NANOTECHNOLOGYIN CANCERMANAGEMENT
NANOTECHNOLOGYIN CANCERMANAGEMENT PreciseDiagnosticsToward PersonalizedHealthCare
Editedby
KAMILREZAKHONDAKAR
CentreforPersonalisedNanomedicine,AustralianInstituteforBioengineeringand Nanotechnology(AIBN),TheUniversityofQueensland,Brisbane,QLD,Australia
AJEETKUMARKAUSHIK
NanoBioTechLaboratory,DepartmentofNaturalSciences,DivisionofSciences,Art, andMathematics,FloridaPolytechnicUniversity,Lakeland,FL,UnitedStates
Elsevier
Radarweg29,POBox211,1000AEAmsterdam,Netherlands
TheBoulevard,LangfordLane,Kidlington,OxfordOX51GB,UnitedKingdom 50HampshireStreet,5thFloor,Cambridge,MA02139,UnitedStates
Copyright©2021ElsevierInc.Allrightsreserved.
Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproducedortransmittedinanyformorbyanymeans,electronicormechanical, includingphotocopying,recording,oranyinformationstorageandretrievalsystem,withoutpermissioninwritingfromthe publisher.Detailsonhowtoseekpermission,furtherinformationaboutthePublisher’spermissionspoliciesandour arrangementswithorganizationssuchastheCopyrightClearanceCenterandtheCopyrightLicensingAgency,canbefoundat ourwebsite: www.elsevier.com/permissions
ThisbookandtheindividualcontributionscontainedinitareprotectedundercopyrightbythePublisher(otherthanasmaybe notedherein).
Notices
Knowledgeandbestpracticeinthisfieldareconstantlychanging.Asnewresearchandexperiencebroadenourunderstanding, changesinresearchmethods,professionalpractices,ormedicaltreatmentmaybecomenecessary.
Practitionersandresearchersmustalwaysrelyontheirownexperienceandknowledgeinevaluatingandusingany information,methods,compounds,orexperimentsdescribedherein.Inusingsuchinformationormethodstheyshouldbe mindfuloftheirownsafetyandthesafetyofothers,includingpartiesforwhomtheyhaveaprofessionalresponsibility.
Tothefullestextentofthelaw,neitherthePublishernortheauthors,contributors,oreditors,assumeanyliabilityforany injuryand/ordamagetopersonsorpropertyasamatterofproductsliability,negligenceorotherwise,orfromanyuseor operationofanymethods,products,instructions,orideascontainedinthematerialherein.
BritishLibraryCataloguing-in-PublicationData
AcataloguerecordforthisbookisavailablefromtheBritishLibrary LibraryofCongressCataloging-in-PublicationData
AcatalogrecordforthisbookisavailablefromtheLibraryofCongress
ISBN:978-0-12-818154-6
ForInformationonallElsevierpublications visitourwebsiteat https://www.elsevier.com/books-and-journals
Publisher: SusanDennis
AcquisitionsEditor: KostasMarinakis
EditorialProjectManager: LizHeijkoop
ProductionProjectManager: JoyChristelNeumarinHonestThangiah
CoverDesigner: VictoriaPearson
TypesetbyMPSLimited,Chennai,India
6Bioinformatics
Listofcontributors
MuqadasAleem
DepartmentofPlantBreedingandGenetics,Universityof Agriculture,Faisalabad,Pakistan;NationalCenterforSoybean Improvement,NanjingAgriculturalUniversity,Nanjing,Jiangsu, China
ShuvashisDey
CentreforPersonalisedNanomedicine,AustralianInstitutefor BioengineeringandNanotechnology,TheUniversityof Queensland,StLucia,QLD,Australia
ShraddhaDorlikar
DepartmentofMicrobiology,RashtrasantTukadojiMaharaj NagpurUniversity,Nagpur,India
NicoletaHickman
DepartmentofNaturalSciences,DivisionofSciences,Art,and Mathematics,FloridaPolytechnicUniversity,Lakeland,FL, UnitedStates
MuhammadSarmadIftikhar
SchoolofAgricultureandFoodSciences,TheUniversityof Queensland,StLucia,QLD,Australia;DepartmentofPlant BreedingandGenetics,UniversityofAgriculture,Faisalabad, Pakistan
PrasantaKalita TerrablueXT,NewDelhi,India
AshishKalkal
DepartmentofBiotechnology,IndianInstituteofTechnology Roorkee,Roorkee,India
AjeetKumarKaushik
NanoBioTechLaboratory,DepartmentofNaturalSciences, DivisionofSciences,Art,andMathematics,FloridaPolytechnic University,Lakeland,FL,UnitedStates
AyubKhan
DepartmentofOrthodontics,AMEDentalCollege,Raichur, India
KamilRezaKhondakar
CentreforPersonalisedNanomedicine,AustralianInstitutefor BioengineeringandNanotechnology(AIBN),TheUniversityof Queensland,Brisbane,QLD,Australia
SaurabhKumar
CentreforNanoScienceandEngineering(CeNSE),Indian InstituteofScience,Bengaluru,India
VidhuMalik
DepartmentofChemistry,DCRUSTMurthal,Sonipat,India
PoojaRawat
DepartmentofAppliedPhysicsandInstituteofNatural Sciences,KyungHeeUniversity,Yongin-si,RepublicofKorea
K.MohsinReza
DepartmentofConservativeDentistryandEndodontics, NavodayaDentalCollege,Raichur,India
JongSooRhyee
DepartmentofAppliedPhysicsandInstituteofNatural Sciences,KyungHeeUniversity,Yongin-si,RepublicofKorea
AppanRoychoudhury
CentreforBiomedicalEngineering,IndianInstituteof TechnologyDelhi,HauzKhas,NewDelhi,India
AmenShamim
DepartmentofMolecularCellBiology,SchoolofMedicine, SamsungMedicalCenter,SungkyunkwanUniversity,Suwon, Korea;CentreofAgriculturalBiochemistryandBiotechnology (CABB),UniversityofAgriculture,Faisalabad,Pakistan
ManuSharma
DepartmentofBiosciences,ShriRamCollegeMuzaffarnagar,India
ParshantKumarSharma
DepartmentofBiotechnology,Dr.A.P.J.AbdulKalamTechnical University,Lucknow,India
GhulamMohyuddinTalha
DepartmentofPlantBreedingandGenetics,Universityof Agriculture,Faisalabad,Pakistan
NishantVats
DepartmentProductionPlanningandControl,VarrocPolymers Pvt.Ltd.,GreaterNoida,India
SurendraK.Yadav
DepartmentofChemistry,NorwegianUniversityofScienceand Technology(NTNU),Trondheim,Norway
Nanotechnologyandits application:areview
ParshantKumarSharma1,ShraddhaDorlikar2, PoojaRawat3,VidhuMalik4,NishantVats5,ManuSharma6, JongSooRhyee3 andAjeetKumarKaushik7
1DepartmentofBiotechnology,Dr.A.P.J.AbdulKalamTechnicalUniversity, Lucknow,India 2DepartmentofMicrobiology,RashtrasantTukadojiMaharaj NagpurUniversity,Nagpur,India 3DepartmentofAppliedPhysicsand InstituteofNaturalSciences,KyungHeeUniversity,Yongin-si,Republicof Korea 4DepartmentofChemistry,DCRUSTMurthal,Sonipat,India 5DepartmentProductionPlanningandControl,VarrocPolymersPvt.Ltd., GreaterNoida,India 6DepartmentofBiosciences,ShriRamCollege Muzaffarnagar,India 7NanoBioTechLaboratory,DepartmentofNatural Sciences,DivisionofSciences,Art,andMathematics,FloridaPolytechnic University,Lakeland,FL,UnitedStates
1.1Introduction
Nanotechnology(“nano,”theGreekwordfor“dwarf”)isthe scienceandengineeringassociatedwithcreation,formation, characterization,andapplicationofmaterialsanddeviceswhose smallestfunctionalunitinatleastonedimensionisonthenanometerscale [1 6].Afamouslectureofphysicsnoblelaureates R.P.FeynmanatthemeetingoftheAmericanPhysicsSocietyin December,1959,entitled“There’splentyofroomatthebottom,” introducedthetermnanotechnology [7].Afterthat,theFeynman ideaofhandlingmatterattheatomicscalewasdemonstratedby manyground-breakingdevelopmentsinchemistry,physics,and biology.In1974NorioTaniguchi(aprofessorattheTokyo UniversityofScience)inventedtheterm“nanotechnology”to describeextra-highprecisionandultra-finedimensions [8]. Therearenumerousdefinitionsofnanotechnology,andaccordingtotheNationalNanotechnologyInitiative,nanotechnologyis thefieldthatincludesthefollowingcharacteristics: 1. Developmentoftechnologyand researchatthemacromolecular,atomic,ormolecularlevels,inthescaleoftheapproximately 1 100nmrange.
