https://ebookmass.com/product/modelling-of-flow-andtransport-in-fractal-porous-media-1st-edition-jianchao-caieditor/
Instant digital products (PDF, ePub, MOBI) ready for you
Download now and discover formats that fit your needs...
Petrophysical Characterization and Fluids Transport in Unconventional Reservoirs Jianchao Cai
https://ebookmass.com/product/petrophysical-characterization-andfluids-transport-in-unconventional-reservoirs-jianchao-cai/
ebookmass.com
Multiphase Fluid Flow in Porous and Fractured Reservoirs 1st Edition Wu
https://ebookmass.com/product/multiphase-fluid-flow-in-porous-andfractured-reservoirs-1st-edition-wu/
ebookmass.com
Wave Fields in Real Media: Wave Propagation in Anisotropic, Anelastic, Porous and Electromagnetic Media 4th Edition José M. Carcione
https://ebookmass.com/product/wave-fields-in-real-media-wavepropagation-in-anisotropic-anelastic-porous-and-electromagneticmedia-4th-edition-jose-m-carcione/ ebookmass.com
Vesuvius, Campi Flegrei, and Campanian Volcanism 1st Edition Benedetto De Vivo (Editor)
https://ebookmass.com/product/vesuvius-campi-flegrei-and-campanianvolcanism-1st-edition-benedetto-de-vivo-editor/
ebookmass.com
Veerarajan
https://ebookmass.com/product/linear-algebra-and-partial-differentialequations-t-veerarajan/
ebookmass.com
eTextbook 978-0136026884 Public Personnel Management
https://ebookmass.com/product/etextbook-978-0136026884-publicpersonnel-management/
ebookmass.com
Corsairs: Bethiah (Corsair Brothers Book 5) Ruby Dixon
https://ebookmass.com/product/corsairs-bethiah-corsair-brothersbook-5-ruby-dixon/
ebookmass.com
Nature-inspired computing paradigms in systems : reliability, availability, maintainability, safety and cost (RAMS+C) and prognostics and health management (PHM)
Michael G. Pecht (Editor)
https://ebookmass.com/product/nature-inspired-computing-paradigms-insystems-reliability-availability-maintainability-safety-and-costramsc-and-prognostics-and-health-management-phm-michael-g-pechteditor/ ebookmass.com
Post-transcriptional Gene Regulation in Human Disease
Buddhi Prakash Jain
https://ebookmass.com/product/post-transcriptional-gene-regulation-inhuman-disease-buddhi-prakash-jain/
ebookmass.com
Taking 8th Edition, (Ebook PDF)
https://ebookmass.com/product/bates-pocket-guide-to-physicalexamination-and-history-taking-8th-edition-ebook-pdf/
ebookmass.com
ModellingofFlowandTransport inFractalPorousMedia ModellingofFlowand TransportinFractal PorousMedia Editedby
JianchaoCai
StateKeyLaboratoryofPetroleumResourcesandProspecting, ChinaUniversityofPetroleum,Beijing;InstituteofGeophysicsandGeomatics, ChinaUniversityofGeosciences,Wuhan,China
LiehuiZhang
StateKeyLaboratoryofOilandGasReservoirGeologyandExploitation, SouthwestPetroleumUniversity,Chengdu,China
WeiWei InstituteofGeophysicsandGeomatics,ChinaUniversityofGeosciences, Wuhan,China
Elsevier
Radarweg29,POBox211,1000AEAmsterdam,Netherlands
TheBoulevard,LangfordLane,Kidlington,OxfordOX51GB,UnitedKingdom 50HampshireStreet,5thFloor,Cambridge,MA02139,UnitedStates
© 2021ElsevierInc.Allrightsreserved.
Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproducedortransmittedinanyformorbyanymeans,electronicor mechanical,includingphotocopying,recording,oranyinformationstorageandretrievalsystem,without permissioninwritingfromthepublisher.Detailsonhowtoseekpermission,furtherinformationaboutthe Publisher’spermissionspoliciesandourarrangementswithorganizationssuchastheCopyrightClearance CenterandtheCopyrightLicensingAgency,canbefoundatourwebsite: www.elsevier.com/permissions.
ThisbookandtheindividualcontributionscontainedinitareprotectedundercopyrightbythePublisher(other thanasmaybenotedherein).
Notices
Knowledgeandbestpracticeinthisfieldareconstantlychanging.Asnewresearchandexperiencebroadenour understanding,changesinresearchmethods,professionalpractices,ormedicaltreatmentmaybecome necessary.
Practitionersandresearchersmustalwaysrelyontheirownexperienceandknowledgeinevaluatingandusing anyinformation,methods,compounds,orexperimentsdescribedherein.Inusingsuchinformationormethods theyshouldbemindfuloftheirownsafetyandthesafetyofothers,includingpartiesforwhomtheyhavea professionalresponsibility.
Tothefullestextentofthelaw,neitherthePublishernortheauthors,contributors,oreditors,assumeanyliability foranyinjuryand/ordamagetopersonsorpropertyasamatterofproductsliability,negligenceorotherwise,or fromanyuseoroperationofanymethods,products,instructions,orideascontainedinthematerialherein.
