogenous bases associated with nucleotides of DNA.
5. Guard cells
11. Cytoplasmic inclusions.
10. DNA and RNA stand for _________ and _________, respectively.
12. (d)
13. (c)
Mastering the concepts are further divided as per Knowledge/ Understanding, and Application/ Analyze
6. Pharynx
5. Define gene.
7. Haemoglobin
8. Alveoli
11. The non-living materials found in cytoplasm are known as _________.
(a) Chloroplast (b) Chromoplast
(d)
(c) Leucoplast (d) Vacuole
10. Identify the similarities between mitochondria and chloroplasts.
17. The functions of cell organelles are controlled by which component of the cell?
A
11. Adenine cannot pair with cytosine. Give reason.
(a) Protoplasm (b) Cytoplasm
6. What is complementary base pairing? What is its significance?
9. Trachea
10. Diffusion
11. Expiration
Directions for questions from 12 to 23: For each of the following questions, for choices have been provided. Select the correct alternatives,
(c) Nucleus (d) Tissue
22. (a)
23. (c)
Application and Analysis
12. (a)
18. Identify the cell organelle which is specialized in detoxification of a cell in animals.
24. (a)
25. (b)
(a) Lysosome (b) Ribosome
MASTERING THE CONCEPTS
13. (b)
12. Protoplasm of a cell comprises cytoplasm along with
(a) Plasma membrane
Knowledge-Based Questions
(b) Cell organelles
(c) Nucleolus
12. Explain the role of DNA in protein synthesis.
(c) Peroxisome (d) Centrosome
mastEring tHE concEpts
1. A cell wall performs the following functions:
(a) Sperm cell
(b) WBC
19. Which of the following is not a part of cell nucleus?
Knowledge and Understanding
(a) Chromatin (b) Nucleolus
13. (a) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is abundant in liver cells, cells in brain and the cells in the muscles of limbs. What are the functions performed by it in the respective cells?
(c) Guard cells of stomata
2. The major components of a cell nucleus are:
(c) Nucleoplasm (d) Ribosome
(d) Nucleus
(a) Provides a framework to the cell
(b) Provides definite shape to the cells
(c) Gives rigidity and support to the plant tissues
1. Respiration is a chemical process which involves breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen to release energy. Breathing is more of a physical process which involves mere intake and release of air, i.e., taking in oxygen and giving out carbon dioxide.
(a) Nuclear membrane
(b) Sarcoplasmic reticulum is the modified form of smooth ER. What is its significance?
4. Lungs are protected from various injuries and shock by a double membrane around it, called pleural membrane. The fluid that is seen between pleural membranes, i.e., pleural fluid, also gives protection to the lungs.
(b) Nuclear sap or nucleoplasm (c) Nucleolus and (d) Chromatin material
14. Diseases related to mitochondria are inherited from female parent only. Give reason.
(d) Gives mechanical strength to the cell to facilitate a plant to support its long and tall body.
2. Respiration is the process by which plants produce energy for their various activities. It involves breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen. During breathing, they take in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide. This oxygen is carried to different parts of the body and cells where it is used to break down glucose to release energy. Respiration can be represented as:
18. What is the difference between the genetic material of prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
19. Explain the role of Golgi apparatus in the processing of proteins synthesized in rough ER.
5. Haemoglobin is the respiratory pigment seen in human blood. It is an iron-containing pigment with red colour. It acts as the main carrier for oxygen transport to all parts of the body.
15. (a) In what way the totipotent cells, pluripotent cells and multi potent cells differ from each other?
(e) Helps in balancing and maintaining osmotic pressure and prevents bursting of cells
3. The basic units of deoxyribose nucleic acid are nucleotides. These are made up of a molecule of pentose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogen base.
6. (A) Pharynx (B) Bronchioles (C) Bronchi (D) Alveoli (E) Diaphragm
+ Oxygen Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
(b) What are stem cells? Where are they located in human body? What is their
20. How are lysosomes formed? In which cells of human body they are found abundantly?
21. The following cells are observed under a microscope. How do you distinguish them with respect to the position of nucleus?
4. The four nitrogen bases associated with the nucleotides are adenine, guanine, thymine and
(a) Mature plant cell
7. When we inhale, ribs are lifted up and diaphragm
Hints and Explanation for key questions along with highlights on the common mistakes that students usually make in the examination