https://ebookmass.com/product/endoscopic-surgery-of-the-
Instant digital products (PDF, ePub, MOBI) ready for you
Download now and discover formats that fit your needs...
Endoscopic Craniosynostosis Surgery: An Illustrated Guide to Endoscopic Techniques David F. Jimenez
https://ebookmass.com/product/endoscopic-craniosynostosis-surgery-anillustrated-guide-to-endoscopic-techniques-david-f-jimenez/
ebookmass.com
Internet Of Things 1st Edition Raj Kamal
https://ebookmass.com/product/internet-of-things-1st-edition-rajkamal/
ebookmass.com
Physics of Spin-Orbit-Coupled Oxides Gang Cao
https://ebookmass.com/product/physics-of-spin-orbit-coupled-oxidesgang-cao/
ebookmass.com
GO! with Microsoft Excel 2016 Comprehensive (GO! for Office 2016 Series) 1st Edition – Ebook PDF Version
https://ebookmass.com/product/go-with-microsoftexcel-2016-comprehensive-go-for-office-2016-series-1st-edition-ebookpdf-version/ ebookmass.com
Boneyard Tides_Amo Jones Jones https://ebookmass.com/product/boneyard-tides_amo-jones-jones/
ebookmass.com
Thermoelectricity and Advanced Thermoelectric Materials
Ranjan Kumar
https://ebookmass.com/product/thermoelectricity-and-advancedthermoelectric-materials-ranjan-kumar/
ebookmass.com
The Palgrave Handbook of Utopian and Dystopian Literatures
1st ed. 2022 Edition Peter Marks
https://ebookmass.com/product/the-palgrave-handbook-of-utopian-anddystopian-literatures-1st-ed-2022-edition-peter-marks/
ebookmass.com
Wish Upon a Cowboy Jennie Marts
https://ebookmass.com/product/wish-upon-a-cowboy-jennie-marts/
ebookmass.com
The Cheerful Granny ~ Chidren Story Book 2nd Edition I Made Rico Surya Wirawan
https://ebookmass.com/product/the-cheerful-granny-chidren-storybook-2nd-edition-i-made-rico-surya-wirawan/
ebookmass.com
https://ebookmass.com/product/the-christmas-clash-suzanne-park/ ebookmass.com
EndoscopicSurgeryoftheOrbit EndoscopicSurgeryoftheOrbit RajSindwani,MD,FACS,FRCS(C) ViceChairmanandSectionHead Rhinology,Sinus&SkullBaseSurgery j HeadandNeckInstitute Co-Director j MinimallyInvasiveCranialBase&PituitarySurgeryProgram RosaEllaBurkhardtBrainTumor&Neuro-OncologyCenter ViceChairofEnterpriseSurgicalOperations j ClevelandClinic Cleveland,Ohio
Elsevier 3251RiverportLane St.Louis,Missouri63043
ENDOSCOPICSURGERYOFTHEORBITISBN:978-0-323-61329-3 Copyright © 2021,ElsevierInc.Allrightsreserved.
SinusandNasalInstituteofFloridaFoundationretainscopyrightfortheoriginal figures/imagesappearinginDr.Lanza’schapter(Chapter29).
Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproducedortransmittedinanyformorbyanymeans,electronicor mechanical,includingphotocopying,recording,oranyinformationstorageandretrievalsystem,without permissioninwritingfromthepublisher.Detailsonhowtoseekpermission,furtherinformationaboutthe Publisher’spermissionspoliciesandourarrangementswithorganizationssuchastheCopyrightClearance CenterandtheCopyrightLicensingAgency,canbefoundatourwebsite: www.elsevier.com/permissions
ThisbookandtheindividualcontributionscontainedinitareprotectedundercopyrightbythePublisher(other thanasmaybenotedherein).
Notices Practitionersandresearchersmustalwaysrelyontheirownexperienceandknowledgeinevaluatingand usinganyinformation,methods,compoundsorexperimentsdescribedherein.Becauseofrapidadvancesin themedicalsciences,inparticular,independentverificationofdiagnosesanddrugdosagesshouldbemade. Tothefullestextentofthelaw,noresponsibilityisassumedbyElsevier,authors,editorsorcontributorsfor anyinjuryand/ordamagetopersonsorpropertyasamatterofproductsliability,negligenceorotherwise,or fromanyuseoroperationofanymethods,products,instructions,orideascontainedinthematerialherein.
LibraryofCongressControlNumber: 2020933845
ContentStrategist: JessicaL.McCool
ContentDevelopmentManager: MeghanB.Andress
PublishingServicesManager: ShereenJameel
SeniorProjectManager: UmaraniNatarajan
DesignDirection: BridgetHoette
PrintedinChina
Lastdigitistheprintnumber:987654321
Thisbookisdedicatedtomydaughters,SiennaandSasha, whosemerepresencemakesmewanttobeabetterpersonandmakeourworldabetterplace. Girls,alwaysrememberthatyourplaceintheworldis wherever and whatever youwantittobe.
Thefactthatthisbooknowexistsinphysicalformisatestamenttothelove, support,andcountlesssacrificesofseveralpeopleinmylife mostnotablymyparentsandmywife, Sangeeta who,first,convincedmethatIreallycoulddoanythingthatIputmymindto, andthen,second,providedmetherunwaytodoit.
RajSindwani,MD,FACS,FRCS(C)
Preface Thistextbookisasuniqueastheevolvingfieldofendoscopic orbitalsurgery.Morethananyothersphere,contemporary approachestotheorbitandskullbasearetheepitomeofmultidisciplinarycareandthe “teamofteams” approachtoproblemsolving.Theseapproachestakeexquisiteadvantageoftheanatomic realitythatthesinonasaltractislargelyanair-filledcolumnofbony cellsthatcanreadilyberemovedwithoutconsequence.Attheir core,theadvantagesofendoscopicapproachestotheorbitclosely paralleltheadvantagesthatwenowroutinelyleverageduringendoscopicskullbasetechniques namely,direct-lineaccesstopathologyinhard-to-reachareasoftheheadthatweareabletomanage throughthenosewithminimalretractiononsensitiveneurovascularstructures.
Withconcurrentimprovementinofficeexaminationtechniquesandimagingtechnology,clinicianswithaninterestindisordersaffectingtheorbitareoftenabletoachieveincreasedprecision inpreoperativediagnosisandoffertheirpatientsmorerefined,and insomecaseslessinvasive,treatmentoptions.Minimallyinvasive orbitaltechniquesofferthepromiseofamorestreamlinedapproach tocomprehensivepatientcare,improvedpatientsatisfactionand experience,andsuperioroutcomes.
Themoderneraofendoscopicsurgeryoftheorbithaswitnessedanunparalleledpartnershipbetweenthespecialtiesof
otolaryngologyandophthalmology.Beyondeventhiscoredyad, however,thecomplexnatureofendoscopicorbitalsurgery requiresacohesive,multidisciplinaryteamconsistingofotolaryngologists,ophthalmologists,neurosurgeons,endocrinologists, medicalandradiationoncologists,andradiologistsandpathologists.Inadditiontoprovidingexpertiseandperspectivesfrom thesevariousspecialties, EndoscopicSurgeryoftheOrbit (1stedition) alsohighlightsthetwo-surgeon,multihandedsurgicaltechniques thathaveusheredinanewerainmanagingcomplexpathologies involvingtheorbitandskullbase.
Infusedwiththeknowledgeandwisdomofglobalthought leaders,itwasmymissiontoprovideacomprehensiveresourcethat couldserveasanauthoritativetexttopractitionersperforming endoscopicorbitalproceduresandcaringforthesepatients.Iam immenselygratefultomydistinguishedcolleaguesandfriends fortheircontributionstothisimportantproject;yourtimeand dedicationareverymuchappreciated.
Itismysincerehopethatreadersfindthisworkinformative, thought-provoking,entertaining,andinspiring.
RajSindwani,MD,FACS,FRCS(C)
Biography RajSindwani,MD,FACS, FRCS(C)
Dr.SindwaniisvicechairmanandheadoftheSection ofRhinology,Sinus&Skull BaseSurgeryoftheHead& NeckInstituteattheCleveland Clinic.Heisalsoco-directorof theMinimallyInvasiveCranial BaseandPituitaryProgramof theRoseEllaBurkhardtBrain TumorandNeuro-Oncology Center.Hehasheldseveral importantleadershiprolesat theClevelandClinicandis currentlyvicechairmanof
EnterpriseSurgicalOperations.Inthisrole,heandhisteamchampionproceduralandsurgicalsafetyandqualitywhileworkingto addressaccess,efficiency,andservice-linedevelopmentacross theClevelandClinichealthsystem.HealsoservesaspresidentelectofthemedicalstaffandisamemberoftheClevelandClinic BoardofGovernors.
Dr.Sindwaniispresentlytheeditor-in-chiefofthe American JournalofRhinology&Allergy andpasteditor-in-chiefofthe Year BookofOtolaryngology. Heservesonseveralhigh-impacteditorial andscientificadvisoryboardsandhastrainedmanyfellowsandresidents.Heisanestablishedauthorityonthemedicalandsurgical managementofconditionsaffectingthesinuses,orbit,andskull baseandhaspioneeredendoscopicsurgicalapproachestothese regions.Hehaspublishedextensivelyinthefieldandhaslectured atmanyinstitutions,instructionalcourses,andscientificsymposia aroundtheworld.
