https://ebookmass.com/product/evidence-based-validation-of-
Instant digital products (PDF, ePub, MOBI) ready for you
Download now and discover formats that fit your needs...
Quality Control and Evaluation of Herbal Drugs: Evaluating Natural Products and Traditional Medicine Pulok K. Mukherjee Dr.
https://ebookmass.com/product/quality-control-and-evaluation-ofherbal-drugs-evaluating-natural-products-and-traditional-medicinepulok-k-mukherjee-dr/ ebookmass.com
Validation of Food Preservation Processes Based on Novel Technologies Tatiana Koutchma
https://ebookmass.com/product/validation-of-food-preservationprocesses-based-on-novel-technologies-tatiana-koutchma/
ebookmass.com
Validation of Food Preservation Processes Based on Novel Technologies Tatiana Koutchma
https://ebookmass.com/product/validation-of-food-preservationprocesses-based-on-novel-technologies-tatiana-koutchma-2/ ebookmass.com
I am the Rage Martina Mcgowan
https://ebookmass.com/product/i-am-the-rage-martina-mcgowan/
ebookmass.com
Intended Consequences Hemant Taneja
https://ebookmass.com/product/intended-consequences-hemant-taneja/
ebookmass.com
Changing Hayden: An Age Gap Second Chance Friends To Lovers Steamy MM Romance (Uptown Heat Book 1) Zack Wish
https://ebookmass.com/product/changing-hayden-an-age-gap-secondchance-friends-to-lovers-steamy-mm-romance-uptown-heat-book-1-zackwish/ ebookmass.com
Networked Collective Actions: The Making of an Impeachment Hyunjin Seo
https://ebookmass.com/product/networked-collective-actions-the-makingof-an-impeachment-hyunjin-seo/
ebookmass.com
Consciousness and Quantum Mechanics 1st Edition Shan Gao (Editor)
https://ebookmass.com/product/consciousness-and-quantum-mechanics-1stedition-shan-gao-editor/
ebookmass.com
Plastic Surgery-Craniofacial, Head and Neck SurgeryPediatric Plastic Surgery 4th Edition Geoffrey C. Gurtner
https://ebookmass.com/product/plastic-surgery-craniofacial-head-andneck-surgery-pediatric-plastic-surgery-4th-edition-geoffrey-c-gurtner/
ebookmass.com
https://ebookmass.com/product/choreomania-dance-and-disorder-1stedition-kelina-gotman/
ebookmass.com
EVIDENCE-BASEDVALIDATIONOF HERBALMEDICINE
TranslationalResearchonBotanicals
SECONDEDITION
EVIDENCE-BASED VALIDATION OFHERBAL MEDICINE
TranslationalResearchonBotanicals
SECONDEDITION
Editedby
PROF.PULOK K.MUKHERJEE,FRSC,FASCT,FNAAS,FNASC Director,InstituteofBioresourcesandSustainableDevelopment(IBSD),DepartmentofBiotechnology,Takyelpat,Imphal,Manipur,India SchoolofNaturalProductStudies,DepartmentofPharmaceuticalTechnology,JadavpurUniversity,Kolkata,India
Elsevier
Radarweg29,POBox211,1000AEAmsterdam,Netherlands TheBoulevard,LangfordLane,Kidlington,OxfordOX51GB,UnitedKingdom 50HampshireStreet,5thFloor,Cambridge,MA02139,UnitedStates
Copyright©2022ElsevierInc.Allrightsreserved.
Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproducedortransmittedinanyformorbyanymeans,electronicor mechanical,includingphotocopying,recording,oranyinformationstorageandretrievalsystem,without permissioninwritingfromthepublisher.Detailsonhowtoseekpermission,furtherinformationaboutthe Publisher’spermissionspoliciesandourarrangementswithorganizationssuchastheCopyrightClearance CenterandtheCopyrightLicensingAgency,canbefoundatourwebsite: www.elsevier.com/permissions ThisbookandtheindividualcontributionscontainedinitareprotectedundercopyrightbythePublisher(other thanasmaybenotedherein).
Notices
Knowledgeandbestpracticeinthisfieldareconstantlychanging.Asnewresearchandexperiencebroadenour understanding,changesinresearchmethods,professionalpractices,ormedicaltreatmentmaybecome necessary.
Practitionersandresearchersmustalwaysrelyontheirownexperienceandknowledgeinevaluatingandusing anyinformation,methods,compounds,orexperimentsdescribedherein.Inusingsuchinformationormethods theyshouldbemindfuloftheirownsafetyandthesafetyofothers,includingpartiesforwhomtheyhavea professionalresponsibility.
Tothefullestextentofthelaw,neitherthePublishernortheauthors,contributors,oreditors,assumeanyliability foranyinjuryand/ordamagetopersonsorpropertyasamatterofproductsliability,negligenceorotherwise,or fromanyuseoroperationofanymethods,products,instructions,orideascontainedinthematerialherein.
ISBN:978-0-323-85542-6
ForinformationonallElsevierpublications visitourwebsiteat https://www.elsevier.com/books-and-journals
Publisher: SusanDennis
AcquisitionsEditor: CharlotteRowley
EditorialProjectManager: TimEslava
ProductionProjectManager: BharatwajVaratharajan
CoverDesigner: MatthewLimbert
TypesetbySTRAIVE,India
Contributors
SayeedAhmad BioactiveNaturalProductLaboratory, DepartmentofPharmacognosy&Phytochemistry,Schoolof PharmaceuticalEducation&Research,JamiaHamdard, NewDelhi,India
MuhammadTayyabAkhtar InstituteofIndustrial Biotechnology,GovernmentCollegeUniversity,Lahore, Pakistan
MdJahangirAlam DepartmentofBiotechnology,National InstituteofPharmaceuticalEducationandResearch(NIPER), Guwahati,Assam,India
AtharAta DepartmentofChemistry,RichardsonCollegefor theEnvironmentalandScienceComplex,TheUniversityof Winnipeg,Winnipeg,Manitoba,Canada
ShivBahadur InstituteofPharmaceuticalResearch,GLA University,Mathura,India
RajibBandyoypadhyay DepartmentofInstrumentationand ElectronicsEngineering,JadavpurUniversity,Kolkata,India
RupeshBanerjee InstituteofBioresourcesandSustainable Development,Takyelpat,Imphal,India
SanjayK.Banerjee DepartmentofBiotechnology,National InstituteofPharmaceuticalEducationandResearch(NIPER), Guwahati,Assam,India
SubhadipBanerjee SchoolofNaturalProductStudies, DepartmentofPharmaceuticalTechnology,Jadavpur University,Kolkata,WestBengal,India
KrzysztofB.Bec InstituteofAnalyticalChemistryand Radiochemistry,CentrumforChemistryandBiomedicine, UniversityofInnsbruck,Innsbruck,Austria
SayantanBera J.B.RoyStateAyurvedicMedicalCollege& Hospital,DepartmentofHealth&FamilyWelfare, GovernmentofWestBengal,Kolkata,India
SantanuBhadra EliLillyServicesIndiaPvt.Ltd.,Bengaluru, Karnataka,India
PardeepK.Bhardwaj InstituteofBioresourcesand SustainableDevelopment(IBSD),Departmentof Biotechnology,MinistryofScienceandTechnology, GovernmentofIndia,Takyelpat,Imphal,Manipur,India
SayanBiswas InstituteofBioresourcesandSustainable Development(IBSD),DepartmentofBiotechnology,Ministry ofScienceandTechnology,GovernmentofIndia,Takyelpat, Imphal,Manipur,India
AnthonyBooker CentreforPharmacognosyand Phytotherapy/ResearchClusterBiodiversityand Medicines,UCLSchoolofPharmacy;ResearchCentrefor OptimalHealth,SchoolofLifeSciences,Universityof Westminster,London,UnitedKingdom
RainerW.Bussmann InstituteofBotany,Departmentof Ethnobotany,IliaStateUniversity,Tbilisi,Georgia
EnginCelep FacultyofPharmacy,Departmentof PharmacognosyandPhytotherapy,YeditepeUniversity, Istanbul,Turkey
HluphekaP.Chabalala IKSBasedTechnologyInnovations, DepartmentofScienceandInnovation,Pretoria, SouthAfrica
JoydebChanda InstituteofBioresourcesandSustainable Development,Takyelpat,Imphal,Manipur,India
RawiwanCharoensup MedicinalPlantsInnovationCenterof MaeFahLuangUniversity;SchoolofIntegrativeMedicine, MaeFahLuangUniversity,ChiangRai,Thailand
DebprasadChattopadhyay ICMR-NationalInstituteof CholeraandEntericDiseasesVirusResearchLaboratory,I.D. &B.G.Hospital,Kolkata,WestBengal;ICMR-National InstituteofTraditionalMedicine(ICMR-NITM),Belagavi, Karnataka,India
SushilK.Chaudhary InstituteofBioresourcesand SustainableDevelopment(IBSD),Departmentof Biotechnology,MinistryofScienceandTechnology, GovernmentofIndia,Takyelpat,Imphal,Manipur,India
AnaL.Chávez-Hernández DIFACQUIMResearchGroup, DepartmentofPharmacy,SchoolofChemistry,National AutonomousUniversityofMexico,MexicoCity,Mexico
Wai-IChik SchoolofChineseMedicine,HongKongBaptist University,HongKongSAR,China
IrenaMariaChoma DepartmentofChromatography,Faculty ofChemistry,MariaCurie-SkłodowskaUniversity,Lublin, Poland
SørenBrøggerChristensen DepartmentofDrugDesignand Pharmacology,UniversityofCopenhagen,Copenhagen Ø, Denmark
GeoffreyA.Cordell NaturalProductsInc.,Evanston,IL; DepartmentofPharmaceutics,CollegeofPharmacy, UniversityofFlorida,Gainesville,FL,UnitedStates
Sharna-kayDaley NaturalProductsInc.,Evanston,IL, UnitedStates
BhaskarDas SchoolofNaturalProductStudies,Department ofPharmaceuticalTechnology,JadavpurUniversity,Kolkata, WestBengal,India
JaydeepDas IndianInstituteofTechnology,Bombay, India
BarunDasGupta SchoolofNaturalProductStudies, DepartmentofPharmaceuticalTechnology,Jadavpur University,Kolkata,WestBengal,India
BarshaDassarma DepartmentofPharmacology,Schoolof Medicine,FacultyofHealthSciences,UniversityoftheFree State,Bloemfontein,SouthAfrica
SudarshanaGhoshDastidar DepartmentofInstrumentation andElectronicsEngineering,JadavpurUniversity,Kolkata, India
HugoJ.deBoer NaturalHistoryMuseum,UniversityofOslo, Oslo,Norway
IndiraDevi InstituteofBioresourcesandSustainable Development,Takyelpat,Imphal,India
ThidaratDuangyod MedicinalPlantsInnovationCenterof MaeFahLuangUniversity;SchoolofIntegrativeMedicine, MaeFahLuangUniversity,ChiangRai,Thailand
ThomasEfferth DepartmentofPharmaceuticalBiology, InstituteofPharmaceuticalandBiomedicalSciences, JohannesGutenbergUniversity,Mainz,Germany
ElenaV.Flisyuk Saint-PetersburgStateChemical PharmaceuticalUniversity,Saint-Petersburg,Russia
E.AlexisFlores-Padilla DIFACQUIMResearchGroup, DepartmentofPharmacy,SchoolofChemistry,National AutonomousUniversityofMexico,MexicoCity,Mexico
DilipGhosh Nutriconnect,Sydney,NSW,Australia
