HERBAL BIOACTIVEBASEDDRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS
ChallengesandOpportunities
Editedby
INDERBIR SINGH BAKSHI
ChitkaraCollegeofPharmacy,ChitkaraUniversity,Rajpura,Punjab,India
RAJNI BALA
ChitkaraCollegeofPharmacy,ChitkaraUniversity,Rajpura,Punjab,India
REECHA MADAAN
ChitkaraCollegeofPharmacy,ChitkaraUniversity,Rajpura,Punjab,India
RAKESH K.SINDHU
ChitkaraCollegeofPharmacy,ChitkaraUniversity,Rajpura,Punjab,India
AcademicPressisanimprintofElsevier
125LondonWall,LondonEC2Y5AS,UnitedKingdom
525BStreet,Suite1650,SanDiego,CA92101,UnitedStates
50HampshireStreet,5thFloor,Cambridge,MA02139,UnitedStates
TheBoulevard,LangfordLane,Kidlington,OxfordOX51GB,UnitedKingdom
Copyright©2022ElsevierInc.Allrightsreserved.
Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproducedortransmittedinanyformorbyanymeans,electronicormechanical, includingphotocopying,recording,oranyinformationstorageandretrievalsystem,withoutpermissioninwritingfromthe publisher.Detailsonhowtoseekpermission,furtherinformationaboutthePublisher’spermissionspoliciesandour arrangementswithorganizationssuchastheCopyrightClearanceCenterandtheCopyrightLicensingAgency,canbefound atourwebsite: www.elsevier.com/permissions
ThisbookandtheindividualcontributionscontainedinitareprotectedundercopyrightbythePublisher(otherthanasmay benotedherein).
Notices
Knowledgeandbestpracticeinthisfieldareconstantlychanging.Asnewresearchandexperiencebroadenour understanding,changesinresearchmethods,professionalpractices,ormedicaltreatmentmaybecomenecessary.
Practitionersandresearchersmustalwaysrelyontheirownexperienceandknowledgeinevaluatingandusingany information,methods,compounds,orexperimentsdescribedherein.Inusingsuchinformationormethodstheyshouldbe mindfuloftheirownsafetyandthesafetyofothers,includingpartiesforwhomtheyhaveaprofessionalresponsibility.
Tothefullestextentofthelaw,neitherthePublishernortheauthors,contributors,oreditors,assumeanyliabilityforany injuryand/ordamagetopersonsorpropertyasamatterofproductsliability,negligenceorotherwise,orfromanyuseor operationofanymethods,products,instructions,orideascontainedinthematerialherein.
ISBN:978-0-12-824385-5
ForInformationonallAcademicPresspublications visitourwebsiteat https://www.elsevier.com/books-and-journals
Publisher: StacyMasucci
AcquisitionsEditor: AndreGerhardWolff
EditorialProjectManager: TracyTufaga
ProductionProjectManager: SreejithViswanathan
CoverDesigner: MarkRogers
TypesetbyMPSLimited,Chennai,India
Listofcontributorsxi Prefacexv
1.Roleofherbalbioactivesandtheir formulationsinthetreatmentof gastrointestinaldisorders1
SarabjitKaur,MonikaSachdeva,HasandeepSingh,Arshdeep Singh,JaipalKaur,ArchanaRani,SarojAroraandBalbirSingh
1.1Introduction1
1.1.1Anatomyandphysiologyof gastrointestinaltract1
1.2Roleofherbalbioactivesandformulations inthetreatmentofgastrointestinaltract disorders2
1.2.1Gastroesophagealrefluxdisease3
1.2.2Pepticulcer5
1.2.3Coloncancer8
1.2.4Constipation9
1.2.5Diarrhea11
1.2.6Irritablebowelsyndrome12
1.2.7Nanotechnology-basedherbal formulationsfortreatmentof gastrointestinaldiseases14
1.3Conclusion16 Acknowledgments16 Conflictofinterests16 Funding16 References17
2.Herbalbioactivesforoculardrug deliverysystems25
EvrenAlgınYapar,M.E.Durgun,I.Esentu¨rk, S.Gu¨ngorandY.Ozsoy
2.1Introduction25
2.2Anatomy,physiology,andpharmacokinetic ofeye26
2.3Herbalmedicineforoculardiseases26
2.4Herbalmedicineforoculardrugdelivery systems27
2.4.1Micro-andnanoparticles27
2.4.2Micro-andnanoemulsions30
2.4.3Nanosuspensions31
2.4.4Micelles32
2.4.5Liposomes32
2.4.6Phytosomes36
2.4.7Dendrimers37
2.4.8Hydrogellingsystems37
2.4.9Ocularinsertsandimplants39
2.5Herbalexcipientsusedinoculardrug deliverysystems40
2.5.1Cellulosederivatives41
2.5.2Alginate42
2.5.3Starch43
2.5.4Pectin43
2.5.5Gumsandmucilages44
2.5.6Cyclodextrins47
2.6Conclusionsandfutureperspectives48 References49
3.Herbalbioactivesforpulmonarydrug deliverysystems63
ReshuVirmaniandKamlaPathak
3.1Introduction63
3.2Asthma64
3.3Chronicobstructivepulmonarydisease69
3.4Lungcancer72
3.5Pulmonaryfibrosis76
3.6Researchandmarketscenario81
3.7Conclusion81 References84
4.Herbalbioactivesintransdermaldrug deliverysystem93
GagandeepKaur,PrabhjotKaur,PiyushMadaan, RishuVerma,ParteekChandel,TwinkleSalgotra, HarnoorKaurandRakeshK.Sindhu
4.1Introduction93
4.2Herbalbioactives94
4.3Meritsanddemeritsofherbaldrug formulations94
4.4Transdermaldrugdeliverysystem95
4.5Novelherbalbioactivecarriersin transdermaldrugdelivery96
4.5.1Liposomes96
4.5.2Phytosomes98
4.5.3Niosomes98
4.5.4Nanoparticles100
4.5.5Emulsions101
4.5.6Ethosomes102
4.5.7Microsphere104
4.5.8Transferosomes105
4.6Proniosomes106
4.7Conclusion106
References107
5.Herbalbioactive based vaginalandrectaldrugdelivery systems111
SanjeevaniShekharDeshkarandJayashriG.Mahore
5.1Introduction111
5.2Vaginalrouteforherbalbioactives112
5.2.1Anatomyofvagina113
5.2.2Vaginalabsorptionandfactors affectingvaginaldrugdelivery113
5.2.3Vaginaldisordersandtheir treatmentusingmedicinalplant extracts114
5.2.4Vaginalherbalformulations basedonplantextracts117
5.2.5Majorherbalbioactivesand theirformulationsforvaginal delivery119
5.3Rectalrouteforherbalbioactives137
5.3.1Anatomyofrectum137
5.3.2Factorsaffectingabsorption throughtherectum138
5.3.3Rectaldosageformsforplant extracts138
5.3.4Deliveryofplantextractsorbioactives throughrectalroute139
5.4Conclusionandfuturescope150
References150
6.Herbalbioactive basednanodrug deliverysystems169
MuhammadSohail,FazleRabbi,AyeshaYounas,AbidHussain, BinYu,YanliLi,SajidIqbal,KamranHidayatUllah, AbdulQadeer,MdAquib,HaroonIqbalandHuiXu
6.1Introduction169
6.2Historyandconventionalapproachesto herbalbioactive171
6.2.1Historyofdeliverysystems173
6.3Principleobjectivesfornanodrugdelivery systemandherbalbioactive173
6.4Recentapproachesofdrugdeliverysystemfor herbalbioactivesubstances174
6.5Whynanodrugdeliveryforherbal bioactive176
6.6Typesofdrugdeliverysystemusedforherbal bioactive176
6.6.1Liposomes176
6.6.2Nanoemulsions179
6.6.3Niosomes181
6.6.4Phytosome182
6.6.5Polymericmicelles183
6.6.6Nanoparticles184
