BigDataAnalysisofNanoscienceBibliometrics, Patent,andFundingData(2000-2019)1stEdition YuliangZhao
https://ebookmass.com/product/big-data-analysis-ofnanoscience-bibliometrics-patent-and-fundingdata-2000-2019-1st-edition-yuliang-zhao/
Instant digital products (PDF, ePub, MOBI) ready for you
Download now and discover formats that fit your needs...
Process Safety and Big Data Sagit Valeev
https://ebookmass.com/product/process-safety-and-big-data-sagitvaleev/
ebookmass.com
Analysis of the Development of Beijing, 2019 1st ed. Edition Zhao Ran
https://ebookmass.com/product/analysis-of-the-development-ofbeijing-2019-1st-ed-edition-zhao-ran/
ebookmass.com
Big Data Anil Maheshwari
https://ebookmass.com/product/big-data-anil-maheshwari/
ebookmass.com
Rethinking Meditation Buddhist Meditative Practice in Ancient and Modern Worlds David L. Mcmahan
https://ebookmass.com/product/rethinking-meditation-buddhistmeditative-practice-in-ancient-and-modern-worlds-david-l-mcmahan/ ebookmass.com
Vector Mechanics for Engineers 12th Edition Ferdinand Pierre Beer
https://ebookmass.com/product/vector-mechanics-for-engineers-12thedition-ferdinand-pierre-beer/
ebookmass.com
Ravana's Kingdom: The Ramayana and Sri Lankan History from Below Justin W. Henry
https://ebookmass.com/product/ravanas-kingdom-the-ramayana-and-srilankan-history-from-below-justin-w-henry/
ebookmass.com
When Life Gives You Vampires: Single. Curvy. Vampire. Gloria Duke
https://ebookmass.com/product/when-life-gives-you-vampires-singlecurvy-vampire-gloria-duke/
ebookmass.com
Boudica: Warrior Woman of Roman Britain Caitlin C. Gillespie
https://ebookmass.com/product/boudica-warrior-woman-of-roman-britaincaitlin-c-gillespie/
ebookmass.com
Gonstead Chiropractic Science & Art: The Methodology of Clarence S .
https://ebookmass.com/product/gonstead-chiropractic-science-art-themethodology-of-clarence-s/
ebookmass.com
https://ebookmass.com/product/robber-barons-and-wretched-refusezeidel/
ebookmass.com
Editedby
YuliangZhao
HongjunXiao XingxingHe
Elsevier
Radarweg29,POBox211,1000AEAmsterdam,Netherlands
TheBoulevard,LangfordLane,Kidlington,OxfordOX51GB,UnitedKingdom 50HampshireStreet,5thFloor,Cambridge,MA02139,UnitedStates
Copyright © 2021ElsevierB.V.Allrightsreserved.
Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproducedortransmittedinanyformorbyanymeans, electronicormechanical,includingphotocopying,recording,oranyinformationstorageand retrievalsystem,withoutpermissioninwritingfromthepublisher.Detailsonhowtoseek permission,furtherinformationaboutthePublisher’spermissionspoliciesandourarrangements withorganizationssuchastheCopyrightClearanceCenterandtheCopyrightLicensingAgency,can befoundatourwebsite: www.elsevier.com/permissions .
Thisbookandtheindividualcontributionscontainedinitareprotectedundercopyrightbythe Publisher(otherthanasmaybenotedherein).
Notices
Knowledgeandbestpracticeinthis fieldareconstantlychanging.Asnewresearchandexperience broadenourunderstanding,changesinresearchmethods,professionalpractices,ormedical treatmentmaybecomenecessary.
Practitionersandresearchersmustalwaysrelyontheirownexperienceand knowledgeinevaluatingandusinganyinformation,methods,compounds,or experimentsdescribedherein.Inusingsuchinformationormethodsthey shouldbemindfuloftheirownsafetyandthesafetyofothers,includingparties forwhomtheyhaveaprofessionalresponsibility.
Tothefullestextentofthelaw,neitherthePublishernortheauthors, contributors,oreditors,assumeanyliabilityforanyinjuryand/ordamageto personsorpropertyasamatterofproductsliability,negligenceorotherwise,or fromanyuseoroperationofanymethods,products,instructions,orideas containedinthematerialherein.
LibraryofCongressCataloging-in-PublicationData
AcatalogrecordforthisbookisavailablefromtheLibraryofCongress
BritishLibraryCataloguing-in-PublicationData
AcataloguerecordforthisbookisavailablefromtheBritishLibrary
ISBN:978-0-323-91311-9
ForinformationonallElsevierpublicationsvisitourwebsiteat https://www.elsevier.com/books-and-journals
Publisher: GlynJones
EditorialProjectManager: NaomiRobertson
ProductionProjectManager: PaulPrasadChandramohan
CoverDesigner: AlanStudholme
TypesetbyTNQTechnologies
Editorsandcontributors
NationalCenterforNanoscienceandTechnology,China
YuliangZhao Director,NationalCenterforNanoscienceandTechnology,China
ZhixiangWei
DeputyDirector,NationalCenterforNanoscienceandTechnology, China
QingDai
DirectorofScience&TechnologyManagement,NationalCenterfor NanoscienceandTechnology,China
HongweiDong
NanoStandardizationAccreditationandStrategicSupportDivision, NationalCenterforNanoscienceandTechnology,China
HongjunXiao
InternationalAffairsOffice,NationalCenterforNanoscienceand Technology,China
ShuxianWu
NanoStandardizationAccreditationandStrategicSupportDivision, NationalCenterforNanoscienceandTechnology,China
Elsevierandothercontributors
XingxingHe
Analyst,ResearchAnalyticsandDataService,Elsevier
BeverleyMitchell
Editor-in-chief,Science-Metrix,Elsevier
ThomasA.Collins DataScientist,ResearchAnalyticsandDataService,Elsevier
HuggettSarah
HeadofAnalyticalServicesAPAC,Elsevier
VanOrdenJohn
StrategyAssociate,Elsevier
ChristianeBarranguet
DirectorofStrategicServices,Elsevier
BasakCandemir
HeadofAnalyticalServicesEurope,Elsevier
ThisbookwascreatedbyElsevierincollaborationwithProfessorYuliangZhao andmembersoftheNationalCenterforNanoscienceandTechnology,China. PrimaryauthorswillincludeXingxingHe,TomThomasA.,andChristiane BarranguetofElsevieraswellasYuliangZhao,ZhixiangWei,QingDai,Hongjun Xiao,HongweiDongandShuxianWufromtheNationalCenterofNanoscience Technology.
