Reproduction in Organisms
1. Clones are
(a) Morphologically similar
(c) Both (a) and (b)
2. The approximate life span of a parrot is
(a) 60 yrs
(c) 15 yrs
3. The approximate life span of a crocodile is
(a) 60 yrs
(c) 150 yrs
(b) Genetically similar
(d) None of the above
(b) 1–2 weeks
(d) 140 yrs
(b) 15 yrs
(d) 140 yrs
4. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their life span
(1) Crocodile
(3) Crow
(a) 1 > 2 > 3 > 4
(c) 4 > 1 > 2 > 3
5. Life span of a tortoise is approx
(a) 50–100 yrs
(c) 150–200 yrs
6. The given diagram shows:
(2) Dog
(4) Parrot
(b) 2 > 3 > 4 > 1
(d) 4 > 1 > 3 > 2
(b) 100–150 yrs
(d) 200–250 yrs
(a) Budding in Bacteria
(c) Budding in yeast
7. Sexual reproduction is characterized by:
(a) Two parent participation
(c) Fusion of gametes
(b) Binary fission in amoeba
(d) Budding in sponge
(b) Formation of gametes
(d) All of the above
8. Asexual reproduction is common among all except:
(a) Unicellular organisms
(c) Animals with simple organization
(b) Plants with simple organization
(d) Animals with complex organization
9. In which of these organisms is cell division in itself a mode of reproduction?
(a) Amoeba
(c) Euglena
10. The given diagram shows:
(a) Budding in Bacteria
(c) Budding in yeast
(b) E. coli
(d) All
(b) Binary fission in amoeba
(d) Budding in sponge
11. Cell division is synonymous with reproduction in:
(a) Plants and Fungi
(c) Protista and Monera
12. Binary fission is seen in:
(a) Amoeba
(c) Vorticella
13. Which of these organisms show budding?
(a) Yeast
(c) Sponge
14. Find the false statement.
(b) Animal and Plant
(d) Monera and Algae
(b) Paramecium
(d) All of these
(b) Hydra
(d) All
(A) In yeast unequal division leads to bud formation.
(B) When offspring is produced by a single parent with or without the involvement of gamete formation, the reproduction is asexual.
(C) Size of crows and parrots are not very different yet their life span shows a wide difference.
(D) In binary fission cell divides in unequal parts.
(a) Only B and D
(c) Only D
(b) Only C
(d) Only A and B
15. Approximate life span of the organism shown in the given diagram is:
(a) 5 yrs
(c) 25 yrs
(b) 15 yrs
(d) 50 yrs
16. Match column-I (Organism) with column-II (reproductive structure).
Column-IColumn-II
(A) Penicillium(1) Conidia
(B) Hydra(2) Exogenous bud
(C) Sponge(3) Gemmules (Endogenous buds)
(D) Paramecium(4) Binary fission
(a) A:1, B:2, C:3, D:4
(c) A:1, B:3, C:4, D:2
17. Select the incorrect statement.
(b) A:4, B:1, C:3, D:2
(d) A:2, B:1, C:4, D:3
(a) Members of the Kingdom Fungi and simple plants such as algae reproduce through special asexual reproductive structures.
(b) Zoospores are generally microscopic motile structures.
(c) Zoospores are usually macroscopic motile structures.
(d) Clones are morphologically and genetically similar individuals.
18. Which are the units of vegetative propagation in plants?
(a) Runners and rhizomes
(c) Tuber and offset
(b) Suckers and bulbs
(d) All of these
19. In plants, the units of vegetative propagation are capable of giving rise to new offspring. These structures are called:
(a) Zoospores
(c) Vegetative propagules
(b) Asexual spores
(d) Rhizomes
20. Match Column-I (Structure) with Column-II (Name of structure and its parent plant).
(a) A:2, B:1, C:3
(c) A:3, B:2, C:1
(b) A:1. B:2, C:3
(d) A:2, B:3, C:1
Column-I
Column-II
A.
1. Bulbil of Agave
B.
2. Leaf buds of Bryophyllum
C.
3. Offset of water hyacinth (Terror of Bengal)
21. Which is the incorrect statement about water hyacinth?
(a) Introduced in India for their lovely flowers and shape of leaves.
(b) It is world’s most problematic terrestrial weed.