6.6.7Nanogels/hydrogel186
6.6.8OtherNDDSherbalformulation186
6.7Futureperspectiveandchallengesofherbal bioactive188
Conflictofinterest190 References190
7.Herbalbioactive basedcosmetics195 KennethC.UgoezeandOluwatoyinA.Odeku
7.1Introduction195
7.1.1Whatiscosmetics?195
7.1.2Historyofcosmetics196
7.1.3Reasonsfortheuseofcosmetics197
7.2Categoriesofcosmetics198
7.2.1Classificationbasedonthephysical stateoftheproduct198
7.2.2Cosmeticsbasedonthetypeof formulation198
7.2.3Cosmeticsbasedonthepartofthe bodyforapplication(LifestyleLounge; Romanowski,2014;Sharma,Gadiyah, &Dhanawat,2018)198
7.2.4Cosmeticsbasedonthefunctionofthe preparation(LifestyleLounge;
Romanowski,2014;Sharmaetal., 2018)199
7.2.5Outlineofvariouscosmeticsproducts (CosmeticInfo)199
7.2.6Fragranceproducts199
7.2.7Dustingpowders200
7.2.8Haircareproducts200
7.2.9Nailproducts200
7.2.10Oralcareproducts200
7.2.11Productsforpersonalcleanliness201
7.3Challenges/disadvantagesofsynthetic-based cosmetic201
7.3.1Adversereactionofcosmetics202
7.4Herbalbioactivecosmeticproducts203
7.4.1Herbalbioactiveconstituentsemployed inthetreatmentofdryskin204
7.4.2Herbalbioactivecomponentsemployed inthetreatmentofeczema205
7.4.3Herbalbioactivecomponentsemployed inthetreatmentofacne,spots,and pimples205
7.4.4Herbalbioactivecomponentsemployed asskinantiagingagents206
7.4.5Herbalbioactivecomponentsemployed forfree-radicalscavengingeffects206
7.4.6Herbalbioactivecomponentsemployed forantiinflammatoryeffects207
7.4.7Herbalbioactivecomponentsemployed inhaircare207
7.5Sourcesofsomenotableherbalbioactive ingredientsandtheiruses210
7.5.1Soy211
7.5.2Silibinin211
7.5.3Pycnogenol212
7.5.4Ginkgobiloba212
7.5.5Greentea212
7.5.6Aloesin212
7.6Standardizationofusefulherbalbioactive ingredientsincosmetics212
7.6.1Sourceofmaterial213
7.6.2Collectionofplantsamples213
7.6.3Authenticationofsample213
7.6.4Morphologicalandmicroscopical evaluations213
7.6.5Physico-chemicalevaluations214
7.6.6Phytochemicalassessment214
7.6.7Standardizationofbioactiveingredients markers214
7.7Patentedherbalbioactive-basedcosmetics214
7.7.1Patenttheapplicationofthenaturalor organic-basedcosmetic215
7.7.2Patenttheformulationofnaturalor organiccosmetic215 References217
8.Herbalbioactive basednutraceuticals usingametabolomicsapproach227
AmirModarresiChahardehiandVuanghaoLim
8.1Introduction227
8.2Nutraceuticalsanddevelopmentin metabolomics228
8.3Metabolomicsinherbalplants232
8.4Techniquesinmetabolomics233
8.5Profilingofbioactivesandclassifications241
8.6Nutraceuticalsbiomarkersfrommetabolomics approaches242
8.7Qualitycontrolandoptimization243
8.8Conclusion250 Acknowledgement251 References251
9.Herbalbioactivesforwoundhealing application259
InderbirSinghBakshi,HiteshChopra,MadhuSharma,Deepak Kaushik,RakeshPahwaandHaryanto
9.1Introduction259
9.1.1Typesofwounds260
9.1.2Varioustypesofwoundhealing260
9.2Stagesofwoundhealing260
9.3Nanotechnologybasedapproachedforwound healing263
9.4Patents274
9.5Futuredirectionsandconclusions274 References277
10.Therapeuticupdatesandfuture prospectsonanticancereffectsof medicinalplantsandphytochemicals283
SevgiGezici
10.1Introduction283
10.2Globalcancerstatistics284
10.3Carcinogenesisandtreatmentstrategies286
10.4Roleofphytochemicalsincancerfor complementarytherapy288
10.5Phytochemicalsandmolecularmechanisms ofactionincancer290
10.6Signaltransductionandsignalingpathways involvedincancer296
10.7Potentialsofmedicinalplantsand phytochemicalsforcancerchemoprevention andtherapy298
10.8Phytochemicalsandclinicaltrialsforcancer chemotherapeutics302
10.9Futurerecommendationsand conclusions303
10.10Conflictofintereststatement306
10.11Financialdisclosure306 References306
11.Herbalbioactive-incorporated scaffoldsforwoundhealing applications311
AmeyaSharma,VivekPuri,InderbirSinghBakshiand PradeepKumar
11.1Background311
11.2Curcumin-incorporatedscaffoldsforwound healingapplications312
11.3Quercetin-incorporatedscaffoldsforwound healingapplications320
11.4EGCG-incorporatedscaffoldsforwound healingapplications323
11.5 Moringa extractincorporatedscaffoldsfor woundhealingapplications325
11.6Miscellaneous325 References327
12.Developmentofnaturalbioactive deliverysystemsthroughpressurized fluids-moderntechniques331
AnaPauladaFonsecaMachado,RobertodePaulaNascimento, AmandaMariaTomaziniMunhozMoya, RafaeladeCarvalhoBaptistaand MarioRobertoMarosticaJunior
12.1Introduction331
12.2Classificationofemergentmethodsbasedon pressurizedfluidfunction:solvent,solute,and antisolvent334
12.3Developmentofdeliverysystemsthrough emergentmethodsandtheirpotential applicationinhumanhealth334
12.3.1Rapidexpansionofsupercritical solutions334
12.3.2Particlesfromgassaturated solutions338
12.3.3Supercriticalantisolvent precipitation343
12.4Conclusion360 Acknowledgment360 References360
13.Nanoformulatedherbalbioactivesfor thetreatmentofneurodegenerative disorders371
SorayaSajadimajd,SeyedZachariahMoradi,ValiAkbari, FaranakAghazandMohammadHoseinFarzaei
13.1Introduction371
13.2Neurodegenerativediseases372
13.3Herbalbioactivesinthetreatmentof neurodegenerativediseases373
13.3.1Plantsandtheirconstituentsfrom traditionalChinesemedicine373
13.3.2Plantsandtheirconstituentsfrom traditionalIndianmedicine (Ayurvedicmedicine)375
13.3.3Plantsandtheirconstituentsfrom Iraniantraditionalmedicine376
13.3.4Plantsandtheirconstituentsfrom SouthAmericanandAfrican traditionalmedicines377
13.4Nanoformulatedherbalbioactivein neurodegenerativediseases377
13.4.1RoleofnanoformulatedCurcuminin neurodegenerativediseases377
13.4.2Roleofnanoformulatedquercetinin neurodegenerativediseases380
13.4.3Roleofnanoformulatedresveratrolin neurodegenerativediseases381
13.4.4Roleofnanoformulatedrutinin neurodegenerativediseases381
13.4.5Roleofnanoformulatedpiperinein neurodegenerativediseases381
13.4.6Roleofnanoformulatedgallicacid andepigallocatechin-3-gallatein neurodegenerativediseases382
13.4.7Roleofnanoformulatedferulicacidin neurodegenerativediseases382
13.4.8RoleofnanoformulatedSeleniumin neurodegenerativediseases382
13.5Conclusion383 References383