Executivesummary
Overthepast2decades,thenumberof nanoscience-relatedscientistsandacademic outputhasproliferated.Theacademicimpactof nano-publicationshassteadilyrisen.
Thisbookpresentsanevaluationofnanotechnology-relatedacademic publicationsandpatentsfrom2000to2019,focusingonnanotechnology’sinfluenceonbasicscientificresearchandindustry.Theassessmentshowsresearchfundingandinternationalcollaborationsin nanosciencetobethedrivingforcesofnanotechnologydevelopments. Thebook’sfindingsarebasedonliteraturecitation,researchanalysis, funding,andpatentdatasourcesfromElsevier’sScopusdatabase, SciVal,FundingInstitutional,andPatentSight.Thefollowingare chapterhighlightsfromthisbook.
Researcheffortsrelatedtonanosciencerapidlyincreased overthepast2decades.
(1) Therewere1.42millionresearchpublicationsonnanoscience, involving2.21millionresearchers.
Theapproximately1.42millionnano-relatedacademicpublications accountedfor4.2%ofpublicationsworldwidebetween2000and2019, accordingtoScopus.Atthesametime,5.2%oftotalpublication authors,about2.21millionresearchers,1 publishedarticlesinthefield ofnanoscience.
(2) Thescholarlyoutputinnanosciencehadanannualgrowthof 14.6%inthepast2 decades,whichwas3.2timestherateofglobal publications.
Globally,thenumberofnano-relatedpublications(nanopublications)increasedfrom11,555in2000to153,455in2019,
1 Researchercountmethod:ThisisbasedontheuniqueauthorIDsinScopus, whichareusedasaproxyincalculatingthenumberofresearchers.
accountingfor1.1%and6.2%oftotalannualacademicpublications, respectively.Thecompoundannualgrowthrate(CAGR)fornanopublicationswas14.6%,whichwas3.2timesthatofworldwide publications.
Meanwhile,thenumberofauthorswhopublishednano-related scholarlyoutputincreasedfrom32,591in2000to498,948in2019, accountingfor2.5%and10.9%,respectively,ofauthorsworldwide. TheCAGRofnanoscience-publishingauthorsbetween2000and 2019was15.4%,whichwas2.3timesthatofglobalauthors.
Thefield-weightedcitationimpact(FWCI)scoreofnanopublicationsinChinaandworldwidewasrising, indicatingastrongeracademicimpactinthefieldof nanotechnologyintheseareas.
(1) TheFWCIofnano-publicationswas1.6timestheglobalaverage.
Forallglobalpublications,theFWCIisbenchmarkedto1.Between 2000and2019,theFWCIofnano-publicationswas1.6.NanopublicationsfromChinaexhibitedasignificantincreaseinFWCI, shiftingfrom1.3in2000to1.9in2019,agrowthrateof43%.In 2019,ChinasurpassedtheUnitedStates’FWCIscoreinnanoscience.
(2) Amongthetop1%highlycitedpublications,11%were nanoscience-related,eventhoughnano-publicationsaccounted foronly4.2%ofthegloballiterature.
Overthepast2decades,11%ofthetop1%highlycitedpublicationswerenano-publications.Thetotalgrewfrom4.2%in2000to 13.6%in2019,reflectingtheessentialcontributionofnano-research insomeofthemosthighlyimpactfulstudies.
Asaninterdisciplinaryfield,nanoscienceservedasa comprehensiveplatformfortheintegrationofbasic research,contributingtomultiplefieldsandadvancing scientificdevelopment.
(1) Nano-publicationsappearedmostfrequentlyinthesubjectsof materialsscience,chemistry,physicsandastronomy,andenergy.
Overthepast2decades,thepercentageofnano-publicationshas increasedinmultiplefields,especiallyinmaterialsscience.From 2000to2019,over10%ofstudiesinfourresearchsubjectswererelevanttonanoscience.Thesesubjectswerematerialsscience(20.7%), chemicalengineering(17.7%),chemistry(16.3%),andphysicsand astronomy(12.8%).With11%ofitspublicationsinnano-research, energywasaddedtothelistfor2010 19.
(2) Thefastest-growingsubfieldswereinnanobiology.
Inimmunologyandmicrobiology,theCAGRofnano-publications was5.1timesthatofallpublicationsinthesamefieldin2000 19. Thisfigurewas4.4inthesubfieldofbiochemistry,genetics,and molecularbiologyand4.0inthesubfieldofpharmacology,toxicology, andpharmaceutics.Despitetherapidgrowth,thevolumeofnanopublicationsinlifesciencesisstillrelativelysmall.
Nanoscienceiscloselyrelatedtothemostprominent researchtopics.
(1) Nanosciencehascoveredsomeofthehottestissuesinscience.
Ofthemostprominentresearchtopics2 between2015and2019, 89%hadatleastonepublicationrelatedtonanoscienceand39% hadstrongconnectionstonanoscience:thatis,atleast10%oftheir publicationswerenano-related.Thedatashowedthatnanoscience wastightlyintegratedwithmanyemergingresearchfields.