(c) It reproduce asexually through offsets
(d) Its botanical name is Eicchorniacrassipes
22. Vegetative propagules of Agave is:
(a) Tuber
(c) Bulbil
23. Vegetative propagules of Solanumtuberosum is:
(a) Tuber
(c) Bulbil
24. Select the odd one out.
(a) Tuber
(c) Bulbil
25. Rhizomes are vegetative propagules of:
(a) Apple
(c) Mango
(b) Rhizome
(d) Runner
(b) Rhizome
(d) Offset
(b) Rhizome
(d) Zoospores
(b) Banana
(d) Grapes
26. Which of these points is false about the diagram?
(a) Belongs to class mammalia
(c) Belongs to genus Elephas
27. Choose the correct statement.
(b) Life span is approx 40 yrs
(d) Crepuscular animal.
(A) Asexual reproduction method is the common method of reproduction in organisms with relatively simple organization like algae and fungi.
(B) Organism with relatively simple organization like algae and fungi shifted to sexual mode of reproduction just before onset of adverse conditions.
(C) Vegetative as well as sexual mode of reproduction is exhibited by the higher plants
(D) Only sexual mode of reproduction is present in most of the animals.
(a) A and B only
(c) C and D only
(b) B and C only
(d) All A, B, C and D
28. Sexual reproduction as compared to asexual reproduction is a:
(A) Slow process
(C) Simple process
(a) A and D only
(c) B and D only
(B) Fast process
(D) Complex process
(b) A and C only
(d) B and C only
29. Plants, animals or fungi differ in all of these aspects except:
(a) External morphology
(c) Physiology
(b) Internal structure
(d) Pattern of sexual mode of reproduction
30. Which of these plants which do not show clear cut vegetative, reproductive and senescent phase?
(a) Annual plant
(c) Perennial plant
(b) Biennial plant
(d) All of these
31. Which information is false about the organism shown in the diagram?
(a) Reproduce by basidiospores
(c) It is conidia of penicillium.
(b) It is a multicellular fungus.
(d) Belongs to ascomycetes.
32. Which of the following flowers only once in their lifetime?
(a) Mango
(c) Bamboo
(b) Neem
(d) All of these
33. Which of the following plant flowers once in 12 years?
(a) Mangiferaindica
(c) Helianthus annus
(b) Strobilanthus Kunthiana (Neelakuranji)
(d) Papversominiferum
34. Which of these statement is true about Strobilanthus Kunthiana?
(a) This plant flowered during September–October 2006.
(b) Its mass flowering transformed large tracks of hilly areas in Kerala, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu into blue stretches.
(c) It flowers once in 12 years.
(d) All of the above
35. In animals, the juvenile phase is followed by – changes prior to active reproductive behaviour.
(a) Morphological changes
(c) Genetical changes
(b) Physiological changes
(d) Both (a) and (b)
36. Which of the following mammals show menstrual cycle?
(a) Monkeys
(c) Humans
(b) Apes
(d) All of these
37. The diagram shows:
(a) Zoospores of hydra
(c) Gemmules in sponge
38. Oestrous cycle occurs in:
(a) Cows
(c) Deer
39. Find the correct statement.
(b) Conidia of Penicillium
(d) Zoospores of chlamydomonas
(b) Rats
(d) All of these
(a) ‘Reproductive phase’ is of same duration in all organisms.
(b) Birds in captivity can be made to lay eggs throughout the year.
(c) Female of non-primates shows cyclical changes during reproductive phase which is known as menstrual cycle.
(d) Perennial plants show clear cut vegetative, reproductive and senescent phase.
40. Most wild mammals are:
(a) Continuous breeder
(b) Seasonal breeder
(c) Continuous for half year, seasonal for next half year.
(d) None of the above
41. Which of these statements is false about the diagram?
(a) It represents asexual reproductive structure of hydra.
(b) It contains archeocyte cells.
(c) It represents asexual reproductive structure of sponges.
(d) It shows gemmules in sponges.