LibraryofCongressCataloging-in-PublicationData
AcatalogrecordforthisbookisavailablefromtheLibraryofCongress
BritishLibraryCataloguing-in-PublicationData
AcataloguerecordforthisbookisavailablefromtheBritishLibrary
ISBN:978-0-12-817797-6
ForinformationonallElsevierpublications visitourwebsiteat https://www.elsevier.com/books-and-journals
Publisher: CandiceJanco
AcquisitionsEditor: AmyShapiro
EditorialProjectManager: LindsayLawrence
ProductionProjectManager: BharatwajVaratharajan
CoverDesigner: MilesHitchen
TypesetbySPiGlobal,India
CONTRIBUTORS.........................................................................................xi
CHAPTER1 Abriefintroductiontoflowandtransportinfractal porousmedia........................................................................1
JianchaoCai,LiehuiZhang,andWeiWei
1Introduction................................................................................1
2Fractalstructuralcharacteristicsofporousmedia..................4
3Transportmodelbasedonfractalgeometryand othertheories.............................................................................5
4Modellingoftransportcharacteristicsand itsapplication.............................................................................6
5Conclusion..................................................................................8
CHAPTER2 Fractalstructuralparametersfromimages:Fractal dimension,lacunarity,andsuccolarity...............................11
YuxuanXia,JianchaoCai,andWeiWei
1Introduction..............................................................................11
2Definitionandphysicalmeaning..............................................12
3Calculatedmethod...................................................................12
4Applicationsinfractalporousmedia.......................................15
4.1Characterizationofcomplexity,heterogeneity, andanisotropy..................................................................15
4.2Fractalmodelofreservoirpermeability.........................17
4.3Fracturedistributioncharacterization............................19
4.4Permeabilityprediction....................................................21
5Conclusions..............................................................................72
Acknowledgments..........................................................................73 References.....................................................................................73
CHAPTER5 Modellingflowandtransportinvariablysaturatedporous media:Applicationsfrompercolationtheoryand effective-mediumapproximation........................................79 BehzadGhanbarianandAllenG.Hunt
1Introduction..............................................................................79
1.1Percolationtheory..... ..............80
1.2Effective-mediumapproximation....................................87
2Combininguniversalscalinglawsfrompercolation theoryandtheeffective-mediumapproximation.... ................90
3Diffusion....................................................................................92
4Electricalconductivity..............................................................93
5Permeability.............................................................................96
5.1Single-phasepermeability...............................................97
5.2Waterrelativepermeability...........................................102
6Conclusion..............................................................................111
Acknowledgment..........................................................................112 References...................................................................................112
CHAPTER6 Fractalanalysisonconductiveheattransfer inporousmedia................................................................119
XuanQin,JianchaoCai,andPengXu
1Introduction............................................................................119
2Exactlyself-similarfractalmodel...... ........121
3Statisticallyself-similarfractalmodel.......... ........................ 125
4Statisticallyself-similarfractalmodelwiththeeffect ofroughsurfaces...................................................................131
5Conclusions............................................................................136
Acknowledgment..........................................................................136 References...................................................................................136
CHAPTER7 Transportpropertyandapplicationoftree-shaped network..............................................................................141
PengXu,BomingYu,ArunS.Mujumdar,and JianchaoCai
1Introductionandbackground.................................................141
2Applicationoftree-shapednetwork... .....143
3Optimizationprinciplefortree-shapednetwork...................144
3.1TheoriginofMurray’slaw.............................................144
3.2Optimizationoftree-shapedstructure..........................147
3.3Fractaltree-shapednetwork.........................................150
CHAPTER8
4Fluidflowintree-shapednetwork.............
Fractalcharacterizationoffracturenetworksand productionpredictionformultiplefracturedhorizontal wellsinunconventionalgasreservoirs............................165 QiZhangandGuanglongSheng 1Introduction............................................................................165
2Fractalfracturepropertydistribution....................................167
2.1Fractaldimensionsofinducedfractures......................167
2.2Fractalfractureporosity,permeability, andcompressibilitydistribution.. 168
2.3Resultsanddiscussion..................................................170 3DMFDEconstruction..............................................................174
3.1Diffusivityequationsofdual-mediasystems...... ..........174
3.2Modelvalidationandapplication...................................182
CHAPTER9 Applicationoffractaltheoryintransientpressure propertiesofhydrocarbonreservoir................................193 LiehuiZhang
1Introduction............................................................................195
2Fractalwelltestingmodelforaverticalwellina homogeneousoilandgasreservoir........................ ............ ..196