(2) Amongallfields,nanosciencehadtheclosestconnectionwith highlyprominenttopicsinphysicalsciences.
Between2015and2019,inthebelow5subjects-materialscience; physicalandastronomy;chemistry;chemicalengineering;energy;and pharmacology,toxicologyandpharmaceutics-therewereatover42% ofthemostprominenttopicsstronglyrelatedtonanoscience,withat least10%ofthetopic’spublicationsbeingnano-related.
2 Themostprominenttopics:ThesearetopicswhosetopicProminencescore ranksamongthetop1%intheworld.See Chapter2 andtheAppendixforthetopic significancescore.
(3) Nanosciencefocusedoncertainprominenttopicclusters.
Between2015and2019,nanosciencehadthehighestscholarly outputinthehighlyprominenttopicsclusters3 ofsolarcells,graphene, lithiumbatteries,plasmonmetamaterials,biosensors,catalysts,semiconductorquantumdots,nanoparticles,andpolymers.
ComparedwithChina,theUnitedStates,Germany,Japan, andtheUnitedKingdomhadahigheracademic corporate collaborationrate4 innano-research,andpatents frequentlycitedtheirresults.
(1) Innanoscience,theUnitedStates,Japan,Germany,andtheUnited Kingdomhaveamoreextensiveacademic corporatecollaboration thandoesChina.
Between2015and2019,bothChinaandtheworldhadacademic corporatecollaborationratesinnano-researchthatwereslightlylower thantheoverallnationalandglobalaverages,respectively.TheUnited States,Japan,Germany,andtheUnitedKingdomhadhigherratesthan China,demonstratingmorefrequentcollaborationbetweenthe academicandcorporatesectorsinthesecountries.
(2) Thepercentageofnano-publicationscitedbypatentswashigher thanaverage.
Between2015and2019,1.04%ofglobalnano-publicationswere citedatleastoncebypatentsfiledunderthelargestfiveintellectual propertyoffices.5 Thisfigurewas89%higherthantheworldaverage of0.55%forallpublications.
3 TopicclusterswithProminencescoresthatrankinthetop5%.
4 Academic corporatecollaborationrate:Literaturecopublishedbyauthorsfrom bothacademiaandindustryisreferredtoasacademic corporatecollaborated publication.Theratioofacademic corporatecollaboratedpublicationstoallpublicationsistheacademic corporatecollaborationrate.
5 Thelargestfiveintellectualpropertyoffices:WorldIntellectualProperty Organization,theUSPatentandTrademarkOffice,EuropeanPatentOffice,Japan PatentOffice,andUnitedKingdom’sIntellectualPropertyOffice.
Thefiveofficesrecordedanaverageof10.4citationsper1000 nano-publications.OfChina,theUnitedStates,Germany,theUnited Kingdom,andJapan,theUnitedStateshadthehighestrate,at23.7 citationsper1000nano-publications,andChinahad6.0.
(3) Nano-relatedpatentsfromChinahavebeenproliferating,but China’spatentcompetitivenesshasroomforimprovement.
Inthepast2decades,therewereabout690,000nano-related patentsworldwide,accordingtodatafromthepatentanalysisplatform PatentSight.Thepercentageofnano-relatedpatentsgrewfrom0.9% in2000to3.8%in2019.Amongthosenano-patents,58%came fromChina.Althoughthecountryhasthelargestnumberofnanorelatedpatents,thereisroomforimprovementinitscompetitiveness.
Amongtheprojectsfundedbymajorglobalfunders,the shareofnano-relatedgrantscontinuedtoincrease.
(1) Theshareofnano-relatedawardswasrising.
AccordingtothefundingdatabaseFundingInstitutional,132,220 awardsweregrantedtonanoscience-relatedprojectsbetween2009 and2018.Thenumberaccountedforapproximately3.6%ofallglobal awardsinthedatabase,andtheCAGRwas3%.Althoughthetotal numberofgrantsinthatperiodremainedthesame,theproportion ofnano-relatedprojectsincreasedfrom3%in2009to4%in2018.
(2) Materialssciencereceivedthehighestshareofnano-related awards.
Amongthefieldsofscience,materialssciencereceivedthemost grantawardsfornano-research.Between2009and2018,29.4%of awardedgrantswererelevanttonanoscienceinmaterialsscience, followedby17.9%inphysicsandastronomy,and14.8%inchemistry.
Thedegreeofinternationalcollaborationinnanoscience washigherthantheaverageforallresearchfields.
(1) Theinternationalcollaborationrateinnanosciencewashigher thanallresearchfieldscombined.
Between2010and2019,theinternationalcollaborationratein nanosciencewas25%,withatotalof277,793nano-publications publishedbycollaboratingauthorsfromdifferentcountriesand regions.Theworldwideinternationalcollaborationrateoverthat periodwas21%,indicatingmorefrequentinternationalcooperation innanoscience.
(2) Chinahasprovenitselfasaglobalallyinthenanosciencefield.
China’sinternationalcollaborationeffortsinnanosciencehave steadilyrisen,andataratemuchfasterthanthoseofotherresearch disciplinesinthecountry.Meanwhile,internationallycollaborated nano-researchwithChinaasapartnerexhibitedahighacademic impact:between2010and2019,internationalnano-publication collaborationsfromChinahadanFWCIof2.5,ahigherscorethan thoseofothercountriessuchastheUnitedStates(2.3),Japan(1.8), Germany(1.8),andtheUnitedKingdom(1.9).
