https://ebookmass.com/product/machine-learning-and-theinternet-of-medical-things-in-healthcare-krishna-kant-singh/
Instant digital products (PDF, ePub, MOBI) ready for you
Download now and discover formats that fit your needs...
Machine Learning Approaches for Convergence of IoT and Blockchain Krishna Kant Singh
https://ebookmass.com/product/machine-learning-approaches-forconvergence-of-iot-and-blockchain-krishna-kant-singh/
ebookmass.com
Machine Learning and the Internet of Things in Education: Models and Applications John Bush Idoko
https://ebookmass.com/product/machine-learning-and-the-internet-ofthings-in-education-models-and-applications-john-bush-idoko/
ebookmass.com
Machine Learning for Healthcare Applications Sachi Nandan Mohanty
https://ebookmass.com/product/machine-learning-for-healthcareapplications-sachi-nandan-mohanty/
ebookmass.com
The Vanished Days Susanna Kearsley
https://ebookmass.com/product/the-vanished-days-susanna-kearsley-3/
ebookmass.com
Mercy in Betrayal : Dark Mafia Romance (Sons of the Mafia Book 4) Vi Carter & E.R. Whyte
https://ebookmass.com/product/mercy-in-betrayal-dark-mafia-romancesons-of-the-mafia-book-4-vi-carter-e-r-whyte/
ebookmass.com
(eBook PDF) Ethics and Professionalism for Healthcare Managers
https://ebookmass.com/product/ebook-pdf-ethics-and-professionalismfor-healthcare-managers/
ebookmass.com
■■■■: 1964-1978 [■■] ■■
https://ebookmass.com/product/%e9%9d%9e%e5%b8%b8%e5%b9%b4%e4%bb%a31964-1978-%e4%b8%8a%e5%8d%b7-%e8%b6%99%e5%9c%92/
ebookmass.com
Social Entrepreneurship and Sustainable Business Models: The Case of India 1st ed. Edition Anirudh Agrawal
https://ebookmass.com/product/social-entrepreneurship-and-sustainablebusiness-models-the-case-of-india-1st-ed-edition-anirudh-agrawal/
ebookmass.com
Investigation of the internal structure of thermoresponsive diblock poly(2-methyl-2-oxazoline)-bpoly[N-(2,2-difluoroethyl)acrylamide] copolymer
nanoparticles 11th Edition David Babuka
https://ebookmass.com/product/investigation-of-the-internal-structureof-thermoresponsive-diblock-poly2-methyl-2-oxazoline-bpolyn-22-difluoroethylacrylamide-copolymer-nanoparticles-11th-editiondavid-babuka/ ebookmass.com
Medical Terminology 2nd Edition Paula Bostwick
https://ebookmass.com/product/medical-terminology-2nd-edition-paulabostwick/
ebookmass.com
MachineLearningand theInternetof MedicalThingsin Healthcare
MachineLearningand theInternetof MedicalThingsin Healthcare
Editedby
KrishnaKantSingh Professor,FacultyofEngineering&Technology, Jain(Deemed-to-beUniversity),Bengaluru,India
MohamedElhoseny CollegeofComputerInformationTechnology, AmericanUniversityintheEmirates,Dubai,UnitedArabEmirates
AkanshaSingh DepartmentofCSE,ASET, AmityUniversityUttarPradesh,Noida,India
AhmedA.Elngar FacultyofComputersandArtificialIntelligence, Beni-SuefUniversity,BeniSuefCity,Egypt
AcademicPressisanimprintofElsevier
125LondonWall,LondonEC2Y5AS,UnitedKingdom 525BStreet,Suite1650,SanDiego,CA92101,UnitedStates 50HampshireStreet,5thFloor,Cambridge,MA02139,UnitedStates TheBoulevard,LangfordLane,Kidlington,OxfordOX51GB,UnitedKingdom
Copyright©2021ElsevierInc.Allrightsreserved.
Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproducedortransmittedinanyformorbyanymeans,electronic ormechanical,includingphotocopying,recording,oranyinformationstorageandretrievalsystem, withoutpermissioninwritingfromthepublisher.Detailsonhowtoseekpermission,further informationaboutthePublisher’spermissionspoliciesandourarrangementswithorganizationssuch astheCopyrightClearanceCenterandtheCopyrightLicensingAgency,canbefoundatourwebsite: www.elsevier.com/permissions.
Thisbookandtheindividualcontributionscontainedinitareprotectedundercopyrightbythe Publisher(otherthanasmaybenotedherein).
Notices
Knowledgeandbestpracticeinthisfieldareconstantlychanging.Asnewresearchandexperience broadenourunderstanding,changesinresearchmethods,professionalpractices,ormedical treatmentmaybecomenecessary.
Practitionersandresearchersmustalwaysrelyontheirownexperienceandknowledgeinevaluating andusinganyinformation,methods,compounds,orexperimentsdescribedherein.Inusingsuch informationormethodstheyshouldbemindfuloftheirownsafetyandthesafetyofothers,including partiesforwhomtheyhaveaprofessionalresponsibility.
Tothefullestextentofthelaw,neitherthePublishernortheauthors,contributors,oreditors,assume anyliabilityforanyinjuryand/ordamagetopersonsorpropertyasamatterofproductsliability, negligenceorotherwise,orfromanyuseoroperationofanymethods,products,instructions,orideas containedinthematerialherein.
BritishLibraryCataloguing-in-PublicationData
AcataloguerecordforthisbookisavailablefromtheBritishLibrary
LibraryofCongressCataloging-in-PublicationData
AcatalogrecordforthisbookisavailablefromtheLibraryofCongress
ISBN:978-0-12-821229-5
ForInformationonallAcademicPresspublications visitourwebsiteat https://www.elsevier.com/books-and-journals
Publisher: MaraConner
AcquisitionsEditor: ChrisKatsaropoulos
EditorialProjectManager: RubySmith
ProductionProjectManager: SwapnaSrinivasan
CoverDesigner: MilesHitchen
TypesetbyMPSLimited,Chennai,India
CHAPTER1Machinelearningarchitectureandframework ........... 1 AshishTripathi,ArunKumarSingh,KrishnaKantSingh, PushpaChoudharyandPremChandVashist
1.1 Introduction....................................................................................1
1.1.1Machinelearningclassification..........................................2
1.2 Architectureofmachinelearning..................................................4
1.2.1Dataacquisition..................................................................5
1.2.2Dataprocessing...................................................................5
1.2.3Datamodeling.....................................................................9
1.2.4Execution(modelevaluation)...........................................12
1.2.5Deployment.......................................................................12
1.3 Machinelearningframework.......................................................12
1.3.1FeaturesofMLframework...............................................12
1.3.2TypesofMLframework...................................................15
1.4 Significanceofmachinelearninginthe healthcaresystem.........................................................................17
1.4.1Machine-learningapplicationsinthe healthcaresystem..............................................................18
1.5 Conclusion....................................................................................19 References....................................................................................20
CHAPTER2Machinelearninginhealthcare:review, opportunitiesandchallenges ..................................... 23 AnandNayyar,LataGadhaviandNoorZaman
2.1 Introduction..................................................................................23
2.1.1Machinelearninginanutshell.........................................24
2.1.2Machinelearningtechniquesandapplications.................25
2.1.3Desiredfeaturesofmachinelearning...............................28
2.1.4Howmachinelearningworks?.........................................29
2.1.5Whymachinelearningforhealthcare?.............................30
2.2 Analysisofdomain......................................................................32
2.2.1Backgroundandrelatedworks.........................................32
2.2.2IntegrationscenariosofMLandHealthcare....................33
2.2.3Existingmachinelearningapplications forhealthcare....................................................................33
2.3 Perspectiveofdiseasediagnosisusingmachinelearning...........37
2.3.1Futureperspectivetoenhancehealthcaresystem usingmachinelearning.....................................................38 2.4 Conclusions..................................................................................41 References....................................................................................41 CHAPTER3Machinelearningforbiomedicalsignal processing
3.1 Introduction..................................................................................47
3.2 ReviewsofECGsignal................................................................48
3.3 PreprocessingofECGsignalusingMLbasedtechniques.........51
3.3.1Leastmeansquare(LMS).................................................54
3.3.2Normalizedleastmeansquare(NLMS)...........................54
3.3.3DelayederrornormalizedLMS(DENLMS) algorithm...........................................................................54
3.3.4Signdataleastmeansquare(SDLMS)............................55
3.3.5Logleastmeansquare(LLMS)........................................57
3.4 FeatureextractionandclassificationofECGsignal usingML-basedtechniques.........................................................58
3.4.1Artificialneuralnetwork(ANN)......................................59