2.1Physicalmodeldescription............................................197
2.2Mathematicalmodelanditssolution............................197
2.3Pressureresponseanalysis..... ..........201
3Fractalnonlinearseepageflowmodelfordeformable dualmediareservoir..............................................................204
3.1Background....................................................................204
3.2Problemsstatement......................................................206
3.3Solutionanalysis............................................................211
3.4Applicationtopressureanalysis........................ ...........220
4Transientpressurefractalanalysisofaverticalwellin acompositereservoir............................................................221
4.1Physicalmodel...............................................................221
4.2Mathematicalmodel......................................................222
4.3Solutiontothemodel....... ..........224
4.4Resultsanalysis.............................................................227
5Fractaltheoryinshalegas reservoir.... ..........233
5.1Background....................................................................233
5.2Fractalmodelforshale.................................................233
5.3Multilayerfractaladsorptionmodel..............................236
5.4Experimentalresultsanddiscussion.. ..........................239
6Conclusions............................................................................246
References...................................................................................246
INDEX...................................................................................................................251
Contributors JianchaoCai StateKeyLaboratoryofPetroleumResourcesandProspecting,ChinaUniversityof Petroleum,Beijing;InstituteofGeophysicsandGeomatics,ChinaUniversityofGeosciences,Wuhan, China
BehzadGhanbarian PorousMediaResearchLab,DepartmentofGeology,KansasStateUniversity, Manhattan,KS,UnitedStates
AllenG.Hunt DepartmentofPhysicsandDepartmentofEarthandEnvironmentalSciences,Wright StateUniversity,Dayton,OH,UnitedStates
ArunS.Mujumdar DepartmentofMiningandMaterialsEngineering,McGillUniversity,Montreal, QC,Canada
XuanQin InstituteofGeophysicsandGeomatics,ChinaUniversityofGeosciences,Wuhan,China
GuanglongSheng SchoolofPetroleumEngineering,YangtzeUniversity,Wuhan,China
ShifengTian StateKeyLaboratoryofCoalMineDisasterDynamicsandControl;SchoolofResources andSafetyEngineering,ChongqingUniversity,Chongqing,China
WeiWei InstituteofGeophysicsandGeomatics,ChinaUniversityofGeosciences,Wuhan,China
YuxuanXia InstituteofGeophysicsandGeomatics,ChinaUniversityofGeosciences,Wuhan,China
XuefuXian StateKeyLaboratoryofCoalMineDisasterDynamicsandControl;SchoolofResources andSafetyEngineering,ChongqingUniversity,Chongqing,China
PengXu CollegeofScience,ChinaJiliangUniversity,Hangzhou,China
KangYang StateKeyLaboratoryofCoalMineDisasterDynamicsandControl;SchoolofResources andSafetyEngineering,ChongqingUniversity,Chongqing,China
BomingYu SchoolofPhysics,HuazhongUniversityofScienceandTechnology,Wuhan,China
LiehuiZhang StateKeyLaboratoryofOilandGasReservoirGeologyandExploitation,Southwest PetroleumUniversity,Chengdu,China
QiZhang SchoolofEarthResources,ChinaUniversityofGeosciences,Wuhan,China
JunpingZhou StateKeyLaboratoryofCoalMineDisasterDynamicsandControl;Schoolof ResourcesandSafetyEngineering,ChongqingUniversity,Chongqing,China
Abouttheeditors JianchaoCai isaprofessorattheStateKeyLaboratoryofPetroleumResources andProspecting,ChinaUniversityofPetroleum(Beijing),andtheInstituteof GeophysicsandGeomatics,ChinaUniversityofGeosciences(Wuhan).Hehas publishedmorethan140peer-reviewedjournalarticles,threebooks,and numerousbookchapters.Heisthefounderandtheeditor-in-chiefof Advances inGeo-EnergyResearch andservesasanassociateeditororeditorialmemberfor severaljournals.HereceivedtheProjectoftheNationalScienceFoundationof ChinaforOutstandingYouthFoundationin2017.
LiehuiZhang isaprofessorattheCollegeofPetroleumEngineeringandthe vicepresidentatSouthwestPetroleumUniversity.Hehaspublishedmorethan 270peer-reviewedjournalarticlesandauthoredorcoeditedeightbooks.He alsoservesonnumerouseditorialboards.HeistherecipientoftheChina NationalFundsforDistinguishedYoungScientistsin2012,awardedbythe NaturalScienceFoundationofChina.HewasalsonamedtheCheungKong Scholars’distinguishedprofessorin2014bytheChineseMinistryofEducation.
WeiWei nowworksattheInstituteofGeophysicsandGeomaticsofChina UniversityofGeosciences(Wuhan).HereceivedhisBScinGeophysicsfrom theGuilinUniversityofTechnologyin2012aswellashisMscinGeological EngineeringandPhDinGeophysicsfromChinaUniversityofGeosciences (Wuhan)in2015and2018,respectively.Hisresearchfocusesonmodelling theelectricalpropertiesofporousmediaaswellasfractaltheoryanditsapplication.Hehaspublished14peer-reviewedjournalarticles,whichhavenearly 550totalcitationsfromtheWebofScience.
Preface Porespaceand/orasolidmatrixofporousmediahavebeenobservedtofollow fractalproperties,includingself-similarityandself-affinity.Featuressuchas power-lawprobabilitydensityfunctionandscaleinvariancecanhelpcapture thecomplexitytostudyflowandtransportphenomenainnaturalporoussystemssuchassoilsandrocks.Asthisisagrowingresearcharea,itisnecessaryto highlightnewcharacteristicsoffractalscalinglawsandilluminatepractical applicationsfromdifferentviewpoints.Scientistshavebeenattemptingtofill thegaptocharacterizeporousmediausingfractaltheoryforalongtime.Inthis book,wetrytoshedfurtherlightontwoconcepts:(1)howtoanalyzethestructuralcharacteristicsofporousmediabymeansoffractaltheory,and(2)howto effectivelyutilizefractalcharacteristicstoinvestigatetheflowandtransportprocess.Therefore,apracticalknowledgeoffractalporousmediawillcontributeto anaccuratecharacterizationoftheirmicrostructuresandanin-depthunderstandingoffluidtransportmechanisms.
Thebookpresentsacomprehensiveoverviewoftheflowandtransportpropertiesoffractalporousmediathatwillenhancethebasicunderstandingofthe theoreticalmodellingandapplicationoftransportphenomena.Itcoversawide rangeofapplicationsusingdifferenttheoretical,mathematical,andnumerical approacheswhilealsoprovidingananalysisoftheflowandtransportpropertiesinfractalporousmedia.
