https://ebookmass.com/product/hybrid-nanofluids-preparationcharacterization-and-applications-zafar-said/
Instant digital products (PDF, ePub, MOBI) ready for you
Download now and discover formats that fit your needs...
Amorphous Nanomaterials: Preparation, Characterization and Applications Lin Guo
https://ebookmass.com/product/amorphous-nanomaterials-preparationcharacterization-and-applications-lin-guo/
ebookmass.com
Two-Dimensional-Materials-Based Membranes: Preparation, Characterization, and Applications Gongping Liu
https://ebookmass.com/product/two-dimensional-materials-basedmembranes-preparation-characterization-and-applications-gongping-liu/
ebookmass.com
Applications of hybrid nanofluids in solar energy, practical limitations and challenges_ A critical review Tayyab Raza Shah & Hafiz Muhammad Ali
https://ebookmass.com/product/applications-of-hybrid-nanofluids-insolar-energy-practical-limitations-and-challenges_-a-critical-reviewtayyab-raza-shah-hafiz-muhammad-ali/ ebookmass.com
Fated to the Alien Warrior: A
Fated Mates Alien Romance (Warriors of Tavikh Book 1) Erin Hale
https://ebookmass.com/product/fated-to-the-alien-warrior-a-fatedmates-alien-romance-warriors-of-tavikh-book-1-erin-hale/ ebookmass.com
Critical Thinking 12th Edition Brooke Noel Moore
https://ebookmass.com/product/critical-thinking-12th-edition-brookenoel-moore/
ebookmass.com
Wiley's 22 Years' JEE Advanced - Wiley Editorial.pdf User
https://ebookmass.com/product/wileys-22-years-jee-advanced-wileyeditorial-pdf-user/
ebookmass.com
The Fossil-Fuelled Climate Crisis: Foresight or Discounting Danger? 1st ed. Edition Raymond Murphy
https://ebookmass.com/product/the-fossil-fuelled-climate-crisisforesight-or-discounting-danger-1st-ed-edition-raymond-murphy/
ebookmass.com
ChatGPT MASTERY 12 Books in 1: Unlocking the Potential of AI, Everything you Need to know to Make Money Mastering AI Irvin
https://ebookmass.com/product/chatgpt-mastery-12-books-in-1-unlockingthe-potential-of-ai-everything-you-need-to-know-to-make-moneymastering-ai-irvin/
ebookmass.com
Ghost Dick; A Port Canyon Chronicle Kincaid
https://ebookmass.com/product/ghost-dick-a-port-canyon-chroniclekincaid/
ebookmass.com
MicroFinTech: Expanding Financial Inclusion with CostCutting Innovation 1st Edition Moro-Visconti
https://ebookmass.com/product/microfintech-expanding-financialinclusion-with-cost-cutting-innovation-1st-edition-moro-visconti/
ebookmass.com
HYBRIDNANOFLUIDS
HYBRIDNANOFLUIDS
Preparation,Characterization andApplications
Editedby
ZAFARSAID
DepartmentofSustainableandRenewableEnergyEngineering,Universityof Sharjah,Sharjah,UnitedArabEmirates
ResearchInstituteforSciencesandEngineering,UniversityofSharjah,Sharjah, UnitedArabEmirates
U.S.-PakistanCenterforAdvancedStudiesinEnergy(USPCAS-E),National UniversityofSciencesandTechnology(NUST),Islamabad,Pakistan
Elsevier
Radarweg29,POBox211,1000AEAmsterdam,Netherlands
TheBoulevard,LangfordLane,Kidlington,OxfordOX51GB,UnitedKingdom 50HampshireStreet,5thFloor,Cambridge,MA02139,UnitedStates
Copyright©2022ElsevierInc.Allrightsreserved.
Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproducedortransmittedinanyformorbyanymeans,electronicor mechanical,includingphotocopying,recording,oranyinformationstorageandretrievalsystem,without permissioninwritingfromthepublisher.Detailsonhowtoseekpermission,furtherinformationaboutthe Publisher’spermissionspoliciesandourarrangementswithorganizationssuchastheCopyrightClearance CenterandtheCopyrightLicensingAgency,canbefoundatourwebsite: www.elsevier.com/permissions.
ThisbookandtheindividualcontributionscontainedinitareprotectedundercopyrightbythePublisher (otherthanasmaybenotedherein).
Notices
Knowledgeandbestpracticeinthisfieldareconstantlychanging.Asnewresearchandexperiencebroadenour understanding,changesinresearchmethods,professionalpractices,ormedicaltreatmentmaybecome necessary.
Practitionersandresearchersmustalwaysrelyontheirownexperienceandknowledgeinevaluatingandusing anyinformation,methods,compounds,orexperimentsdescribedherein.Inusingsuchinformationormethods theyshouldbemindfuloftheirownsafetyandthesafetyofothers,includingpartiesforwhomtheyhavea professionalresponsibility.
Tothefullestextentofthelaw,neitherthePublishernortheauthors,contributors,oreditors,assumeany liabilityforanyinjuryand/ordamagetopersonsorpropertyasamatterofproductsliability,negligence orotherwise,orfromanyuseoroperationofanymethods,products,instructions,orideascontained inthematerialherein.
LibraryofCongressCataloging-in-PublicationData
AcatalogrecordforthisbookisavailablefromtheLibraryofCongress
BritishLibraryCataloguing-in-PublicationData
AcataloguerecordforthisbookisavailablefromtheBritishLibrary ISBN:978-0-323-85836-6
ForinformationonallElsevierpublications visitourwebsiteat https://www.elsevier.com/books-and-journals
Publisher: MatthewDeans
AcquisitionsEditor: EdwardPayne
EditorialProjectManager: LeticiaM.Lima
ProductionProjectManager: PremKumarKaliamoorthi
CoverDesigner: GregHarris
TypesetbySTRAIVE,India
Chapter4Hydrothermalpropertiesofhybridnanofluids.
