https://ebookmass.com/product/green-sustainable-process-for-
Instant digital products (PDF, ePub, MOBI) ready for you
Download now and discover formats that fit your needs...
Green Sustainable Process for Chemical and Environmental Engineering and Science: Carbon Dioxide Capture and Utilization Dr. Inamuddin
https://ebookmass.com/product/green-sustainable-process-for-chemicaland-environmental-engineering-and-science-carbon-dioxide-capture-andutilization-dr-inamuddin/ ebookmass.com
Green Sustainable Process for Chemical and Environmental Engineering and Science: Switchable Solvents Dr. Inamuddin
https://ebookmass.com/product/green-sustainable-process-for-chemicaland-environmental-engineering-and-science-switchable-solvents-drinamuddin/
ebookmass.com
Green Sustainable Process for Chemical and Environmental Engineering and Science: Green Solvents for Biocatalysis 1st Edition Inamuddin (Editor)
https://ebookmass.com/product/green-sustainable-process-for-chemicaland-environmental-engineering-and-science-green-solvents-forbiocatalysis-1st-edition-inamuddin-editor/
ebookmass.com
Toxic at Work: Surviving your psychopathic workmates, from the dominant bullies to the charming manipulators David Gillespie
https://ebookmass.com/product/toxic-at-work-surviving-yourpsychopathic-workmates-from-the-dominant-bullies-to-the-charmingmanipulators-david-gillespie/ ebookmass.com
Reading Greek Tragedy with Judith Butler Mario Telò
https://ebookmass.com/product/reading-greek-tragedy-with-judithbutler-mario-telo/
ebookmass.com
eTextbook 978-0134444284 Cryptography and Network Security: Principles and Practice (7th Edition)
https://ebookmass.com/product/etextbook-978-0134444284-cryptographyand-network-security-principles-and-practice-7th-edition/
ebookmass.com
Cambridge IGCSE® & O Level Complete Physics Student Book Fourth Edition Stephen Pople
https://ebookmass.com/product/cambridge-igcse-o-level-completephysics-student-book-fourth-edition-stephen-pople/
ebookmass.com
Emery's Elements of Medical Genetics E-Book Turnpenny
https://ebookmass.com/product/emerys-elements-of-medical-genetics-ebook-turnpenny/
ebookmass.com
12 Men for Christmas Phillipa Ashley
https://ebookmass.com/product/12-men-for-christmas-phillipa-ashley/
ebookmass.com
https://ebookmass.com/product/understanding-financial-risk-toleranceinstitutional-behavioral-and-normative-dimensions-caterina-cruciani/
ebookmass.com
GREENSUSTAINABLE PROCESSFOR CHEMICALAND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERINGAND SCIENCE GREENSUSTAINABLE PROCESSFOR CHEMICALAND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERINGAND SCIENCE SupercriticalCarbonDioxide asGreenSolvent Editedby
INAMUDDIN
DepartmentofChemistry,KingAbdulazizUniversity,SaudiArabia
ABDULLAHM.ASIRI
DepartmentofChemistry,KingAbdulazizUniversity,SaudiArabia
ARUNM.ISLOOR
DepartmentofChemistry,NationalInstituteofTechnology
Karnataka,India
Elsevier
Radarweg29,POBox211,1000AEAmsterdam,Netherlands
TheBoulevard,LangfordLane,Kidlington,OxfordOX51GB,UnitedKingdom 50HampshireStreet,5thFloor,Cambridge,MA02139,UnitedStates
© 2020ElsevierInc.Allrightsreserved.
Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproducedortransmittedinanyformorbyanymeans,electronicormechanical, includingphotocopying,recording,oranyinformationstorageandretrievalsystem,withoutpermissioninwriting fromthepublisher.Detailsonhowtoseekpermission,furtherinformationaboutthePublisher’spermissionspolicies andourarrangementswithorganizationssuchastheCopyrightClearanceCenterandtheCopyrightLicensingAgency, canbefoundatourwebsite: www.elsevier.com/permissions
ThisbookandtheindividualcontributionscontainedinitareprotectedundercopyrightbythePublisher(otherthanas maybenotedherein).
Notices
Knowledgeandbestpracticeinthisfieldareconstantlychanging.Asnewresearchandexperiencebroadenour understanding,changesinresearchmethods,professionalpractices,ormedicaltreatmentmaybecomenecessary.
Practitionersandresearchersmustalwaysrelyontheirownexperienceandknowledgeinevaluatingandusingany information,methods,compounds,orexperimentsdescribedherein.Inusingsuchinformationormethodsthey shouldbemindfuloftheirownsafetyandthesafetyofothers,includingpartiesforwhomtheyhaveaprofessional responsibility.
Tothefullestextentofthelaw,neitherthePublishernortheauthors,contributors,oreditors,assumeanyliabilityfor anyinjuryand/ordamagetopersonsorpropertyasamatterofproductsliability,negligenceorotherwise,orfromany useoroperationofanymethods,products,instructions,orideascontainedinthematerialherein.
LibraryofCongressCataloging-in-PublicationData
AcatalogrecordforthisbookisavailablefromtheLibraryofCongress
BritishLibraryCataloguing-in-PublicationData
AcataloguerecordforthisbookisavailablefromtheBritishLibrary ISBN:978-0-12-817388-6
ForinformationonallElsevierpublicationsvisit ourwebsiteat https://www.elsevier.com/books-and-journals
Publisher: SusanDennis
AcquisitionEditor: KostasKIMarinakis
EditorialProjectManager: MichaelLutz
ProductionProjectManager: VigneshTamil
CoverDesigner: ChristianBilbow
TypesetbySPiGlobal,India
Contributors PoonamAggarwal
DepartmentofFoodScienceandTechnology,PunjabAgriculturalUniversity,Ludhiana, India
MuktaAgrawal
RungtaCollegeofPharmaceuticalSciencesandResearch,Bhilai,Chhattisgarh,India
MudasirAhmad
DepartmentofFoodScienceandTechnology,UniversityofKashmir,Srinagar,India
Ajazuddin
RungtaCollegeofPharmaceuticalSciencesandResearch,Bhilai,Chhattisgarh,India
SumiaAkram UniversityofEducation,BankRoadCampus,Lahore,Pakistan
AmitAlexander RungtaCollegeofPharmaceuticalSciencesandResearch,Bhilai,Chhattisgarh,India
FrancoRicoAmado
MaterialsandEnvironmentLaboratory(LAMMA),StateUniversityofSantaCruz—UESC, Ilheus,Brazil
AndrewN.Amenaghawon
DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,FacultyofEngineering,UniversityofBenin,BeninCity, Nigeria
NanjangudVAnilKumar
DepartmentofChemistry,ManipalInstituteofTechnology,ManipalAcademyofHigher Education,Manipal,India
ChineduL.Anyalewechi
DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,FacultyofEngineering,UniversityofBenin,BeninCity, Nigeria
RaoufAslam
DepartmentofProcessingandFoodEngineering,PunjabAgriculturalUniversity,Ludhiana, India
MojhdehBaghbanbashi
DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,AmirkabirUniversityofTechnology(Tehran Polytechnic),Tehran,Iran