Thisbookprovidesasuitablereferenceforgraduateandupperlevelundergraduatestudents,andforpractitionersintheresearchanddevelopmentofresource andenergyinacademiaandindustry.Itconsistsofninechapterstointroduce ModellingofFlowandTransportinFractalPorousMedia. Chapter1 presentsabrief summarizationrelatedtotheflowandtransportpropertiesoffractalporous media,whichcanenhanceresearchers’basicunderstandingoffractaltheoreticalmodellingandtheapplicationoftransportphenomenainporousmedia. Chapter2 analyzeshowtoapplyfractalparameterizationtoevaluatethestructuralcharacteristicsofporousmediafromtheviewsofcomplexity,heterogeneity,andanisotropywhilealsoprovidingafeasiblerelationshipbetween
transportpropertiesandfractalfeatures. Chapter3 presentsaframeworkofcalculatingthetortuosityfortheelectricalandhydraulictransportinfractal porousmediaanddiscussesthepower-lawrelationshipbetweentortuosity andfractaldimensions.In Chapter4,theadsorptionandflowcharacteristics areanalyzedwithfractalparameters,andanoverviewisprovidedontherelationshipbetweenthemostcommonmethodsofcapturingporestructuralcharacteristicsandfractaldimensions. Chapter5 reviewstheapplicationsof percolationtheoryandeffective-mediumapproximationformodellingthe flowandtransportinunsaturatedporousmediaandfindsthemodelsof transportproperties,includinghydraulicandelectricalconductivityaswell asgas/solutediffusionrelatedtoporesizedistribution. Chapter6 explores theapplicationoffractaltheoryintheheattransferofporousmedia,and obtainsgeneralizedmodelsforeffectivethermalconductivitybasedonthe effectivemediummodel,theSierpinskimodel,andthefractalroughsurface model. Chapter7 proposesaprospectiveviewoftree-shapednetworkstostudy thetransportpropertiesoffluidflow,andpresentstheoptimalprincipleoftreeshapednetworksthatcanprovideanin-depthanalysisforpulsatilefluidflow, heatconduction,andelectricaltransfer. Chapter8 developsacoupledmethod tocorrelatethefractalcharacteristicsoffractureapertureandfracturespacing, andemploysthisapproachintheflowsimulationformultiplefracturedhorizontalwellsinunconventionalgasreservoirs. Chapter9 solvesthedetailed analyticalprocessofafractalmodelforahomogeneousoilandgasreservoir, adeformabledualmediareservoir,acompositereservoir,andashalegasreservoirbasedontheLaplaceintegraltransform.
Theeditorsacknowledgethecontributingauthors.Specialthanksaredueto AmyShapiro,LindsayLawrence,BharatwajVaratharajan,andMilesHitchen ofElsevier’sbookproductiongroupforeditingthisbook.Wealsoacknowledge theNationalNaturalScienceFoundationofChina(Nos.51534006, 41722403,42004086)forsupportingourseriesofstudiesonflowandtransportinfractalporousmedia.
Abriefintroductiontoflowandtransport infractalporousmedia JianchaoCaia,b,LiehuiZhangc,andWeiWeib aStateKeyLaboratoryofPetroleumResourcesandProspecting,ChinaUniversityofPetroleum, Beijing,China, bInstituteofGeophysicsandGeomatics,ChinaUniversityofGeosciences,Wuhan, China, cStateKeyLaboratoryofOilandGasReservoirGeologyandExploitation,Southwest PetroleumUniversity,Chengdu,Sichuan,China
1Introduction Innature,porousmediaaswellasitsmatrix,pores,andfracturesconstitutea complexmicrosystem,forexample,soils,rocks,buildingmaterials,andbiologicaltissues.Thestructuralfeaturesofthesesystems,includingpore(grain)size distribution,fracturelengthdistribution,andsurfaceroughness,usuallyshowa statisticalpowerlawwithmeasuredscale.Thesestructuresarereferredtoasselfsimilarinfractaltheory,thustheporousmediaisusuallyknownasfractal porousmedia.Thestudyoffractalporousmediahasreceivedsubstantialattentionbyresearchersinthelastdecades.Itcanbeseenin Fig.1 thatthepublished paperskeepincreasingwithtime.Italsomeansthatthemodelandtheoryof fractalporousmediaaremoreconvenienttodescribethecomplexporestructurecomparedwithregularandtraditionalapproaches.
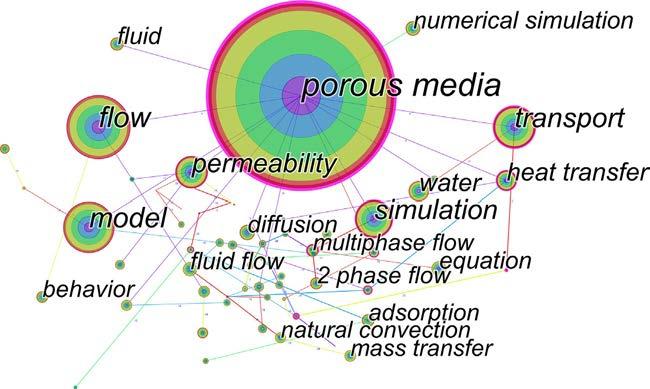
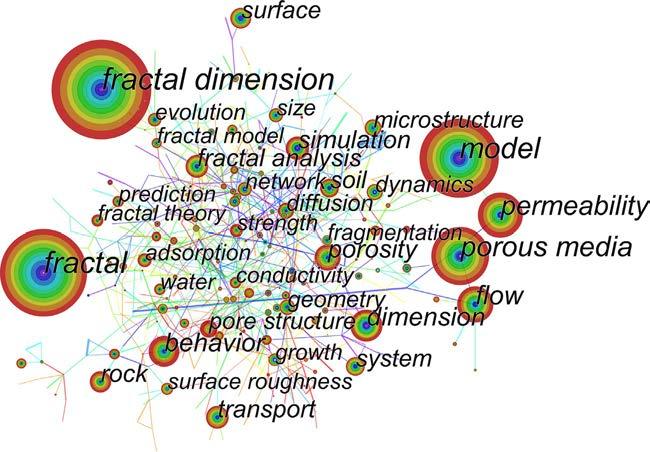
Therelationofthetopic“porousmedia”mainlyconnectedwithflow/transport fromthedatabaseoftheWebofScienceCoreCollectionisshownin Fig.2.It alsoindicatesthatthesolutionfortheflow/transportprobleminporousmedia isalong-termresearchtheme.Theflowmechanismofporousmediaisaffected byfluidproperties,porestructure,andmatrixconstituent.Forfractalporous media,thetransportprocessadditionallyneedstoconsidertheinfluenceof theself-similarporestructureandthemultiordersofmagnitudeoftheporesize. Fromsearchresultsonthetopic“fractalporousmedia,”asshownin Fig.3,we findthatthefocuspointisthefractaldimensionofthemicrostructure,and obtainingtheflowortransportbehaviorofporousmedia.Severaltheories andmethodsareusedtoanalyzetherelationshipbetweentransportcharacteristicsandpore/fracturegeometryparameters,suchasthepercolationtheory, theeffectivemediumtheory,thefractaltheory,andtheporenetworkmodel.