L.SyamSundar,E.VenkataRamana,ZafarSaid,andAntonioC.M.Sousa 4.1Introduction.............................
4.3Frictionfactor............................
4.4Pressuredrop............................
Chapter5Rheologicalbehaviorofhybridnanofluids...
AbdullaAhmadAlshehhi,ZafarSaid,andMahamAslamSohail
5.2Experimentalandnumericalstudiesonrheology.
ArunKumarTiwari,AmitKumar,andZafarSaid
Chapter7Theoreticalanalysisandcorrelationsforpredicting
ArunKumarTiwari,AmitKumar,andZafarSaid
ZafarSaidandMahamAslamSohail
10.6Degradationoforiginalproperties...........
10.7Increasedfrictionfactor,pumpingpower,and
10.8Selectingsuitablehybridnanofluids.........
Contributors
ElhamAbohamzeh DepartmentofEnergy,Materials,andEnergy ResearchCenter(MERC),Karaj,Iran
AbdullaAhmadAlshehhi SpaceMissionsDepartment,UAESpace Agency,AbuDhabi,UnitedArabEmirates
NeetiArora DepartmentofMechanicalEngineering,GuruJambheshwar UniversityofScienceandTechnology,Hisar,Haryana,India
Z.Ebrahimpour DepartmentofMechanicalEngineering;Renewable EnergySystemsandNanofluidApplicationsinHeatTransfer Laboratory,BabolNoshirvaniUniversityofTechnology,Babol,Iran
MunishGupta DepartmentofMechanicalEngineering,Guru JambheshwarUniversityofScienceandTechnology,Hisar,Haryana, India
MehdiJamei FacultyofEngineering,ShohadayeHoveizehCampusof Technology,ShahidChamranUniversityofAhvaz,DashteAzadegan, Iran
AmitKumar MechanicalEngineeringDepartment,Instituteof Engineering&Technology,Dr.A.P.J.AbdulKalamTechnicalUniversity, UttarPradesh,Lucknow,India
E.VenkataRamana I3N,DepartmentofPhysics,UniversityofAveiro, Aveiro,Portugal
ZafarSaid DepartmentofSustainableandRenewableEnergy Engineering;ResearchInstituteforSciencesandEngineering, UniversityofSharjah,Sharjah,UnitedArabEmirates;U.S.-Pakistan CenterforAdvancedStudiesinEnergy(USPCAS-E),National UniversityofSciencesandTechnology(NUST),Islamabad,Pakistan
M.Sheikholeslami DepartmentofMechanicalEngineering;Renewable EnergySystemsandNanofluidApplicationsinHeatTransfer Laboratory,BabolNoshirvaniUniversityofTechnology,Babol,Iran
MahamAslamSohail DepartmentofSustainableandRenewable EnergyEngineering,UniversityofSharjah,Sharjah,UnitedArab Emirates
AntonioC.M.Sousa CentreforMechanicalTechnologyandAutomation (TEMA-UA),DepartmentofMechanicalEngineering,Universityof Aveiro,Aveiro,Portugal
L.SyamSundar CentreforMechanicalTechnologyandAutomation (TEMA-UA),DepartmentofMechanicalEngineering,Universityof Aveiro,Aveiro,Portugal
ArunKumarTiwari MechanicalEngineeringDepartment,Instituteof Engineering&Technology,Dr.A.P.J.AbdulKalamTechnicalUniversity, UttarPradesh,Lucknow,India
Preface
“SeekknowledgefromtheCradletotheGrave.”
ProphetMuhammad(peacebeuponhim)
Hybridnanofluidisintroducedasanewclassforengineering applicationscomprisingsolidparticleswithasizetypicallyranging from1to100nmdispersedinbasefluids.Nanoparticlessuspendedintraditionalheattransferfluidenhancethermalconductivity.Theadditionofthesenanoparticlestotheconventionalheat transferfluidsenhancestheheattransferrate.Inthiswork,thehistoryofhybridnanofluids,preparationtechniques,thermoelectricalproperties,rheologicalbehavior,opticalproperties,theoretical modelingandcorrelations,andtheeffectofallthesefactorsonthe potentialapplicationssuchassolarenergy,electronicscooling, heatexchangers,machining,andrefrigerationarediscussedin detail.Inaddition,futurechallengesandfutureworkscopehave beenincluded.Theinformationfromthisbookwillenablethe readersdevelopnoveltechniques,resolveexistingresearchlimitations,andcomeupwithnovelhybridnanofluids,whichcanbe implementedforheattransferapplications.Thesubjectofthe bookisthecurrentcomprehensiveresearchanddevelopmentof hybridnanofluids,theirimplementationinvariousapplications, anddirectionsforvariousresearchgapsthatarestillrequiredin preparations,stability,characterization,andapplicationstoovercomethechallengesbeingfacedbybothresearchersandthe industryforlarge-scaleapplications.Thus,thisbookisthemost recentsourceofguidelinesforfuturetrends.