14.Standardizationofherbal bioactives393
ShashikantBagade,DipakD.PatilandAtulShirkhedkar
14.1Introduction393
14.2Standardizationofherbals394
14.2.1Presentscenariowithstandardization ofbioactivematerial394
14.2.2Herbaldrugsinpharmacopeia395
14.3Analyticalmethodsforherbal standardization396
14.3.1Hyphenatedtechniques397
14.3.2Pharmacopeialstandard material399
14.4Somepracticalaspectsofextraction400
14.5Challengeswhileworkingwithdrugdelivery systemcontainingbioactiveconstituents400
14.5.1Factorsaffectinginvitro,invivo bioactivitystudies401
14.6Directionsforfurtherstudies402
14.7Conclusion403 Acknowledgment403 References403
15.Enhancementofthepropertiesof herbalbioactivesfordrugdelivery application409
YotsananWeerapolandPornsakSriamornsak
15.1Introduction409
15.2Enhancementoftheabsorptionofherbal bioactives410
15.2.1Sizereduction410
15.2.2Emulsiontechnology410
15.2.3Modificationofsurface properties412
15.2.4Micro-andnanocarriers412
15.3Therapeuticmodifications414
15.4Approachestoimprovethestabilityof herbalbioactives414
15.4.1Storageconditions415
15.4.2Antioxidantaddition415
15.4.3Adsorbentuse416
15.5Conclusion416 References416
16.Regulatoryconsiderationsofherbal bioactive basedformulations419
SureshKumar,RamanpreetWalia,ShikhaSaxena, PoojaDeyandReechaMadaan
16.1Introduction419
16.2Classificationofherbalmedicines420
16.2.1Category1:Indigenousherbal medicines420
16.2.2Category2:Herbalmedicinesin systems420
16.2.3Category3:Modifiedherbal medicines420
16.2.4Category4:Importedproducts withaherbalmedicinebase421
16.3Factsandstatisticsofherbalmedicinal products421
16.4Needforherbalregulations421
16.5Challengesinregulationofherbal medicines422
16.5.1Lackofknowledgeaboutherbal medicineswithinnationaldrug authorities422
16.5.2Standardizationchallenges423
16.5.3Safetychallenges423
16.5.4Qualitychallenges423
16.5.5Clinicaltrialschallenges423
16.5.6Pharmacovigilancechallenges423
16.6Indianregulatorybody424
16.6.1MinistryofAYUSH424
16.6.2Legistationsandlegalstatus425 16.7UnitedStatesregulatorybody426
16.7.1Herbalmedicinesasbotanical drugs426
16.7.2Legislationsandlegalstatus427 16.8Europeanregulatorysystem427
16.8.1Legistationsandlegalstatus427
16.9Legalstatusandregulatoryguidelinesof variouscountries428
16.10Conclusion434
16.11Recommendations435 References435
17.Modernextractiontechniquesfor herbalbioactives437
YoussefElRayess,MichellaDawraandMarcElBeyrouthy
17.1Introduction437
17.2Pulsedelectricfield assistedextraction438
17.3Ultrasound-assistedextraction440
Contents
17.4Microwave-assistedextraction441
17.5Pressurizedliquidextraction445
17.6Supercriticalfluidextraction448
17.7Conclusionandfuturechallenges449
References452
Index457
Listofcontributors
FaranakAghaz NanoDrugDeliveryResearch Center,HealthTechnologyInstitute, KermanshahUniversityofMedicalSciences, Kermanshah,Iran
ValiAkbari DepartmentofBiology,Facultyof Science,RaziUniversity,Kermanshah,Iran; ResearchCenterofOilsandFats,Research InstituteforHealthTechnology,Kermanshah UniversityofMedicalSciences,Kermanshah, Iran
EvrenAlgınYapar Departmentof PharmaceuticalTechnology,Facultyof Pharmacy,SivasCumhuriyetUniversity, Sivas,Turkey
MdAquib DepartmentofPharmaceutics, SchoolofPharmacy,ChinaPharmaceutical University,Nanjing,P.R.China
SarojArora DepartmentofBotanicaland EnvironmentalSciences,GuruNanakDev University,Amritsar,India
ShashikantBagade Departmentof PharmaceuticalChemistry,SVKM’sNMIMS SchoolofPharmacyandTechnology Management,Shirpur,India
InderbirSinghBakshi ChitkaraCollegeof Pharmacy,ChitkaraUniversity,Patiala,India
RafaeladeCarvalhoBaptista SchoolofFood Engineering,UniversityofCampinas (UNICAMP),Campinas,Brazil
AmirModarresiChahardehi Advanced MedicalandDentalInstitute,UniversitiSains Malaysia,KepalaBatas,Malaysia
ParteekChandel ChitkaraCollegeof Pharmacy,ChitkaraUniversity,Punjab,India
HiteshChopra ChitkaraCollegeofPharmacy, ChitkaraUniversity,Patiala,India
MichellaDawra ChemicalEngineering Laboratory,ToulouseUniversity,CNRS, INPT,UPS,Toulouse,France
SanjeevaniShekharDeshkar Departmentof Pharmaceutics,Dr.D.Y.PatilInstituteof PharmaceuticalSciencesandResearch, Pimpri,Pune,India
PoojaDey AmityInstituteofPharmacy, AmityUniversity,Noida,India
M.E.Durgun DepartmentofPharmaceutical Technology,FacultyofPharmacy,Istanbul University,Istanbul,Turkey
MarcElBeyrouthy DepartmentofAgriculture andFoodEngineering,Schoolof Engineering,HolySpiritUniversityofKaslik, Jounieh,Lebanon
YoussefElRayess DepartmentofAgriculture andFoodEngineering,Schoolof Engineering,HolySpiritUniversityofKaslik, Jounieh,Lebanon
I.Esentu ¨ rk DepartmentofPharmaceutical Technology,FacultyofPharmacy,University ofHealthSciencesTurkey,Istanbul,Turkey
MohammadHoseinFarzaei Facultyof Pharmacy,KermanshahUniversityof MedicalScience,Kermanshah,Iran; DepartmentofTraditionalPharmacy,Faculty ofTraditionalMedicine,TehranUniversityof MedicalScience,Tehran,Iran
SevgiGezici MolecularBiologyandGenetics, DepartmentofScienceandLiterature, AdvancedTechnologyApplicationand ResearchCenter,Kilis7AralikUniversity, Kilis,Turkey
S.Gungor DepartmentofPharmaceutical Technology,FacultyofPharmacy,Istanbul University,Istanbul,Turkey
Haryanto SchoolofNursingScienceof Muhammadiyah,STIKMuhammadiyah Pontianak,KabupatenKubuRaya,Indonesia
AbidHussain SchoolofLifeSciences,Beijing InstituteofTechnology,Beijing,P.R.China; AdvancedResearchInstituteof MultidisciplinaryScience,BeijingInstituteof Technology,Beijing,P.R.China;Institute ofEngineeringMedicine,BeijingInstituteof Technology,Beijing,P.R.China;Key LaboratoryofMolecularMedicineand Biotherapy,BeijingInstituteofTechnology, Beijing,P.R.China
HaroonIqbal CollegeofPharmaceutical Sciences,SoochowUniversity,Suzhou,P.R. China
SajidIqbal SchoolofPharmaceuticalSciences, CheelooCollegeofMedicine,Shandong University,Shandong,P.R.China
GagandeepKaur DepartmentofChemistry andBiochemistry,UniversityofWindsor, Windsor,ON,Canada
HarnoorKaur ChitkaraCollegeofPharmacy, ChitkaraUniversity,Punjab,India
JaipalKaur DepartmentofPharmaceutical Sciences,GuruNanakDevUniversity, Amritsar,India