MingBao
StateKeyLaboratoryofFineChemicals,DalianUniversityofTechnology,GanjingziDistrict, DalianChina;SchoolofPetroleumandChemicalEngineering,DalianUniversityof Technology,LiaodongwanNewDistrict,Panjin,China
DanielAssumpc ¸ a˜oBertuol
EnvironmentalProcessesLaboratory(LAPAM),ChemicalEngineeringDepartment,Federal UniversityofSantaMaria—UFSM,SantaMaria,Brazil
F.W.F.Bezerra
TechnologyInstitute,ProgramofPost-GraduationinFoodScience,Technologyand Engineering,FederalUniversityofPara ´ ,Belem,Brazil
P.N.Bezerra
TechnologyInstitute,ProgramofPost-GraduationinFoodScience,Technologyand Engineering,FederalUniversityofPara ´ ,Belem,Brazil
R.N.CarvalhoJunior
TechnologyInstitute,ProgramofPost-GraduationinFoodScience,Technologyand Engineering;TechnologyInstitute,ProgramofPost-GraduationinAmazonNaturalResources Engineering,FederalUniversityofPara ´ ,Belem,Brazil
RajeshChandra
BioenergyResearchLaboratory,DepartmentofPolymer&ProcessEngineering,IndianInstitute ofTechnologyRoorkee(SaharanpurCampus),Saharanpur,India
A.M.J.ChavesNeto
TechnologyInstitute,ProgramofPost-GraduationinAmazonNaturalResourcesEngineering; LaboratoryofPreparationandComputationofNanomaterials,FederalUniversityofPara ´ , Belem,Brazil
AhmadCheikhyoussef UniversityofNamibia,Windhoek,Namibia
NataschaCheikhyoussef MinistryofHigherEducation,TrainingandInnovation,Windhoek,Namibia
Gun-HeanChong
FacultyofFoodScienceandTechnology,UniversitiPutraMalaysia,Serdang,Selangor, Malaysia
R.M.Cordeiro
TechnologyInstitute,ProgramofPost-GraduationinAmazonNaturalResourcesEngineering, FederalUniversityofPara ´ ,Belem,Brazil
EstevanDornelesCruz
EnvironmentalProcessesLaboratory(LAPAM),ChemicalEngineeringDepartment,Federal UniversityofSantaMaria—UFSM,SantaMaria,Brazil
V.M.B.Cunha
TechnologyInstitute,ProgramofPost-GraduationinFoodScience,Technologyand Engineering,FederalUniversityofPara ´ ,Belem,Brazil
W.A.daCosta
TechnologyInstitute,ProgramofPost-GraduationinAmazonNaturalResourcesEngineering, FederalUniversityofPara ´ ,Belem,Brazil
J.N.daCruz
LaboratoryofPreparationandComputationofNanomaterials,FederalUniversityofPara ´ ,Belem, Brazil
M.S.deOliveira
TechnologyInstitute,ProgramofPost-GraduationinFoodScience,Technologyand Engineering,FederalUniversityofPara ´ ,Belem,Brazil
AnaLu ´ ciaBarbosadeSouza
UniversityCenterSENAICIMATEC,HealthInstituteofTechnologies(CIMATECITS), NationalServiceofIndustrialLearning—SENAI,Salvador,Bahia,Brazil
NoorUDinReshi
DepartmentofChemistry,UniversityofKashmir,Srinagar,India
JaniceIzabelDruzian
FederalUniversityofBahia(UFBA),FacultyofPharmacy,Salvador,Bahia,Brazil
SunilKumarDubey DepartmentofPharmacy,BirlaInstituteofTechnologyandScience,Pilani,Rajasthan, India
AdilGani
DepartmentofFoodScienceandTechnology,UniversityofKashmir,Srinagar,India
SandraGonc ¸ alves FacultyofSciencesandTechnology,MeditBio,UniversityofAlgarve,Faro,Portugal
NaghmehHadidi
DepartmentofClinicalResearchandElectronicMicroscope,PasteurInstituteofIran,Tehran, Iran
NoorHadzuinNikHadzir
FacultyofFoodScienceandTechnology,UniversitiPutraMalaysia,Serdang,Selangor, Malaysia
ShahryarJafarinejad
DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,CollegeofEngineering,TuskegeeUniversity,Tuskegee, AL,UnitedStates
JunaidKhan
UniversityTeachingDepartment(Pharmacy),SantGahiraGuruUniversity,Sarguja,Ambikapur, Chhattisgarh,India
HeriSeptyaKusuma
DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,FacultyofIndustrialTechnology,InstitutTeknologi SepuluhNopember,Surabaya,Indonesia
Wan-JunLee
FacultyofFoodScienceandTechnology,UniversitiPutraMalaysia,Serdang,Selangor, Malaysia
XinLiu
StateKeyLaboratoryofFineChemicals,DalianUniversityofTechnology,GanjingziDistrict, DalianChina;SchoolofPetroleumandChemicalEngineering,DalianUniversityof Technology,LiaodongwanNewDistrict,Panjin,China
BrunaAparecidaSouzaMachado
UniversityCenterSENAICIMATEC,HealthInstituteofTechnologies(CIMATECITS), NationalServiceofIndustrialLearning—SENAI,Salvador,Bahia,Brazil
MahfudMahfud
DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,FacultyofIndustrialTechnology,InstitutTeknologi SepuluhNopember,Surabaya,Indonesia
LeonidasMatsakas
BiochemicalProcessEngineering,DivisionofChemicalEngineering,DepartmentofCivil, EnvironmentalandNaturalResourcesEngineering,Lulea ˚ UniversityofTechnology,Lulea ˚ , Sweden
SyedKazimMoosvi
SchoolEducationDepartment,J&KGovernment,Srinagar,India
MuhammadMushtaq
DepartmentofChemistry,GCUniversity,Lahore,Pakistan
RavishPatel
RamanbhaiPatelCollegeofPharmacy,CharotarUniversityofScienceandTechnology, CHARUSATCampus,Changa,Ta-Petlad,Anand,Gujarat,India
AlokPatel
BiochemicalProcessEngineering,DivisionofChemicalEngineering,DepartmentofCivil, EnvironmentalandNaturalResourcesEngineering,Lulea ˚ UniversityofTechnology,Lulea ˚ , Sweden
GholamrezaPazuki
DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,AmirkabirUniversityofTechnology(Tehran Polytechnic),Tehran,Iran
FernandoLuizPellegriniPessoa
UniversityCenterSENAICIMATEC,HealthInstituteofTechnologies(CIMATECITS), NationalServiceofIndustrialLearning—SENAI,Salvador,Bahia,Brazil
R.H.H.Pinto
TechnologyInstitute,ProgramofPost-GraduationinFoodScience,Technologyand Engineering,FederalUniversityofPara ´ ,Belem,Brazil
JagbirRehal DepartmentofFoodScienceandTechnology,PunjabAgriculturalUniversity,Ludhiana,India
Joa˜oHenriquedeOliveiraReis
FederalUniversityofBahia(UFBA),FacultyofPharmacy,Salvador,Bahia,Brazil
MasoodAhmadRizvi DepartmentofChemistry,UniversityofKashmir,Srinagar,India
AnabelaRomano FacultyofSciencesandTechnology,MeditBio,UniversityofAlgarve,Faro,Portugal
ShailendraSaraf
UniversityInstituteofPharmacy,Pt.RavishankarShuklaUniversity,Raipur,Chhattisgarh,India
SwarnlataSaraf
UniversityInstituteofPharmacy,Pt.RavishankarShuklaUniversity,Raipur,Chhattisgarh,India
KmSartaj
MolecularMicrobiologyLaboratory,BiotechnologyDepartment,IndianInstituteofTechnology (IIT-R),Roorkee,India
SabahuddinSiddique PatelCollegeofPharmacy,MadhyanchalProfessionalUniversity,Bhopal,MadhyaPradesh,India
M.P.Silva
TechnologyInstitute,ProgramofPost-GraduationinFoodScience,Technologyand Engineering,FederalUniversityofPara ´ ,Belem,Brazil
EmmaSuali
FacultyofEngineering,JalanUMS,UniversitiMalaysiaSabah,KotaKinabalu,Sabah,Malaysia
NorhidayahSuleiman
FacultyofFoodScienceandTechnology,UniversitiPutraMalaysia,Serdang,Selangor,Malaysia