VideoContents 13-1EndoscopicDacryocystorhinostomy
JessicaW.Grayson
21-1OpticNerveDecompression
NicoleI.Farber
29-1Endoscopic-AssistedOrbitalExenteration
DonaldCharlesLanza
30-1RightOrbitalSubperiostealAbscessDrainage
RonMitchell
33-1EndoscopicRepairofaMedialOrbitalWallFacture
Withthe “MilanTechnique” MarcoMolteni
33-2EndoscopicMedialOrbitalWallReconstructionAfter RemovalofanOrbitalMassViaaTransnasalApproach MarcoMolteni
Contributors OmarH.Ahmed,MD
Fellow,RhinologyandCranialBaseSurgery
DepartmentofOtolaryngology
UniversityofPittsburghMedicalCenter Pittsburgh,PA,UnitedStates
ShaheryarF.Ansari,MD Fellow,PacificNeuroscienceInstitute JohnWayneCancerInstitute Providence’sSaintJohn’sHealthCenter SantaMonica,CA,UnitedStates
LeopoldArkoIV,MD
MinimallyInvasiveEndoscopicSkull BaseFellow
DepartmentofNeurologicalSurgery
WeillCornellMedicalCollege NewYorkPresbyterianHospital NewYork,NY,UnitedStates
CatherineBanks,MD,FRACS
Fellow/ClinicalInstructorinRhinologyandSkull BaseSurgery DepartmentofOtolaryngology
MassachusettsEyeandEarInfirmary HarvardMedicalSchool Boston,MA,UnitedStates
GarniBarkhoudarian,MD,PhD
AssociateProfessor DepartmentofNeuroscienceandNeurosurgery JohnWayneCancerInstitute SantaMonica,CA,UnitedStates
FedericoBiglioli,MD
ProfessorandChair MaxillofacialSurgeryUnit SantiPaoloeCarloHospital,Universitàdegli StudidiMilano Milan,Italy
BenjaminS.Bleier,MD AssociateProfessor DirectorofEndoscopicSkullBaseSurgery Co-DirectorCenterforThyroidEye DiseaseandOrbitalSurgery DepartmentofOtolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery MassachusettsEyeandEarInfirmary HarvardMedicalSchool Boston,MA,UnitedStates
KofiBoahene,MD Professor DepartmentofOtolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery JohnsHopkins Baltimore,MD,UnitedStates
HamidBorghei-Ravazi,MD AssistantProfessor DepartmentofNeurosurgery ClevelandClinicFlorida Weston,FL,UnitedStates
ZacharyJ.Cappello,MD Otolaryngologist CharlotteEye,Ear,Nose,andThroatAssociates Charlotte,NC,UnitedStates
AnaisL.Carniciu,MD DepartmentofOphthalmology UniversityHospitalsClevelandMedicalCenter CaseWesternReserveUniversitySchoolofMedicine Cleveland,OH,UnitedStates
RicardoL.Carrau,MD Professor
DepartmentsofOtolaryngology – Headand NeckSurgery NeurologicalSurgery,andCommunicationSciences andDisorders TheOhioStateUniversity Columbus,OH,UnitedStates
MatthewCassidy,CNIM
IntraoperativeNeuromonitoringWorkleader IntraoperativeNeuromonitoring ClevelandClinicFoundation Cleveland,OH,UnitedStates
RakeshChandra,MD Professor DepartmentofOtolaryngology VanderbiltUniversityMedicalCenter Nashville,TN,UnitedStates
ChandalaChitguppi,MD Fellow,DivisionofRhinologyandSkullBaseSurgery DepartmentofOtolaryngologyandHeadandNeckSurgery ThomasJeffersonUniversity Philadelphia,PA,UnitedStates
BrianH.Chon,MD OculofacialPlasticSurgery ClevelandClinicFoundation,ColeEyeInstitute Cleveland,OH,UnitedStates
GiacomoColletti,MD StaffPhysician MaxillofacialSurgeryUnit SantiPaoloeCarloHospital,UniversitàdegliStudidiMilano Milan,Italy
GustavoCoy,MD Mr. SãoPauloENT&SkullBaseCenter EdmundoVasconcelosHospital SãoPaulo,Brazil
IacopoDallan,MD UnitofOtolaryngology,AudiologyandPhoniatrics UniversityofPisa Pisa,Italy
JacksonDeere,BS MedicalStudent SchoolofMedicine UniversityofTexasSouthwesternMedicalCenter Dallas,TX,UnitedStates
NoraDewart,BSc(Hon) DepartmentofOtolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery UniversityofToronto Toronto,ON,Canada
EricM.Dowling,MD ResidentPhysician DepartmentofOtorhinolaryngology – Head andNeckSurgery MayoClinic Rochester,MN,UnitedStates
CharlesS.Ebert,Jr.,MD,MPH AssociateProfessor DepartmentofOtolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery UNCSchoolofMedicine UniversityofNorthCarolina ChapelHill,NC,UnitedStates
JeanAndersonEloy,MD,FACS,FARS ProfessorandViceChair DepartmentsofOtolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery, NeurologicalSurgery,Ophthalmologyand VisualScience
RutgersNewJerseyMedicalSchool Newark,NJ,UnitedStates
JamesJ.Evans,MD Professor DepartmentofNeurologicalSurgeryandOtolaryngology ThomasJeffersonUniversityHospital Philadelphia,PA,UnitedStates
NicoleI.Farber,MD Resident DepartmentofOtolaryngology RutgersNewJerseyMedicalSchool Newark,NJ,UnitedStates
NyssaFoxFarrell,MD Fellow DepartmentofOtolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery OregonHealth&ScienceUniversity Portland,OR,UnitedStates
JuddH.Fastenberg,MD Fellow,DivisionofRhinologyandSkullBaseSurgery DepartmentofOtolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery ThomasJeffersonUniversity Philadelphia,PA,UnitedStates
GiovanniFelisati,MD ProfessorandChair OtorhinolaryngologyUnitandHeadandNeckDepartment SantiPaoloeCarloHospital,UniversitàdegliStudidiMilano Milan,Italy
JuanC.Fernandez-Miranda,MD Professor DepartmentofNeurosurgery SurgicalDirector BrainTumor,SkullBaseandPituitaryCenters StanfordUniversity Stanford,CA,UnitedStates
PaulA.Gardner,MD
AssociateProfessor
DepartmentsofNeurologicalSurgeryand Otolaryngology UniversityofPittsburghSchoolofMedicine Co-Director CenterforCranialBaseSurgery UniversityofPittsburghMedicalCenter Pittsburgh,PA,UnitedStates
InbalGazit,MD
DepartmentofOphthalmology AssafHarofehMedicalCenter Tzrifin,Isreal
ChristosGeorgalas,MD,PhD,MRCS(England), DLO,FRCS(ORL-HNS)
ConsultantandOtolaryngologist – Headand NeckSurgeonDirectorofEndoscopicSkull BaseCenter
HygeiaHospital Athens,Greece ProfessorofSurgery St.George’sMedicalSchoolatNicosiaUniversityProgram Nicosia,Greece
KyleJ.Godfrey,MD
DivisionofOphthalmicPlastic,Reconstructive, andOrbitalSurgery DepartmentofOphthalmology WeillCornellMedicalCollege NewYork,NY,UnitedStates; DivisionofOculoplasticandOrbitalSurgery DepartmentofOphthalmology HarknessEyeInstitute ColumbiaUniversityMedicalCenter NewYork,NY,UnitedStates
EzequielGoldschmidt,MD,PhD Intra-ResidencyFellow,OpenandEndoscopic CranialBaseSurgery DepartmentofNeurosurgery UniversityofPittsburgh Pittsburgh,PA,UnitedStates
JessicaW.Grayson,MD RhinologyandSkullBaseResearchGroup AppliedMedicalResearchCentre UniversityofNewSouthWales AustralianSchoolofAdvancedMedicine MacquarieUniversity Sydney,Australia
AshleighA.Halderman,MD AssistantProfessor DepartmentofOtolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery UniversityofTexasSouthwesternMedicalCenter Dallas,Texas,UnitedStates
JohnF.Hardesty,MD DepartmentofOphthalmologyandVisualSciences WashingtonUniversitySchoolofMedicine St.Louis,MO,UnitedStates
MorrisE.Hartstein,MD,FACS Director,OphthalmicPlasticandReconstructive Surgery DepartmentofOphthalmology AssafHarofehMedicalCenter Zerfin,Israel ClinicalAssociateProfessor DepartmentofOphthalmology SaintLouisUniversity St.Louis,MO,UnitedStates
RichardJ.Harvey,MD,PhD Professor RhinologyandSkullBaseSurgery,AppliedMedicalResearch Centre UniversityofNewSouthWales Sydney,Australia Professor FacultyofMedicineandHealthScience MacquarieUniversity Sydney,Australia
StephenC.Hernandez,MD AssistantProfessor LSUSchoolofMedicine NewOrleans,LA,UnitedStates
EricHink,MD AssociateProfessor DepartmentsofOtolyngology – HeadandNeck SurgeryandOphthalmology UniversityofColoradoSchoolofMedicine Aurora,CO,UnitedStates
JohnBryanHolds,MD,FACS OphthalmicPlasticandCosmeticSurgery,Inc. DesPeres,MO,UnitedStates DepartmentsofOphthalmologyandOtolaryngology – Head andNeckSurgery SaintLouisUniversity St.Louis,MO,UnitedStates
WayneD.Hsueh,MD AssistantProfessor DepartmentofOtolaryngology – Headand NeckSurgery CenterforSkullBaseandPituitarySurgery Neurologica lInstituteofNewJersey RutgersNewJerseyMedicalSchool Newark,NJ,UnitedStates
CatherineJ.Hwang,MD
OculofacialPlasticSurgery
ClevelandClinicFoundation
ColeEyeInstitute Cleveland,OH,UnitedStates
ChristopherKarakasis,MD AssociateStaff
DivisionofNeuroradiology ClevelandClinic Cleveland,OH,UnitedStates AssistantProfessor DiagnosticRadiology LernerCollegeofMedicineofCaseWestern ReserveUniversity Cleveland,OH,UnitedStates
MichaelKazim,MD
DivisionofOculoplasticandOrbitalSurgery DepartmentofOphthalmology HarknessEyeInstitute ColumbiaUniversityMedicalCenter NewYork,NY,UnitedStates
DanielF.Kelly,MD Director,PacificNeuroscienceInstitute DepartmentofNeurosurgery PacificNeuroscienceInstitute SantaMonica,CA,UnitedStates
KathleenM.Kelly,MD ResidentPhysician
DepartmentofOtolaryngology – Headand NeckSurgery UTSouthwesternMedicalCenter Dallas,TX,UnitedStates
AdamJ.Kimple,MD,PhD AssistantProfessor Otolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery UNCSchoolofMedicine UniversityofNorthCarolinaatChapelHill ChapelHill,NC,UnitedStates
ToddT.Kingdom,MD Professor
DepartmentsofOtolyngology – HeadandNeckSurgery andOphthalmology UniversityofColoradoSchoolofMedicine Aurora,CO,UnitedStates
CourtneyLynnKraus,MD DepartmentofOphthalmology JohnsHopkinsUniversity Baltimore,MD,UnitedStates
HowardKraus,MD ProfessorofSurgery DirectorofEye,Ear&SkullBaseCenter JohnWayneCancerInstitute ProvidenceSaintJohn’sHealthCenter SantaMonica,CA
VarunR.Kshettry,MD Physician DepartmentofNeurosurgery ClevelandClinic Cleveland,OH,UnitedStates
EdwardC.Kuan,MD,MBA AssistantProfessor DepartmentofOtolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery UniversityofCalifornia,Irvine Irvine,CA,UnitedStates
AndrewP.Lane,MD Professor DepartmentofOtolaryngology – Headand NeckSurgery JohnsHopkinsUniversitySchoolofMedicine Baltimore,MD,UnitedStates