42. ‘Humans’ are:
(a) Seasonal breeder
(c) Both
(b) Continuous breeder
(d) None of these
43. Which of the following can be considered as one of the parameter of senescence or old age?
(a) End of Juvenile or vegetative phase
(c) Hormonal imbalance
44. Pre-fertilization events among these are:
(a) Syngamy
(c) Formation of zygote
45. Gametes are generally:
(a) Haploid
(c) Diploid
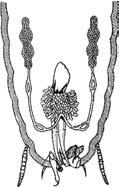
46. The diagram shows:
(a) Homogametes of cladophora
(c) Hetrogametes of Cladophora
47. Which of the following is/are male gametes?
(b) End of Reproductive phase
(d) Slowing of metabolism due to disease
(b) Gametogenesis and Gamete transfer
(d) Embryogenesis
(b) Triploid
(d) Hexaploid
(b) Heterogametes of Fucus
(d) Heterogametes of Fungus
(a) Egg (b) Ovum
(c) Antherozoids
(d) Zygote
48. Count the total number of organisms which are monoecious.
Cucurbits, Coconut, Papaya, Date palm, Chara, Marchantia
(a) 1
(c) 3
49. Archegoniophore is present in:
(a) Chara
(c) Marchantia
50. Select the incorrect statement.
(a) Unisexual male flower is staminate.
(b) Unisexual female flower is pistillate.
(b) 2
(d) 4
(b) Papaya
(d) Fucus
(c) Heterothallic and dioecious are terms used to describe unisexual condition.
(d) Cockroach is a hermaphrodite.
51. Select the example/s of hermaphrodite organism/s among these.
(a) Earthworm
(b) Tapeworm
(c) Leech (d)
52. Identify A, B, C in the diagram. A
(a) A: Nodes, B: Buds, C: Adventitious root (b) A: Buds, B: Nodes, C: Top root
(c) A: Adventitious root, B: Nodes, C: Buds (d) A: Tape root, B: Nodes, C: Buds
53. Monoecious plants means:
(A) Only male flowers are present in the plant
(B) Only female flowers are present in the plant
(C) Bisexual flowers are present in the plants
(D) Separate male and female flowers are present in the same plant.
(a) Only A
(c) Only C
(b) Only D
(d) C and D both
54. Which of these organisms has/have haploid parental body?
(a) Monera and fungi
(c) Bryophytes
(b) Algae
(d) All of these
55. Which of these organisms has/have diploid parental body?
(a) Pteridophyte and gymnosperm
(c) Most of animals
56. Anthridiophore is present in:
(a) Chara
(c) Marchantia
57. The diagram shows:
(b) Angiosperm
(d) All of the above
(b) Fucus
(d) Sweet potato
(a) Homogametes of cladophora (b) Homogametes of Fucus
(c) Hetrogametes of cladophora (d) Heterogametes of Fungus
58. Find out total number of organism whose gametes contain odd number of chromosomes.
Rat, Housefly, Dog, Cat, Apple, Rice, Maize, Potato, Onion
(a) 3
(c) 5
(b) 4
(d) 6
59. Meiocyte of which organism contain maximum number of chromosomes?
(a) Fruit fly
(b) Butterfly (c) Ophiglossum (a fern) (d) Human
60. Meiocyte of cat contains how many chromosomes?
(a) 8 (b) 12
(c) 42
61. Identify the plant shown in the given diagram.
(d) 38
62. Water is a medium for gamete transfer in:
(a) Bryophytes
(b) Pteridophyte
(c) Algae (d) All of these
63. Which of these are carriers of male gamete in seed plants?
(a) Microspore mother cell
(c) Anther
(b) Megasporemother cell
(d) Pollen grains
64. Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma is known as:
(a) Emasculation (b) Pollination (c) Bogging (d) Fertilization
(1) Branches Axis (2)
(3) (4) Dwarf shoot Long shoot Seeds
65. Most critical event in sexual reproduction is:
(a) Gametogenesis
(c) Fertilization (Syngamy)
(b) Gamete transfer
(d) Embryogenesis
66. Match column-I (Organism) with column-II (Chromosome number in meiocyte).
Column-I
Column-II
(A) Housefly (1) 12
(B) Apple (2) 34
(C) Rice (3) 24
(D) Rat (4) 42
(E) Onion (5) 32
(a) A:1, B:2, C:3, D:4, E:5
(c) A:5, B:4, C:3, D:2, E:1
(b) A:2, B:3, C:1, D:4, E:5
(d) A:3, B:2, C:1, D:4, E:5
67. Select the incorrect statement from the following.
(a) Few fungi and algae have motile male and motile female gametes.
(b) Most vital event of sexual reproductive is the fusion of gametes.
(c) Pea is a bisexual self fertilizing plant.
(d) In majority of organisms male gamete is non-motile and female gamete is motile.