3.4.2Fuzzylogic(FL)...............................................................60
3.4.3Wavelettransforms...........................................................61
3.4.4Hybridapproach................................................................62
3.5 Discussionsandconclusions........................................................63 References....................................................................................63
CHAPTER4Artificialitelligenceinmedicine ............................... 67 ArunKumarSingh,AshishTripathi,KrishnaKantSingh, PushpaChoudharyandPremChandVashist 4.1 Introduction..................................................................................67
4.1.1Disease..............................................................................67 4.1.2Medicine............................................................................70
4.1.3HistoryofAIinmedicine.................................................73
4.1.4Drugdiscoveryprocess.....................................................75
4.1.5Machine-learningalgorithmsinmedicine........................77
4.1.6Expertsystems..................................................................82
4.1.7Fuzzyexpertsystems........................................................83
4.1.8Artificialneuralnetworks.................................................83
4.2 Conclusion....................................................................................84 References....................................................................................85
CHAPTER5Diagnosingofdiseaseusingmachinelearning ........ 89
PushpaSingh,NarendraSingh, KrishnaKantSinghandAkanshaSingh
5.1 Introduction..................................................................................89
5.2 Backgroundandrelatedwork......................................................90
5.2.1Challengesinconventionalhealthcaresystem.................91
5.2.2Machine-learningtoolsfordiagnosisandprediction.......91
5.2.3Python................................................................................92
5.2.4MATLAB..........................................................................93
5.3 Typesofmachine-learningalgorithm..........................................93
5.4 Diagnosismodelfordiseaseprediction.......................................95
5.4.1Datapreprocessing............................................................95
5.4.2Trainingandtestingdataset.............................................95
5.4.3Classificationtechnique....................................................96
5.4.4Performancemetrics.........................................................97
5.5 Confusionmatrix..........................................................................97
5.6 Diseasediagnosisbyvariousmachine-learningalgorithms........98
5.6.1Supportvectormachine(SVM)........................................98
5.6.2K-nearestneighbors(KNN)............................................100
5.6.3Decisiontree(DT)..........................................................101
5.6.4Naivebayes(NB)............................................................103
5.7 MLalgorithminneurological,cardiovascular, andcancerdiseasediagnosis......................................................104
5.7.1Neurologicaldiseasediagnosisbymachine learning............................................................................104
5.7.2Cardiovasculardiseasediagnosisbymachine learning............................................................................105
5.7.3Breastcancerdiagnosisandprediction: acasestudy.....................................................................105
5.7.4Impactofmachinelearninginthehealthcare industry............................................................................106
5.8 Conclusionandfuturescope......................................................107 References..................................................................................107
CHAPTER6Anovelapproachoftelemedicinefor managingfetalconditionbasedonmachine learningtechnologyfromIoT-basedwearable medicaldevice .......................................................... 113 AshuAshuandShilpiSharma
6.1 Introduction................................................................................113
6.2 Healthcareandbigdata..............................................................113
6.3
6.8.1Researchonrevolutionaryeffectoftelemedicine
6.8.2Roleofmachinelearningintelemedicine/healthcare.........120
6.8.3Roleofbigdataanalyticsinhealthcare.........................122
6.8.4Challengesfacedinhandlingbigdatain
6.8.5Researchdoneontracingthefetalwell-being usingtelemedicineandmachinelearningalgorithms....125
7.3.3Diagnosticservices.........................................................138 7.3.4Inpatientservices............................................................138
CHAPTER8Examiningdiabeticsubjectsontheircorrelation withTTHandCAD:astatisticalapproachon exploratoryresults .................................................... 153
SubhraRaniMondalandSubhankarDas
8.1 Introduction................................................................................153
8.1.1Generalapplicationprocedure........................................154
8.1.2Medicinalimaging..........................................................154
8.1.3BigdataandInternetofThings......................................156
8.1.4Artificialintelligence(AI)andmachine learning(ML)..................................................................156
8.1.5BigdataandIoTapplicationsinhealthcare...................158
8.1.6Diabetesanditstypes.....................................................159
8.1.7Coronaryarterydisease(CAD)......................................161
8.2 Reviewofliterature....................................................................163
8.3 Researchmethodology...............................................................164
8.3.1Trialsetup.......................................................................164
8.4 Resultanalysisanddiscussion...................................................166
8.4.1TTHcannotbe................................................................169
8.5 Originalityinthepresentedwork..............................................170
8.6 Futurescopeandlimitations......................................................171
8.7 Recommendationsandconsiderations.......................................171
8.8 Conclusion..................................................................................172 References..................................................................................173
CHAPTER9Cancerpredictionanddiagnosishinged onHCMLinIOMTenvironment ................................. 179
G.S.PradeepGhantasala,NalliVinayaKumari andRizwanPatan
9.1 Introductiontomachinelearning(ML).....................................179
9.1.1Somemachinelearningmethods....................................179
9.1.2Machinelearning............................................................179
9.2 IntroductiontoIOT....................................................................181
9.3 ApplicationofIOTinhealthcare...............................................182
9.3.1Redefininghealthcare.....................................................183
9.4 Machinelearninguseinhealthcare..........................................185
9.4.1Diagnoseheartdisease..................................................185
9.4.2Diabetesprediction.......................................................186
9.4.3Liverdiseaseprediction................................................187
9.4.4Surgeryonrobots..........................................................187
9.4.5Detectionandpredictionofcancer...............................188
9.4.6Treatmenttailored.........................................................188
9.4.7Discoveryofdrugs........................................................190
9.4.8Recorderofintelligentdigitalwellbeing......................190
9.4.9Radiologymachinelearning.........................................190
9.4.10Studyandclinicaltrial..................................................191
9.5 Cancerinhealthcare...................................................................192
9.5.1Methods...........................................................................192
9.5.2Result...............................................................................192 9.6 BreastcancerinIoHTML..........................................................193
9.6.1Studyofbreastcancerusingtheadaptivevoting algorithm.......................................................................193
9.6.2Softwaredevelopmentlifecycle(SDLC)....................193
9.6.3PartsofundertakingdutyPDRandPER.....................194
9.6.4Infostructure.................................................................195
9.6.5Inputstage.....................................................................195