Chapter1 focusesonhybridorcompositenanofluids,which aredevelopedasanovelclassofnanofluidssynthesizedbycombiningtwoormorenanoparticlescontainingmetalormetaloxide orcombiningbothparticlesinabasefluid.Thepreparationprocessisasignificantstepinthenanocompositestofurtherimprove thethermalconductivityofheattransferfluids.Thermophysical propertiesofhybridnanofluidsshowgoodenhancementascomparedwithmononanofluids.Highervolumefractionsresultin enhancedvaluesofthermophysicalproperties.Severalinvestigationshavebeenreportedonhybridnanofluids’thermalconductivityandviscosity,butresearchonotherpropertieslikedensity, specificheat,thermaldiffusivity,andmagneticislimited.Hybrid
nanofluidsarepromisingandcanbeutilizedinseveralapplicationssuchasheattransfer,electricalandenginecooling,refrigeration,machining,desalination,nuclearPWR,heatexchangers, andsolarcollectors.However,somechallengesstillneedtobe identified,suchasstability,increasedpumpingpower,andproductioncosttobeemployedinindustrialapplications.
Chapter2 providesinsightintothepreparation,stability,and characterizationofhybridnanofluids.Thechapterpresentsthe synthesis,stabilityevaluation,andstabilityenhancement methodsofhybridnanofluidsinbrief.Properpreparationof hybridnanofluidsisnecessaryforenhancingthermophysical propertiesandtheirstability.Thestabilityofnanofluidsplaysa vitalroleintheirproperworkinginthermalsystems.Variousstabilityevaluationmethodslikesedimentation,zetapotential,spectralabsorbance,andelectronmicroscopyaredeliberatedtogain importantindicativeinformationaboutthestabilityofnanofluids.Forimprovingthestabilityofnanofluids,variousstability enhancementtechniquessuchasultrasonication,surfactant addition,surfacemodificationsofnanoparticles,andpHchange arealsodescribedinthechapter.Properselectionofnanomaterialsisobligatoryforpreparinghybridnanofluidsaccordingto theirsynergylevel.Attheendofthechapter,somechallenges andoutlooksabouthybridnanofluidshavebeendiscussedfor theirworldwideapplications.
Chapter3 outlinesthepromisingthermophysical,electrical, magnetic,anddielectricpropertiesofhybridnanofluidsthatdisplayconsiderablepotentialinheattransferapplications.Hybrid nanofluidsexhibitaremarkableimprovementinheattransfer performanceascomparedwithmononanofluids.Thechapter presentstherecentadvancementsintheaugmentationofhybrid nanofluids’thermophysicalproperties.Ataugmentedparticle loadingsandtemperaturesofhybridnanofluids,thethermophysicalpropertiesofthermalconductivityandspecificheatare enhanced.Moreover,thedynamicviscosityanddensityofhybrid nanofluidsdecreasewithtemperatureandincreasewithvolume concentration.Thus,temperatureandvolumeconcentrationare thesignificantparametersthataffectthethermophysicalpropertiesofhybridnanofluids.Thechapteralsopresentsstudiesonthe propertiessuchasmagneticanddielectricproperties.
Chapter4 outlineshybridnanofluids’hydrothermalproperties,demonstratingthattheypossesshigherheattransferrates overthesinglenanoparticle-basednanofluids.Propertieslikesurfacetension,pumpingpower,pressuredrop,frictionfactor,and foulingfactorarediscussed.Surfacetension,frictionfactor,pressuredrop,andpumpingpowerareaugmentedwithhigher
particleloadings.Increasedfoulingfactorindicatesareductionin heattransfercoefficientwiththeuseofhybridnanofluids.Recent challengesarealsopresented,anditisreportedthatfurtherinvestigationisrequiredtostudyvarioustypesofhybridnanoparticles, thestabilityofthenanofluid,thermophysicalproperties,heat transfer,lessfrictionfactor,pumpingpower,andpressuredrop characteristics.
Chapter5 focusesontherheologicalbehaviorofhybridnanofluids.Recently,thefieldofnanofluidshasgainedenormousinterestduetotheirgreatadvantagesoverconventionalfluids.The presenceofnanosizedparticleswithinconventionalfluidsledto anincreaseinthethermalconductivitycoefficientscomparedwith basefluids.Researchersacrosstheglobecontinuouslywork towardfurtheradvancementandimprovementsofthenanofluids’ behavior.Therheologicalbehaviorofananofluidisdescribedby therelationshipbetweenthesharedstressanditsrate.Thechapter outlinestherheologicalbehaviorofhybridnanofluidswitha reviewofpastandrecentstudiesandfindingsofamixtureofdual nanometer-sized(<100nm)particleswithvariantbasefluidsand variantvolumefraction.Itisobservedthatthesizeofthenanoparticle,shearrate,andvolumefractionofthenanoparticlesaffectthe rheologicalbehaviorofthenanofluidssignificantly.
Chapter6 focusesontheradiativetransportofhybridnanofluids.Thesehybridnanofluidscanbeusedfordirectabsorption solarthermalsystemsasaworkingfluid.So,itbecomesessential tostudytheopticalpropertiesofthehybridnanofluids.Different nanoparticleshavedifferentproperties.Fordirectsolarabsorptionapplications,itisessentialtoestimatetheopticalproperties ofthehybridnanofluids.Differenttheoriespredicttheextinction coefficient,outofwhichMiescatteringtheoryisthemostsuitable theory.Differenttheorieshavebeendiscussedinthepresent studytocalculatetheextinctioncoefficienttheoretically,and thesetheoreticalvaluesoftheextinctioncoefficientarecompared withexperimentallyobtainedvalues.
Chapter7 discussesthetheoreticalanalysisandcorrelations forpredictingthepropertiesofhybridnanofluids.Themain objectiveofthechapteristoprovideacomprehensivereviewof thethermophysicalpropertiesofhybridnanofluidsuptodate andthecorrelationusedforpredictingthoseproperties.Themain contributingfactorsthataffectthethermophysicalproperties, suchasstability,nanoparticletype,size,volumeconcentration, typeofbasefluid,temperature,surfactant,pHvalue,andsonicationtime,arealsoaddressed.Inaddition,variousempiricalcorrelationsdevelopedbyresearchersforthethermophysical propertiesofthehybridnanofluidsarecompiledandreported.