ElviraGille NationalInstituteofResearchandDevelopment forBiologicalSciencesBucuresti/StejarulBiologicalResearch Centre,PiatraNeamt,Romania
L.Gori UnitofEmergencyMedicine,USLCentroToscana, SanGiuseppeHospital,Empoli,Italy
JustynaGrabska InstituteofAnalyticalChemistryand Radiochemistry,CentrumforChemistryandBiomedicine, UniversityofInnsbruck,Innsbruck,Austria
De-anGuo ShanghaiResearchCenterforModernizationof TraditionalChineseMedicine,NationalEngineering LaboratoryforTCMStandardizationTechnology,Shanghai InstituteofMateriaMedica,ChineseAcademyofSciences, Shanghai,China
ArunGupta AyuSwasthPvtLtd.,Faridabad,India
PallabKantiHaldar SchoolofNaturalProductStudies, DepartmentofPharmaceuticalTechnology,Jadavpur University,Kolkata,WestBengal,India
RanjitK.Harwansh InstituteofPharmaceuticalResearch, GLAUniversity,Mathura,India
MichaelHeinrich CentreforPharmacognosyand Phytotherapy/ResearchClusterBiodiversityandMedicines, UCLSchoolofPharmacy,London,UnitedKingdom
PaulHolloway DepartmentofBiology,RichardsonCollege fortheEnvironmentalandScienceComplex,TheUniversity ofWinnipeg,Winnipeg,Manitoba,Canada
ChristianW.Huck InstituteofAnalyticalChemistryand Radiochemistry,CentrumforChemistryandBiomedicine, UniversityofInnsbruck,Innsbruck,Austria
BruceHugman WriterandCommunicationsSpecialist, Oxford,UnitedKingdom
MuhammadJahangir DepartmentofFoodScience& Technology,UniversityofHaripur,KhyberPakhtunkhwa, Pakistan
DeborahJohnston LondonSouthBankUniversity(LSBU), London,UnitedKingdom
AmitKar InstituteofBioresourcesandSustainable Development(IBSD),DepartmentofBiotechnology,Ministry ofScienceandTechnology,GovernmentofIndia,Takyelpat, Imphal,Manipur,India
C.K.Katiyar EmamiLtd.,Kolkata,India
WernerKnoss FederalInstituteforDrugsandMedical Devices,Bonn,Germany
PulokKumarMukherjee InstituteofBioresourcesand SustainableDevelopment(IBSD),Departmentof Biotechnology,MinistryofScienceandTechnology, GovernmentofIndia,Takyelpat,Imphal,Manipur;Schoolof NaturalProductStudies,DepartmentofPharmaceutical Technology,JadavpurUniversity,Kolkata,WestBengal, India
TemitopeO.Lawal DepartmentofPharmacyPractice, CollegeofPharmacy,WHOCollaboratingCentrefor TraditionalMedicine,UniversityofIllinoisatChicago, Chicago,IL,UnitedStates;Departmentof PharmaceuticalMicrobiology,UniversityofIbadan, Ibadan,Nigeria
IrinaMacovei FacultyofPharmacy,GrigoreT.Popa UniversityofMedicineandPharmacy,Iasi,Romania
GailB.Mahady ClinicalPharmacognosyLaboratories, DepartmentofPharmacyPractice,CollegeofPharmacy, PAHO/WHOCollaboratingCentreforTraditional Medicine,UniversityofIllinoisatChicago,Chicago,IL, UnitedStates
AnanyaDasMahapatra ICMR-National InstituteofCholera andEntericDiseasesVirusResearchLaboratory,I.D.& B.G.Hospital,Kolkata,WestBengal,India
KalyanMajumdar DepartmentofInstrumentationand ElectronicsEngineering,JadavpurUniversity,Kolkata, India
MotlalepulaGilbertMatsabisa Departmentof Pharmacology,SchoolofMedicine,FacultyofHealth Sciences,UniversityoftheFreeState,Bloemfontein,South Africa
SubirK.Maulik IndianCouncilofMedicalResearch, MinistryofHealth,NewDelhi,India
JoseL.Medina-Franco DIFACQUIMResearchGroup, DepartmentofPharmacy,SchoolofChemistry,National AutonomousUniversityofMexico,MexicoCity,Mexico
F.Menichetti UnitofCardiology,USLCentroToscana,San GiuseppeHospital,Empoli,Italy
IrinaYu.Mikhailovskaya Saint-PetersburgStateChemical PharmaceuticalUniversity,Saint-Petersburg,Russia
AncaMiron FacultyofPharmacy,GrigoreT.PopaUniversity ofMedicineandPharmacy,Iasi,Romania
AchintyaMitra CentralAyurvedaResearchInstitute, CCRAS,MinistryofAYUSH,GovernmentofIndia,Kolkata, India
SonaliMukherjee AYUSHWing,DepartmentofHealth& FamilyWelfare,GovernmentofWestBengal,Swasthya Bhavan,Kolkata,India
LutfunNahar LaboratoryofGrowthRegulators,Instituteof ExperimentalBotanyASCR&PalackýUniversity,Olomouc, CzechRepublic
IgorA.Narkevich Saint-PetersburgStateChemical PharmaceuticalUniversity,Saint-Petersburg,Russia
SaminaNaz DepartmentofChemistry,RichardsonCollege fortheEnvironmentalandScienceComplex,TheUniversity ofWinnipeg,Winnipeg,Manitoba,Canada
NeeleshK.Nema NutraceuticalDivision,CVJCreative Centre,SynthiteIndustriesPvt.Ltd.,Kolenchery,India
HannaNikolaichuk DepartmentofChromatography, FacultyofChemistry,MariaCurie-SkłodowskaUniversity; DepartmentofBioanalytics,FacultyofBiomedicine,Medical UniversityofLublin,Lublin,Poland
Nadire Ozenver DepartmentofPharmacognosy,Facultyof Pharmacy,HacettepeUniversity,Ankara,Turkey; DepartmentofPharmaceuticalBiology,Instituteof PharmaceuticalandBiomedicalSciences,Johannes GutenbergUniversity,Mainz,Germany
PravareePhuneerub MedicinalPlantsInnovationCenterof MaeFahLuangUniversity;SchoolofIntegrativeMedicine, MaeFahLuangUniversity,ChiangRai,Thailand
RittichaiPimpa MedicinalPlantsInnovationCenterofMae FahLuangUniversity;SchoolofIntegrativeMedicine,Mae FahLuangUniversity,ChiangRai,Thailand
OlgaN.Pozharitskaya MurmanskMarineBiologicalInstitute oftheRussianAcademyofSciences(MMBIRAS),Murmansk, Russia
CharuPundir KLEUniversity’sCollegeofPharmacy, Belagavi,Karnataka,India
XueQiao StateKeyLaboratoryofNaturalandBiomimetic Drugs,SchoolofPharmaceuticalSciences,PekingUniversity, Beijing,China
AncuțaCristinaRaclariu-Manolica NaturalHistoryMuseum, UniversityofOslo,Oslo,Norway;StejarulResearchCentrefor BiologicalSciences,NationalInstituteofResearchand DevelopmentforBiologicalSciences,PiatraNeamț,Romania
MukhlesurRahman SchoolofHealth,Sportsand Bioscience,UniversityofEastLondon,London, UnitedKingdom
NishikantRaut DepartmentofPharmacyPractice,College ofPharmacy,WHOCollaboratingCentreforTraditional Medicine,UniversityofIllinoisatChicago,Chicago,IL, UnitedStates;DepartmentofPharmaceuticalSciences, RashtrasantTukadojiMaharajNagpurUniversity,Nagpur, India
A.P.Sampieri DepartmentofRadiology,USLCentro Toscana,SanGiuseppeHospital,Empoli,Italy
SatyajitD.Sarker CentreforNaturalProducts Discovery,SchoolofPharmacyandBiomolecularSciences,
LiverpoolJohnMooresUniversity,Liverpool, UnitedKingdom
BilgeSener H.E.J.ResearchInstituteofChemistry, InternationalCenterforChemicalandBiologicalSciences, UniversityofKarachi,Karachi,Pakistan
KhozirahShaari NaturalMedicinesandProductsResearch Laboratory(NaturMeds),InstituteofBioscience,Universiti PutraMalaysia,Serdang,Selangor,Malaysia
AnamAminShami InstituteofIndustrialBiotechnology, GovernmentCollegeUniversity,Lahore,Pakistan
NanaochaSharma InstituteofBioresourcesandSustainable Development(IBSD),DepartmentofBiotechnology,Ministry ofScienceandTechnology,GovernmentofIndia,Takyelpat, Imphal,Manipur,India
AlexanderN.Shikov Saint-PetersburgStateChemical PharmaceuticalUniversity,Saint-Petersburg,Russia
DilipSing DepartmentofInstrumentationandElectronics Engineering,JadavpurUniversity,Kolkata,India
SouadSkalli FacultyofScience,MohammedVUniversityin Rabat,Morocco
Satyajit Tripathy DepartmentofPharmacology,Schoolof Medicine,FacultyofHealthSciences,UniversityoftheFree State,Bloemfontein,SouthAfrica
ShravanKumarUppulapu DepartmentofBiotechnology, NationalInstituteofPharmaceuticalEducationandResearch (NIPER),Guwahati,Assam,India
RoyUpton AmericanHerbalPharmacopoeia,ScottsValley, CA,UnitedStates
S.Vanni UnitofEmergencyMedicine,USLCentroToscana, SanGiuseppeHospital,Empoli,Italy
Prof.Dr.RobertVerpoorte NaturalProductsLaboratory, IBL,LeidenUniversity,Leiden,TheNetherlands
Jia-boWang SchoolofTraditionalChineseMedicine,Capital MedicalUniversity,Beijing,China
MinYe StateKeyLaboratoryofNaturalandBiomimetic Drugs,SchoolofPharmaceuticalSciences,PekingUniversity, Beijing,China
ErdemYesilada FacultyofPharmacy,Departmentof PharmacognosyandPhytotherapy,YeditepeUniversity, Istanbul,Turkey
Hong-JieZhang SchoolofChineseMedicine,HongKong BaptistUniversity,HongKongSAR,China
Chen-LiangZhao SchoolofChineseMedicine,HongKong BaptistUniversity,HongKongSAR;GuizhouUniversity ofTraditionalChineseMedicine,Guiyang, China
Jia-jingZhou StateKeyLaboratoryofNaturaland BiomimeticDrugs,SchoolofPharmaceuticalSciences,Peking University,Beijing,China
Foreword
Someyearsago,Prof.Pulokaskedmetowritetheforewordforabookheeditedonthevalidationofherbal medicines.Iacceptedthatinvitation,andIwroteabriefdiscussionontheurgentneedforevidence-baseduseof medicinalplants.Now,thereisasecondeditionofthisbook,withcontributionsfromtheauthorsofthefirst editionplus50%morenewcontributions.Also,thistime,partofitisonstudiesaimedatevidence-baseduseof traditionalmedicine,andpartofitisondevelopingnovelleadsfromtraditionalmedicines.Inthepastdecade,the omicstechnologiesandsystemsbiologybecamethekeywordsforbiologicalandmedicinalresearch.Thisgave manynewinsights,forexample,theroleofthegastrointestinaltractmicrobiomeforhumanhealth,andevidence ontheactivityofanumberofmedicinalplants.
Thetoolsoftheomicstechnologiescanbeusedasadouble-edgedswordinmedicinalplantresearch. Transcriptomicsandproteomicswillhelptoidentifythetargetsofactivecompounds.Themetabolomicscanbe usedtoseewhichsignalscorrelatewithactivity.Thisinformationcanthenbeusedtoidentifythecompoundsand seeiftheycouldserveasleadsforfurtherdrugdevelopment.Themetabolomicsinformationcanalsobeusedto defineafingerprintforqualitycontrolofherbalmedicines.Theleadfindingapproachissomethingforthelong term;tofindaleadandeventuallydevelopitintoadrugisa10-to15-yearproject,withestimatedcostsbeing1–2 billioneuros.Theuseofmetabolomicsdataandtheircorrelationwiththebiologicalactivityin invivo testsare immediatelyapplicableforevidence-basedherbalmedicines.Eventually,metabolomicsdatawillbeimportantfor qualitycontrolofherbalmedicines.