9.6.6Outputdesign................................................................195
9.6.7Responsibledevelopersoverview.................................195
9.6.8Dataflow.......................................................................196
9.6.9Cancerpredictionofdataindifferentviews................196
9.6.10Cancerpredicationinusecaseview............................196
9.6.11Cancerpredicationinactivityview..............................196
9.6.12Cancerpredicationinclassview..................................196
9.6.13Cancerpredicationinstatechartview.........................198
9.6.14Symptomsofbreastcancer...........................................198
9.6.15Breastcancertypes.......................................................198
9.7 Casestudyinbreastcancer........................................................200
9.7.1Historyandassessmentofpatients.................................201
9.7.2Recommendationsfordiagnosis.....................................201
9.7.3Discourse.........................................................................202
9.7.4Outcomesofdiagnosis....................................................203
10.4 Datacollection...........................................................................214
10.4.1Recordingprocedure.....................................................214
10.4.2Noisereduction.............................................................215
10.5 Speechsignalprocessing...........................................................215
10.5.1Samplingandquantization...........................................216
10.5.2Representationofthesignalintimeand frequencydomain..........................................................217
10.5.3Frequencyanalysis........................................................219
10.5.4Shorttimeanalysis........................................................221
10.5.5Short-timefourieranalysis............................................222
10.5.6Cepstralanalysis...........................................................222
10.5.7Preprocessing:thenoisereductiontechnique..............223
10.5.8Frameblocking.............................................................225
10.5.9Windowing....................................................................226
10.6 Featuresforspeechrecognition.................................................226
10.6.1Typesofspeechfeatures...............................................226
10.7 Speechparameterization............................................................228
10.7.1Featureextraction..........................................................228
10.7.2Linearpredicativecoding(LPC)..................................229
10.7.3Linearpredictivecepstralcoefficients(LPCC)............231
10.7.4Weightedlinearpredictivecepstralcoefficients (WLPCC)......................................................................233
10.7.5Mel-frequencycepstralcoefficients.............................234
10.7.6Deltacoefficients..........................................................239
10.7.7Delta deltacoefficients...............................................240
10.7.8Powerspectrumdensity................................................240
10.8 Speechrecognition.....................................................................242
10.8.1Typesofspeechpatternrecognition.............................244
10.9 Speechclassification..................................................................244
10.9.1Artificialneuralnetwork(ANN)..................................245
10.9.2Supportvectormachine(SVM)....................................245
10.9.3Lineardiscriminantanalysis(LDA).............................246
10.9.4Randomforest...............................................................246
10.10 Summaryanddiscussion............................................................246 References..................................................................................248
11.1 Aleapintothehealthcaredomain.............................................251
11.2 Therealfactsofhealthrecordcollection..................................253
11.3 Aproposalforthefuture............................................................254
11.4 Discussionsandconcludingcommentsonhealthrecord collection....................................................................................255
11.5 Backgroundofelectronichealthrecordsystems.......................256
11.5.1Thedefinitionofanelectronichealth record(EHR).................................................................256
11.5.2Ashorthistoryofelectronichealthrecords.................257
11.6 Reviewofchallengesandstudymethodologies........................257
11.6.1AnalyzingEHRsystemsandburnout..........................257
11.6.2AnalyzingEHRsystemsandproductivity...................258
11.6.3AnalyzingEHRsystemsanddataaccuracy.................259
11.7 Conclusionanddiscussion.........................................................260 References..................................................................................261
Listofcontributors
GauravAggarwal
SchoolofComputingandInformationTechnology,ManipalUniversityJaipur, Jaipur,India
IshpreetAneja
DepartmentofDataScience,RochesterInstituteofTechnology,Rochester,NY, UnitedStates
AshuAshu
DepartmentofComputerScience,AmityUniversity,Noida,India
PushpaChoudhary
DepartmentofInformationTechnology,G.L.BajajInstituteofTechnologyand Management,GreaterNoida,India
SubhadipChowdhury
DurgapurSocietyofManagementScienceCollege,KNU,Asansol,India
SubhankarDas
ResearcherandLecturer,HonorsProgramme,DuyTanUniversity,DaNang, Vietnam
RitamDutta
SurendraInstituteofEngineeringandManagement,MAKAUT,Kolkata,India
LataGadhavi
ITDepartment,GovernmentPolytechnicGandhinagar,Gandhinagar,India
G.S.PradeepGhantasala
DepartmentofComputerScienceandEngineering,ChitkaraUniversity InstituteofEngineering&Technology,Chandigarh,India
SaradaPrasadGochhayat
VirginiaModeling,AnalysisandSimulationCentre,SimulationandVisualization Engineering,OldDominionUniversity,Suffolk,VA,UnitedStates
NalliVinayaKumari
DepartmentofComputerScienceandEngineering,MallaReddyInstituteof TechnologyandScience,Hyderabad,India
SubhraRaniMondal
ResearcherandLecturer,HonorsProgramme,DuyTanUniversity,DaNang, Vietnam
AnandNayyar
FacultyofInformationTechnology,GraduateSchool,DuyTanUniversity, DaNang,Vietnam
RizwanPatan
DepartmentofComputerScienceandEngineering,VelagapudiRamakrishna SiddharthaEngineeringCollege,Vijayawada,India
VandanaPatel
DepartmentofInstrumentationandControlEngineering,LalbhaiDalpatbhai CollegeofEngineering,Ahmedabad,India
AnjuS.Pillai
DepartmentofElectricalandElectronicsEngineering,AmritaSchoolof Engineering,AmritaVishwaVidyapeetham,Coimbatore,India
VijayalakshmiSaravanan
FacultyinDepartmentofSoftwareEngineering,RochesterInstituteof Technology,Rochester,NY,UnitedStates
AnkitK.Shah
DepartmentofInstrumentationandControlEngineering,LalbhaiDalpatbhai CollegeofEngineering,Ahmedabad,India
ShilpiSharma
DepartmentofComputerScience,AmityUniversity,Noida,India
AkanshaSingh
DepartmentofCSE,ASET,AmityUniversityUttarPradesh,Noida,India
ArunKumarSingh
DepartmentofInformationTechnology,G.L.BajajInstituteofTechnologyand Management,GreaterNoida,India
KrishnaKantSingh
FacultyofEngineering&Technology,Jain(Deemed-to-beUniversity), Bengaluru,India
LatikaSingh
AnsalUniversity,Gurugram,India
NarendraSingh
DepartmentofManagementStudies,G.L.BajajInstituteofManagementand Research,GreaterNoida,India
PushpaSingh
DepartmentofComputerScienceandEngineering,DelhiTechnicalCampus, GreaterNoida,India
AshishTripathi
DepartmentofInformationTechnology,G.L.BajajInstituteofTechnologyand Management,GreaterNoida,India
PremChandVashist
DepartmentofInformationTechnology,G.L.BajajInstituteofTechnologyand Management,GreaterNoida,India
HongYang
DepartmentofDataScience,RochesterInstituteofTechnology,Rochester,NY, UnitedStates
NoorZaman
SchoolofComputerScienceandEngineeringSCE,Taylor’sUniversity,Subang, Jaya,Malaysia
Machinelearning architectureandframework
1
AshishTripathi1,ArunKumarSingh1,KrishnaKantSingh2,PushpaChoudhary1 andPremChandVashist1
1DepartmentofInformationTechnology,G.L.BajajInstituteofTechnologyandManagement, GreaterNoida,India 2FacultyofEngineering&Technology,Jain(Deemed-to-beUniversity),Bengaluru,India
1.1 Introduction
In1959,ArthurSamuelproposedthetermMachineLearning(ML).Hewasthe masterofartificialintelligenceandcomputergaming.Hestatedthatmachine learninggivesalearningabilitytocomputerswithoutbeingexplicitly programmed.
In1997arelationalandmathematical-baseddefinitionofmachinelearning wasgivenbyTomMitchellinthatacomputerprogramusesexperience“e”to learnfromsometask“t.”Itapplies“p”asaperformancemeasureon“t”that automaticallyimproveswith“e.”
Inrecentyears,machinelearninghasbeenappearingasthemostsignificant technologyaroundtheglobetosolvemanyreal-lifeproblems.So,itisemerging asaverypopulartechnologyamongtheresearchersandindustrypeopleforproblemsolving.
