https://ebookmass.com/product/biomass-biofuels-biochemicals-
Instant digital products (PDF, ePub, MOBI) ready for you
Download now and discover formats that fit your needs...
Biomass, Biofuels, Biochemicals – Biochemicals and Materials Production From Sustainable Biomass Resources Hu Li
https://ebookmass.com/product/biomass-biofuels-biochemicalsbiochemicals-and-materials-production-from-sustainable-biomassresources-hu-li/
ebookmass.com
Biomass, Biofuels, Biochemicals: Advances in Enzyme Catalysis and Technologies 1st Edition Sudhir P. Singh (Editor)
https://ebookmass.com/product/biomass-biofuels-biochemicals-advancesin-enzyme-catalysis-and-technologies-1st-edition-sudhir-p-singheditor/
ebookmass.com
Biomass, Biofuels, Biochemicals : Microbial Fermentation of Biowastes Le Zhang
https://ebookmass.com/product/biomass-biofuels-biochemicals-microbialfermentation-of-biowastes-le-zhang/
ebookmass.com
Structural engineering handbook 5th Edition Edwin Henry Gaylord (Editor)
https://ebookmass.com/product/structural-engineering-handbook-5thedition-edwin-henry-gaylord-editor/
ebookmass.com
Visualization, Modeling, and Graphics for Engineering Design 2nd Edition – Ebook PDF Version
https://ebookmass.com/product/visualization-modeling-and-graphics-forengineering-design-2nd-edition-ebook-pdf-version/
ebookmass.com
A Handbook for Wellbeing Policy-Making: History, Theory, Measurement, Implementation, and Examples Frijters
https://ebookmass.com/product/a-handbook-for-wellbeing-policy-makinghistory-theory-measurement-implementation-and-examples-frijters/
ebookmass.com
Christmas at Home Carolyn Brown
https://ebookmass.com/product/christmas-at-home-carolyn-brown-3/
ebookmass.com
https://ebookmass.com/product/%e8%bf%99%e6%89%8d%e6%98%af%e4%b8%ad%e5%
ebookmass.com
Smith’s Anesthesia for Infants and Children 9th Edition
Peter J. Davis
https://ebookmass.com/product/smiths-anesthesia-for-infants-andchildren-9th-edition-peter-j-davis/
ebookmass.com
https://ebookmass.com/product/etextbook-978-1305505490-macroeconomicsa-contemporary-introduction/
ebookmass.com
BIOMASS,BIOFUELS,BIOCHEMICALS
CircularBioeconomy:TechnologiesforWaste
Remediation
SeriesEditor:AshokPandey
DistinguishedScientist,CentreforInnovationandTranslationalResearch, CSIR-IndianInstituteofToxicologyResearch,Lucknow,India
BIOMASS,BIOFUELS, BIOCHEMICALS
CircularBioeconomy: TechnologiesforWaste
Remediation
Editedby
SUNITA VARJANI
ScientificOfficer,GujaratPollutionControlBoard,Gandhinagar,Gujarat,India
ASHOK PANDEY
DistinguishedScientist,CentreforInnovationandTranslationalResearch,CSIR-IndianInstituteofToxicology Research,Lucknow,India
MOHAMMAD J.TAHERZADEH
Professor,SwedishCentreforResourceRecovery,UniversityofBora ˚ s,Bora ˚ s,Sweden
HUU HAO NGO
ProfessorofEnvironmentalEngineering,UniversityofTechnologySydney,Sydney,Australia
R.D.TYAGI
ChiefScientificofficer,BOSK-Bioproducts,QuebecCity,Quebec,Canada
Elsevier
Radarweg29,POBox211,1000AEAmsterdam,Netherlands
TheBoulevard,LangfordLane,Kidlington,OxfordOX51GB,UnitedKingdom 50HampshireStreet,5thFloor,Cambridge,MA02139,UnitedStates
Copyright©2022ElsevierInc.Allrightsreserved.
Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproducedortransmittedinanyformorbyanymeans,electronicor mechanical,includingphotocopying,recording,oranyinformationstorageandretrievalsystem,without permissioninwritingfromthepublisher.Detailsonhowtoseekpermission,furtherinformationaboutthe Publisher’spermissionspoliciesandourarrangementswithorganizationssuchastheCopyrightClearance CenterandtheCopyrightLicensingAgency,canbefoundatourwebsite: www.elsevier.com/permissions.
ThisbookandtheindividualcontributionscontainedinitareprotectedundercopyrightbythePublisher (otherthanasmaybenotedherein).
Notices
Knowledgeandbestpracticeinthisfieldareconstantlychanging.Asnewresearchandexperiencebroadenour understanding,changesinresearchmethods,professionalpractices,ormedicaltreatmentmaybecome necessary.
Practitionersandresearchersmustalwaysrelyontheirownexperienceandknowledgeinevaluatingandusing anyinformation,methods,compounds,orexperimentsdescribedherein.Inusingsuchinformationormethods theyshouldbemindfuloftheirownsafetyandthesafetyofothers,includingpartiesforwhomtheyhavea professionalresponsibility.
Tothefullestextentofthelaw,neitherthePublishernortheauthors,contributors,oreditors,assumeanyliability foranyinjuryand/ordamagetopersonsorpropertyasamatterofproductsliability,negligenceorotherwise,or fromanyuseoroperationofanymethods,products,instructions,orideascontainedinthematerialherein.