2. Designingandusingstructures,equipment,andsystems thathaveuniquepropertiesandfunctionbecauseoftheir tinyorintermediatesize.
3. Abilitytooperateontheatomicscale.
Nanotechnologymeansaprocessthatinvolvestheuseof matterattheatomicandmolecularlevelandexploitationofits uniquecapabilitiesandpropertiescreatedattheatomicand molecularscale [9].Nanotechnologyhasabroadrangeofapplications,anditsdevelopmentbringsrapidchangestoresearch fieldandindustries,detectionandtreatmentofdiseasesand drugdelivery,monitoring,environmentalprotection,foodsector,agriculture,andbuildingcomplexstructureforelectriccircuitorairplanes [10 13].
Numerousresearchhasbeendoneinthefieldofnanotechnology,butthereislessstudyinthe fieldofnanobiotechnology. Nanobiotechnologyisthefieldthatappliesthenanoscienceto biosystemsandusesbiologicalprincipleandmaterialtocreatea newdeviceandsystemintegratedfromthenanoscale [14].The applicationofdeviceslikenanosensors,nanoparticles,anddeliverysystemtoagricultureandfoodhasthemostpromisinguse [15 19].Nanotechnologyhasmadeanimportantadvanceinbiomedicalandpharmacologyapplication.Thematerialanddevice aredesignwithahighdegreeoffunctionalspecificityandallow interactingwithcellandtissuesatthemolecularlevel [4,20]. Thesenanomaterialsaredesignedinsuchafashionthatthey interactwithcellsatthemolecular level.Thesesynthesizednanomaterialshavepropertiessuchasbeinghardtobreak,havehigh electricandthermalconductivity,andareveryreactivedueto theirsmallsize.Theeffectivenessofnanomaterialscanbe increasedbysurfacemodification,changingshapeandsizeand usingdifferentmaterials.
Pesticidesareusedinagriculturetoremovethepest,pathogens,andunwantedplantweeds,butthesepesticidesaccumulate inthesoilmakingthelandnon-fertileforagriculture [21 24]. Somepesticidesremaininthesoilwithoutanydegradationcausinglossofsoildiversityandthesepesticidesenterwaterbodies withsurfacewaterrunoffaffectingthemarineaquaticbiodiversity andcanenterthebodyofmarine animalcausingmutation,loss offertility,increasespH,andifthesepollutantsgetaccessinto drinkingwaterreservoircanenterhumancausingcancer,protein damage,ordamagetoDNA [23].Nanotechnologyhaspotentialto increaseproductivityofcrop,geneticimprovementinhuman,and liposomecanbeusedforgenetherapyaswellasfordrugdelivery.
Nanospheres,nanotubes,nanoparticlesofmetalandmetaloxides,andnanoencapsulesaresynthesizedfromdifferentsources
andusedagainstpathogensforbioremediation,removaloftoxic metals,nanoencapsulationoffertilizerandbiopesticides,nutrients,andgrowthhormonesinthefieldareveryusefulandreduce theexcesslossofagrochemicals.Applicationofnanotechnology toagriculture,medical,watertreatment,andtovariousfieldsis lesscostlyandeconomicalovertheconventionalmethod.
Inthischapter,wedescribetheapplicationofnanotechnologytoabiologicalsystemandenablethedevelopmentofanew classofbioactivesystems.
1.2Applicationofnanotechnology
Nanotechnologyhasvariousapplicationsindifferentfields. Nanobiosensors,Nanotubes,Nanoparticles,nanospherequantumdots,anddifferentnanomaterialshaveabroadrangeof applicationstobiologicalsystemsusedfornumerouspurposes inadifferentfield.Forinstance,inmedicalfieldsitisusedto studycancercellsandtoimprovedrugdeliverysystems.Inagriculture,itisusedtoimprovecropproductivity.Nanotechnology hasgreatpotentialinwaterandwastewatertreatmenttoimprove treatmentefficiency.Applicationofnanotechnologytobiological systemisdiscussedinthefollowingsections.
1.2.1Nanotechnologyinbiomedical
Nanotechnologyhasbeendiscoveredasamajorbreakthroughformedicalfields [25 30].Nanocapsulesandnanotubescanbeusedasadrugdeliveryvehicle;nanoprobesare synthesizedforcellimaging;andvariousnanoparticlesaresynthesizedfrombacteria,fungus,orplantfortheirantimicrobial activityagainstdisease-causingmultipledrug-resistantbacteria. Drugdeliveryusingnanoparticlesofferaccurate,effectivetreatmentagainstdiseases.Theapplicationofnanotechnologyin medicalfieldshavehelpedinthediagnosesofvariousdiseases.
1.2.1.1Drugdelivery
Themajorandmostcommonapplicationofnanotechnology inmedicalfieldsisfordrugdelivery [30 35].Usingnanotechnology,hydrophobicdrugscouldbedeliveredtothetargetsite, andalesseramountisrequiredbecausethedrugisdelivered directlyatthesiteofaction;drugdeliveryusingnanoparticlesis veryeffectivebecauseitcancrossthemembrane,andtheside effectoftheharmfulmedicationcanalsobeavoidedthrough capillaryactionandpenetrateddeeptothetargetsitetoshow
itseffect.Liposomescanbeusedfordrugdeliveryinsidethe cellastheycanpassthroughthelipidbilayer [36,37].Asliposomescrossthelipidbilayertheyarealsousedforgenetherapy. Drugorligandcovalentsareboundtothenanoparticlesand thenboundtothetargetcellhavingareceptorforaligandon theirsurface.Drugdeliveryusingnanoparticlesasavector hastheadvantagethatasthedrugspecificallykillsthetargetedcell,harmtonormalsurroundingcellsreduced,which mainlyhappensduetothetoxicityofthetherapeutic.When thesynthesizednanoparticlescoatedwithpolyethyl-glycol (PEG),thePEGincreasesitsaccumulationandcirculation timeinthebloodandalsoprotectsitfrombloodclearance andsurfacechangesduetotheactionofproteinorother enzymes [38,39] .
ManyresearchershavebeenworkingtoinhibitthereplicationofHIVfrompreventingAIDS;noneofthetreatmentcan cureHIVinfection.Evenhighlyactiveantiretroviraltherapy, whichconsistsofthreeantiretroviraldrugs,failedtheleadto viralresistance [40 42].LievenBaertetal.workedondevelopmentoflong-actinginjectableformulationwithnanoparticles ofrilpivirine(TMC278)forHIVtreatment [41].Nanosuspension ofnonnucleosidereversetranscriptaseinhibitorrilpivirinewere preparedasbaseorHClbywetmillinginanaqueouscarrier, andtheparticlessizewere200nm,400nm,and800nm.They foundonsingle-doseadministration,theplasmaconcentration showedtheconstantreleaseofrilpivirineover3monthsindogs and3weeksinmice.Theycomparedsubcutaneousandintramuscularinjectionsof5mg/kg(200nm)indogs,andresults showedthatthesubcutaneousroutehadthemoststableplasma levelwhile200nmnanosuspensionhadhigherandlessflexible plasmaconcentrationascomparedto400and800nmsuspension.Inmice,thepharmacokineticsof20mg/kg(200nm)were similartotwodifferentsurfactants,thatis,poloxamer338and Dalpha-tocopherylpolyethyleneglycol1000succinate.Fromthe followingresulttheyconcludedthat200nmsizedrilpivirine nanosuspensioncouldfunctionasalong-actinginjectable.