68. Parthenogenesis is shown by:
(a) Rotifers
(c) Some lizards and birds (turkey)
(b) Honeybees
(d) All of above
69. Which of these statements is false about the diagram?
(a) It belongs to family solanaceae.
(b) It is a modified root meant for storage.
(c) It is a modified stem meant for reproduction.
(d) Eyes of the above structure are axillary buds.
70. External fertilization is seen in all of these except:
(a) Algae
(c) Fishes
71. Find the incorrect statement.
(b) Amphibians
(d) Mammals
(a) Large number of gametes are released in surrounding water in external fertilization
(b) Offspring produced by external fertilization are extremely vulnerable to predators.
(c) External fertilization is shown by bony fishes and frogs.
(d) In seed plant motile male gametes are carried to female gamete by pollen tubes.
72. Internal fertilization is seen in:
(a) Reptiles
(c) Mammals
73. Internal fertilization is seen in:
(a) Bryophytes
(c) Gymnosperm and Angiosperm
(b) Birds
(d) All of these
(b) Pteridophytes
(d) All of the above
74. Which of these characteristics belong to organisms showing internal fertilization?
(a) Eggs are formed inside the female body where they fuse with male gamete.
(b) Male gametes are motile
(c) Number of eggs produced less in number
(d) All of the above
75. Development of embryo from zygote is:
(a) Parthenogenesis
(c) Blastulation
76. Life in all organism starts from:
(a) Single cell zygote
(c) Single cell embryo
(b) Embryogenesis
(d) Gastrulation
(b) Two celled zygote
(d) Multicellular embryo
77. Select the total number of Correct true statements.
(A) In organisms belonging to fungi and algae, the zygote develops a thick wall that is resistant to dessication and damage.
(B) Formation of diploid zygote is universal in all sexually reproducing organisms.
(C) Syngamy occurs inside the body of the organism in internal fertilization.
(D) In organism with haplontic life cycle zygote divides by meiosis to form haploid spores that grow into haploid individuals.
(a) 1
(c) 2
78. Following are oviparous except:
(a) Crocodile
(c) Parrot
(b) 2
(d) 4
(b) Crow
(d) Horse
79. In oviparous animals like birds and reptiles the fertilized egg in covered by shell made up of
(a) SiO2
(c) CaCO3
(b) Na2CO3
(d) MgCO3
80. Chances of survival of the young one is greater in:
(a) Internal fertilization
(c) Oviparous animals
(b) External fertilization
(d) Viviparous animals
81. After fertilization which part of flower generally withers and falls off?
(a) Sepals
(c) Stamens
82. Select the false statement.
(a) Ovule develops into seed.
(b) Petals
(d) All of these
(b) Ovary develops into fruit.
(c) Zygote develops into embryo. (d)
83. A, B, C and D shows which type of placentation respectively?
(a) A: Marginal, B: Free central, C: Perietal, D: Axile
(b) A: Perietal, B: Marginal, C: Axile, D: Free central
(c) A: Axile, B: Free central, C: Marginal, D: Perietal
(d) A: Axile, B: Perietal, C: Free central, D: Marginal
84. Gametes in haploid organisms are produced by:
(a) Amitosis
(c) Meiosis
85. Embryonal protection and care are better in:
(a) Oviparity
(c) Viviparity
(b) Mitosis
(d) Cleavage
(b) Parthenogenesis
(d) Polyembryony
86. After fertilization in angiosperms, ovules develop into:
(a) Pericarp
(c) Seed
87. ‘A’ in the diagram shows:
(a) Testis of a male cockroach
(c) Testis of an earthworm
(b) Fruit
(d) Embryo
(b) Ovary of a female cockroach
(d) Ovary of an earthworm
88. The progenitor of the next generation inside the mature seed is known as:
(a) Micropyle
(c) Embryo
(b) Pericarp
(d) Zygote
89. Identify the ploidy of the following parts of flowering plants.
Ovary, Anther, Egg, Pollen, Male gamete and Zygote
(a) 2n, 2n, n, n, n, 2n
(c) 2n, n, n, n, n, 2n
90. Select the correct statement from the following.
(b) 2n, 3n, n, n, 2n, 2n
(d) 2n, 2n, n, 2n, n, 2n
(A) In flowering plants, the zygote is formed inside the ovule.