CONTENTS 1.Introduction..... 1
2.Fractalstructural characteristicsof porousmedia... 4
3.Transportmodel basedonfractal geometryand othertheories.. 5
4.Modellingof transport characteristics andits application....... 6
5.Conclusion....... 8
Acknowledgments 8 References........... 8
FIG.1
Thenumberofpublishedpapersforthetopic“fractalporousmedia”from2010to2019.Thesearch criteriaare"fractal"and(“porousmedia”or“soil”or“rock”or“fiber”or“building”or“biological”or “reservoir”or“material”);thisdataistakenfromtheWebofScienceCoreCollection.
FIG.2
Morethan14,000paperswerepublishedfrom2015to2019relateddirectlyorindirectlytovarious aspectsofflow/transportinporousmedia.ThisdataistakenfromtheWebofScienceCoreCollection.
FIG.3
About5000paperswerepublishedfrom2010to2019,relateddirectlyorindirectlytovariousaspectsof thetopic“fractalporousmedia.”Thesearchcriteriaare“fractal”and(“porousmedia”or“soil”or“rock”or “fiber”or“building”or“biological”or“reservoir”or“material”);thisdataistakenfromtheWebofScience CoreCollection.
Thesetheories/methodscouldeffectivelydescribethefluidflowprocessin porousmediafromdifferentviews.
Fractalgeometryisasuccessfulmethodtocharacterizethestatisticalrelation betweenthegeometrystructureversuslengthscale.Thescalingexponentand fractaldimensioncouldsimplifythemathematicalexpressionfordepicting complexstructuralfeaturesofporousmedia.Besides,theanalysisoftheheterogeneityandconnectivityofthepore-throatstructurealsohasgoodperformance basedonotherfractalparameters,suchaslacunarityandsuccolarity.Combiningwithotheranalyticalmethods,fractalgeometryisnowconsideredtobean integratedtooltomodeltheflowandtransportinporousmedia.Asthistoolhas obtainedmanyachievementsinseveralfieldsofproduction(e.g.,reservoirengineering,geologicalsequestrationofcarbondioxideandgeothermalenergy),systematicallyunderstandingtheapplicationoffractaltheoryforflowand transportinporousmediaisofmoreconcern.
Inthischapter,wepresentabriefsummarizationrelatedtotheflowandtransportpropertiesoffractalporousmediathatwillenhanceourbasicunderstandingofthetheoreticalmodellingandapplicationoftransportphenomenain differentfields.Thischapterincludesthreeparts:thefractalstructuralcharacteristicsofporousmedia,thetransportmodelbasedonfractalgeometryand
othertheories,andmodellingthetransportcharacteristicsanditsapplication. Itcoversawiderangewithdifferenttheoretical,mathematical,andnumerical approachesaswellastheanalysisofflowandtransportphenomenainfractal porousmedia.
2Fractalstructuralcharacteristicsofporousmedia Infractaltheory,therearemainlythreeparameterstodescribethecomplex microstructureofporousmedia:fractaldimension,lacunarity,andsuccolarity [1–3].Bytheapplicationofthethreeparameters,thestructuralcharacteristics ofporousmediacanbeevaluatedfromtheviewofcomplexity,aggregation, andconnectivity,respectively.Thefractaldimensionrepresentshowmuchan objectoccupiesthemetricspace.Lacunaritydenotestheclusterdegreeofpores (fractures);moregenerally,itquantifiestheheterogeneity.Succolarityreflectsthe abilityofafluidflowinginaporousmedium.However,exceptingthefractal dimension,thecalculationoflacunarityandsuccolarityiscumbersomeand time-consumingfortheheterogenousstructureinthemicro-andnanometer scale.Fortunately,withthedevelopmentofimagingtechnologyandhighperformancecomputers,thebox-countingmethodforlacunarityandsuccolarity candealwiththestructureimagingofhighresolutionwell [4–6]
Althoughthecomplexity,heterogeneity,andanisotropyofporousmediacan beaccuratelycharacterizedbycombiningthethreeparameters,theemphasisof thethreefractalparametersisclearlydifferent.IntheworkofXiaetal. [7,8], theyusefractaldimension,lacunarity,andsuccolaritytoestimatethepermeability.Akeyfindingisthatthesuccolaritycouldbetterfitthepermeability ofsandstonethanotherparameters.Theyillustratethereasonthatpermeability iscloselyrelatedtoporeinterconnectioninlow-permeabilityrock,andthe valueofsuccolarityissensitivetotheinterconnectionofporousmedia.