Machinelearningisasubdomainofartificialintelligence(AI)thathelps machinestoautomaticallylearnfromexperienceandimprovetheirabilitytotake decisionstosolveanyproblemwithouttakinganyexplicitinstructions.Thefocus ofMListodevelopandapplycomputerprogramsthatareabletolearnfromthe problemdomainandmakebetterdecisions [1]
ThelearningprocessinMLstartswithobservingandanalyzingthedata throughdifferenttechniques,suchasusingexamples,experiences,relyingonpatternmatchingindata,etc.,thatallowsmachinestotakedecisionswithoutany assistancefromhumansoranyotherintervention [2]
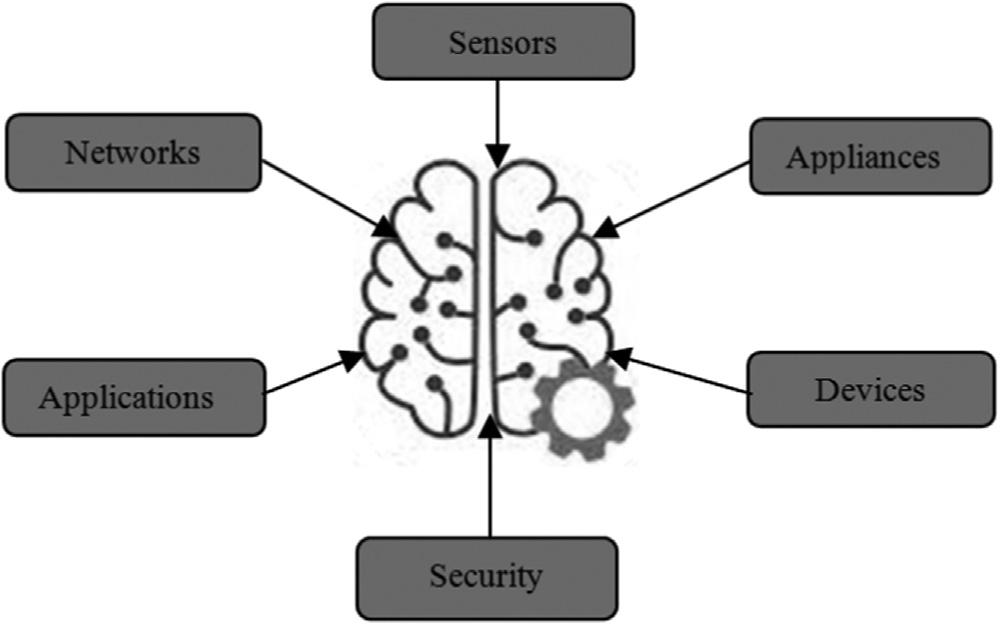
Machine-learningalgorithmstakeasampledatasetasaninput,whichisalso knownasthetrainingdataset,tobuildandtrainamathematicalmodel(MLsystem).Inputdatamayincludetext,numerics,audio,multimedia,orvisualthings andcanbetakenfromvarioussourcessuchassensors,applications,devices, networks,andappliances.
MachineLearningandtheInternetofMedicalThingsinHealthcare.DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-821229-5.00005-7 Copyright © 2021ElsevierInc.Allrightsreserved.
Themathematicalmodelisusedtoextractknowledgefromtheinputdata throughanalyzingitselfwithoutanyexplicitprogrammingintervention.
Afterprocessingthedata,itgivessomeresponseasanoutput.Theoutput maybeintheformofanintegervalueorafloating-pointvalue [3]. Fig.1.1 showsthelearningofaMLsystemfromdatawithexplicitprogrammingsupport.
Unlikeconventionalalgorithms,MLalgorithmsareapplicableindifferent applications,suchascomputervision,filteringofemails,ecommerce,healthcare systems,andmanymore,toprovideeffectivesolutionswithhighaccuracy.
1.1.1 Machinelearningclassification
Learningcanbeunderstoodasaprocessthatconvertsexperienceintoexpertise. So,thelearningshouldbemeaningfulinrespecttosometask.Itisaclearly definedprocessthattakessomeinputsandproducesanoutputaccordingly.
Machine-learningalgorithmshavethreemajorclassificationsthatdependon thetypeandnatureofdataprovidedtothesystem,whichareasfollows:
1.1.1.1 Supervisedlearning
Supervisedlearningstartswithadatasetwhichcontainsbothinputandexpected outputdatawithlabels.Theselabelsareusedforclassificationandprovideabase forlearning [4].Thishelpsinfuturedataprocessing.
Thetermsupervisedlearningisconsideredtobeasystemwhichcontains pairsofinputsandoutputstoprovidetrainingtothemachinetocorrelateinputs andoutputsbasedoncertainrules [5]
Indeed,supervisedlearningistotrainthemachinehowthegiveninputsand outputscanbemappedorrelatedtogether.Theobjectiveofthislearningisto
FIGURE1.1 LearningofaMLsystemfromdifferentdatasources.
makethemachinecapableenoughbyproducingamappingfunctiontopredict thecorrectoutputonthegiveninputstothesystem.
Supervisedlearningisapplicableinvariousapplications,suchasself-driving cars,chatbots,facialrecognition,expertsystems,etc.
ArtificialNeuralNetworks [6,7],LogisticRegression [8],SupportVector machine [9],K-NearestNeighbor [10],andNaıveBayesClassifier [11] aresome examplesofsupervisedlearningalgorithms.
Unsupervisedlearningproblemsaregroupedunderclassificationand regression.
• Classification:itisatechniquethathelpstocategorizetheinputsintotwoor moreclassesbasedonthefeaturesoftheinputs.Itisusedtoassignthe correctclasslabeltotheinputs [12].Inclassification,predictionisbasedon yesorno [13].Asuitableexampleofclassificationisspamfilteringinwhich inputsareemailmessagesandthecorrespondingclassesarespamandnot spam.Otherexamplesaresentimentanalysistoanalyzethepositiveand negativesentiment,labelingofsecureandunsecureloans,andtoclassify whetherthepersonismaleorfemale.
• Regression:inregression,acontinuousorrealratherthandiscretevalueis obtainedastheoutput [14].
Forexample,thepredictionofhousepricebasedonsizeorquantifyingheight basedontherelativeimpactofgender,age,anddiet.
1.1.1.2 Unsupervisedlearning
Unsupervisedlearningisusedwherethedataarenotlabeledorclassifiedtotrainthe system [15].Thereisnolabeledsampledataavailableforthetrainingpurposes. Thislearningsystemitselfworkstoexploreandrecognizethepatternsand structuresintheinputdatatoobtainapredictedvalueorclassificationofan object [16].
Unsupervisedlearningdoesnotclaimtogivetheexactfigureoftheoutput. Thisformoflearningisappliedonunlabeleddatatotrainthesystemto exploreandexploitthehiddenstructure.Ithelpstocategorizetheunclassified andunlabeleddatabasedonfeatureextraction [17].Thislearningsystemworks inareal-timescenarioandhencethepresenceoflearnersistheprimenecessity tolabelandanalyzetheinputdata [18]
Thusinthislearning,humaninterventionforanalyzingandlabelingtheunlabeleddataisrequired,whichisnotfoundinsupervisedlearning [19].
Unsupervisedlearningcanbeunderstoodbyanexample:anunseenimage containinggoatandsheephasbeengivenforidentifyingbothseparately.Thusin theabsenceoftheinformationaboutthefeaturesofboththeanimals,themachine isnotabletocategorizeboth.But,wecancategorizeboththesheepandgoat basedontheirdifferences,similarities,andpatterns.First,weneedtoseparatethe picturesofgoatsandsecondlycollectallpicturesofsheepfromtheimage.Here, inthetask,therehasnotbeenanytrainingorsampledatausedtotrainthe
machinepreviously.Mappingofnearestneighbor,valuedecomposition,selforganizingmaps,andk-meansclusteringarethemostusedunsupervisedlearning techniques.
Unsupervisedlearningproblemsaregroupedintoclusteringandassociation problems.
• Clustering:thisconceptdealswithfindingagroupofuncategorizeddatabased oncertainfeatures,patterns,orstructures [20].Theclusteringalgorithmsare responsibleforidentifyinggroups/clustersofdata.Forexample,considering purchasingbehaviorofcustomerstoidentifyagroupofcustomers.
• Association:thisallowstheestablishmentofassociationamongdataobjects fromthelargesetofyourdata [18,21].Thiscanbeunderstoodby,for example,anassociationexistsifapersonthatbuysanobjectxthenalsohasa tendencytobuyobjecty.
1.1.1.3 Reinforcementlearning
Reinforcementlearninginvolvesinteractionwiththesurroundingenvironment anditappliesatrialanderrorapproachtoobtainrewardsorerrors.Algorithms identifythoseactionswhichcontainthebestrewards [22].