DhanyaSunil DepartmentofChemistry,ManipalInstituteofTechnology,ManipalAcademyofHigher Education,Manipal,India
EduardoHiromitsuTanabe
EnvironmentalProcessesLaboratory(LAPAM),ChemicalEngineeringDepartment,Federal UniversityofSantaMaria—UFSM,SantaMaria,Brazil
NaderVahdat
DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,CollegeofEngineering,TuskegeeUniversity,Tuskegee, AL,UnitedStates
Wan-HuiWang
StateKeyLaboratoryofFineChemicals,DalianUniversityofTechnology,GanjingziDistrict, DalianChina;SchoolofPetroleumandChemicalEngineering,DalianUniversityof Technology,LiaodongwanNewDistrict,Panjin,China
PoojaYadav
RungtaCollegeofPharmaceuticalSciencesandResearch,Bhilai,Chhattisgarh,India
MudasirYaqoob DepartmentofFoodScienceandTechnology,PunjabAgriculturalUniversity,Ludhiana,India
GiovaniL.Zabot
LaboratoryofAgroindustrialProcessesEngineering(LAPE),FederalUniversityofSantaMaria (UFSM),CachoeiradoSul,Brazil
PoojaYadava,MuktaAgrawala,AmitAlexandera,RavishPatelb, SabahuddinSiddiquec,ShailendraSaraf d,Ajazuddina
aRungtaCollegeofPharmaceuticalSciencesandResearch,Bhilai,Chhattisgarh,India bRamanbhaiPatelCollegeofPharmacy,CharotarUniversityofScienceandTechnology,CHARUSATCampus,Changa, Ta-Petlad,Anand,Gujarat,India
cPatelCollegeofPharmacy,MadhyanchalProfessionalUniversity,Bhopal,MadhyaPradesh,India dUniversityInstituteofPharmacy,Pt.RavishankarShuklaUniversity,Raipur,Chhattisgarh,India
Inthepastfewdecades,polymershavebecomeanimportantpartofdailylife.Their feasiblesynthesisandprocessingareneededforvariousapplications.Insteadofusingconventionalsolvents,nowtheresearchhasbeenshiftedtosupercriticalfluids.Thesupercriticalfluidsaredescribedasamaterialmaintainedataconditionoftemperatureand pressuremorethanitscriticalvalues.Itholdstheuniquecombinationofviscosity(like gas)anddensity(likeliquid)whichmakesasupercriticalfluidanexcellentsolvent [1,2] Supercriticalcarbondioxide(SCO2)isanon-toxicsolvent,whichisthebestalternative
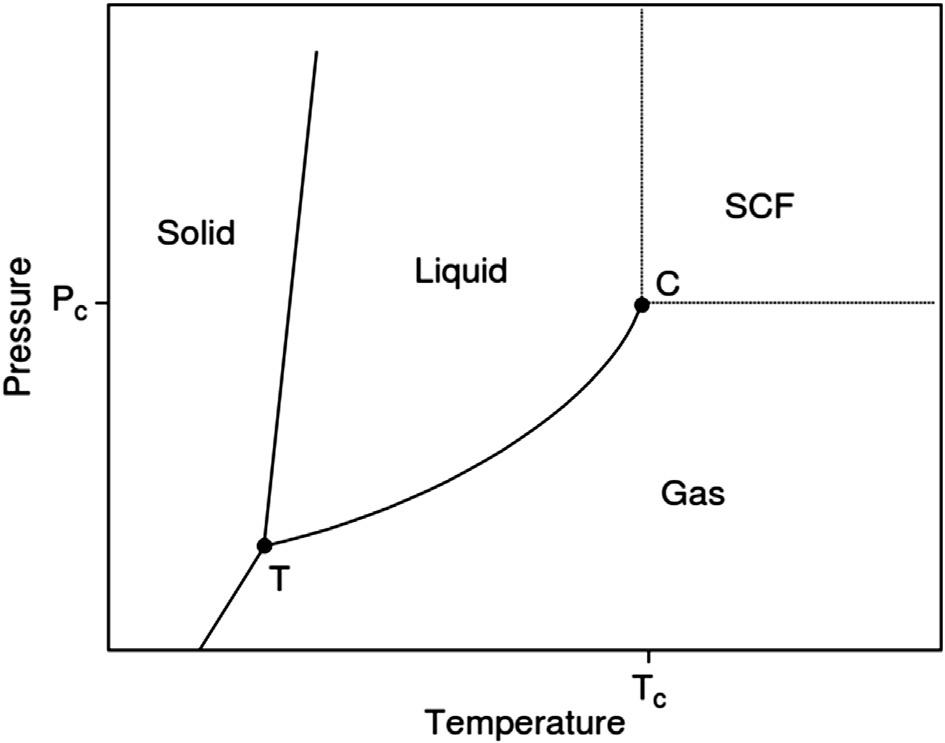
Fig.1 Schematicrepresentationoftemperature–pressurephasediagramofthepurecomponent, surroundedbytriplepoint(T)andcriticalpoint(C). (AdaptedfromS.P.Nalawade,F.Picchioni,L.P.B.M. Janssen,Supercriticalcarbondioxideasagreensolventforprocessingpolymermelts:processingaspects andapplications,Prog.Polym.Sci.31(1)(2006)19–43.)
fornoxiousorganicsolventsandchlorofluorocarbons.Owingtotheirimmensephysical propertiessuchasnon-flammability,chemicallyinertness,andcheapness,thesefindapplications,notonlyinpolymersynthesis,butalsoinpolymerproduction.Thesupercritical conditionsofcarbon-dioxide(CO2)caneasilybeachieved(Tc ¼ 304Kand Pc ¼ 7.38 MPa)(Fig.1)andextractedoutfromthereactionbysimplydepressurizingthereactor. ThehighyieldandincreasedproductqualityattracttheusageofSCO2 [4]
Moreover,CO2 isagasinambientconditions,whichmakesiteasytoremovefrom thepolymericproductinsteadofusingcostlymethodsofsolventevaporationordrying. Mixturesofsolventsareusedtoenhancethestrengthofchemicalreactionduringthe synthesisandprocessingofpolymers [5].However,byincorporatingSCO2 intothe responsegivesadvantagesoverconventionalsolvents,suchas:
•itpossessesenvironmentallybenigncharacteristicssuchasbeingnon-toxic,nonflammable,andlowcost;
•easyremovalofthesolventafterthereaction;
•fasterrateofreactionatmildconditions;and
•higherselectivityandhigheryieldinchemicalreactions(obtainedduetotemperature andpressureabovecriticalvalues).
2.PropertiesofsupercriticalCO2 SCO2 haswidelygainedimportanceinrecentyearsbecauseofitsassureddiffusivityand density.Thesecanchangetheglasstransitiontemperature(Tg)ofthepolymersleadingto theirreducedviscosity [6].Undeniably,eventhoughCO2,duetoitsdistinctsymmetrical
structure,hasnodipolemoment,itcanshowinviolablequadruplemoment(actingata smallerdistancethandipolarinteraction),henceincreasingthesolubility [7,8].TheCO2 itselfshowsexcellentsolubilizingpowerandisthereforeusedasasolventandantisolvent. CO2 ispreferredasapolymerizationmediumbecause:
•thesearecost-effective,non-flammable,non-toxic,andarereadilyobtainablein pureform;
•solventrecoverybecomeseasyduetotheuseofCO2;
•thehighsolubilityofvariouspolymerswithinCO2 findsitsapplicationfortheir synthesis;
•forporouspolymerstobesynthesized,thesupercriticalfluidhavingCO2 facilitatesas non-solvatingpowerandactsasanorganicdiluent;and
•carbondioxideusuallydoesn’tinteractwiththestrongnucleophiles(e.g.,alkoxides, primaryamines,etc.),andhenceitcanbesuggestedpolymerizationinCO2 is generallythroughtheanionicmechanism.
Thenonpolarmolecules,havinglowmolecularweight,canbereadilysolubilizedin supercriticalCO2 ratherthanwaterandioniccompoundsbecausesupercriticalCO2 hasarelativelysmalldielectricconstant(ε ¼ 2).SCO2,owingtoitstremendousphysiochemicalproperties,isalsocheap,non-toxic,andnon-flammable,hencefindingapplicationsintheproductionandrefinementofpolymers.Owingtothehighmasstransfer, lowviscosity,andlowtoxicityprofile,thesupercriticalcarbondioxidecanbepotentially usedinpolymerprocessing,whichalsoovercomestheTrommsdorffeffect.Also,with supercriticalCO2,drypolymerscanbeeasilymadebymerelydepressurizingthereactor afterpolymerization [9,10]
3.ApplicationsofSCO2 inpolymerproductionandprocessing 3.1Purificationofpolymers Apriorquantitativeanalysisoftheextractedcompoundfromthepolymericmatrixbydifferentconventionalmethods,likeduringsynthesisorprocessingofpolymers,isessential becausethereisachancetoobtainby-productsorresidualrawmaterialsthathavetobe extracted.Theconventionalmethodsforpurificationofpolymersincludevariousmethods suchassolvent-intensive,Soxhletextraction,orpolymerdissolutionmethod [11].SCO2 possessestheabilitytoextractouttheseby-productsbyfirstlyswellingthepolymerand thenpermeatingwithinthematrixwheretheseimpuritiesgetsolubilizedintothe SCO2 andagainuponreducingthepressure,SCO2 iseasilydiffusedoutofthepolymer. Interestingly,thesolvatingpowerofSCO2 isregulatedbyslightmodificationinpressure andtemperature.Hence,itisusedinpurificationofpolymers [12,13].Moreover,thesedo notleaveanyharmfulresidue,representingthenon-toxicbehaviorofSCO2.Inaddition, thesecanbeeasilyrecycledduetotheirvolatilenature.Comparedtotheconventional extractionprocesses,ifweuseadrymembranethatispre-treatedwithsupercriticalcarbon dioxide,thiscanresultinlessshrinkageandimprovedwaterpermeability [14,15].