(B) In reptiles and birds, the fertilized eggs covered by hard calcareous shell (Cleidoic) are laid in a safe place in environment,
(C) In organisms belonging to fungi and algae, the zygote develops a thick wall that is vulnerable to dessication and damage.
(D) During embryogenesis, zygote undergoes cell division and cell differentiation
(a) A and C only
(c) C and D only
91. Which of these statements is true about chara?
(b) A, B and C only
(d) A, B and D only
(a) Oogonium and Anthredium are present on different plants.
(b) Oogonium is placed in the upper part andAnthredium in the lower part.
(c) Oogonium is placed in the lower part andAnthredium in upper part
(d) Chara belongs to angiosperm
92. Identify A and B in this diagram.
(a) A: Anther, B: Sepals
(c) A: Stamen, B: Carpel
(b) A: Petals, B: Anther
(d) A: Pistil, B: Stamen
93. Find the chromosome numbers in gamete (n) of the following organisms respectively.
Human, Housefly, Rat, Dog, Cat, Fruitfly, Apple, Rice, Maize, Potato, Butterfly, Onion
(a) 23, 12, 12, 39, 19, 6, 17, 12, 10, 24, 190, 16
(b) 23, 12, 21, 39, 19, 6, 17, 12, 20 24, 190, 16
(c) 23, 6, 21, 39, 19, 4, 17, 12, 10, 24, 190, 16
(d)
94. Identify A, B, C in the diagram.
(a) A: Heterogametes of Chlamydomonas
B: Homogametes of fucus
C: Hetrogametes of Homo Sapiens
(b) A: Homogametes of Chara
B: Heterogametes of Fucus
C: Heterogamete of Homo Sapiens
(c) A: Homogamete of Claldophora (a bryophyte)
B: Heterogamete of Fucus (an alga)
C: Heterogamete of Homo Sapiens
(d) A: Isogametes of Cladophora (an alga)
B: Heterogametes of Fucus (an alga)
C:Heterogametes of Homo Sapiens
95. Adventitious buds arise from the notches present at margins of leaves in:
(a) Potato
(c) Bryophyllum
(b) Offset
(d) Turmeric
96. Most of the animals shows which type of reproduction?
(a) Asexual
(b) Vegetative
(c) Sexual
(d) Gemmules formation
97. What is the number of non-primate mammals in this series?
Cow, Sheep, Rat, Deer, Dog, Tiger, Monkey, Human and Ape
(a) 3
(c) 6
98. Rhizomes are present in:
(a) Banana
(c) Potato
(b) 4
(d) 7
(b) Ginger
(d) Both (a) and (b)
99. Identify A, B and C in the figure.
(a) A: Zoospores of chlamydomonas, B: Conidia of Penicillium, C: Buds in Hydra
(b) A: Zoospores of chlamydomonas, B: Conidia of yeast, C: Buds in Hydra
(c) A: Conidia of Penicillium, B: Zoospores of Chymydomonas, C: Buds in Hydra
(d) A: Zoospores of chlamydomonas, B: Ascospores of Penicillium, C: Buds in Hydra
100. Bulbils are vegetative propagules in:
(a) Water hyacinth
(c) Potato
(b) Agave
(d) Tomato
Answer Keys
(a)
(c)
(b)
41. (a) 42. (b) 43. (b)
(b)
(d)
(d) 71. (d) 72. (d) 73. (d) 74. (d)
(b)
(d) 81. (d) 82. (d) 83. (a) 84. (b) 85. (c) 86. (c) 87. (a) 88. (c) 89. (a) 90. (d) 91. (b) 92. (c) 93. (c) 94. (d) 95. (c) 96. (c) 97. (c) 98. (d) 99. (a) 100. (b)
Conida (C)
Mouth
Bud
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plant
1. Flowers convey important human feelings such as (a) Love and affection (b) Happiness and grief (c) Mourning (d) All of the above
2. Flowers are considered as object of (a) Aesthetic value
(b) Ornamental value (c) Religious and cultural value (d) All of the above
3. Biologist consider flower to be objects of (a) Morphological marvels
(b) Embryological marvels (c) Sites of sexual reproduction (d) All of the above
4. When does plant decides to flower?
(a) In embryonic development (b) When flower bud appears (c) Before the actual flower appear on plant (d) All are correct