Finally,challengeswiththestabilityandthermophysicalpropertiesoftheircorrelationsaresummarized.
Chapter8 providesabriefoverviewoftheapplicationsof hybridnanofluids.Thechemicalandphysicalfeaturesofdifferent materialsarecombinedinthehybridmaterialsimultaneously, providingthecharacteristicsinahomogeneousphase.Theeffectiveviscosityanddensityofhybridnanofluidsmaybeofthesame orderasthatofmononanofluids,whiletheirthermalconductivity mightbesubstantiallyhigherthanthatofmononanofluidsconsideringsynergisticeffects.Theoutstandingenhancementin thermaltransferpropertiesofnanofluidsledresearcherstouse theminvariousengineeringapplications,includingnuclearcooling,desalination,machining,refrigeration,enginecooling,heat exchangers(HEX),solarcollectors,andelectronicscooling.This chaptergivesabriefoverviewoftheapplicationsofhybridnanofluids,thechallengesassociatedwiththem,andthewayforward forresearchgapsthatstillneedattention.
Chapter9 shedslightontherecentadvancesinpredicting nanofluids’thermophysicalpropertiesusingartificialintelligence (AI).Recently,methodshavebeenwidelywelcomedduetothe weaknessoftraditionalregression-basedmethodsandtheirlow accuracyinnonlinearproblemsrelatedtothestudyofthermophysicalpropertiesofnanofluids.Inrecentyears,variousinvestigationshavebeendevotedtoapplyingAIinestimatingthe thermophysicalpropertiesofnanofluidsandenergyapplications, mostofwhichhavefocusedonsinglenanofluids.AI-basedinvestigationsonthermophysicalpropertiesofnanofluidsdemonstratedthatmostoftheapplicationsofmachinelearningand data-drivenmodelsarerelatedtothermalconductivityandviscosityofmonofluids,andlimitedresearchhasbeenconductedto modelhybridnanofluids.However,giventheincreasingcapabilitiesofAImethodsandtheirintegrationwithrobustoptimization algorithms,itcanbehopedtosolvenonlinearproblemsofhybrid nanofluidswithmanyinputvariablestoachievepromisingresults. Inthisdirection,thechapterprovidesanoverviewoftherecent advancesinAIforpredictingthethermophysicalpropertiesof nanofluids.
Chapter10 focusesonthechallengesbeingfacedbythe researchersandscholarsinthecommercializationofnanofluids andthewayforward.Severalkeychallengessuchasfoamformation,stability,highcost,increasedfrictionfactor,pressuredrop, pumpingpower,degradationoforiginalproperties,predicting modelsforthermophysicalproperties,safety,environmentalconcerns,andsuitablehybridmaterialsareselectedanddiscussed. Futuredirectionsandpossibleresearchgapsareprovidedaswell.
Acknowledgments
Thisbookwouldnothavebeenpossiblewithoutthededicated andinsightfulworkofthechapterauthors.Iamgratefultothe authorsfortheirprecioustimeandefforttothisadventure.I appreciatetheirkindness,dedication,andexcellenceinproviding high-qualitychaptersthatsummarizethemaincharacteristics, challenges,andapplicationsofhybridnanofluids.Itwasapleasureandanhonorworkingwithyouallonthiscrucialmilestone inthisemergingarea.Thebookwouldnothavebeenpossible withoutthecontinuousdedicationandsupportfromtheUniversityofSharjahandmyfamily,especiallymyparents,wifeandson.
Next,IgenuinelythanktheexcellentsupportfromtheElsevier team.Theirkindness,patience,continuoussupport,technical expertise,andinsightswereessentialtomakingthisbookareality. Ithasbeenanabsolutepleasuretobeassociatedwithyou!
Finally,beingthefirstbookinthishighlydynamicarea,Ihope thatthisworkwillbecomeamilestonetofurtherfosterincreasing scientificandengineeringeffortsandthathybridnanofluidswill increasinglybecomeimplementedasanewclassofhighperformanceheattransferfluidssupportingamoresustainable future.