3.2Impregnationandsupercriticaldyeing CO2 canbeusedasasolventtointroducenumerousdyesandmetalcomplexesintothe polymerichosts.Hence,itmaybeapplicableduringdyeing.Adopingsolutebehaving likeaguestisintroducedwithinthehostpolymermatrixduringpolymerimpregnation anddyeing.ThesupercriticalpropertiesofSCO2,includinglowsurfacetension,higher diffusivity,andeasyrecoveryofsolvent,assiststhepreparationofanewpolymer [16,17] Impregnationisthetechniquetoabsorbtheliquidswithinthepolymermatrix.During impregnationusingSCO2,thetherapeuticdrugisdissolvedintothesolventandthen impregnatedwithinthepolymermatrix,whichcanbepreparedfordrugdelivery.There aretwomechanismsforSCO2 infiltrationasadditivesinthepolymericmatrix.Thefirst mechanismdealswiththesolute,whichgetssolubilizedintotheSCO2 andthenispassed throughthepolymermatrix.Afterreducingthepressure,CO2 vacatesthepolymer matrix,andthesoluteparticlesbecomestrappedwithinthepolymer [4,18].Thesecond mechanismdealswiththepartitioningofsolutewithinthepolymermatrixbecauseof theirlowsolubilityinSCO2.Thehighaffinityofsolutetowardspolymeristheprimary factorforsuccessfulsupercriticaldyeing [19]
3.3Particleproduction Normalmillingandgrindingmaydeterioratethepolymerparticles;therefore,administeringSCO2 asasuitablesolvent,orantisolvent,couldofferamorepromisingapproachto reducetheparticlesizeandcontrolthemorphologicalpropertiesofthepolymer.Inadditiontothis,adjustingtheprocessparameterssuchaspressure,temperature,rateofdepressurization,andnozzlediametercanalsoresultindifferentparticlesize [20].Althoughahigh pressureisrequiredfortheparticleformationwhileusingSCO2 insteadofusingorganic solvents,whichtendtoproduceundesirablesolventresidues,itisbeneficialtouseSCO2 wherenosuchtoxicwastesaregenerated.Themicronsizedparticlescanbeproducedby low-meltingpolyestercoatings,acryliccoating,andpolyester-epoxysystems [21].Either ofthetwomethodscanformpolymericparticles,precipitationgenerallythrougharapid expansion,whichinvolvestheuseofSCO2 orbyusingSCO2 asanantisolvent.
3.4Polymermodification MonomersandinitiatorscangetdissolvedwithintheCO2 leadingtoenhanceddiffusion withinthepolymermatrixandcanthereforeeasilymodifythemorphologyofpolymer. Graftingofchemicalgroupswithinthepolymersubstratecanbedonethroughadditional reactions [22].
Theisopropyl-isocyanategraftingonethylene-vinylalcoholcopolymers(EVOH) baretheadvantageofSCO2 providingaselectivedispersionmethodinadditiontofrequentreactionsofthemonomerinamorphousformofEVOHmaintainingtheircrystallinenature [23].
4.Polymerproduction 4.1Step-growthpolymerization Inthismethod,thefunctionalgroupofdifunctionalmonomersiscondensed.Byusing SCO2,polycondensationofcomponentssuchaspolyesters,polyamides(nylon),polyurethanes,andpolyureasispossible(Fig.2).
Thenameitselfshowsthatthepolymerizationprocesswillbestepwisefromdimersto largemoleculesandthentopolymerchains.Themainproblemassociatedwiththisprocessistediousremovalofhighviscosityby-products,whichcanlargelybeovercomeby supercriticalCO2,showinganexcellentplasticizingeffectthatwilldecreasetheviscosity ofthawinfluencingfinerstirring.Predominantly,supercriticalCO2 permitsextractionof by-products [8,24,25]
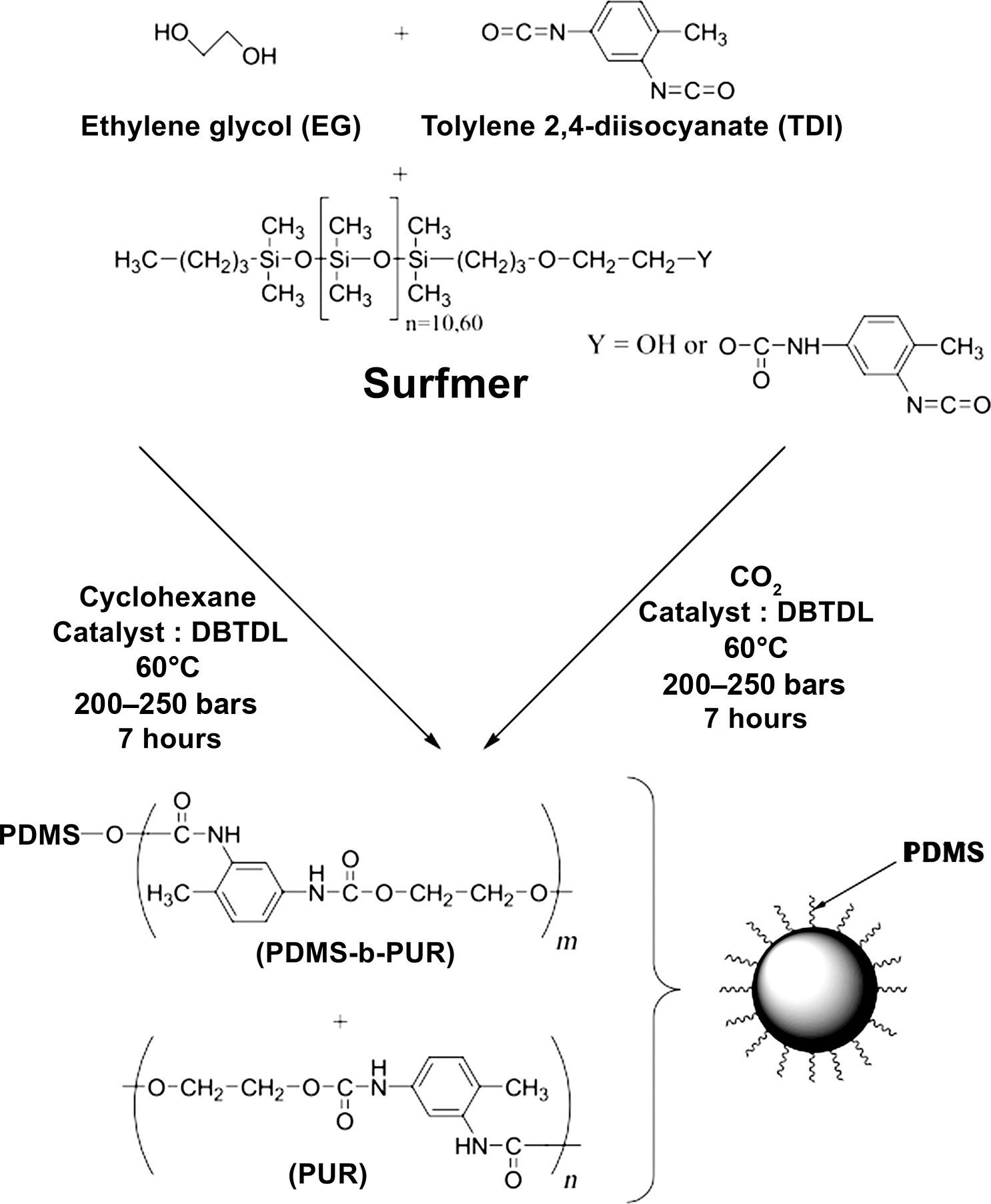
PolycarbonatescanbesynthesizedbyincorporatingSCO2 inthetransesterification ofBisphenolAusingdiphenylcarbonate.Here,SCO2 hasatendencytoremovethe phenolby-productsandenhancethediffusivityofphenolduringsolidstatepolymerizationprocess [8,26].Similarly,polyurethanesandpolydimethylsiloxane(PDMS) weresynthesizedusingSCO2 asdispersantmediaat60°Candabove200barpressure whereethyleneglycolandtolylene-2,4-diisocyanateactasmonomersandhydroxyorisocyanate-terminatedpolydimethylsiloxaneserveasasurfmer(Fig.3) [8,27]
Fig.2 Schematicrepresentationofstep-growthpolymerizationusingSCO2. (AdaptedfromC.Boyère, C.Jer ^ ome,A.Debuigne,Inputofsupercriticalcarbondioxidetopolymersynthesis:anoverview,Eur.Polym. J.61(2014)45–63.)
Fig.3 Reactionbetweentolylene2,4-diisocyanate,andethyleneglycolinthepresenceofsurfmer. (AdaptedfromP.Chambon,E.Cloutet,H.Cramail,T.Tassaing,M.Besnard,Synthesisofcore-shell polyurethane–polydimethylsiloxaneparticlesincyclohexaneandinsupercriticalcarbondioxideusedas dispersantmedia:acomparativeinvestigation,Polymer46(4)(2005)1057–1066.)