Reinforcementlearninghasthreemaincomponents:environment,actions,and agent.Heretheagentworksasadecision-maker,actionsdenotethestepsthataretaken bytheagent,andtheenvironmentisthedomaininwhichtheagentdoestheinteraction [23].Togetthemaximumlevelofperformancefrommachine/softwareagents,this learninghelpstodecidetheidealbehaviorautomaticallyforaparticularcontext.
Thistypeoflearningtechniqueusesareinforcementsignalthatrequiresfeedbackforguidingtheagenttodecidethebestamongalltheavailableactions. Additionally,ithelpstodecidetotakeaction,whereitishardtopredictthelevel ofseverityforcertainsituationsbasedongoodnessorbadness [24].Thislearning enablesmachinestolearnandplaygames,drivevehicles,etc.
So,themainobjectiveofreinforcementlearningistoapplythebesttechnique toachieveafastbusinessoutcomeasearlyaspossible.
1.2 Architectureofmachinelearning
Therequiredindustryinteresthasbeenincorporatedinthearchitectureof machinelearning.
Thustheobjectiveistooptimizetheuseofexistingresourcestogettheoptimizedresultusingtheavailabledata.Also,thishelpsinpredictiveanalysisand dataforecastinginvariousapplications,especiallywhenitislinkedwithdatasciencetechnology.
Thearchitectureofmachinelearninghasbeendefinedinvariousstages.Each stagehasdifferentrolesandallstagesworktogethertooptimizethedecisionsupportsystem.
FIGURE1.2 Phasesofmachinelearningarchitecture.
Thearchitectureofmachinelearninghasbeendividedintofivestages,such asdataacquisition,dataprocessing,datamodeling,execution,anddeployment. Thesestagesareshownin Fig.1.2
Thedetailsareasfollows:
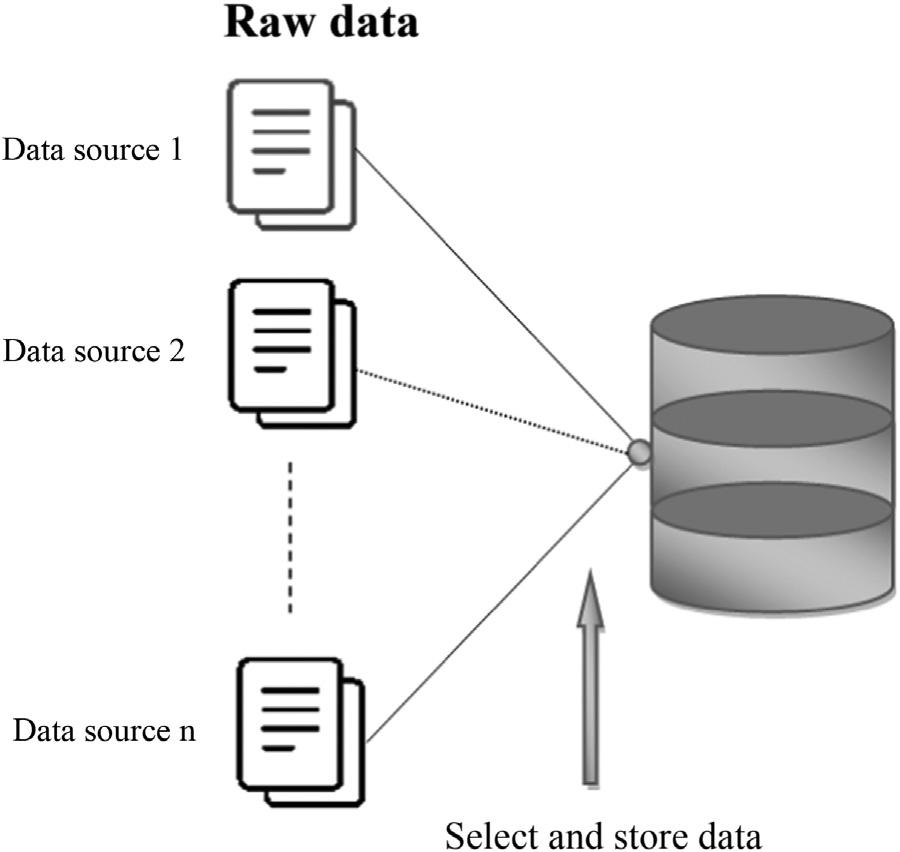
1.2.1 Dataacquisition
Itiswell-knownthattheacquisitionofdataisproblem-specificanditisunique foreachMLproblem.Theexactestimationofdataisverydifficultinorderto obtaintheoptimalutilitywithrespecttomachinelearningproblems.Itisvery toughtopredictwhatamountofdataisrequiredtotrainthemodelintheearly stageofdataacquisition.
Insomeresearchactivities,itisfoundthatmorethantwo-thirdsofthecollecteddatamaybeuseless.Also,atthetimeofdatacollection,itisverydifficult tounderstandwhichportionofthedatawillbeabletoprovidethesignificantand correctresultbeforethetrainingbeginsforamodel.Thereforeitbecomesessentialtoaccumulateandstoreallkindsofdata,whetheritisrelatedtostructured, unstructured,online,offline,open,andinternal.Sothisphaseofdataacquisition shouldbetakenveryseriouslybecausethesuccessoftheMLmodeltraining dependsontherelevanceandqualityofdata.
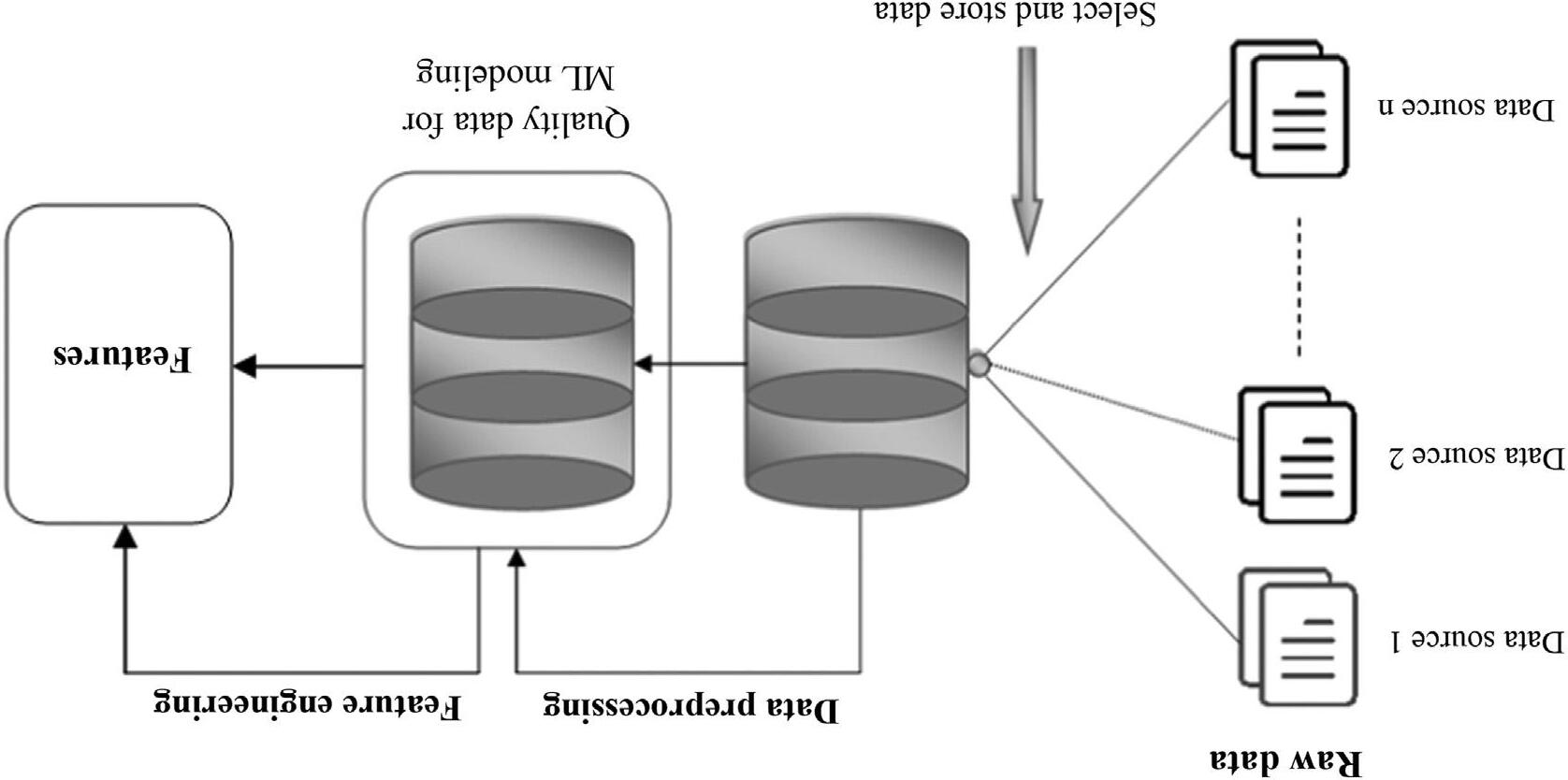
ThereforethedataacquisitionisthefirstphaseinMLarchitecturethatapplies toaccumulatetheessentialdatafromdifferentsources [25],asshownin Fig.1.3.