ZafarSaid
1
Introductiontohybridnanofluids
ZafarSaida,b,c,∗ andMahamAslamSohaila
aDepartmentofSustainableandRenewableEnergyEngineering,Universityof Sharjah,Sharjah,UnitedArabEmirates. bResearchInstituteforSciencesand Engineering,UniversityofSharjah,Sharjah,UnitedArabEmirates. cU.S.-PakistanCenterforAdvancedStudiesinEnergy(USPCAS-E),National UniversityofSciencesandTechnology(NUST),Islamabad,Pakistan
∗Correspondingauthor:zsaid@sharjah.ac.ae,zaffar.ks@gmail.com
Chapteroutline
1.1Introduction 2
1.1.1Developmentofnanomaterialsandnanofluids 4
1.1.2Drawbacksofmononanofluids 7
1.1.3Developmentofhybridnanofluids 7
1.2Preparationofhybridnanofluids 10
1.3Propertiesofhybridnanofluids 13
1.3.1Thermalconductivity 14
1.3.2Viscosity 16
1.3.3Density 17
1.3.4Specificheatcapacity 17
1.3.5Thermaldiffusivity 17
1.3.6Electrical,magnetic,dielectric 18
1.4Applicationsofhybridnanofluids 19
1.4.1Electroniccooling 19
1.4.2Solarcollectors 20
1.4.3Heatexchangers 20
1.4.4NuclearPWR 21
1.4.5Enginecooling 21
1.4.6Refrigeration 21
1.4.7Machining 21
1.4.8Desalination 22
1.5Challengesandoutlook 22
1.6Conclusion 23
References 23
HybridNanofluids:Preparation,CharacterizationandApplications. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-85836-6.00001-6
1.1Introduction
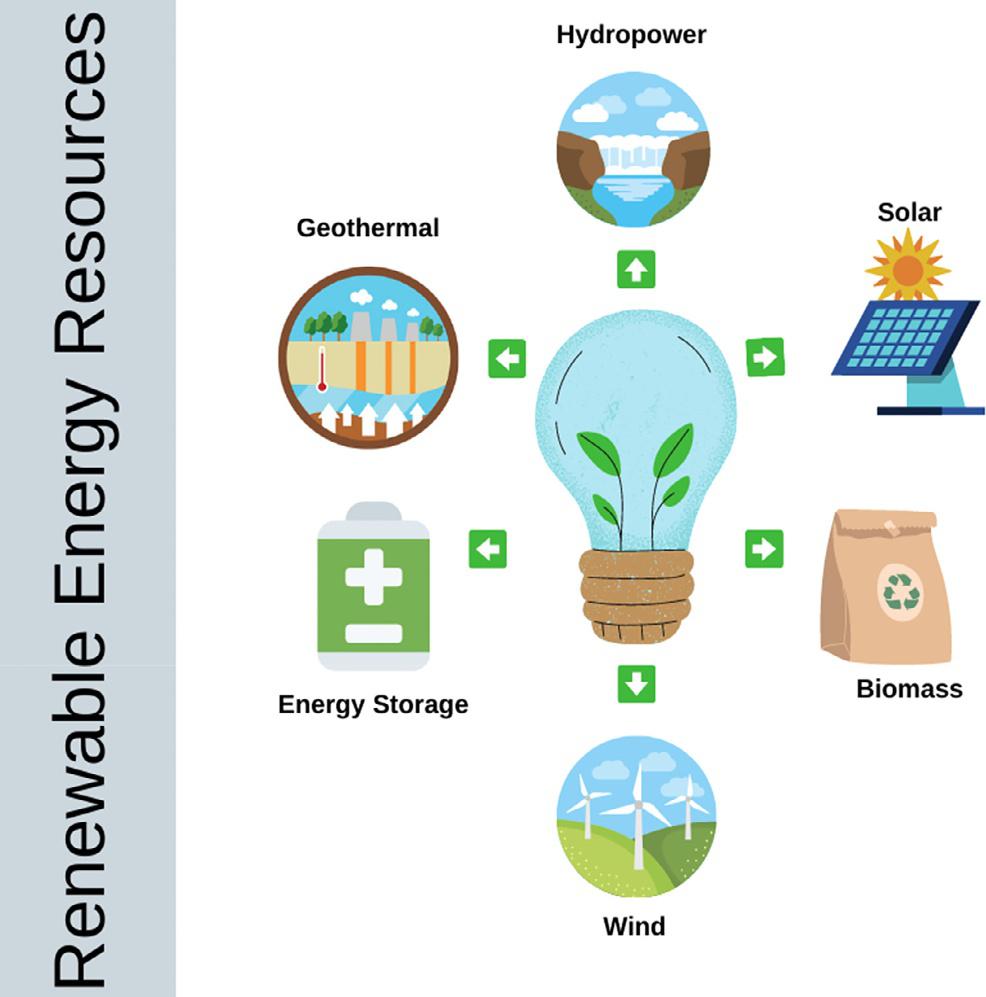
Energyresourcesarestronglydominantwiththelargestshare onfossilfuelsforenergyproduction,whichsignificantlyimpact theenvironment.Carbonfootprintmodificationisacriticalissue duetotheincreasingconcernsaboutglobalclimatechange. In-depthstudiesarebeinginvestigatedtoobtainsustainablesolutionsasitisregardedtobeoneofthemajordrivers [1–3]. Acontinuousdecreaseinfossilfuelresourcesandincreasedcarbonemissionsmadethedevelopednationsprogresstoward renewableenergysources [4].Energyspecialisstsandpolicymakerssuggestthatifsuitableinvestmentsaremadetodevelop renewableenergyforpowergeneration,theeconomiespresently supportedonfossilfuelswillbecomeindependentfromnonrenewablesourcessoonerorlater [3,5].Renewableenergysources areforecastedtodeliver70%–85%ofpowerby2050,significantly reducingcarbonemissions (Fig.1.1)[6].Renewableenergyconsistsofasequenceofinfiniteandenvironment-friendlyenergy sourceswithouthumaninvolvement,suchassolarenergy,wind energy,biomass,hydropower,geothermal,andenergystorage.
Withthereductionoffossilfuelreserves,solarenergyisconsideredaplentifulrenewablesource [7].Solarenergyisamain elementincleanenergytechnologiesbecauseitdeliversinfinite, clean,andenvironmentallyfriendlyenergy [8].Theearthaccommodatessolarradiationofabout170PW,inwhich30%ofthis reflectsbacktospace,andtheremainderisabsorbedbytheearth andsea [9].Itcanbestoredandemployedinvarioustechnologies suchassolarthermalandphotovoltaic(PV)systems.Solarphotovoltaics(PV)isconsideredareliabletechnologythatconverts solarradiationdirectlytoelectricity [10].Solarthermaltechnologyconsistsofthesolarradiationharnessedforusefulthermal energyandincludesapplicationareasinsolardesalination [11], solar-thermalpowerplants [12],residentialorcommercialheating [13],absorptioncooling [14],andsoon.Therefore,howto efficientlytransferorstoresolarenergyhasanovelpointtoconsiderforthescientificandresearchcommunityinthepresentday andfuture.Photovoltaic/thermal(PV/T)systemsconsistofphotovoltaic(PV)andsolarthermalcomponentsystemsthatcangenerateheatandelectricity.Theyhaveapromisingpotentialfor energysavingsandremarkableefficiency.PV/Tsystemsare emergingasastrongcandidateforpowergenerationshortly.
