EmergingCarbonCaptureTechnologies:Towardsa SustainableFutureMohammadKhalid
https://ebookmass.com/product/emerging-carbon-capturetechnologies-towards-a-sustainable-future-mohammad-khalid/
Instant digital products (PDF, ePub, MOBI) ready for you
Download now and discover formats that fit your needs...
Carbon Capture Technologies for Gas-Turbine-Based Power Plants Hamidreza Gohari Darabkhani
https://ebookmass.com/product/carbon-capture-technologies-for-gasturbine-based-power-plants-hamidreza-gohari-darabkhani/
ebookmass.com
Carbon Capture Technologies for Gas-Turbine-Based Power Plants Hamidreza Gohari Darabkhani
https://ebookmass.com/product/carbon-capture-technologies-for-gasturbine-based-power-plants-hamidreza-gohari-darabkhani-2/
ebookmass.com
Marketing Tourist Destinations in Emerging Economies: Towards Competitive and Sustainable Emerging Tourist Destinations Ishmael Mensah
https://ebookmass.com/product/marketing-tourist-destinations-inemerging-economies-towards-competitive-and-sustainable-emergingtourist-destinations-ishmael-mensah/ ebookmass.com
Embryology and the Rise of the Gothic Novel Diana Pérez
Edelman
https://ebookmass.com/product/embryology-and-the-rise-of-the-gothicnovel-diana-perez-edelman/
ebookmass.com
The GAME of Innovation: Gamify Challenges, Level Up Your Team, and Play to Win 1st Edition David Cutler
https://ebookmass.com/product/the-game-of-innovation-gamifychallenges-level-up-your-team-and-play-to-win-1st-edition-davidcutler/
ebookmass.com
(Original PDF) Crime Control in America What Works 4th Edition by John
L. Worrall
https://ebookmass.com/product/original-pdf-crime-control-in-americawhat-works-4th-edition-by-john-l-worrall/
ebookmass.com
A Gentleman Will Never… Forget A Lady: The Governess Chronicles - Book Three Windsor
https://ebookmass.com/product/a-gentleman-will-never-forget-a-ladythe-governess-chronicles-book-three-windsor/
ebookmass.com
Set
My Heart Bonfire (Blueball Band of Brothers Book 4) Marika Ray
https://ebookmass.com/product/set-my-heart-bonfire-blueball-band-ofbrothers-book-4-marika-ray/
ebookmass.com
Social Media Marketing For Dummies, 4th Edition Shiv Singh
https://ebookmass.com/product/social-media-marketing-for-dummies-4thedition-shiv-singh/
ebookmass.com
https://ebookmass.com/product/978-1848726680-handbook-of-prejudicestereotyping-and-discrimination-2nd-edition/
ebookmass.com
EmergingCarbonCaptureTechnologies
Thispageintentionallyleftblank
EmergingCarbon CaptureTechnologies
TowardsaSustainableFuture
Editedby MohammadKhalid
GrapheneandAdvanced2DMaterialsResearchGroup,Schoolof EngineeringandTechnology,SubangJaya,Selangor,Malaysia
SwapnilA.Dharaskar
CO2 ResearchGroup,DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,Schoolof TechnologyPanditDeendayalEnergyUniversity,Gandhinagar, Gujarat,India
MikaSillanpa¨a ¨
DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,SchoolofMining,Metallurgyand ChemicalEngineering,UniversityofJohannesburg,Doornfontein, SouthAfrica
HumairaSiddiqui
DepartmentofBiologicalSciences,SchoolofMedicineandLifeSciences, SunwayUniversity,Malaysia
Elsevier
Radarweg29,POBox211,1000AEAmsterdam,Netherlands TheBoulevard,LangfordLane,Kidlington,OxfordOX51GB,UnitedKingdom 50HampshireStreet,5thFloor,Cambridge,MA02139,UnitedStates
Copyright 2022ElsevierInc.Allrightsreserved.
Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproducedortransmittedinanyformorbyanymeans, electronicormechanical,includingphotocopying,recording,oranyinformationstorage andretrievalsystem,withoutpermissioninwritingfromthepublisher.Detailsonhowto seekpermission,furtherinformationaboutthePublisher’spermissionspoliciesandour arrangementswithorganizationssuchastheCopyrightClearanceCenterandtheCopyright LicensingAgency,canbefoundatourwebsite: www.elsevier.com/permissions .
Thisbookandtheindividualcontributionscontainedinitareprotectedundercopyrightby thePublisher(otherthanasmaybenotedherein).
Notices
Knowledgeandbestpracticeinthis fieldareconstantlychanging.Asnewresearchand experiencebroadenourunderstanding,changesinresearchmethods,professional practices,ormedicaltreatmentmaybecomenecessary.