DonaldCharlesLanza,MD,MS Director Rhinology&SkullBaseSurgery SinusandNasalInstituteofFloridaFoundation St.Petersbrug,FL,UnitedStates
VictoriaS.Lee,MD AssistantProfessor DepartmentofOtolaryngology – Headand NeckSurgery UniversityofIllinoisatChicagoCollegeof Medicine Chicago,IL,UnitedStates
RiccardoLenzi,MD,PhD ConsultantOtorhinolaryngologist AziendaUSL,Toscana,NordOvest UnitofOtorhinolaryngology ApuaneHospital Massa,Italy
JamesK.Liu,MD,FACS,FAANS Professor DepartmentsofOtolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery andNeurologicalSurgery CenterforSkullBaseandPituitarySurgery NeurologicalInstituteofNewJersey RutgersNewJerseyMedicalSchool Newark,NJ,UnitedStates
LisaD.Lystad,MD
Neuro-Ophthalmology ColeEye ClevelandClinicFoundation Cleveland,OH,UnitedStates
RobiNicolasMaamari,MD OphthalmicPlasticandCosmeticSurgery,Inc. DesPeres,MO,UnitedStates; DepartmentofOphthalmologyandVisual SciencesOculoplasticsfellow WashingtonUniversitySchoolofMedicine St.Louis,MI,UnitedStates
JoãoMangussi-Gomes,MD SãoPauloENT&SkullBaseCenter EdmundoVasconcelosHospital SãoPaulo,Brazil
RalphB.Metson,MD Professor DepartmentofOtolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery MassachusettsEyeandEar HarvardMedicalSchool Boston,MA,UnitedStates
KapilMishra,MD ResidentPhysician DepartmentofOphthalmology WilmerEyeInstitute JohnsHopkinsHospital Baltimore,MD,UnitedStates
RonMitchell,MD ProfessorandChief DepartmentofOtolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery SchoolofMedicine UniversityofTexasSouthwesternMedicalCenter Dallas,TX,UnitedStates
KrisS.Moe,MD,FACS ProfessorandChief,DivisionofFacialPlasticSurgery DepartmentsofOtolaryngologyandNeurologicalSurgery UniversityofWashingtonSchoolofMedicine Seattle,WA,UnitedStates
LucaMuscatello,MD
AziendaUSLToscanaNordOvest UnitofOtorhinolaryngology ApuaneHospital Massa,Italy
DileepNair,MD SectionHeadofAdultEpilepsy EpilepsyCenter ClevelandClinic Cleveland,OH,UnitedStates
JohnNguyen,MD AssociateProfessor FellowshipDirector
OphthalmicPlastic&ReconstructiveSurgery DepartmentofOphthalmology&VisualSciences WestVirginiaUniversity Morgantown,WV,UnitedStates
LeahNovinger,MD,PhD Resident DepartmentofOtolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery IndianaUniversitySchoolofMedicine Indianapolis,IN,UnitedStates
GurstonG.Nyquist,MD AssociateProfessor DivisionofRhinologyandSkullBaseSurgery DepartmentofOtolaryngologyandNeurologicalSurgery ThomasJeffersonUniversityHospital Philadelphia,PA,UnitedStates
LiorOr,MD DepartmentofOphthalmology AssafHarofehMedicalCenter Tzrifin,Israel
JamesN.Palmer,MD ProfessorofOtorhinolaryngology DivisionofRhinology DepartmentofOtorhinolaryngology – HeadandNeck Surgery UniversityofPennsylvania Philadelphia,PA,UnitedStates
JulianD.Perry,MD OculofacialPlasticSurgery ClevelandClinicFoundation,ColeEyeInstitute Cleveland,OH,UnitedStates
AnastasiaPiniara,MD,MSc ConsultantandOtolaryngologist – HeadandNeckSurgeon HygeiaHospital Athens,Greece
DanielM.Prevedello,MD Professor DepartmentofNeurologicalSurgery TheOhioStateUniversity Columbus,OH,UnitedStates
MindyR.Rabinowitz,MD AssistantProfessor DivisionofRhinologyandSkullBaseSurgery DepartmentofOtolaryngologyandNeurologicalSurgery ThomasJeffersonUniversity Philadelphia,PA,UnitedStates
HassanRamadan,MD ProfessorandChairman DepartmentofOtolaryngology
WestVirginiaUniversity Morgantown,WV,UnitedStates
PabloF.Recinos,MD
SectionHead,SkullBaseSurgery DepartmentofNeurosurgery
BrainTumorandNeuro-OncologyCenter ClevelandClinic Cleveland,OH,UnitedStates
RoxanaY.Rivera,MD
Director,OculoplasticandOrbitalSurgeryService UniversityHospitalsClevelandMedicalCenter AssistantProfessorofOphthalmology CaseWesternReserveUniversitySchoolofMedicine Cleveland,OH,UnitedStates
MarcR.Rosen,MD
Professor,DivisionofRhinologyandSkullBaseSurgery DepartmentofOtolaryngologyandNeurologicalSurgery ThomasJeffersonUniversityHospital Philadelphia,PA,UnitedStates
ChristopherR.Roxbury,MD AssistantProfessor DivisionofOtolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery UniversityofChicago Chicago,IL,UnitedStates
PaulRuggieri,MD Chief DivisionofNeuroradiology ClevelandClinic Cleveland,OH,UnitedStates
CharlesSaadeh,MD Resident DepartmentofOtolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery SchoolofMedicine UniversityofTexasSouthwesternMedicalCenter Dallas,TX,UnitedStates
RaymondSacks,MD
RhinologyandSkullBaseResearchGroup AppliedMedicalResearchCentre UniversityofNewSouthWales; AustralianSchoolofAdvancedMedicine MacquarieUniversity; DepartmentofOtolaryngology UniversityofSydney Sydney,Australia
SoumyaSagar,MBBS ClinicalResearchFellow DepartmentofNeurosurgery BrainTumorandNeuro-OncologyCenter ClevelandClinic Cleveland,OH,UnitedStates
AlbertoMariaSaibene,MD,MA StaffPhysician OtorhinolaryngologyUnit SantiPaoloeCarloHospital UniversitàdegliStudidiMilano Milan,Italy
GriffinD.Santarelli,MD AssistantProfessor BarrowNeurologicalInstitute Phoenix,AZ,UnitedStates
JamieLeaSchaefer,MD Fellow DepartmentofOphthalmology &VisualSciences WestVirginiaUniversity Morgantown,WV,UnitedStates
TheodoreH.Schwartz,MD
ProfessorofNeurosurgery,Otolaryngologiy,Neurology andNeuroscience DepartmentofNeurologicalSurgery WeillCornellMedicalCollege NewYorkPresbyterianHospital NewYork,NY,UnitedStates
RajeevD.Sen,MD
Resident DepartmentofNeurologicalSurgery UniversityofWashingtonSchool ofMedicine Seattle,WA,UnitedStates
GopiShah,MD AssistantProfessor DepartmentofOtolaryngology – Headand NeckSurgery DivisionofPediatricOtolaryngology SchoolofMedicineandChildren's MedicalCenter UniversityofTexas SouthwesternMedicalCenter Dallas,TX,UnitedStates
RajSindwani,MD,FACS,FRCS(C) ViceChairmanandSectionHead Rhinology,Sinus&SkullBaseSurgery HeadandNeckInstitute Co-Director
MinimallyInvasiveCranialBase&Pituitary SurgeryProgram RosaEllaBurkhardtBrainTumor&Neuro-Oncology Center ViceChairofEnterpriseSurgicalOperations ClevelandClinic Cleveland,OH,UnitedStates
ArunD.Singh,MD ColeEyeInstitute ProfessorofOphthalmology Director,OphthalmicOncology ClevelandClinicFoundation Cleveland,OH,UnitedStates
CarlH.Snyderman,MD,MBA Professor
DepartmentsofOtolaryngologyandNeurological Surgery
UniversityofPittsburghSchoolofMedicine Pittsburgh,PA,UnitedStates Co-Director CenterforCranialBaseSurgery UniversityofPittsburghMedicalCenter Pittsburgh,PA,UnitedStates
AldoC.Stamm,MD,PhD SãoPaulo,ENT&SkullBaseCenter EdmundoVasconcelosHospital SãoPaulo,Brazil
HeinzStammberger,MD(Deceased) Professor DepartmentofGeneralOtorhinolaryngology,Headand NeckSurgery MedicalUniversityofGraz Graz,Austria
JanaleeK.Stokken,MD AssistantProfessor DepartmentofOtorhinolaryngology – Headand NeckSurgery MayoClinic Rochester,MN,UnitedStates
EricSuccar,MD Instructor DepartmentofOtolaryngology VanderbiltUniversityMedicalCenter Nashville,TN,UnitedStates
PeterF.Svider,MD DepartmentofOtolaryngology – Headand NeckSurgery
RutgersNewJerseyMedicalSchool Newark,NJ,UnitedStates
LuisamTarrats,MD,JD Director DepartmentofRhinologyandSkullBaseSurgery LaClínicadeRinosinusitis,LLC Cayey,PuertoRico AssistantProfessor DepartmentofOtolaryngology – Headand NeckSurgery UniversityofPuertoRico SanJuan,PuertoRico
BrianD.Thorp,MD AssistantProfessor DepartmentofOtolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery UNCMedicalSchool UniversityofNorthCarolinaatChapelHill ChapelHill,NC,UnitedStates
JonathanY.Ting,MD,MS,MBA InterimChair DepartmentofOtolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery IndianaUniversitySchoolofMedicine Indianapolis,IN,UnitedStates
PeterValentinTomazic,MD,PhD AssociateProfessor DepartmentofGeneralOtorhinolaryngology – Head andNeckSurgery MedicalUniversityofGraz Graz,Austria
KyleK.VanKoevering,MD AssistantProfessor,CranialBaseSurgery Otolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery UniversityofMichigan AnnArbor,MI,UnitedStates
ErichVyskocil,MD DepartmentofOtorhinolaryngologyHeadandNeckSurgery MedicalUniversityofVienna Vienna,Austria
EricW.Wang,MD AssociateProfessor
DepartmentsofOtolaryngology,NeurologicalSurgery andOphthalmology DirectorofEducation,CenterforCranialBaseSurgery UniversityofPittsburghMedicalCenter Pittsburgh,PA,UnitedStates
IanJ.Witterick,MD,MSc,FRCSC ProfessorandChair
DepartmentofOtorhinolaryngology – Headand NeckSurgery UniversityofToronto Toronto,ON,Canada
PeterJ.Wormald,MD,FAHMS,FRACS,FRCS(Ed), FCS(SA),MBChB
ProfessorOtolaryngologyHeadandNeckSurgery ProfessorSkullBaseSurgery DepartmentofOtolaryngologyHeadsandNeckSurgery UniversityofAdelaide Adelaide,Australia
HabibZalzal,MD Physician Otolaryngology WestVirginiaUniversity Morgantown,WV,UnitedStates
AdamM.Zanation,MD AssociateProfessor DepartmentofOtolaryngology – HeadandNeckSurgery UNCSchoolofMedicine UniversityofNorthCarolinaatChapelHill ChapelHill,NC,UnitedStates
EndoscopicOrbitalSurgery: TheRhinologist’sPerspective RALPHB.METSON,MD
Thespecialtiesofotolaryngologyandophthalmologyare separatedbylittlemorethanthewidthofthelamina papyracea.Thispaper-thinbonethatformstheboundary betweentheorbitalandsinonasalcavitiesservesasametaphorfor thealignedinterestsoftwospecialtieswhosepractitionersoften findthemselvesoperatingincloseanatomicproximity.Indeed, cooperativesurgicalendeavorsbetweenotolaryngologistsandophthalmologistshaverisenrapidlysincetheintroductionofnasal endoscopestotreatpatientswithorbitaldisorders.