KatherineA.Redmondetal.workedonalltransretinoicacid nanodisk [43].Theysynthesizedthenanodiskofphospholipid bilayerassociatedwithATRAasadeliveryagentonhumanhepatomacell.ATRAisthederivativeofvitaminA,whichiswaterinsolubleandcontrolsthecellgrowthandapoptosisofacell.In cancercellstherearedefectsinthemechanismofretinoicacid [44].Intheirstudytheyfoundthatthenanodiskassociatedwith ATRAinhibitedthecellgrowthofhumanhepatomacellsand requiredfewerdosesasthesenanodisksinjectedintravenously.
WhereasLesegoTshweuworkedonnanoencapsulationofthe water-solubledrug,lamivudine,usingadoubleemulsionspraydryingtechniqueforimprovingHIVtreatment [11].Varioussecondarydiseasescausedbyvirusesduetoloweredimmunityof HIVpatients.Theantiretroviraldrugmayhavesideeffectsand toxicityaswell.Theydevelopedbiodegradablenanoparticlesas adrugdeliverysystemtoovercomethisproblemassociated withtheuseoftheantiretroviraldrug.Polyepsiloncaprolactone (PCL)nanoparticlesweresynthesizedbydoubleemulsionspraydryingmethodusingsolventandexcipient,loadeditwithlamivudine [45].Lamivudineisananti-HIVhydrophilicdrughaving aplasmahalf-lifeof5 6h.Drugreleaserateincreasedfor4 daysatpH1.3,pH4.5,andpH6.8,whichisverysignificant becausetheconditionissimilartothatwithinthegastrointestinaltract.ThisstudyshowsthepotentialofPCLloadedwith lamivudineforcontrolledrelease.Likewise,LebogangKatata etal.alsoworkedonthedesignandformulationofnanosized spray-driedefavirenzpartI:influenceofformulationparameters [46].Theproducednanoparticlesweremoralnanoencapsulation ofefavirenz,whichiswater-insolublenonnucleosidereverse transcriptaseinhibitorusedinHIVtreatment.
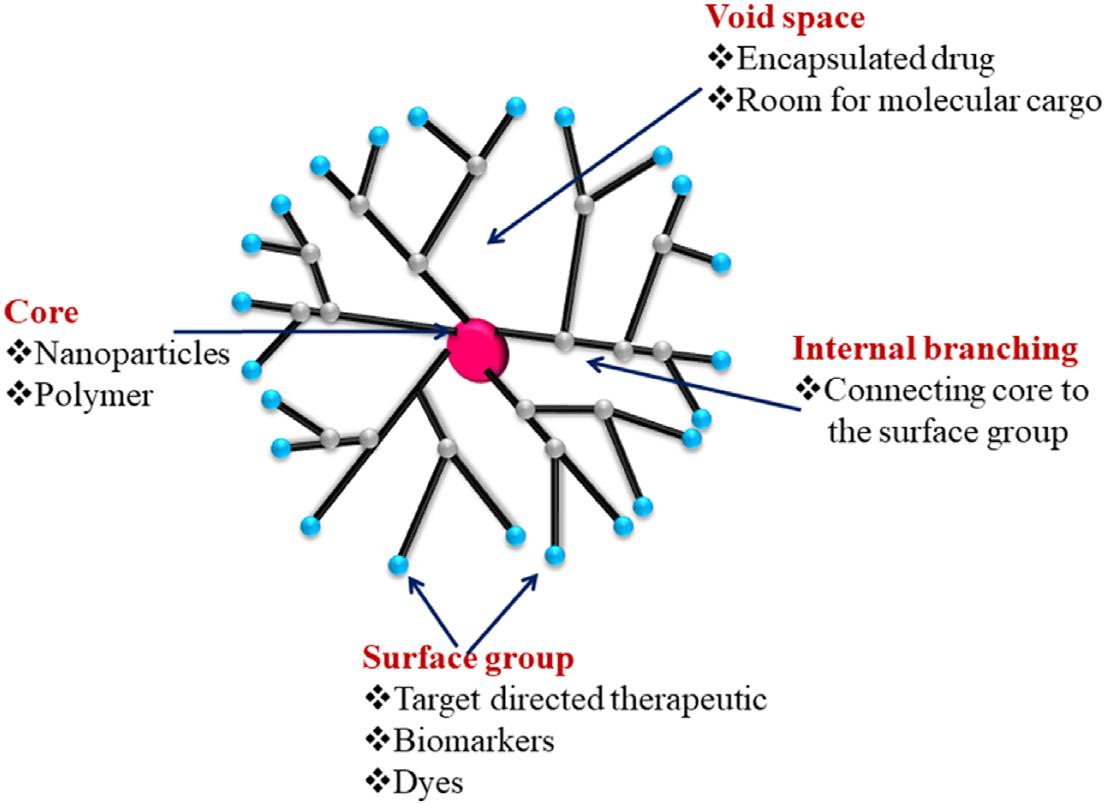
Researcherssynthesizeddifferentnanoparticlestofacilitate drugdelivery.Dendrimersarealsousedfordrugdelivery [47,48]. Theyarehavingbranchstructureandtheirsizeissimilartoprotein(Fig.1.1).Asdendrimerswithalargesurfacearedifferent therapeuticorbiologicallyactivecompoundsareattachedand delivered.Dendrimercanuseforimagingalso,alsoforthe
Figure1.1 Dendrimers showingthedifferentgroups andspaceforthedrug delivery [48].
identificationofdetectedcellbyattachingbiomarker.Biosensors notonlyhaveapplicationsinagriculturebutcanalsohaveapplicationsinthemedicalfield.Forexample,theycanbeusedto monitorbloodglucoselevelinblood.Notonlytheglucoselevel buttheyareusedtocontrolthecholesterol,thyroid,andurea level.Nanobiosensorscansensethechangeinleveltotake thenecessaryaction.Also,nanoencapsulescanbeusedfor controlled-releaseenzymeswheneverthereisthechangeinthe concentrationinthebody,forexample,insulinreleaseinthe bodytomaintainthebloodglucoselevelinthebody.ClaudiaR. Gordijoetal.workedonNanotechnology-EnabledClosed-Loop InsulinDeliveryDevice:InVitroandInVivoEvaluationof Glucose-RegulatedInsulinReleaseforDiabetesControl.They usedthebioinorganicnanocompositemembrane,whichreleases theinsulininresponsetotheglucoselevelinblood [49].
1.2.1.2Bioimaging
Nanotechnologyalsocanbeusedforthetreatmentofdiseasesinthesymptomlessstage.Fordiseaseslikecancer,ifidentifiedataveryearlystage,itcouldbeeasytotreatthepatient [50].Imagingofcanceratanearlystagehelpsinearlyrecognitionofthedisease.Quantumdotcanbeusedforcancercell imaging.Thesecrystalsemitlightwhenstimulatedwithlight. Thisnanodevicecanbeusedtoidentifytheparticularregionin theDNAthathelpsinidentifyingthecellthatisalteredorto identifythecelldifferentfromothernormalcellstodistinguish betweennormalandmutatedcell.Thequantumdotsgivea wealthofinformation,whichishelpfulinrecognition/identification.Thatiswhythequantumdothasapplicationincancer treatment.Butquantumdotsmayhavesometoxicity,socarbon dotsareusedforcancercellimaging [50 53].SusantaKumar Bhuniaetal.workedontheImagingCancerCellsExpressing theFolateReceptorwithCarbonDotsProducedfromFolicAcid [52].Carbondotwassynthesizedusingfolicacidasacarbon sourceandtheseC-dotsthenbindtotargetcancercells,which expressedthefolatereceptorsandfluorescentwhenstimulated withlight.Henceitiseasytodistinguishcancerthroughbioimagingandhelpinthediagnosisofcancer.Goldnanoparticles (AuNPs)arealsousedforbioimaging.Carbondotsaresynthesizedbyusingnaturalprecursorandusedinbioimagingor manymedicalfields [54 57].