AbouttheNationalCenterfor NanoscienceandTechnology andElsevier
NationalCenterforNanoscienceandTechnology
TheNationalCenterforNanoscienceandTechnology,China (NCNST),establishedinDecember2003,isco-foundedbythe ChineseAcademyofSciences(CAS)andtheMinistryofEducation asaninstitutiondedicatedtofundamentalandappliedresearchin thefieldofNanoscienceandtechnology,especiallyresearchwith importantpotentialapplications.NCNSTisoperatedunderthesupervisionoftheGoverningBoardandaimstobecomeaworld-class researchcenter,aswellasapublictechnologicalplatformandyoung talenttrainingcenterinthefield,andtoactasanimportantbridgefor internationalacademicexchangeandcollaboration.
Elsevier
ThisbookhasbeenpreparedandpublishedbyElsevier’sAnalytical Services,partofElsevier’sResearchIntelligenceportfolioofproducts andservices.Forover140years,researchersandhealthcareprofessionalshavetrustedandrelieduponElsevier’sportfolioofjournals, includingiconicpublicationssuchasTheLancet,CellPress,and Gray’sAnatomy.Today,Elsevierisagloballeaderininformation andanalytics,helpingresearchcommunitiesadvancescienceand improvehealthoutcomesforthebenefitofsocietybyfacilitating insightsandcriticaldecision-makingforcustomersacrosstheglobal researchandhealthecosystems.
Foreword
Nanoscience,acriticalfrontierfieldinscienceandtechnologyinthe 21stcentury,haslonghadanimpactoneconomicandsocialdevelopmentandthushasbeenafocusofglobalattention.Itisahighlyinterdisciplinaryfieldwithapplicationsacrossawiderangeofsectors, fromaviationtoclinicalsolutionstotheenergyindustry.Withits numerousapplicationsandinterdisciplinarynature,understanding howresearchinthefieldofnanotechnologyhasevolvedinrecent yearsisessentialtosuccessfullysolvingthemodernstrategicand societalchallengesfacedbyallnations.
Overthepast2decades,thefieldofnanosciencehasbecome increasinglyaccelerated,inpartowingtoimprovedcollaboration acrossdisciplinesthroughthelaunchofdedicatedprograms,research centers,andothergovernmentinitiativesaroundtheworld.Inthe UnitedStates,theNationalNanotechnologyInitiativewasfounded in2000tocoordinatenano-relatedresearchandresourcesacross20 differentfederaldepartments.Morerecently,China’s14thFive-Year Planoutlinestheimportanceoffrontierareasinscienceandtechnologywhileactingoninnovation-drivendevelopmentstrategies.Thus,it isunsurprisingtofindhigh-endsmartmaterialssuchasshapememory alloys,self-healingmaterials,andnano-functionalmaterialssuchas grapheneandmetamaterialsamongthe100majorprojectsofthe 14thFive-YearPlan.Theplanalsoidentifiesfrontiernano-research asoneoftheNationalKeyResearchandDevelopmentObjectives toadvancescientificexplorationatthenanometerscale.Asthe importanceofnanoscienceisincreasinglyrecognized,Ibelieve moreandmorededicatedresearchorganizationsaroundtheworld willarisetonourishitsgrowth.
Ofcourse,muchprogresshasalreadybeenmadeinnanoscience thatneedstobecelebrated.Asthisin-depthandcomprehensive analyticalbookreveals,thesubjecthasseenenormousgrowthin researchoutput,withvariedindustrypartnersacrossmanydifferent sectorsbetween2000and2019.Infact,nano-relatedresearchhas risenfromonly1.1%ofallglobalresearchin2000toanimpressive 6.2%by2019.Suchprogressmeritshighlightinginanaccessible manner,forbothexpertsandnonscientistsalike,todemonstratebetter
thefundamentalroleofnanoscienceintechnologyandeveryday qualityoflife.
Lookingforward,futureprogresswillundoubtablyrelyon strengtheningbasicresearchinthefield,coupledwithanenhanced awarenessandimprovedutilityofthepartnershipsacrossindustries thatdriveresearch.Itisalsocriticaltoplanforbestpracticesto transformthosebasicresearchresultsintoappliedtechnological products.Thisisoneofthemostrelevantstrategicgoalsintermsof thedevelopmentofnanotechnologyinChina,aswellasglobally.
NanoscienceandNanotechnologyinaGlobalLandscape aimsto furtheranunderstandingofthedevelopmentofnanosciencefrom fiveperspectivesbasedonbibliometricanalysis.Itreviewsthedevelopmentofnanoresearchoverthepast20years,revealingtheimpact ofnanoscienceonotherresearchfieldsandclarifyingthedevelopment ofnanoresearchfrombasicresearchtoindustryapplications.Italso summarizeskeycountries’nanoresearchdevelopmentstrategybased onfundinganalysisandresearchfocusanalysisandanticipates upcomingfrontierresearchinthenanofield.
Thebookinitsentiretyprovidesanoverallexplanationofthecurrentstatusandfuturedevelopmentofnanosciencefromamacro perspective,andprovidesextremelyvaluabledatasupportandfactual referencesfortherealizationofscientificandtechnologicalpolicyas wellasmajorbreakthroughsinthefieldofnanoscience.
Itismysincerehopethatthefieldofnanosciencewilladvancewith eachpassingday,andthatthenanoindustrywillcontinuouslyfind newandambitiouswaystobenefitoursociety.Ibelievethatifwe continuetowatchthefield’srapidpaceofevolutionclosely,wewill notbedisappointed.
Dr.ChunliBai President,UniversityofChineseAcademyofSciences Formerpresident,ChineseAcademyofSciences
Introduction
THEFUTUREDEVELOPMENTOFSCIENCEWILL CONTINUETOMAKEINROADSINTOTHEMACROAND MICROWORLDS.