ISBN:978-0-323-88511-9
ForinformationonallElsevierpublications visitourwebsiteat https://www.elsevier.com/books-and-journals
Publisher: SusanDennis
SeniorAcquisitionsEditor: KatieHammon
EditorialProjectManager: AndreaDulberger
ProductionProjectManager: JoyChristelNeumarinHonestThangiah
CoverDesigner: GregHarris
TypesetbySTRAIVE,India
Contributorsix
Prefacexiii
Solidwasteremediationand sustainabilityinacircular bioeconomy
1.Sustainablebiowasterecyclingtoward zerowasteapproaches
XiunaRen,TaoLiu,YueZhang,XingChen,MukeshKumarAwasthi, andZengqiangZhang
1Introduction3
2Biowastegeneration,collection,and characteristics5
3Biowasterecyclingandresourcerecovery7
4Publicengagementfortheimplementationof wastereductionandrecyclingpolicies8
5Possibletechnologyandmanagementoptionfor biowaste9
6Treatmentandusesofashandbiowasteresidues afterprocessing16
7Bio-basedrecyclingandcirculareconomy17
8Perspectivesforacircularbioeconomy19
9Conclusions19 References19
2.Compostingasasustainabletechnology forintegratedmunicipalsolidwaste management
TaoLiu,HongyuChen,YuwenZhou,SanjeevKumarAwasthi, ShiyiQin,HuiminLiu,ZengqiangZhang,AshokPandey, SunitaVarjani,andMukeshKumarAwasthi
1Introduction23
2Understandingtheprocesstowardsustainable wastemanagementapproach25
3Typesofcompostingandtheirintegratedprocess27
4Roleofcompostingforattenuationofpersistent organicandinorganiccompounds29
5Thecriticalaspectsofcompostingprocess improvementtowardanovelcleancomposting strategy30
6Sustainabilityassessmentandtechnologygapof cleanercomposting31
7Impactofcompostapplicationinsoilbiological propertiesandclimatechange33
8Economicfeasibilityanalysisofcomposting34
9Cerspectivesforcircularbioeconomy35
10Conclusions35 Acknowledgments36 References36
3.Integratedterrestrialweedmanagement andgenerationofvaluableproductsina circularbioeconomy
KrishnaChaitanyaMaturi,IzharulHaq,andAjayS.Kalamdhad
1Introduction41
2Plantsmorphology42
3Weeds43
4Adverseeffectsandtoxicityassessmentofterrestrial weedsoncrops46
5Weedmanagementpractices50
6Perspectivesforcircularbioeconomy57
7Conclusions60 References60
4.Hydrothermalliquefactionofbiomass forthegenerationofvalue-added products
J.Nallasivam,P.FrancisPrashanth,andR.Vinu
1Introduction65
2Roleofoperatingparametersinhydrothermal liquefactionprocesses66
3Feedstocksforhydrothermalliquefaction69
4Coliquefaction74
5Typesofreactorsforhydrothermalliquefaction processes74
6Hydrothermalliquefactionprocessintegration withexistingrefineries80
7Characteristicsofhydrothermalliquefaction products82
8Applicationsofhydrothermalliquefaction products87
9Processeconomics92
10Challengesandopportunities94
11Perspectivesforcircularbioeconomy96
12Conclusions98 References98
5.Circularbioeconomyinagriculturalfood supplychainandvalueaddition
ArvindKumar,V.DavidChellaBaskar,UmanathMalaiarasan, TanujMisra,ManmohanDobriyal,andAnilKumar
1Introduction109
2Presentsituationofagriculturalproduction andconsumptionproblems110
3Linearfoodproductionsystem(LFS)110
4Circulareconomyandfoodsupplychain116
5Perspectivesforcircularbioeconomy119
6Conclusions119 References120
II
Industrialwastewaterremediation andsustainabilityinacircular bioeconomy
6.Sustainableconversionoffoodwaste intohigh-valueproductsthrough microalgae-basedbiorefinery
Jia-XingGuo,Long-LingOuyang,Zhi-GangZhou,CarolSzeKiLin, andZhengSun
1Introduction125
2Classificationoffoodwaste126
3Treatmentmethods129
4Microalgae-basedbioconversionoffoodwaste132
5Techno-economicassessment140
6Perspectivesforacircularbioeconomy145
7Conclusions146
Acknowledgment146
References146
7.Sustainablewastewaterremediation technologiesforagriculturaluses
AnitaSingh,KaushikGautam,andMadhoolikaAgrawal
1Introduction153
2Wastewatergeneration154
3Wastewatertreatmenttechnologiesforusein agriculture157
4Policiesandguidelinesforwastewatertreatmentfor agriculturaluses167
5Perspectivesforcircularbioeconomy168
6Conclusions172
Acknowledgments172
References172
8.Sustainableaquaculturewastewater remediationthroughdiatomandbiomass valorization
BhartiMishraandArchanaTiwari
1Introduction181
2Compositionofaquaculturewastewater184
3Cultivationofdiatomsinaquaculture184
4Roleofdiatomsinaquaculturewastewater remediation187
5Potentialapplicationofdiatomsbasedaqua feed188
6Biocontrolefficacyofdiatoms191
7Diatomsasasourceofhigh-valueproducts194
8Diatomsforbiofuels195
9Perspectivesforcircularbioeconomy196
10Conclusions198
Acknowledgment198
References198
9.Membranebioreactorforthetreatment ofemergingpharmaceuticalcompounds inacircularbioeconomy
PunitKumar,MrinalKantiMandal,SupriyaPal,HirokChaudhuri, andKashyapKumarDubey
1Introduction203
2Membranebioreactor(MBR)205
3Membranefoulingmechanisms206
4Methodstocontrolthemembranefouling208
5Removalofemergingpharmaceuticalcompounds usingMBR210
6Factorsaffectingmembranebioreactors (MBRs)212
7Comparisonofmembranebioreactors(MBRs)with conventionalprocesses215
8Perspectivesforacircularbioeconomy215
9Conclusions216
Acknowledgments217
References217
10.Circularbioeconomyperspectiveof agro-waste-basedbiochar
MuhammadKashifShahid,AyeshaKashif,YounggyunChoi, SunitaVarjani,MohammadJ.Taherzadeh,andPrangyaRanjanRout
1Introduction223
2Feedstockforbiocharproduction224
3Conversiontechnologies227
4Applicationsofbiochar228
5Environmentalimpactofbiochar233
6Perspectivesforcircularbioeconomy234
7Conclusions235
Acknowledgments235 References236
11.Sustainableanaerobictechnologiesfor biogasandbiohythaneproduction
YuQin,HuiCheng,andYu-YouLi
1Introduction245
2Fundamentalsinanaerobictechnologies246
3Operatingfactors247
4Anaerobiccodigestion249
5Anaerobicmembranebioreactor253
6Biohythaneproduction259
7Perspectivesforcircularbioeconomy263
8Conclusions264
Acknowledgment265
References265
12.Microbialbiomassforsustainable remediationofwastewater
NeeluNawani,AminurRahman,andAbulMandal
1Introduction271
2Typesofwastewaters,sourcesandtheireffectonthe environment272
3Microbialtechnologiesusedinwastewater remediationwithspecialreferencetoheavy metals276
4Commerciallyviabletechnologiesforwastewater remediation279
5Newdimensionstowastewatertreatmentandallied processes284
6Perspectivesforacircularbioeconomy286
7Conclusions288
Acknowledgment288
References288
13.Integratedtechnologiesfor thetreatmentofandresourcerecovery fromsewageandwastewaterusingwater hyacinth
ManjushaAnipeddi,SameenaBegum,andGangagniRaoAnupoju
1Introduction293
2Harvestingofwaterhyacinth295
3Utilizationofwaterhyacinthbiomass305