Practitionersandresearchersmustalwaysrelyontheirownexperienceandknowledgein evaluatingandusinganyinformation,methods,compounds,orexperimentsdescribed herein.Inusingsuchinformationormethodstheyshouldbemindfuloftheirownsafety andthesafetyofothers,includingpartiesforwhomtheyhaveaprofessionalresponsibility.
Tothefullestextentofthelaw,neitherthePublishernortheauthors,contributors,or editors,assumeanyliabilityforanyinjuryand/ordamagetopersonsorpropertyasamatter ofproductsliability,negligenceorotherwise,orfromanyuseoroperationofanymethods, products,instructions,orideascontainedinthematerialherein.
ISBN:978-0-323-89782-2
ForinformationonallElsevierpublicationsvisitourwebsite at https://www.elsevier.com/books-and-journals
Publisher: SusanDennis
EditorialProjectManager: MicaEllaOrtega
ProductionProjectManager: KumarAnbazhagan
CoverDesigner: MilesHitchen
TypesetbyTNQTechnologies
5.NovelsolventsforCO2
5.1.Amine-basedsolventsystem
5.2.Non-amine-basedsolventsystem
5.3.Ionicliquids
5.4.Deepeutecticsolvents
5.9.Physicalabsorptionsolvents
6.Absorptioncostandenergyrequirement
6.1.Capitalcostestimationbasedonbaremodulecost(CBM)54
6.2.Energyrequirement
7.Recyclingandregenerationcriteria
3.CO2 capturebyadsorption
BaharehSadeghalvad,HamidEbrahimiandAmirrezaAzadmehr
1.Introductiontogas-solidadsorption
2.Conventionalsolidadsorbents
2.1.Activatedcarbon66
2.2.Zeolites66
3.Flexibleadsorbents
4.Noveladsorbentmaterials
4.1.Metalorganicframework(MOFs)68
4.2.Carbonnanomaterials69
4.3.Hybridmaterials71
4.4.Amine-basedsolidmaterials72
5.Recentdevelopmentsinadsorptiontechnology 73
5.1.Utilizingrenewableenergy73
5.2.Hybridprocessesoracombinationofprocesses74
6.Adsorptioncostmodelandenergyrequirement
7.Challengesandfutureperspective
4.ChemicalloopingcombustionforinherentCO2 capture
HariC.Mantripragada
2.Chemicalloopingcombustion(CLC)
2.1.Calciumlooping(CaL)forpostcombustionCO2
3.Fuelsforchemicalloopingcombustion
4.Oxygencarriersforchemicalloopingcombustion
5.Reactorsystemsforchemicalloopingcombustion
5.1.Reactorsforgaseousfuels
5.2.Reactorsforsolidfuels
6.Performancemodelforchemicalloopingcombustion
6.1.Massbalanceequations
5.MembraneforCO2 separation
HarriNieminen,ArtoLaariandTuomasKoiranen
1.Introduction
2.Membranecontactors
2.1.Backgroundandtheory123
2.2.MembranecontactorsinCO2 absorption
2.3.Absorbentsolutions
2.4.MembranecontactorsinCO2 stripping
2.5.Feasibilityanddemonstrations
3.Gasseparationmembranes
3.1.Backgroundandtheory
3.2.Membranematerials
3.3.Processdesign,optimization,andcostestimates148
4.Challengesandfutureprospects
5.Conclusions
6.Electrochemicalreductionofcarbondioxideto hydrocarbons:techniquesandmethods ReyadShawabkeh,AkramAl-Absi,MohamedShamlooh, MazenKhaledandIbnelwaleedA.Hussein
1.Introduction 161
2.Reactionmechanism 162
2.1.Firstpathway162
2.2.Secondpathway163
3.Techniquesandconceptsinelectrochemistry 163
3.1.Cyclicvoltammetry163
3.2.Linearsweepvoltammetry168
3.3.Chronopotentiometry169
3.4.Chronoamperometry170
3.5.Faradaicefficiency
3.6.Overpotential
4.Experimentalinvestigations
4.1.Electrodestructure
4.2.Gasdiffusionelectrodes
4.3.Electrolyte
4.4.Temperatureandpressureeffects
4.5.Rotatingdiskelectrode(RDE)
5.Analyticaltechniquesforformicacid/formate
7.Hydrate-basedCO2 separation TinkuSaikiaandAbdullahSultan
1.Introduction
2.CO2 separationtechnologies
2.1.Absorption194
2.2.Adsorptiontechnology195
2.3.Membranetechnology196
2.4.Cryogenicseparation197
3.TechnicaldrawbacksassociatedwithconventionalCO2 separationtechnologies 197
4.Gashydrates 198
4.1.Gashydrateformationanddissociationkinetics199 4.2.Nucleation200
4.3.Hydrategrowth201
5.Gashydrate basedCO2 capture 202