Aswecansee,theaforementionedfractalparametershaveadvancedperformance,buttheyaredifficulttodescribetheflowlengthoftheelectricalor hydraulictransportprocessinporousmedia.Oneofthedifficultiesisthatthe tortuosityofthefluidflowchangesconstantlywiththelocaldifferenceofpore configuration.WheatcraftandTyler [9] assumedthattortuosityhasaself-similar behaviorandpresentedthecalculationmethodoftortuositybasedonfractal theory.Theyutilizedthemeasuredlengthandthefractaldimensiontoexpress thetortuosityinadifferentscale.Thetransportbehaviorrelatedtotortuosity alsocanbecharacterizedbythefractaldimension.However,theapplication offractaltheoryforcalculatingtortuosityholdsseveraluntowardpoints [10,11].Oneofthemostimportantpointsishowtoobtainthefractaldimensioninthepower-lawexponentparameterbetweentortuosityandlengthscale.
Forthesolutionofthepower-lawexponent,Weietal. [12] presentedaframeworktocalculatethetortuosityfortheelectricalflowlengthinfractalporous
media.Thisresultshowsthatthepower-lawexponentbetweentortuosityand measuredscalecanbecalculatedbytwofractaldimensions,thetortuosityfractaldimensionandthefractaldimensionoftherandomwalker.Theyfoundthat thedifferencevalueofthepower-lawexponentfromtwofractaldimensions approaches1.TheanalysisfromCaietal. [13] indicatesthatthedifferent calculatingmethodoftortuosityalsocaninfluencethepower-lawexponent, namelythatthetortuositysuchaselectricalandhydraulicflowcannotberepresentedinthesametortuositymodel.
Intheprogressoffractalparametersandtortuositycalculation,thestructural imagingandstatisticsofporousmediaalsoneedtobenoticed.Themostcommonlyusedcharacterizationmethods,suchasopticalmicroscope,scanning electronmicroscopy,nanoCT-scan,mercuryinjectioncapillarypressure, CO2 adsorption,N2 adsorption,andnuclearmagneticresonancetests,can reflectthefractaldimensionsofporousmedia [14–16].However,fractal dimensionsindifferenttestmethodsaredissimilar.Forexample,theporefractaldimensioncanbecalculatedbyscanningelectronmicroscopyorgasadsorption.Thefractaldimensionfromscanningelectronmicroscopyisbasedon imageanalysis,whilethefractaldimensioncalculatedbygasadsorptionisfrom theanalysisofadsorptioncapacityinfluidinjectionprocess.Especially,the transportcapacityofshalewithorganicmatterporesisrelatedtothemineral matrixorparticles,interparticle,intraparticle,andfracturepores.Thesecomponentscanaffectthetestresultsforthefractalcharacteristicsofporestructure obtainedfromdifferentmethods.
Forthesetestmethods,Zhouetal. [16–18] providedafindingthattheadsorptionandgasflowbehaviorsinshalearedifferentduetotherangeofporesize distribution,whichmeansthattheapplicationofreasonablefractalparameters indifferentporecharacterizationmethodsissignificant.Therefore,acombinationofaseriesofporecharacterizationmethodsisneededtoobtainthefull-scale poresizedistributionofshale.Furthermore,fractaltheoryindifferentporecharacterizationmethodsiseffectivetoreflecttheheterogeneousporesatdifferent sizeranges.
3Transportmodelbasedonfractalgeometryand othertheories Thecapacitytodescribetheself-similarbehaviorofporousmediaisoneofthe advantagesoffractaltheory.However,forsomespecialinfluencesfortransport propertiesresultingfromtheinhomogeneousdistributionofporousmedia, suchastheeffectivestatisticalinformationofporestructureandpercolation status,theapplicabilityoffractaltheoryisrelativelyweak [19,20].Applying acombinationofdifferenttheories/methodstoanalyzethetransportcharacterizationhasbeenapopularideaintheexplanationofafractalporesystem.
Amongthesetheories,theeffectivemediumtheoryandpercolationtheorycan effectivelymakeupthedisadvantagesoffractaltheory,especiallyintheprocess offractalgeometrydescribingthebundle-of-tubesstructureofporousmedia.
Thedrawbackfromthepoordescriptionforporeinterconnectivityinporous mediacanbeperfectlysolvedbycombiningthefractalbundle-of-tubesmodel withthepercolationtheoryandeffectivemediumtheory [21].Themethods havebeensuccessfullyappliedtodescribefluidflowandtransportinlattices, porenetworks,andporousmedia [22–24].Therearemoreadvantagessuchas thepresenceofapercolationthresholdbelowwhichthefluidwithinthepore spacelosesitsconnectivity,andaccordinglymacroscopictransport coefficients [25]
Thecombinationofseveraltheoriescanbettercharacterizethetransportproperties,includinghydraulicandelectricalconductivityandgas/solutediffusion. Theaccuratedescriptionofheattransferinporousmediaisavailablebasedon fractalgeometryandeffectivemediumtheory.Relativetothefluidflowprocess inporousmedia,theheattransferneedstoconsiderthethermalconductivityof eachphase,suchasgas,grain,andfluid.Oneofthecommonlyusedmodelsfor thermalconductivitycharacterizationinporousmediaistheMaxwell-Eucken model,wheresphericalporesareassumedtobewidelydispersedinacontinuousmedium [26].Theeffectivemediumtheoryisanapproximatedmethodto modelthethermalconductivityofmacroscopicallyhomogeneousandisotropicmediacontainingrandomlydistributedgrainsandpores.However,the impactsofmicrostructuressuchassolid/poregeometryandsize,tortuosity, andtheroughsurfacesofmicroporesonthethermalconductionofporous mediaremaindemanding [27]
Onthebasisofaneffectivemediumapproach,thethermalconductivityof porousmediaisstronglyinfluencedbythemicrostructuralfeaturesofporous media,whichcanbewellcharacterizedbyfractalgeometry.Inarecentwork, Qinetal. [27,28] derivedageneralizedmodelforeffectivethermalconductivity dependingontheeffectivemediummodel,theSierpinskimodel,andthefractal roughsurfacemodel.Thesemodelsconsidertheinfluenceofgrainandporesize distributions,liquidsaturation,androughsurface,whichisinagreementwith thepublishedexperimentaldataandnumericalsimulationdata.