4Perspectivesforcircularbioeconomy310
5Conclusions311
Acknowledgments312 References312
14.Techno-economicanalysisand life-cycleassessmentofvermi-technology forwastebioremediation
SanketDeyChowdhury,RupamBandyopadhyay,and PuspenduBhunia
1Introduction315
2Mechanismofvermi-technology316
3Applicationofvermi-technology321
4Life-cycleassessment(LCA)studieson vermi-technology330
5Environmentalbenefitsof vermi-technology337
6Economicalperspectivesandlinkagetocircular bioeconomy339
7Conclusions343
Acknowledgment344
References344
15.Integratedtechnologiesforthe remediationofpaperindustrywasteina circularbioeconomy
IzharulHaq,AnshuSingh,andAjayS.Kalamdhad
1Introduction351
2Anoverviewofpaperindustry352
3Paperindustrywaste352
4Remediationofwastegeneratedfrompaper industry353
5Developmentofvaluableproductfromwaste356
6Challenges357
7Perspectivesforcircularbioeconomy357
8Conclusions358
Acknowledgment359 References359
16.Constructedwetlandsystemforthe treatmentofwastewaterinacircular bioeconomy
RajatChandrakantPundlik,RajeshRoshanDash,and PuspenduBhunia
1Introduction365
2Constructedwetlands367
3Enhancedconfigurationforperformance growth370
4Hybridconstructedwetlandsystemsforacircular bioeconomyapproach374
5Environmentbenefitsofconstructedwetlands379
6Challengesofconstructedwetlands380
7Perspectivesforacircularbioeconomy380
8Conclusions382 References383
17.Productionandenvironmental applicationsofactivatedsludgebiochar
AbhishekGupta,AnuradhaSingh,TalatIlyas,PankajChowdhary, andPreetiChaturvedi
1Introduction387
2Processingofactivatedsludge388
3Valorizationofbiowaste390
4Applicationsofactivatedsludgebiochar392
5Perspectivesforcircularbioeconomy396
6Conclusions398
Conflictsofinterests398
Acknowledgments399 References399
18.Waste-derivedvolatilefattyacids forsustainableruminantfeed supplementation
AmirMahboubi,SwarnimaAgnihotri,ClarisseUwineza, UmarinJomnonkhaow,andMohammadJ.Taherzadeh
1Introduction407
2Organicwastes,digestion,andvolatilefattyacids inacircularbioeconomy409
3Ruminaldigestionandfermentation411
4Volatilefattyacidsasfeedadditivesinruminant diet413
5Waste-derivedvolatilefattyacids(VFA)417
6Perspectivesforcircularbioeconomy423
7Conclusions424 References424
19.Sustainablemanagementofalgal bloomsinpondsandrivers
OmarAshrafElFar,NurulSyahirahMatAron,KitWayneChew,and PauLokeShow
1Introduction431
2Characteristicsandtypesofalgae432
3Potentialofconvertingalgaeinto bioresources432
4Hazardsofalgalbloom433
5Harvestingofalgaefromalgalbloomsites436
6Extractionofbioproductsfromalgalblooms437
7Strategiestoharvestandutilizealgalbloom biomassinindustry5.0438
8Perspectivesforcircularbioeconomy438
9Conclusions440
References440
Index445
Contributors
SwarnimaAgnihotri SwedishCentrefor ResourceRecovery,UniversityofBora ˚ s,Bora ˚ s, Sweden
MadhoolikaAgrawal CenterofAdvanced StudyinBotany,InstituteofScience,B.H.U., Varanasi,UttarPradesh,India
ManjushaAnipeddi Bioengineeringand EnvironmentalSciences(BEES)Division, DepartmentofEnergyandEnvironmental Engineering(DEEE),CSIR-IndianInstituteof ChemicalTechnology,Hyderabad,India
GangagniRaoAnupoju Bioengineeringand EnvironmentalSciences(BEES)Division, DepartmentofEnergyandEnvironmental Engineering(DEEE),CSIR-IndianInstituteof ChemicalTechnology,Hyderabad;Academy ofScientificandInnovativeResearch(AcSIR), Ghaziabad,India
NurulSyahirahMatAron Departmentof ChemicalandEnvironmentalEngineering, FacultyofScienceandEngineering,University ofNottinghamMalaysia,Semenyih,Malaysia
MukeshKumarAwasthi CollegeofNatural ResourcesandEnvironment,NorthwestA&F University,Xianyang,China
SanjeevKumarAwasthi CollegeofNatural ResourcesandEnvironment,NorthwestA&F University,Xianyang,China
RupamBandyopadhyay Schoolof Infrastructure,IndianInstituteofTechnology, Bhubaneswar,Odisha,India
V.DavidChellaBaskar RaniLakshmiBai CentralAgricultureUniversity,Jhansi,India
SameenaBegum Bioengineeringand EnvironmentalSciences(BEES)Division, DepartmentofEnergyandEnvironmental Engineering(DEEE),CSIR-IndianInstituteof ChemicalTechnology,Hyderabad,India
PuspenduBhunia SchoolofInfrastructure, IndianInstituteofTechnology,Bhubaneswar, Odisha,India
PreetiChaturvedi AquaticToxicology Laboratory,EnvironmentalToxicologyGroup, CouncilofScientificandIndustrialResearchIndianInstituteofToxicologyResearch (CSIR-IITR),Lucknow,UttarPradesh,India
HirokChaudhuri DepartmentofPhysics, NationalInstituteofTechnology,Durgapur, India
HongyuChen CollegeofNaturalResources andEnvironment,NorthwestA&FUniversity, Xianyang,China
XingChen CollegeofNaturalResourcesand Environment,NorthwestA&FUniversity, Xianyang,China
HuiCheng SchoolofEnvironmentaland ChemicalEngineering,ShanghaiUniversity, Shanghai,China
KitWayneChew SchoolofEnergyand ChemicalEngineering,XiamenUniversity Malaysia,Sepang,Malaysia
YounggyunChoi Departmentof Environmental&ITEngineering,Chungnam NationalUniversity,Daejeon,SouthKorea
PankajChowdhary AquaticToxicology Laboratory,EnvironmentalToxicology Group,CouncilofScientificandIndustrial Research-IndianInstituteofToxicology Research(CSIR-IITR),Lucknow,UttarPradesh, India
RajeshRoshanDash SchoolofInfrastructure, IndianInstituteofTechnology,Bhubaneswar, Odisha,India
SanketDeyChowdhury Schoolof Infrastructure,IndianInstituteofTechnology, Bhubaneswar,Odisha,India
ManmohanDobriyal RaniLakshmiBaiCentral AgricultureUniversity,Jhansi,India
KashyapKumarDubey Bioprocess EngineeringLaboratory,Schoolof Biotechnology,JawaharlalNehruUniversity, NewDelhi,India
OmarAshrafElFar SchoolofPharmacy,Faculty ofScienceandEngineering,Universityof NottinghamMalaysia,Semenyih,Malaysia
KaushikGautam CenterofAdvancedStudyin Botany,InstituteofScience,B.H.U.,Varanasi, UttarPradesh,India
Jia-XingGuo KeyLaboratoryofExploration andUtilizationofAquaticGeneticResources, MinistryofEducation;InternationalResearch CentreforMarineBiosciences,Ministryof ScienceandTechnology;National DemonstrationCentreforExperimental FisheriesScienceEducation,ShanghaiOcean University,Shanghai,China
AbhishekGupta AquaticToxicology Laboratory,EnvironmentalToxicologyGroup, CouncilofScientificandIndustrialResearchIndianInstituteofToxicologyResearch (CSIR-IITR),Lucknow,UttarPradesh,India
IzharulHaq DepartmentofCivilEngineering, IndianInstituteofTechnologyGuwahati, Guwahati,Assam,India
TalatIlyas AquaticToxicologyLaboratory, EnvironmentalToxicologyGroup,Councilof ScientificandIndustrialResearch-Indian InstituteofToxicologyResearch(CSIR-IITR), Lucknow,UttarPradesh,India