EndoscopicDacryocystorhinostomy Beforetheendoscopicage,attemptstosurgicallytreatorbitaldisease throughatransnasalapproachwereoftenfraughtwithpoorvisualizationandpooroutcome.Thebestdocumentedattempttoperform adacryocystorhinostomy(DCR)throughthenosewasdescribedin 1921byHarrisP.Mosher,whothenservedaschairmanofthe DepartmentofOtologyandLaryngologyatHarvardMedical School.1 Usingaheadlightandnasalspeculum,hedescribedthe drainageofpusfromtheinfectedlacrimalsacsof12patients. Althoughthisintranasalapproachavoidedtheneedforafacialincision,apostoperativeorbitalinfectiondevelopedinonepatientwho almostlosthereye,promptingMoshertoabandontheprocedurein favorofacombinedexternal-intranasalapproach.Inhiswords, “Wherelightispossibleitisfollytoworkinthedark.Thebestsurgeryisdonebysight.” Forthenext70years,DCRswereperformed almostexclusivelyinanexternalmannerthroughamedialcanthal incision,andlargelybyophthalmologists.
Withtheadventofsmall-diameter,high-resolutionnasalendoscopesforsinussurgeryinthemid-1980s,arenewedinterestdevelopedinthepossibilityofaccessingorbitalpathologythroughthe nose.Otolaryngologistsfoundthemselvesroutinelyoperatingin thevicinityofthelacrimalsacastheycleareddiseasefromadjacent ethmoidaircellsunderexcellentvisualization.Whiledoingso,the potentialtoreadilyaccessthemedialorbitalstructuresviaatransnasalapproachbecamereadilyapparent,andearlyreportsinthe literaturesupportedtheconcept.2
In1989,IwasapproachedbyDanielTownsend,anophthalmologistatMassachusettsEyeandEarInfirmary,whohadrecently performedanexternalDCRona52year-oldwoman,onlytohave hertroublesometearingreturn3monthslater.WhenIexamined thepatientintheofficewithanasalendoscope,adensescarband couldbeseenoverlyingtheregionofthelacrimalsacalongthe
lateralnasalwall.Sheappearedtobeanidealcandidatetorevisit Mosher’sintranasalDCRapproach,thistimewiththenecessary “light” andvisualizationtoperformasafeandeffectivesurgery.
Thetriptotheoperatingroomprovedtobeafruitfulone.The ophthalmologistpassedlacrimalprobesthroughthecanaliculito localizetheobstructedlacrimalsacwhileIresectedthescartissue andmadeawideopeningaroundtheprobesintothesac.The patienttoleratedthe90-minuteprocedurewell,andherepiphora hasnotreturnedinmorethan30years.
TheearlysuccessofendoscopicDCRledtoitsrelativelyrapid adoptionbyothersurgeonsatourhospitalandacrossthecountry. ThebenefitsofavoidingafacialincisionandreducingpatientmorbidityofferedbyendoscopicDCRwereobvious.However,notso obviousatthetimewerethesubtletiesofpatientselectionandsurgicaltechniquethataffectedclinicaloutcome.
Onesuchexamplewastheuseofsurgicallasers,whichwere quitepopularatthetime,fortheperformanceofendoscopic DCR.3 Althoughlaserfiberscouldbepassedthrougheitherthe tearductornosetoremoveboneoverlyingthelacrimalsac,their useledtopostoperativescarformationandrestenosis.LaserendoscopicDCRhadasuccessrateof78%comparedwitharateof morethan90%forconventionalDCR.Becauseoftheseearlysetbacks,endoscopicDCRlostfavoramongmanyophthalmologists whocontinuedtoperformconventionalexternalDCR.Nevertheless,withincreasingclinicalexperience,theperformanceofendoscopicDCRwasrefinedanditsadoptiongrewworldwide. Numerousreportsoverthepastdecadehavedescribedthesafety andefficacyofthistechniquewithresultscomparabletothose ofexternalDCR.4
KeyConceptsandLessonsLearned Overthepast30years,personalexperiencesupportedby evidenced-basedstudieshastaughtmemanylessonsregarding theperformanceofendoscopicDCR.Theselessonshavebeen reinforcedbythemorethantwodozenreferringophthalmologists withwhomIhavesharedthisjourney.Thefollowinglistenumeratessomeofthelessonslearned.
1. Thebenefitsofateamapproach. PatientswhoundergoendoscopicDCRarebestservedwhentheircareisprovidedbyboth anophthalmologistandotolaryngologist.Thecomplementary skillsetsofthesespecialistsallowsforoptimaltreatmentofthese patients,includingpreoperativeirrigationofthelacrimal
apparatus,intraoperativeintubationofthecanaliculi,andpostoperativedebridementofthesurgicalsite.
2. Startingwithrevisioncases. WhenlearningtoperformendoscopicDCRs,keepinmindthatrevisioncasesareusuallyeasier thanprimaryones,becausethethickboneoverlyingthesachas alreadybeenremoved.Inaddition,ophthalmologistsaremore likelytoreferoneoftheirpatientsinwhomexternalDCRwith recurrentepiphorahasfailed.Suchinitialcasesoftenleadto happypatientsandahappyreferringophthalmologist.
3. Adequateexposureofthelacrimalsac.Thetechniqueusedto removethickboneoverlyingthelacrimalsac drill,rongeur, ultrasonicaspirator isnotnearlyasimportantasthelocation andamountofboneremoved.Theimportantthingisto removethethickboneanteriortothemaxillarylinetoprovide adequateexposureoftheentiremedialsacwall.
4. Placementoflacrimalstents. Althoughplacementofastent throughthenewlycreatedinternallacrimalostiumattheconclusionofendoscopicDCRmaynotbenecessaryinmostcases, doingsohaslowpatientmorbidityandmayhelpwithpostoperativedebridementandhealing.
5. Visualizationoftheinternalcommonpunctumattheconclusionofsurgery. ThegoalofendoscopicDCRisnasalization oftheinternalcommonpunctum.Thispunctumisvisibleas theopeningthroughwhichthelacrimalstententersthelateral sacwall.Ifthispunctumisvisibleattheconclusionofsurgery, thechancesarehighforasuccessfulsurgicaloutcome.
6. PerformanceofseptoplastyattimeofendoscopicDCR. Ifa superiorseptaldeflectionlimitsaccesstotheregionofthe lacrimalsac,thepractitionershouldhavealowthresholdfor performingseptoplastyimmediatelybeforeendoscopicDCR. Adequatevisualizationandexposurearekeytosafeandeffective endoscopicsurgery.
7. Postoperativedebridement. Removaloftissueanddebris fromthesurgicalsiteunderendoscopicguidance1weekafter surgeryisjustasimportantafterDCRasitisaftersinussurgery. Movementofthelacrimalstentwithblinkingasseenonendoscopyatthetimeofdebridementsuggestspatenttearflowandis apositiveprognosticsignforsuccessfulsurgery.
8. IntranasalcausesofDCRfailure. Themostcommoncauses ofDCRfailure,whetherperformedthroughanendoscopicor externalapproach,areduetointranasalpathology.Suchpathology,includingadhesionsandobstructingturbinates,canbe readilyvisualizedonpostoperativeendoscopicexamination andaddressedatthetimeofrevisionendoscopicDCR.