5.1.CO2 capturemechanism 202
5.2.Operationalparametersofhydrate-basedCO2 separation204
6.CO2 hydrate-basedseparationprocessandreactordesigns 206
6.1.Continuousprocess206
6.2.Stirredreactors207
6.3.Ejector-typeloopreactor(basedonmicrobubble technology) 208
6.4.Fixed-bedreactor 210
6.5.Unstirredreactor 213
7.Differenthydratepromoters(chemicaladditives) 214
7.1.Tetra-n-butylammoniumbromide 214
7.2.Tetrahydrofuran 217
7.3.Propane 218
7.4.Cyclopentane 219
7.5.Surfactants 220
8.Costcomparisoncalculationforhydrate-based CO2 separation 224
9.Conclusions 226 Acknowledgment226 References226
8.Innovationsincryogeniccarboncapture
TusharPatil,SwapnilA.DharaskarandB.RajasekharReddy
1.Introduction
2.CO2 captureapproachesandtechnologies
3.Cryogenictechnologies
3.1.Cryogenicdistillation
3.2.Cryogenicpackedbed
3.3.CryoCellprocess
3.4.Antisublimation(AnSU)
3.5.Externalcoolingloopcryogeniccarboncapture technology(CCCECL)
3.6.Stirlingcoolersystemtechnique
4.Benefitsofcryogeniccarboncapturetechniques
4.2.HighpurityofCO2 product
5.Challengesandlimitationsofcryogeniccarboncapture techniques
5.1.Operatingcost
5.2.Operationefficiency
5.3.Impurities
9.CO2 capturefromtheatmosphericairusing nanomaterials
MohammedAlHinaai
10.CO2 transportation:safetyregulationsandenergy requirement
AhmadK.SleitiandWahibA.Al-Ammari
11.Techno-economicanalysisandoptimizationmodels forCO2 captureprocesses TeroTynjala 1.Introduction
3.Economicalparametersandcostfunctions
12.Modelingandmolecularsimulationmethods forCO2 capture AbhishekKumarGupta
1.Introduction
2.Molecularsimulationsofmaterialsemployedfor CO2
13.BiologicalprocessesforCO2 capture RameshK.Guduru,AnuragAteetGuptaandUttakanthaDixit 1.Introduction
2.BiologicalapproachesforCO2 capture
2.1.Approachesbasedonphotosyntheticalgae
3.TheextentofCO2 fixationbymicroalgae
3.1.Suspendedgrowthreactors
3.2.Attachedgrowthreactors
3.3.Bioscrubbers
4.Approachesbasedonnonphotosynthetic organisms
5.Approachesbasedonbioelectrochemicalsystems
6.ForestationforCO2 capture
6.1.Forestryactivitiestomitigateclimatechange391
7.Improveforestrytechniquestoreduceemissions
8.Carbonsequestrationonagriculturallands
9.1.Theoceancarboncycle
9.2.Ecosystemrestoration
9.3.Large-scaleseaweedcultivation
10.Challengesandfuturetrends
11.Conclusions
14.Decarbonization:regulationandpolicies
MohamedChakerNecibi,YoussefBrouziyneand AbdelghaniChehbouni
2.TheParisAgreement
2.1.Overview402
2.2.EstimatedimpactsoftheParisAgreement403
2.3.WeakpointsoftheParisAgreement406
2.4.FutureendeavorsrelatedtothePA406
3.Carbontaxandcredit 407
4.Roleofgovernmentinenforcingthepolicies:Morocco asacasestudy 410
4.1.Moroccoinbrief410
4.2.Emissionspattern410
4.3.Politicalcommitment412
4.4.Mainsectorsofaction413
4.5.Opportunitiesandchallenges415
4.6.Currentchallengesandfuturetrendsincarbon capture416
4.7.Challengesandbarriers 416
4.8.Futuretrendsofcarboncapture 419
4.9.Connectingwithbigdataandartificialintelligence421 5.Conclusion 422
15.Circularcarboneconomy
RickySaputra,MohammadKhalid,RashmiWalvekarand AgamuthuPariatamby
2.Movingtowardalowcarboneconomyusingcircular
3.Thecirculareconomyopportunityforindustries
3.1.Opportunityinmanufacturingandconstruction
3.2.Opportunityinfoodindustry444
3.3.Opportunityinthemobilityindustry446
4.Policyleversforalowcarboncirculareconomy
Listofcontributors
AkramAl-Absi,DepartmentofChemicalandPetroleumEngineering,Universityof Calgary,Calgary,Canada
WahibA.Al-Ammari,DepartmentofMechanical&IndustrialEngineering,College ofEngineering,QatarUniversity,Doha,Qatar
MohammedAlHinaai,A’SharqiyahUniversity,CollegeofAppliedandHealth Sciences,DepartmentofBasicSciences,Ibra,Oman