Theinventionofthescanningtunnelingmicroscopein1981gavebirth tonanoscienceandnanotechnology,whichaidedscientists’explorationofthemicroscopicworldbetweennanometers,ametricunitof lengththatdescribesabillionthofameter.Nanoscienceandnanotechnologyrefertotheresearchofquantumpropertiesandinteractionsof substancesatthenanoscale,suchasatomsandmolecules.Thesealso seektoinvestigatetheinterdisciplinarysciencesandtechnologiesthat leveragethesecharacteristics.Throughthelensofnanoscienceand nanotechnology,humankind’sunderstandingoftheworldextends, andnewmeanstoshapetheworldattheatomicandmolecularlevel emerge.Nanotechnologistsaimtoproduceproductswithspecific functionsbasedonnanoscalesubstances’novelphysical,chemical, andbiologicalproperties1.
Byassessingandchangingtheworld’sfutureonemicronatatime, thefieldofnanoscienceandnanotechnologyhasbeendrastically expandingsincethe20thcentury.Asayounganddynamicresearch andapplicationfield,itistransformingtheworldasweknowit,deliveringrevolutionaryadvancementstoindustriessuchasmanufacturing andhealthcare.Aidedbytheirinterdisciplinary,comprehensive,and fundamentalcharacteristics,nanoscienceandnanotechnologyhave becomethedrivingforceinsciencedevelopment.
Nanotechnologyhasalsoestablisheditsvalueinvariouseconomic sectors.Besidesthenanomaterialsfieldinthenewmaterialindustry, nanotechnologyapplicationsintheareasofenergyandenvironment, biomedicine,informationdevices,andgreenmanufacturinghave becomeincreasinglyprominent,withpromisingprospects.
1 Bai,Chunli.(2005).Nanoscience&technology:Dreamandreality.Proceedings ofthe2004ChinaNanotechnologyApplicationSymposium.
Giventhestrategicsignificanceofnanoscienceandnanotechnology, itisessentialtoevaluateandpredicttheirdevelopmentaltrends.This bookisbasedonthelargestabstractandcitationdatabaseof peer-reviewedliterature,Elsevier’sScopus,alongwiththeresearch evaluationplatformSciVal.Thefundingandpatentanalysisdatafor thebookarefromFundingInstitutionalandPatentSight,respectively. ThisbookprovidesanevaluationofNanoscience’sscientificoutput, role,contribution,andimpact throughbibliometricanalysis,combinedwithbigdataindicatorsofnanosciencescientificresultsandpatentsfrom2000to2019.
PleaserefertotheAppendixforthedefinitionofnano-publications andtheindicatorsusedinthebook.
Scholarlyoutputand academicimpactof nanoscience
Keyfindings
4.2% ofglobalscholarly outputwere nano-publications (2000 19).
1.6 wasthefield-weighted citationimpactfor nano-publications, whichwas1.6times theworldaverage (2000 19).
11% ofoutputinthetop1% citationswasnanorelated(2000 19).
2,211,585 authorspublished nano-publications (2000 19).
28.8 citationsperpaper werereceivedbynano publications,whichis 48%morethanthe worldaverage (2000 19).
25% ofoutputinthetop1% citationsinChinawas nano-related (2000 19).
Thegrowthrateofnanosciencewasseveraltimestheaveragefor manykeyindicators,whichreflectsthefullflourishingofnanoscience (Table1.1).
BigDataAnalysisofNanoscienceBibliometrics,Patent,andFundingData(2000 2019)
https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-91311-9.00001-3
Copyright © 2021ElsevierB.V.Allrightsreserved.
2 CHAPTER1 Scholarlyoutputandacademicimpactofnanoscience
Table1.1 Globaltotalsfornano-relatedauthors,scholarlyoutput,andoutputintop1% highlycitedpublications(2000 19).
CAGR,compoundannualgrowthrate. FromScopus.
1.1 Overviewofscholarlyoutputandacademic impactofnanoscience
Thissectionprovidesanevaluationofglobalnano-relatedresearch outputanditsacademicimpactbetween2000and2019.Assessment indicatorsincludescholarlyoutput,citationcount,authorcount, field-weightedcitationimpact(FWCI),andpublicationoutputinthe top1%citations.Detailsaboutthedefinitionsoftheseindicators andvaluescanbefoundin AppendixA.Furtherinformationabout thedataispresentedin Fig.1.1.
Basedonthesedataonnanoscienceacademicoutputandimpact, furtherfindingsarepresentedsubsequently.
(1) Nanosciencecontributedsignificantlytoglobalscientificresearch. Theglobalshareofnanoscienceresearchoutputwasrelatively high:4.2%ofglobalresearchoutputwasrelatedtonanoscience. Approximately1.4millionpublicationsinnanoscience(nanopublications)hadatotalcitationcountabout40.9million, contributingto6.4%ofallcitationsworldwide.
FIGURE1.1
Overallnanosciencescholarlyoutputandimpactintheworld (2000 19). FWCI,field-weightedcitationimpact.
FromScopus.
(2) TheFWCIofnano-publicationswashigherthanthatoftheworld average.Acitationreferstothesourceofinformation,suchas academicliterature,usedinotherresearchwork.Thecitation countisoneofthemostwidelyrecognizedindicatorsforevaluatingacademicimpact.However,assessingapublication’sinfluenceischallengingbecauseofdifferencesincitationpractices acrossfields,publicationyears,anddocumenttypes.Toaddress theissue,Elsevierdevelopedastandardizedimpactindicator,the FWCI,toappraiseresearchacademicimpactofpublications. Thisbookincludesrelativeindicators,suchascitationsper publicationandhighlycitedpublications,topresentfull academicimpactofnanoscience.
Someoverallstatisticsfrom2000to2019are:
•WhereastheglobalaverageFWCIwas1,theFWCIofnanopublicationsworldwidewas1.6,indicatingthatnanopublications’academicimpactwas1.6timestheglobalaverage.