EndoscopicOrbitalDecompression NotlongafterthesuccessfulintroductionofendoscopicDCR, sinussurgeonsbegantoconsiderotherpossibilitiesfortransnasal treatmentoforbitalpathology.Atthecompletionofroutineethmoidectomyforchronicrhinosinusitis,theskeletonizedlamina papyraceawasinfullview,yetitspenetrationwasassiduously avoidedforfearofexposingorbitalfatandcausinginjuryto intraorbitalstructures.
Thoseofuswhotrainedinotolaryngologybeforetheendoscopic erawerefamiliarwiththeWalsh-Oguratransantralapproachfor treatmentofpatientswithexophthalmosfromGraves’ disease.5 Surgerystartedwithatransoralincisiontoopenthemaxillaryand ethmoidsinuses.Thebonyorbitalfloorandlaminapapyraceawere thenremoved,resultinginorbitaldecompressionwithimmediate reductioninproptosis.Butcouldsimilarsurgerybeperformed
throughanendoscope?Theanswercamein1990whenDavid Kennedyandhisophthalmologiccolleague,NeilMiller,atJohns Hopkinsdescribedthesuccessfultreatmentofeightpatientswith Graves’ orbitopathyusinganendoscopictechnique.6 Twoofthe patientsunderwentsimultaneousWalsh-Oguraprocedurestoverify thatadequatebonehadbeenremovedendoscopicallyalongthe orbitalfloor.
Laterthatyear,IwasapproachedbyJohnShore,aninnovative ophthalmologistatMassachusettsEyeandEar,whohada38-yearoldpatientwithaseverecaseofGraves’ orbitopathy.Hewasparticularlyconcernedaboutimpendingvisionlossinthisindividual whohadalreadyhadavision-threateningcornealabrasionandwas inneedofathoroughdecompression,includingtheregionofthe orbitalapex,whichcanbedifficulttovisualizethroughaconventionalapproach.
Whenwetookthisfirstpatienttotheoperatingroom,theophthalmologistwasamazedattheexcellentvisualizationintheregion oftheorbitalapexaffordedbytheendoscope.Afterremovalofthe entirelaminapapyracea,Iincisedtheperiorbitainaposterior-toanteriordirection,resultinginimmediateprolapseoforbitalfat andreductioninthepatient’sproptosis.Atenseorbitwasnowsoft, andthereferringphysicianwasnowsoldontheadvantagesofan endoscopicapproachtothemedialorbit.Aweekaftersurgery,the patient’sexophthalmoswas8mmlessthanitspreoperativelevel, buthedidnothavethepostoperativefacialswelling,numbness, andecchymosisassociatedwithnonendoscopicapproachesto theorbit.Theenhancedvisualizationandreducedpatientmorbidityaffordedbytheapproachtothemedialorbitledtoarapid growthinthenumberofendoscopicdecompressionsperformed nationwideduringthe1990s.7
Withinthefirst5yearsofperformingorbitaldecompressions, however,anunanticipatedproblembecameevident:development ofnew-onsetdiplopiathatwasdifficultforthestrabismussurgeons tocorrect.Wehadknownformanyyearsthatdoublevisionwasan expectedsequelatoorbitaldecompressioninmanypatients,but theseverityandincidenceofthediplopiawastroubling.Ananalysisofourresultssuggestedthattheproblemwasduetothethoroughnessofmedialorbitaldecompressionwhenperformedwith endoscopicinstrumentationcomparedwithconventionaltransantralortransorbitalapproaches.Removaloftheentirelaminapapyraceaandperiorbitaresultedinagreaterprolapseoforbitalfatand herniationofthemedialrectusmuscleintothesinonasalcavities thanoccurredwithconventionalapproaches.Thisfindingwasparticularlyapparentinpatientswhohadundergoneonlymedial decompressionwithoutaconcurrentlateraldecompression.
Similarfindingswerereportedbyotherauthorswhorecommendedtheuseofa “balanceddecompression” techniquewith concurrentmedialandlateraldecompressionsatthesameoperative setting.8 Thisbalanceddecompressionresultedinasignificantly lowerincidenceofpostoperativediplopia.Itmadesensethatthe lateraldecompressionrelievedinwardpressureontheorbitalcontents,resultinginlessmedialdisplacementoftheorbitalcontents, includingthemedialrectusmuscle,andtherebycausedlessdouble vision.BalanceddecompressionsarenowperformedonthemajorityofpatientswithGraves’ diseaseinmypracticewhorequiresurgicaldecompression.Onlythosewithrelativelymildproptosisand noopticneuropathyundergomedialdecompressionalone.
AnotherproceduredevelopedtoreducetheincidenceofpostoperativediplopiainpatientswithGraves’ orbitopathyisknownas the “orbitalsling” technique.A10-mmwidestripoftheperiorbita overlyingthemedialrectusmuscleispreservedtopreventmedial displacementofthemuscleduringsurgery.Orbitalfatisfreeto
herniateaboveandbelowthefascialsling,providingadequate decompressionoftheorbitalcontents.Whenabalancedtechnique isusedinthemajorityofpatients,supplementedbytheuseofan orbitalslinginselectpatients,theresultsofendoscopicorbital decompressionarecomparabletothoseoftransantralandtransorbitaltechniques,includingthedegreeofdecompressionachieved andrelativelylowincidenceofpostoperativecomplications.9,10
UnlikeendoscopicDCR,ophthalmologistsgravitatedrelatively quicklytotheconceptofendoscopicorbitaldecompression.They realizedtheobviousadvantagesofendoscopicinstrumentationfor suchsurgery,includingbettervisualizationalongtheskullbaseand amorecompleteremovalofthelaminapapyraceathancouldbe achievedwithconventionalapproaches.Themajorityoforbital decompressionsperformedtodayuseateamapproach.Itiscommonfortheororhinolaryngologisttoperformthemedialportion ofthedecompressionwhiletheophthalmologistfollowswiththe lateraldecompression.
KeyConceptsandLessonsLearned Specifictechniquesusedfororbitaldecompressionaredependent ontheindividualpatient’spathologyandthesurgeon’spreferences.Nevertheless,personalexperienceoverthepastthree decades,combinedwithevidenced-basedstudies,hasledtoageneralsetofprinciplesthatIapplyinthetreatmentofpatientsrequiringendoscopicorbitaldecompression:
1. Endoscopicorbitaldecompressionisonlythefirststepinthe rehabilitationofmanypatientswithGraves’ orbitopathy. Oncetheproptosishasbeensuccessfullyreduced,aseriesofadditionalsurgicalproceduresperformedbytheophthalmologistare oftennecessarytoachievethedesireddegreeofnormalfunction andappearance.Theseproceduresmayincludeloweringthepositionoftheuppereyelid,whichisoftenelevatedinGraves’ disease, andstrabismussurgerytoaddressanyresidualdiplopia.
2. Abalanceddecompressiondecreasestheincidenceofpostoperativediplopia. Postoperativediplopiaisanexpectedsequela, notacomplication,ofendoscopicorbitaldecompressionin manypatients.Nevertheless,theincidenceofdoublevision canbereducedbytheperformanceofconcurrentmedialandlateralorbitaldecompressioninthesameoperativesetting.
3. Theuseofanorbitalslingtechniquecanfurtherdecreasethe incidenceofpostoperativediplopiainselectpatients. Preservationofa10-mmwidestripoftheperiorbitaoverlyingthe medialrectusmusclehelpstostabilizethemusclepositionand function,particularlyinpatientswithoutpreexistingdiplopia.
4. Patientswhopresentwithopticneuropathyshouldhave completeremovaloflaminapapyraceaintheregionofthe orbitalapex. Decompressionoftheorbitalapexregioneffectivelyremovespressureontheopticnerveandleadstoimproved visioninmanypatientswithvisuallossfromopticneuropathy.
5. Preservetheanterior,notposterior,inframedialorbital strut(IOS). TheanteriorportionoftheIOS(locatedanterior tothemaxillaryostium)isroutinelyleftinplaceduringendoscopicmedialorbitaldecompression.PreservationoftheposteriorportionofIOSmakesdecompressiontechnicallymore difficultandalterspostoperativediplopiaonlytothedegreethat itreducesthedegreeoforbitaldecompression.
6. Revisionorbitaldecompressionisbeneficialinselect patients. Incasesofpersistentorrecurrentproptosisafter decompressionsurgery,removalofanyremainingbonealong themedialorbitwallorfloormayresultintheadditional desireddegreeofdecompression.
EndoscopicOpticNerveDecompression Endoscopicopticnervedecompressionisanaturalextensionof orbitaldecompression.Boneremovalalongtheposteriororbitis continuedintothesphenoidsinusfollowingtheopticcanalasit coursesalongthelateralsphenoidwall.Inthe1990s,arelatively largenumberofopticnervedecompressionswereperformedon patientswholostvisionafterheadtrauma,particularlyduring motorvehicleaccidents.Therewasmuchdebateatthetimeas tothebestsurgicalapproachtousetodecompresstheopticnerve inpatientswholostvisionafterheadtrauma endoscopic,open, transorbital,ortranscranial.Thedebateendedwhenhigh-dosesteroidswerefoundtobejustaseffectiveassurgicaldecompressionof theopticcanalinthesepatients.10
Mostindividualswhopresentwithopticneuropathyas acomponentofGraves’ orbitopathydoverywellafterendoscopic orbitaldecompressionalone.Providedadequateboneisremoved todecompresstheregionoftheorbitalapex,theirneuropathy, includingtheassociatedcolorblindnessandvisualfieldloss, usuallyresolves.Someophthalmologists,however,dofavor decompressionoftheopticcanalattimeofendoscopicorbital decompressioninpatientswithsevereopticneuropathy.