Obviously,academicresearchcreatesafoundationonwhichbothnoveldrugsandtraditionalmedicinecanbe furtherdeveloped.Worldwide,somegovernmentsinvestintheresearchoftraditionalmedicine,whereasbig pharmaceuticalindustriesmovetowardthebiologicals.COVID-19showedthat,intheshortterm(withinayear), anovelvaccinecanbebroughttothemarket,whereasanovelcureortreatmentforCOVID-19willtakeat least10years.Shorterperiodswouldbepossiblewitharepurposingapproachinwhichknownregistereddrugs aretestedforotherapplications,likeCOVID-19.Inthatapproach,themajorbottlenecksofdrugdevelopment,i.e., toxicityandsafetystudies,wouldbecircumvented.Moreover,theclinicaltrialscanfullyfocusonactivity,as safetyisalreadyknownfrompreviousregistrationwiththeFDAorEMA.
Becauseofthecomplexityoftraditionalmedicines,theidentificationofthemodeofactionisnottrivial.Multitargetdependentpeffects,antagonists,agonists,synergy,prodrugs,etc.mayallplayaroleinthis.Areductionistapproach withsinglemoleculartargetsisnotthemethodofchoice,becauseofthecomplexityofplantextracts.Modelsfor activityshouldbelivingcellsororganisms.Nowadays,italsoincludesgeneticallymodifiedcellsororganisms inwhichspecificactivitiescanbeeasilymeasured.Clinicaltrials,ofcourse,beingthemostdirectapproach,but whensafetyisnotyetestablished,biologicalactivitycanbestudiedin,animalexperiments,forexample,Zebrafish (Daniorerio), Caenorhabditiselegans,and Artemiasalina.Thissequencegetsgeneticallyfurtherawayfromhumans, butthesemodelsstillshareseveralbasicbiologicalprocesses.Particularly,metabolomicsdataincombinationwith transcriptomicsandproteomicsdatawillbeveryusefultoseetheeffectsofplantextractsonthewholesystem. Finally,aftersafetyhasbeenestablishedbymetabolomics,standardizedpreparationscanbesubjectedtoclinicaltrials. Butweshouldberealistic.Thementionedmethodsarenotpanaceathatsolveallourproblemsandgiveanswersto allourquestions.Theomicstechnologiesareverypowerfulinproducinghugeamountsofdata,infact,morethanwe candealwith.Consequently,inthepastyears,majorprogressinthefieldcamefromnovelchemometricmethodsand artificialintelligence(AI)thatcananalyzelargedatasets.Oneshouldbeverycarefulindealingwiththeresultsand searchforproperwaystovalidatetheoutcomeofourexperiments.Forexample,metabolomicscanidentifyand quantifyallmoleculesinanorganismoracell.Also,largemoleculeslikeproteins,polysaccharides,RNA,and DNAcanbecharacterizedandquantified.Butwhatdoesallthesedatamean?Ifwehaveallthesedataforasingle cell,whycan’twejustputallthesecompoundstogetherinonepot,mixit,andobtainalivingcell?Ofcourse,it raisesthequestion: “Whatislife?” Itismorethanacomplexmixtureofdifferentcompounds;itisanorganized systemthatactsasascaffoldforallkindsoffunctions.Timeandspacearetheframeworkoftheseactivities.
Particularly,physicochemistryisnowneededtofindmodelsthatexplainhowallthesecompoundsareorganizedin differentcellsandcellorganelles,withcellmembranescreatingdifferentcompartmentstoseparatethevariousfunctions. Thesephilosophicalthoughtsbringmebacktothisbookandparticularlytodrugdevelopment,wherenetwork pharmacologyispresentlyusedasamodeltovisualizeallactivitiesandinteractionsofmedicinesinthehuman “ omes ”.Forallmajormedicines,thetargetshavebeenmappedand,inthenetwork,onecanseewhichtargetsare connectedonthelevelsofgenes,proteins,andmetabolites.Forallmajorailments,onecanseewhatthemajor therapeutictargetsare.Thisisveryusefultoclassifynovelcompounds:dotheyalreadyfitknownclassesordo theyhavedifferentprofilesoftargets,andthuscouldbeanovel,first-in-classdrugwithanewmodeofaction? Moreover,workingwithmedicinalplants,theeffectsofcombinationsofdifferentcompoundscanbevisualized, e.g.,synergy.
Thenetworkisbasedontherapeuticdosesofthedrugs.Inmedicinalplantresearch,manystudiesarenowbasedon thisnetwork,thoughoftenonlyinaqualitativeway.Thegeneralprocedureistofirstfindallcompoundsthathavebeen identifiedinthemedicinalplantofinterest.Thiscanbefrompreviousstudies,aswellasfromcurrentmetabolomics measurements.Thesecondstepistocollectallthedataonthebiologicalactivitiesforallthecompoundsfoundinthe firststep.Subsequently,thesedataarequalitativelyplacedinthenetwork.Basedonthisqualitativesurvey,themost likelymodeofactionoftheherbalmedicineisdeduced.Nowordaboutthelevelsoftheactivecompoundsinthe plant,nocriticalanalysisoftheusedinformation,andnoestimationoftheapproximatedoseapatientgetsofthe medicinalplantandthusoftheactivecompounds.ItislikethemindexperimentsImentionedearlier;justputtingall thedatatogetheronaqualitativebasisdoesnotmeanthatoneunderstandsthelivingsystem.Mostabundantand easy-to-isolatecompoundsfromplantshavebeentestedinavarietyofactivities,andwithoutacriticalanalysisof whatisaphysiological/pharmacologicalreasonabledose,anyplantwillhaveaprofile,alsoforourdailyfood.But theseprofilesarebasedonverylooseground.Apropervalidationofallthedataintroducedinthenetworkis needed,andthesameappliesforthefinalconclusionsfromthenetworkanalysis.
WhydoIgivetheseexamples?Asaneditor,Ialwaysfeelsadtorejectapaper,andasaresearcherIseeallthose metastudiesthatconcernmedicinalplantsandmedicines(e.g.,Cochranereviews)wherealargepartofthepublished studiesisnotconsidered,e.g.,becauseofnotfulfillingbasicrequirementsforagoodclinicaltrial.Alargepartofwhat ispublishedcannotbeusedtodrawanyconclusions.Thatmeansmuchofthepublishedworkdoesnot serveanything.Theymeanalossofprecioustimefortheauthors,aswellasforthecolleagueswhoreadthe papers.Toeventuallyhavesomeimpactasresearchersinacademiaandgovernmentalorganizations,wemustdo better.Weshouldeventuallycomeupwithnoveldrugsorevidence-basedmedicinalplants.Toproducerealevidence, weneedtofollow “goodpractices” rules.
Atthesametime,asIalsomentionedinmyforewordtothefirstedition,thereisanurgentneedforprotectingthe rightsofthedevelopmentofanevidence-basedtraditionalmedicine,justasforanynovelsinglecompoundmedicine. Thepresentpatentlawswillnotacceptthedevelopmentofanexample,traditionalantidiabeticmedicineasan innovation;consequently,whenthatevidencehasbeenobtained,anyonemayusethatinformationandproduce andmarketthemedicine.Inotherwords,thereisaneedforaneconomicincentivefordevelopingtraditionalmedicine.
Inthisbook,thestate-of-the-artresearchofmedicinalplantscanbefound.Itincludes,amongothers,goodpractices, bioassays,systemsbiology,newmethods,regulatoryinstitutions,successfulexamples,etc.IwanttocongratulateProf. PulokK.Mukherjeewiththisexcellentsecondeditionofhowtovalidatetraditionalmedicinesanddevelopnovel leads.Thisbookwillbeofgreatvaluetoteachthenextgenerationofresearchersandtoupdateourcolleaguesall overtheworldaboutthelatestdevelopmentsinmedicinalplantresearch.Forallstakeholders,thisbookisamust tohelpincreasethequalityofresearchinourfieldandtoensurethatnootherpublicationswillberejectedor uncitedbecauseofnothavingtherequiredstandards.
Prof.Dr.RobertVerpoorte NaturalProductsLaboratory,IBL,LeidenUniversity, Leiden,TheNetherlands
Preface
Herbalmedicineplaysanimmenseroleinthemanagementofhumanhealth.Whileitsusageintherapeuticsisbecoming increasinglypopular,traditionalmedicineisstillopentofascinatingrealmsofresearch.Highthroughputscreening-based developmentofsecondarymetabolitesandleadsfromnaturalproductsofferexcitingfrontiersoffutureresearch.The secondeditionofthebook Evidence-BasedValidationofHerbalMedicines bringstogethercurrentthinkingandpractices intheareasofvalidationandevaluationofnaturalproducts.Themainaimofthebookistodescribedifferent approachesandtechniquesforevaluatingthequality,safety,andefficacyofherbalmedicineincludingthemethodsto assesstheactivityofherbalmedicine.Consideringtheculminationoftraditionalandmodernusageofherbal medicine,thisbookhighlightsthetrendsinvalidationandvalueadditionofherbalmedicinewithdifferentscientific approachesusedintherapeutics.
Developmentofnaturalproductsrequiresaconfluenceofmoderntechniquesandintegratedapproachesinvarious fieldsofscienceandtechnology.Thisbookisanefforttobringtogethertheviews,expertise,andexperienceofscientific expertsinthefieldofmedicinalplantresearchanddevelopmentwiththeaimtoshowwhatisexpectedandrequiredfor theevidence-basedvalidationofmedicinalplants.Itcontainsallaspectsofevaluationanddevelopmentofmedicines fromplantsources,includingtheircultivation,collection,phytochemicalandphyto-pharmacologicalevaluation, andtherapeuticpotential.Thus,itwillprovidecurrentcutting-edgescientificresearchonnaturalremedies, discussingseveralaspectsofnaturalproductstoassesstheiractivityandunderlyingmechanismsofaction,witha viewtoimprovestandardsusedindifferentsystemsofmedicine.Emphasisisplacedondescribingthefullrangeof evidence-basedanalyticalandbioanalyticaltechniquesusedtocharacterizenaturalproducts,including omictechnologies,phytochemicalanalysis,hyphenatedtechniques,andmanymore.
Theeditedvolumeprovidesstate-of-the-artreviewsfromresearchersaroundtheworldonvariousaspectsfor evaluationofherbalmedicineandwillhelpresearchersknowabouttheirvalidationtoexploittraditional medicines(TMs)fordrugdiscoveryanddevelopment.Itwillbeaveryusefulpublication,whichwillnotonly serveasahandytoolforstudentsandresearchersinthisareabutwillalsoprovidethemostrecentmethodologies developedforevidence-basedvalidation,andphytochemicalandpharmacologicalevaluationofherbaldrugsin allaspectsleadingtothetranslationalapproaches.Withemerginginterest,thisvolumewillencouragecontinuing effortstounderstandTM-inspireddrugdevelopmentaswellastherolesofTMinglobalhealthcareatlarge.This bookwillimprovealevelofunderstandingofvariousaspectsonevaluationofnaturalproductsandprovidea comprehensivevalidationofherbalmedicine,sothattheycanbeusedwithgreaterconfidence,raisinga scientificallysoundevidencebaserelatingtodifferentaspectsofthetranslationalresearchonbotanicals.