Ji-HoParketal.workedonMicellarHybridNanoparticlesfor SimultaneousMagnetofluorescentImagingandDrugDelivery [58].Intheirworktheycreatedhybridnanoformulationwhich
consistsofquantumdotsandmagneticironoxidenanoparticlesandalsodoxorubicin,ananticancerdrugwithinmicellar madeupofpolyethyleneglycol.Thismicellarhybridnanoparticleenablesthedetectionofcancerortumorcellsbynearinfraredfluorescenceimagingandmagneticresonanceimaging (MRI)oftissuesandtheirtreatmentbytargetdrugdelivery. Variousmultifunctionalnanoformulationcanbesynthesized, whichcanworktwoormoresimultaneously.
Today,computedtomography(CT)imagingisusedbydoctorstocheckifthereisanydamagefromatumorinsidethe bodyandfordiagnosis.InCTimagingiodineisusedasacontrastagent.ButCTimagingisnotspecific,andalsoonceiodine getsclearedbykidneythenimagingisnotpossible [59].
RachelaPopovtzeretal.workedonTargetedGoldNanoparticles EnableMolecularCTImagingofCancer.Theysynthesizedgold nanorodsandconjugateditwiththeUM-A9antibodyandused thisagainstsquamouscellcarcinoma [59].Thesynthesized AuNPsconjugatedwithUM-A9antibodybindstothecancer cellsandgavedistinguishCTimageasAuNPsattachedtoa cancercellinhighdensitythanthattoothertissues.Thisway theAuNPscouldhaveprovedtobemolecularimagingofcancer cellsandalsothesizeofthecancercell [60].
1.2.1.3Nanotechnologyfordiagnosisandtreatment
Nowadays,theuseofAuNPsforcancerdiagnosisbecauseof theirnontoxicitytothebody.ThesurfaceofAuNPsismodified withpolymerortherapeuticagents,whichspecificallytarget cancercells.Thenanoparticlesselectivelyinvadethecancer cell,andafterinvadingthetherapeuticdissociateandrelease thetoxin,resultinginapoptosisofcancer.Thisisusedtotreat tumorsthatcannotberemovedbysurgery.MoustafaR.K.Ali etal.studiednuclearmembrane-targetedAuNPsthatinhibit cancercellmigrationandinvasion [61].Resultsobtained showedthatAuNPshadheldbackcancercellinvasionspeedas wellasinhibitmetastasis,whichcauseddeathinmostcancer patients.TheyfoundthattheAuNPswhichweretrappedinthe nuclearmembraneincreasedthestiffnessofthenucleusand thusretardedcancercellinvasion.TheAuNPcanalsobeused asatoolforcancercellimagingoverCTscan,MRI,andX-rays. RachelaPopovtzeretal.alsomentionedtheuseofAuNPsfor molecularimagingofcancercell [59].
Metalslikecopper,silver,gold,brassnickel,iron,etc.exhibit antimicrobialactivityagainstawidenumberofmicroorganism capableofcausingdiseases [59 64].Butahighlevelofsome
metalinthebodycanbetoxic.Sousingnanotechnology,nanoparticlesofthesemetalsbemadeandused.Thenanoparticles canpenetratedeepinsidethecellandinthecapillary,andshow itsactioneveninminuteconcentrations.Researcherfoundvariousapplicationofnanotechnologytodealwithvirusesanddiseasescausingbacteria.Forinstance,PonnusamyManogaran etal.studiedmycosynthesis,characterization,andantibacterial activityofsilvernanoparticles(AgNPs)againstmultidrugresistant(MDR)bacterialpathogensoffemaleinfertilitycases [65] AgNPsweresynthesizedfromfungusoxysporumNGDandcharacterizedthemusingX-diffraction,scanningelectronmicroscopy,UV Visspectroscopy,energydispersivespectroscopy.The resultsoninhibitorypotentialofAgNPson Pseudomonasaeruginosa,Klebsiellapneumoniae,Enterobacterspp.,and Escherichia coli.showedthatAgNPshavehighinhibitoryeffectagainstthese bacteria.OtherthanAgNPs,whicharecoupledwithampicillin, alsoshowinhibitoryaction.Theyfoundthatascomparedto AgNPs,AgNPscoupledwithampillinesensitizethebacteriamore. MarwahM.Mohamedetal.studiedtheantibacterialeffectof AuNPsagainst Corynebacteriumpseudotuberculosis [66].Thecausativeagentofchroniccaseouslymphadenitisingoatsandsheep is C.pseudotuberculosis.TheyusedAuNPsandAuNPscombined lasertherapyagainstthisbacterium.TheyfoundthattheAuNPs penetratedeepinsidethecellwallandthelasercombinedtherapy helptoimprovetheantibacterialeffectofAuNPs.
G.PrasannarajandP.VenkatachalamstudiedonEnhanced Antibacterial,Anti-biofilmandAntioxidant(ROS)Activitiesof BiomoleculesEngineeredSilverNanoparticlesagainstClinically IsolatedGramPositiveandGramNegativeMicrobialPathogens [67].Intheirstudy,theyused10speciesofmedicinalplantsuch as Alstoniascholaris,Andrographispaniculata,Aeglemarmelos, Centellaasiatica,Ecliptaprostrata,Moringaoleifera leavesand barksof Thespesiapopulnea,Terminaliaarjuna androotbarkof Plumbagozeylanica,and Semecarpusanacardiumnuts tosynthesisAgNPs.Thesynthesizednanoparticleswerethentestedfor theirantibacterialandantibiofilmactivityagainstbacterialspecies Staphylococcusaureus,Staphylococcusepidermidis,P.aeruginosa,E.coli,K.pneumoniae,Proteusvulgaris,whichwere isolatedfrompatients.Theresulttheyobtainedshowedthat AgNPssynthesizedfromthesemedicalplantsareveryeffective asantibacterialandalsoinhibitthebiofilmformationby S.epidermidis and P.aeruginosa,andalsoincreasetheantioxidant generation.SimilarstudywasperformedbyU.Jinuetal.biofabricationofCubicPhaseSilverNanoparticlesLoadedwith Phytochemicalsfrom Solanumnigrum LeafExtractsforPotential
Antibacterial,AntibiofilmandAntioxidantActivitiesagainstMDR HumanPathogens.TheysynthesizedAgNPsfromleafextractof S.nigrum [68].Thesestudiesshowedthatnanoformulationof plantextractveryeffectiveagainstMDRstrainandarerequired inaverysmallamounttoitseffect.
1.2.1.4Nanotechnologyfortreatmentofcancer
Cancerdefinedasamultistepcarcinogenesisprocessrequiringvariousphysiologicalarrangementssuchascellapoptosis andimaging,causingitahighlyuncoherentandcomplexdisease.Themajorfactorforthebetterorsuccessfultreatmentof cancerisitsearlydetection.Chemotherapy,surgery,andradiationtherapyarethelimitedcancertreatment.Togetmore achievementtowardthetreatmentofcancerpatients,nanotechnologycanplayanimportantroletoredefineitinbetter, cheaper,andeasierways [69 71].