UmarinJomnonkhaow Departmentof Biotechnology,FacultyofTechnology,Khon KaenUniversity,KhonKaen,Thailand
AjayS.Kalamdhad DepartmentofCivil Engineering,IndianInstituteofTechnology Guwahati,Guwahati,Assam,India
AyeshaKashif DepartmentofSeniorHealth Care,EuljiUniversity,Daejeon,SouthKorea
AnilKumar RaniLakshmiBaiCentral AgricultureUniversity,Jhansi,India
ArvindKumar RaniLakshmiBaiCentral AgricultureUniversity,Jhansi,India
PunitKumar DepartmentofMorphologyand Physiology,KaragandaMedicalUniversity, Karaganda,Kazakhstan
Yu-YouLi DepartmentofCiviland EnvironmentalEngineering,GraduateSchool ofEngineering,TohokuUniversity,Sendai, Japan
CarolSzeKiLin SchoolofEnergyand Environment,CityUniversityofHongKong, Kowloon,HongKong
HuiminLiu CollegeofNaturalResourcesand Environment,NorthwestA&FUniversity, Xianyang,China
TaoLiu CollegeofNaturalResourcesand Environment,NorthwestA&FUniversity, Xianyang,China
AmirMahboubi SwedishCentreforResource Recovery,UniversityofBora ˚ s,Bora ˚ s,Sweden
UmanathMalaiarasan MadrasInstituteof DevelopmentStudies,Chennai,India
AbulMandal SchoolofBiosciences,University ofSkovde,Skovde,Sweden
MrinalKantiMandal DepartmentofChemical Engineering,NationalInstituteofTechnology, Durgapur,India
KrishnaChaitanyaMaturi DepartmentofCivil Engineering,IndianInstituteofTechnology Guwahati,Guwahati,Assam,India
BhartiMishra DiatomResearchLaboratory, AmityInstituteofBiotechnology,Amity University,Noida,UttarPradesh,India
TanujMisra RaniLakshmiBaiCentral AgricultureUniversity,Jhansi,India
J.Nallasivam DepartmentofChemical EngineeringandNationalCenterfor CombustionResearchandDevelopment, IndianInstituteofTechnologyMadras, Chennai,India
NeeluNawani MicrobialDiversityResearch Centre,Dr.D.Y.PatilBiotechnologyand BioinformaticsInstitute,Dr.D.Y.Patil Vidyapeeth,Pune,India
Long-LingOuyang KeylaboratoryofEast ChinaSeaFisheryResourcesExploitation, MinistryofAgricultureandRuralAffairs,East
ChinaSeaFisheriesResearchInstitute,Chinese AcademyofFisherySciences,Shanghai,China
SupriyaPal DepartmentofCivilEngineering, NationalInstituteofTechnology,Durgapur, India
AshokPandey CentreforInnovationand TranslationalResearch,CSIR-IndianInstitute ofToxicologyResearch,Lucknow,India
P.FrancisPrashanth DepartmentofChemical EngineeringandNationalCenterfor CombustionResearchandDevelopment, IndianInstituteofTechnologyMadras, Chennai,India
RajatChandrakantPundlik Schoolof Infrastructure,IndianInstituteofTechnology, Bhubaneswar,Odisha,India
ShiyiQin CollegeofNaturalResourcesand Environment,NorthwestA&FUniversity, Xianyang,China
YuQin DepartmentofCivilandEnvironmental Engineering,GraduateSchoolofEngineering, TohokuUniversity,Sendai,Japan
AminurRahman SchoolofBiosciences, UniversityofSkovde,Skovde,Sweden
XiunaRen CollegeofNaturalResourcesand Environment,NorthwestA&FUniversity, Xianyang,China
PrangyaRanjanRout Departmentof Biotechnology,SchoolofEnergyand Environment,ThaparInstituteofEngineering andTechnology,Patiala,Punjab,India
MuhammadKashifShahid ResearchInstitute ofEnvironment&Biosystem,Chungnam NationalUniversity,Daejeon,SouthKorea
PauLokeShow DepartmentofChemicaland EnvironmentalEngineering,FacultyofScience andEngineering,UniversityofNottingham Malaysia,Semenyih,Malaysia
AnitaSingh CenterofAdvancedStudyin Botany,InstituteofScience,B.H.U.,Varanasi, UttarPradesh,India
AnshuSingh DefenceInstituteofBio-energy Research-DRDO,Haldwani,Uttrakhand,India
AnuradhaSingh AquaticToxicology Laboratory,EnvironmentalToxicologyGroup, CouncilofScientificandIndustrialResearchIndianInstituteofToxicologyResearch (CSIR-IITR),Lucknow,UttarPradesh,India
ZhengSun KeyLaboratoryofExplorationand UtilizationofAquaticGeneticResources, MinistryofEducation;InternationalResearch CentreforMarineBiosciences,Ministryof ScienceandTechnology;National DemonstrationCentreforExperimental FisheriesScienceEducation,ShanghaiOcean University,Shanghai,China
MohammadJ.Taherzadeh SwedishCentrefor ResourceRecovery,UniversityofBora ˚ s,Bora ˚ s, Sweden
ArchanaTiwari DiatomResearchLaboratory, AmityInstituteofBiotechnology,Amity University,Noida,UttarPradesh,India
ClarisseUwineza SwedishCentreforResource Recovery,UniversityofBora ˚ s,Bora ˚ s,Sweden
SunitaVarjani GujaratPollutionControlBoard, Gandhinagar,Gujarat,India
R.Vinu DepartmentofChemicalEngineering andNationalCenterforCombustionResearch andDevelopment,IndianInstituteof TechnologyMadras,Chennai,India
YueZhang CollegeofNaturalResourcesand Environment,NorthwestA&FUniversity, Xianyang,China
ZengqiangZhang CollegeofNaturalResources andEnvironment,NorthwestA&FUniversity, Xianyang,China
YuwenZhou CollegeofNaturalResourcesand Environment,NorthwestA&FUniversity, Xianyang,China
Zhi-GangZhou KeyLaboratoryofExploration andUtilizationofAquaticGeneticResources, MinistryofEducation;InternationalResearch CentreforMarineBiosciences,Ministryof ScienceandTechnology;National DemonstrationCentreforExperimental FisheriesScienceEducation,ShanghaiOcean University,Shanghai,China
Preface
Thebooktitled CircularBioeconomy:TechnologiesforWasteRemediation isapartofthe comprehensiveseries Biomass,Biofuels,Biochemicals (SeriesEditor:AshokPandey).The leapfrogincreaseinsolidwasteandwastewaterbyindustrialactivitiesandwastematerialsgeneratedbyhumanactivity,duetothe potentialharmfuleffectsontheenvironment andpublichealth,ledtoincreasingawareness aboutthealarmingneedforthedevelopment ofnoveltechnologiesforthemanagementof bothsolidwasteandwastewater.Onthe onesidethereisaneedtominimizewaste generationandontheothersidethereisa needtoreuseandrecyclethem.Thetechnologiesformanaging/treatingsuchwastesplay animportantroleinmitigatingissuescreated bywastegeneration.Apartfromthis,recoveryofenergyandfuelsfromwastesbyvarioustechnologiesleadstonotablereduction inthetotalquantityofwastegenerated, whichneedstobedisposedoffinallyinacontrolledmannerwhilemeetingpollutioncontrolstandards.Reductioninthequantumof solidandliquidwasteisacriticalissue,particularlyinlightoffiniteavailabilityofdisposalsitesatmanypartsaroundtheglobe. Althoughtreatmentplantsforwastestreams andby-productrecoveryprocesseshavebeen introducedinmanysectors,lifecycleassessmentandtechno-economicfeasibilityprovide detailedunderstandingforadaptingtechnologyforsustainability,whichformsanintegral partofthecircularbioeconomy.Integrationof biological,thermal,andchemicalprocessesin resourcerecoveryfromsolidwasteand wastewaterintovalue-addedproductswould
helpimplementthecircularbioeconomyapproachincludingsocialaspects.