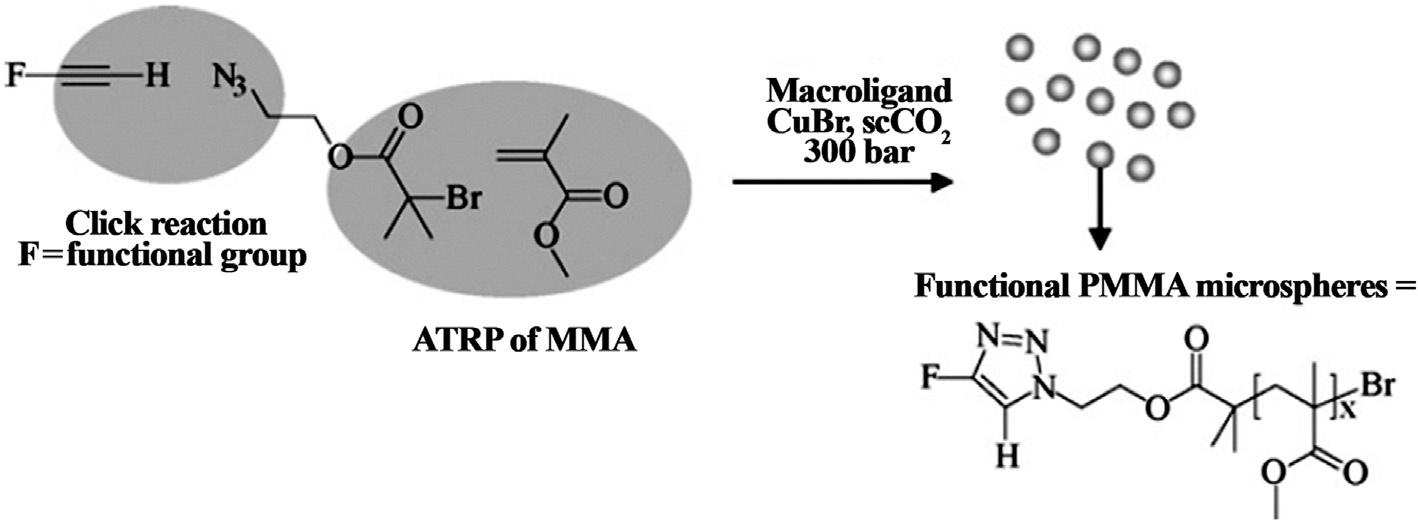
4.2Chaingrowthpolymerization SupercriticalCO2 isbestsuitedforradicalpolymerizationwhereallthethree components,i.e.,monomer,initiator,andcontrolreagents,areeffortlesslysolubilized insupercriticalCO2 [28].Itactsasagreensolventforthesynthesisofvariousfluorinated andnon-fluorinatedpolymersbyatomtransferradicalpolymerization(ATRP).Moreover,itplaysabinaryrolebystabilizingthegrowingchainsofPMMAandcomplexionof thecoppersaltinthesynthesisofpoly(methylmethacrylate)(PMMA)usingATRP [29, 30].Aone-potprocessusingdispersionATRPandazide-alkyne1,3-dipolarHuisgen’s cycloadditionwasemployedforpreparingfunctionalizedpolymers(Fig.4) [31].
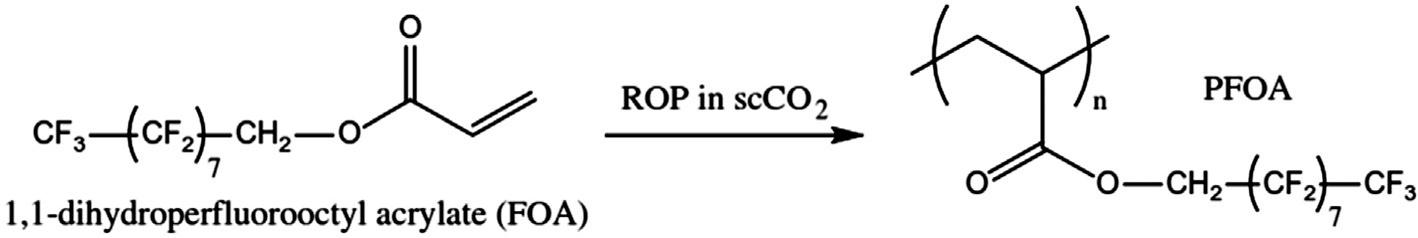
4.2.1Homogeneouspolymerization ThefluoropolymerscanbesynthesizedbyusingSCO2 viacationicpolymerizationor freeradicalpolymerization [32].Thehomogeneouspolymerizationof1,l-dihydroperfluorooctylacrylate(FOA)andazobisisobutyronitrile(AIBN)usingSCO2 yieldsvarious fluoropolymersassociatedwithFOA [8,33].Furthermore,FOAcanbe co-polymerized usingvinylhydrocarbonmonomersinthepresenceofSCO2,whichyieldspoly(1,ldihydroperfluorooctylacrylate)(PFOA)(Fig.5).
Anotherco-polymertetrafluoroethylene(TFE)canbeusedforthesynthesisofvariousfluoropolymers;althoughTFEasamonomercausesrapidexplosions,whencombinedwithCO2 itformsa“pseudo”azeotrope,whichmakesiteasiertohandle.Various TFE-basedfluoropolymershavebeensynthesizedusingCO2 suchasfluorinatedethylenepropylene(FEP),perfluoroalkoxyalkanes(PFA),ethylenetetrafluoroethylene (ETFE),TFE/vinylacetate,Nafiontypematerials,andTeflon-AF-typematerials (Fig.6) [35] .
Fig.4 ReactionbetweendispersionATRPandclickreactioncontainingfunctionalgroupforthe formationoffunctionalPMMAmicrospheres. (AdaptedfromB.Grignard,C.Calberg,C. Jerome,C.Detrembleur, “One-pot” dispersionATRPandalkyne-azideHuisgen’s1,3-dipolar cycloadditioninsupercriticalcarbondioxide:towardstheformationoffunctionalmicrospheres,J. Supercrit.Fluids53(1)(2010)151–155.)
Fig.5 HomogeneouspolymerizationPFOAfromFOAmonomerusingSCO2. (AdaptedfromC.Boyère, C.Jer ^ ome,A.Debuigne,Inputofsupercriticalcarbondioxidetopolymersynthesis:anoverview,Eur.Polym. J.61(2014)45–63.)
Fluorinated ethylene propylene resin
Perfluoroalkoxy resin (FEP)
tetrafluoroethylene resin
Fig.6 DifferentTetrafluoroethylene-basedfluoropolymerssynthesizedbyusingcarbondioxide (AdaptedfromC.D.Wood,A.I.Cooper,J.M.DeSimone,Greensynthesisofpolymersusingsupercritical carbondioxide,Curr.Opin.SolidStateMater.Sci.8(5)(2004)325–331.)
CF2
Ethylene
Tetrafluoroethylene-co-vinyl acetate (ETFE) (PFA)
However,TFEandSCO2 basedfluoropolymersproducehighmolecularweight polymersduetothepresenceofmuchlessacidicendgroups.Hence,itbecomesnecessarytoaddfurtherchaintransferagents,whichwilldecreasemolecularweightandoptimizemeltprocessabilityofthepolymer [36].SCO2 playsadualroleherebyfacilitating themonomerintothepolymerphase(becauseoftheplasticizingpropertyofCO2)and favoringcrosspropagationduetodecreasedtemperature [34,37].
4.2.2Precipitationpolymerization Assuch,vinylmonomersarereadilysolubleinCO2 buttheirrespectivepolymersafter synthesisprecipitateoutfromthesolution.TheuseofSCO2 heresignifiesthatuponsimpledepressurizationofthereactor,theprecipitatedpolymerswillcrystallizeoutindry formwithnosolventleftoverbehind [38]
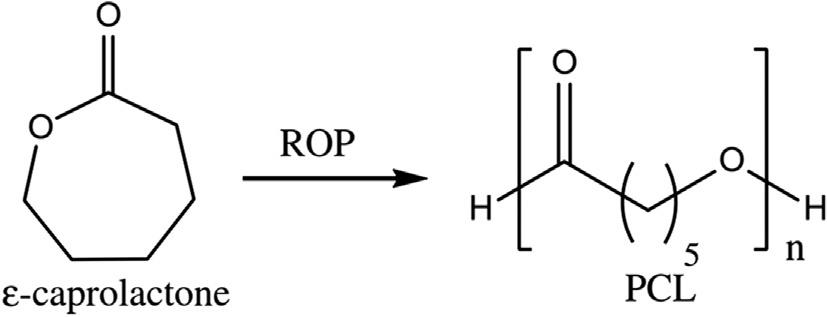
Semi-crystallinefluoropolymerscanbetreatedusingthemethodofprecipitation polymerization,whichyieldshighmolecularweightpolymers.ByusingTFEandperfluoro(propylvinylether)copolymers,highmolecularweightpolymerswereproduced andconfirmedbyusingFT-IRanalysiswheretheroleofSCO2 wasalsotoeliminatethe unwantedendgroups [8,39].Polymersthatarethermoresponsivewerealsosynthesized byusingN-isopropylacrylamide(NIPAM),whichreactedwithacrylicacid(AA).These weresubjectedtohydration-dehydrationbehaviortoanalyzethetemperatureresponse [40].Similarworkwasdonebyusing2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate(HEMA) [41] and vinylidenefluoride(VDF) [42].Insolublealiphaticpolyesterswereproducedfromfeedstocksofnon-petrochemicalcompoundsbyringopeningpolymerization(ROP)of lactones [43].Thereactionresultedindeleteriousenvironmentalhazardsinthepresence ofLewisacidcatalyst.Therefore,theROPwasperformedusingCO2.Thealiphatic polyesterswereinsolubleinCO2.Hence,thelatterwaspolymerizedusingprecipitation polymerization(Fig.7) [8,44]
4.2.3Dispersionpolymerization Indispersionpolymerization,thepolymerisobtainedbypolymerizingthemonomerand initiatorintoCO2 byusingastabilizer,whichtendstostabilizethedispersedpolymer
Fig.7 ROPofe-caprolactoneactingasmonomeranditscorrespondingpolycaprolactone(PCL). (AdaptedfromC.Boyère,C.Jer ^ ome,A.Debuigne,Inputofsupercriticalcarbondioxidetopolymer synthesis:anoverview,Eur.Polym.J.61(2014)45–63.)