PrabhjotKaur ChitkaraCollegeofPharmacy, ChitkaraUniversity,Punjab,India
SarabjitKaur DepartmentofPharmaceutical Sciences,GuruNanakDevUniversity, Amritsar,India
DeepakKaushik Departmentof PharmaceuticalSciences,MaharshiDayanand University,Rohtak,India
PradeepKumar WitsAdvancedDrugDelivery PlatformResearchUnit,Departmentof PharmacyandPharmacology,Schoolof TherapeuticSciences,FacultyofHealth Sciences,UniversityoftheWitwatersrand, Johannesburg,SouthAfrica
SureshKumar DepartmentofPharmaceutical SciencesandDrugResearch,Punjabi University,Patiala,India
YanliLi SchoolofPharmacy,Collaborative InnovationCenterofAdvancedDrug
DeliverySystemandBiotechDrugsin UniversitiesofShandong,KeyLaboratoryof MolecularPharmacologyandDrug Evaluation,MinistryofEducation,Yantai University,Yantai,P.R.China
VuanghaoLim AdvancedMedicalandDental Institute,UniversitiSainsMalaysia,Kepala Batas,Malaysia
AnaPauladaFonsecaMachado Schoolof FoodEngineering,UniversityofCampinas (UNICAMP),Campinas,Brazil
PiyushMadaan ChitkaraCollegeof Pharmacy,ChitkaraUniversity,Punjab,India
ReechaMadaan ChitkaraCollegeof Pharmacy,ChitkaraUniversity,Punjab,India
JayashriG.Mahore Departmentof Pharmaceutics,Dr.D.Y.PatilInstituteof PharmaceuticalSciencesandResearch, Pimpri,Pune,India
MarioRobertoMarosticaJunior Schoolof FoodEngineering,UniversityofCampinas (UNICAMP),Campinas,Brazil
SeyedZachariahMoradi Pharmaceutical SciencesResearchCenter,HealthInstitute, KermanshahUniversityofMedicalSciences, Kermanshah,Iran;MedicalBiologyResearch Center,KermanshahUniversityofMedical Sciences,Kermanshah,Iran
AmandaMariaTomaziniMunhoz Moya SchoolofFoodEngineering, UniversityofCampinas(UNICAMP), Campinas,Brazil
RobertodePaulaNascimento SchoolofFood Engineering,UniversityofCampinas (UNICAMP),Campinas,Brazil
OluwatoyinA.Odeku Departmentof PharmaceuticsandIndustrialPharmacy, FacultyofPharmacy,UniversityofIbadan, Ibadan,Nigeria
Y.Ozsoy DepartmentofPharmaceutical Technology,FacultyofPharmacy,Istanbul University,Istanbul,Turkey
RakeshPahwa InstituteofPharmaceutical Sciences,KurukshetraUniversity, Kurukshetra,India
KamlaPathak PharmacyCollegeSaifai,Uttar PradeshUniversityofMedicalSciences, Saifai,India
DipakD.Patil DepartmentofPharmaceutical Chemistry,H.R.PatelInstituteof PharmaceuticalEducationandResearch, Shirpur,India
VivekPuri ChitkaraUniversitySchoolof Pharmacy,ChitkaraUniversity,Kalujhinda, India
AbdulQadeer KeyLaboratoryofAnimal ParasitologyofMinistryofAgriculturaland RuralAffairs,ShanghaiVeterinaryResearch Institute,Shanghai,P.R.China
FazleRabbi DepartmentofPharmacy,Abasyn UniversityPeshawar,Peshawar,Pakistan
ArchanaRani DepartmentofPharmaceutical Sciences,GuruNanakDevUniversity, Amritsar,India
MonikaSachdeva FatimaCollegeofHealth Sciences,AlAin,UnitedArabEmirates
SorayaSajadimajd DepartmentofBiology, FacultyofScience,RaziUniversity, Kermanshah,Iran
TwinkleSalgotra ChitkaraCollegeof Pharmacy,ChitkaraUniversity,Punjab,India
ShikhaSaxena AmityInstituteofPharmacy, AmityUniversity,Noida,India
AmeyaSharma ChitkaraUniversitySchoolof Pharmacy,ChitkaraUniversity,Kalujhinda, India
MadhuSharma AmravatiEnclave,Surajpur, India
AtulShirkhedkar Departmentof PharmaceuticalChemistry,R.C.Patel InstituteofPharmaceuticalEducationand Research,Shirpur,India
RakeshK.Sindhu ChitkaraCollegeof Pharmacy,ChitkaraUniversity,Punjab,India
ArshdeepSingh Departmentof PharmaceuticalSciences,GuruNanakDev University,Amritsar,India
BalbirSingh DepartmentofPharmaceutical Sciences,GuruNanakDevUniversity, Amritsar,India
HasandeepSingh Departmentof PharmaceuticalSciences,GuruNanakDev University,Amritsar,India
MuhammadSohail SchoolofPharmacy, CollaborativeInnovationCenterofAdvanced DrugDeliverySystemandBiotechDrugsin UniversitiesofShandong,KeyLaboratoryof MolecularPharmacologyandDrug Evaluation,MinistryofEducation,Yantai University,Yantai,P.R.China
PornsakSriamornsak Pharmaceutical BiopolymerGroup(PBiG),Facultyof Pharmacy,SilpakornUniversity,Nakhon Pathom,Thailand;FacultyofPharmacy, SilpakornUniversity,NakhonPathom, Thailand;AcademyofScience,TheRoyal SocietyofThailand,Bangkok,Thailand
KennethC.Ugoeze Departmentof PharmaceuticsandPharmaceutical Technology,FacultyofPharmaceutical Sciences,UniversityofPortHarcourt,Port Harcourt,Nigeria
KamranHidayatUllah Departmentof Pharmacy,Quaid-I-AzamUniversity, Islamabad,Pakistan
RishuVerma ChitkaraCollegeofPharmacy, ChitkaraUniversity,Punjab,India
ReshuVirmani SchoolofPharmaceutical Sciences,MVNUniversity,Palwal,India
RamanpreetWalia AmityInstituteof Pharmacy,AmityUniversity,Noida,India
YotsananWeerapol FacultyofPharmaceutical Sciences,BuraphaUniversity,Chonburi, Thailand;PharmaceuticalBiopolymerGroup (PBiG),FacultyofPharmacy,Silpakorn University,NakhonPathom,Thailand
HuiXu SchoolofPharmacy,Collaborative InnovationCenterofAdvancedDrug DeliverySystemandBiotechDrugsin UniversitiesofShandong,KeyLaboratoryof MolecularPharmacologyandDrug Evaluation,MinistryofEducation,Yantai University,Yantai,P.R.China
AyeshaYounas DepartmentofPharmaceutics, CollegeofPharmaceuticalSciences, ZhengzhouUniversity,Zhengzhou,P.R. China
BinYu SchoolofPharmacy,Collaborative InnovationCenterofAdvancedDrug
DeliverySystemandBiotechDrugsin UniversitiesofShandong,KeyLaboratoryof MolecularPharmacologyandDrug Evaluation,MinistryofEducation,Yantai University,Yantai,P.R.China
Preface
Herbalremedieshavebeenusedforthe treatmentofdifferentillnessessinceancient times.Arangeofbioactivecompoundsin herbsandspiceshavebeenstudiedfor therapeuticpropertiesinanimalsaswellas humans.Traditionalherbalmedicineand herbalbioactivesarebeingusedastherapeuticsubstitutesorascomplementary treatmentstoaugmentexistingtherapies. Thedrugdeliverysystemusedforadministeringtheherbalmedicinetothepatient istraditionalandobsolete,resultingin reducedefficacyofthedrug.Ifthenovel drugdeliverytechnologyisappliedin herbalmedicine,itmayplausiblyhelpin increasingtheefficacyandreducingthe sideeffectsofvariousherbalcompounds. Herbalbioactivescanbeincorporatedin variousnoveldrugdeliverysystemssuch asnanoparticles,microemulsions,matrix systems,soliddispersions,liposomes,and solidlipidnanoparticles.