Thisbookismeantforaglobalreadership,aimedatprovidingastructuredapproachtotheevidence-based evaluationofherbsandherb-derivedproducts.Itwillactasanessentialreferenceforanyonewhoseprofessional lifeimpingesontheuseofnaturalresourcesforthoseinvolvedinthefieldsofherbalmedicine,traditionalremedies, pharmaceuticalsciences,andnaturalproductresearch.
Prof.PulokK.Mukherjee InstituteofBioresourcesandSustainableDevelopment (IBSD),DepartmentofBiotechnology, Takyelpat,Imphal,Manipur,India SchoolofNaturalProductStudies, DepartmentofPharmaceuticalTechnology, JadavpurUniversity,Kolkata,India
Acknowledgments
Theenormousgrowthofherbalmedicinalproductsworldwidehasbeenoneofthemostinterestingaspectsof healthcare.Harmonizationofthedifferentfacetsofdevelopmentofherbalmedicine includingquality,safety, efficacy,validation,andregulation isbestpossiblethroughinternationalcoordination.
Theintentionofthisbookistodescribeandassessvariousapproachesforevidence-basedvalidationofherbal medicine,especiallytranslationalresearchonBotanicals,whichhavebeendescribedindifferentchaptersofthis editedvolumebyeminentscientistsandtechnologistsfromdifferentcountries.Iwouldliketoexpressmygratitude toallofthemfortheirvaluablecontributions.Itwillprovidecurrentcutting-edgescientificresearchonnatural remediesleadingtotranslationalcomponentsofnaturalremedies;anessentialreadforeveryoneinterestedin evidence-basedvalidationofnaturalresources.
IexpressmyheartfeltthankstoProf.RobertVerpoorte,Leiden,theNetherlands,forhissupportand encouragementforallmyworkthroughoutandparticularlyforwritingtheForewordforthisbook.
Itwouldnothavebeenpossibletocompletethisworkwithouttheactivehelpfrommyresearchgroup.Igratefully acknowledgethehelpandsupportrenderedbyDr.AmitKar,Dr.SushilChaudhury,Dr.PallabK.Haldar, Dr.NanaochaSharma,Dr.PardeepBhardwaj,Mr.SubhadipBanerjee,Mr.BhaskarDas,Dr.JoydebChanda, Mr.PradipDebnath,Mrs.SehaSingha,Dr.SayanBiswas,Mr.BarunDasgupta,Mr.RupeshBanerjee,Ms.Akanksha Sharma,Mr.DilipSingh,Mr.ShibuNarayanJana,Mr.SandipanJana,Ms.SuparnaGhosh,andothersfortheir activehelp.
IextremelyappreciatetheinteresttakenbyElsevier,UnitedStates,forproducingthiseditedvolume.Igratefully acknowledgethecooperationandsupportreceivedfromMs.KathrynEryilmaz,Ms.VeronicaSantos,Ms.Swapna Praveen,Mr.TimEslava,andMr.BharatwajVaratharajanfromElsevierinbringingoutthisbook.
Myfather,ShriHariharMukherjee,inspiredmealotinallmyworks,amanIintenselyadmire,andhecontinuesto liveinmyheart.Iamthankfultomyfamily,mymotherMrs.SudhaRaniMukherjee;mybrothersAloke,Tilok,and AmitMukherjee;mywifeDr.KakaliMukherjee;daughterMaria;andsonManishforallthesupportandlovethey givetomealways;youarethereasonbehindmyeverysuccessfulstep.
Prof.PulokK.Mukherjee InstituteofBioresourcesandSustainableDevelopment (IBSD),DepartmentofBiotechnology,Takyelpat, Imphal,Manipur,India SchoolofNaturalProductStudies, DepartmentofPharmaceuticalTechnology, JadavpurUniversity,Kolkata,India
1
Evidence-basedvalidationofherbalmedicine:
Translationalapproach
PulokKumarMukherjeea,b,SubhadipBanerjeeb,BarunDasGuptab, andAmitKara
aInstituteofBioresourcesandSustainableDevelopment(IBSD),DepartmentofBiotechnology,MinistryofScienceand Technology,GovernmentofIndia,Takyelpat,Imphal,Manipur,India bSchoolofNaturalProductStudies,Departmentof PharmaceuticalTechnology,JadavpurUniversity,Kolkata,WestBengal,India
Abbreviations
WHO WorldHealthOrganization
AYUSH Ayurveda,Yoga,Unani,SiddhaandHomeopathy
TM Traditionalmedicine
IUPAC InternationalUnionofPureandAppliedChemistry
USFDA UnitedStatesFoodandDrugAdministration
GACP GoodAgriculturalandCollectionPractices
CDSCO CentralDrugsStandardControlOrganization CYP450 CytochromeP450
EMEA EuropeanMedicinesAgency
T&CM TraditionalandComplementaryMedicine
1Healthcarethroughherbalmedicine
Herbalmedicinesattracttheinterestofbothpatients andscientists,inallaspectsofdrugdevelopmentfromnaturalproductsandalsoforvalidationoftraditionalmedicine(TM).SeveraldevelopingcountriesrelyonTM becauseoftheiraccessibilityandaffordabilityandscientistsallovertheworldconsiderherbalspeciesasasource fornewchemicalentitiesandusedthemtoisolatecompounds,suchasdigoxin,morphine,taxol,atropineand vinblastine [1].TMhasproventobeaboonfortheimpecuniouswhoaredevoidofthemoderntreatmentfacilities [2].Herbalmedicineshaveanimportantpositioninhealth caresystemsworldwide,theircurrentassessmentand qualitycontrolareamajorbottleneck.Manyadverse eventsofherbalmedicinescanbeattributedtothepoor qualityoftherawmaterialsorthefinishedproducts.Qualityissuesofherbalmedicinescanbeclassifiedintotwocategories,externalandinternal.Externalissuesincludetoxic metals,pesticidesresidues,microbes,adulterationand misidentificationofmedicinalplants.Theinternalissues
affectingthequalityofherbalmedicinesarecomplexity andnon-uniformityoftheingredients.TheIndiansubcontinentisalwaysknownforitsmonumentalwidespreadof medicinallyactiveplants.Duetolargerforestareascoveringmostofthevillagestheadaptivenatureofhumans havehelpedcertainhealthcarepractitionerstochannel thepotentialofnaturalresourcesintopotentmedications [2].TheconceptofAyurvedaisthelivingproofofexperiencebasedtreatmentofdifferentailmentsthroughTM. ManyAyurvedictextsandbookslikeCharakSamhita, SushrutSamhita,AshtangaHridaya,MadhavaNidana, BhavaPrakashaandmanymorehavealwaysboostednaturalproduct-basedhealthcareresearch [3]
Throughtheuseofmodernanalyticalmethodsand pharmaceuticaltechniques,previouslyunsolvedinternal issueshavebecomesolvable [4].Theincreasingsearch fortherapeuticagentsderivedfromplantspeciesisjustifiedbytheemergenceofdiseases.Medicinalplantsserve asmostvaluablesourceforcuringmanydiseases.Herbal medicinesincludeherbalextracts,herbaldrugpreparationsandherbaldrugs.Herbaldrugsareunprocessedpart ofplantsorwholeplants [5].Herbsincludecrudeplant materialsuchasleaves,flowers,fruit,seed,stems,wood, bark,roots,rhizomesorotherplantparts,whichmaybe entire,fragmentedorpowdered.Herbalpreparations includecomminutedorpowderedmaterialsorextracts, tincturesandfattyoilsofherbalmaterials,whichmay beproducedbyextraction,fractionation,purification,concentrationorotherphysicalorbiologicalprocesses [6].
Modernallopathicmedicinehasdevelopedfrom ancientmedicine,anditislikelythatmanyimportant newremedieswasdiscoveredandcommercialized
followingtheleadsprovidedbytraditionalknowledge andexperiences.Thestudyofthesetraditionsnotonly providesaninsightintohowthefieldhasdeveloped butitisalsoafascinatingexampleofourabilityto developadiversityofculturalpractices [7].Theadministeringofapurechemicaloraplantextractcontainingthe samechemicalentityisessentiallydifferent.Thedifferenceismainlyduetothecomplexityofaplantextractthat introducesmanyvariablestoconventionalphytomedicinalresearch,whichcouldpossiblycontributeto chemicalcomplexityandbioactivity.Onadministration ofplantmaterialof Artemisiaannua versuspuredrug e.g.artemisininshowedthatthebioavailabilityfrom theleaveswas45timesmorethanthatofthepuredrug [8].Thusthecomplexityoftheplantextractcouldhave contributedtotheincreasedbioavailabilityandthus thebioactivity.Shiftintheparadigmfrom “singlecompoundsingletarget” to “singlecompoundmultiple targets” and “multiplecompoundssingletarget” the modernresearchersareabletodevelopnovelandtherapeuticallyactivedrugs [3].Agenuineinterestonvarious traditionalpracticesnowexistsamongpractitionersof modernmedicineandnumbersofpractitionersoftraditional,indigenousoralternativesystemsarebeginning
toacceptandusesomeofthemoderntechnologies. Propermethodologiesfortheresearchanddevelopment, manufacturingandqualitycontroloftheformulationsin TMandinvestigationsofthetherapeuticpotentialsof plantsusedinthosesystemswithsupportofscientific methodsmayhelptousethemwithmaximumpossible efficacy [9,11]
2Integratedapproachesfordevelopmentof herbalmedicine
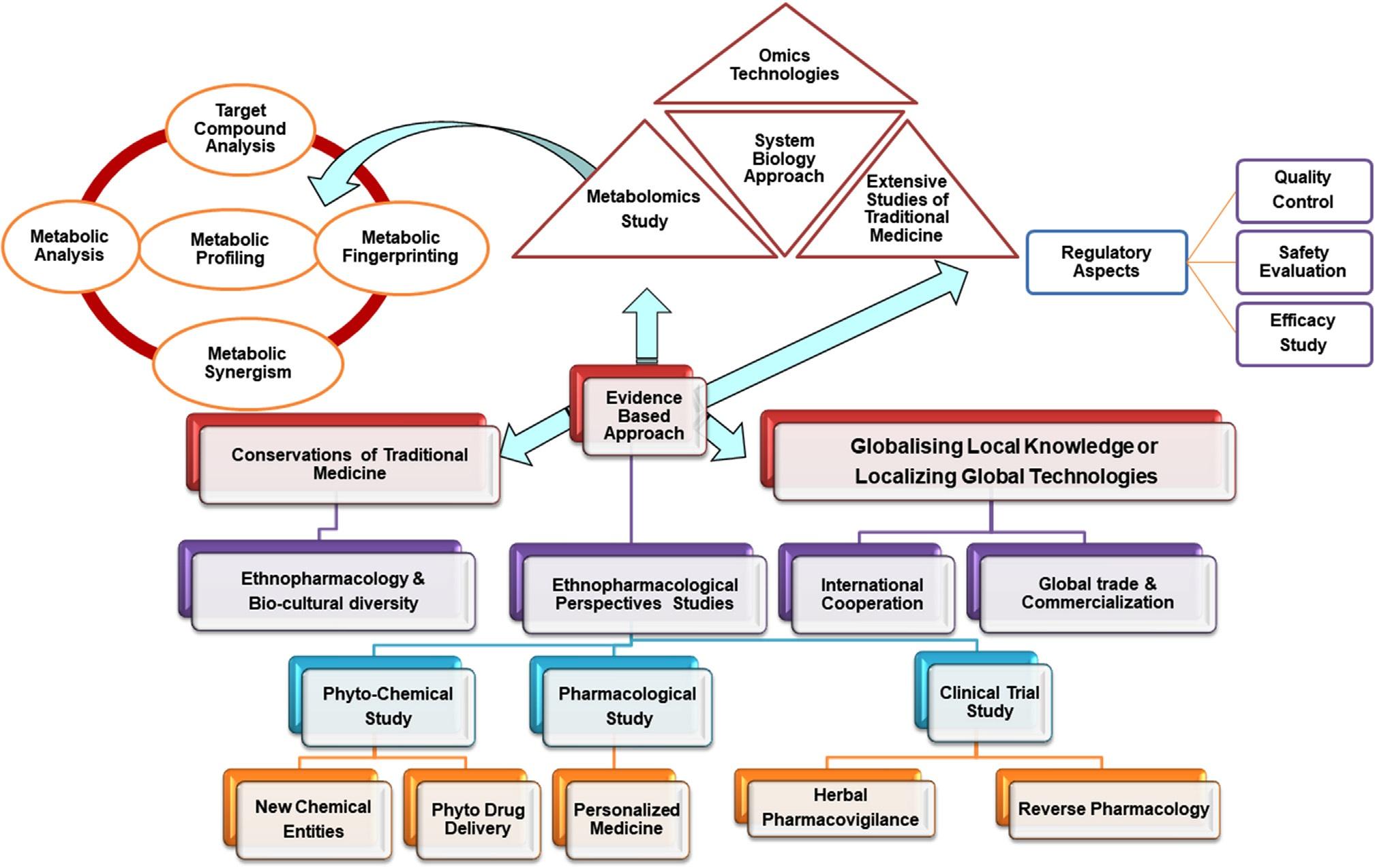
Theinternationaltradeinherbalmedicinehasattracted mostofthepharmaceuticalcompanies,includingthemultinationals.Untilafewyearsago,onlysmallcompanies hadinterestinthemarketingofherbalmedicines.Currently,severallargemultinationalcompaniesareinterestedincommercializingherbaldrugs [9].Theworld marketforherbalmedicine,includingherbalproducts andrawmaterials,hasbeenestimatedtohaveanannual growthrateupto15%.Severalintegratedapproachesin herbalresearchforpromotionanddevelopmentofnatural productsareshownin Fig.1
FIG.1
2.1Opportunitiesandchallengesinherbal medicine