Amongvariousenvironmentalproblems, effectivesolidwasteandwastewatermanagement/treatmentareimportantsectors thatneedmoreattention.Thepresentsystem dealingwithmanagement/treatmentofboth sectorsisstillnotuptothemarkformeeting societalneedsofthegrowingworldpopulation.Thisbooktouchesuponvariousaspects ofsolidwasteandwastewatermanagement/treatment.Itcoverstechnologicalinterventionsinwastemanagementinavery straightforwardandscientificmanner.The bookalsocoverstrendsandperspectives forcircularbioeconomyinthetreatmentof wastestreams(solidwasteandwastewater) andproductionofvalue-addedproducts fromthewastes.Thebookprovidesinformationabouttheproductionofvalue-added productsthroughdifferentwaystoincrease productselectivitywiththeintegrationof technologies.Theeditorshavemadeserious attemptstoensurethatthisbookisasrelevanttoallaspectsaspossible,addressing burningissuesinthefieldofwasteremediationandsustainabilityandtherationale underpinningthem.
Thisbookcoversin-depthinformation aboutthestrategiesandapproachesfacilitatingtheintegrationoftechnologiesforwastewaterandsolidwasteremediation.Thebook highlightsthemodelsdevelopedtovalorize wastesfortheproductionofbio-basedproducts.Wastewatersandsolidwastearean abundantsecondarysourceforfiniteresources;hence,nutrientremovalfromwaste
streamsisimportantinacircular bioeconomy.Remediation/valorizationof solidwasteorwastewaterwouldreduceenvironmentalpollution.Integrationoftechnologies,includinglifecycleanalysisand techno-economicanalysisofsuchprocesses tovalorizethewastesforvalue-addedproducts,isoneoftheaspectsofthecirculareconomythatneedtobegivenaholisticandallinclusiveapproach,andthishasbeen addressedinthebook.
Variouschapterspresentedinthebook havefocusedonthesustainabilityapproaches asthecenterthemeinordertofacilitateindustriesandpolicymakersforadoptingcircular economygoals.Sincetheprincipalideaisto makeatransitionfromlineareconomytoa circularbioeconomy,itinvolvesadvanced technologicalanddesigningbreakthroughs toreducewastewithaclose-loopedsystem. Thispioneersacradle-to-cradleandwasteto-resourcesapproach.Integrationofvarious technologieshasbeenconsideredaspossibly thebestwaytoutilizethewastes. Chapter1 dealswiththesustainablebiowasterecycling towardzerowasteapproaches,whichemphasizesthatitisessentialtosatisfytherequirementsofzerowastetorecycle biowastesinasustainableway.Inorderto improveandmakebetteruseofthesebiotechnologiesinactualproduction,moreefforts mustbemade. Chapter2 describescompostingasasustainabletechnologyforintegratedmunicipalsolidwaste,which reviewstherecentdevelopmentsinthecompostingoforganicmanureasasustainable technologyforintegratedsolidwastemanagement. Chapter3 examinestheefficiency, toxicity,andviableoptionforconvertingterrestrialweedsintovalue-addedproducts throughabiologicalmanagementcompostingtechniqueinacircularbioeconomy. Chapter4 discussesthepossibilitiesof derivingchemicals,fuelmolecules,andbioproductsfromarangeoffeedstocksvia
HTLtechnology,withspecialemphasison (a)characteristicsandapplicationsofdifferentproductsfromHTL,(b)possibilitiesoftailoringtheselectivitytospecificchemicalsby usingcatalysts,(c)challengesandopportunitiesinintegratingtheHTLproductsinthe existingrefineryinfrastructure,and (d)industrialpotentialandeconomicsofthe process. Chapter5 presentsacircular bioeconomyintheagriculturalfoodsupply chainandvalueaddition. Chapter6 focuses onthesustainableconversionofwasteinto high-valueproductsthroughamicroalgaebasedbiorefinery. Chapter7 presentsdifferentsustainabletechnologiesusedtoreduce theriskrateofwastewaterutilization.Itisalso correlatedwiththeperspectiveofacircular bioeconomy,i.e.,shiftfrom“useandthrow” toa“use,treat,andreuse.”Theobjectiveof thecircularbioeconomycanonlybefulfilled byrecoveringtheresourcesfromwastewater sothattheycanbereusedforthebetterment oftheenvironmentandbenefitofthesociety. Chapter8 highlightsthediverseroleof microalgaeinaquaculturewastewaterquality evaluation,remediation,andaquafeedpotentialasasustainablesolution. Chapter9 discussesmembranebioreactorsforthe treatmentofemergingpharmaceuticalcompoundsinacircularbioeconomy. Chapter10 focusesonthesynthesisandapplicationofagro-waste-basedbiocharwitha perspectiveofthecircularbioeconomy. Chapter11 focusesontheapplicationofanaerobictechnologiesforcircularbioeconomy. Therealizationofrecyclingsocietyrequires accelerationtodrivethebiomassflowing alongthecycles,whiletheanaerobicapproachesaregenerallyslow. Chapter12 compilesthelatesttechnologiesinwhich microbial/bacterialbiomasswasusedfor wastewatertreatmentandremediation,with aspecialfocusontheremediationofwastewaterscontaminatedwithheavymetalsdescribingthebasictechnologiesaswellas
smarttechnologies.Emphasisisgivento thecircularbioeconomyandhowitcanbe implementedinwastewatertreatment. Chapter13 describesthenumerouswaysof valorizingwaterhyacinth,whichmayhave ahugepotentialtocreateanicheinthecircularbioeconomy. Chapter14 presentsatechnoeconomicanalysisandlifecycleassessment ofvermintechnologyforwastebioremediation. Chapter15 providesupdateddetails ontheproductionofpaperandthegeneration ofwastewateranditscharacteristicsandtoxicity.Biologicalandphysicochemicalprocesseshavealsobeendiscussedforthe treatmentofwastewaterfromthepaperindustry. Chapter16 presentsthepossibleapplicationofconstructedwetlandsfocused ondesign,optimization,sustainability,and resourcegenerationtowardacircularbioeconomy. Chapter17 providescomprehensiveinformationoninnovativetechnologies andstrategiesforgreenerwastemanagement andsustainableeconomicdevelopment. Chapter18 discusseswaste-derivedvolatile fattyacidsasasustainablesourceofanimal feed.Finally, Chapter19 focusesontherelationshipofalgalbloomandeutrophication withparticularfocusontheapplicationand implicationofalgal.Agriculturalcultivation
ofalgaeisoneofthepromisingsolutionsto improvetheproductionandefficiencyof bio-basedproducts,reductionofgreenhousegasemissions,andextractionofconstituentsthatareusedasdiagnosticand medicinetools.Thechapteralsodiscusses stepstoidentifyandharvestalgaefromthealgalbloomsites.