Thisbookisasystematiccompilationof herbalbioactive-baseddifferentdrugdeliverysystemsforgastrointestinal,ocular,
transdermal,pulmonary,andvaginal administration.Variousnovelapproaches forthedeliveryofherbalbioactivesand commonissuesrelatedtoherbalbioactive suchassolubility,bioavailability,andtaste couldbemodifiedfordesigninganeffectivedrugdeliverysystemhavebeen addressedconspicuously.Herbalcosmetics, standardization,andregulatoryissues relatedtoherbalbioactivesarediscussedin separateandindividualizedchapters.The students,researchers,andscientistsworkinginthedomainofherbal/naturalmaterials/compounds,polymersciences,drug delivery,cosmetics,standardization,regulatoryconsiderationscouldreferthebook forconceptualenhancementandacquiring thoroughinsightintothetopic.
InderbirSinghBakshi RakeshK.Sindhu ReechaMadaan RajniBala
Thispageintentionallyleftblank
Roleofherbalbioactivesandtheir formulationsinthetreatmentof gastrointestinaldisorders
SarabjitKaur1,MonikaSachdeva2,HasandeepSingh1, ArshdeepSingh1,JaipalKaur1,ArchanaRani1,SarojArora3 andBalbirSingh1
1DepartmentofPharmaceuticalSciences,GuruNanakDevUniversity,Amritsar,India 2Fatima CollegeofHealthSciences,AlAin,UnitedArabEmirates 3DepartmentofBotanicaland EnvironmentalSciences,GuruNanakDevUniversity,Amritsar,India
1.1Introduction
Thereisplethoraofnutrientspresentinthe foodweconsume,andtheirpresencehelpsto buildnewtissuesandrepairsthedamagedtissuesinbody.Foodistheprincipalsourceof energyforthehumanbody;thereforeitisofcrucialimportanceforsustenance.Foodcontains largemoleculesthatarenoteasilyprocessedbythebodycells,thereforeitisbrokenintosmall moleculesthatenterthecellsofbodybymeansofdigestion.Thebreakdownandabsorptionof allthefoodproductsrequiredforhealthylifeoccursinthegastrointestinal(GI)system.
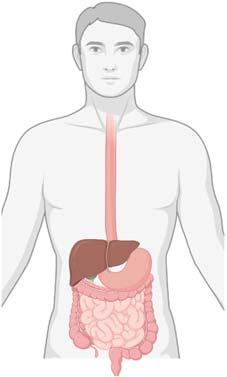
Thegastrointestinaltract(GIT)isahollowmusculartubethatoriginatesfromoralcavityand continuestopharynx,esophagus,stomach,andintestinestorectumandanus.Therearealsoaccessoryorganssuchassalivaryglands,liver,pancreas,andgallbladder,whichassistindigestionand metabolismoffoodbysecretingvariousenzymesasshownin Fig.1.1 (Martini,2001;Moore,1999). TheprimaryfunctionsoftheGITaremobility,secretiondigestion,absorption,anddefecation.
1.1.1Anatomyandphysiologyofgastrointestinaltract
TheGITcomprisesoffourlayersknownastunics.Eachlayeriscomposedofdifferent tissuesandperformsdifferentfunctions.Thefourtunicsareknownasmucosa,submucosa,muscularis,andserosa.
2 1.Roleofherbalbioactivesandtheirformulationsinthetreatmentofgastrointestinaldisorders
1.1.1.1Mucosa
FIGURE1.1 Thegastrointestinaltract.
Mucosaismadeupofepitheliumcells,thinconnectivetissue,anditistheabsorptive andsecretorylayerofGIT.Thegobletcellsarepresentinthemucosa,whichsecretes mucusthroughouttheGIT.Thevilliandmicrovilliarealsopresentinmucosalayer.
1.1.1.2Submucosa
Itservesthemucosaandishighlyvascularandrelativelythick.Theelementsthatare absorbedandpassthroughthemucosaarepickedupfromthebloodvesselspresentin submucosa.Theglandsandnerveplexusesarepresentinsubmucosa.
1.1.1.3Muscularis
Theperistalticmovementsandsegmentalcontractionsarecarriedoutbymuscularisin GIT.Themuscularisismadeupoftwomusclelayers,thatis,innercircularandouterlongitudinal.Thechurningandmovementoffoodmixesitwithdigestiveenzymesdownthe GItractiscarriedbymuscularis.
1.1.1.4Serosa
Itisaprotectivelayerthatiscomposedofsimplesquamousepitheliumandvascular connectivetissue,whichsecreteslubricatingserousfluid.Itisvisiblelayerandisoutside theorgan(Chen&Chen,1989;Ernst,1997;Kenney,1986;Scanlon&Sanders,2018).
1.2Roleofherbalbioactivesandformulationsinthetreatmentof gastrointestinaltractdisorders
TheGITcanbeaffectedbyvariouspathologicalconditionsthatcanimpairdigestion andhaveimpactonoverallhealth.CommonGIdisordersincludeconstipation,diarrhea,
1.2Roleofherbalbioactivesandformulationsinthetreatmentofgastrointestinaltractdisorders
gastroesophagealrefluxdisease(GERD),pepticulcer,irritablebowelsyndrome(IBS),and coloncancer.
Tomaintainhealthandcurediseases,herbalformulationshavebeeninusesincethe dawnofcivilization.Nowadaysaswell,thepopularityofherbalbioactivesinthefieldof medicinehasincreasedinadrasticway.AccordingtotheWorldHealthOrganization (WHO),aboutthree-fourthoftheglobalpopulationreliesmoreontheherbalformulation thanthatonallopathicdrugs.InIndia,47%oftheelderlypeopleuseherbaldrugsfor treatmentofanydisease(Tugume&Nyakoojo,2019).
Somecommonreasonswhytheemergenceofherbaldrugshaveincreasedare:
1. costeffectiveness,
2. highcorrespondencewithpatientsideology,and
3. lesseradverseeffectsthansyntheticmedicines.
Herbalmedicinesarelargelyusedforthepromotionofhealthandasatherapyfor chronicandlife-threateningdiseases.Moreover,theuseofsuchmedicationsgets enhancedwhentheconventionalmedicinetherapiesareinadequateinthetreatmentof chronicdiseases.Herbalmedicinesaregenerallyusedasofthebeliefthatthey“aresafe andarenottoxic.”Butthisstatementisnotalwaystrue,especiallywhentheherbalproductsareusedalongwiththeprescriptiondrugsorover-the-counter(OTC)medications orherbs(Ekor,2014).
1.2.1Gastroesophagealrefluxdisease
GERDisachronicGIdisorder.InGERD,thegastriccontentisregurgitatedintothe esophagus(foodpipe).InUnitedStates,itisthemostcommonlydiagnoseddigestivedisorderandhasaprevalenceofabout20%(Kahrilas,1996).GERDcanbecausedbymultiplemechanismsthatcanbestructuralorintrinsic,oritcanbebecauseofboth.GERD disruptstheesophagigastricjunction,whichleadstoexposureofacidicgastriccontents intotheesophagus.
GERDexistswithextra-esophagealsymptomsincludingpaininchest,chroniccough, inflammationoflarynx,dentalerosions,orasthma(Hom&Vaezi,2013;Vakil,vanZanten, Kahrilas,Dent,&Jones,2006).
Generally,forthemanagementofGERD,lifestylemodifications,protonpumpinhibitors(PPIs),GIprokineticagents,andmucosalprotectiveagentshavebeenthemainstay overtheyears(Hosseini,Salari,Shariatmaghani,Birjandi,&Salari,2017).However,the widespreaduseofherbalformulationsforthemanagementofGERDisincreasingdayby day.SomeoftheherbalformulationsusedinthemanagementofGERDarediscussedas follows.