Withtheglobalincreaseinthedemandformedicinal plantorplant-derivedmedicines,thereisacallforensuringthequalityandsafetyofherbaldrugsusingseveral modernanalyticaltechniques.Chemicalconstituentsin herbalmedicinemayvarydependingonharvestseasons, plantorigins,dryingprocessesandotherrelatedfactors. Thus,itseemstobenecessarytodeterminemostofthe phytochemicalconstituentsofherbalproductsinorder toensurethereliabilityandrepeatabilityofpharmacologicalandclinicalresearch,tounderstandtheirbioactivities andpossiblesideeffectsofactivecompoundsandto enhancethequalityoftheherbalproducts [10].TheLack ofchemicalmarkersremainsamajorproblemforthe qualitycontrolofherbalmedicines.Inmanycases,we donothavesufficientchemicalandpharmacologicaldata ofchemicalmarkers.Further,therearemanytechnical challengesintheproductionofmarkers.Forexample, temperature,lightandsolventsoftencausedegradation and/ortransformationofpurifiedcomponents;isomers andconformationsmayalsocausechangesinthemarkers. However,aconceptofunderstandingthecomplexprinciplesofherbalmedicinemustbedevelopedthrough markerprofilingandrelatedapproachessoastodevelop evidence-basedpracticeofherbalmedicine [11].Itis importanttocharacterizeallthephytoconstituentsina planttoensureasafeandefficaciousherbalmedicine [2].Evidence-basedsubmissionsforregulatoryapproval andinterlinkingofvariouspharmacopoeialandmonographswouldbehelpfulfortheherbalmanufacturersto regulatemarketsacrosstheworld.Ageneralcomparison ofthepharmacopoeialstandardsrevealsthatthereisa widevariationinplantspecificparameters,qualitystandardsofthedifferentnations.WithrespecttoSouthEast Asia,Indiaisamongtheleadingcountrieswithrespect todevelopmentofpharmacopoeialstandardsaswellas modificationofexistingregulatoryguidelines [12].
Themajorchallengesforthedevelopmentand promotionofTMincludethechemo-profiling,safety evaluations,qualitycontrolandeffectiveregulatory guidelinesforherbalmedicines [13].Wisdomandcompassion,enhancedglobalcollaborationandleadership areneededtochangethecontemporaryparadigmsand developnewstrategiesfortheenhancementofTMs anddietarysupplements.Researchthroughcollaboration andcooperationacrossthenationcanhelptoahigh extentinthepromotionanddevelopmentoftheTMfor thebettermenthealthcareglobally [14].Thiswould developasystemtobringrepresentativestogethertodiscusstheglobalissuesandimplicationsinnewstrategic terms,withanewsetofgoals,anewagenda,butmost importantly,anewvigor,andisvitalfortheglobal
development [2,14].Developmentandevaluationof medicinalplantderivedproductsarebeingcontrolled andimplementedthroughvariousagenciesindifferent countries.Thisprovidestheuniqueadvantagesfor researchersandthepharmaceuticalindustrytoenhance drugdiscoveryanddevelopment [15].
2.2Severalaspectsforrevitalizationofmedicinal plants
Inordertorevitalizetheherbalmedicineinlinewith themodernmedicine,variousstrategicareasinmedicinalplantresearcharebeingconsidered.Scientistsare convincedthattheintegrationofherbalmedicinewith moderntoolswouldnotonlybenefittheirowndevelopment,butalsohelptofightagainstmanycomplexdiseasesthroughdevelopmentofnewentities [16,17] Numerousmethodsexistinordertoevaluatethequality ofeithernaturalorsyntheticsubstances.Several invitro, invivo,andhighthroughputscreeningmethodsarecurrentlyinvolvedinthetraditionaldrugdiscovery approaches [18].Duringthepastdecades,publicinterest innaturaltherapies,namelyherbalmedicine,has increaseddramaticallynotonlyindevelopingcountries butmainlyinindustrializedcountries [19].Thishas increasedtheinternationaltradeinherbalmedicine enormouslyandhasattractedmostofthepharmaceuticalcompanies,includingthemultinationals.Indiaisone ofthefewcountriesthatarecapableofproducingmost oftheimportantplantsusedinmodernaswellastraditionalsystemsofmedicine.Inmodernerathecombinatorialchemistryandhighthroughputscreeningarevery usefulmethodandsomanynewdrugmoleculesare comingoutfromherbalresources.Thetraditionaluse ofmedicinalplantsneedstobesystematicallyinvestigatedandstandardizedintheprospectiveofthequality, safetyandefficacy [15].Oneofthemostimportantissues involvedinanyresearchstudyisthequalityofthetest material.Astudycannotbeconsideredscientifically validifthematerialtestedwasnotauthenticatedand characterizedsuchthatthematerialcanbereproduced. Inthecaseofbotanicals,theremaybemisidentification ofthecollectedplant,adulterationwithotherspecies,or contaminationwithextraneousingredients [7].
3UseofherbsinTM
TMgenerallyreferstothosemedicalandhealthcare systemsthatarepracticedinatraditionalmannerfrom ancienttimes,andthisdisciplineisnotconsideredto beapartofconventionalmodernmedicine.Overseveral years,thissystemhasevolvedonthebasisofreligious
beliefsandsocialedificesofseveralindigenouspeoples byexploitingthenaturalresourcesandmorerecently bydevelopingascientificmethodforvalidatingtherapeuticandpreventiveapproaches [20].However,TMis notalwaysdocumentedproperlythroughevidenced basedscientificvalidationasinconventionalmodern medicine.TMsaremoreeasilyacceptedbymostpeople duetotheirstrongbelief,faith,practicalbenefits,economicaladvantage,easyaccess,andmanyotherreasons thathaveregional,religious,andsocialbases,etc. [21].. TheIndianmaterialmedicaincludesapproximately 2000drugsofnaturalresources,nearlyallofwhichare derivedfromdifferenttraditionalsystemsofmedicine andIndianfolklorepractices.Manyconventionalmoderndrugsoriginatefromdifferentnaturalsourcesespeciallymedicinalplants:acenturyago,mostofthe effectivedrugswereplantbased [22].Drugdevelopment frommedicinalplantscontinues,withdrugmanufacturingcompaniesengagedinlarge-scalepharmacological screeningofherbs.InTM,somepopularherbssuchas Turmeric,Neem,Ginger,HoliBasil,Ashwagandha, andRauwolfia.,createarevivalofinterestinherbalproductsatagloballevel [23].Around60%oftheglobalhealth careproductmarketisdominatedbymedicinallyuseful formulationsandotherhealthproducts,derivedordevelopedfrombotanicals.InIndia,around25,000traditional andfolkmedicinaleffectiveplant-originatedformulationsareused.InIndia,morethan1.5millionconsultants areusingtraditionalmedicinalsystemsforhealthcare, andmorethan7800manufacturingunitsareinvolved intheproductionofnaturalhealthproducts(NHP)and traditionalplantoriginatedformulations [12].Thereis worldwideemerginginterestinexecutingtraditional practicesinthehealthcaresystembyexploringtheirtherapeuticaswellaspreventivepotential.InTM,various regulationsandcontrolontheuseofbotanicalshave comeup,whichwillnotonlyhelptocuredifferentailmentsthroughindigenousnaturalresourcesbutwillalso helpinthescreeningandevaluationofthemedicinal plantsinabetterwaytousethemintraditionalhealthcaresystems [24]
4GlobalizationofTM
TMhasbeendefinedasskillsandapracticebasedon thetheories,beliefs,andexperiencesthatareindigenous todifferentcultures.Itisusedinthemaintenanceof healthcareaswellasintheprevention,diagnosis,and treatmentofphysicalandmentalillnesses [25].Scientists aroundtheworldarehighlyemphasizingonmedicinal plantsasalternativemedicineandtheircommercial potentialinhealthcare.GlobalizationofTMisnecessary fortheestablishmentofevidence-basedhealthcare, basedonTMinconsiderationofitssafety,efficacy,
therapeutic,andclinicalevidence [26].Moderntechnologyandsciencehavedevelopedmanytechniquesand systemsforcoredisciplinesincludingethnomedicine, ethnobotany,ethnopharmacology,andmedicalanthropologytopromoteTMcompoundsglobally [11].Establishmentofglobaland/orregionalregulatory harmonizationisobligatoryforitsdevelopmentandpromotionthroughscientificvalidation.Thedevelopmentof TMandnaturalproductsrequirestheconvergenceof moderntechniquesandintegratedapproachesrelated totheirevidence-basedresearchinvariousfieldsofsciencethroughcoordinationandcooperation [27].Tocombatthegrowingmarketdemand,thereisanurgencyto expeditiouslyutilizeandscientificallyvalidatemore medicinallyusefulplantsglobally,whichneedsglobalizinglocalknowledgeandlocalizingglobaltechnologies, throughinternationalcollaborationandcooperation. ThemajorlimitsfortheglobalizationofTMsaredueto havingdifferentstandardsofTMproductsandpractices, includingvariedterminologyandphilosophical approaches.Developmentofeffectiveguidelinesfor safety,efficacy,andqualityisregardedasafundamental requirementinordertoestablishtheevidencebasefor TM [28].TheInternationalUnionofPureandApplied Chemistry(InternationalofPureandAppliedChemistry (IUPAC))haspublishedaseriesofprotocolsonquality control,safety,efficacy,standardization,anddocumentationofherbalmedicineinwhichvarioussignificant aspectsandfeaturesofphytochemistryandanalytical chemistryhavebeendescribed.Ifthesestrategiesare fullyimplementedbytheIUPAC,theWorldHealth Organization(WHO)willexploreTMfromitspessimistic viewtomodernmedicine [29].