AmirrezaAzadmehr,DepartmentofMining&MetallurgicalEngineering,Amirkabir UniversityofTechnology,Tehran,Iran
YoussefBrouziyne,MohammedVIPolytechnicUniversity(UM6P),International WaterResearchInstitute(IWRI),GreenCityBenguerir,Morocco
AbdelghaniChehbouni,MohammedVIPolytechnicUniversity(UM6P),International WaterResearchInstitute(IWRI),GreenCityBenguerir,Morocco
SukantaKumarDash,CO2 ResearchGroup,DepartmentofChemicalEngineering, PanditDeendayalEnergyUniversity,Gandhinagar,Gujarat,India
AnirbanDey,CO2 ResearchGroup,DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,Pandit DeendayalEnergyUniversity,Gandhinagar,Gujarat,India
SwapnilA.Dharaskar,CO2 ResearchGroup,DepartmentofChemicalEngineering, SchoolofTechnologyPanditDeendayalEnergyUniversity,Gandhinagar,Gujarat, India
UttakanthaDixit,DepartmentofMechanicalEngineering,PanditDeendayalEnergy University(PDEU),Gandhinagar,Gujarat,India
HamidEbrahimi,WilsonCollegeofTextiles,NorthCarolinaStateUniversity, Raleigh,NC,UnitedStates
RameshK.Guduru,DepartmentofMechanicalEngineering,PanditDeendayal EnergyUniversity(PDEU),Gandhinagar,Gujarat,India
AbhishekKumarGupta,DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,Schoolof Technology,PanditDeendayalEnergyUniversity,Gandhinagar,Gujarat,India
AnuragAteetGupta,DepartmentofMechanicalEngineering,PanditDeendayal EnergyUniversity(PDEU),Gandhinagar,Gujarat,India
IbnelwaleedA.Hussein,GasProcessingCenter,CollegeofEngineering,Qatar University,Doha,Qatar;ChemicalEngineeringDepartment,CollegeofEngineering, QatarUniversity,Doha,Qatar
MazenKhaled,DepartmentofChemistryandEarthSciences,QatarUniversity,Doha, Qatar
MohammadKhalid,GrapheneandAdvanced2DMaterialsResearchGroup,School ofEngineeringandTechnology,SubangJaya,Selangor,Malaysia;ElastiCities ResearchCluster,SunwayUniversity,SubangJaya,Selangor,Malaysia
NiyayeshKhorshidi,DepartmentofMining&MetallurgicalEngineering,Amirkabir UniversityofTechnology,Tehran,Iran
TuomasKoiranen,DepartmentofSeparationScience,LUTSchoolofEngineering Science,Lappeenranta-LahtiUniversityofTechnologyLUT,Lappeenranta, Finland
ArtoLaari,DepartmentofSeparationScience,LUTSchoolofEngineeringScience, Lappeenranta-LahtiUniversityofTechnologyLUT,Lappeenranta,Finland
BishnupadaMandal,DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,IndianInstituteof TechnologyGuwahati,Guwahati,Assam,India
HariC.Mantripragada,DepartmentofChemicalandPetroleumEngineering, SwansonSchoolofEngineering,UniversityofPittsburgh,Pittsburgh,PA,United States
MohamedChakerNecibi,MohammedVIPolytechnicUniversity(UM6P),InternationalWaterResearchInstitute(IWRI),GreenCityBenguerir,Morocco
HarriNieminen,DepartmentofSeparationScience,LUTSchoolofEngineering Science,Lappeenranta-LahtiUniversityofTechnologyLUT,Lappeenranta, Finland
AgamuthuPariatamby,JeffreySachsCenteronSustainableDevelopment,Sunway University,SubangJaya,Selangor,Malaysia
TusharPatil,CO2 ResearchGroup,DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,Schoolof TechnologyPanditDeendayalEnergyUniversity,Gandhinagar,Gujarat,India
B.RajasekharReddy,DepartmentofFuel,Minerals&MetallurgicalEnigineering, IndianInstitueofTechnology(IndianSchoolofMine)Dahnbad,Jharkhand,India; DelawareEnergyInstitute,UniversityofDelaware,Newark,DE,UnitedStates
BaharehSadeghalvad,DepartmentofCivil,Environmental,andConstruction Engineering,TexasTechUniversity,Lubbock,TX,UnitedStates
TinkuSaikia,DepartmentofPetroleumEngineeringandCenterforIntegrative PetroleumResearch,KingFahdUniversityofPetroleum&Minerals,Dhahran, SaudiArabia
RickySaputra,SchoolofComputerScienceandEngineering,Taylor’sUniversity LakesideCampus,SubangJaya,Selangor,Malaysia
MohamedShamlooh,GasProcessingCenter,CollegeofEngineering,QatarUniversity, Doha,Qatar