Anotherseriouschallengethatresearchersandengineersface intoday’spracticalapplicationsisheatexchangebetweenseveral devices.Itiscertaintoapplyheatexchangersandheatsinksfor heattransferinseveralapplications [15].Electroniccomponents
Fig.1.1 Differentresourcesofrenewableenergy.
insuchdevicesproduceundesirableheatbydecreasingtheefficiencyorcausedevicefailure.Advancementinheattransferplays asignificantpartinindustrialapplicationsforcostsavingsand energysavingsasthedemandforhigh-performancedevicesis increasingnowadayswiththeprogressinscienceandtechnology [16].Inthepastdecade,severalinvestigationsweredevelopedto enhanceheattransferdevices’efficiencybyvarioustechniques suchasdifferentshapesoffinsandtheiroptimization.Theperformanceandefficiencyofheattransfercanpotentiallyimpactthe boundaryconditionsandthermophysicalpropertiessuchasthermalconductivity,viscosity,density,andspecificheatofthe
workingfluid.Thisworkingfluidperformsasubstantialroleinthe heattransferrate.Conventionalfluidssuchaswater,ethyleneglycol,andoilarewidelyusedinseveralheattransferapplications andpossesslowthermalconductivity [17].Duetolowthermal conductivity,thesefluidscouldnotmeettheever-increasing demandforenhancedheattransfertechnologyastheirperformancewasnoteffectiveandcausedhighpumpinglosses [18] NobelscientistMaxwell [19] proposedanideabyintroducingmillimeterormicrometer-sizedparticlesinthebasefluidtoenhance thethermalconductivityandperformance,butthiscausedthe followingchallengesintheliquidsduetolargeparticles,which areunfavorableforpracticalapplications:
•Sedimentation
•Clogging
•Increasedpumpingpower
•Corrosion
Masudaetal. [20] observedsimilarchallengesofsedimentation,greaterpumpingpowerlossesbyinvestigatingmicro-sized solidparticlesdispersedinthebasefluid.Fromthen,several investigationswereconductedbyresearchersandscholarsto boostthepoorthermalconductivityoffluidsbyaddingsolid particles.
1.1.1Developmentofnanomaterialsandnanofluids
Nanomaterialshavegainedextensivesignificanceinthepresentday,havingthepromisingpotentialtoperformaninnovative roleinpracticalapplications.BasedontheInternationalOrganizationforStandardization(ISO),theprefixnanodefinesasasize rangingfrom1to100nm.Forinstance,thecarbonatomisabout 0.25nmindiameter,andthedistancebetweencarbonatomsis about0.15nm.Therefore,nanomaterialsarebiggerthanindividualatomsorsmallgroupsofatoms.Theyhavedistinctivepropertiessuchasthermal,magnetic,electrical,optical,andmechanical propertiesduetotheirlargespecificarea,latticestructure,altered electronicstates,etc. [21].Nanomaterialsareextensivelyinvestigatedinvariousapplicationssuchassolarcells [22],watertreatment [23],improvedheattransfer [24],batteries [25],biosensors [26],etc.Nanomaterialsareclassifiedintofourcategories [27–31]:
•Zero-dimensional(0D):Thisincludesquantumdots,fullerenes(hollowspheres),goldnanoparticles,etc.
•One-dimensional(1D):Thisincludesnanofibers,nanotubes, nanowires,andnanorods.
•Two-dimensional(2D):Thisincludesthinfilms,nanocoatings, andnanoplates.
Nanospheres, clusters
• Fullerenes
•
Quantum dots
• Gold nanoparticles
CLASSIFICATION OF NANOMATERIALS
Nanotubes, wires, rodsBulk nanomaterials, polycrystals
• Metal nanotubes
Carbon nanotubes
• Metallic nanotubes
•
•
Gold nanowires
•
Liposome
• Polycrystalline
• Dendrimer
Thin films, layered structures
• Graphene sheets
•
Carbon coated nanoplates
• Layered nanomaterials
Fig.1.2 Classificationofnanomaterials.
•Three-dimensional(3D):Thisincludesnanocomposites, nanostructuredmaterials,andpolycrystals.
Nanomaterialshaveawiderangeofapplicationsindifferent sectorssuchasaerospace,chemicals,construction,cosmetics, energy,electronics,automobile,engineering,environment,medicine,military,andsports(Fig.1.2).
Withthesignificantdevelopmentofmodernnanotechnology andnanomaterials,thediscoveryofnanofluidsthatcontained nanosizedparticlesdispersedinbasefluidscompletelychanged thepicture.Choiandhisteam [32] proposedtheterm “nanofluid,”anovelkindofnanotechnology-basedheattransfer fluidsdefiningasanengineeredcolloidalsuspensionof nanometer-sizedparticlestypicallyrangingfrom1to100nmdispersedinthebasefluid (Fig.1.3).Theprogressinnanofluid-based technologieshasgainedsignificantattentionfromseveral researchersduetotheirexcellentthermalconductivityandstabilityinseveralscientificfieldssuchasenergy-basedapplications [33–35],airconditioning [36],electronics,medicine,andenergy andfuelmanagement [37–39].Apartfromthehighthermalconductivity,nanoparticlesaredesirableforheattransferapplicationsastheyreducecloggingpumpingpower,whichhelpsin energysavings [40].Nanoparticlesoccupyahighersurfacearea
0D1D2D3D
Base Fluid
Nanoparticles
Nanofluids
• Ethylene glycol
• Oil
• Bio-fluids
• Polymer solutions
• Metals
•
• Metallic and non-metallic oxides
• Metal carbides and nitrides
• Carbon nanotubes, graphite, diamond, etc
• Functionalized nanoparticles
• Phase change materials
Fig.1.3 Graphicalrepresentationofnanofluids.