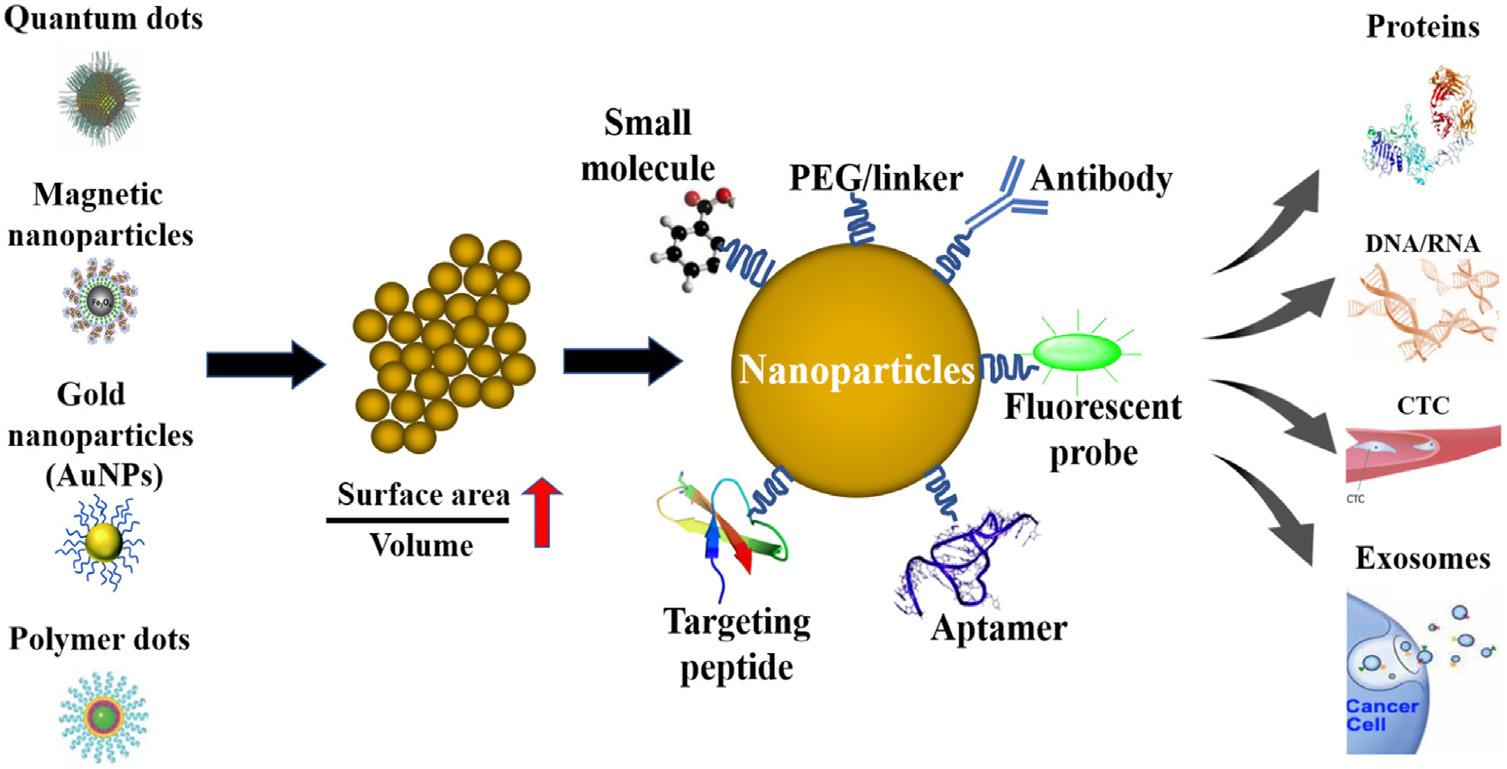
Oncomparingwiththebulkmaterials,largesurfaceareato volumeratioofnanoparticlemakesthemapotentialcandidate forthecancerdetectionshownin Fig.1.2.Insomecancers, bothradiotherapyandchemotherapyremainineffective.Today, therearelotofresearchgoingonfortheuseofnanotechnology incancertreatment.Nanoparticlescandetectcancerinearly stagebyattachingtocancermarkertargetingantibodies.This opensadoorfornanotechnologytowarditsapplicationsfor cancertreatment.Therearevarioustherapybasedon
Figure1.2 Nanotechnologyimprovescancerdetectionanddiagnosis [71].
nanotechnologyhavebeenusedforthetreatmentofcancer. Fewofthemareexplainedbelow:
1. Nanotechnology-basedphotodynamictherapy(PDT):Itis basedontheactivationofphotosensitizer.Inthis,aspecific wavelengthoflightcausesareleaseofreactionoxygenspeciestokillcancerouscellaswellastumor-associatedvasculature.Itleadstobreakingoftumorinfraction.UseofpH sensitivenanoparticleasapotentialcandidatefortumortargetingandPDTwasperformedbyPengetal. [72]
2. Nanotechnology-basedgenetherapy:Thistherapyrelieson theconceptthattoproduceatumoricidaleffect,aspecific exogenousgenecanbeplacedintothetumorcellgenome. Thistherapyisoneofthemostrapidlyimprovinganddevelopingareasinclinicalcancerresearch.Jereetal. [73] have efficientlydeliveredAkt1small-interference-RNA-loadedbiodegradablenanopolymericcarrier,leadingtosilencingof Akt1proteinandreducedcancercellsurvival,proliferation, malignancy,andmetastasis.
3. Nanotechnology-basedcancertheragnostics:Theragnostics isthecombinationofdiagnosisandtherapyusedinthebiomedicalfieldforcancertreatment.Theprimarygoaloftheragnosticsistodeveloptherapeuticaccuracyforselectively target-specific(diseased)tissuesorcellstomakethemsafer, shorter,andmoreefficient.Shimetal.showsthetheragnosticstudiesforcancertreatment [74].Theyhavecoated AuNPsonsmall-interfering-RNA-encapsulatingpolyplexes viaacid-cleavablelinkagestoexplorethepossibilityofgettingcombinedstimuli-responsivemultimodalopticalimagingandstimuli-enhancedgenesilencing.
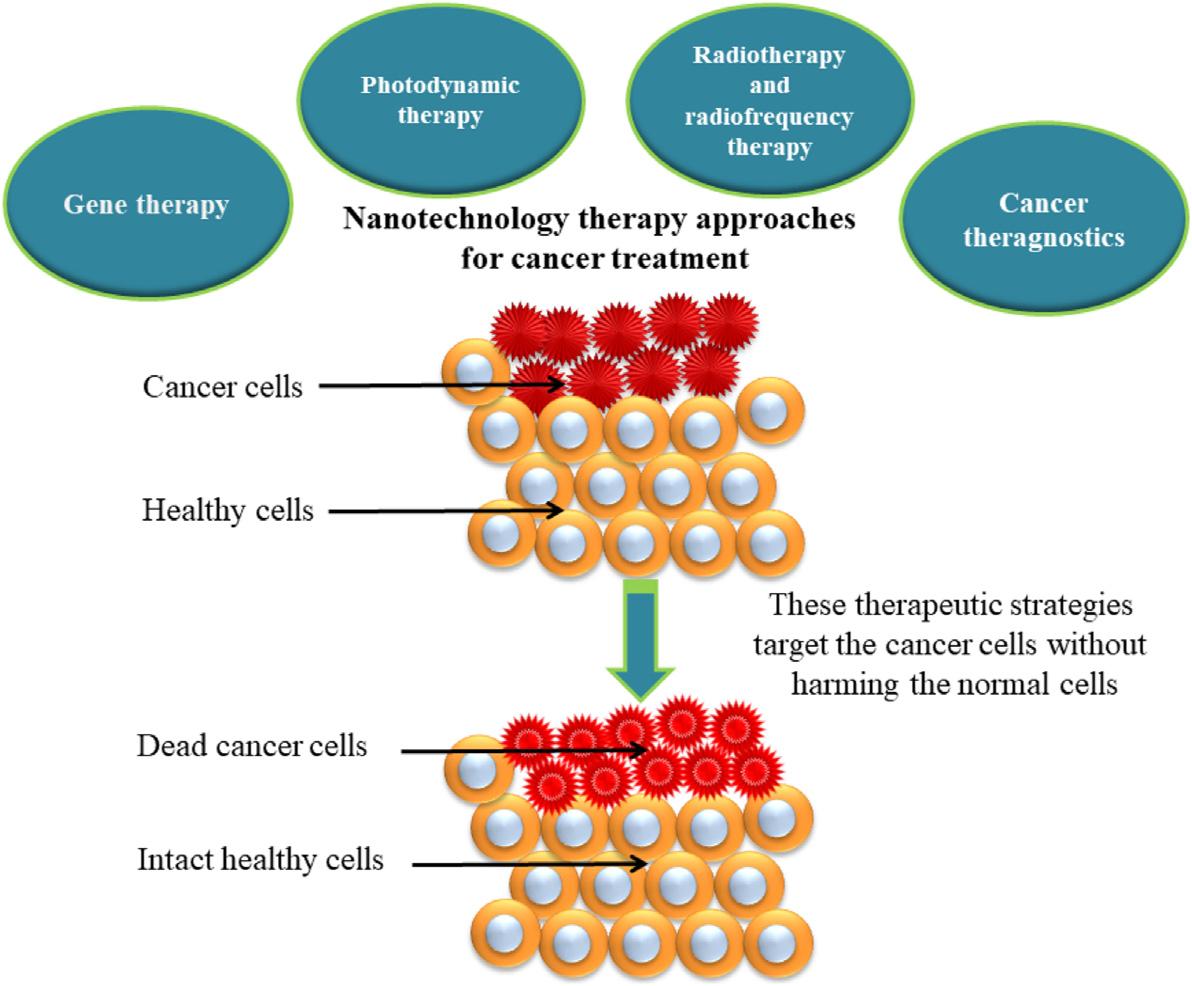
4. Nanotechnology-basedradiotherapyandradio-frequencytherapy:Fromlongtimeuseofhighatomicnumberhasbeenused fortheenhancementofradiationdose.Fortheclinicalusefulness,aradiosensitizershouldbeeasilyutilized,readilyavailable, nontoxic,andhavehightherapeuticratio.Nanogold(AuNPs) showeddose-enhancingeffectsincellexperiments.Changetal. [75] haveinvestigatedthedose-enhancingeffectandapoptotic potentialofAuNPsincombinationwithsingle-doseclinicalelectronbeamsonB16F10melanomatumor-bearingmice. Forcancerandothermedicalapplications,threeimportant functionsrequiresareimagingwithsingleanddualmodality, targetingusingoneormoreligandsanduseofdifferenttherapy (Fig.1.3).Itgivesvariousopportunitiesforthetuningofdifferentpropertiesthatareimpossibleforothertherapeuticdrugs. Becauseofthistheyhaveabrightandlongfuturetowardthe cancertherapeutics.