ReyadShawabkeh,DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,UniversityofJordan, Amman,Jordan
AhmadK.Sleiti,DepartmentofMechanical&IndustrialEngineering,Collegeof Engineering,QatarUniversity,Doha,Qatar
AbdullahSultan,DepartmentofPetroleumEngineeringandCenterforIntegrative PetroleumResearch,KingFahdUniversityofPetroleum&Minerals,Dhahran, SaudiArabia
TeroTynja ¨ la ¨ ,LUTSchoolofEnergySystems,Lappeenranta-LahtiUniversityof TechnologyLUT,Lappeenranta,Finland
RashmiWalvekar,DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,SchoolofEnergyand ChemicalEngineering,XiamenUniversityMalaysia,Sepang,Selangor,Malaysia
Thispageintentionallyleftblank
Abouttheeditors
Dr.MohammadKhalid isaResearchProfessorandHeadofGrapheneand Advanced2DMaterialsResearchGroupatSunwayUniversity,Malaysia.His researchinterestslieintheareaofadvancednanomaterialsynthesis,heat transferfluids,energyharvesting,andstorage.Heisamongthetop2%ofscientistsinthefieldofmaterials,withover200researchpublicationsinpeerreviewedinternationaljournals.Hehassupervisedmorethan30postgraduate studentsandhasover15yearsofresearchandteachingexperience.Heisalsoa FellowoftheHigherEducationAcademy,UK.
ProfessorMikaSillanpa ¨ a ¨ receivedhisM.Sc.(English)andD.Sc.(English)degreesfromAaltoUniversity,wherehealsocompletedanMBAdegree in2013.Hehassupervisedover50PhDsandbeenareviewerinover250 academicjournals,manyofwhicharetop-rankedintheirfields.Heisalsoa highlycitedresearcherwithover900researcharticlesinpeer-reviewed internationaljournals.MikaSillanpa ¨ a ¨ hasservedontheeditorialboardsof severalscholarlypublications.HeiscurrentlyanEditorinInorganicChemistryLetters(Elsevier),anAssociateEditorinEnvironmentalChemistry Letters(Springer),andaFieldChiefEditorinFrontiersinEnvironmental Chemistry.
Dr.SwapnilA.Dharaskar isanAssociateProfessorandHeadofthe ChemicalEngineeringDepartment,SchoolofTechnologyatPanditDeendayal EnergyUniversity,Gandhinagar,Gujarat.HisresearchinterestsareCO2 separations,deepeutecticsolvents/ionicliquids,desulfurizationprocess,and nanotechnology.HeistheprincipalinvestigatorofaCO2 separationproject fundedbytheDepartmentofScienceandTechnology,India,aspartofthe MissionInnovationcarboncapturescheme.Hehassupervised6PhDsand20 MTechstudentsandhaspublishedover50researchpapersininternational journals.Heisamemberofvariousprofessionalorganizations,including IIChE,AIChE,ACS,IWA,IEI,ISTE,IAENG,ISRD,IAN,etc.Healsoserves ontheeditorialboardsofseveralprestigiousinternationaljournals.
HumairaSiddiqui graduatedwithabachelor’sdegreeinbiotechnology engineeringfromIntegralUniversity,India.ShecompletedherM.Sc.fromthe SchoolofMedicineandLifeSciences,SunwayUniversity,Malaysia.Her researchfocusesoncarbonicanhydraseenzyme-mediatedcarboncapturefrom extremophiles.
Thispageintentionallyleftblank
Preface
Thesecondwarmestyearin141yearsforbothoceanandlandsurfacecombined wastheyear2020.AtmosphericCO2 levelsarereachingnewheightswitheach passingyear.Theglobaltemperatureneedstoremainbelow1.5 Cabove preindustriallevelsasagreedinthe2015ParisAgreement.TheIntergovernmental PanelonClimateChangehasurgedtobringdowntheCO2 emissionlevelsby 45%.Failuretodosohaspredictedanincreaseinglobaltemperaturebetween 3.7and4.8 Cbytheyear2100.TherecentCOP26madethesignatoriesof UnitedNationsFrameworkConventiononClimateChangetosetoutambitious yetrealisticgoalsforclimateaction.However,theparticipatingcountries havesignaledtophaseoutorphasedowntheuseoffossilfuelswhichisthechief contributortoclimatechange.Westillneedtoputourmitigationstrategies inplaceforCO2 captureatemissionsitesuntiltheuseoffossilfuelsbecomes history.