Thedataisfurtherprocessedbythesystemtomakeadecisionforsolvinga givenproblem.Thisincludesdifferentactivitiessuchasgatheringcomprehensive andrelevantdata,case-baseddatasegregation,andvalidinterpretationofdatafor storingandprocessingaspertherequirements [26].
Actually,thedataisgatheredfromdifferentsourcesinanunstructuredformatand everysourcehasadifferentformatwhichisnotsuitableforanalysispurposes [27].
1.2.2 Dataprocessing
Thisstageacceptsdatafromthedataacquisitionlayertoapplyfurtherprocessing whichincludesdataintegration,normalization,filtering,cleaning,transformation, andencodingofdata.
Processingofdataalsodependsonthelearningtechniqueswhichhavebeen usedtosolvetheproblem [28].Forexample,inthecaseofsupervisedlearning, datasegregationisperformedwhichcreatessampledatainseveralsteps.The sampledataisfurtherappliedtotrainthesystemandthusthecreatedsampledata isgenerallycalledthetrainingdata [29].
Inunsupervisedlearning,theunlabeleddataismainlyusedforanalysispurposes.Thusthislearningtechniquemainlydealswithunpredictabledatathatare morecomplicatedandrequirecomplexprocessingascomparedtootherexisting learningtechniques [29]
Inthiscasedataaregroupedintoclustersandeachclusterbelongstoaspecificgroup.Eachclusterisformedbasedonthegranularityofthedata.
Thekindofprocessingisanotherfactorofdataprocessingwhichisbased onthefeaturesandactiontakenonthecontinuousdata.Also,itmayprocess upondiscretedata.Processingondiscr etedatamayneedmemoryboundprocessing [30]
So,theobjectiveofthisstageistoprovideacleanandstructureddataset. Sometimes,thisstageisalsoknownasthepreprocessingstage.Somemajorsteps comeunderthisphaseofMLarchitecture,whichareasfollows:
1.2.2.1 Arrangementofdata
Thestoreddataarerequiredtobearrangedinsortedorderwiththefiltering mechanism.Thishelpstoorganizethedatainsomeunderstandableform.
FIGURE1.3 Dataacquisition.
Itbecomesveryeasytoretrievetherequiredinformation,whichisnecessaryfor thevisualizationandanalysispurposesofthedata.
1.2.2.2
Analysisofdata
Thein-depthanalysisstartstounderstandthedataintermsofitstype,anymissingparts,valueofdata,correlationamongdata,andmuchmore,inordertotake furtheractiononthedata.Indataanalysis,dataisevaluatedbasedonthelogical andanalyticalreasoningtoexploreandexplaineachelementofthedataprovided toreachafinalconclusion.
1.2.2.3
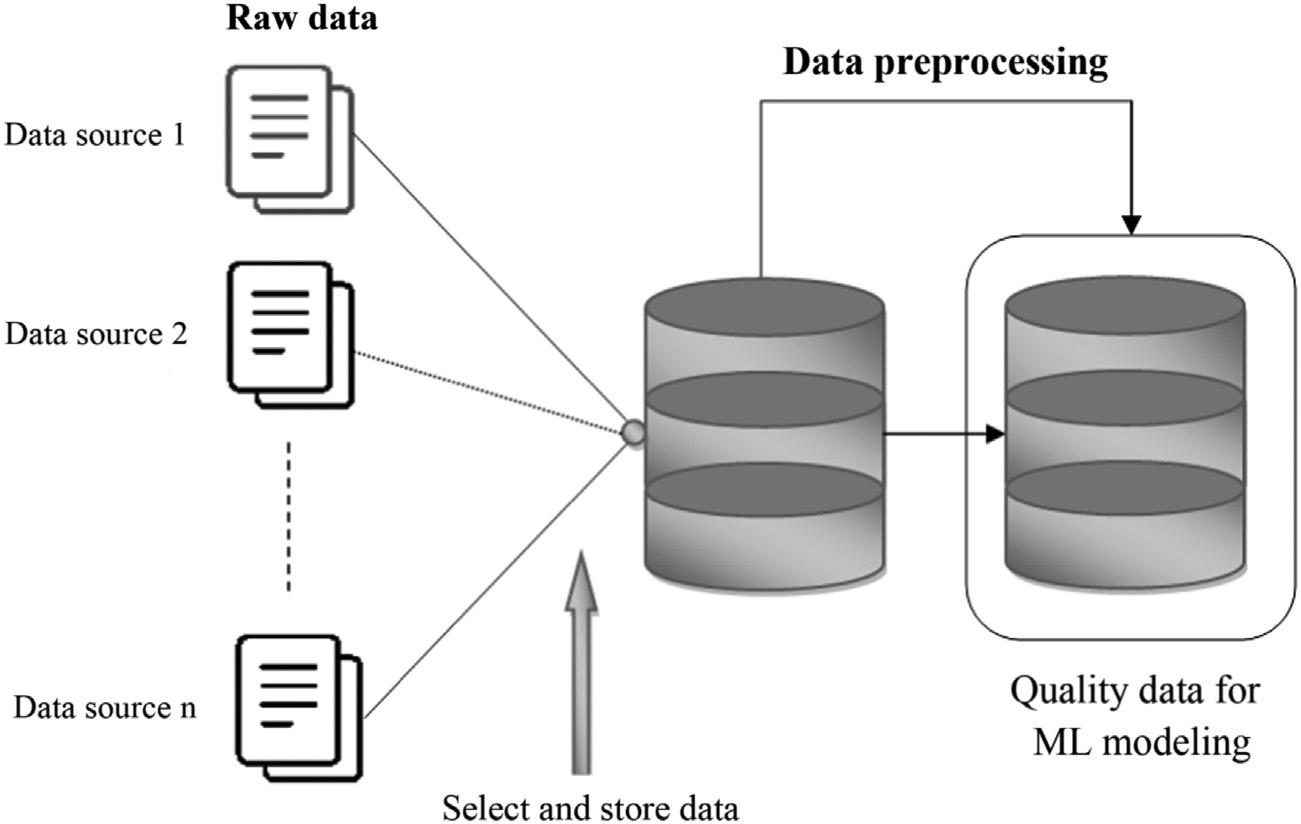
Preprocessingofdata
Datapreprocessingisatechniquethatperformsthenecessaryconversionofthe rawdataintotheformwhichcanbeacceptedbythemachinelearningmodelas shownin Fig.1.4.Initiallythedataarecollectedinanunstructuredmannerfrom differentsourcesduringthedatacollection,thusthedatarequiresrefiningbefore involvementinthemachinelearningmodeling.Toprovidequalitydatasome approachesarerequiredtobetakensuchasformattingofdata,datacleaning (handleincompletedataduetonoiselikemissingvalues),andsamplingofdata. Thereforetheconversionfrominconsistent,incomplete,anderror-pronedata intoanunderstandable,clean,andstructuredformallowstheenhancementofthe accuracyandefficiencyoftheMLmodel.Asaresult,theenhancedMLmodel mightbeabletoprovidepreciseandoptimalresults.