1.2.1.1Rikkunshito
RikkunshitoisatraditionalJapanesemedicinethatconsistsofeightcrudeherbsandis generallyusedbythepeopleofJapanforvariousGIdisordersandsymptomsrelatedto respectivedisorderssuchasnausea,anorexia,andvomiting.Itenhancestheeffectsrelated togastricfunctionsmediatedbynitricoxideforimprovedgastricemptying.Itincreases
thelevelsofghrelin,whichisapotentstimulantinvolvedingastricemptyingandGI motility(Suzuki,Inadomi,&Hibi,2009)AsmallstudyconductedinchildrenwithGERD showedthatRikkunshitoreducedacidexposuretothedistalpartofesophagusby improvingacidclearance(Kawaharaetal.,2007).Combinedtherapyofrabeprazole (10mgday 1)withRikkunshitoshowedresistantsymptomsafter4-weektherapyin patientshavingrefractoryGERD.Furthermore,Rikkunshitostronglybindstobilesalts andhelpedinabsorptionofbilesalts,thusservingapotentialroleinthemanagementof refractoryGERD(Araki,Mukaisho,Fujiyama,Hattori,&Sugihara,2012).
1.2.1.2Faringel
Faringelcontainsherbalcomponentssuchas Matricariarecutita L.,aloevera,honey, Propolisgel,and Calendulaofficinalis alongwithsodiumbicarbonateandalginate.Thefirst twoelementsareactuallyinvolvedinproducingantirefluxactionbydintoftheirabilityof neutralizinggastricacidity(Kwiatek,Roman,Fareeduddin,Pandolfino,&Kahrilas,2011; Mandel,Daggy,Brodie,&Jacoby,2000).Uponcomingincontactwiththegastriccontent, theycreatearaft,whichactsasaphysicalbarrierintheupperpartofthestomach,thereby preventingrefluxepisodes.Theherbalcomponentsinvolvedinthecompositionarecapableofproducingmildantiinflammatory,analgesiceffects,andtheyfavorthehealing capacityofhumanmucosa(Amsterdametal.,2009;Ansorge,Reinhold,&Lendeckel, 2003;Lotfy,Badra,Burham,&Alenzi,2006;Parenteetal.,2012).
Alginatehasauniquepropertyofformingafoamygelandisananionicpolysaccharide thatispresentinnaturallyoccurringbrownalgae.Whenalginateandbicarbonateinteract withthegastriccontent,theyresultintheformationofafoamygelthatactsasaraft, floatsonthesurfaceofgastriccontent,therebycreatingarelativepH-neutralbarrier (Mandeletal.,2000).Thisformulationreducesthepostprandialsymptomsbyneutralizing theacidicgastriccontent.Itdisplacestheacidiccontentfromtheesophagogastricjunction byformingafoamygelbarrierandthuscanhelpinprotectingesophagealmucosa.This formulationhasanimmediateandfastonsetofaction(within1hofadministration)than PPIswithlongerdurationandhigherefficacythansomeofthetraditionalantacidsinprovidingrelieffromrefluxsymptoms(Kwiateketal.,2011;Zentilinetal.,2005).
1.2.1.3Cannabisandcannabinoids
VariouscannabinoidreceptorsandtheirendogenousligandsarereportedinGITwhich areinvolvedinvariousGIfunctionssuchasrelaxingloweresophagealsphincter,fluid secretions,gastricemptying,gastricacidsecretion,andGImotility(Izzo&Sharkey,2010; Massa&Monory,2006).
Patientssmokingcannabisfor2daysormoreinaweekwereassociatedwithlowgastricacidoutput(Nalinetal.,1978).Severalpreclinicalstudieshavebeendoneontherats subjectedtopylorus-ligationfor2 4h,andtheresultssuggestedthatcannabisandother individualcannabinoidsinhibitedthegastricacidsecretioninrats(Castilloetal.,2006). CannabinoidsactonCB1(cannabinoidtype1)receptorslocatedonthevagalefferent pathways,andtheinhibitoryeffectofcannabinoidsongastricacidsecretionmightbe mediatedbyactingonthesereceptors(Coruzzietal.,2006).Cannabisalsoaffectedthe CB1receptorslocatedonparietalcells,whichresultedininhibitinggastricacidsecretion byloweringthecentralefferentvagalactivity(Coruzzietal.,2006).Furthermore,when
1.2Roleofherbalbioactivesandformulationsinthetreatmentofgastrointestinaltractdisorders
theethanolextractof Cannabissativa wasadministeredinrats,itwasobservedtoraisethe gastricpH.AriseingastricpHwasnoticedinratswhentreatedwith Cannabis extractat doseof0.1and0.3gkg 1,respectively(Castilloetal.,2006).Somepreclinicalstudiesalso supportedcannabisorcannabinoidshavingaprotectiveeffectinstomach.Whengiven subcutaneouslyorviaoralroute,tetrahydrocannabinolinhibitedtheproductionofgastric ulcersinducedbypyloricligation.
Ingastricmucosa,thecannabisexertedantioxidantandantiinflammatoryeffects,thus protectingitbyactivatingcentralcannabinoidreceptors(Abdel-Salametal.,2015;Allen& Flemstrom,2005;Calatayud,Barrachina,&Esplugues,2001;Wallace&Miller,2000; Whittle,1993).Becauseofalltheseconcomitantbenefits,itisusuallyusedinthetreatment ofpepticulcersandmostimportantlyintreatingGERD.
1.2.1.4SiniZuojindecoction
DecoctionmadebythecombinationofSinipowderandZuojinpilliscalled“Sini Zuojindecoction”(SNZJD),aChinesemedicinethatisusedasabasicrecipeforthetreatmentofGERD.InChina,Japan,SouthKorea,andinsomeotherregionsoftheworld,this herbalformulationcombinedwithfixedherbsiswidelyacceptedandstudied(Daietal., 2017;Lingetal.,2015;Teschke,Wolff,Frenzel,Eickhoff,&Schulze,2015;Tominaga& Arakawa,2015;Xiaoetal.,2018).Thecompositionofthisformulationincludes Citrusaurantium L.(ZhiShi,AurantiiFructusImmaturus), Bupleurumchinense DC.(ChaiHu, BupleuriRadix), Glycyrrhizauralensis Fisch.exDC.(GanCao,GlycyrrhizaeRadixet Rhizoma), Paeonialactiflora Pall.(BaiShao,PaeoniaeRadixAlba), Coptischinensis Franch (HuangLian),and Tetradiumruticarpum (A.Juss.) T.G.Hartley (Lietal.,2020).
SNZJDactondopamineD2receptorspresentinGImyentericplexusorstimulatethe5HT4receptorsofGImyentericplexusandthusimprovethemovementofesophagusto theproximalsmallintestine.SNZJD’sareusedtotreatGITdisorders,adversity,clearthe heat,andharmonizethestomachfunctions.However,SNZJD’sbenefitsintreatingGERD areuncertaintillnowbecausethemechanisminvolvedisnotappropriate(Travagli& Anselmi,2016).