Theabsolutenecessitytodevelopacommercialmethod,process,and technologytocaptureanthropogenicCO2 fromtheemittingsitehasledtothe creationofaportfolioofseveralcarboncaptureandstorage(CCS)strategies. Thisincludesapproachesthathavemadeittothedeploymentstage,whilemany needtobetechnicallyimprovedandmadeeconomicallyfeasible.Additionally, variousimprovedandnovelCCSstrategiesareprogressingundertheresearch, development,anddemonstrationstage,intendingtoprovideacost-effectiveand sustainablesolutiontothecarbonemissioncrises.
Thisbooktraversesthereadersthroughthevariouschemical,biological,and simulation-basedcarboncaptureapproachesfromthermalpowerplantsand atmospheretotransportationandstorageoftheCO2,techno-economicanalysis andoptimizationmodel,regulationsandpoliciesinvolvingCO2 capture,and circularcarboneconomy.
ThebookaimstoprovideacomprehensiveandtechnicaloverviewofCCS approachesthatareavailableatdifferentstagesoftheirmaturity,hopingto providethetechnicalbackgroundtostudentsinSTEM,researchers,decisionmakers,policymakers,andupcomingyoungengineerswhowishtounderstand andhelpinprovidinganovelandtechnologicalsolutionstotacklethebiggest problemofthiscentury.
Thispageintentionallyleftblank
Chapter1
Introductiontocarboncapture
AnirbanDey1,SukantaKumarDash1 andBishnupadaMandal2 1CO2 ResearchGroup,DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,PanditDeendayalEnergy University,Gandhinagar,Gujarat,India; 2DepartmentofChemicalEngineering,IndianInstitute ofTechnologyGuwahati,Guwahati,Assam,India
1.Carboncycle:sourcetosink
Carbonisexchangedor“cycled”amongEarth’slithosphere,hydrosphere, biosphere,andatmosphere.Allorganicmatterismadeupofcarboncompounds,afundamentalbuildingblockofalllivingorganisms,andanessential componentofmanychemicalprocesses.Carboniscontinuouslycirculating throughtheentirerealmoftheecosysteminvariousformssuchasatmospheric CO2 (carbondioxide),carbohydrates(CnH2nOn),orsugarinthelivingspecies, calciumcarbonate(CaCO3)inmineralsandrocks,etc.Thecarbonpassage amongthedifferentecosystemcomponentscanberepresentedintheformof theCarbonCycleshownin Fig.1.1 [1].Thenumbersassociatedwitheach componentofthecarboncycleinthefigureindicatetheamountofcarbon storedincarbonsinksingigatonscarbon(GtC).Atthesametime,thearrows representthefluxofCO2 movementingigatonscarbon/year(GtC/year)betweenthedifferentcomponentsoftheenvironment.Carbonpresentinthe systemcanbecirculatedacrossthebiosphereandtheoceansoverawidertime scalethatcanvaryfromfewerdaystomillionsofyears.Forinstance,itcanbe eitherconservedunderthedeephorizonwithintheocean’ssedimentsforan extendedperiod,oritmightgetreturnedtotheatmospherewithinashorttime. Inthiscontext,itbecomesveryimportantfortheresearcherstounderstandthe mechanismandprocessesofvarioussourcesandsinksofcarboninorderto interpretandanalyzetheinfluenceofvarioushumanactionsonthenatural carboncyclescheme[2].Atypicalsourcerepresentedinthecarboncyclecan berelatedtoanyactivityortheprocessbywhichCO2 isdischargedoremitted totheair.Greenhousegasemissions,includingCO2,canresultfromboth naturalandanthropogenicactions.Ontheotherhand,sinksarenaturalor artificialbodiesthatcanabsorbandstorecarbonfromtheatmosphere[3].The land-basedsinkmainlyrelatestotheintegrationofCO2 intothephotosynthesisproductsproducedbytheterrestrialgreenplants.Atthesametime,the ocean-basedsinkincludestheincorporationinthephotosynthesisproducts
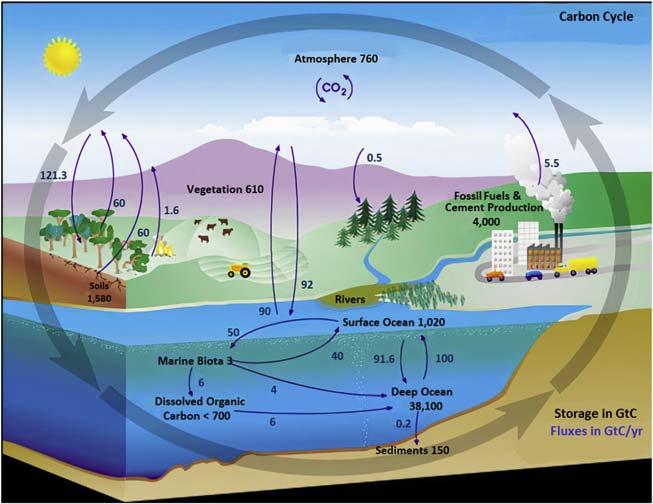
formedviaphytoplanktonaswellasamalgamationbyseveralacid-based reactions,dissolution,andcarbonateformingreactionsofnumerousmarine organisms.