•Citationsperpaperfornano-publicationstotaled28.8,48% higherthantheworldaverage,whichwas19.4.
•Ofthetop1%highlycitedpublications,11%werenano-related, foratotalof54,052publications.
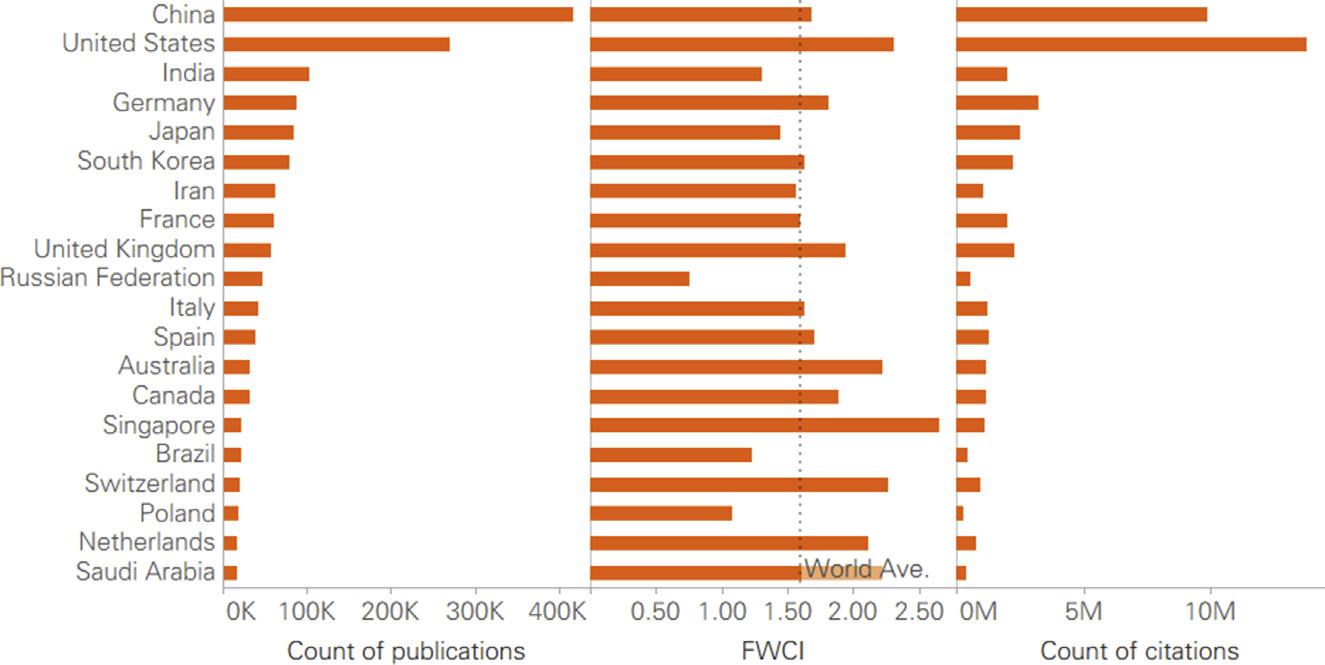
FIGURE1.2
Top20countriesbynano-publicationoutput(2000 19). Ave.,Average; FWCI,field-weightedcitationimpact.
FromScopus.
(3) Chinarankedfirstfornano-publicationoutputworldwide. Amongthe20countrieswiththehighestscholarlyoutputsin nanosciencebetween2000and2019,thetopfivewereChina,the UnitedStates,India,Germany,andJapan(Fig.1.2).Thefive countries’nano-publicationsaccountedfor29.4%(416,554 publications),19%(269,747publications),7.3%(102,904publications),6.1%(87,164publications),and5.9%(54,079publications)ofglobalnano-publications,respectively. Between2000and2019,thetopfiveamongthe20countrieswith thehighestFWCIscoresfornano-publicationswereSingapore (2.65),theUnitedStates(2.31),Switzerland(2.26),Australia (2.22),andtheNetherlands(2.12).Inthesameperiod,the averageworldFWCIofnano-publicationswas1.6.However,the outputvolumesofnano-publicationsinSwitzerland,the Netherlands,andSingaporewerelowerthanforotherleading countries.
ThetopfivecountriesbytotalcitationcountweretheUnited States(13,762,200),China(9,854,878),Germany(3,222,746), Japan(2,498,856),andtheUnitedKingdom(2,270,916).To provideacomprehensivecomparisonbasedonthevolumeand impactofacademicoutputinnanoscienceacrosscountriesbetween2000and2019,thebookselectedthesefivecountriesas thekeycomparatorsforfurtheranalysis.
1.2 Trendsinscholarlyoutputinnanoscience
Thenumberofnanoresearchersworldwideisrising Researchtalentisacrucialelementforscienceadvancement.This sectionassessescurrentdevelopmentsinnanosciencebyanalyzing publicationauthors.Referto AppendixA fordescriptionsofthestatisticalmethodsused.
Thenumberofauthorswhopublishednano-publicationscontinued growingbetween2000and2019(Fig.1.3),indicatingarisein scientistsengagedinnanoscience-relatedworkorintegratingnanotechnologyintotheirfield.Thetotalnumberofauthorspublishing nano-relatedresearchgrewfrom32,591in2000to498,948in2019, accountingfor2.5%and10.9%,respectively,oftheresearcherpopulationworldwide.Overthepast2decades,thecompoundannual growthrate(CAGR)ofauthorsinnanosciencewas15.4%,which was2.3timestheglobalCAGR.
FIGURE1.3
Numberandglobalshareofauthorswithnano-publications(2000 19). FromScopus.