4.1StrategiesforglobalizationofTM
Theterm “globalization” meanstheincreasedmobility ofindividuals,information,goods,services,labor,technology,andcapitalthroughouttheworld.Therearehuge databasesofTM,whichareusedbyancientpeopleasfolk medicine,andthisevidencewasfoundinmanywritten textbooks [30].ThereareseveralstrategiesfortheexpansionofTMsuchas(1)additioninthehealthcaresystem, (2)promotionofsecureandvaluableuse,(3)increasing itsaccess,(4)increasingcommunication,and(5)cooperationingenerationanddistributionofTM-relatedinformation.Thesestrategiesbasedoninformation,botany, chemistry,andbiologyofmedicinalplantvalidation andqualitycontrolareessential [31].Intheeraofmodern research,somenewdrugmoleculesareemergingwith thehelpofcombinatorialchemistryandhigh-throughput screeningfromherbalresources.Astudycannotbeconsideredscientificallyvalidifthematerialtestedwasnot authenticatedandcharacterizedsuchthatthematerial

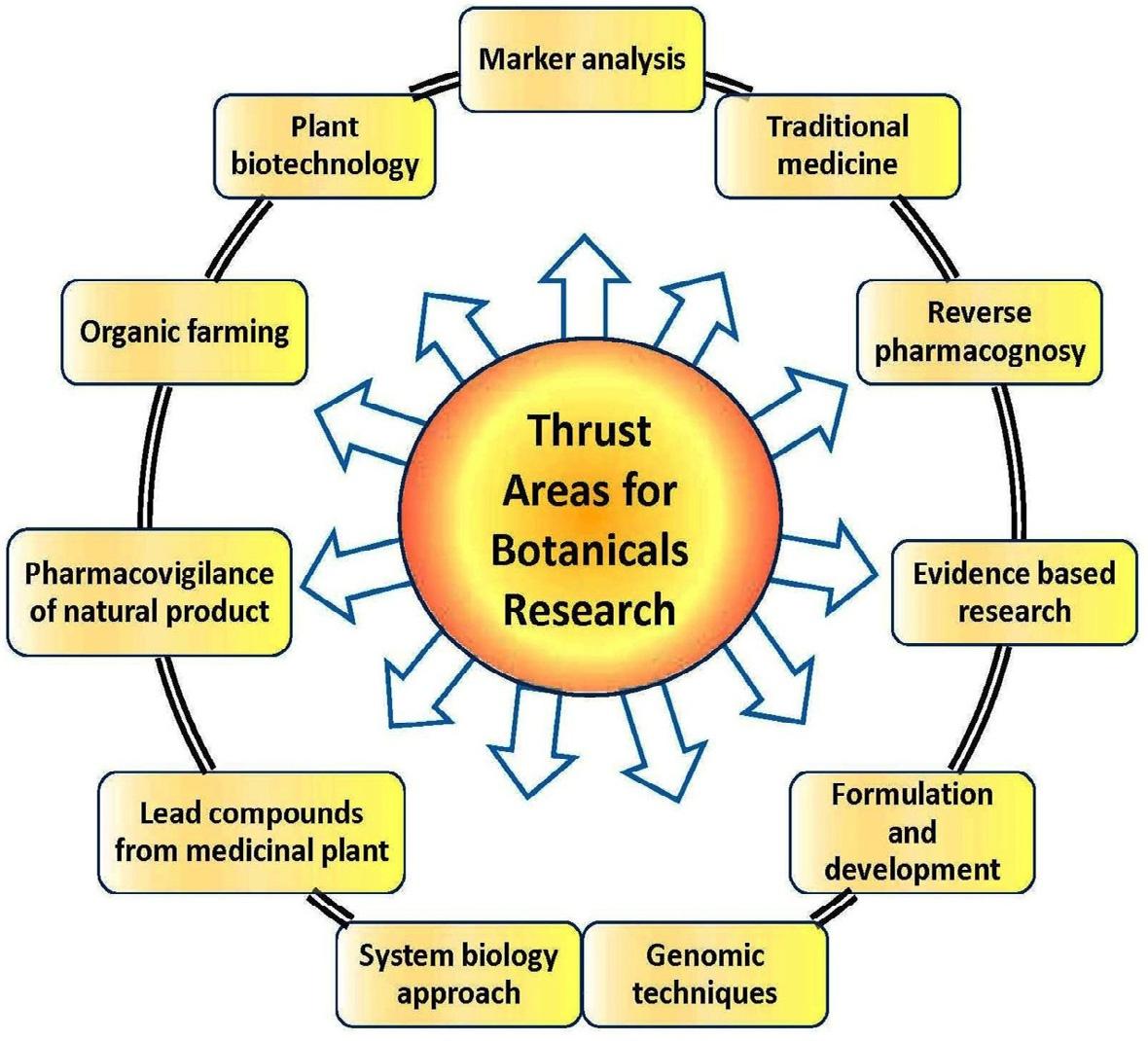
canbereproduced.Inthecaseofbotanicals,theremaybe misidentificationofthecollectedplant,adulterationwith otherspecies,orcontaminationwithextraneousingredients.Fromtheperspectiveofaregulatoryaction,these casesmayrangefromsimplemisleadinglabelingtofrank poisoningduetotoxiccontaminants.Itcanoftenbedifficulttocomparereportedefficacyortoxicitystudies evenwhen “standardized” materialhasbeenused.Many studiesrefertotheuseofstandardizedbotanicalmaterial,whichusuallyimpliesachemicalstandardization [32].InterdisciplinaryapproachofworkonTMistobe exploredforthediscoveryofnovelbioactivecompounds. Issuesrelatedtotheappropriatenessofconventionalbiomedicalandclinicalmodelsforevaluatingtheefficacyof TMaresometimesverycrucial.Aholisticapproachbased onsystemsbiologyseemsmuchmoresuitedtostudythe therapeuticefficacyandpharmacodynamicsof TM-baseddrugdevelopment [11].Approachesfordrug developmentbasedontraditionalleadsaredescribed in Fig.2
MostoftheIndianandChineseherbalformulationscontainamixtureofherbs,andseveralmethodsareavailableto classifythem.Whentwoormoreherbswiththeirbioactive compoundsarecombinedtoprepareformulations,theycan beobservedtohavethefollowingeffects [33]:
• Synergisticsignificance
• Synergisticimprovement
• Co-counteraction
• Mutualrepression
• Communalaggression
• Communalinappropriateness
Themainingredientisacomponentthatprovidesthe maintherapeuticaction;thesecondingredientpotentiatesthetherapeuticactionsoftheother,whichisknown assynergisticreaction,andthecomponentissynergism. Therestserveoneofthefollowingfunctions:
• Treataccompanyingsymptoms,
• Moderatetheruggednessortoxicityoftheprimary ones,
• Targetthemedicinetotheproperorgans,
• Exertacomplementaryeffect.
Insomecases,standardizedbioactivecompoundsare subjectedtoanimalmodelstocorrelatethepresenceof certainphytoconstituentswithapathophysiologicalconditionofthehumanbody [34].Inthecontextofmodern biomedicalresearch,thereshouldalsobenecessaryprerequisitesforclinicaltrials.
5TMinspireddrugdiscoveryanddrug development
Inordertorevitalizeherbalmedicineinlinewithmodernmedicine,variousstrategicareasinmedicinalplant
FIG.2 Drugdevelopmentbasedontraditionalclaims.
researcharetobeconsideredofglobalimportance [35] Integrationofherbalmedicineandmoderntoolswould notonlybenefittheirowndevelopmentbutwillalsohelp tofightagainstmanycomplexdiseasesthroughthedevelopmentofnewentities.Suchdedicatedresearchwouldbe beneficialonlywithsupportfromadvancedapproaches andnovelstrategies [36].Therearevariousthrustareas thatplayaverysignificantroleforresearchanddevelopmentofnaturalproductsasrepresentedin Fig.3.
TMishelpfulinallaspectsofdrugdevelopmentfrom naturalresources.Afewexamplesofdrugsfromnatural productswouldbetterexplainthehistoryofitsowntradition.SeveralapproachesondrugdiscoveryanddevelopmentfromTMhadbeenpracticedbyscientistsformany years.Severaltherapeuticallypotentialconstituentswere isolatedfromplantssuchasartemisinin(antimalaria),vincristine,vinblastine,camptothecinpodophyllotoxin,etoposide,teniposide,andpaclitaxel(anticancer) [37].The developmentofdrugsfromayurvedicplantsisongoing, withpharmaceuticalcompaniesengagedinlarge-scale pharmacologicscreeningofherbs. “Sushruta-Samhita,” a SanskrittextonAyurvedawrittenin600BCnotedthat theplant Commiphoramukul Hookwasusefulinthetreatmentofobesityandrelateddiseases.Inrecentyears,aconfluenceofspectacularadvancesinchemistry,molecular biology,genomics,andchemicaltechnologyandthecognatefieldsofspectroscopy,chromatography,andcrystallographymayinfluenceseveraltherapeuticallypotent leadingcompoundsfromTM [12].
Therearemanyapproachesforthesearchofnewbiologicallyactiveprinciplesfrombotanicals.Onecansimplylookfornewchemicalconstituentsandfinda biologistwhowilltestthesubstancepharmacologically. Thisisnotconsideredtobeaveryvalidapproach. Asecondapproachissimplytocollecteveryreadily availableplant,prepareextracts,andtesteachextract foroneormoretypesofpharmacologicalactivity.This testingwillhelpinthestandardizationofextractsand thebioassay-guidedisolationoftheactiveconstituents. Thephytoconstituentsobtainedcanthenbetakenfurther forstructure-activityrelationshipstudies [38].Onceall thesefactorsaredetermined,theconstituent/extract obtainedcanbefurtherexaminedforitstoxicityand safetyevaluation,followedbyclinicaltrials.Thisrandom collectionandextensivescreeningmethodisareasonable andthemosteffectiveapproachthateventuallyshould produceusefuldrugs,whichcanbewellproducedand formulatedinindustries.Theclassicmethodofpharmacologicscreeninginvolvessequentialtestingofherbal extractsorphytoconstituentsfrombiologicalmaterials inisolatedorgansfollowedbytestinginwholeanimals, mostlyinratsandmice.Mostofthedrugsinusetodayas therapeuticagentshavebeenfoundandevaluatedwith thesemethods [39].However,fortheevaluationofTM, weshouldnotfollowthereductionistapproach,butgo backtotheholisticinvivoapproach.Thiscanbedone intwodifferentways:oneisthroughclinicaltrials;the otheristhroughanimalexperiments.Besidestheclassic
FIG.3 Thrustareasforbotanicalresearch.
physiologicobservationsthatcanbemadebyinvivo experiments,forexample,bloodpressure,analgesic activity,andsedation,nowadays,itisalsopossibleto measuregeneexpression,theproteome,andthemetabolome.Thesemethodsopenupacompletelynewworldof possibilitieswithseveralnewtechnologiesnowgivinga muchbetterinsightintothepossiblechangesinthe organism,inaholisticway.Itwillgiveusthepossibility tobetterunderstandthemodeofactionbycomparingthe changesinthetranscriptome,proteome,andmetabolomicpatternswhencomparedwiththoseobservedwith knowndrugs.Suchanapproachisnowknownasthesystemsbiologyapproach.Themetabonomicapproach requiresthestatisticalanalysisoflargedatasetsby methodssuchasmultivariateandprinciplecomponent analysistoextracttheinformationfromthesedata [40] Moreover,byusingthesystemsbiologyapproachfor theorganismcombinedwithmetabolomicdataforthe differentextractsofthemedicinalplantorfractions thereof,itshouldbefeasibletomakecorrelations betweentheoccurrenceofcertaincompoundsinthe extractandtheactivity.