1.2.1.5Nanotechnologyingeneticmaterialsequencing
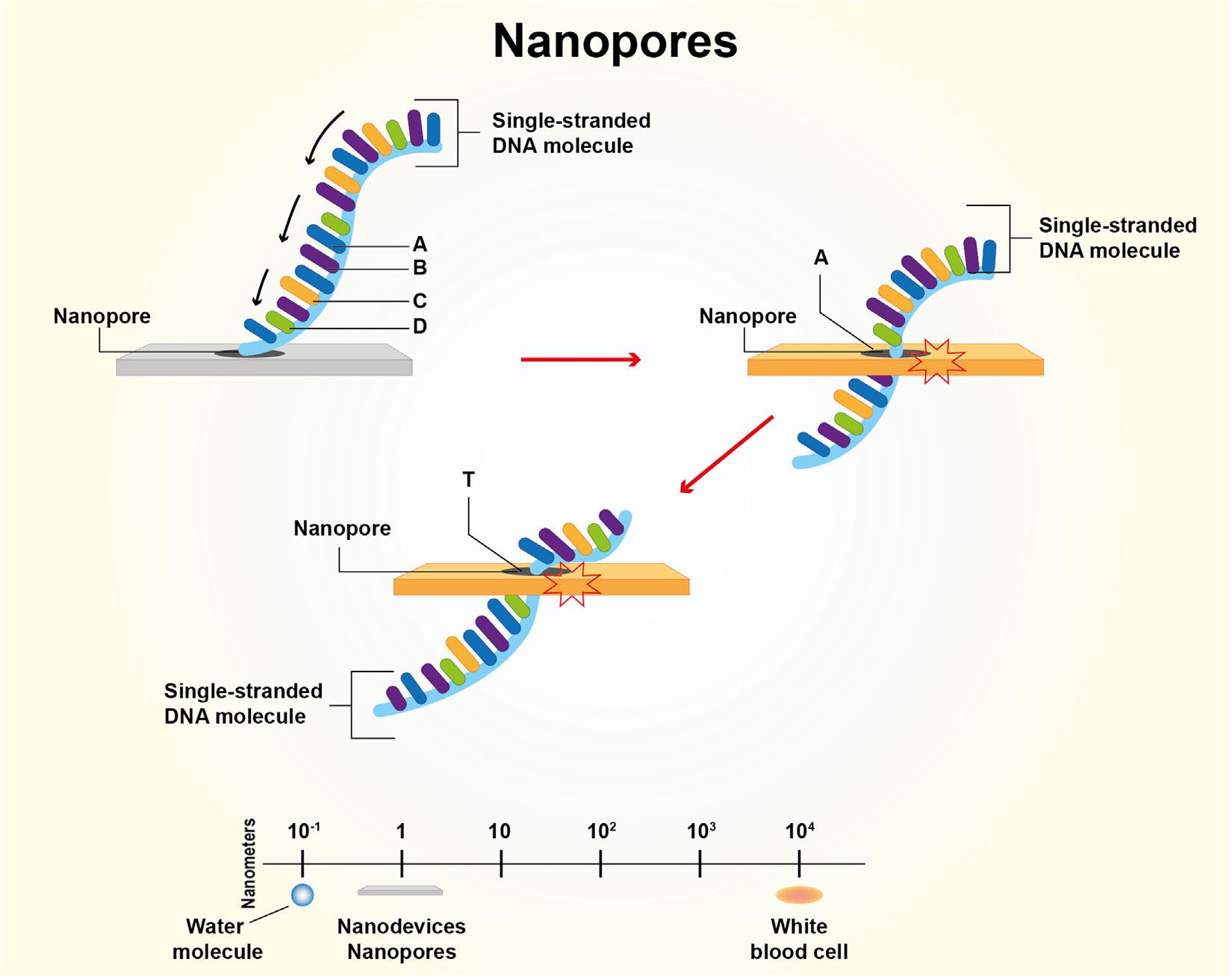
Nanoporetechnologyisanotheremergingaspect.Nanopore technologyisusedforsequencingDNAorRNA [76 78].Ituses polymermembranecontainingproteinnanopores,whichareelectricallyresistant.AnyonestrandofDNAorRNAisallowedtopass throughthenanopore,andthechangeincurrentdependson whichbasepasses.Itoffersquickandreliablesequencinginvery lessercostascomparedtotheconventionaltechnique.Thisnanoporetechnologyfortheidentificationofcancer,ascancercellmay differentDNAsequenceascomparedtoothernormal(Fig.1.4)so offerearlyidentification.Notonlyforcancercellidentificationbut thistechniquecanbeusedforwholegenomeidentificationof virusesorbacteria,detectionofanymutationinhumangenome, etc.Thistechniqueoffersquick,rapidanalysisoftheDNA sequence.Moleculardiagnosticsareapartofgeneticmaterial sequencingandalsoextendsitslimitstonanoscaleusingnanotechnology.Conversionofnucleicacid intostringsofnucleotidesusing nanoporetechnologyandthendirectlyintoelectronicsignalshas alsobeenanalyzed [79].
1.2.1.6Nanotechnologyinbiosensors
Nanobiosensorsarethesmallbiosensorsincorporatedinthe biologicallyderivedsensitizedelementslinkedtophysicochemical
Figure1.3 Applicationof differentnanotechnology therapyforcancertreatment [71].
Figure1.4 Nanoporeactingasananodeviceforreadinggeneticcode [50].
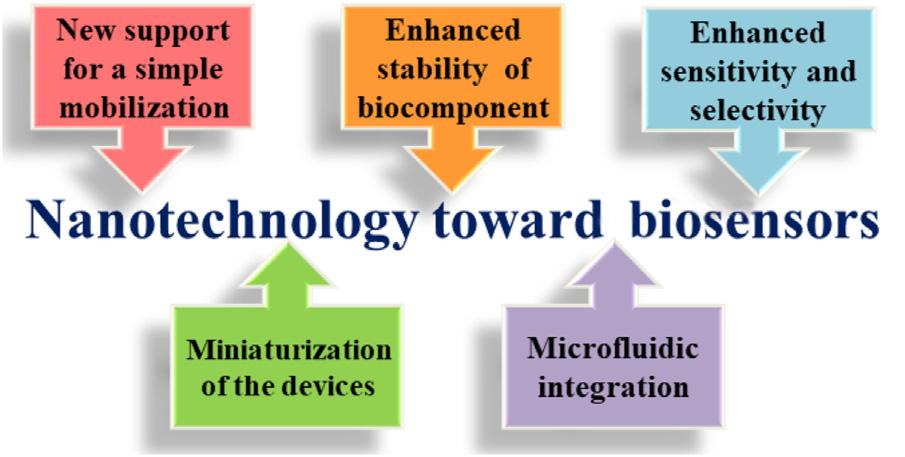
Figure1.5 Advancementin nanotechnologytoward biosensorapplication.
transducersandusedtodetectthepresenceorconcentrationof variousmolecules,toxiccompounds,ormicroorganisms. Biosensorscompriseofbioreceptorsandtransducers,whichsense elements,andtransducersdetectthissignalandconvertthesignal toelectricsignal [80,81].Applicationofnanotechnologytowardthe biosensorhasbeenshownas Fig.1.5
Ifthecompoundsorpathogensarepresentinasmallnumber,nanobiosensorcaneasysenseandproduceasignal.They candetectthepresenceofcompoundspresentintheminute concentrationintheenvironment.Therearedifferenttypesof biosensorsdevelopeddependingontransducingmechanism.