Endoscopicopticnervedecompressionremainsanexcellent procedureinthosepatientswhosevisuallossisduetocompression oftheopticnervewithinthesphenoidsinusfromneoplasms,such asmeningiomas,orosseouslesions,suchasfibrousdysplasia.Experiencehasshownthatunroofingthebonycanalintheaffectedarea issufficienttorestorevisioninmostcases.Incisionoftheoptic nervesheathisnotnecessary.10
EndoscopicResectionofOrbitalTumors Theinferiorandmedialrectusmusclesareroutinelyexposedduringendoscopicorbitaldecompression.Manipulationofthesemusclestogainaccesstotheintraconalregionoftheorbitwasanatural extensionofthissurgicalapproach.Successfulendoscopicremoval oftumorsofthemedialorbithasbeendescribedbyanumberof authors.11 Mostoftheearlyexperiencewaswithresectionoforbital hemangiomas,whicharenotonlythemostcommonintraorbital tumorencounteredbutalsoarewellencapsulated,facilitatingtheir dissectionfromsurroundingorbitalcontents.Asexperiencewith thesetechniqueshasadvanced,thesize,location,andpathology oforbitaltumorssuccessfullyresectedthroughanendoscopic approachhavealsoadvanced.
FutureDirections Thehistoryofendoscopicorbitalsurgeryoverthepast30years reflectsanaturalprogressionofsurgicalexploration:fromsuperficialtodeep,frommedialtolateral.Asboththetechniquesand technologiesassociatedwithendoscopicorbitalsurgeryadvance, sotoowilltheindications,extent,andsuccessoftheseprocedures. Iforeseethedaywhenotolaryngologistswillworkwithophthalmologiststoperformsurgeryonextraocularmuscles retrieval oflostmusclesduringstrabismussurgery,andremodelingofdiseasedmusclesfromGraves’ disease.Endoscopicinstrumentation alsohaspotentialbenefitsinthefieldofneuroophthalmology placementofretinalandopticnerveimplants,fenestrationof theopticnervefortreatmentofpatientswithvisuallossfromintracranialhypertension,anddecompressionoftheopticnervein patientswithischemicneuropathy.
Conclusion Thefieldsofotolaryngologyandophthalmologywereonceasingle specialty.Theadventofendoscopictechniquestotreatpatients withorbitaldisordershasservedtofosterthecollaborativeefforts ofsurgeonsinthesetwospecialtiesonceagain.Withthegrowing useofendoscopicinstrumentationtotreatorbitaldisease,the futureofendoscopicorbitalsurgeryisabrightone,enablingsurgeonsandtheirpatientstotruly “seethelight.”
References 1.Mosher,H.P.(1921).Re-establishingintranasaldrainageofthe lacrymalsac. Laryngoscope, 31,492–512.
2.McDonogh,M.,&Meiring,J.H.(1989).Endoscopictransnasal dacryocystorhinostomy. JournalofLaryngologyandOtology, 103(6), 585–587.
3.Metson,R.,Wong,J.J.,&Puliafito,C.A.(1994).Endoscopiclaser dacryocystostomy. Laryngoscope, 104(8Pt1),269–274.
4.Kingdom,T.T.,Barham,H.P.,&Durairaj,V.D.(2019).Long-term outcomesafterendoscopicdacryocystorhinostomywithoutmucosal flappreservation. Laryngoscope https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.27989
5.Walsh,T.E.,&Ogura,J.H.(1957).Transnasalorbital decompressionformalignantexophthalmos. Laryngoscope , 67(6). 544 – 568.
6.Kennedy,D.W.,Goldstein,M.L.,Miller,N.R.,&Zinreich,S.J. (1990).Endoscopictransnasalorbitaldecompression. Archivesof Otolaryngology–HeadNeckSurgery, 116(3),275–282.
7.Metson,R.,Dallow,R.L.,&Shore,J.W.(1994).Endoscopicorbital decompression. Laryngoscope, 104(8Pt1),950–957.
8.Kacker,A.,Kazim,M.,Murphy,M.,Trokel,S.,&Close,L.G. (2003). “Balanced” orbitaldecompressionforsevereGraves’ orbitopathy:techniqueandtreatmentalgorithm. Otolaryngology–HeadNeck Surgery, 128(2),228–235.
9.Yao,W.C.,Sedaghat,A.R.,Yadav,P.,Fay,A.,&Metson,R.(2016). Orbitaldecompressionintheendoscopicage:Themodifiedinferomedialorbitalstructure. Otolaryngology–HeadNeck Surgery, 154(5), 963–969.
10.Pletcher,S.D.,Sindwani,R.,&Metson,R.(2006).Endoscopic orbitalandopticnervedecompression. OtolaryngologicClinicsof NorthAmerica, 39(5),943–958.
11.McKinney,K.A.,Snyderman,C.H.,Carrau,R.L.,Germanwala,A. V., Prevedello,D.M.,Stefko,S.T.,etal.(2010).Seeingthelight: Endoscopicendonasalintraconalorbitaltumorsurgery. Otolaryngology–HeadNeckSurgery, 143(5),600–701.
2 EndoscopicOrbitalSurgery: TheOphthalmologists ’ Perspective: FormationoftheOphthalmologyOtolaryngologyTeam ROBINICOLASMAAMARI,MD,JOHNF.HARDESTY,MD, ANDJOHNBRYANHOLDS,MD,FACS
Endoscopicorbitalsurgeryhasrapidlyestablisheditselfasa highlyevolvingmultidisciplinarysurgicalfield,relyingon theexpertiseandtechnicalskillsofophthalmologistsand otolaryngologists.In1978,NorrisandCleasbyfirstdescribed theuseoftheendoscopefororbitalsurgeryintheophthalmicliterature. 1 Threeyearslater,in1981,theyreporteda15-patientcase seriesdescribingtheirexperienceusingatransorbitalendoscopic approachfororbitaltraumaevaluation,foreignbodyremoval, andtumorbiopsy.2 Theadoptionoftransorbitalendoscopicsurgerybytheophthalmiccommunitywaslimitedowingtorisks ofirrigation-relatedintraorbitalpressureelevation,tissueedema, andcompressiveinjury.Asaresult,mostophthalmologistsand oculofacialsurgeonsuseendoscopictechniquesmainlywhenperformingendoscopicdacryocystorhinostomies(Fig.2.1)andendoscopicbrowlifts.
Incontrast,theintroductionofendoscopicsurgeryinthefield ofotolaryngologyhasrevolutionizedthetreatmentofsinusand allergicdisease.Thewidespreaduseoftheendoscopictransnasal approachhasresultedinrapiddevelopmentandimplementation oftechnologicalinnovations.Theseadvanceshaveledtoanexpansionoftheclinicalutilityofthetransnasalendoscopicapproach, withavarietyofapplicationsaddressingpathologyanddisease intheadjacentanatomicregions,includingtheskullbase andorbit.