Forimplementingeffectivemitigationstrategies,itisessentialtocategorizethenaturalandanthropogenicsourcesofCO2.Oneoftheprimenatural sourcesofatmosphericCO2 istheemissionrelatedtothemicrobialdecay processofdeadremainsofplantsandanimals.Atthesametime,volcanoes andforestfiresrepresenttheothersignificantclassofnaturalcontributors.The burningoffossilfuelsforenergy-relatedapplicationsisoneofthepotential anthropogenicCO2 sources.Powerplantsarethemajorconsumersoffossil fuels,asthechemicalenergystoredinthehydrocarbon-derivedfossilfuelsis convertedintoenergyviacombustionprocess[2].Thisprocessgeneratesa largevolumeoffluegascontainingaconsiderableamountofSOx,NOx,CO, andCO2 asthemajoremissionproduct.Theotherpotentialanthropogenic sourcesaredeforestationaswellasmass-scaleburningofsolidwasteand woodforenergyconsumption.
Greenplantspresentintheecosystemplayanincrediblycrucialroleinthe carboncycleglobally.TheyextracttheatmosphericCO2 andproducesugars comprisingprimarilyofcarbonviathephotosynthesisprocess.Inthefirststep, plantstrapthesunlightinsmallpacketsofenergycalledphotons.Thisenergy isfurthertransformedchemicallyintoATP(adenosinetriphosphate).
FIGURE1.1 Thecarboncycle. Reproduced: http://ete.cet.edu/gcc/?/globaltemp_carbon_cycle/.
TheenergystoredintheformofATPcanbeutilizedtoproducesugar (C6H12O6)andoxygen(O2)inthepresenceofCO2 andwaterviasecondstep. Thenetchemicalreactionofphotosynthesisprocesscanbeexpressedin reaction (1.1) [1]:
Inaddition,theanimalbodiessplitdownthecarbohydratespresentinthe plantspecies,releasingCO2 intotheatmosphereviarespirationprocess.Italso contributestotherespirationprocessbybreakingdowntheavailableorganic moleculesandreleasingtheinherentstoredenergy.Thenetchemicalreaction fortheprocessofrespirationistheexactoppositeofphotosynthesisshownin reaction (1.2) [1]:
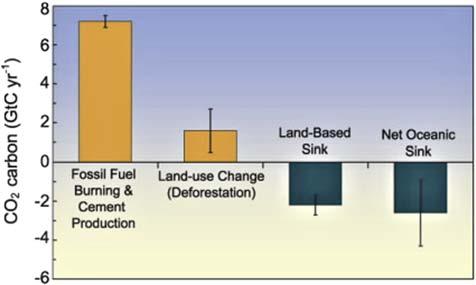
Whenthedeadremainsoftheplantandanimalspeciesslowlyundergo decompositionathighertemperaturesandpressure,theyaresubsequently convertedintoareservoirofenergysourcesknownas fossilfuels.Thesefossilderivedfuelsarelaterburnedtoreleasetheenergystoredinthem.Inorderto meettherisingenergydemandglobally,theburningoffossilfuelsis increasing,whichcontributestothehugeamountofcarbondioxideemitted intotheatmosphere.Theimpactofmajorsourcesandsinksofthecarboncycle ispresentedin Fig.1.2 [4].
Fromthefigure,itcanbeinterpretedthatfossilfuelcombustionand processindustriesemissionssuchascementproductiongloballyareresponsibleformorethan75%ofanthropogenicCO2 emissions.Deforestation, changingagriculturalpractices,andotherlandusechangesareresponsiblefor therest.Typically,theoverallsourcesandsinksofthenaturalcarboncycle shouldbalanceoneanother.Forexample,thecarbonemittedduringrespirationisoffsetbyphotosynthesis.However,theadditionofanthropogenic
FIGURE1.2 Majorsourcesandsinksofatmosphericcarbondioxide. Reproduced: https://www. acs.org/content/acs/en/climatescience/greenhousegases/sourcesandsinks.html.