BiosensorsTransducing
ResonantbiosensorsAnacousticwavetransducersiscoupledbioelements,which measurethefrequencychangeduetochangeinthemassof membranetowhichbioelementattached.
OpticalbiosensorsSignalmeasuredislight.Thechangeinrefractiveindexofthe mediumduetochangeintheabsorbanceorfluorescence causedinthereaction.
Thermaldetection biosensors
Ion-sensitive biosensors
Electrochemical biosensors
Amperometric biosensors
Potentiometric biosensors
Inbiologicalreaction,heatgenerateschangesthetemperature ofthemediuminwhichreactionhappens.Thebiosensor sensesthetemperature.Measurementoftemperatureof temperatureisdoneusingthermistors,thatis,enzyme thermistors.
Theyaresemiconductorfieldeffecttransistorhavingionsensitivesurface.Whenionandsemiconductors,thesurface potentialchangeswhichmeasured.
Ionsorelectorsproducesinthechemicalreactionchangesthe electricpropertiesofthesolution.Electrochemicalbiosensors areusedtomeasurethisvariation.
Thesebiosensorssenseelectroactivetypeinthebiological samples.
Measurestheoxidationorreductionpotentialofthe electrochemicalreaction.
1.2.1.7Nanotechnologyincontrolledrelease
Apartfromtheuseofabiosensor,differentcarriervehiclesare usedforcontrolledreleaseofagrochemicalinthefield.Thesecarriervehiclesareeasybiodegradable,cheap,andlowtoxic.Theuse ofcontrolled-releasesystemtoagricultureallowcontrolleddeliveryofagrochemical,whichreduces thequantitiesofagrochemical requiredandsoreducesthetoxicitytohumanhealthandenvironment.Biofertilizersconsistoflivingmicroorganisms,whichhelps toconvertorganicmaterialintosimplecompoundessentialfor plantgrowth,maintainthefertilityofsoil,increasescropyield, andmaintainssoilquality.ButthesearetemperatureandpHsensitive.Sothecontrolled-releasesystemreducesthelossofagrochemicalsduetoleaching,evaporation,andotheraspects [82 86].Nanocapsulesaremade,whichactasacarriervehiclefor
controlledreleaseofvarious agrochemicalsinthefield. Nanocapsulesarethehollownanoparticles,whicharemadeupof nontoxicpolymer.Fertilizerandpesticidesareencapsulatedfor controlledrelease.Theoutershellprotecttheagrochemicalfrom damagebyvariousouterfactorpresentinsurroundingandhelps topenetratedeepinthetissue.Theopeningoftheshellcanalso becontrolledbychangingtheexternalenvironment.Liposomes andpolymershavebeenmadeforthispurpose.
Estefa ˆ niaVangelieRamosCamposetal.workedonPolymeric andSolidLipidNanoparticlesforSustainedReleaseof CarbendazimandTebuconazoleinAgriculturalApplications [87]. Intheirstudytheyusedcarbendazimandtebuconazole,which arecommonlyusedasafungicidalintheagriculturalfield.They preparedthesolidlipidnanoparticlesandpolymericnanocapsulesasacarriersystemforthemixtureofcarbendazimand tebuconazole.Theythenobservedforthereleaseprofileofthese fungicidesandalsofortheircytotoxicity.Theyfoundthatboth thenanoparticlesshowed99%associationefficiencyandthere wasadecreaseincytotoxicityofthesefungicides.Similarly, JhonesLuizdeOliveiraworkedonSolidLipidNanoparticlesColoadedwithSimazineandAtrazine:Preparation,Characterization, andEvaluationofHerbicidalActivity [88].Theyusedatrazineas wellassimazineherbicidesfortheirstudy.Solidlipidnanoparticles,havingtheseherbicides,wereprepared.Theyfoundthatuse ofsolidlipidnanoparticlesimprovedthereleaseprofileofthese herbicidesinwater.Thetreatmentofspecies Raphanusraphanistrum withthenanoparticlescontainingherbicidesshowedthe effectivenessofthisformulation,andthetoxicityoftheseherbicidesinthepresenceofsolidlipidnanoparticleswasdecreased.
HarrisonWanyikaworkedonsustainedreleaseoffungicide metalaxylbymesoporoussilicananospheres [89].Heused nanoparticlesforthedeliveryofthepesticides.Hepreparedthe mesoporoussilicananoparticlesbysol gelprocessandloaded metalaxylmoleculesintotheporesofmesoporoussilicananoparticlesbyarotaryevaporationmethod.Hefoundthatnearly 76%offreemetalaxylwasreleasedinthesoilwithin30days whileonly47%ofmetalaxylwasreleasedbymesoporoussilica nanoparticlesinthesoilwithinthesametimeperiod.This showsthattheuseofnanoparticleasacarrierforthecontrolled releasecansignificantlydecreasedtheirreleaseinsoil.
SrinivasaRaoYearlaandKolliparaPadmasreeworkedon Exploitationofsubabulstemligninasamatrixincontrolledreleaseagrochemicalnanoformulations:acasestudywithherbicidediuron [90].Inthisstudytheyexploitedtheabilityofsubabul stemligninasamatrixmaterialforagrochemicalformulation.
Theyemployedthenanoprecipitationmethodthenoptimizedto fabricateastableherbicide“diuronnanoformulation”(DNF).This optimizedDNF(ODNF)havenonlinearbiphasicreleasenature fordiuron.ODNFefficiencyforreleaseofdiuronwastestedusing Canola (Brassicarapa). B.rapa seedlingwasgrowninthesoilsupplementedwithODNF.Theyobservedthatthe B.rapa showed earlysignofleafchlorosisandmortalityinsoilcomparedwith B.rapa growninthesoilsupplementedwithcommercialdiuron formulationandbulkdiuron.Throughthisstudytheyalsoconcludedthatsubabulstemlignincouldbeutilizedasamatrixfor anotheragrochemicalalsowhichareassociatedwithgrowthand developmentoftheplant.Similarly,El-RefaieKenawyandM.A. SakranalsoworkedonControlledReleaseFormulationsof AgrochemicalsfromCalciumAlginate [91].Intheirstudy,calcium alginatewasusedasamatrixforcontrolledreleaseof1naphthaleneaceticacidandpentachlorophenolwhichactasa growthregulatorandplantherbicide(Fig.1.6).Inadditionthey alsousedpoly(ethyleneimine)(PEI)forcoatingalginatebeads. TheyfoundthataftercoatingthegelbeadsbyPEI,thereleaserate fromthegelbeadsretarded.Thereleaserateaftercoatingvaried completely.SothecoatingofbeadswithPEIcanincreasethe durationofthereleaseofagrochemical.