4Modellingoftransportcharacteristicsandits application
Thepurposeofusingfractaltheory/methodsistosolvethevariedproblemsin transportingforporousmedia.Thetree-shapedstructureusuallyisappliedto
optimizethetransportprocessinindustrialengineering.However,akeyproblemishowtoeffectivelyutilizethetree-shapedstructuretodesignthenatural transfersystems.SimilartoHagen-PoiseuillelawandFick’slaworiginating fromabiologicalcontext,Murray’slawisproposedinabiologicalsystem andisabasicphysicalprincipleforbothlivingandnonlivingtree-shapedtransfernetworks.Thepreviousresearchofthetree-shapedstructurebasedonMurray’slawhasbeenextendedtothestudyofthetransportperformanceofporous media [29,30].Theoptimizationofthetree-shapedstructureismainlyfrom fourparameters:theminimumsurfacearea,theminimumvolume,theminimumdrag,andtheminimumpower.Therefore,thebalanceofthefourparametersintree-shapednetworksneedstobefurtherinvestigated.
Fromtheviewofoptimizationofthetree-shapednetwork,Xuetal. [31–33] gaveanapplicationframeoftree-shapednetworkstostudythetransportpropertiesoffluidflow.Furthermore,theypresentedtheoptimalprincipleoftreeshapednetworksthatprovidesin-depthanalysisforpulsatilefluidflow,heat conduction,andelectricaltransfer.Theoptimalresultsshowedthattheflow featuresarerelatedtothemacroscopictransportpropertiesandmorphological parametersoftree-shapednetworksbasedonfractalgeometry.Thesefeaturesof thetree-shapednetworkscouldhelpresearcherstounderstandtheflowmechanismofreservoirrock.
Inunconventionalreservoirs,suchascoalformation,shale,andtightreservoirs,fractaltheoryalsoplaysanimportantrole.Itcanbeappliedtoanalyze theinducedfracturespacingandapertureintheprocessofconnectingthepreexistingnaturalfractures [34] ,andsolvetheanalyticalsolutionofwellbore pressureforthetransientflow [35,36].Theresultsareserviceableformatchingandpredictingproductionrateofreservoirs.Asthedevelopmentofthe calculatingmethodoftortuosityindex,fractaldimension,fractureporosity, permeability,andcompressibilityare graduallyusedtodescribethecoupled relationshipbetweentheapertureandthespacinginfractal-induced fracture [37].
Forhydrocarbonreservoirs,thestudyoftheapplicationoffractaltheoryin transientflowmodelsisgraduallygrowing [38,39].Anonlineartransientflow modelofdualfractalmediacanbeestablishedbasedonembeddingthetreeshapedfractalnetworksintoafractalporousmedia.Inthederivativecurvefor thewelltestingorexperimentaldata,thetransientflowmodelsshowthatthe flowregimesarerecognizable,whichmeansthatthefractalmodelsaresuitable foramajorityofreservoirs [38,39].Inseveralcases [40–42],theresultsshowed thatthemicrostructuralevaluationoffractalporousmediaaswellastheevaluationofoilandgasresourceabundancearepromisinginprovidingnewideas andmethodsforoilandgasexplorationanddevelopment.
5Conclusion Linkingthemodellingofflowandtransportwithfractalporousmedia,itis recognizedthatfractaltheoryhasbeenasuccessfulapproachtodescribethe characterizationofthecomplexstructureofaporoussystem.Inthisbook, wepresentacomprehensiveoverviewrelatedtotheflowandtransportpropertiesoffractalporousmedia.Thebookfurtherexploresandextendstherecent applicationoffractaltheoryinthemodellingofthefluidtransportprocess basedonutilizingthenovelfractalstructuralparameters,combiningothertraditionaltheories,andsolvingseveralnewmathematicaltransportmodels.It willhelpmoreresearcherslearnadvancedideasaboutthestudyofflowand transportinfractalporousmedia.
Acknowledgments Wewouldliketothanktheindividualchapterauthorsofthebookfortheirinspiringcontributions anddiligentworks.WespeciallyacknowledgetheElsevierpressforprovidingtheopportunityto bringthisbooktoreaders.J.CaialsoacknowledgetheNationalNaturalScienceFoundationof China(Nos.41722403,41572116)forsupportingtheseriesofstudiesonthemodellingofflow andtransportinfractalporousmedia.
References [1] A.Roy,E.Perfect,W.M.Dunne,etal.,Lacunarityanalysisoffracturenetworks:evidencefor scale-dependentclustering,J.Struct.Geol.32(2010)1444–1449.
[2] J.-W.Kim,M.C.Sukop,E.Perfect,etal.,GeometricandhydrodynamiccharacteristicsofthreedimensionalsaturatedprefractalporousmediadeterminedwithLatticeBoltzmannmodeling, Transp.PorousMedia90(2011)831–846.
[3] A.Roy,E.Perfect,Lacunarityanalysesofmultifractalandnaturalgrayscalepatterns,Fractals 22(2014)1440003.
[4] M.J.Blunt,B.Bijeljic,H.Dong,etal.,Pore-scaleimagingandmodelling,Adv.WaterResour. 51(2013)197–216.