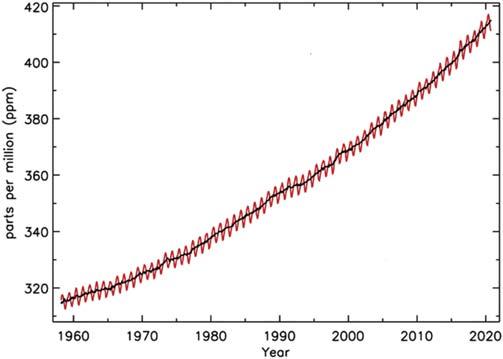
sourcessuchastheburningoffossilfuels,deforestation,etc.,disruptthe completecycleandincreasestheconcentrationofCO2 prevailinginthe atmosphere[5].Onaglobalscale,theoverallCO2 emissionshaveincreased bymorethan400%since1950onaccountofhumanactions[6].Itcanalsobe interpretedfromtheliteraturesourcesthatinthelastdecadetheCO2 concentrationhasincreasedalarminglybyover2ppm[7].Thenetincreaseinthe atmosphericCO2 overtheyearscanbeobservedfromthereferencedata (Fig.1.3)collectedfromtheMaunaLoaObservatoryinHawaii.Thecurrent CO2 concentrationintheatmospherestandsatalltimehighvalueof 415.52ppmasofJanuary2021[8].
2.SectorsresponsibleforanthropogenicCO2 emission
Drivenbyhigherenergydemandglobally,theCO2 emissionfromtheenergyrelatedsourcesincreased1.7%toahistorichighof33.1GtofCO2 in2018[9]. Thiswasthehighestevergrowthrecordedsince2013and70%higherthanthe annualaverageratesince2010.Theglobalenergydemandhasbeenrising substantially,anditisexpectedtorisealarminglybyover67%by2030[10]. Fossilfuelswillcontinuetobethemajorenergysourcetomeettheever increasingenergydemandandgenerateaconsiderableamountofCO2 and othergreenhousegases.Apparently,itiscrucialtocategorizethemajorsectors ofCO2 emissionsothatadequatepreventivemeasurescanbelaiddownto reducetheemissions.TheanthropogeniccontributionsofCO2 andother greenhousegasesoriginatemainlyfromthefollowingsectors:
(i) PowerGenerationSector Thefossilfuel basedpowerindustry mostlyderivesitsenergybyburningthefossilfuelssuchascoaland
FIGURE1.3 AtmosphericcarbondioxidemeasuredatMaunaLoaobservatory,Hawaii. Reproduced: https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/
naturalgas.Althoughrenewableenergysourcesaregainingpopularityin thecurrentscenario,thepowersectorcontinuestobethehighestCO2 emittertotheatmosphere.Carboncapture,storage,andUtilization (CCSU)willplayanessentialroleincombatingthemassemissionfrom large-scalestationarysources.
(ii) Transportation
Thecombustionoffossil-derivedfuelsources,mainly coal,petrol,anddieselinautomobileengines,contributesmajorlyto large-scaleCO2 resultinginglobalwarming.Theseareconsideredasthe nonstationarysourceemittinghighvolumesofCO2.Thegradualintroductionofbiofuel-basedalternativesources,aswellaselectricvehicles, cansignificantlycontributetoloweringtheemissionfromtheautomobile sector[11].
(iii) BuildingSector
Theresidential,commercial,andindustrialbuilding complexesalsoshareanimportantsegmentintheemissionofCO2 along withotherpotentialgreenhousegasessuchasCH4 andSO2.Theemission mainlyarisesfromfossilfuelcombustionforenergy-relatedapplications andtheusageofcertainGHGconcentratedmaterials[12,13].Theconcept ofgreenbuildingsandotherrevolutionarystrategiesshouldbewidely implementedinthesesectorstominimizetheeffectofallthesesources.
(iv) IndustrialProcessSector TheCO2 emissionfromtheindustrial processsectormainlyincludestheemissionsresultingfromchemical, mineral,andmetallurgicaltransformationprocesses,aswellaswaste managementoperations.Italsocompriseson-sitefossilfuel(mainlycoal, petroleum,andnaturalgas) poweredenergygenerationfacilities[12,13]. Amoredetaileddescriptionofthemajorprocessindustriesandtheir associatedCO2 dischargeishighlightedin Section5
(v) Agriculture,Forestry,andLandUse Thegreenhousegases,mainly CO2,methane(CH4),andnitrousoxide(N2O),arereleasedintothe atmospherebydifferentmechanismssuchascombustionoffuels,plant biomassdecomposition,andorganicmatterinthesoil.Variousanthropogeniclanduse basedactivitiessuchasmanagementofforests, grasslands,croplands,conversionofgrasslandsforpossiblecroplands, andcultivationcanalsocontributesignificantlytowardtheemissionof CO2 alongwithothergreenhousegasesintotheatmosphere[13].
3.EnergyCO2-nexusandclimatechange
Scientificpredictionrevealedthatglobalwarmingresultsfromgreenhouse gases(GHG),especiallyCO2 accumulationintheatmosphereduetotherapid industrializationandenergytransition.Globalwarmingisconsideredthe majorenvironmentalchallengeofthe21stcenturyasenergyconsumptionand theresultingCO2 emissionswillcontinuetoriseinthenearfuture.Thereare manyreportsontherelationbetweenCO2 emissionandenergyconsumption.