particleswhilethereisachangeinthereactionmediumfromhomogeneoustoheterogeneous [45].Thestabilizeractsbyinducingstericrepulsionbetweenthegrowing particles.However,nowadaystheresearchhasshiftedtowardsnon-fluorinatedstericstabilizer,whichismorebeneficialinpolymerizationinvolvingdispersionusingSCO2 Recently,hydrocarbonblockcopolymerswereemployedasstabilizersbut,duetolack ofsolubilityinCO2,resultedinagglomeratedpolymerparticles [46].Interestingly,some polyvinylesterslikepolyvinylacetateandpolyvinylpivalatewereabetterreplacement fortheconventionalfluorinatedsurfactants [47–50]
4.2.4Suspensionpolymerization Inoppositiontodispersionpolymerizati on,heretheseformaheterogeneousmedia whereneithermonomernorpolymeraresolubleinthemedia.Themonomerforms dropswhentheinitiatorisaddedtoitwiththeaidofmechanicalstirring.Suspension polymerizationyieldedsubmi cron-sizedwater-solublepolymersbyN-ethylacrylamide.Thesizeofthepolymerparticlesvarieswidely,dependinguponmonomerconcentration,stabilizer,initiator,and,moreimportantly,uponvaryingthepressureand temperature [8,51] .Thepoly(3-O-methacryloyl- D -glucopyranose)-b-PFOMA a is usedasanemulsifierforthesuspensionpo lymerization,whichisanamphiphilic di-blockcopolymer [52] . Recently,variouspolymerssuchaspoly(acrylicacid)(PAA) [53],poly(lactide-codioxanone)(PLDO) [41],andcopolymersofN-isopropylacrylamide(NIPA) [54] were alsosynthesizedbysuspensionpolymerizationinSCO2.
4.2.5Emulsionpolymerization Emulsionpolymerizationdealswithbiphasicliquids/organicsolventmixturescontaining stabilizers,whichwillmodifythestructureofpolymersafterpolymerization.This methodofpolymerizationyieldshighmolecularweightpolymersbecausethesegenerally donotdependupontheviscosity;rather,theelongatingchainsremainwithintheparticlesatlowconcentrations.ThestableemulsioncanbeformedbyusingsurfactantshavingCO2-phillicandCO2-phobicpartsattached,whichwilldeterminethenatureof emulsionformed,i.e.,CO2-in-waterorwater-in-CO2 typeemulsion.Ifwehavehydrophilicmonomersundergoingwater-in-CO2 (W/C)polymerization,thenwater-soluble polymerswillformandviceversa.
InthecaseofaW/Csystem,surfactanttendstoformmicellewithahydrophilic monomer,whichuponpolymerizationbecomessolubilizedwithintheaqueousphase andresultsinsuspendedparticleswithinSCO2 (Fig.8).
a Poly(3-O-methacryloyl-D-glucopyranose)-b-1,1-dihydroperfluorooctylmethacrylate.
Fig.8 Graphicalillustrationofheterogeneousmicroemulsionpolymerizationtechniqueusing(A)W/C and(B)CO2-in-water(C/W)systems,whichresultsinformationofsolidparticlesandporousmaterial, respectively. (AdaptedandmodifiedfromC.Boyère,C.Jer ^ ome,A.Debuigne,Inputofsupercriticalcarbon dioxidetopolymersynthesis:anoverview,Eur.Polym.J.61(2014)45–63.)
5.Polymerprocessing
5.1Plasticizationofpolymers
SupercriticalCO2 hasthepotentialtolowertheglasstransitiontemperature(Tg)of glassypolymers.ThesepolymerstendtoabsorbsupercriticalCO2 andhenceforthswell andreformtheirphysicalandmechanicals trength.Theinteractionofafunctional groupofpolymersandsupercriticalSCO2 tendtodecreasethechain-chaininteraction andelevatethemobilityofpolymers [55,56] .PlasticizationofpolymersusingsupercriticalSCO2 canbemeasuredbydifferentmethodssuchasgassorption,permeability [57,58] ,andpolymerswelling [59,60]
5.2Viscosityreduction
Highmolecularweightpolymersaredifficulttoprocessduetothehighviscositysolvents usedduringtheprocessing.However,viscositycanbereducedifweapplyahightemperaturetothesystem,asweknowthatbyincreasingthetemperature,duetotheincrease
inkineticenergy,molecularvibrationsincreases,andtheviscositydecreases.Indeed,the increaseintemperaturecanresultinpolymerdegradation.Therefore,asuitablesolvent suchasSCO2 canbeusedtoreducetheviscosityatlowtemperature [61].SCO2 hasa goodplasticizationeffectonpolymers.CO2 isreadilysolubilizedinpolymers,decreasing theirTg,andthusthedecreaseinthemeltingpointofpolymersalsoreducestheviscosity.
Duetotheelongationofpolymermoleculesduringsynthesis,CO2 couldnotescape fromthefibers;hence,aftersolidification,inadditiontoreducedviscosity,wegetalowdensitypolymer [3]
5.3Microcellularfoam Amicrocellularfoamedpolymerconsistsofacelldiameteroffewerthan10 μmandacell densityofmorethan100cells/cm3 [17].MicrocellularfoamcanbeformedbyasinglephasesolutionwhereafterdepressurizingtheSCO2,supersaturationoccurs,leadingto nucleationofcells.Drugentrapmentwithinthepolymerfoamusingsupercritical CO2 hasbecomeaninterestingtopicforresearch.Inarecentinvestigation,hydrophilic druggentamicinandhydrophobicdrugcurcuminhavebeenloadedasmicrocellular foamusingpoly(lactic-co-glycolicacid)(PLGA)polymerwiththeaidofSCO2.The entrapmentefficiencywasfoundtobe75%byusingthedrug:apolymerratioof 75:25 [62].Thefoamingprocessisgenerallycompletedintwobasicsteps: (a)dissolutionofCO2 inthepolymericmatrixunderanoptimumpressureforminga polymer/gassolution;and(b)nucleationandgrowthoftheparticlesuponadecrease inpressureoranincreaseintemperature [12]
5.4Polymerblending Forprocessingandblending,interactionsassociatedwiththesupercriticalmediaandthe functionalgroupofpolymershavetobekeptinmind.Theirratiooftheviscositieswill determinethesizeofthephases.Thesupercriticalmediabehavesdifferentlywithevery componentoftheblendbecauseoftheirvaryingmolecularstructures,whichwillhavea differenteffectontheTgofeachelement.Therefore,theplasticizingeffectofeachcomponentwillbedifferent.Duringextrusionusingsupercriticalfluid,thesolubilityofCO2 playsanimportantroleuponvaryingtemperature,pressure,andshearrate.Afteremploying SCO2,theshearthinningisdecreasedandafinedispersionisobtained.Therefore,onecan easilymanipulatethemorphologyofpolymerblendandtuneitssizeeasily [63].Byblending thepolymerwithinitiatorandSCO2,apolymercompositecanalsobeformed.
6.Futureprospects Duringthemanufactureoffluoropolymers,SCO2 showsincreasedsafetyaswellaspolymerproperties.Therefore,thesecanfindapplicationduringhandlingofexplosive
monomers.SCO2 canbefoundadvantageouswhenconsideringthedrawbacksassociatedwiththescaffoldfabricationmethod.Thesedrawbacksnotonlycanmanipulatescaffoldporositybutcanalsobeusedtomakebiocompositesandpreserveproteinactivity.As discussedabove,CO2 notonlyisabetteralternativeforpolymerproduction,butinmany casesisthemostneededone.AwiderangeofapplicationsassociatedwithSCO2 suggest ittobeapromisingsolvent,butfurtherinvestigationsrelatedtotheinteractionofthe polymerandSCO2 systemarerequired.