1.2.2Pepticulcer
Aninjuryofthedigestivetractresultsinmucosalbreaksreachingthesubmucosa.Loss ofprotectiveelementsresultsinmucosalerosionandcausesdisturbancesinGImucosa, whichresultsintheoccurrenceofpepticulcer.Pepticulcersaremainlyfoundinproximal duodenumandstomach,buttheirprevalencecanalsobefoundinesophagus(DelValle, 2015).Stress,smoking,familyhistory,andhypersecretoryacidicenvironment,alongwith dietaryfactorswerethoughttobetheonlycausesforthedevelopmentofpepticulcers (Rotter,1983),butnowadays,interventionof Helicobacterpylori infectionandnonsteroidal antiinflammatorydrugtherapyisfoundtobemajorcauseofpepticulcers.Theorganism createsthealkalineenvironmentbytheproductionofurease,whichcountsessentialfactorsforitssurvival(DelValle,2015).Evidencesuggeststhatoxidativestressalsoplaysa roleinthepathophysiologyofGIinflammationandgastriculcers(Repetto&Llesuy, 2002).Incaseofpepticulcers,reactiveoxygenspecieswerefoundtobeinvolvedinthe
ulcersinducedbypylorusligationandethanol-inducedulcers(Sen,Chakraborty,De,& Mazumder,2009).DifferenttherapeuticagentssuchascombinationofaPPI,twoantibioticsgenerallyclarithromycinandamoxicillinormetronidazoleandsomeherbalpreparationsareusedfortreatmentofpepticulcer.Theseagentsactbyinhibitingtheacid secretionorenhancingthemucousproduction,therebyboostingthemucosaldefense mechanism(Kamadaetal.,2021).Theherbaldrugsandherbalformulationsusedfortreatmentandpreventionofpepticulcerarediscussedasfollows.
1.2.2.1 Capsicumannuum (chili)
Themainactiveconstituentofchiliiscapsaicin.Originally,chilieswerethoughttoexacerbatethepepticulcers,butrecentresearchhasshownsomethingcontrarytothat.Studies showedthattheindividualshavingahighdietaryintakeofchiliesareknowntohaveless chanceforpepticulcers(Kang,Teng,Wee,&Chen,1995;Kang,Yeoh,etal.,1995; Satyanarayana,2006).Inratshavingethanol-oraspirin-inducedpepticulcers,capsaicin showedaprotectiveproperty(Kang,Teng,etal.,1995;Kang,Yeoh,etal.,1995).In double-blindtrials,thepatientstaking2.5mgday 1 chilipepperfor5weekswereknown tobeeffectiveagainstepigastricpainandsymptomsrelatedtodyspepsia(Bortolotti, Coccia,Grossi,&Miglioli,2002;Lambrecht,Burchert,Respondek,Muller,&Peskar,1993).
Protectivemechanismmayalsoinvolvethevanilloidreceptors,andbothcapsaicinand resiniferatoxinactonvanilloidreceptors.Resiniferatoxin,anultrapotentanalogofcapsaicin,alsodisplayedprotectivepropertiesagainstpepticulcers(Basith,Cui,Hong,&Choi, 2016).
1.2.2.2 Azadirachtaindica (neem)
Neemhasbeeninuseforthousandsofyearsforcureofseveraldiseasessuchasdiabetes,epistaxis,parasites,asthma,andepigastricpain.Clinicalstudieshavesuggestedthat takingneembarkextractat30mgfor10daysreducesthesecretionofgastricacidby77% andpromotesthehealingofduodenalulcerswhentakencontinuouslyfor10weeks (Bandyopadhyayetal.,2004).Neeminhibitsprotonpumpandhassimilarpharmacology asthatofPPIs(Bandyopadhyayetal.,2002).
1.2.2.3 Glycyrrhizaglabra (licorice)
Forthetreatmentofepigastricpainanddyspepsia,licoricehasbeenusedsincetheprimevalEgyptiantimesandforatleast4000yearsinChina(Shibata,2000).Glycyrrhizicacid(triterpenoidalsaponin)isamainactiveconstituentoflicoriceandisreportedtopossess antiulceractivity(Takagi,Okabe,&Saziki,1969).Themainactiveconstituentoflicorice,glycyrrhizinicacidshowedantiulcereffectbyincreasingtheprostaglandinsconcentration,which promotesthecellproliferationandmucoussecretioninstomach.Previousstudyalsoreported theactivityof Extractumliquiritiae (EL),glycyrrhizicacid,glycyrrhetinicacid,andanovellipophilicderivativeofglycyrrhetinicacidmonoglucuronide(GAMG),acetylatedGAMGagainst 29 H.pylori strains,suggestingtheirbeneficialeffectonpepticulcers(Krausse,Bielenberg, Blaschek,&Ullmann,2004;Lohar,Wankhade,Faisal,&Jagtap,2020).
Licoriceistheoldestherbusedinthetreatmentofpepticulcers.Themechanismofantiulcereffectoflicoricepertainstotheantioxidant,prostoglandinformationbooster,andantiinflammatoryeffects(Jalilzadeh-Amin,Najarnezhad,Anassori,Mostafavi,&Keshipour,2015).
1.2Roleofherbalbioactivesandformulationsinthetreatmentofgastrointestinaltractdisorders
Inaddition,theflavonoid-richfractionoflicoriceextractpossesses H.pylori activitybyreducingthehydroxy-folatereductaseenzyme,proteinsynthesis,andDNAgyraseenzyme(Asha etal.,2013).Furthermore,theconstituentsoflicoriceincreasethemucoussecretioninalimentarycanalandenhancethelifespanofcellsurfacesinstomachwiththeirantipepsineffect (Aly,Al-Alousi,&Salem,2005).Moreover,thevariousconstituentsoflicoricesuchasglabrene,licochalconeA,glabridin,licoricidin,andlicoiso flavanBactasinhibitorsof H.pylori reproduction(Fukaietal.,2002).
1.2.2.4
Vacciniumoxycoccos (cranberry)
Cranberryhastheabilitytoeliminate H.pylori inthepatientsdrinking500mLjuice dailyfor3months.Inaninvitrostudyofhumangastriccells,cranberryimpairedthe adhesionof H.pylori tothegastriccellwall(Burgeretal.,2002).
1.2.2.5 Curcumalonga
(turmeric)
InChineseandAyurvedicmedicinesystem,turmerichasbeeninuseforcenturies, mainlyforthetreatmentofdyspepsiaandepigastricpain.Inpatientshavingpepticulcers, administrationof600mgturmericrootfivetimesadaywasreportedtoresolvetheulcers in4weeksin48%andin12weeksin76%patients(Prucksunand,Indrasukhsri, Leethochawalit,&Hungspreugs,2001).Asignificantimprovementinthesymptomsof dyspepsiain1 2weeksbyturmerichasalsobeenreported(Prucksunandetal.,2001).In invitrostudies,turmericderivativesareknowntohaveactivityagainst H.pylori,butthe abilityofturmerictoeradicate H.pylori completelyisstillnotfullydemonstratedinclinicaltrials(DiMarioetal.,2007).TurmericisalsoknowntohaveH2-blockingproperty, whichexplainsitspotentialtohealulcers(Kimetal.,2005;Yuetal.,2009).
1.2.2.6Avipattikarchurna
ItisanAyurvedicpolyherbalformulationthatisknownforpossessingantiulcerproperties.Itiscomposedof14differentingredientssuchasela(Amomumsubulatum ),maricha (Pipernigrum),pippali(Piperlongum),haritaki(Terminaliachebula),vidanga(Embeliaribes), vibhitaka(Terminaliabellerica),aamalaki(Emblicaofficinalis),shunthi(Zingiberofficinale), musta(Cyperusrotundus),salt(Vidalavana),patra(Cinnamomumtamala),lavanga(Syzgium aromaticum),sharkara(sugarcandy),andtrivrit(Operculinaterpethum).
Trivrit,lavanga,andsugarcandyarepresentin11,44,and66parts,respectivelyand everyothercomponentispresentin1 1parteach.Intotal,3 6gofchurnawithwater beforeorafterthemealisgivenasatherapeuticdose(Gyawalietal.,2013).
Haritaki,maricha,andpippalipreventedthegastricmucosathroughtheircytoprotectiveeffects(Khandare,Gulecha,Mahajan,Mundada,&Gangurde,2009;Raju,Ilango, Chitra,&Ashish,2009; Zaveri,Khandhar,Patel,&Patel,2010).Gastricsecretionsare decreasedbyshunthi,anditalsohelpedincreasemucosalresistanceanddefensivefactors ofgastricmucosa(AlYahyaetal.,1990).Lavangamaintainedthebasalgastricmucosal bloodflow,andanincreaseinmucussecretionswerenoted(Santinetal.,2011).