FIGURE1.4
Dataprocessing:datapreprocessing.
1. Dataformatting:theimportanceofdataformattinggrowswhendatais acquiredfromvarioussourcesbydifferentpeople.Thefirsttaskforadata scientististostandardizerecordformats.Aspecialistcheckswhether variablesrepresentingeachattributearerecordedinthesameway.Titlesof productsandservices,prices,dateformats,andaddressesareexamplesof variables.Theprincipleofdataconsistencyalsoappliestoattributes representedbynumericranges.
2. Datacleaning:thissetofproceduresallowsfortheremovalofnoiseandthe fixingofinconsistenciesinthedata.Adatascientistcanfillinmissingdata usingimputationtechniques,e.g.,substitutemissingvalueswithmean attributes.Aspecialistalsodetectsoutliers’observationsthatdeviate significantlyfromtherestofdistribution.Ifanoutlierindicateserroneous data,adatascientistdeletesorcorrectsthem,ifpossible.Thisstagealso includesremovingincompleteanduselessdataobjects.
3. Datasampling:bigdatasetsrequiremoretimeandcomputationalpowerfor analysis.Ifadatasetistoolarge,applyingdatasamplingisthewaytogo. Adatascientistusesthistechniquetoselectasmallerbutrepresentativedata sampletobuildandrunmodelsmuchfaster,andatthesametimetoproduce accurateoutcomes.
1.2.2.4
Transformationofdata
ThisstepinvolvestheconversionofdataintoaformsuitablefortheMLmodel. Fordatatransformationthefollowingtechniquesareused:
1. Scalingofdata:thisisalsoknownasthenormalizationofdata.Ifattributes (features)ofdataarenumericthenthescalingoftheattributesbecomes essentialtoputthemintoacommonscale.Thenumericattributesofdata havedifferentranges,suchaskilometers,meters,andmillimeters, representingthedatavalue.Forexample,scalingofanattributefora minimumvaluemaybeintherange0to10,andforthemaximumvalue,it maybein-between11and100.
2. Decompositionofdata:itbreaksthecomplexdataintosmallerpartwhich makesiteasiertounderstandthedatapatterns.Decompositionisatechnique thatovercomestheissueofthecomplexconceptofattributesandbreaksthe complexfeaturesintosimplesubfeaturesthatmakesthedatamore understandableandmeaningful.Also,itguidesthemachinetowherethenew featurescanbeadded.Decompositionismostlyapplicablefortheanalysisof timeseriesdata.Estimatingademandforgoodspermonthforlocalvendors, amarketanalysisbasedonthedataofbigorganizationstoknowthedemand ofgoodsperthreemonths,orpersixmonths,areexamplesofdecomposition.
3. Aggregationofdata:aggregationcanbeunderstoodasthereverseprocessof decomposition.Inaggregation,severalfeaturesarecombinedintoasingle featureandwheneverrequiredallfeaturescanbeexplored.Inotherwords, theaggregationrepresentsthesummarizedformofthecollecteddatawhich
canbeusedfurtherfordataanalysis.Thisisthesignificantstepofdata transformation,wherethequalityandamountofdatadecidetheaccuracyof thedataanalysis.Therearevariousapplicationswheredataaggregationcan beused,whichmayincludethefinancesector,marketingplans,productionrelateddecisions,andproductpricing.
4. Featureengineering:thisisasignificanttaskinMLarchitectureinwhichthe requiredfeaturesareselectedandextractedfromthedata,whichisrelevantto thetaskormodeltobedeveloped,asshownin Fig.1.5.Therelevantfeatures ofdataarefurtherusedtoenhancethepredictiveefficiencyMLalgorithms. Thereforefeatureengineeringshouldbedonecorrectly,otherwiseitwill affecttheoveralldevelopmentoftheMLmodel.Featureengineeringinvolves foursubtasks:(1)featureselection:itdealswithselectingthemostusefuland relevantfeaturesfromthedata;(2)featureextraction:selectedfeaturesare extractedfromthedatafordatamodeling;(3)featureaddition:existing featuresareaddedwithnewfeaturesselectedandextractedfromnewly gathereddata;and(4)featurefiltering:irrelevantfeaturesarefilteredoutto makeMLmodelmoreefficientandeasytohandle.
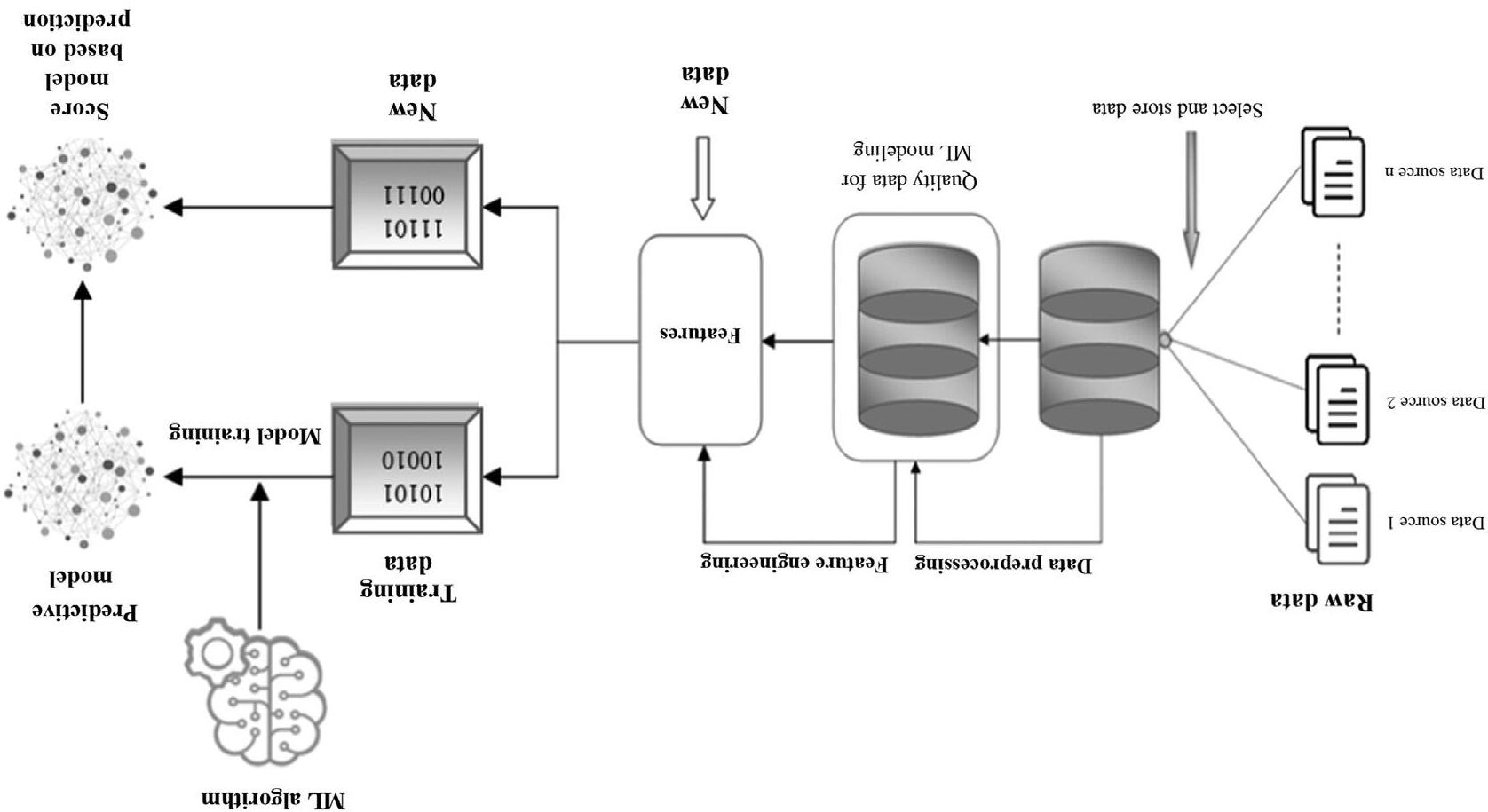
1.2.3 Datamodeling
Datamodelinginvolvestheselectionofanappropriatealgorithmwhichshouldbe mostadaptableforthesystemtoaddresstheissuesintheproblemstatement [31]. ItinvolvesprovidingtrainingtoaMLalgorithmtodopredictionsbasedonthe availablefeatures,parametertuningasperthebusinessneeds,anditsvalidation onthesampledata.Thealgorithmsinvolvedinthisprocessareevolvedthrough learningtheenvironmentandapplyingthetrainingdatasetusedinthelearning process [32].Atrainedmodelreceivedaftersuccessfulmodelingisusedforinferencewhichallowsthesystemtodopredictionsonnewdatainputs.Theprocess ofdatamodelingisshownin Fig.1.6
Inthedatamodelingstage,variousmodelsaretrainedbythedatascientist. Theobjectiveofthisstageistoidentifythemodel,whosepredictionaccuracyis betterincomparisontoothers.