7.Challengesahead AlargevolumeofSCO2 isneededduringtheencapsulationofdrugsintopolymerichosts whichprovedtobelimited.Anotherchallengeisthehighsolubilityofmonomers requiredforpolymerprocessingandsynthesis.HighlySCO2 solublepolymersshowsignificantpolymerprocessingability.Overall,ithasbecomeclearthatSCO2 hasmoved aheadfromscientificcuriosity,butitstillneedstobemorecommercializedconcerning polymerprocessing.Akeychallengeistomakealargenumberofdrugstobeprocessedin SCO2.However,usingSCO2 asanantisolventwithotheradditionalsolventsovercomes thisproblem.Hence,SCO2 willplayanessentialroleinfuturedrugdeliveryapplications.
8.Conclusion SCO2 isanexcitingsubstituteforvariousorganic/non-polarsolventsinmultipleapplicationssuchasextraction,purification,impregnationofpolymers,andsupercriticaldyeing.Itcanalsobeusedindifferentpolymerizationtechniquesincludinghomogeneous polymerization,dispersion,suspension,precipitation,andemulsionpolymerizations. VariousprocessingstrategieshaveemergedthatdependonsupercriticalCO2 because ofitsplasticizingandantisolventproperties.Insummary,supercriticalfluidsofferatremendousopportunityinresearchassociatedwithpolymers,andprovidegreatscopefor developmentofmorepromisingandsustainabletechnologiestothepolymericindustry.
References [1] M.Champeau,J.M.Thomassin,T.Tassaing,C.Jerome,DrugloadingofpolymerimplantsbysupercriticalCO2assistedimpregnation:areview,J.Control.Release209(2015)248–259.
[2] A.Aguiar-Ricardo,V.D.Bonifacio,Supercriticalcarbondioxidedesignstrategies:fromdrugcarriers tosoftkillers,Philos.Trans.AMath.Phys.Eng.Sci.373(2057)(2015).
[3] S.P.Nalawade,F.Picchioni,L.P.B.M.Janssen,Supercriticalcarbondioxideasagreensolventforprocessingpolymermelts:processingaspectsandapplications,Prog.Polym.Sci.31(1)(2006)19–43.
[4] A.I.Cooper,S.G.Kazarian,M.Poliakoff,Supercriticalfluidimpregnationofpolyethylenefilms,anew approachtostudyingequilibriainmatrices;thehydrogenbondingoffluoroalcoholsto(η5-C5Me5)Ir (CO)2andtheeffectonC-Hactivation,Chem.Phys.Lett.206(1)(1993)175–180.
[5] O.R.Davies,A.L.Lewis,M.J.Whitaker,H.Tai,K.M.Shakesheff,S.M.Howdle,Applicationsof supercriticalCO2inthefabricationofpolymersystemsfordrugdeliveryandtissueengineering, Adv.DrugDeliv.Rev.60(3)(2008)373–387.
[6] J.Zhou,Applicationofsupercriticalfluidinnanolithographicprocesses,RecentPat.Nanotechnol. 4(2)(2010)78–84.
[7]K.MF,Supercriticalcarbondioxideforsustainablepolymerprocesses,in:M.T.KemmereMF(Ed.), SupercriticalCarbonDioxide:inPolymerReactionEngineering,FRG:Wiley-VCHVerlagGmbH& Co,Weinheim,2006.
[8] C.Boye ` re,C.Jer^ ome,A.Debuigne,Inputofsupercriticalcarbondioxidetopolymersynthesis:an overview,Eur.Polym.J.61(2014)45–63.
[9] P.Sheth,H.Sandhu,D.Singhal,W.Malick,N.Shah,M.S.Kislalioglu,Nanoparticlesinthepharmaceuticalindustryandtheuseofsupercriticalfluidtechnologiesfornanoparticleproduction,Curr.Drug Deliv.9(3)(2012)269–284.
[10] M.Bhamidipati,A.M.Scurto,M.S.Detamore,Thefutureofcarbondioxideforpolymerprocessingin tissueengineering,TissueEng.PartBRev.19(3)(2013)221–232.
[11] K.Khosravi-Darani,E.Vasheghani-Farahani,Applicationofsupercriticalfluidextractioninbiotechnology,Crit.Rev.Biotechnol.25(4)(2005)231–242.
[12] E.DiMaio,E.Kiran,Foamingofpolymerswithsupercriticalfluidsandperspectivesonthecurrent knowledgegapsandchallenges,J.Supercrit.Fluids134(2018)157–166.
[13] E.Kiran,Supercriticalfluidsandpolymers—Theyearinreview—2014,J.Supercrit.Fluids110(2016) 126–153.
[14] G.Brunner,Calculationofphaseequilibriaandtheirrelationtoseparationwithsupercriticalfluids, J.Supercrit.Fluids134(2018)2–11.
[15] Y.Hiraga,A.Duereh,R.L.Smith,Aspectsofsolventpolarityandsolventpropertiesindeveloping efficientsystemsforprocessingbiomasswithionicliquidmixturesandsupercriticalCO2, J.Supercrit.Fluids134(2018)12–20.
[16] M.Tang,T.-Y.Wen,T.-B.Du,Y.-P.Chen,Synthesisofelectricallyconductivepolypyrrole–polystyrenecompositesusingsupercriticalcarbondioxide:II.Effectsofthedopingconditions,Eur. Polym.J.39(1)(2003)151–156.
[17] C.L.Higginbotham,J.G.L.Yons,J.E.Kennedy,13-Polymerprocessingusingsupercriticalfluids, in:S.Thomas,Y.Weimin(Eds.),AdvancesinPolymerProcessing,WoodheadPublishing,2009, pp.384–401.
[18] M.Miya,R.Iwamoto,S.Mima,FT-IRstudyofintermolecularinteractionsinpolymerblends, J.Polym.Sci.Polym.Phys.Ed.22(1984)1149–1151.
[19] J.vonSchnitzler,R.Eggers,MasstransferinpolymersinasupercriticalCO2-atmosphere,J.Supercrit. Fluids16(1)(1999)81–92.
[20] T.J.Yoon,Y.-W.Lee,Currenttheoreticalopinionsandperspectivesonthefundamentaldescription ofsupercriticalfluids,J.Supercrit.Fluids134(2018)21–27.
[21] E.Weidner,M.Petermann,K.Blatter,V.Rekowski,Manufactureofpowdercoatingsbysprayingof gas-enrichedmelts,Chem.Eng.Technol.24(5)(2001)529–533.
[22] G.Y.Friedmann,J.M.Catala,ModificationchimiquedepolymeresenmilieuCO2supercritique Greffagedegroupsisocyanate-isopropylesurunechainedepoly(ethylene-coalcoolvinylique),Eur. Polym.J.36(2000)13–20.
[23] A.Alexander,J.Ajazuddin,S.Khan,S.Saraf,S.Saraf,Poly(ethyleneglycol)-poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)basedthermosensitiveinjectablehydrogelsforbiomedicalapplications,J.Control.Release 172(3)(2013)715–729.
[24] O. Ihata,Y.Kayaki,T.Ikariya,SynthesisofThermoresponsivepolyurethanefrom2-Methylaziridine andsupercriticalcarbondioxide,Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.43(6)(2004)717–719.
[25] B.Tan,H.M.Woods,P.Licence,S.M.Howdle,A.I.Cooper,SynthesisandCO2solubilitystudiesof poly(ethercarbonate)sandpoly(etherester)sproducedbystepgrowthpolymerization, Macromolecules38(5)(2005)1691–1698.
[26] S.M.Gross,G.W.Roberts,D.J.Kiserow,J.M.DeSimone,Crystallizationandsolid-statepolymerizationofpoly(bisphenolacarbonate)facilitatedbysupercriticalCO2,Macromolecules33(1)(2000) 40–45.
[27] P.Chambon,E.Cloutet,H.Cramail,T.Tassaing,M.Besnard,Synthesisofcore-shellpolyurethane–polydimethylsiloxaneparticlesincyclohexaneandinsupercriticalcarbondioxideusedasdispersant media:acomparativeinvestigation,Polymer46(4)(2005)1057–1066.
[28] P.B.Zetterlund,F.Aldabbagh,M.Okubo,Controlled/livingheterogeneousradicalpolymerizationin supercriticalcarbondioxide,J.Polym.Sci.APolym.Chem.47(15)(2009)3711–3728.
[29] B.Grignard,C.Calberg,C.Jer^ ome,W.Wang,S.Howdle,C.Detrembleur,SupportedATRPof fluorinatedmethacrylatesinsupercriticalcarbondioxide:preparationofscCO2 solublepolymerswith lowcatalyticresidues,Chem.Commun.(44)(2008)5803–5805.