Nano-relatedacademicoutputisrising
Inthisbook,academicoutputismeasuredbythenumberofnanopublications.Thevolumeofglobalnano-relatedoutputproliferated between2000and2019,itsshareofworldwideresearchoutputrose aswell.Thenumberofnano-publicationsincreasedfrom11,555in 2000to153,455in2019,accountingfor1.1%and6.2%,respectively, ofglobalpublicationsineachyear(Fig.1.4).WhereastheCAGRfor globalpublicationswas4.5%,theCAGRofnano-publicationsinthe past2decadeswas3.2timeshigher,at14.6%.
Thenano-relatedacademicoutputandimpactofkeycountries (China,Germany,Japan,theUnitedStates,andtheUnitedKingdom) areanalyzedinthisbook.Ingeneral,thenumberofnano-publications ineachkeycountrygrewsteadily.TheCAGRofnano-publicationsin thesecountriesexceededeachcountry’saverageCAGRforallacademicoutput(Fig.1.5).Theanalysisshowstherapiddevelopment ofnanoscienceinthesecountries.
FIGURE1.4
Numberandglobalshareofnano-publications(2000 19). FromScopus.
FIGURE1.5
Scholarlyoutput(left)andcompoundannualgrowthrate(CAGR)(right) ofnano-publicationsinkeycountries(2000 19). CHN,China; DEU,Germany; JPN,Japan; UK,UnitedKingdom; USA,UnitedStates; WLD,world.
FromScopus.
Chinahadthehighestgrowthrateforthenumberofnanopublicationsamongthecomparators(Fig.1.5),anditsoutput accountedforthehighestpercentageofglobalnano-publications. China’snanosciencepublicationsgrewfrom1,341in2000to 59,349in2019,whichaccountedfor11.6%and38.7%of nano-publicationsworldwideforeachyear.TheCAGRofChinapublishednanoscienceresearchwas22%,whichwas1.6timesthe nation’stotalacademicoutputgrowthrate(CAGR ¼ 14%).Over thesameperiod,theamountofUS-publishednanoscienceoutput increasedfrom3,115in2000to21,608in2019,accountingfor 27%and14.1%ofnano-publicationsworldwide,withaCAGRof 12%.Thegrowthrateinthefieldwasfourtimestheaverageofthe growthrateforallpublicationsintheUnitedStates(CAGR ¼ 3%) inthesameperiod.
Theanalysisshowedthatthepercentageofnano-publicationsfrom Chinahadbeencontinuouslygrowing(Fig.1.6).Theshareofnanopublicationsalsovariedineachcountry(Fig.1.7),theresultof differentfocusesofhigh-yieldresearchineachcountry.Statistics fromtheScopusdatabasefor2000 19indicatethatthebiggestfour researchfieldsinChinawereengineering,materialsscience,physics andastronomy,andchemistry,whicharesubjectscloselyrelatedto
FIGURE1.6
Shareofglobalnano-publicationspercountry(2000 19). CHN,China; DEU,Germany; JPN,Japan; UK,UnitedKingdom; USA,UnitedStates; WLD,world.
FromScopus.
FIGURE1.7
Nano-publications’shareofallpublicationspercountry(2000 19). CHN,China; DEU,Germany; JPN,Japan; UK,UnitedKingdom; USA, UnitedStates; WLD,world.
FromScopus.
nanoscience.IntheUnitedStates,fieldswiththehighestacademic outputweremedicineandbiochemistry,genetics,andmolecular biology.Todate,nano-relatedresearchinthesefieldsislessthanin engineering,materialsscience,physicsandastronomy,andchemistry. SimilardisciplinarydifferenceswerealsoexistedinGermany,the UnitedKingdom,andJapan.
1.3 Trendsintheacademicimpactofnanoscience
Nano-publicationsscoredahigherfield-weighted citationimpactthantheglobalaverage,andChina’s field-weightedcitationimpactofnano-publicationshad steadilyincreased
FWCIisanindicatorofthecitationimpactofapublication.Itiscalculatedbycomparingthenumberofcitationsreceivedbyapublication withthenumberofcitationsexpectedtobereceivedbyapublication ofthesamedocumenttype,publicationyear,andsubject.AnFWCIof morethan1.00indicatesthattheentity’spublicationshavebeencited morethanwouldbeexpectedbasedontheglobalaverageforsimilar publications.Forexample,anFWCIof2.11meansthepublicationsof theentityinquestionwerecited111%morethantheworldaverage. Forfurtherdetailsaboutthisindicator,pleasereferto AppendixA.