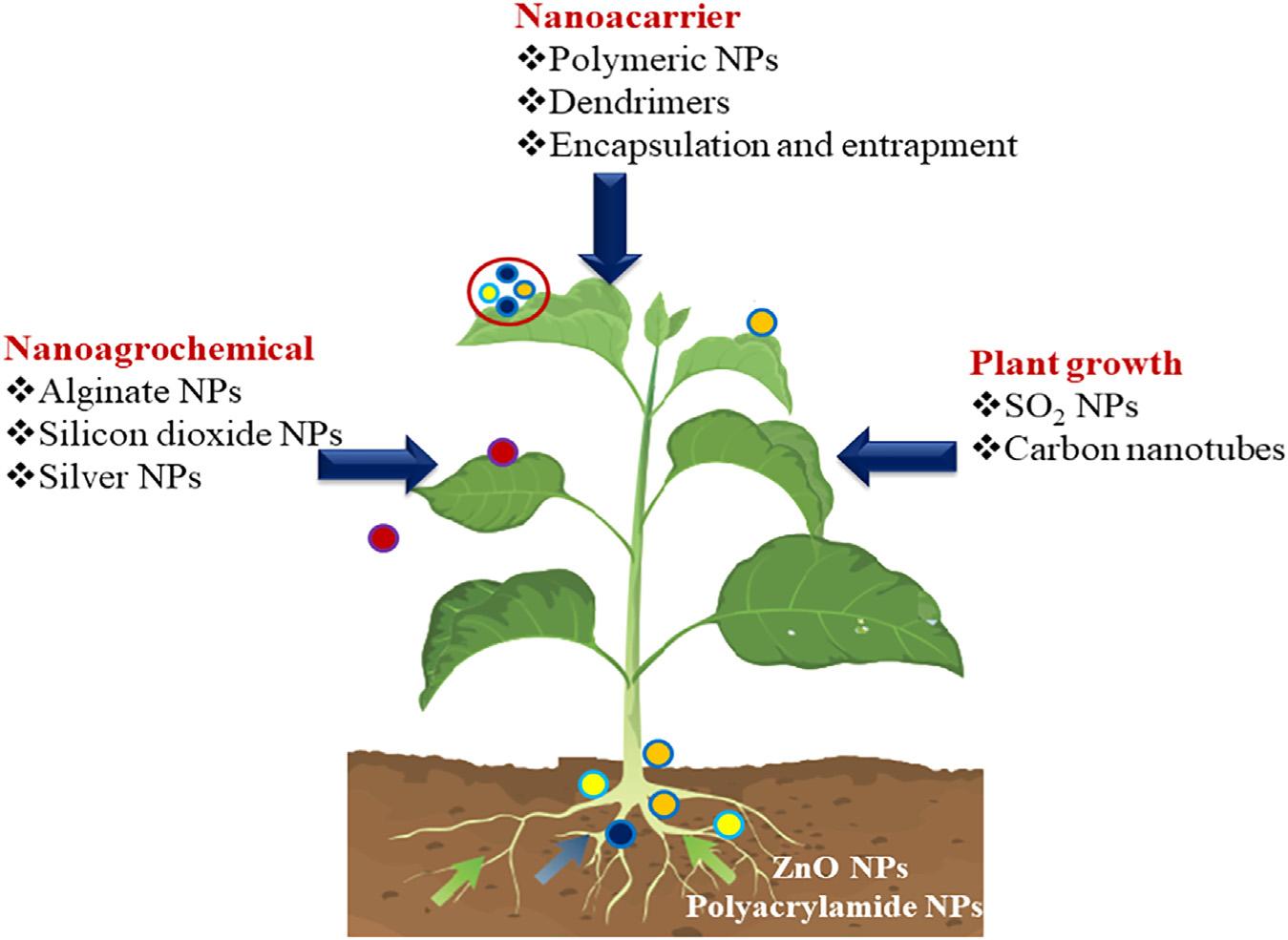
Figure1.6 Interactionofdifferentnanoparticleswithplant.
1.2.1.8Nanotechnologyinbioremediation
Bioremediationisuseofmicrobesforremovalofpollutant fromenvironment.Pesticidesandherbicidesareusedtoprotect theplantfromdiseasesandfromattackbypests.Butthesepesticidesgetaccumulatedintheenvironment.Nanotechnology playsthekeenroleinthecleaningoftheenvironment. Nanotechnologyhasapplicationinthebioremediationofpollutantssuchasresistantpesticides [92 95].Accumulationof thesepesticidescanaffectthesoilqualityoftheagricultural fieldanddisturbthebiodiversityofsoilmicroflora,whichhelps inthefixationofvariouselementsinthesoil.Thispollutant comesfromvariousindustries,agriculture,anddomesticwaste, andfromthedegradationofanorganiccompoundandthis resistantpollutantorcompoundpersistsforalongertimeand hasaharmfuleffectontheenvironmentaswellasonthe humanandanimalhealth.Titaniumdioxide(TiO2)enhances thegrowthandphotosynthesisinplantandalsoshowsitsactivityinthedegradationofpesticides.ManymetaloxidenanoparticleslikeZnO,CuO,andTiO2 nanoparticlescanbeusedfor removalofresistantpesticides(Fig.1.7) [94,95].Ifthese
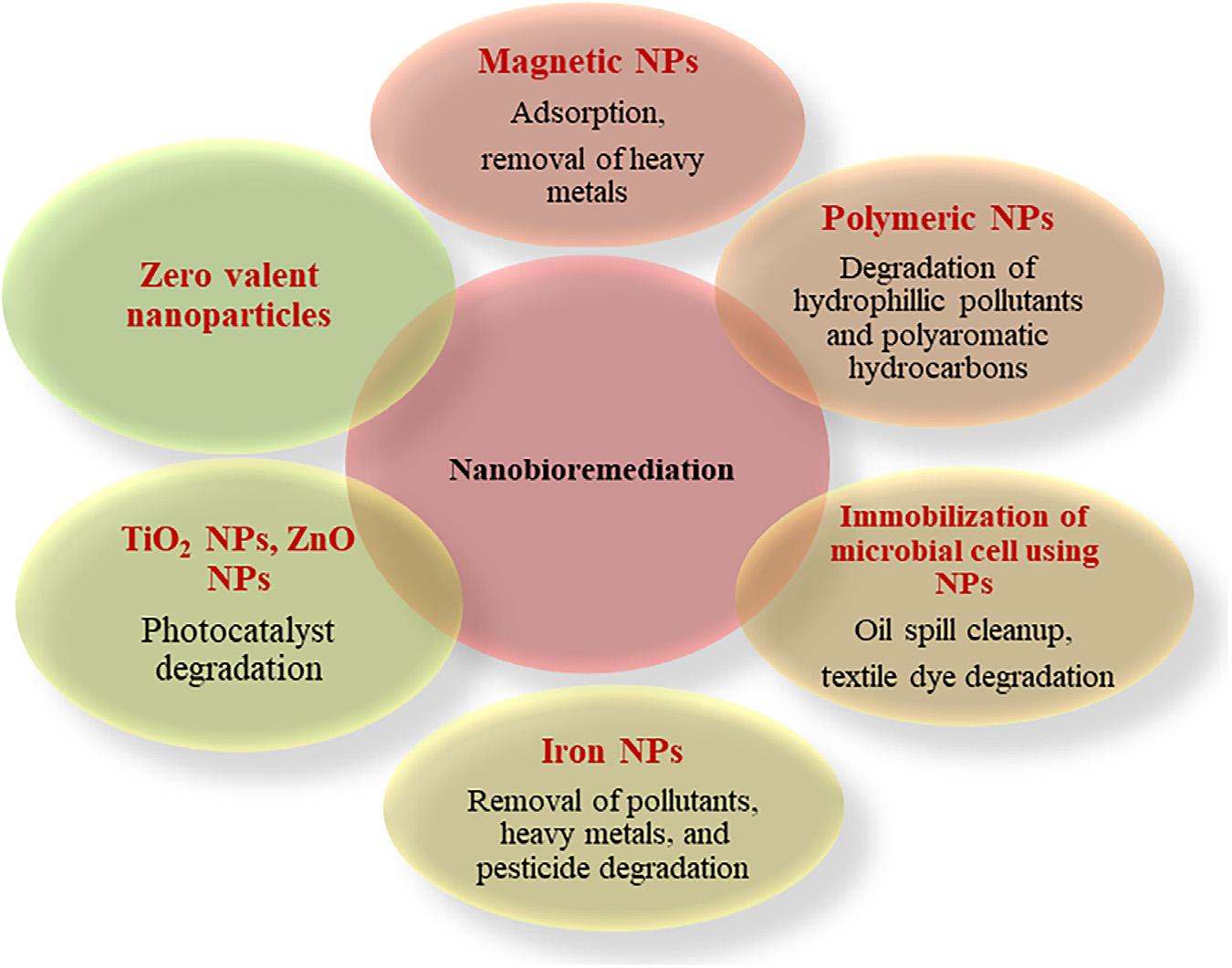
Figure1.7 Nanoparticlesforbioremediation.