Thechurnadecreasedthevolumeofgastriccontents,loweredthenumberofulcers,shortenedthelengthofulcers,alsodecreasedthegastricirritancyindexand increasedthegastric pH.Inpyloricligationinducedgastriculcers,theAvipattikarchurnashowedantisecretoryand antiulcerpropertiessimilartoranitidine(Yadav,Sharma,Kumar,&Sharma,2019).
8 1.Roleofherbalbioactivesandtheirformulationsinthetreatmentofgastrointestinaldisorders
1.2.2.7DHC-1
DHC-1isaherbalformulationthatconsistsofmethanolextractsof G.glabra L., E.officinalis Gaertn., Bacopamonnieri L., S.aromaticum L.,and Mangiferaindica L.Thisformulation reducedthegastricfluidvolumeandtotalacidityandincreasedthepH,thusimparting theantiulceractivity(Bafna&Balaraman,2004).
Ininvivostudies,ithasbeenobservedthatoxidativestressisalsoinvolvedinthe developmentofpylorusligation induced(Rastogi,Patnaik,&Dikshit,1998)andethanolinducedgastricmucosalinjury(Pihan,Regillo,&Szabo,1987).Superoxidedismutaseand catalaseenzymesarethepreventiveantioxidentsandserveasthefirstlineofdefense againstreactiveoxygenspecies(Misra&Fridovich,1972).TreatmentwithDHC-1ledtoa markedincreaseinsuperoxidedismutaseandcatalaseanddecreasedthelevelofglutathione(Balaraman,Bafna,&Kolhapure,2004).
1.2.3Coloncancer
Thethirdleadingcauseofcancerdeathintheworldiscoloncancer,anditsoccurrence isontheriseindevelopingnations(Rawla,Sunkara,&Barsouk,2019).Itisfoundthat maincausesofcoloncanceraresubstantialalcoholconsumption,processedmeat,red meat,abdominalfat,bodyfat,andthefactorsthatcanleadtogreateradult-attainedheight (Stewart,2003).Theriskofcoloncancerincreasesifthepatientsarealreadysufferingfrom inflammatoryboweldisease(Crohn’sdiseaseandulcerativecolitis).Arecentmetaanalysis reportedthatpeopleaffectedbyCrohn’sdiseaseareatahigherrisktodevelopcoloncancer(VonRoonetal.,2007).
Epidemiologicalmodeling-basedstudieshavedemonstratedthatherbaltreatment whenusedasanadjuvanttherapymayimproveprognosisinadvancedcoloncancer patients(Auyeung&Ko,2010;Au-Yeungetal.,2008).ThemechanismsbywhichtraditionalChinesemedicineactsinmetastaticcancerhavebeendescribedaccordingtodualisticantiproliferationandhypotheticalmodelsoftumorinvasivenessandreduction(Baak, Gyllenhaal,Liu,Guo,&Block,2011).
1.2.3.1Triphala
Abilityofcancerstemcells(CSCs)todrivecontinuedexpansionleadstoanincreasein populationofmalignantcells.Thereforeaneffectiveapproachagainstcoloncancerwould betheuseofstrategiesthattargetCSCs(Chen,Wu,Tanaka,&Zhang,2014).Triphala,a widelyusedIndiantraditionalformulation,showedantiproliferativeandproapoptotic effortsonhumancolonCSCsandcoloncancercells,thatis,HCT116(Vadde, Radhakrishnan,Reddivari,&Vanamala,2015).
HerbalformulationTriphalachurnaisacombinationof Terminaliabellirica Roxb., E.officinalis Gaertn.,and Terminaliachebula Retz.,whichareaddedinequalproportions.Itwas observedtoinhibitthedevelopmentofthymiclymphoma,pancreaticcancer,andstomach cancerinmice(Sandhya,Lathika,Pandey,&Mishra,2006;Shi,Sahu,&Srivastava,2008). Avarietyofflavonoids,namely,homoorientin,quercetin,naringin,isorhamnetin,and hypaconitinewerefoundtobepresentinthemethanolextractoftriphala(MET).Naringin specificallyinhibitedtheprogressionofbreastcancercellsbymodulationofWnt/
β-cateninpathway(Lietal.,2013).ProliferationofvascularsmoothmusclecellsweresuppressedbynaringinbytargetingcyclinD1(Kimetal.,2008;Lee,Moon,Choi,Kim,& Moon,2008).ThetranscriptionfactorsofT-cellfactor/lymphoidenhancerfactor(TCF/ LEF)familyinthenucleuswasblockedbytheflavonoids,therebydecreasingtheexpressionofoncogenicproteins(Amadoetal.,2014;Leonardietal.,2010).Thedecreased humancoloncancerstemcells(HCCSC)proliferationwasduetodownregulationofcMycandcyclinD1inducedbytriphalaextract(Amendolaetal.,2009).METsuppressed theproliferation,whichisindependentofp53statusinHCT116andinHCCSCs.Elevated levelsofcleavedpolyadenosinediphosphate-ribosepolymerase(PARP)clearlyindicated thatMETalsoinducesp53-independentapoptosisinHCCSCs.Accordingtothedata obtainedbywesternblotting,METsuppressedtheproteinlevelsofc-MycandcyclinD1, whicharemainlyresponsibleforinductionofapoptosisandsurvivalofCSCs(Chenetal., 2014;Hoffman&Liebermann,2008;Niuetal.,2015;Wangetal.,2008).
Dietaryplantextracts,especiallyvegetables,fruits,andherbs,holdstrongevidencein preventionofcoloncancer(Kim,Yang,Lee,&Ju,2021).Bioactivecompoundssuchas polyphenols,glucosinolates,andcarotenoidsareabundantlypresentintheseplantextracts andinhibitionofcellproliferation,inducingapoptosis,andscavengingfreeradicalsare someofthechemopreventivepropertiesofthesecompounds(Longetal.,2021).
1.2.3.2C168
C168isamixtureofeightherbs,includingcinnamon,ginger,atractylodes,carthamus, angelica,turmeric, Glycyrrhiza and Astragalus.C168methanolextract(CME)exertedantiproliferativeactivitiesonHepG2hepatocellularcarcinomacellsandcolorectalcarcinomacells,but itwasunabletoshowanyeffectonlymphoblasticleukemiacells,V79 4Chinesehamster lungfibroblastsandCCD-841-CoNnormalcolonepithelialcells.CMEinducedG2/McellcyclearrestandapoptosisinHCT116cells.DNAdamagewasreportedasanearlysignalof CME-inducedapoptosisasCMEincreasedtheH2AXphosphorylationandtailmomentvalue inHCT116cells(Leong,Chan,Hamid,Latip,&Rajab,2016).
1.2.3.3Resveratrol
Resveratrol,abioactivecompoundpresentingrapeskin,showedsuppressionofcolon cancercellproliferation.Itactsviaactivationofp53andsuppressionofIGF-1R/Akt/Wnt signalingpathways,resultinginelevatedapoptosis(Vanamala,Reddivari,Radhakrishnan, &Tarver,2010).
1.2.4Constipation
Constipationoccurswhenthereisunsatisfactorydefecationcomprisinginfrequent stoolsanddifficultstoolpassageorboth,occurringthreeorafewtimesaweek.Itaffects approximately12% 35%ofworld’spopulation(Werth,Williams,Fisher,&Pont,2019). Thesymptomsariseeitherfromanacuteeventthatcanberemediedwithhighfluidand dietaryintakeorbecauseofachronicconditionthatrequiresdailyinterventions. AvarietyofOTCmedicationsareavailableforconstipation.However,manypatients aredisappointedbycurrentconventionaltreatments(Ramkumar&Rao,2005;Youssef,