5. Identify A, B, C and D in this figure?
(a) A: Pollen grains, B: Filament (Stalk), C: Line of dehiscence, D: Pollen sacs
(b) A: Line of dehiscence, B: Filament (Stalk), C: Pollen sacs, D: Pollen grains
(c) A: Filament (Stalk), B: Pollen grains, C: Line of dehiscence, D: Pollen sacs
(d) A: Line of dehiscence, B: Pollen sacs, C: Pollen grains, D: Filament (Stalk)
6. The initiation and development of floral primordium takes place by (a) Only by hormonal changes in plant
(b) Only structural changes in plant
(c) Changes in seasonal variation
(d) Both by hormonal and structural changes in plant
7. Where of stamens in flower represent
(a) Gynoecium
(b) Androecium
(c) Calyx (d) Corolla
8. Whorl of carpel in flower represents (a) Gynoecium
(b) Androecium (c) Calyx (d) Corolla
9. What indicates “A” in below figure?
(a) Pollen grains
(c) Generative cell
10. Whorl of petals in flower represents (a) Gynoecium
(b) Pollen sacs
(d) Vacuoles
(b) Androecium (c) Calyx (d) Corolla
11. Whorl of sepals in flower represents (a) Androecium
(b) Gynoecium (c) Calyx (d) Corolla
12. Stamens consist of the following parts
(a) Filament
(b) Style, stigma (c) Anther
(d) Both (a) and (c)
13. The number and length of stamens in flowers are
(a) Variable in different species
(b) Same in plants present in similar climatic condition
(c) Variable and depend on the amount of hormonal secretion
(d) Variable in different species and depend on the seasonal variation
14. Typical angiosperm anther is
(a) Unilobed and dithecous
(c) May be both (a) and (b)
15. The anther in transverse section appears to be
(a) Diagonal
(c) Unilobed
16. What are A, B, C and D in this figure?
(b) Bilobed and dithecous
(d) Bilobed and tetrathecous
(b) Tetragonal
(d) Mosaic
(a) A: Thalamus, B: Style, C: Ovary, D: Stigma
(b) A: Style, B: Ovary, C: Stigma, D: Thalamus
(c) A: Stigma, B: Style, C: Ovary, D: Thalamus
(d) A: Ovary, B: Stigma, C: Thalamus, D: Style
17. Tetragonal anther consist of
(a) One microsporangia
(c) Three microsporangia
(b) Two microsporangia
(d) Four microsporangia
18. How many microsporangia are there in each lobe of anther?
(a) One microsporangia
(c) Three microsporangia
19. Pollen sacs develop from
(a) Microspore
(c) Microsporangium
(b) Two microsporangia
(d) Four microsporangia
(b) Microspore mother cell
(d) Megaspore
20. Typical microsporangium appear ________ in transverse section.
(a) Wavy
(c) Oval
(b) Circular
(d) Irregular
21. Which one amongst the given perform the function of protection in typical microsporangium?
(A) Epidermis
(C) Tapetum
(a) A and B
(c) A and D
(B) Endothecium
(D) Middle layer
(b) A and C
(d) A, B and D
22. Which of the following layer of microsporangium provide nourishment to the developing anther?
(a) Middle layers
(c) Endothecium
(b) Tapetum
(d) Epidermis
23. Outer three layers of microsporangium, perform the function of
(a) Protection to developing pollen
(b) Provide nourishment to developing pollen
(c) Help in dehiscence of anther to release pollen
(d) Both (a) and (c)
24. Identify the parts A to I in this figure.
(a) A: Ovary, B: Anther, C: Filament, D: Nectariferous area, E: Sepal, F: Stigma, G: Style, H: Ovule, I: Petal
(b) A: Anther, B: Ovule, C: Stigma, D: Anther, E: Petal, F: Filament, G: Sepal, H: Nectariferous area, I: Ovary
(c) A: Ovary, B: Ovule, C: Nectariferous area, D: Sepal, E: Filament, F: Petal, G: Anther, H: Stigma, I: Style
(d) A: Style, B: Stigma, C: Anther, D: Petal, E: Filament, F: Sepal, G: Nectariferous area, H: Ovule, I: Ovary
25. The microsporangium cells which posses dense cytoplasm and have more than one nucleus is the characteristic of
(a) Middle layers
(c) Endothecium
(b) Tapetum
(d) Epidermis
26. In young anther the tissue occupying the centre of each microsporangium is called as (a) Megaspore mother cell
(b) Sporogenous tissue (c) Parietal tissue
27. Identify A to E in this figure?
(d) None of the above