Evidence-basedmedicineresearchshouldbeconductedwiththeinvolvementofpatientsandfunding bodiestoestablisharoleofmedicalpractitionersindecisionmaking [41].Awidespreadrevolutioninphytochemistryhasbeenobservedthroughstrengtheningits importancewiththeapplicationofnewtechnologies toenhancetheoriginallinkbetweenphytochemistry andTM.Evidence-basedrese archincludesdeveloping policies,regulatorycriteria,andtechnicalguidelines thatwouldensureandprovidethecontinuedavailabilityofquality,safety,andeffectivetraditionalmedicinal products,whichcouldsupportinclusioninhealthcare systems,insuranceprograms,andonessentialmedicine lists [29].Evidencebasedsubmissionsforregulatory authorizationandinterlinkingofvariouspharmacopoeiaandmonographswouldmakeiteasyforherbal manufacturersandtheywillgaingreateraccesstoregulatedmarketsacrosstheworld [42] .Itisunderthese circumstancesthatsomeofthe rationalists,scientists, scholars,andprotagonistsofalternativemedicinesdedicatedthemselvestothedevelopmentofthesealternativesystemsfordrugdevelopmentfromnatural resources,whichrequire dtobeharmonizedthrough internationalcoordination.
6Qualitycontrolandqualityassuranceofherbal medicine
Qualitycontrolandqualityassuranceofherbalmedicinesareveryimportanttoprotecttheintegrityofthe herbalextracts/productsforthemanagementofpharmaceuticalquality.Theyhaveanimportantroleforthe
reproducibilityoftheeffectoftheactiveingredientsfrom batch-to-batchuniformity.Tomaintainandcomplywith standardconditionswithrespecttoquality,safety,and efficacyofherbalmedicine,itisrequiredtofollowsome importantstepsforthestandardization [43].Thisincludes the(1)properauthenticationandtaxonomicassignment, suchasthroughDNAfingerprintingandDNAbarcoding; (2)structuralelucidationofallisolatedcompoundsofthe medicinalplant;(3)identificationandcharacterizationof thebioactiveconstituentsforthepharmacologicalactivity; (4)standardizationofthesingleextractsthroughspectroscopicanalysesinthemulti-compoundextracts;(5)internationalharmonizationofspecificstandardization processesundertheumbrellaoftheInternationalFederationofPharmaceuticalManufacturersAssociations.Therefore,itisveryclearthatmajorrequisitesfor standardizationofherbalproductscomplywithinternationalstandards.Thereareseveralvariablesthatcaninfluencethestandardizationprocess.Therefore,itis compulsorytooptimizeallaspectsofcultivation,harvesting,samplepreparation,andsampleprocessingtoensure reproducibilityandeventuallystandardizationofthe herbaldugs.Therearevariousnewhyphenatedtechnologiespresentsuchaschromatographicandspectroscopic analyses,whichneedtobeeffectivelyincorporatedto ensurethatsufficientqualitycontrolmeasuresareimplemented.Byusingseveralchromatographicandspectroscopictechniques,itispossibletoanalyzethefullherbal productandthusgenerateastandardized “metabolic fingerprint” ofspecificherbaldugs.Metabolicprofiling canthenbeincorporatedtoidentifyalltheconstituents [44].Thechemicalfingerprintsobtainedfromchromatographicorspectroscopictechniquesshouldbesimilarin differentsamples.Spectroscopicandchromatographic techniquesarenowbeingusedtogether,whichleadsto effectivechemometricapproaches.Whenthese approachesareusedincombinationwithchemometrics profiles,moreprecisedatacanbeobtainedthatwillbe helpfulintheestablishmentoftheintegrityoftheherbal productandsimilaritiesanddifferencesoftheobserved datawillbeproduced [31]
Generally,itisbelievedthattheriskassociatedwith herbaldrugsisveryless,butreportsonseriousreactions indicatetheneedforthedevelopmentofeffectivemarker systemsforisolationandidentificationoftheindividual components [45].Standardizationofherbalmedicine includestheauthenticationofgenuinedrugs,harvesting ofthebestqualityrawmaterial,assessmentofintermediateandfinishedproduct,anddetectionofharmfuland toxicingredients [46].Severalmarkerssuchastaxonomic, chemical,genomic,proteomicmarkersaidintheidentificationofherbaldrugcomponents.Chemicalmarkershelp intheidentificationofadulterants,confirmationofcollectionsite,andqualityevaluationanddiagnosisofherbal intoxication.AspertheWHOdefinition,therearethree

kindsofherbalmedicinesthatareobtainedfromrawplant material,processedplantmaterial,andmedicinalherbal products [40].Herbalmedicineproductsaredietarysupplementsthatpeopletaketoimprovetheirhealthand aremarketedastablets,capsules,powders,extracts,and freshordriedplants.Herbalsaretraditionallyconsidered harmlessandincreasinglybeingconsumedbypeople, withoutanyprescription.Theevidenceforthetherapeutic actionsofherbaldrugsisdocumentedinIndian,Chinese, European,andAfricansystemsofmedicine [24].Thereare severalimportantaspectsforqualitycontrolofherbal medicinethatareshownin Fig.4
TheWHOhasrecognizedtheimportanceofthequalitycontrolofherbalmedicineanddevelopedaseriesof guidelinestoassistseveralnationstodeveloptheirstrategiesforthequalitycontrolofherbalmedicinesandfor conductingresearchonTMs [47].TheWHOhadpublishedthe “QualityControlMethodsforMedicinalPlant Materials,” acollectionofrecommendedtestprocedures forassessingtheidentity,purity,andcontentofmedicinalplantmaterialstoassistnationallaboratoriesengaged indrugqualitycontrol [48].TheWHOpublishedthe “Guidelinesongoodagriculturalandcollectionpractices (GACP)formedicinalplants” andin2007,anewguideline “WHOguidelinesforassessingqualityofherbal medicineswithreferencetocontaminantsandresidues” wereformulated.TheEuropeanUnion,China,andJapan havedevelopedregionalandnationalguidelinesfor goodagriculturalandcollectionpracticesformedicinal plantsthatensurethatsoilandirrigationwaterused forherbalmaterialcultivationandpropagationare withinthelimitsorarefreefromharmfulheavymetals, pesticides,herbicides,andtoxicologicallyhazardoussubstances.Thecertificationforthisisbasedonparameters suchasidentification,watercontent,andchemicalassay ofactiveingredients,inorganicimpurities(toxicmetals),
microbiallimits,mycotoxins,pesticides,andothers [49] Fromthecultivationtothefinalherbalproductdevelopmentofherbalproducts,therearesomanysignificant factorsthatcaninfluencethequalityofherbalproducts. Somesignificantissuesrelatedtothequalitycontrolof herbalmedicinearebeingdescribedbrieflyinthesubsequentsection.
6.1Contamination
Therearesomanycontaminantsmostlyfoundinmedicinalherbsincludingpesticides,heavymetals,microbes, andmycotoxins.Contaminationsalsopresentserious obstaclesforthetradeofherbalmedicines [50].Heavy metalshavebeenfoundinherbalmedicineswithsomeregularity.Threemostcommonlydetectedtoxicmetalsare mercury,arsenic,andlead.Thesecontaminationsmay occurdueto(1)theaccumulationofheavymetalsinthe environment(e.g.,fromcontaminatedsoiloratmosphere); (2)unintentionalpollutionduringtheproductionprocess; (3)deliberateaddition.Insomeoftheherbalproducts,residuesofpesticidesincludingtheirmetabolitesanddepredatedproductsremainedinplants,andsuchresidues havebecomeanotablesourceofcontaminationforherbal medicines [51].
6.2Adulteration
Adulterationinherbalmedicineincreasestheimpurity byaddingsomeextraneous,improper,orinferioringredients.Herbalmedicinesareadulteratedwithconventionaldrugs,andplantmaterialshaverepeatedlybeen documented.Adulterationscanbedoneinthefollowing wayincludingadditionoforthodoxdrugs,substitution offakeorinferiorplantmaterials,andadditionofforeign materials [36].
FIG.4 Importantstepsforqualitycontrolofherbs.
6.3Misidentification
Conflictingtoadulterationorsubstitutions,misidentificationofherbalmedicinemostlyhappensunintentionally.Falseidentificationcanoccurwhenanimporteror retailermistakesoneherbforanother,duetoincorrect labelingandsimilarappearanceoftheherbalmaterials. Confusingnomenclaturecanbeoneofthereasons, becauseoneherbmaybeknownbymanynames:one ormorecommonnames,aLatinname,localnames, andthebrandname.Somedifferentmedicinalherbsof differentplantspecieswithdifferentconstituentsmay havesimilarnames.Theproblembecomesevenmore complexthroughconfusingterminologiesandtheuse ofdifferentlanguagesindifferentcountries [52].The commonnamesofherbsusuallydonotreflectdifferences inscientifictaxonomy;andthedescriptionandmicroscopicidentificationofanherbcannotidentifyitsconstituents.Thus,astudyofancientdocumentsandtheuseof modernanalysistechniquesareoftennecessarytoproperlyauthenticateherbalmaterials.
6.4Nonuniformchemicalconstituents
Thechemicalcompositionofherbalproductsvaries anddependsonthegrowingconditionsandgeographic region.Severalenvironmentalfactorsthatincludeatmospherichumidity,rainfallpattern,soil,altitude,seasonal variation,temperature,lengthofdaylight,mayaffectthe concentrationofchemicalconstituentsinmedicinal plants.Someotherrelevantfactors,suchasgenetic make-up,seedingtime,useofpesticidesandfertilizers, plantingdensity,alsoplayasignificantrole.Variousprocessingstepsofrawmaterialscanalsochangethepharmacologicalactivityoftheplantextract.Therefore,batchto-batchstandardizationisveryessentialtomaintainthe uniformityofactiveconstituents [53]
6.5Pharmacopoeialstandardsforevaluationof herbalproducts
Safetyandefficacyassessmentforanypharmaceutical mustbetakenintoaccountforthequalityoftheprepared formulation.Minimumstandardsforacceptablequality aregenerallylaiddowninpharmacopoeialmonographs, whichprovideallthedetailsoftheacceptablesubstance andgivethenicetiesofsignificantteststodetermineits identityandpurity.OnetypeofpharmacopoeialmonographisfoundintheBritishorEuropeanpharmacopoeias,whichgiveonlydetailsoftheteststobeusedto establishquality,withveryconcisenotesaboutitstherapeuticapplication.Anothertypeofmonographismore concernedwiththecompleteinformationaboutamedicinalplantandconsistsofalltheinformationaboutits
chemicalconstituents,pharmacology,toxicology,clinical studiesandusage [54].