Wegratefullyacknowledgealltheauthors fortheircontributionstothisbook.Wethank thereviewerswhoprovidedvaluablesuggestionstoimprovedifferentchapters.We greatlyappreciateDr.KostasMarinakis,FormerSeniorBookAcquisitionManager; Ms.KatieHammon,SeniorBookAcquisition Manager;AndreaDulberger,EditorialProjectManager;KumarAnbazhagan,ProductionManager;andothersatElsevierfor theirsupporttowardpublishingthebook. Weareconfidentthatthebookwouldbeof greatvalueforacademiciansandresearchers aswellasforpolicyplannersandindustry persons.
SunitaVarjani AshokPandey
MohammadJ.Taherzadeh HuuHaoNgo R.D.Tyagi
Solidwasteremediationand sustainabilityinacircular bioeconomy
Sustainablebiowasterecyclingtoward zerowasteapproaches
XiunaRen,TaoLiu,YueZhang,XingChen, MukeshKumarAwasthi,andZengqiangZhang CollegeofNaturalResourcesandEnvironment,NorthwestA&FUniversity,Xianyang,China
1Introduction
AccordingtotheWorldResourcesInstitution(WRI),theworldwidepopulationis expectedtoreach10billionpeopleby2050,withtheprosperityanddevelopmentofsocial economy [1].Hugeenergydemandwillinevitablyaggravatethedepletionandscarcityof nonrenewableresourceswhilealsobringingaboutseriousecologicalandsocioeconomic challengessuchashugewastegeneration,environmentalpollution,andclimatechange [2].Hence,sustainabledevelopmentisthebestwaytomanagebiowaste.Biorefineriesareespeciallynecessaryinthecircularbioeconomy.Thetransitionfromasinglelineardevelopmentmodeltoasustainableeconomywhichgasgraduallytriggeredpeopleattention [3].
Biowasteisconsideredtobewastefromtheagriculturalproductionprocessaswellas wastefromthedevelopmentofcompositematerials.Biorefinery,amaintechnologyofsustainabledevelopment,couldnotonlyimproveutilizationefficiencyofbiomassresources,but alsopreventenvironmentalpollutionthrougheffectivemanagement.Besides,theproducts generatedinthebiorefineryprocesslikebiofertilizer,biochemistry,bioenergy,andothers werebeneficialforeconomicdevelopment [4].Asanindispensablerenewableresourcefor energyandconsumerproducts,biowastehasaninestimablepotentialvalueinthebiological developmentfieldtobiorefineriesduetoitslargequantityanddiversecomposition.Nizami [5] reportedthattheworldgenerates1.3billiontonsayearofbiowaste,andcouldreach2.2 billiontonsayearby2025.TheWorldEnergyCouncil(WEC)reportedthatbiofuelsextracted frombiomasswillreplaceabout40%ofthepetroleumusedintransportationin2050 [3].To achievesustainabilityofbiowastemanagement,thereareaseriesofbiotechnologiesin recyclingbiowaste,includingthermaltreatmentaswellasaerobicandanaerobictreatment.
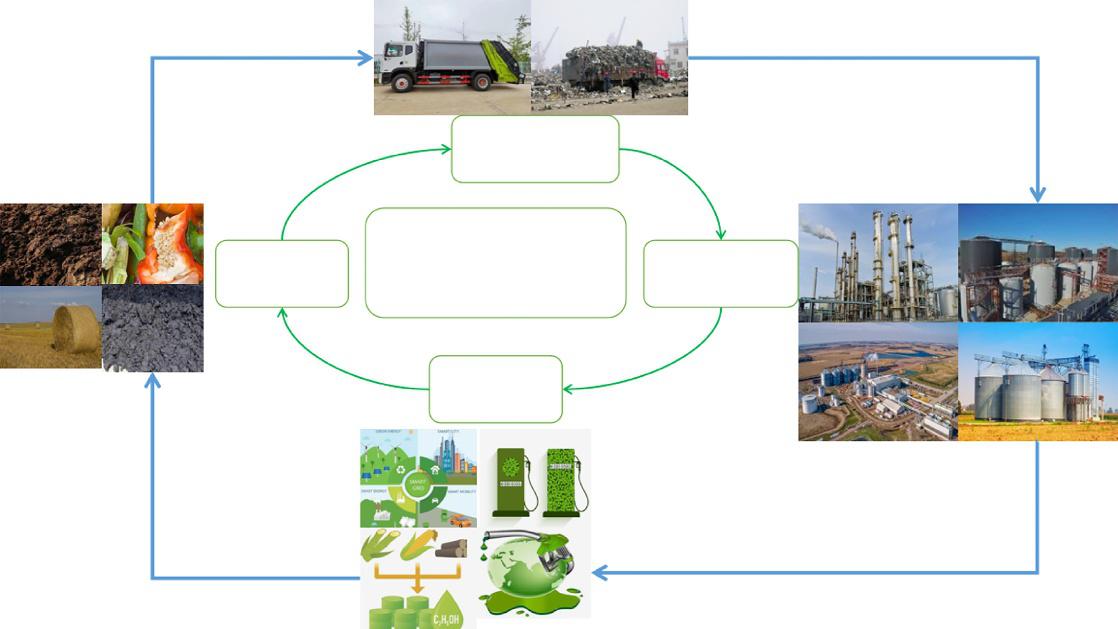
Thesetechnologiessucceededinthebioconversionofwasteintofuel,heatsources,electrical energy,andbioproducts(i.e.,biochemical,biofuel,bioenergy) [6].Accordingtotheenvironmentallyfriendlytarget,thebioeconomyutilizedorganicresourcestogenerateproductsthat hadinestimableeconomicandsocialvalue.Thedevelopmentofthebioeconomyhashuge opportunities,potential,andbroadprospects.TheEuropeanCommissionproposeda bioeconomystrategyin2012,updatedin2018,thatrecommendedreinforcingbio-relatedindustriesandpromotingabioeconomiclayout.Itwasimportanttoexploitthepotentialof biowasteandprotecttheecosystemtoachieveanenvironmentallyfriendlyrecycling bioeconomyandworldwidechallenges(i.e.climatechange) [7].Fromanenergypointof view,biorefineriesareconsideredtobeaneffectivemethodofbiowastemanagement,providingcost-effectiveandprospectiveapproachesforenhancingenergysustainabilityand achievingsustainablewastetreatmenttorealizeacircularbioeconomy [8].Usingthemethod shownin Fig.1,thedevelopmentfromtraditionalthermoelectricfuelstobioagricultureand bioenergyutilizationtoachievesustainableofbiowaste.Duetothevarietyofnaturalrawmaterials,thedifferencesinapplicablepractices,geographyandbiomassavailability,insufficientinfrastructure,lowinvestmentandmarketization.Thereareavarietyoftechnology andfinanceobstaclesaswellassocietychallenges [9].Thesustainabledevelopmentof bioeconomyisclosetothecontributionofbiotechnologytotheeffectiveusingofbiowaste, optimizingtheincentivemechanism,strengtheninnovationandpromoteindustrialization.