[5] X.Liu,B.Nie,Fractalcharacteristicsofcoalsamplesutilizingimageanalysisandgasadsorption,Fuel182(2016)314–322.
[6] J.Lai,G.Wang,Z.Wang,etal.,Areviewonporestructurecharacterizationintightsandstones, EarthSci.Rev.177(2018)436–457.
[7] Y.X.Xia,J.C.Cai,W.Wei,etal.,Anewmethodforcalculatingfractaldimensionsofporous mediabasedonporesizedistribution,Fractals26(2018)1850006.
[8] Y.Xia,J.Cai,E.Perfect,etal.,Fractaldimension,lacunarityandsuccolarityanalysesonCT imagesofreservoirrocksforpermeabilityprediction,J.Hydrol.579(2019)124198.
[9] S.W.Wheatcraft,S.W.Tyler,Anexplanationofscale-dependentdispersivityinheterogeneous aquifersusingconceptsoffractalgeometry,WaterResour.Res.24(1988)566–578.
[10] M.Wu,J.Wu,J.Wu,etal.,Athree-dimensionalmodelforquantificationoftherepresentative elementaryvolumeoftortuosityingranularporousmedia,J.Hydrol.557(2018)128–136.
[11] W.Xu,Y.Jiao,Theoreticalframeworkforpercolationthreshold,tortuosityandtransportpropertiesofporousmaterialscontaining3Dnon-sphericalpores,Int.J.Eng.Sci.134(2019) 31–46.
[12] W.Wei,J.C.Cai,X.Y.Hu,etal.,Anumericalstudyonfractaldimensionsofcurrentstreamlines intwo-dimensionalandthree-dimensionalporefractalmodelsofporousmedia,Fractals 23(2015)1540012.
[13] J.C.Cai,W.Wei,X.Y.Hu,etal.,Electricalconductivitymodelsinsaturatedporousmedia:a review,EarthSci.Rev.171(2017)419–433.
[14] L.Zhou,Z.H.Kang,FractalcharacterizationofporesinshalesusingNMR:acasestudyfrom theLowerCambrianNiutitangFormationintheMiddleYangtzePlatform,SouthwestChina, J.Nat.GasSci.Eng.35(2016)860–872.
[15] S.W.Zhou,G.Yan,H.Q.Xue,etal.,2Dand3Dnanoporecharacterizationofgasshalein LongmaxiformationbasedonFIB-SEM,Mar.Pet.Geol.73(2016)174–180.
[16] J.P.Zhou,S.Xie,Y.D.Jiang,etal.,InfluenceofsupercriticalCO2exposureonCH4andCO2 adsorptionbehaviorsofshale:implicationsforCO2sequestration,EnergyFuels32(2018) 6073–6089.
[17] H.Yin,J.P.Zhou,X.F.Xian,etal.,Experimentalstudyoftheeffectsofsub-andsuper-critical CO2saturationonthemechanicalcharacteristicsoforganic-richshales,Energy132(2017) 84–95.
[18] J.P.Zhou,M.H.Liu,X.F.Xian,etal.,MeasurementsandmodellingofCH4andCO2adsorptionbehaviorsonshales:implicationforCO2enhancedshalegasrecovery,Fuel251(2019) 293–306.
[19] A.G.Hunt,Applicationsofpercolationtheorytoporousmediawithdistributedlocalconductances,Adv.WaterResour.24(2001)279–307.
[20] A.G.Hunt,G.W.Gee,Applicationofcriticalpathanalysistofractalporousmedia:comparison withexamplesfromtheHanfordsite,Adv.WaterResour.25(2002)129–146.
[21] A.G.Hunt,M.Sahimi,Flow,transport,andreactioninporousmedia:percolationscaling, critical-pathanalysis,andeffectivemediumapproximation,Rev.Geophys.55(2017) 993–1078.
[22] B.Ghanbarian,A.G.Hunt,M.Sahimi,etal.,Percolationtheorygeneratesaphysicallybased descriptionoftortuosityinsaturatedandunsaturatedporousmedia,SoilSci.Soc.Am.J. 77(2013)1920–1929.
[23] B.Ghanbarian,A.G.Hunt,T.E.Skinner,etal.,Saturationdependenceoftransportinporous mediapredictedbypercolationandeffectivemediumtheories,Fractals23(2015)15400046.
[24] B.Ghanbarian,C.Torres-Verdin,T.H.Skaggs,Quantifyingtight-gassandstonepermeability viacriticalpathanalysis,Adv.WaterResour.92(2016)316–322.
[25] B.Ghanbarian,A.G.Hunt,Universalscalingofgasdiffusioninporousmedia,WaterResour. Res.50(2014)2242–2256.
[26] J.K.Carson,S.J.Lovatt,D.J.Tanner,etal.,Thermalconductivityboundsforisotropic,porous materials,Int.J.HeatMassTransf.48(2005)2150–2158.
[27] X.Qin,J.C.Cai,P.Xu,etal.,Afractalmodelofeffectivethermalconductivityforporousmedia withvariousliquidsaturation,Int.J.HeatMassTransf.128(2019)1149–1156.
[28] X.Qin,Y.Zhou,A.P.Sasmito,Aneffectivethermalconductivitymodelforfractalporous mediawithroughsurfaces,Adv.Geo-Energ.Res.3(2019)149–155.
[29] B.R.Masters,Fractalanalysisofthevasculartreeinthehumanretina,Annu.Rev.Biomed.Eng. 6(2004)427–452.
[30] P.Perdikaris,L.Grinberg,G.E.Karniadakis,Aneffectivefractal-treeclosuremodelforsimulatingbloodflowinlargearterialnetworks,Ann.Biomed.Eng.43(2015)1432–1442.