Pharmacopoeialmonographsforthemedicinalherbs dealwithalltypesofpharmaceuticalsandplantmaterialswhichhavebeenincludedsincetheearliesteditions withauthorizationatanation alorinternationallevel. Itisinterestingtotracetheevolutionofamonograph foroneparticularmedicinalplantbecauseitreflects developmentsinanalyticaltechniques,theincreasing knowledgeofthechemicalcompoundspresent,and thegrowingbodyofknowledgethatlinksthecompoundspresenttothedesiredb iologicalorclinicaleffect [55] .MorerecenteditionsoftheBritishPharmacopoeia andEuropeanPharmacopoeiahaveincludedmonographsformanymoreherbaldrugsandmoresophisticatedchromatographicme thods,especiallyliquid chromatography(LC),havebeenintroducedforboth identitytests,impuritiestests,andforassayprocedures. Therefore,moreattentionshouldbegivenforthebiologicalactivityrelevanttothereputationandclaimsfor treatingparticulardiseasesassociatedwithherbal medicines [36]
TheIndianPharmacopoeia2007includespharmacopoeialspecificationswithmonographsforsomemedicinal plantsbeingmostcommonlyusedastherapeuticagents. Thespecificationsincludethenameofthedrug(along withitscommonname),itsbiologicalsource(Latinname), thepartoftheplantunderconsideration,itsdescription, macroscopicandmicroscopicstudy,identification,several qualitycontrolparameters,andassayswithrespecttothe phytochemicalreferencestandardsorbotanicalreference standards [56].TheAyurvedicPharmacopoeiaofIndia isanotherofficialcompendiumpublishedbytheMinistry ofHealthandFamilyWelfare,GovernmentofIndia.This describesdifferentmethodsforqualitycontrolandstandardizationofmedicinalplantsandherbalpreparations. Severalspecificationsforqualityevaluationofnatural productsasprescribedintheAyurvedicPharmacopoeia includemorphologicalstudy,determinationofquantitativedata(e.g.,extractivevaluesandforeignmatter),limit tests,anddifferentphysicaltests(e.g.,boilingrange, refractiveindex,andpH) [57]
7Markeranalysisandstandardizationof botanicals
ChemoprofilingofNHPhelpsinidentifyingthe majormetabolitesandisusefultoassessbiological effects.Thedevelopmentofmarker-basedmedicines requiresacomprehensiveunderstandingofplantsystemsincludingbiological,chemical,genetic,andagronomicaspects.Chemicalconsistencyatallstagesof manufacturingprocessesismostimportanttoensure medicinalefficacyandconsumersafety.Thisincludes
allthestagessuchasextraction,stability,shelflife,and purityofherbalmedicines. Differentmethodsforcharacterizationofherbaldrugssuchasmorphologicalidentification,anatomicalidentification,andchemical analysis,suchasthinlayerchromatography(TLC), high-performancethinlayerchromatography (HPTLC),high-performanceliquidchromatography (HPLC),capillaryelectrophoresis(CE),Liquid chromatography-massspectrometry(LC-MS),andproteinanalysisareextensivelyused [28] . AccordingtotheEuropeanMedicinesAgency(EMEA), markersmaybedefinedaschemicalconstituentsor groupsofconstituentsofaherbalmedicinalproductthat areveryimportantforqualitycontrolpurposesregardless ofwhethertheypossessanytherapeuticeffect.Chemical markersarebasicallycategorizedintotheanalytical markersandactivemarkers.Analyticalmarkersarethe constituentsorgroupsofconstituentsthatservesolely foranalyticalpurposes,whereasactivemarkersarethe constituentsorgroupofconstituentsthatcontributeto therapeuticactivities [58].Secondarymetabolitesas markershavebeenwidelyusedinqualitycontroland standardizationofherbalmedicines.Herbalproducts derivedfrombotanicalsaremostlyobtainedfromwild sourcesandhavethegreatestchallengesforensuringconsistentproductquality.Theseareusedformakingmedicineswherethestandardizationandqualitycontrolwith properintegrationofscientifictechniquesandtraditional knowledgeisvitalrequirement [30].Markercompound selectionisgenerallybaseduponavarietyofdifferentfactorsincludingstability,easeofanalysis,timeandcostof analysis,relevancetotherapeuticeffectandindicatorof productqualityorstability.Chemicalmarkersarefrequentlyusedforassuringqualityconsistencyofnatural productsderivedfrombotanicalsources [59].Anideal chemicalmarkerforanaturalproductshouldnotbeonly acharacteristicconstituentbutalsothetherapeuticconstituent.Markercompoundsarenotnecessarilypharmacologicallyactiveallthetimebuttheirpresenceiswell establishedinproductswithcharacteristicchemicalfeatures.Markercomponentsmaybeclassifiedasactiveprinciples,activemarkersandanalyticalmakers,while biomarkersmaybedefinedaspharmacologicallyactive [60].Herbalmanufacturersandresearchersneedto addressthesecriticalquestionstoaidintheharmonization ofspecificationsandanalyticalmethodologiesfornatural products.Usually,determinationofsingleorseveral markercompoundsbyadevelopedmethodisrequired forqualitycontrolpurpose [61].Standardizationmethods throughchemicalfingerprintingshouldtakeintoaccount foralltheaspectsthatcontributethequalityoftheherbal medicine,includingcorrectidentificationofsample,pharmacognosticevaluation,organolepticevaluation,volatile matter,quantitativeevaluation(ashvalues,extractive value,foreignmatter),phytochemicalevaluation,
xenobioticstesting,toxicitytesting,microbialloadtesting andbiologicalactivitydetermination [41].Medicinal plantscontainseveralphyto-constituentsincertainratios andinstandardizedextracts.Theratioofthesechemical constituentsmustbeconstantwithinnarrowlimitsfrom onebatchtoanother [62].Chemicalfingerprintsobtained bychromatographic,spectroscopic,thermogravimetric analysis,capillaryelectrophoresisandpolarographytechniqueshavebecomethemostimportanttoolsforquality controlandstandardizationherbalmedicines [13].
Forensuringconsistentquality,theuseofmarkers, standardization,chemicalandDNAfingerprinting,bioassays,andtheemergingfieldofphytomicsarevery important [63].Somemedicinallyimportantplantsare listedin Table1.Markerselectionmaybebasedupona varietyofdifferentfactorsincludingstability,easeof analysis,timeandcostofanalysis,relevancetotherapeuticeffect,indicatorofproductquality,orstabilityorprevioususebyothermanufacturersorresearchers [60]
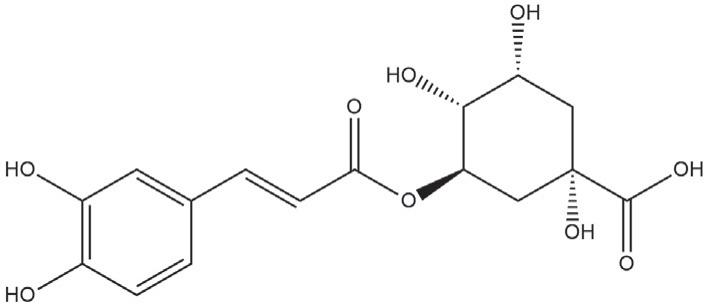
Alistofseveraltherapeuticallypotentphyto-markers fromplantspecieshasbeenshownin Table1.Developmentofleadcompoundsfromthesemedicinalplants andtheirevaluationmayhelptopromotenaturalproductsbasedontheirqualityefficacyandsafety.Marker analysisofseveralherbaldrugsincludingpolyherbalformulationsfromIndiansystemofmedicinehasbeenperformed.ThefingerprintprofilesofEmodin(1)from Aloe vera,Gallicacid(2)from Terminaliachebula,Boswellic acids(3)from Boswelliaserrata,Capsaicin(4)from Capsicumannum,Glycyrrhizin(5)from Glycyrrhizaglabra,epicatechin(6)from Camelliasinensis,Eugenol(7)from Eugeniacaryophyllata,Ferulicacid(8)from CoffeaArabica, Garlicin(9)from Alliumsativum,Genistein(10)from Glycine max,Ellagicacid(11)from Punicagranatum andPiperine(12)from Piperbetel, Syringicacid(13)from Tagetes erecta, Anthocyanidin(14)from Paulliniacupana, Apigenin(15)from Matricariarecutita and Stereospermum suaveolens, Ascorbicacid(16)from Citrussinensis, Berberine(17)from Berberisaristata, Curcumin(18)from Curcumalonga, Gingerol(19)from Zingiberofficinale, Naringenin(20)from Citruslemon, Resveratrol(21)from Vitisvinifera, Lapacholfrom Stereospermumsuaveolen, and theirpharmacologicalactivitieshavebeenreported. MarkeranalysisofGlycyrrhizinfrom G.glabra hasbeen reportedthroughHPTLCdensitometry.ThisisavalidatedmethodaspertheInternationalConferenceon Harmonizationguidelinewheretheamountofglycyrrhizinwasdeterminedintheextractof G.glabra through HPTLC.Themethodwasvalidatedintermsofspecificity,linearity,precision,detectionlimit,andquantification limit [64,65].
Chlorogenicacid(22)wasquantifiedfromthemedicinalplantsofthecucurbitaceaefamilylike Sechiumedule, Trichosanthescucumerina,LuffaacutangulaandTrichosanthesdioica withasuitablesolventsystemofethyl
TABLE1 Somemedicinallyimportantplantsandtheirknownphyto-markers.
ScientificnameFamilyPartsusedMarkercompound
Aloevera LiliaceaeLeavesEmodin(1)
Terminaliachebula CombretaceaeFruitGallicacid(2)
Amaranthustricolor AmaranthaceaeAerialparts
Boswelliaserrata BurseraceaeResinBoswellicacids(3)
Capsicumannum SolanaceaeFruitsCapsaicin(4)
Glycyrrhizaglabra LeguminaceaeRootGlycyrrhizin(5)
Camelliasinensis TheaceaeLeavesEpicatechin(6)
Eugeniacaryophyllata MyrtaceaeFlowerbudEugenol(7)
Coffeaarabica RubiaceaeSeedFerulicacid(8)
Hemidesmusindicus ApocynaceaeWholeplant
Alliumsativum AmaryllidaceaeBulbGarlicin(9)
Glycinemax FabaceaeSeedGenistein(10)
Punicagranatum PunicaceaeFruitEllagicacid(11)
Piperbetel PiperaceaeLeavesPiperine(12)
Tageteserecta AsteraceaeLeavesSyringicacid(13)
Paulliniacupana SapindaceaeSeedAnthocyanidin(14)
Matricariarecutita AsteraceaeFloweringheadApigenin(15)
Stereospermumsuaveolens BignoniaceaeBark
Citrussinensis RutaceaeFruitAscorbicacid(16)
Berberisaristata BerberidaceaeBerriesBerberine(17)
Curcumalonga ZingiberaceaseRhizomeCurcumin(18)
Zingiberofficinale ZingiberaceaseRhizomeGingerol(19)
Citruslemon RutaceaeFruitNaringenin(20)
Vitisvinifera VitaceaeFruitResveratrol(21)
Sechiumedule CucurbitaceaeFruitChlorogenicacid(22)
Trichosanthescucumerina
Luffaacutangula
Trichosanthesdioica
Inularacemose
Lagenariasiceraria
Benincasahispida
Momordicacharantia
Cocciniagrandis
Cucurbitapepo
Luffaacutangula
Cultivarsof Cucumissativus
Myristicafragrans
AsteraceaeWholeplant
CucurbitaceaeFruitCucurbitacinE(23)
MyristicaceaeWholeplantQuercetin(24)
Amaranthustricolor AmaranthaceaeAerialpartsQuercetin,Rutin(25)
Ayapanatriplinervis CompositaeLeavesAyapanin(26)
Continued
TABLE1 Somemedicinallyimportantplantsandtheirknownphyto-markers—cont’d
ScientificnameFamilyPartsusedMarkercompound
Dilleniaindica DilleniaceaeFruitsBetulinicacid(27)
Swertiachirata GentianaceaeLeavesUrsolicacid(28)
Andrographispaniculata AcanthaceaeAerialpartsAndrographolide(29)
Bacopamonnieri ScrophulariaceaeRootBacosideA(30)
Centellaasiatica MackinlayaceaeWholeplantAsiaticoside(31)
Emodin (1)
Gallic acid (2)
Boswellic acid (3)
Capsaicin (4)
Glycyrrhizin (5)
Epicatechin (6)
Eugenol (7)
Ferulic acid (8)
Garlicin (9)
Genistein (10)
Ellagic acid (11)
Piperine (12)
TABLE1 Somemedicinallyimportantplantsandtheirknownphyto-markers—cont’d
Syringic acid (13)
Anthocyanidin (14)
Apigenin (15)
Ascorbic acid (16)
Berberine (17)
Curcumin (18)
Gingerol (19)
Naringenin (20)
Resveratrol (21)
Chlorogenic acid (22)
Cucurbitacin E (23)
Quercetin (24)