[30] A.Alexander,M.Ajazuddin,M.Swarna,M.Sharma,D.Tripathi,Polymersandpermeation enhancers:Specializedcomponentsofmucoadhesives,StamfordJ.Pharmaceut.Sci.4(1)(2011)91–95.
[31] B.Grignard,C.Calberg,C.Jerome,C.Detrembleur,“One-pot”dispersionATRPandalkyne-azide Huisgen’s1,3-dipolarcycloadditioninsupercriticalcarbondioxide:towardstheformationoffunctionalmicrospheres,J.Supercrit.Fluids53(1)(2010)151–155.
[32] A.Alexander,J.Ajazuddin,S.Khan,S.Saraf,S.Saraf,Formulationandevaluationofchitosan-based long-actinginjectablehydrogelforPEGylatedmelphalanconjugate,J.Pharm.Pharmacol.66(9)(2014) 1240–1250.
[33] J.M.DeSimone,Z.Guan,C.S.Elsbernd,SynthesisofFluoropolymersinsupercriticalcarbondioxide, Science(NewYork,N.Y.)257(5072)(1992)945–947.
[34] C.D.Wood,A.I.Cooper,J.M.DeSimone,Greensynthesisofpolymersusingsupercriticalcarbon dioxide,Curr.Opin.SolidStateMater.Sci.8(5)(2004)325–331.
[35] A.Alexander,J.Ajazuddin,S.Khan,S.Saraf,S.Saraf,Polyethyleneglycol(PEG)-poly(Nisopropylacrylamide)(PNIPAAm)basedthermosensitiveinjectablehydrogelsforbiomedicalapplications,Eur.J.Pharm.Biopharm.88(3)(2014)575–585.
[36] K.Takahashi,Polymeranalysisbysupercriticalfluidchromatography,J.Biosci.Bioeng.116(2)(2013) 133–140.
[37] A.I.Cooper,Polymersynthesisandprocessingusingsupercriticalcarbondioxide,J.Mater.Chem. 10(2)(2000)207–234.
[38] A.Alexander,S.Saraf,S.Saraf,UnderstandingtheroleofPoloxamer407basedThermoreversible insitugellinghydrogelfordeliveryofPEGylatedMelphalanconjugate,Curr.DrugDeliv.13(4) (2016)621–630.
[39] T.J.Romack,J.M.DeSimone,T.A.Treat,SynthesisofTetrafluoroethylene-based,nonaqueousFluoropolymersinsupercriticalcarbondioxide,Macromolecules28(24)(1995)8429–8431.
[40] L.Cao,L.Chen,W.Lai,PrecipitationcopolymerizationofN-isopropylacrylamideandacrylicacidin supercriticalcarbondioxide,J.Polym.Sci.APolym.Chem.45(5)(2007)955–962.
[41] X.-H.Wang,L.-Q.Cao,L.-J.Zhang,J.-D.Wang,Precipitationpolymerizationof2-hydroxyethyl methacrylateinsupercriticalcarbondioxide,Polym.Adv.Technol.23(3)(2012)529–533.
[42] J.Liu,H.Tai,S.M.Howdle,PrecipitationpolymerisationofvinylidenefluorideinsupercriticalCO2 andreal-timecalorimetricmonitoring,Polymer46(5)(2005)1467–1472.
[43] C.Jerome,P.Lecomte,Recentadvancesinthesynthesisofaliphaticpolyestersbyring-openingpolymerization,Adv.DrugDeliv.Rev.60(9)(2008)1056–1076.
[44] A.-F.Mingotaud,F.Cansell,N.Gilbert,A.Soum,Cationicandanionicring-openingpolymerization insupercriticalCO2.Preliminaryresults,Polym.J.31(1999)406.
[45] E.J.Park,A.P.Richez,N.A.Birkin,H.Lee,N.Arrowsmith,K.J.Thurecht,S.M.Howdle,Newvinyl estercopolymersasstabilisersfordispersionpolymerisationinscCO2,Polymer52(24)(2011) 5403–5409.
[46] H.Lee,E.Terry,M.Zong,N.Arrowsmith,S.Perrier,K.J.Thurecht,S.M.Howdle,SuccessfuldispersionpolymerizationinsupercriticalCO2usingPolyvinylalkylatehydrocarbonsurfactantssynthesizedandanchoredviaRAFT,J.Am.Chem.Soc.130(37)(2008)12242–12243.
[47] Y.Wang,L.Hong,D.Tapriyal,I.C.Kim,I.-H.Paik,J.M.Crosthwaite,A.D.Hamilton,M.C.Thies, E.J.Beckman,R.M.Enick,J.K.Johnson,DesignandevaluationofNonfluorousCO2-solubleoligomersandpolymers,J.Phys.Chem.B113(45)(2009)14971–14980.
[48] E.Girard,T.Tassaing,S.Camy,J.-S.Condoret,J.-D.Marty,M.Destarac,Enhancementofpoly(vinyl ester)solubilityinsupercriticalCO2bypartialfluorination:Thekeyroleofpolymer–polymerinteractions,J.Am.Chem.Soc.134(29)(2012)11920–11923.
[49] M.Altarsha,F.Ingrosso,M.F.Ruiz-Lopez,AnewglimpseintotheCO2-Philicityofcarbonylcompounds,ChemPhysChem13(14)(2012)3397–3403.
[50] B.Tan,J.-Y.Lee,A.I.Cooper,IonichydrocarbonsurfactantsforemulsificationanddispersionpolymerizationinsupercriticalCO2,Macromolecules39(22)(2006)7471–7473.
[51] W.Ye,J.M.DeSimone,EmulsionpolymerizationofN-Ethylacrylamideinsupercriticalcarbondioxide,Macromolecules38(6)(2005)2180–2190.
[52] W.Ye,J.M.DeSimone,Synthesisofsugar-containingAmphiphilesforliquidandsupercriticalcarbon dioxide,Ind.Eng.Chem.Res.39(12)(2000)4564–4566.
[53] Y.A.Hussain,T.Liu,G.W.Roberts,Synthesisofcross-linked,partiallyneutralizedpoly(acrylicacid) bysuspensionpolymerizationinsupercriticalcarbondioxide,Ind.Eng.Chem.Res.51(35)(2012) 11401–11408.
[54] P.O’Connor,R.Yang,W.M.Carroll,Y.Rochev,F.Aldabbagh,Facilesynthesisofthermoresponsive blockcopolymersofN-isopropylacrylamideusingheterogeneouscontrolled/livingnitroxidemediatedpolymerizationsinsupercriticalcarbondioxide,Eur.Polym.J.48(7)(2012)1279–1288.
[55] S.G.Kazarian,M.F.Vincent,F.V.Bright,C.L.Liotta,C.A.Eckert,Specificintermolecularinteraction ofcarbondioxidewithpolymers,J.Am.Chem.Soc.118(7)(1996)1729–1736.
[56] S.G.Kazarian,K.L.Chan,Micro-andmacro-attenuatedtotalreflectionFouriertransforminfrared spectroscopicimaging,PlenaryLectureatthe5thInternationalConferenceonAdvancedVibrational Spectroscopy,2009,Melbourne,Australia,Appl.Spectrosc.64(5)(2010)135a–152a.
[57] E.S.Sanders,S.M.Jordan,R.Subramanian,Penetrant-plasticizedpermeationinpolymethylmethacrylate,J.Membr.Sci.74(1)(1992)29–36.
[58] J.-S.Wang,Y.Naito,Y.Kamiya,Effectofpenetrant-inducedisothermalglasstransitiononsorption, dilation,anddiffusionbehaviorofpolybenzylmethacrylate/CO2,JPolymSciB34(12)(1996) 2027–2033.
[59] R.G.Wissinger,M.E.Paulaitis,Glasstransitionsinpolymer/CO2mixturesatelevatedpressures, JPolymSciB29(5)(1991)631–633.
[60] Y.Han,H.Zheng,X.Jing,L.Zheng,Swellingbehaviorofpolyesterinsupercriticalcarbondioxide, J.CO2Utiliz.26(2018)45–51.
[61] L.J.Gerhardt,C.W.Manke,E.Gulari,Rheologyofpolydimethylsiloxaneswollenwithsupercritical carbondioxide,JPolymSciB35(3)(1997)523–534.
[62] Y.X.J.Ong,L.Y.Lee,P.Davoodi,C.-H.Wang,Productionofdrug-releasingbiodegradablemicroporousscaffoldusingatwo-stepmicro-encapsulation/supercriticalfoamingprocess,J.Supercrit.Fluids 133(2018)263–269.
[63] S.G.Kazarian,ApplicationsofFTIRspectroscopytosupercriticalfluiddrying,extractionandimpregnation,Appl.Spectrosc.Rev.32(4)(1997)301–348.