Takingintoaccountthehugedevelopmentpotentialofthebiowastesustainablemodel, basedontheabundantbiowasteresourcesandstrongmarketdemand,inthischapter,we giveacomprehensiveexplanationofitscurrentsituationaswellaspublicparticipationin
implementingwastereductionandrecyclingpoliciesandmeasuresforthereasonablemanagementandutilizationofbiowaste.Meanwhile,thetechnology,managementoption,stateof recyclingandcirculareconomywassucceedimplementationintheconceptofbiowaste sustainability.
2Biowastegeneration,collection,andcharacteristics
Biowasteisatypeofwastematerialthathastheabilitytodegradeorganicmatter(OM) underananaerobicoraerobicprocess.Biomasscomesfromlivingthings,includingbiosolids (sewagesludge),animals,andwoodandgreenwaste [10,11].TheconcentrationofOMand nutrientsrequiredbyplantsinbiowasteisincreased,makingitagoodsoilfertilizer.Commercialresourcesfromforests,agriculturalproducts,animalcarcasses,manure,sewage sludge,andfoodwasteshavebeenwidelyused.Householdresourcescontainkitchenand gardenwaste,paperandcardboard,andnaturaltextilesthatalsoformpartofbiowaste. Rapidpopulationgrowth,vigorousurbanization,andimprovementoflivingstandardshave increasedenergydemandandwasteproduction.Biowastewillcausepollutioninallaspects, includingproducingodorseasily,pollutingwaterandsoil,andincreasingGHG,allofwhich aremajorchallengesfacingtheenvironment.Itisnecessarytoexploresustainableapproaches toimprovetheecology [12].Biowastecomesfromvariablesourceswithdifferenthuman activities,includingagriculturalandindustrialactivitieswithheterogeneousandvariable characteristics.Proteins,sugars,andmineralscontainedinbiowastearevaluableresources forthegenerationofbioproductsthroughcomprehensivebioprocesses.However,dueto differencesineconomicconditionsandindustrialstructures,wastecomponentsindifferent regionsaredifferent,anddisposalmethodsarenotthesame.
Agriculturalactivitiesproducelargeamountsoflignocellulose,containingteaseeds,crop waste(straw,stems,andshells),peels,andotherseeds,mainlycomposedofcellulose(35%–50%),hemicellulose(25%–30%),andlignin(25%–30%) [5].Organicsolidwasteproducedin agriculturecontainshighlignocellulose,whichcandevelopandproducevaluablebiological products.Theyarewidelyusedinindustrialbiorefineriesandtransformedintofuel,biochar, organicfertilizer,andcompositematerials.Withtherapiddevelopmentofindustrialization, biowastehasattractedwidespreadattention,involvingvarioussourcessuchasplants,poultryprocessing,slaughterhouses,andthewood,sugar,andpaperindustries.Forexample,a varietyofproducts(ethanol,methane,oil,enzymes,andnanocellulose)areextractedfrom orangepeelsthroughmicrobialengineeringtechnology [13].Thefoodandpaperindustry arethemostimportantwaste-sustainingsector.Itiswidelyreportedthatfoodwasteishighly degradableandhaspotentialforenergybiotransformation.Amongthem,vegetablesand fruitsaresuitableforthecompositionoforganicacidsandvitalenzymes.Animalmeat,which isabundantwithproteinandhair,iscombinedwithanaerobicdigestiontogenerateproteases.Fatandproteinflowoutduringfishprocessing,andtheyaresuitableforproducingesterasethatisbeneficialtochemicalproduction [13].Withtherapidincreaseofpopulationand urbanization,urbanbiowastehasturnedintoaninevitablebarriertosocialdevelopment. Householdwasteandcateringwastearecommonbiowasteswhosemaincomponentsareorganicandcanbeusedforabiorefinery [12].Inparticularly,foodwastecomesfromfood
processing,producing,distribution,andconsumptioninresidentialkitchens,commercial restaurants,andmarketshops.Thecompositionofhouseholdwasteiscomplex,containing paper,bread,noodles,rice,andvegetables.Theyallcontainorganicingredientssuchasfat, cellulose,andprotein.Becausebiowasteisextremelyperishable,itcanunpleasantodors, GHGs,andotherpollution.Itstreatmentfacesseverechallenges. Table1 showsthedifferent typesofbiowastestrategictechnologies.
TABLE1 Differenttypesofbiowastestrategictechnologies.
Typeof biorefineryBiowasteStrategictechnologyRemarksoncirculareconomyReferences
WasteSawdust,rice husk,pig manure
WasteLivestock manure
WasteChicken manure, Caragana microphylla straw
WasteFoodwaste, dryleaves
LignocelluloseAgriculture waste
LignocelluloseAgriculture waste
Reactorcomposting, staticcomposting, windrow composting
Electricfield-assisted aerobiccomposting
Biocharandfluegas desulfurization, gypsum cocomposting
Consideringtheimprovedtreatment efficiencyandtheenvironmental benefits,reactorcompostingmayhave morepotentialinthedevelopmentof sustainablecompostingtechnology
Thisopensanewwaytorecoverwaste heatduringaerobiccompostingand acceleratecompostmaturity
Theeffectofbiocharcombinedwith gypsumoncompostqualitywasclosely associatedwithmicrobialactivitiesand functions,andplayedapivotalrolein determiningtheagronomic performanceofcompost [16]
ReactorcompostingThisstudycouldprovidethe appropriateconditionsforsmall-scale compostingwithfoodwasteanddry leaves
Enzymatic saccharification
Proteomics-basedsaccharificationand fermentationcompoundtechnologyhas hugepotentialforglobalcommercial benefits
AnaerobicdigestionIthashugepotentialtotransformitinto asustainableplatformwithvalueaddedproducts/chemicals/biofuels. ThebyproductsofPHA,bioplastics, andorganicacidsmeetsocialneedsand development [19]
WasteFoodwasteIntegrated biorefinery
Lacticacidandbiogasdemonstratethe opportunitytotransformfromalinear bioeconomytoacircularbioeconomy, supportingregenerationandrepair systemsbypreventingwasteand economicprofitability [20]
Therearemanykindsofbiologicalwaste.Thethreetypeswiththehighestyieldarethe mostcommon:agriculturalresidue,foodwaste,andsewagesludge.Wasteproductscan beconvertedintovaluableresourcesbyincineration,anaerobicfermentation,orcomposting, generatinglargeamountsofheat,electricity,orfertilizer.
3.1Livestockandpoultrymanure
Producedintheprocessoflivestockandpoultrybreedingpollutionisthemainsourceof agriculturalnonpointsourcepollution,occurringintheprocessoflivestockandpoultry breedinglivestockandpoultrydungbesidescontainrichorganicnitrogenphosphorus andpotassium,alsocontainsmetalelements,pathogenicmicroorganisms,allkindsofcolloid andhasnotbeenfullydigestplantresidues,haveabadodor,willdirectlyorindirectlyleadto soilandatmosphericpollutionandeutrophicationofwaterbodies,afterreasonableusecan bearesource [2,3].
3.2Renewal
Withtheoperationofthebiogasproject,renewalandbiogasslurrydisposalbecomesdifficult,renewalbiogasslurrycontainsnutrientsneededforplantgrowth,thesurvivalofthe pathogenicmicroorganismquantityislittle,andrichinadvantageoforganicmatterinsoil improvementandsmallmoleculehumusiseasytobeabsorbedbyplants,thuscomposting isrenewalbiogasslurry,isoneofthemainwaysofusingnotonlycanproduceorganicfertilizer,stillcanreducelandresources,reduceenvironmentalpollution,increasetheeconomic benefit [2].