•Volumeconcentrationofnanoparticles [55,56] Water
thanmicroparticles,increasingheatconductionofnanofluids, andpossessremarkablestability.Thenanoparticlesconsistof metalssuchascopper(Cu) [41],nickel(Ni) [42],gold(Au) [43], andsilver(Ag) [44],metaloxidessuchasaluminumoxide (Al2O3),zincoxide(ZnO),titaniumdioxide(TiO2),copperoxide (CuO),silicondioxide(SiO2),iron(III)oxide(Fe2O3),andmany more,oxideceramics,metalcarbidesandnitrideslikealuminum nitride(AlN),siliconcarbide(SiC),boronnitride(BN),carbon nanotubes,graphite,diamond,andfunctionalizednanoparticles [45].Researchfromuniversitiesandresearchcentersaroundthe globehasstudiedorinvestigatednanofluidsinvariouscontexts andhasanalyzedtheeffectsofvariousfactorsonheattransfer, thermalconductivity,viscosity,andboilingheattransfer [46, 47].Numerousresearchersandscientistshavemadepotential breakthroughsinthedevelopmentofthermalpropertiesofnanofluids,proposingexceptionalnanofluidanalysismodels [48,49]. MichaelandIniyan [50] madeasignificantadvancementinnanofluids’thermalperformancecomparedwithwater.Choietal. [51] noticedanincrementinnanofluids’thermalconductivityupto twotimescomparedwithconventionalfluidsatalowvolume fractionoflessthan1vol.%.Yuetal. [52] examinedthethermal conductivityandviscosityofEG-basednanofluidsexperimentally.Nanofluidscanflowsmoothlywithoutcloggingatsuch lowparticleconcentration,andhighheattransferefficiencycan beattained.Thepromisingpropertiesofnanofluidsdependon thefollowingparameters:
•Temperature [53,54]
•Sizeandshapeofnanoparticles [57,58]
•Ultrasonicationduration [59,60]
•pHvalueofnanofluids [61–63]
•Surfactant-basedornonsurfactant-basednanofluids [64,65]
1.1.2Drawbacksofmononanofluids
Aluminumoxide(Al2O3),alsoknownasalumina,isoneofthe mostwidelyinvestigatedandpromisingnanofluids.Ithasbeen observedthatAl2O3-basednanofluidsexhibitexcellentimprovementinthermalconductivityrangingfrom0.3%to38% [66, 67].Sundaretal. [68] investigatedAl2O3-water/EG-basednanofluidswithoutusingsurfactantandobserved32.3%enhancement for1.5vol.%concentrationfor20:80%EG/H2Oandatatemperatureof60 °C.Withtheprolongationinnanofluidsresearch, researchersandscholarsstudiedfurthertoenhancethepropertiesofnanofluids.Mononanofluidsdonotretainallfavorable propertiesthatarerequisiteforspecializedapplications.For instance,aluminumoxide(Al2O3)hasapropertyofbetterchemicalinertnessandstability,butithasadrawbackoflowthermal conductivity.Metallicnanoparticlessuchascopper,silver,and aluminumexhibitremarkablethermalconductivity,butthey arechemicallyreactiveandunstable;therefore,theyhaveeither abetterthermalpropertyorabetterrheologicalproperty.To trade-offbetweenproperties,hybridnanofluidshavebeenintroducedtoacquireenhancedproperties,suitableforapplications thatinvolveremarkablethermal,optical,andrheologicalpropertiesoftheworkingfluid [69].
1.1.3Developmentofhybridnanofluids
Hybridnanofluidsasanadvancedgroupofnanofluidsare engineeredbydispersingcompositenanoparticlesortwodifferenttypesofnanoparticlesinthebasefluid,representingnoteworthyphysicochemicalpropertiesthatareabsentinindividual nanoparticles [70].Inrecentinvestigations,hybridnanofluids areconsideredtoincreasethermalconductivityandtheperformanceofsolarenergysystems,i.e.,PVTsystems,solarcollectors, andstoragesystems,andthismakesthemremarkableduetothe synergisticimpactofindividualnanoparticles [71,72].Theprincipalpurposeofhybridnanofluidsistoobtainpromisingpropertiessuchasexcellentthermalconductivityandstability,physical strength,mechanicalresistance,reducedpumpingpowerlosses, heattransferperformancerate,betteraspectratio,andreduced productioncostofnanofluids.