Thedatausedformodeltrainingarecategorizedintotwosubsets.Thefirst subsetofthedataisknownasatrainingdatasetwhichisusedastheinputto assisttheMLalgorithmduringthetrainingofthemodel.Theinputdataisthen processedbytheMLalgorithmwhichgivesamodelforpredictiveanalysison newdata.
Thetrainingcontinuesuntilwegetthedesiredmodel.Thetraininghelpsthe modeltoimproveitspredictivehypothesisfornewdata.Inotherwords,wecan saythatthismakesthemodelabletopredicttheintendedvaluefromthenew data.Thetrainingdatacanbelabeledorunlabeled.
Thelabeleddatahasthevalueassociatedwithit,whiletheunlabeleddatahas nopredefinedvalue.
FIGURE1.5 Dataprocessing:featureengineering.
Datamodeling:modeltrainingandscoringmodelbasedonnewdata.
FIGURE1.6
Thesecondsubsetofdataisknownastestdata.Thetestdataisusedtotest thepredictivehypothesisofthemodelwhichiscreatedduringthetraining.The overallobjectiveofthedatamodelingistodevelopsuchamodel,whichisable todothepredictiveanalysisoffuturedatawithhighaccuracy.
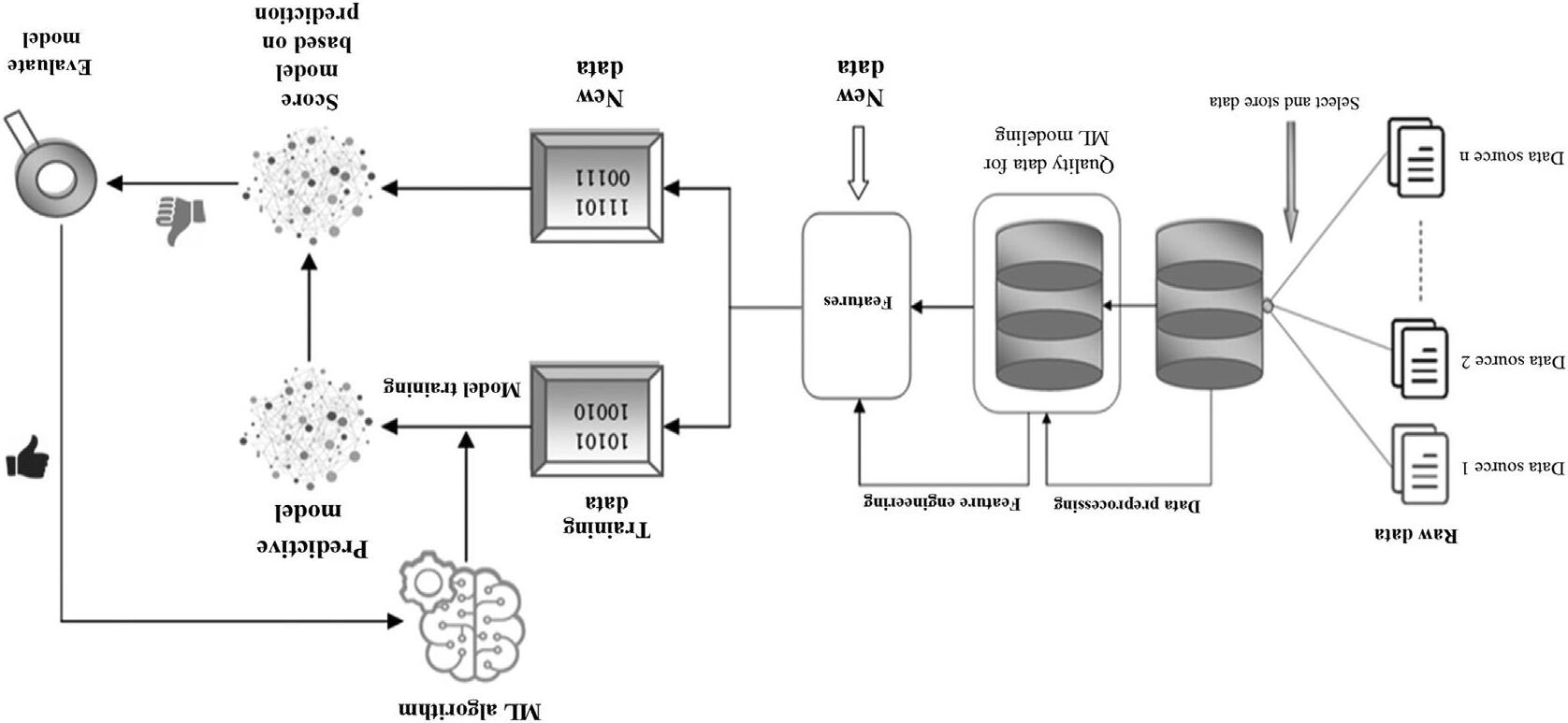
1.2.4 Execution(modelevaluation)
Theexecutionstageinvolvesapplication,testing,andfinetuningofthealgorithm (model)ontestdataset(unseendata).Theobjectiveofthisstageistoretrieve theexpectedoutcomefromthemachineandtooptimizethesystemperformance atthemaximumlevel [33].
AtthisstageofMLarchitecture,thesolutionprovidedbythesystemiscapableenoughtoexploreandprovidetherequireddatafordecision-makingbythe machine [34],asshownin Fig.1.7.
1.2.5 Deployment
Deploymentisthecrucialstagewhichdecideshowthemodelwillbedeployed intothesystemfordecision-making.Atthisstagethemodelactuallyisappliedin arealscenarioandalsoundergoesfurtherprocessing.Furthertheoutputofthe workingmodelisappliedasaninstructionintothesystemfordecision-making activities [35]
TheoutputoftheMLoperationsisdirectlyappliedtothebusinessproduction whereitplaysasignificantroleinenablingthemachinetotakeoutput-based expertdecisionswithoutdependencyonotherfactors.ThedeploymentofML modelisshownin Fig.1.8
1.3 Machinelearningframework
TheMLframeworkcanbeunderstoodasalibrary,aninterface,oratoolthat helpsworkingprofessionalstodevelopmodelsofmachinelearningwithease withoutworryingabouttheunderlyingprinciplesandcomplexitiesofthealgorithms [36].Theframeworkprovidestheoptimizedandprebuiltcomponentsto buildeasy,meaningful,andquickMLmodelsandotherrelatedtasks.
1.3.1 FeaturesofMLframework
Tochoosetherightframework,oneshou ldkeepthefollowingkeyfeatures inmind [37] ( https://hackernoon.com/top-10-ma chine-learning-frameworksfor-2019-h6120305j ).
• Frameworkshouldbeabletoprovideoptimizedperformance.
• Itshouldbeeasyandfriendlytohandlebythedevelopercommunity.
FIGURE1.7
Execution:modelevaluation.