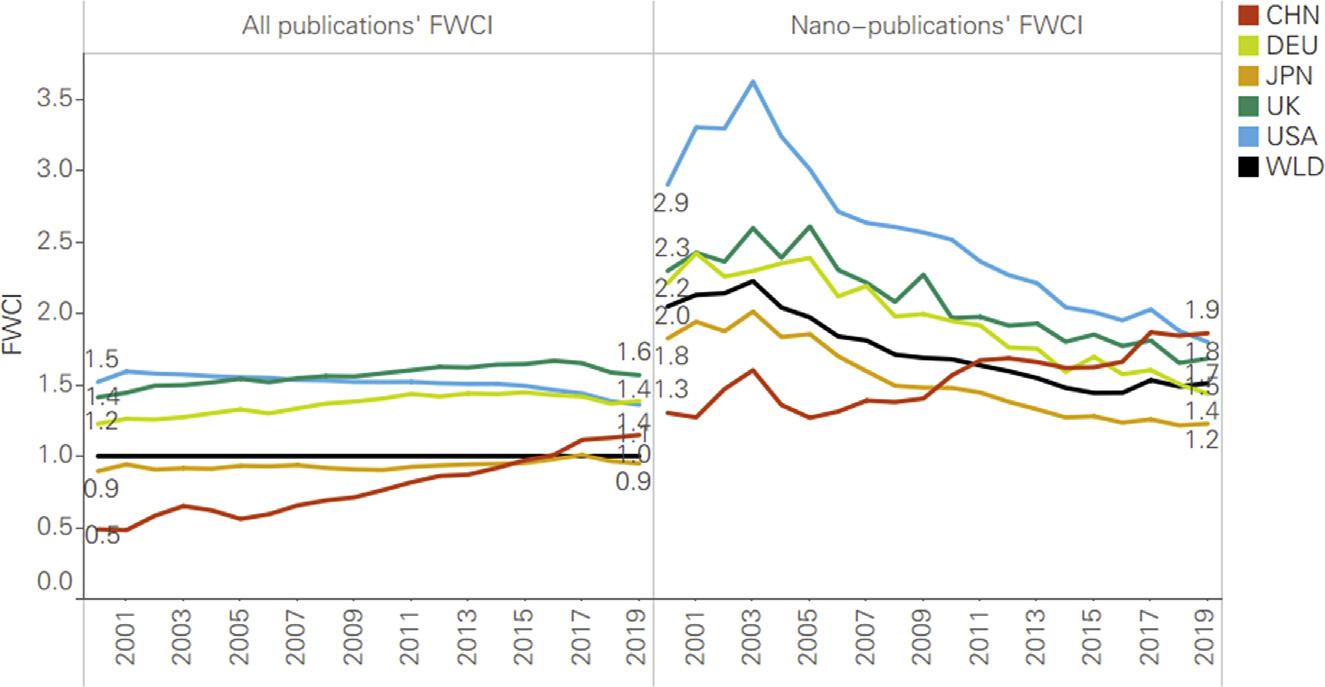
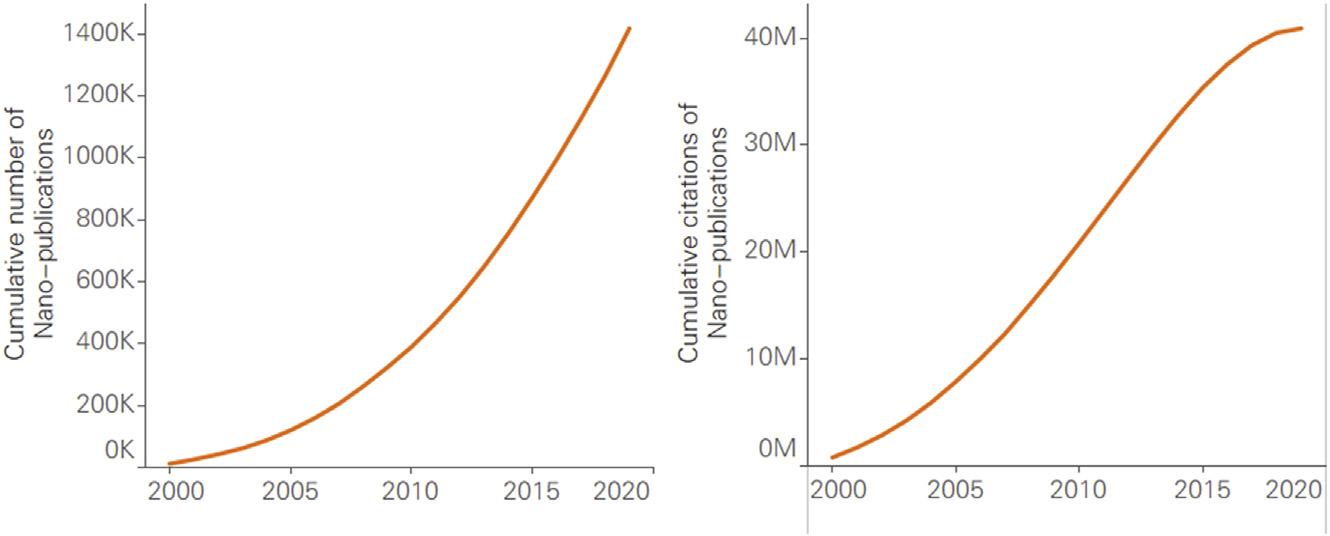
Between2000and2019,theoverallFWCIofnanosciencepublicationsdeclinedslightly.However,theFWCIscoresincreasedslightly between2015and2019.Inaddition,thefigureswerehigherthan theworldwideaverageforallpublications(Fig.1.8).Thedeclinein theFWCIofglobalnano-publicationsresultedfromtherapidgrowth innewnano-research,inwhichaccumulatednano-publicationsoutnumberedaccumulatedcitations(Fig.1.9).Thisdropinimpactisa commonoccurrencewhenthereishighgrowthofpublicationoutput. Intheearlydevelopmentstagesofnanoscience,in2000 05,many high-profilepublicationsthatwereconsideredtobeclassicswerecited intensively,spikingtheFWCIofnano-publicationsintheearlydays.
AtthenationallevelforChina,thenano-publicationFWCI increasedfrom1.3in2000to2.9in2019,achievinga43%growth
FIGURE1.8
Trendsinnano-publicationfield-weightedcitationimpact(FWCI)forthe worldandleadingcountries(2000 19). CHN,China; DEU,Germany; JPN,Japan; UK,UnitedKingdom; USA,UnitedStates; WLD,world.
FromScopus.
FIGURE1.9
Trendsinaccumulatedscholarlyoutputandcitationcountofglobal nano-publications(2000 19).
FromScopus.
overthetwodecades.Nano-relatedresearchhasdriventheincreasein theoverallFWCIinChina,contributingsignificantlytoChina’sacademicresearchimpact.TheFWCIofUSnano-publicationsremained relativelyhighbetween2000and2005andhasdeclinedsince then.However,theUnitedStatesstillhasthehighestimpactfor