3.3Agriculturalwaste
Agriculturalwastesareorganicsubstancesderivedfromagriculturalproduction,includingplantandanimalwaste.Agriculturalwastesaremainlylignocellulosicmaterials consistingoflignin,hemicellulose,andcellulose.Byfarthemostcommonusesarecompostingandincineration [21].Biodegradablepolymers,suchaspolylacticacid(PLA)andvarious polylacticacidbiocomposites,canbemadefromagriculturalwaste.Agriculturalresidues withlowmoisturecontent(cornstalks)canbeusedasfuel [22].Livestockmanurecontains alargeamountofusefulmicrobialresources,isanunderutilizedsourceofnitrogenfertilizer, andcanimprovesoilqualityandincreasecropoutput [23].
3.4Kitchenwaste
Aboutone-thirdoftheediblefoodproducedgloballyiswastedeachyear.Foodwaste includeshouseholdandrestaurantresidues,processedwaste,andcropresidues [24].Such wastescontaincarbohydrates(starch,hemicellulose,andcellulose),lignin,fats,proteins, andlargeamountsofwater.Kitchenwasteisincineratedorburiedwithothercombustible
waste [25] .Anaerobicdigestion,aerobiccomposting,andchemicalhydrolysiscanallturn foodwasteintobiofertilizer.Only40% – 60%ofthematerialsusedinprocessinganimal productsareusedinfoodproduction.Therestoftheskinandfatisrecycled,mostlyin theformofmeatandbonemealforanimalfeedproductionduetoitslowproteincontent. Thesematerialscanalsobeusedasanelementforthegenerationofthermoplasticand thermosettinggoodsaswellascoagulantsand flocculantsutilizedinwastewatermanagement [22] .Bonesareexcellentphosphatefert ilizer,evenwool,andcanbetreatedas fertilizer.
3.5Sewagesludge
Withthebiologicalwastewaterprocess,alotofresidueswillbeproducedintheformof sludge(biologicalsolids).Phosphorusinsewagesludgecanberecycled [26].Sewagesludge removestoxiccompounds,pathogens,andunpleasantodors,andafterstabilization,thiscan beusedinagriculture.Anaerobicdigestionisthemostcommonlyusedmethodforsewage sludgetreatment,followedbyimprovedbiologicalphosphorusremovalorphosphateremovalbysedimentationofstruvite.Thealgalbiomassinthewastewateralgalsystemcould beutilizedtorecycleupto44%ofthenitrogenand91%ofthephosphorusconcentrationin thestruvitegeneration,withhigheconomicvalue [27]
4Publicengagementfortheimplementationofwastereductionand recyclingpolicies
Solidwasteisproducedduetopeople’sdailyactivitiesandhabits.Therefore,public engagementshouldbeanecessaryconditionforwastedisposal [27].The“3R”method—reduce, reuse,andrecycling—istheoptimizedmethodtomanagewaste.Publicengagementisrequired toimplement3Rpoliciesintopractice.Thelevelandextentofpublicparticipationinwaste treatmentactivitieshavegraduallyexpanded.Long-termandeffectiveparticipationinwaste treatmentactivitiescancultivatepublicawareness,whichisconducivetopublicsupportand thesustainabilityofprojectactivities.
Ingeneral,manyareasandlevelscanbeutilized“3R”policesbythepublicengagement. Theseincludewaste-decreaseactivities,resourceisolationfromwaste,engagementin communityreuseactivities,thepurchaseof“green”products,adviceonwastetreatmentprogramsandinfrastructure,andparticipationintheassessmentofwastedisposalactivities [28] suchaswastecollectionandpreventionoflittering.Thisarrangementisachievedthroughthe contractemploymentofcollectorsofrecyclablewasteforindividualsandcommunities.Publicawarenessoftheuseofthenoveltywastetreatmentprojects.Thesearemainlythe importantaspectsofpublicengagementinwastemanagementprocesses.
Implementationofacomprehensivesolidwastetreatmentplans:Firstofall,wemustunderstandhowtoplayaroleinthisgenerationandtheneedsofmanyinterestsinvolvedin ordertoformulateeffectiveplanningandsustainablewastemanagementregulations [29], collection,reuse,transportanddisposalofsolidwasteandintheprovisionofservices.
Siteandtechnicalselectionforwastetreatment:Selectingtheappropriatetechnologyand placingthefacilities(recyclingstations,landfills,wastefrompowerplants,etc.)intheright placeinvolvecomplexprocessesandareusuallyperformedbyexpertsandtechnicians.
Effectivesupervisionandassessment:Publicengagementcouldalsocontributesignificantlytotheeffectiveandimpartialmonitoringofwastemanagementservicesinboththe publicandprivatesectors.
Educationandawareness:Wastedisposaltoagreatextentinvolvestheactionsofindividuals.Becomingperformanceandattitudesarethereforethefirststepgotoeffectivepublic participation.Thisawarenessisimportantforpeopletounderstandtheconnectionbetween theirperformanceandtheenvironment,sothatpeoplecaneffectivelyparticipateinenvironmentallyfriendlymanagement.
Correctassessmentandrecognitionarecriticaltomaintainthespiritofpubliceffort.
Avarietyofservicefacilitiesandinfrastructure:Withappropriate,convenient,andaffordablealternativesandinfrastructuresupport,thepubliccancoordinateandparticipatein wastereductionandseparationactivities.
Strictlyimplementpoliciesandplans:Asystemofstrictandenforcedrulesandpenalties forviolationsisonemethodtoconfirmhigherengagement.
Institutionalarrangementsforpublicparticipationingovernmentdepartments:Alotof localinstitutionshavespecialdepartmentstopromotecommunityengagementinwaste treatmentactivities [30]
Underthesolidwastetreatmentprocess,publicengagementisessential.Legislationin somewayshasfacilitatedpublicparticipation.Thecommunitycouldgivethoseparticipating inwastemanagementactivitiesrewardsandrecognition.Tosumup,wastereductionand recyclingareinevitablyassociatedwithpeople’sbehaviorandsoundpolicy,soincreasing publicparticipationisthebestwaytomaximizewastemanagement. 5Possibletechnologyandmanagementoptionforbiowaste
5.1Thermaltreatmentandprocessing
5.1.1Incineration
Definitionofincineration
Incinerationwastheoxidativecombustionreactwhichincludedthecombinationofwastes andoxygeninthehightemperatureunderaerobicconditions.Afterthat,theheatenergyis releasedandtransformedintohightemperaturegasandsolidresidue [31].Moreover,the biomasswasreducedgreatly.Thesolidresiduecouldbeutilizedinlandfillandbuilding rawmaterialswhilethegascanbeusedasaheatresource [32].Thehazardouschemicals andpathogensinthewasteweredegradedandruinedunderthehightemperature [33]. Badodorsandorganicwastegasarealsodecomposedbyhightemperature.
Theprocessofincineration
Itisgenerallybelievedthatthecombustionofsolidwastecouldbeseparatedintothree stages:drying,combustion,andburnout.