Inparticular,therehasbeenatremendousincreaseintheotolaryngologyliteraturedescribingtheendoscopictransnasalorbital decompressiontechniqueinthemanagementofthyroideyedisease andcompressiveopticneuropathy.In1990,Kennedyetal.introducedthetransnasalendoscopicapproachfororbitaldecompression.3 Inthisstudy,theyreportedameanimprovementin Hertelexophthalmometrymeasurementsof4.7mminfivepatients
aftermedialandinferiorwalldecompressionusingthistransnasal endoscopictechnique.Sincethen,severalmodificationstothis approachhavebeendescribedtoimproveoutcomesanddecrease complicationrisks.Forexample,theincidenceofnew-onsetdiplopiainearlyreportsofendoscopicdecompressionsoccurredin upto45%ofcases.4 However,preservationoftheinferomedial orbitalbonestrutinendoscopicorbitaldecompressionhasresulted inatremendousreductioninnew-onsetpostoperativediplopia.5 Asidefromtheimprovementinpatientoutcomes,thismodificationhighlightstheimportanceofanestablishedinterdisciplinary relationshipandcollaborationbetweentheoculoplasticsurgery andotolaryngologyfields,asthistechniquewasadoptedfrom theworkdescribedbyGoldberg,Shorr,andCohenintheoculoplasticsurgeryliteraturein1992.6 Theanatomicexpertiseofboth fieldshasimprovedourunderstandingoftheorbitalstrutandsuspensoryligamentcomplexandthesinusanatomytopreservethe positionoftheglobeafterendoscopicsurgery.Furthermore,the preservationofastripoftheperiorbitamedialtothemedialrectus musclehasalsobeenintroducedtolimitmedialrectusmuscleprolapseintotheethmoidcavity.7 This “orbitalsling” techniqueisan additionalmodificationthatcanbeusedtoimprovetheversatility ofthetransnasalendoscopicapproachfororbitaldecompression. Thegrowinguseoftheendoscopicapproachfororbital decompressionsinthesurgicalmanagementofthyroideyedisease hasfosteredastrongrelationshipbetweentheophthalmologist andotolaryngologist.In1993,oneauthor(J.B.H.)beganacollaborativerelationshipfororbitaldecompressiontoachievea lowerriskofcomplicationsandimprovepatientcareandsafety. In1999,GrahamandCarterdescribedthecombined-approach orbitaldecompressionasasafe,efficient,andefficaciousjointserviceprocedure,whereintheotolaryngologistperformedthe
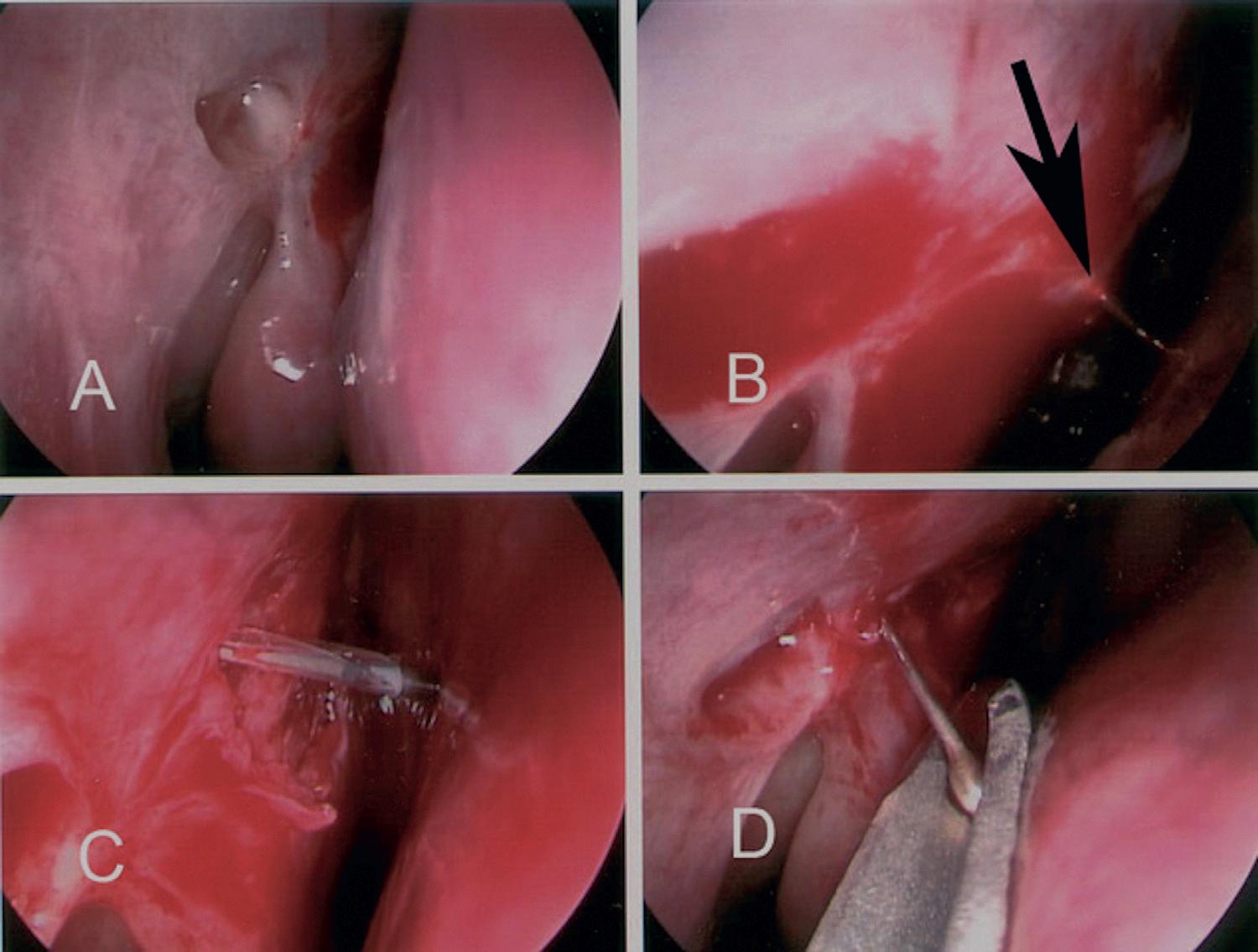
• Fig.2.1 Endoscopictransnasalsurgicaltechniqueslargelydevelopedinotolaryngologyhavebeenadopted byophthalmologistsandoculofacialsurgeonsforlacrimalandorbitalsurgery.Imagesfromanendoscopic revisiondacryoycystorhinostomyshow(A)thenonfunctionallacrimalostium;(B)asharpdilator(arrow)penetratingatthesiteoftheproposedostium;(C)aballooncatheterabouttobeinflatedtoensureanadequate openingaftertheremovalofsomemucosa;(D)retrievaloftheCrawfordlacrimalstentswithanasalgroove director.
endoscopicmedialwalldecompressionandtheophthalmologist completedtheexternal,transorbitalinferior,andlateralwall decompressions.8 Thiscollaborativeeffo rtleveragestheadvantageousfeaturesofeachapproach .Theendoscopicapproachprovidesimprovedvisualizationofth eposteriormedialwall,limiting thepotentialforsurgicalopticnerveinjuryandmaximizingthe extentofdecompressionattheorbitalapex.Theseadvantages areofparticularimportancein casesrequiringdecompression forprogressivethyroiddisease– relatedopticneuropathy.The external,transconjunctival,andlateralcanthalapproachprovides directvisualizationoftheinfraorbitalnervetoenableextensive inferiorwalldecompression,bothmedialandlateraltotheinfraorbitalnerve.Additionally,thesimultaneousthree-walldecompressionfacilitatesmaximalreductioninexophthalmosina singleoperation,whilealsoreducingtheincidenceofpostoperativediplopiaowingtothebalancingeffectwhenboththemedial andlateralwallsaredecompressed.9
Theremarkableadvancesinendoscopyinthepastdecades haveintroducedadditionalteam-basedsurgicalopportunitiesfor theotolaryngologistandophthalmologists.Specifically,several recentstudieshavehighlightedthebenefitsofacombinedprocedurewithcomplexposteriorandapicalorbitalmasses.10–12 Curragh,Halliday,andSelvadescribedthepotentialutilityofa dual-routetechniquewhereintheorbitalapicalmassisaccessed viaatransnasalendoscopicapproachandatranscaruncular
orbitotomyissimultaneouslyusedtoassistinmanipulationand removalofthemass.13 Additionally,theydescribetheadvantageousincorporationofanexternaltransconjunctivaldisinsertion ofthemedialrectusmuscletoincreaseendoscopicexposureduring orbitalbiopsiesandexcisions,whichcanbereinsertedattheconclusionoftheprocedure.
Surgicalnavigationandlocalizationisanareaofrapidprogress andevolutionthatenhancespatientsafetyandsurgicaloutcomes. Thesesystemsalsoplayanintegralroleinroboticsurgery.Initially usedinneurosurgeryandotolaryngologyforlocalizationinareasof criticalanatomyortoallowforsmallincisionapproaches,thesesystemshavebeenadoptedinophthalmologyandoculofacialsurgery toenhancepatientsafety(Fig.2.2).Severalreportsintheophthalmicplasticsurgeryliteraturehighlighttheutilityofstereotactic imageguidancesystemsasadjunctivetoolsinorbitaltumorexcisionsandorbitaldecompressions.14,15
Throughthedevelopmentoftheseinnovativesurgical approachesandtechniques,weareestablishingandsolidifying anevolvingrelationshipbetweenthefieldsofophthalmology andotolaryngology.Asaresult,wemayobserveatransitionin thestandardofcareandsurgicalmanagementofasubsetoforbital andapicaltumors,withimprovedpatientoutcomesbasedonacollaborativepracticethatreliesontheotolaryngologist’sfamiliarityof sinusanatomyandtheophthalmologist’sstructuralexpertiseinthe intraorbitalanatomicrelationships.
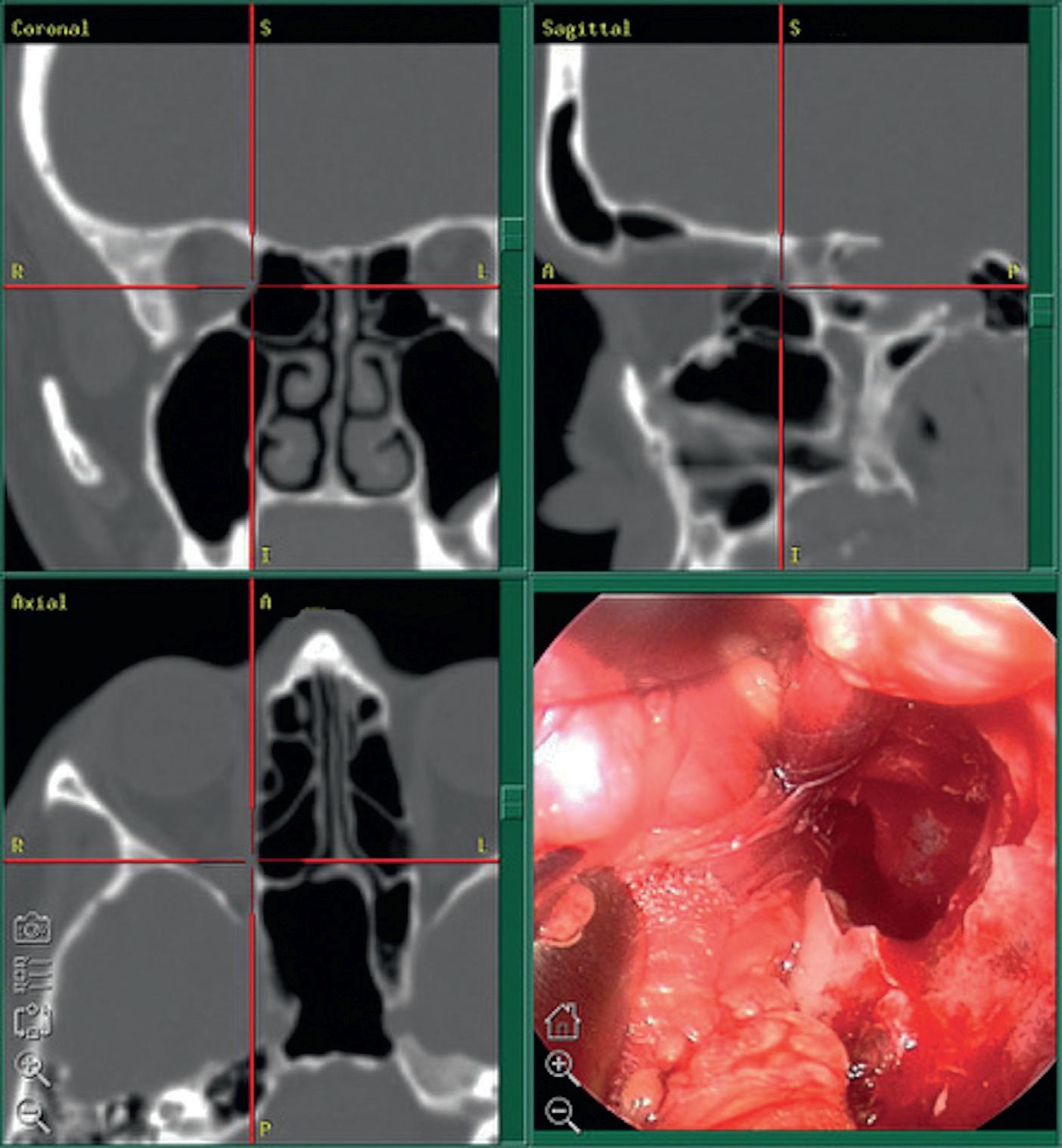
• Fig.2.2 Endoscopicvisualizationthroughtheorbitandsinus(bottomright)andastereotacticlocalization system(topleft,coronal;topright,sagittal;bottomleft,axial)areusedtoenhancepatientsafetyintheresectionofanapicalorbitaltumorbetweenthemedialrectusmuscleandtheopticnerve.