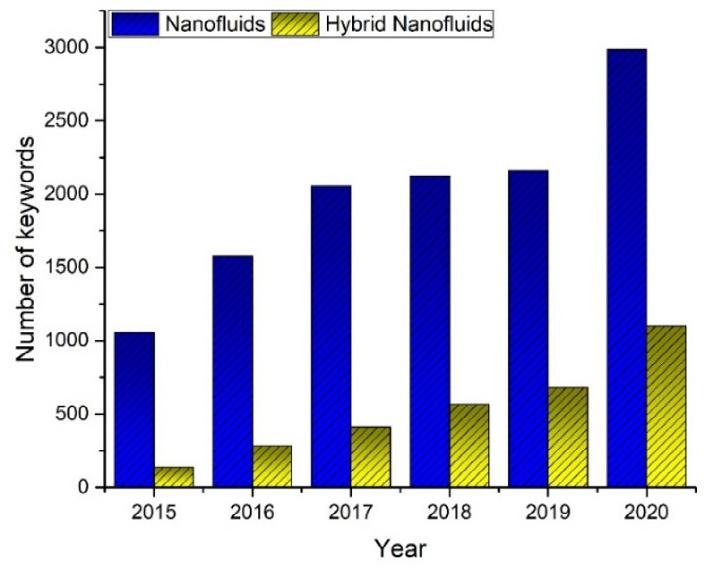
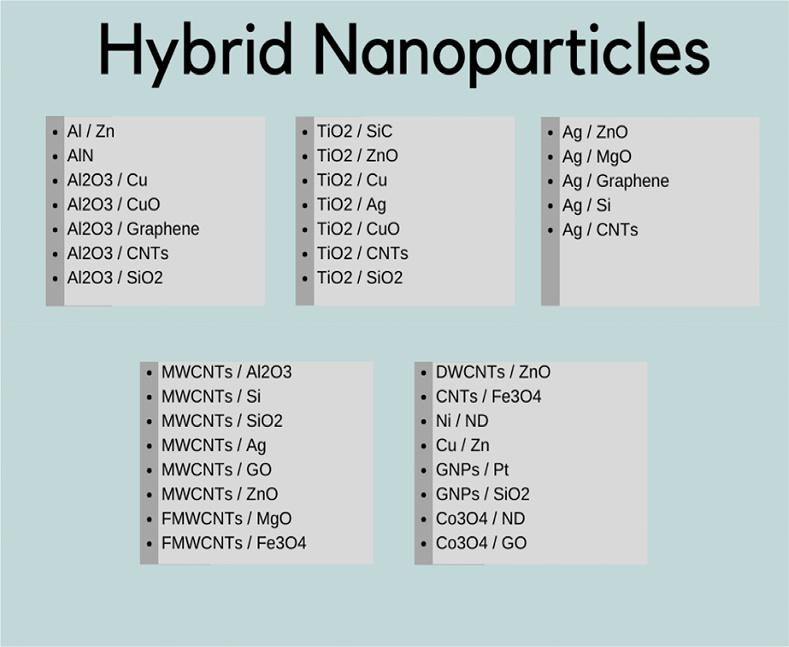
Researchersfromthepast2decadeshaveinvestigatedhybrid nanofluids,mostlyfocusedonthesynthesis,characterization,properties,andapplicationsforseveralindustrialandcommercialapplications [73].Severalpapersarepublishedfromthelastdecadewith numericalandexperimentalinvestigations,andthegrowthcanbe clearlyobservedfrom Fig.1.4.Thecurrentprogressofhybridnanofluidsinthisdevelopingareaismostapparentfromtheincreasing numberofkeywordsascomparedwiththenanofluids.Thedata for Fig.1.4 istakenfromElsevierfortheyears2015–2020.Thenanoparticlesorcompositesinvestigatedsofararegraphene-Ag, MWCNT-MgO,Fe3O4-graphene,Al2O3-CNT,Al2O3-SiO2,Al2O3-Cu, Al2O3-MEPCM,diamond-Ni,SiO2-CNT,Ag-MnO,Ag-TiO2, Ag-CNT,Cu-TiO2,Cu-Zn,Fe2O3-CNT,SWCNT-MgO,andmany moreinvariousheattransferapplications(Fig.1.5).Themetallic ormetaloxide-basedhybridnanofluidsshowexceptionalthermophysicalandrheologicalproperties [74,75].
Basedonthepromisingproperties,thefollowingarethework donebydifferentscholarsandresearchersinthefieldofhybrid nanofluids.
•Turcuetal. [76] wasthefirstonewhoinvestigatedthefabrication ofhybridnanocompositescontainingpolypyrrole-carbonnanotube(PPY-CNT)andMWCNTonmagneticFe2O3 nanoparticles.
•Niihara [77] andOhetal. [78] investigatedAl2O3-Cuhybrid nanocompositesandobservedimprovementinmechanical andthermalproperties.
Fig.1.4 Numberofkeywordsusedyearlyformonoandhybridnanofluids.Thedata istakenfromElsevier.
Fig.1.5 Differenttypesofhybridnanoparticles.
•JhaandRamprabhu [79] investigatedexperimentallyMWCNTAu/H2O-basedhybridnanofluidsandnoticedenhancementin thermalconductivityofaround28%,ascomparedwithCNT/ H2O-basednanofluidwheretheenhancementwasaround15%.
•Madheshetal. [80] investigatedCu-TiO2 aqueoushybridnanofluidsandobservedanimprovementof52%inheattransfer coefficientataparticleloadingof1vol.%andpressuredrop of14.7%.Theyalsoobservedthatbyincreasingthevolume concentration,theheattransfercoefficientisreduceddueto nanoparticles’agglomerationintothebasefluid.
•Baghbanzadehetal. [81] examinedthermophysicalproperties ofSiO2-MWCNTs/H2Ohybridnanofluidsandobserved improvementinthermalconductivityupto22%at1vol.%.
•Akiluetal. [82] analyzedthethermophysicalcharacteristicsof glycerolandEGmixture-basedSiO2-CuO/Chybridnanofluid, anditwasobservedthatthethermalconductivityenhancedup to26.9%,indicatingthathybridisapotentialheattransferfluid forsolarenergytransportation.
•Weietal. [83] investigatedthethermophysicalpropertyofSiCTiO2/diathermicoilhybridnanofluidsandnoticedexcellent thermalconductivityascomparedwithmononanofluids.
•Tiwarietal. [48] studiedexperimentallythethermalconductivityofCeO2 +MWCNT/H2O-basedhybridnanofluidwith