References 1.Norris,J.L.,&Cleasby,G.W.(1978).Anendoscopeforophthalmology. AmericanJournalofOphthalmology, 85(3),420–422. https:// doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9394(14)77741-4
2.Norms,J.L.,&Cleasby,G.W.(1981).Endoscopicorbitalsurgery. AmericanJournalofOphthalmology, 91(2),249–252. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/0002-9394(81)90183-5
3.Kennedy,D.W.,Goodstein,M.L.,Miller,N.R.,&Zinreich,S.J. (1990).Endoscopictransnasalorbitaldecompression. Archivesof Otolaryngology–HeadandNeckSurgery, 116(3),275–282. https:// doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1990.01870030039006
4.Yao,W.C.,Sedaghat,A.R.,Yadav,P.,Fay,A.,&Metson,R. (2016).Orbitaldecompressionintheendoscopicage:Themodified inferomedialorbitalstrut. Otolaryngology–HeadandNeckSurgery, 154(5),963–969. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599816630722
5.Wehrmann,D.,&Antisdel,J.L.(2016).Anupdateonendoscopic orbitaldecompression. CurrentOpinioninOtolaryngology&Head andNeckSurgery, 25(1),73–78. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOO. 0000000000000326.
6.Goldberg,R.A.,Shorr,N.,&Cohen,M.S.(1992).Themedical orbitalstrutinthepreventionofpostdecompressiondystopiain dysthyroidophthalmopathy. OphthalmicPlasticandReconstructive Surgery, 8(1),32–34.
7.Metson,R.,&Samaha,M.(2002).Reductionofdiplopiafollowing endoscopicorbitaldecompression:Theorbitalslingtechnique. Laryngoscope, 112(10),1753–1757. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537200210000-00008
8.Graham,S.M.,&Carter,K.D.(1999).Combined-approachorbital decompresionforthyroid-relatedorbitopathy. ClinicalOtolaryngology andAlliedSciences, 24(2),109–113. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.13652273.1999.00219.x
9.Hernández-García,E.,San-Román,J.J.,González,R.,Nogueira,A., Genol,I.,Stoica,B.,etal.(2017).Balanced(endoscopicmedialand transcutaneouslateral)orbitaldecompressioninGraves’ orbitopathy. ActaOto-Laryngologica, 137(11),1183–1187. https://doi.org/10. 1080/00016489.2017.1354394
10.Stokken,J.,Gumber,D.,Antisdel,J.,&Sindwani,R.(2016).Endoscopicsurgeryoftheorbitalapex:Outcomesandemergingtechniques. Laryngoscope, 126(1),20–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.25539
11.Sun,M.T.,Wu,W.,Yan,W.,Tu,Y.,&Selva,D.(2017).Endoscopicendonasal-assistedresectionoforbitalschwannoma. OphthalmicPlasticandReconstructiveSurgery, 33,S121–S124. https://doi. org/10.1097/IOP.0000000000000528
12.Yao,W.C.,&Bleier,B.S.(2016).Endoscopicmanagementoforbital tumors. CurrentOpinioninOtolaryngology&HeadandNeckSurgery, 24(1),57–62. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOO.0000000000000215
13.Curragh,D.S.,Halliday,L.,&Selva,D.(2018).Endonasalapproach toorbitalpathology. OphthalmicPlasticandReconstructiveSurgery, 34(5),422–427. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0000000000001180
14.Ali,M.J.,Naik,M.N.,Kaliki,S.,&Dave,T.V.(2016).Interactive navigation-guidedophthalmicplasticsurgery:Theusefulnessof computedtomographyangiographicimageguidance. Ophthalmic PlasticandReconstructiveSurgery, 32(5),393–398. https://doi.org/ 10.1097/IOP.0000000000000736.
15.Lee,K.Y.C.,Ang,B.T.,Ng,I.,&Looi,A.(2009).Stereotaxyfor surgicalnavigationinorbitalsurgery. OphthalmicPlasticandReconstructiveSurgery, 25(4),300–302. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP. 0b013e3181ab6795.
3 EndoscopicOrbitalSurgery: TheNeurosurgeon ’sPerspective LEOPOLDARKOIV,MDANDTHEODOREH.SCHWARTZ,MD Neurosurgicalapproachestotheorbitareoftendonewiththe aidofophthalmologistorotolaryngologist,toaddress intraorbitallesionsinvadingintracranialspacesor,more recently,togainskullbaseexposure.Dandyfirstreporteduseofafrontotemporalcraniotomytoresectlesionsfromtheorbitthatthengrew intracranial.1 TheapproachDandydescribedhasnowevolvedintothe skullbaseworkhorseapproachesnowcommonlyusedforlesionsofthe orbitaswellasanteriorandmiddlecranialfossa.Thedevelopmentby Yasargilofthepterionalcraniotomyallowedforeasyexposureof lesionsintheanteriorandmiddlefossa.2 Orbitalpathologyalong thelateraledgeoftheorbitandthe superiororbitalfissurecouldbe approachedfromthetraditionalversionofthisexposure.Lateradditionofasupraorbitalcraniotomy3 tothepterionalapproachcreated theorbitozygomaticcraniotomy,whichallowedforfurtherexposure oftheorbit.4,5 Thepurposeoftheorbitalremovalwiththisexposure wasnotonlytotreatintraorbitalpathologybuttogainskullbaseexposureregardlessoforbitalinvolvement.Lesionsofthesuperolateralarea oftheorbitaswellaslesionsextendingintotheanteriorandmiddle cranialfossacouldsafelyberesectedfromthisapproach.However, therearedownsidesoftraditionalcraniotomies,includingalargescar, temporalisatrophy,cerebrospinalfluidleak(CSF),andinfection.
Subfrontalcraniotomiesareanothercommonlyusedapproachto lesionsoftheorbitandanteriorcranialfossa.Theseapproachesusually includeavariationofabicoronalincisionwithremovalofaportionof thefrontalbarbilaterallyorunilaterallydependingonthepathology.6 Subfrontalretractionthenallowsforviewsofthesuperiororbitalong withextendedviewsofthesuperolateralorsuperomedialorbit.The requiredcranialexposureandretractionofabifrontalcraniotomycan beextensive.Thereforeattemptshavealsobeenmadetodecreasethe amountofcraniotomyneededtoexposetheanteriorfossa.Oneof thesemoreminimalapproachesincludesthesupraorbitalcraniotomy, whichallowsforanteriorfossaexposurewhileminimizingfrontallobe retraction.Visualizationofferedwiththesupraorbitalcraniotomyhas greatlybeenexpandedwithuseoftheendoscopeandcombiningthe supraorbitalapproachwithendonasalapproaches.7
Endoscopicendonasalapproachesweredevelopedinthelate 1990sbyJho,firstforapproachestosellarpathology.8 Later, expandedapproacheswereabletoexposetheinferomedialorbital apexaswellastheanteriorcranialfossa.9 Thefirstattempttouse theendoscopethroughtheorbitwascompletedinthe1980s,but thistechniquewasnotadvancedbecauseofthelackofhigh-quality imagingandnavigationalcapability.10 Thepotentialoftransorbital surgeryasacorridortointracranialpathologywouldnotbeadvanced againuntil2010.11 Thistransorbitalcorridorwasdevelopedinlarge
partbecauseofthetoolsdevelopedforendonasalapproaches,the advancementinimaging,andneuronavigation.Theuseoftheendoscopeallowedforsmallorbitalcraniotomieswithmoredirectroutes tosurgicalpathologyoftheanteriorandmiddlecranialfossa,leading tominimizationofbrainretraction.Transorbitalapproacheshave nowopenedtheorbitasanextensiveintracranialcorridor.
TransorbitalApproaches Transorbitalapproacheshaveaclassificationbasedonthesurgical target.Orbitalendoscopicsurgeryisforaccesstotheorbitand opticnervewithintheorbit;transorbitalendoscopicsurgeryor transorbitalneuroendoscopicsurgery(TONES)isfortargeting intracranialpathology.12 Theseapproachesofferacorridorto thelateralaspectoftheanteriorandmiddlefossa,asopposedto thedirectapproachtothecentralanteriorfossaprovidedbyendoscopicendonasalapproaches.Thechoiceoftransorbitalapproach dependsonthetargetedanatomicalregion.Endoscopicorbital approachesincludethesuperioreyelidcreaseapproach(SLC), theprecaruncularapproach(PC),lateralretrocanthalapproach (LRC),andpreseptallowereyelid(PS)approach(Fig.3.1).11,12 Alltheseapproacheshavebeentestedinbothclinicalandpreclinicalsettingsfordifferentpathologies.
SuperiorEyelidCreaseApproach TheSLCapproachinvolvesasuperioreyelidincisionwithcareful dissectionalongthesuperiororbitalrim.11 Initialclinicaluseof thisexposurewasusedtorepairCSFleaks,fractures,andorbital compressionasdescribedbyMoeetal.11,13,14(Table3.1).With thisexposure,alargeportionofthesuperiorandlateralorbit canbevisualized.Withdrillingoftheposteriororbit,theanterior andmiddlecranialfossacanbereachedthroughthisexposure.The SLCapproachlimitsincludethesuperomediallimitdefinedby thesuperiororbitalfissure,theinferiorlimitdefinedbytheinferior orbitalfissure,andthelaterallimitdefinedbythetemporalismuscle(Fig.3.2).15 Preclinicalcadaverstudieshavethoroughlyevaluatedthepotentialofthisapproach(Table3.2).Thefirstuseof thisapproachforintracranialpathologywasdescribedasatheoreticalapproachforanamygdalohippocampectomy.Bydrillingofthe orbitadjacenttotheinferiororbitalfissure,thetemporalpolewas exposedandintraduralexposureofthemesialtemporallobewas completed.16 Furthercadaverstudieshaveshownthatthelateral cavernoussinus,includingthecavernouscarotid,gasserian